Submitted:
24 May 2024
Posted:
27 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
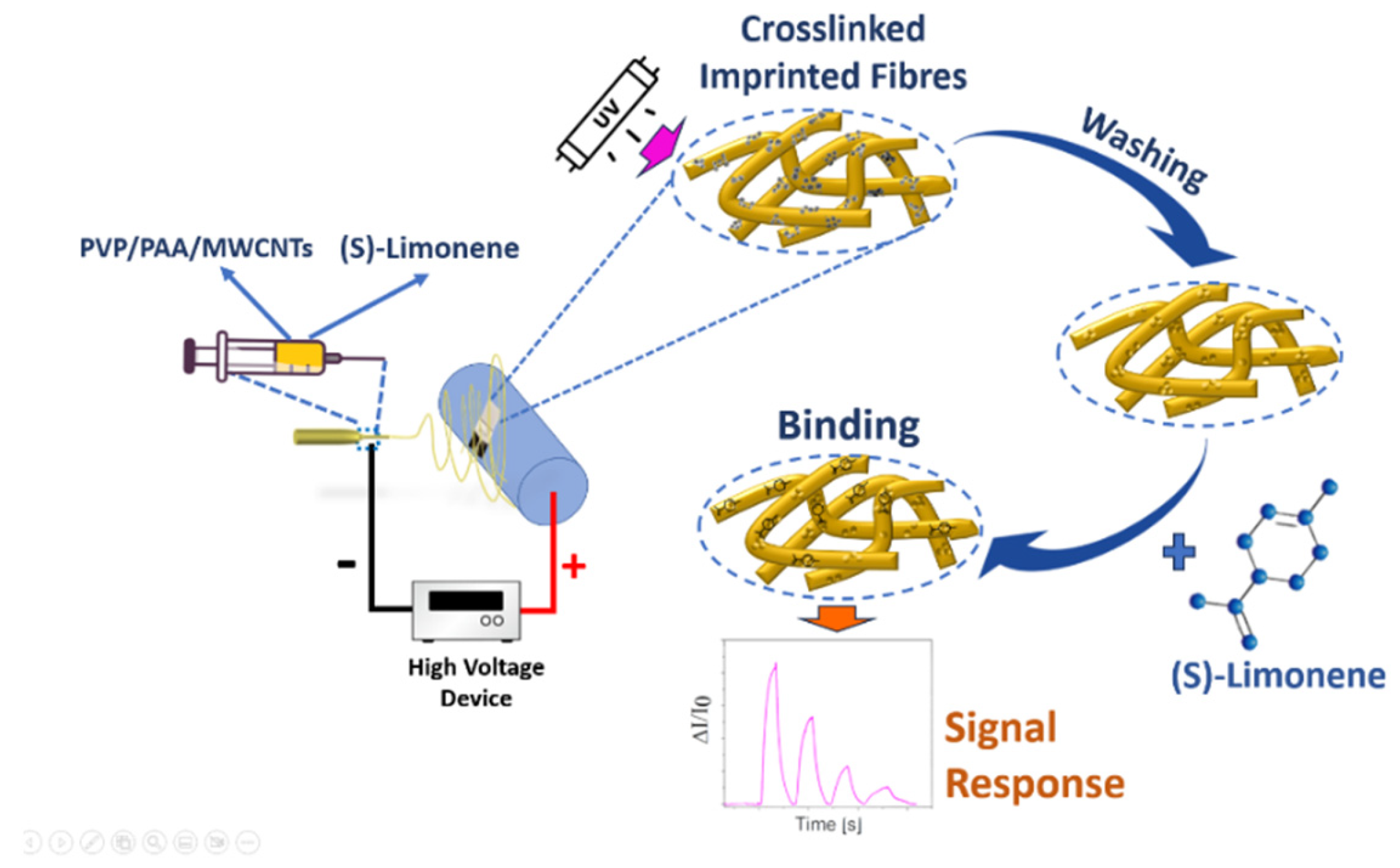
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning Solutions
2.3. Electrospinning Conditions and Device Fabrication
2.4. UV Crosslinking Process
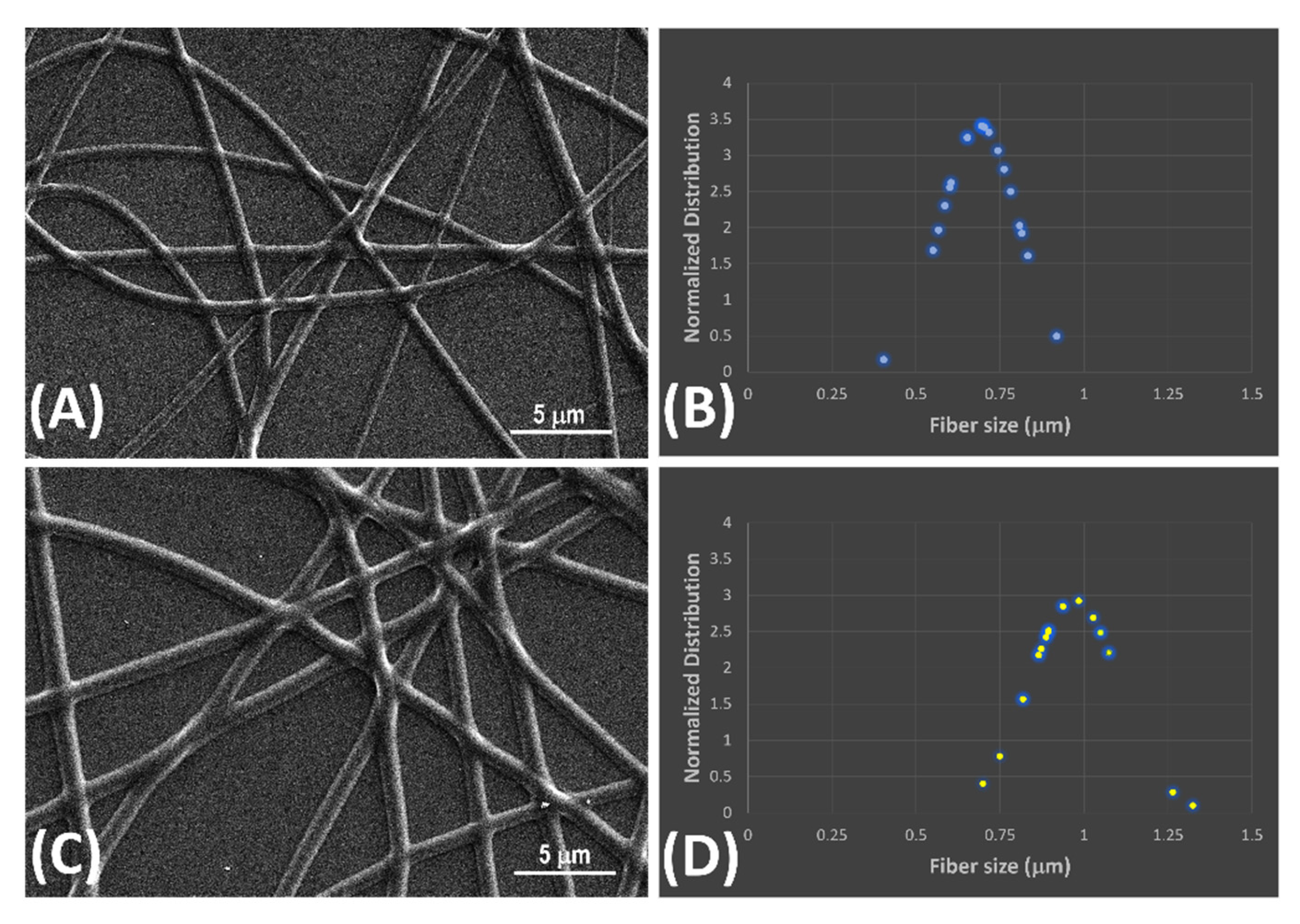
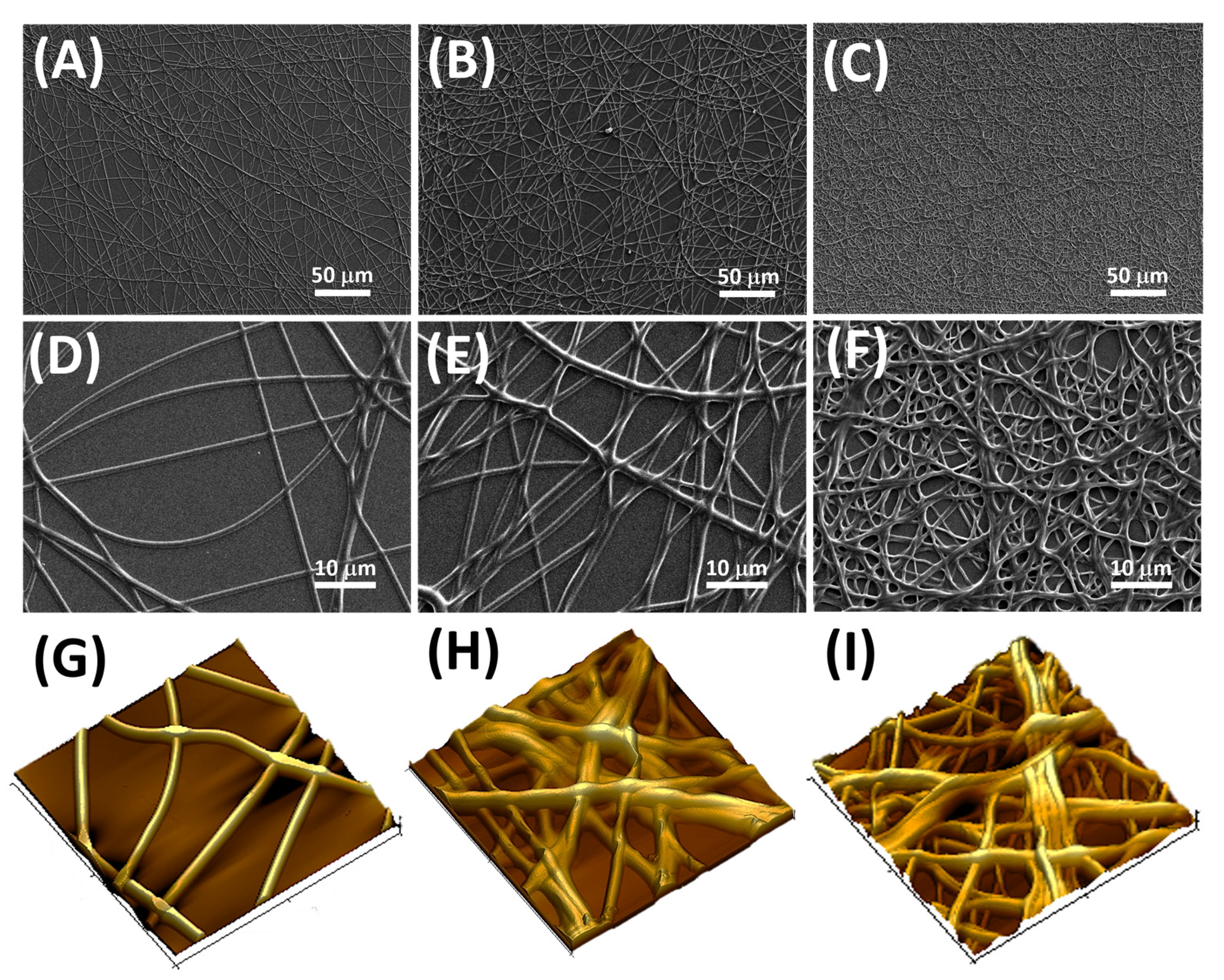
2.5. Scanning Electronic Microscopy
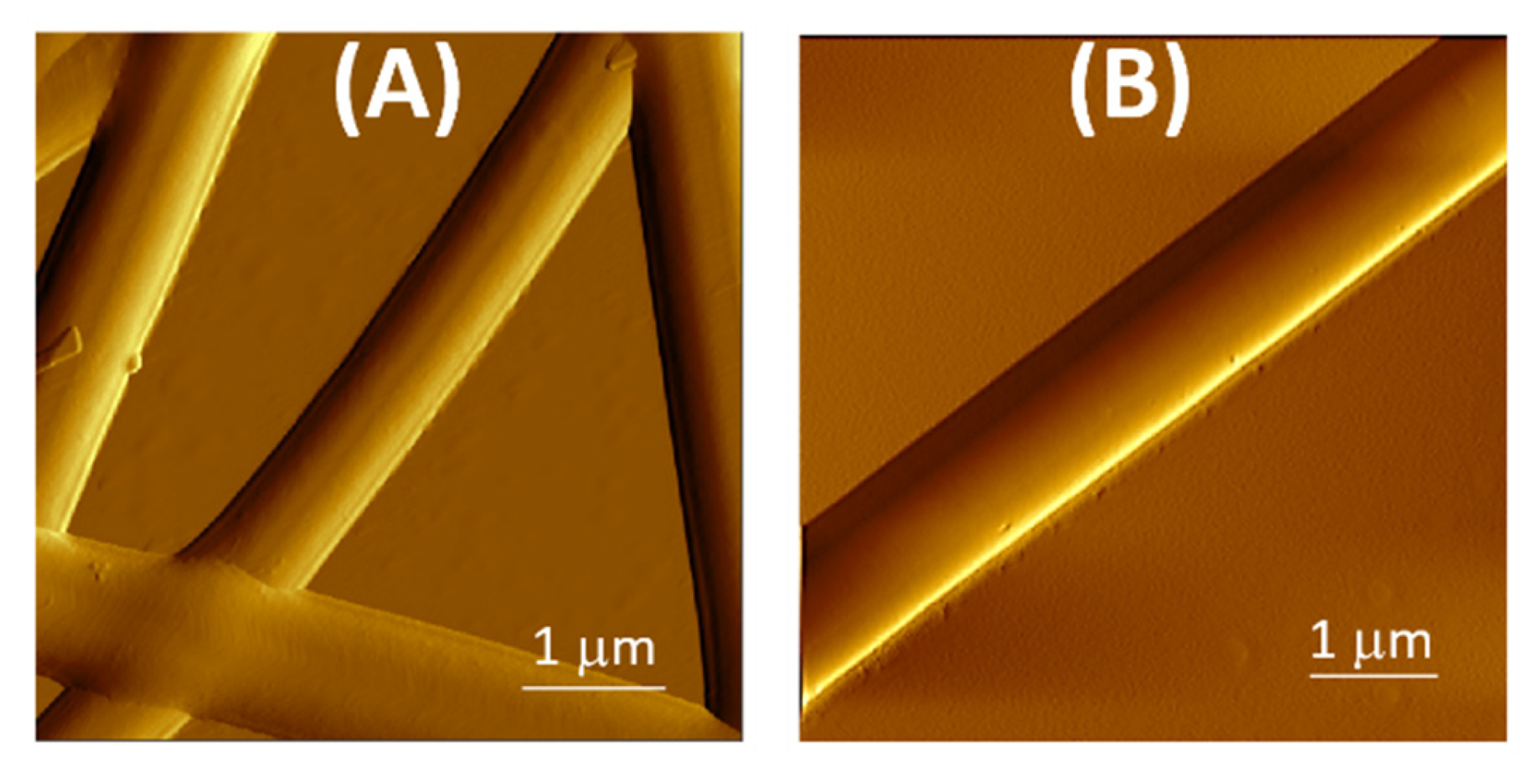
2.6. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscope
2.8. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
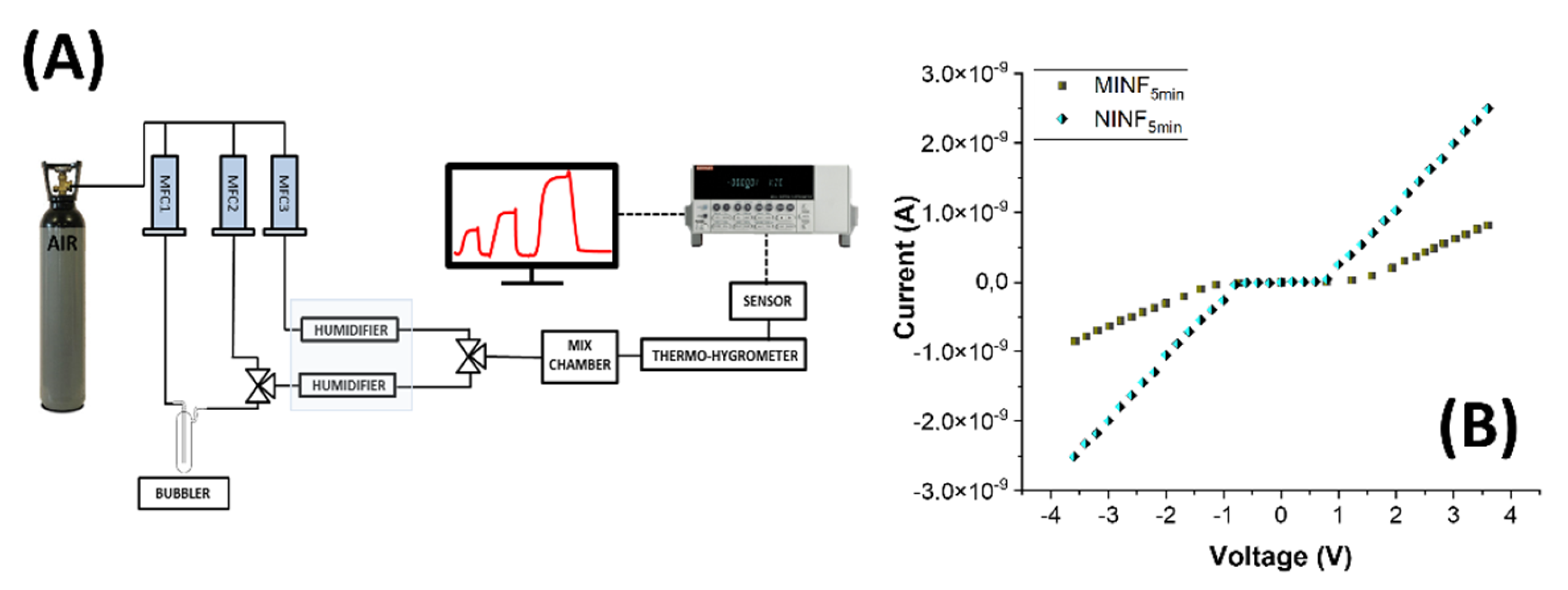
2.9. Electrical Measures
3. Results and Discussion
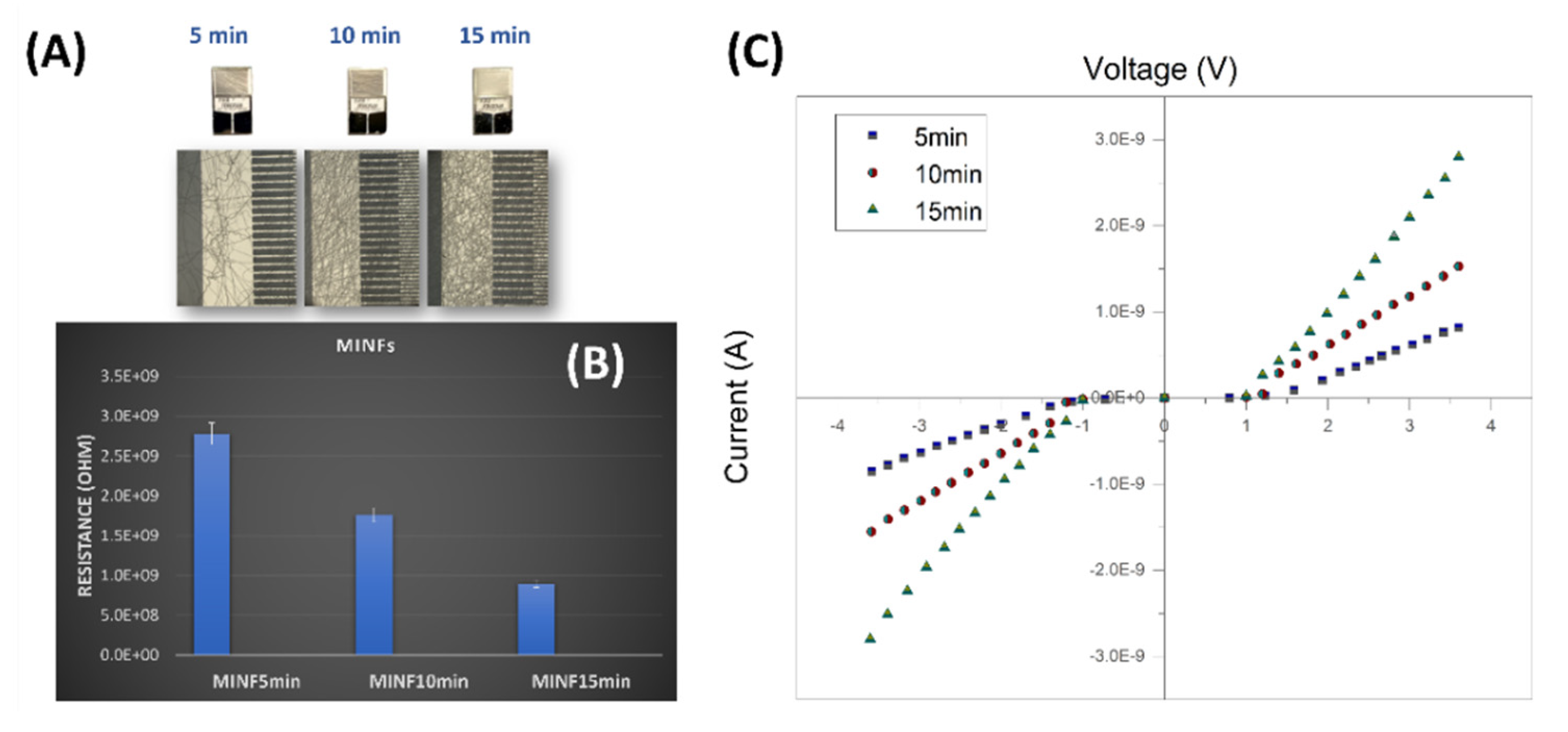
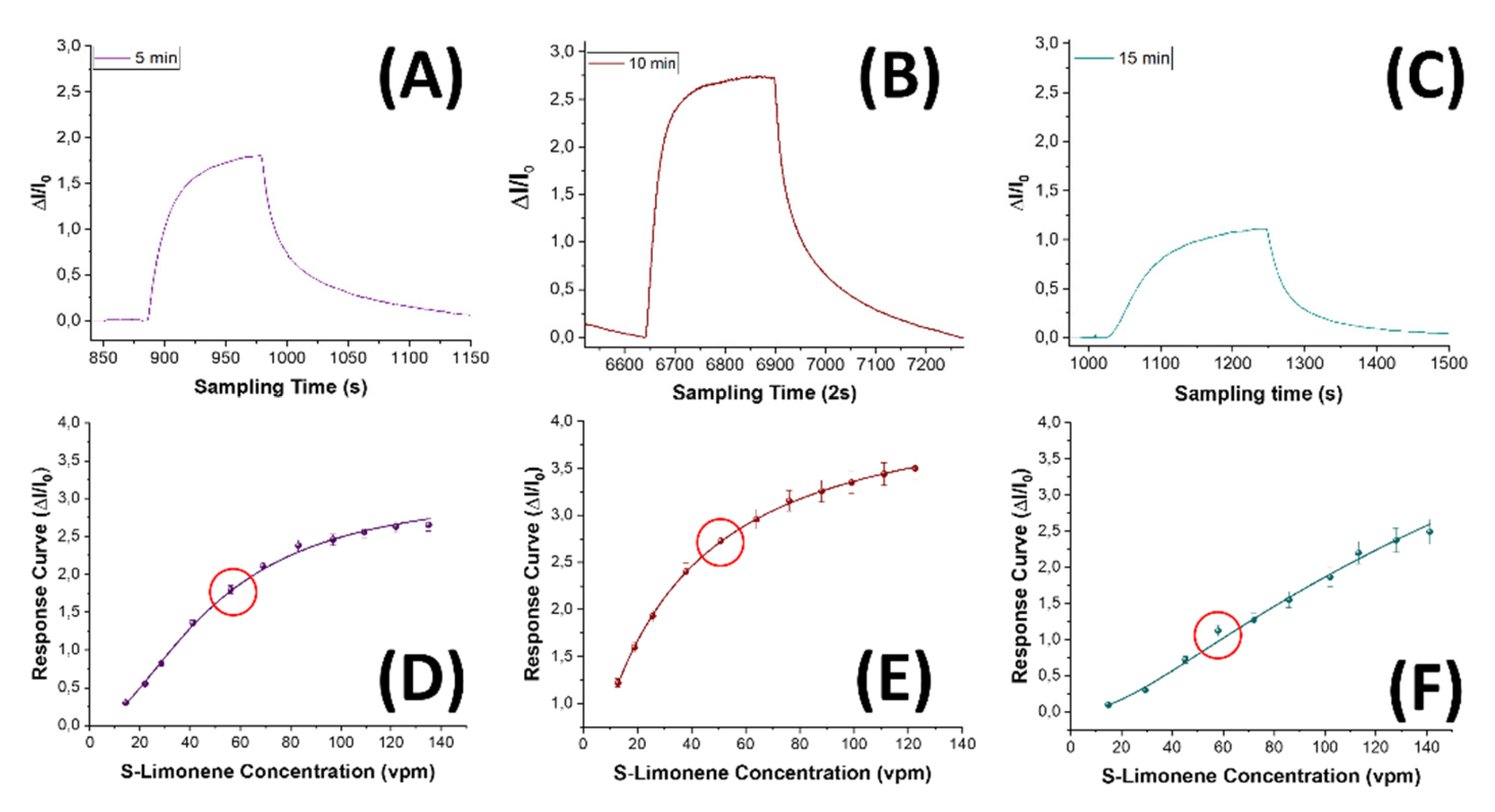
3.1. Fibers Characterization
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
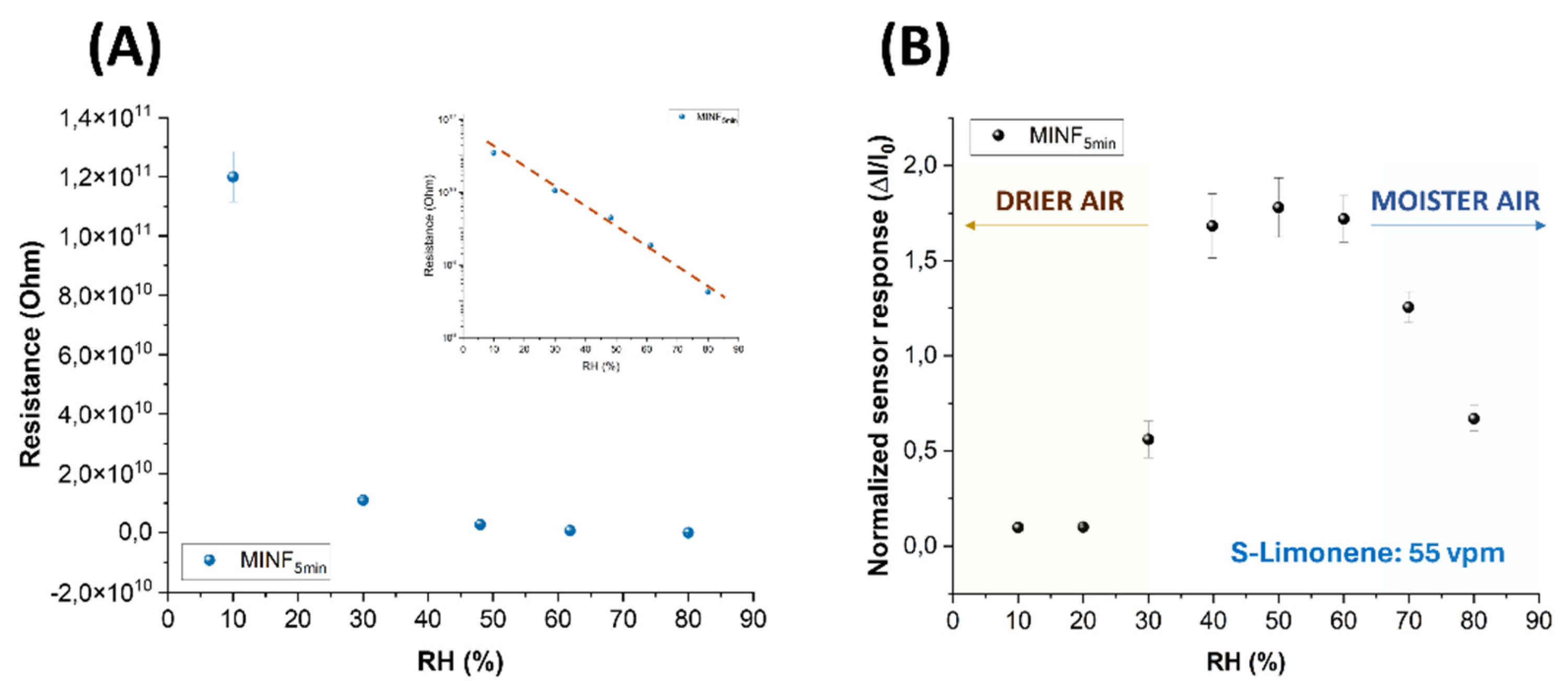
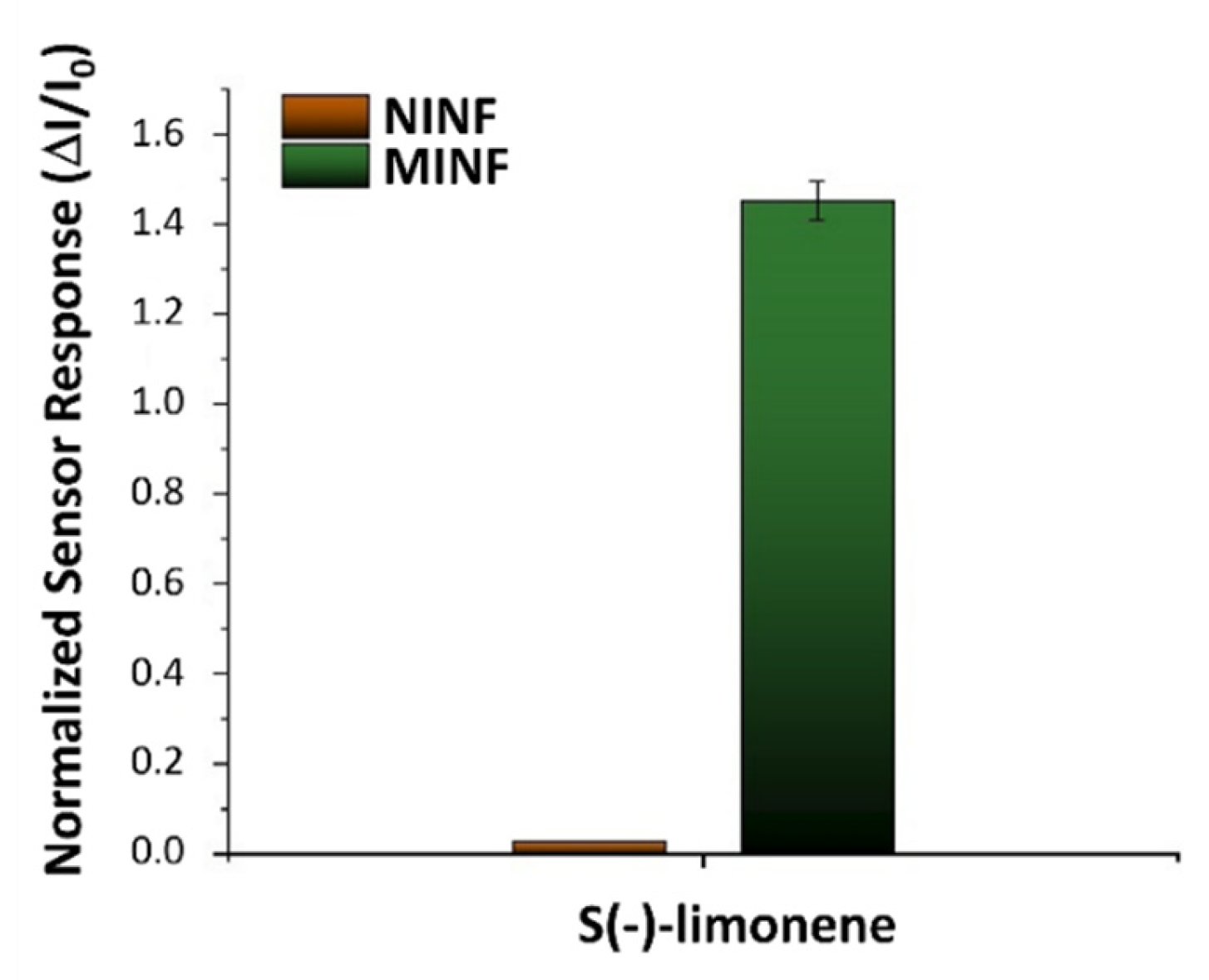
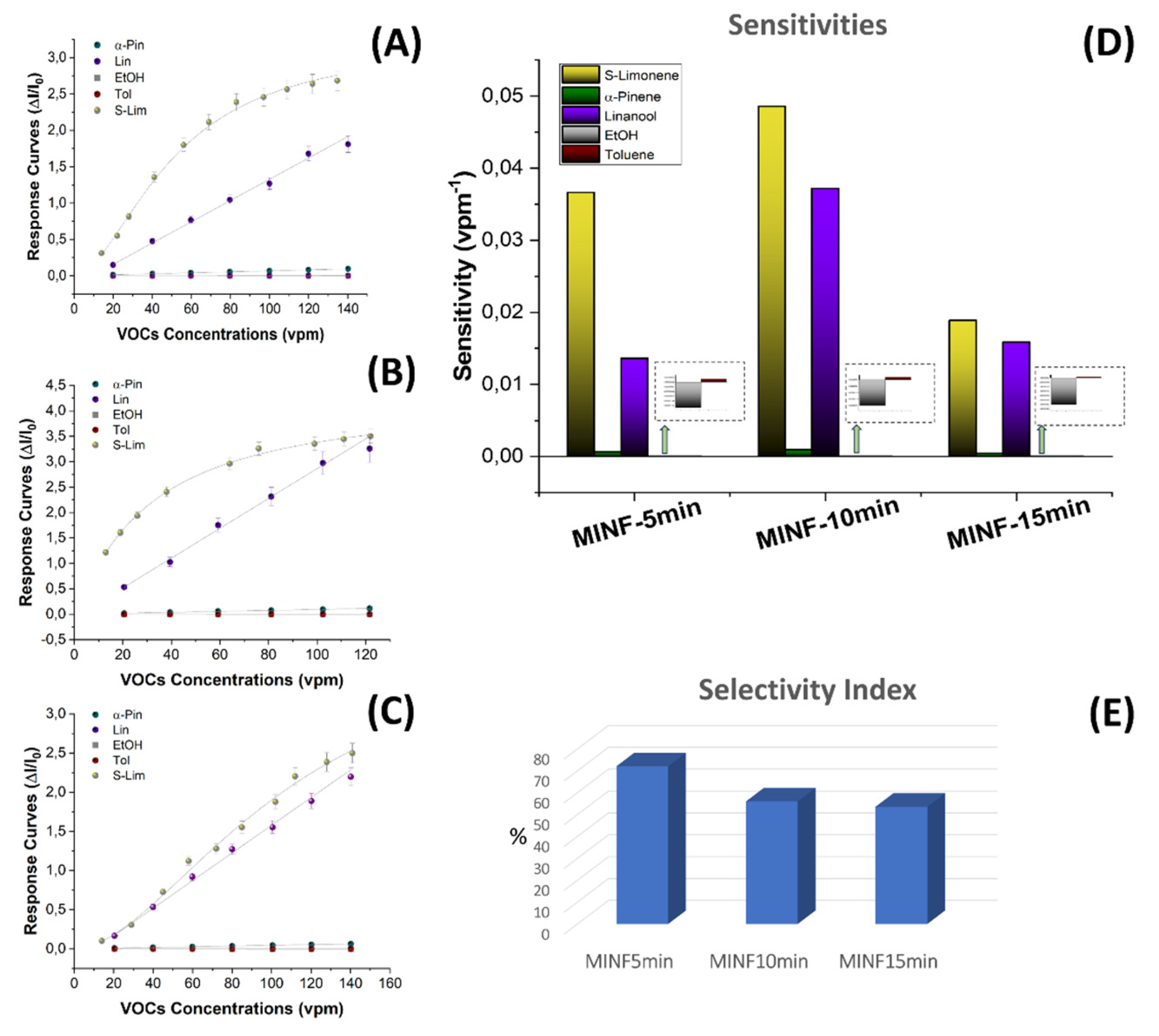
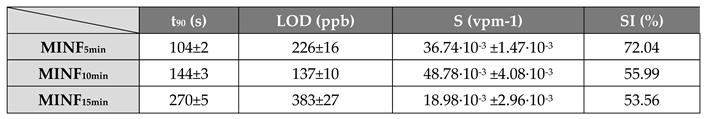
3.3. Electrical and Sensing Features
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
References
- S. Datta, I. Hamim, D.K. Jaiswal, R. Sungthong, Sustainable agriculture, BMC Plant Biol. 23 (2023) 588. [CrossRef]
- Galieni, N. D’Ascenzo, F. Stagnari, G. Pagnani, Q. Xie, M. Pisante, Past and Future of Plant Stress Detection: An Overview From Remote Sensing to Positron Emission Tomography, Front. Plant Sci. 11 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Cagliero, G. Mastellone, A. Marengo, C. Bicchi, B. Sgorbini, P. Rubiolo, Analytical strategies for in-vivo evaluation of plant volatile emissions - A review, Anal. Chim. Acta. 1147 (2021) 240–258. [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, R. Kumar, Sensing Methodologies in Agriculture for Monitoring Biotic Stress in Plants Due to Pathogens and Pests, Inventions. 6 (2021) 29. [CrossRef]
- M. Cai, C. An, C. Guy, A scientometric analysis and review of biogenic volatile organic compound emissions: Research hotspots, new frontiers, and environmental implications, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 149 (2021) 111317. [CrossRef]
- G.F. Bennett, Volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere, J. Hazard. Mater. 50 (1996) 245–246. [CrossRef]
- J.K. Holopainen, J. Gershenzon, Multiple stress factors and the emission of plant VOCs, Trends Plant Sci. 15 (2010) 176–184. [CrossRef]
