Submitted:
02 July 2025
Posted:
03 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