- J. Poveda, Beneficial effects of microbial volatile organic compounds (MVOCs) in plants, Appl. Soil Ecol. 168 (2021). [CrossRef]
- L. NERI, F. SILLO, E. ZAMPIERI, E. LUMINI, G. MARTURANO, C.D. ESPOSTI, G. PETRUZZELLI, B. GIOLI, A. ZALDEI, R. BARALDI, R. BALESTRINI, A combined analysis based on microbial communities and volatile organic compounds as a tool to study soil quality in an urban environment, Pedosphere. 33 (2023) 670–675. [CrossRef]
- X. Bao, W. Zhou, L. Xu, Z. Zheng, A meta-analysis on plant volatile organic compound emissions of different plant species and responses to environmental stress, Environ. Pollut. 318 (2023) 120886. [CrossRef]
- C. Faiola, D. Taipale, Impact of insect herbivory on plant stress volatile emissions from trees: A synthesis of quantitative measurements and recommendations for future research, Atmos. Environ. X. 5 (2020) 100060. [CrossRef]
- Mozaffar, N. Schoon, A. Bachy, A. Digrado, B. Heinesch, M. Aubinet, M.L. Fauconnier, P. Delaplace, P. du Jardin, C. Amelynck, Biogenic volatile organic compound emissions from senescent maize leaves and a comparison with other leaf developmental stages, Atmos. Environ. 176 (2018) 71–81. [CrossRef]
- V. Ninkuu, L. Zhang, J. Yan, Z. Fu, T. Yang, H. Zeng, Biochemistry of Terpenes and Recent Advances in Plant Protection, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (2021) 5710. [CrossRef]
- Munawar, Y. Xu, A.S. Abou El-Ela, Y. Zhang, J. Zhong, Z. Mao, X. Chen, H. Guo, C. Zhang, Y. Sun, Z. Zhu, I.T. Baldwin, W. Zhou, Tissue-specific regulation of volatile emissions moves predators from flowers to attacked leaves, Curr. Biol. 33 (2023) 2321-2329.e5. [CrossRef]
- Z. Gan, Q. Zhou, C. Zheng, J. Wang, Challenges and applications of volatile organic compounds monitoring technology in plant disease diagnosis, Biosens. Bioelectron. 237 (2023) 115540. [CrossRef]
- F. De Cesare, E. Di Mattia, S. Pantalei, E. Zampetti, V. Vinciguerra, F. Canganella, A. Macagnano, Use of electronic nose technology to measure soil microbial activity through biogenic volatile organic compounds and gases release, Soil Biol. Biochem. 43 (2011) 2094–2107. [CrossRef]
- R.K. Murali-Baskaran, P. Mooventhan, D. Das, A. Dixit, K.C. Sharma, S. Senthil-Nathan, P. Kaushal, P.K. Ghosh, The future of plant volatile organic compounds (pVOCs) research: Advances and applications for sustainable agriculture, Environ. Exp. Bot. 200 (2022) 104912. [CrossRef]
- N. Dudareva, F. Negre, D.A. Nagegowda, I. Orlova, Plant Volatiles: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives, CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 25 (2006) 417–440. [CrossRef]
- M.E. Maffei, Sites of synthesis, biochemistry and functional role of plant volatiles, South African J. Bot. 76 (2010) 612–631. [CrossRef]
- F. Loreto, J.-P. Schnitzler, Abiotic stresses and induced BVOCs, Trends Plant Sci. 15 (2010) 154–166. [CrossRef]
- M. Rosenkranz, Y. Chen, P. Zhu, A.C. Vlot, Volatile terpenes – mediators of plant-to-plant communication, Plant J. 108 (2021) 617–631. [CrossRef]
- Aina, O.O. Bakare, A.O. Fadaka, M. Keyster, A. Klein, Plant biomarkers as early detection tools in stress management in food crops: a review, Planta. 259 (2024) 60. [CrossRef]
- R. Malheiro, S. Casal, S.C. Cunha, P. Baptista, J.A. Pereira, Identification of leaf volatiles from olive (Olea europaea) and their possible role in the ovipositional preferences of olive fly, Bactrocera oleae (Rossi) (Diptera: Tephritidae), Phytochemistry. 121 (2016) 11–19. [CrossRef]
- C. Malitesta, E. Mazzotta, R.A. Picca, A. Poma, I. Chianella, S.A. Piletsky, MIP sensors – the electrochemical approach, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 402 (2012) 1827–1846. [CrossRef]
- M. Cieplak, W. Kutner, Artificial Biosensors: How Can Molecular Imprinting Mimic Biorecognition?, Trends Biotechnol. 34 (2016) 922–941. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, X. Wang, W. Lu, X. Wu, J. Li, Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications, Chem. Soc. Rev. 45 (2016) 2137–2211. [CrossRef]
- M. Ávila, M. Zougagh, Á. Ríos, A. Escarpa, Molecularly imprinted polymers for selective piezoelectric sensing of small molecules, TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 27 (2008) 54–65. [CrossRef]
- Y. Hua, Y. Ahmadi, K.H. Kim, Molecularly imprinted polymers for sensing gaseous volatile organic compounds: opportunities and challenges, Environ. Pollut. 311 (2022). [CrossRef]
- S. Antwi-Boampong, K.S. Mani, J. Carlan, J.J. BelBruno, A selective molecularly imprinted polymer-carbon nanotube sensor for cotinine sensing, J. Mol. Recognit. 27 (2014) 57–63. [CrossRef]
- X. Tang, J.-P. Raskin, D. Lahem, A. Krumpmann, A. Decroly, M. Debliquy, A Formaldehyde Sensor Based on Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer on a TiO2 Nanotube Array, Sensors. 17 (2017) 675. [CrossRef]
- M.F. Koudehi, S.M. Pourmortazavi, R. Zibaseresht, S. Mirsadeghi, << MEMS-Based PVA/PPy/MIP Polymeric- Nanofiber Sensor Fabricated by LIFT-OFF Process for Detection 2,4-Dinitrotoluene Vapor, IEEE Sens. J. 21 (2021) 9492–9499. [CrossRef]
- T. Alizadeh, F. Rezaloo, A new chemiresistor sensor based on a blend of carbon nanotube, nano-sized molecularly imprinted polymer and poly methyl methacrylate for the selective and sensitive determination of ethanol vapor, Sensors Actuators B Chem. 176 (2013) 28–37. [CrossRef]
- T. Alizadeh, F. Rezaloo, Toluene chemiresistor sensor based on nano-porous toluene-imprinted polymer, Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 93 (2013) 919–934. [CrossRef]
- A.J. Kadhem, G.J. Gentile, M.M. Fidalgo de Cortalezzi, Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) in Sensors for Environmental and Biomedical Applications: A Review, Molecules. 26 (2021) 6233. [CrossRef]
- K.D. Patel, H.W. Kim, J.C. Knowles, A. Poma, Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Electrospinning: Manufacturing Convergence for Next-Level Applications, Adv. Funct. Mater. 30 (2020). [CrossRef]
- M. Keshvardoostchokami, S.S. Majidi, P. Huo, R. Ramachandran, M. Chen, B. Liu, Electrospun Nanofibers of Natural and Synthetic Polymers as Artificial Extracellular Matrix for Tissue Engineering, Nanomaterials. 11 (2020) 21. [CrossRef]
- R.M.D. Soares, N.M. Siqueira, M.P. Prabhakaram, S. Ramakrishna, Electrospinning and electrospray of bio-based and natural polymers for biomaterials development, Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 92 (2018) 969–982. [CrossRef]
- A.R. Borah, P. Hazarika, R. Duarah, R. Goswami, S. Hazarika, Biodegradable Electrospun Membranes for Sustainable Industrial Applications, ACS Omega. 9 (2024) 11129–11147. [CrossRef]
- Macagnano, E. Zampetti, E. Kny, eds., Electrospinning for High Performance Sensors, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Macagnano, V. Perri, E. Zampetti, A. Bearzotti, F. De Cesare, Humidity effects on a novel eco-friendly chemosensor based on electrospun PANi/PHB nanofibres, Sensors Actuators B Chem. 232 (2016) 16–27. [CrossRef]
- M. Asadnia, A.G.P. Kottapalli, K.D. Karavitaki, M.E. Warkiani, J. Miao, D.P. Corey, M. Triantafyllou, From Biological Cilia to Artificial Flow Sensors: Biomimetic Soft Polymer Nanosensors with High Sensing Performance, Sci. Rep. 6 (2016) 32955. [CrossRef]
- S. Sankar, C.S. Sharma, S.N. Rath, S. Ramakrishna, Electrospun nanofibres to mimic natural hierarchical structure of tissues: application in musculoskeletal regeneration, J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 12 (2018) e604–e619. [CrossRef]
- S. Chigome, G. Darko, N. Torto, Electrospun nanofibers as sorbent material for solid phase extraction, Analyst. 136 (2011) 2879. [CrossRef]
- S. Chigome, N. Torto, A review of opportunities for electrospun nanofibers in analytical chemistry, Anal. Chim. Acta. 706 (2011) 25–36. [CrossRef]
- Ghorani, N. Tucker, M. Yoshikawa, Approaches for the assembly of molecularly imprinted electrospun nanofibre membranes and consequent use in selected target recognition, Food Res. Int. 78 (2015) 448–464. [CrossRef]
- S.A. Zaidi, Recent developments in molecularly imprinted polymer nanofibers and their applications, Anal. Methods. 7 (2015) 7406–7415. [CrossRef]
- K. Yoshimatsu, L. Ye, P. Stenlund, I.S. Chronakis, A simple method for preparation of molecularly imprinted nanofiber materials with signal transduction ability, Chem. Commun. (2008) 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Yoshimatsu, L. Ye, J. Lindberg, I.S. Chronakis, Selective molecular adsorption using electrospun nanofiber affinity membranes, Biosens. Bioelectron. 23 (2008) 1208–1215. [CrossRef]
- S. Piperno, B. Tse Sum Bui, K. Haupt, L.A. Gheber, Immobilization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles in Electrospun Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanofibers, Langmuir. 27 (2011) 1547–1550. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhang, Y. Guo, W. Chi, H. Shi, H. Ren, T. Guo, Electrospun nanofibers containing p-nitrophenol imprinted nanoparticles for the hydrolysis of paraoxon, Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 32 (2014) 1469–1478. [CrossRef]
- F. Liu, Q. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, Y. Wan, K. Gao, Y. Huang, W. Xia, H. Wang, Y. Shi, Z. Huang, B. Lu, Molecularly imprinted nanofiber membranes enhanced biodegradation of trace bisphenol A by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Chem. Eng. J. 262 (2015) 989–998. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wu, Y. Zhang, M. Zhang, F. Liu, Y. Wan, Z. Huang, L. Ye, Q. Zhou, Y. Shi, B. Lu, Selective and simultaneous determination of trace bisphenol A and tebuconazole in vegetable and juice samples by membrane-based molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and HPLC, Food Chem. 164 (2014) 527–535. [CrossRef]
- P. Zahedi, M. Fallah-Darrehchi, S.A. Nadoushan, R. Aeinehvand, L. Bagheri, M. Najafi, Morphological, thermal and drug release studies of poly (methacrylic acid)-based molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles immobilized in electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibers as dexamethasone delivery system, Korean J. Chem. Eng. 34 (2017) 2110–2118. [CrossRef]
- M. Hassanzadeh, M. Ghaemy, S.M. Amininasab, Z. Shami, An effective approach for fast selective separation of Cr(VI) from water by ion-imprinted polymer grafted on the electro-spun nanofibrous mat of functionalized polyacrylonitrile, React. Funct. Polym. 130 (2018) 70–80. [CrossRef]
- M. Demirkurt, Y.A. Olcer, M.M. Demir, A.E. Eroglu, Electrospun polystyrene fibers knitted around imprinted acrylate microspheres as sorbent for paraben derivatives, Anal. Chim. Acta. 1014 (2018) 1–9. [CrossRef]
- L. Li, H. Liu, X. Lei, Y. Zhai, Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes Containing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) for Rhodamine B (RhB), Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 02 (2012) 266–274. [CrossRef]
- F.N. Molinari, F. De Cesare, A. Macagnano, Housing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles in Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Nanofibers to Detect Chiral Terpene Vapors, in: Eurosensors 2023, MDPI, Basel Switzerland, 2024: p. 96. [CrossRef]
- I.S. Chronakis, B. Milosevic, A. Frenot, L. Ye, Generation of Molecular Recognition Sites in Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers via Molecular Imprinting, Macromolecules. 39 (2006) 357–361. [CrossRef]
- X. Xue, R. Lu, Y. Li, Q. Wang, J. Li, L. Wang, Molecularly imprinted electrospun nanofibers for adsorption of 2,4-dinitrotoluene in water, Analyst. 143 (2018) 3465–3471. [CrossRef]
- W.J. Kim, J.Y. Chang, Molecularly imprinted polyimide nanofibers prepared by electrospinning, Mater. Lett. 65 (2011) 1388–1391. [CrossRef]
- Macagnano, F.N. Molinari, T. Mancini, S. Lupi, F. De Cesare, UV Light Stereoselective Limonene Sensor Using Electrospun PVP Composite Nanofibers, in: Eurosensors 2023, MDPI, Basel Switzerland, 2024: p. 131. [CrossRef]
- F. Molinari, A. V. Medrano, A. Bacigalupe, M. Escobar, L.N. Monsalve, Different dispersion states of MWCNT in aligned conductive electrospun PCL/MWCNT composites, Fullerenes, Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures. 26 (2018) 667–674. [CrossRef]
- T. Ito, S. Yamaguchi, D. Soga, T. Yoshimoto, Y. Koyama, Preparation of a Bioadhesive Poly(Acrylic Acid)/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Complex Gel and Its Clinical Effect on Dental Hemostasis, Gels. 8 (2022) 462. [CrossRef]
- D’Arco, M. Di Fabrizio, T. Mancini, R. Mosetti, S. Macis, G. Tranfo, G. Della Ventura, A. Marcelli, M. Petrarca, S. Lupi, Secondary Structures of MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins Revealed by Infrared Vibrational Spectroscopy, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (2023) 9550. [CrossRef]
- H. Kaczmarek, A. Szalla, A. Kamińska, Study of poly(acrylic acid)–poly(vinylpyrrolidone) complexes and their photostability, Polymer (Guildf). 42 (2001) 6057–6069. [CrossRef]
- W. Salalha, Y. Dror, R.L. Khalfin, Y. Cohen, A.L. Yarin, E. Zussman, Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in Oriented Polymeric Nanofibers by Electrospinning, Langmuir. 20 (2004) 9852–9855. [CrossRef]
- P. Poulin, B. Vigolo, P. Launois, Films and fibers of oriented single wall nanotubes, Carbon N. Y. 40 (2002) 1741–1749. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhu, P. Lu, W. Chen, J. Dong, Studies of UV crosslinked poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) hydrogels by FTIR, Raman and solid-state NMR spectroscopies, Polymer (Guildf). 51 (2010) 3054–3063. [CrossRef]
- H. Kaczmarek, M. Metzler, F. Ścigalski, Photochemical stability of poly(acrylic acid)/silver nanocomposite, Mater. Lett. 135 (2014) 110–114. [CrossRef]
- J. Janata, M. Josowicz, Conducting polymers in electronic chemical sensors, Nat. Mater. 2 (2003) 19–24. [CrossRef]
- R. Sarabia-Riquelme, J. Craddock, E.A. Morris, D. Eaton, R. Andrews, J. Anthony, M.C. Weisenberger, Simple, low-cost, water-processable n-type thermoelectric composite films from multiwall carbon nanotubes in polyvinylpyrrolidone, Synth. Met. 225 (2017) 86–92. [CrossRef]
- Ding, M. Wang, X. Wang, J. Yu, G. Sun, Electrospun nanomaterials for ultrasensitive sensors, Mater. Today. 13 (2010) 16–27. [CrossRef]
- F.M. Ernsberger, The Nonconformist Ion, 1983.
- X. Pan, Q. Xue, J. Zhang, Q. Guo, Y. Jin, W. Lu, X. Li, C. Ling, Effective Enhancement of Humidity Sensing Characteristics of Novel Thermally Treated MWCNTs/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Film Caused by Interfacial Effect, Adv. Mater. Interfaces. 3 (2016) 1600153. [CrossRef]
- S.K.S. Basha, G.S. Sundari, K.V. Kumar, M.C. Rao, Structural and Dielectric Properties of PVP Based Composite Polymer Electrolyte Thin Films, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 27 (2017) 455–466. [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.F.A. Bakar, T.H. Ling, N. Ideris, Z.H.M. Zain, N. Radacsi, Morphology and conductivity evaluation of electrospun polyacrylic acid (PAA) microfiber, Mater. Today Proc. 17 (2019) 574–583. [CrossRef]
- T. Khan, M.S. Irfan, M. Ali, Y. Dong, S. Ramakrishna, R. Umer, Insights to low electrical percolation thresholds of carbon-based polypropylene nanocomposites, Carbon N. Y. 176 (2021) 602–631. [CrossRef]
- P. Rani, M.B. Ahamed, K. Deshmukh, Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in Polymer Nanofibers by Electrospinning, in: Handb. Carbon Nanotub., Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2022: pp. 943–977. [CrossRef]
- J. Abraham, S. Thomas, N. Kalarikkal, Handbook of carbon nanotubes, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T.T. Moore, W.J. Koros, Gas sorption in polymers, molecular sieves, and mixed matrix membranes, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 104 (2007) 4053–4059. [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, C. Di Natale, A contribution on some basic definitions of sensors properties, IEEE Sens. J. 1 (2001) 183–190. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Al-Ghouti, D.A. Da’ana, Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review, J. Hazard. Mater. 393 (2020) 122383. [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A. Afzal, F.L. Dickert, Transitioning from Supramolecular Chemistry to Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Chemical Sensing †, Sensors. 23 (2023) 1–13. [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





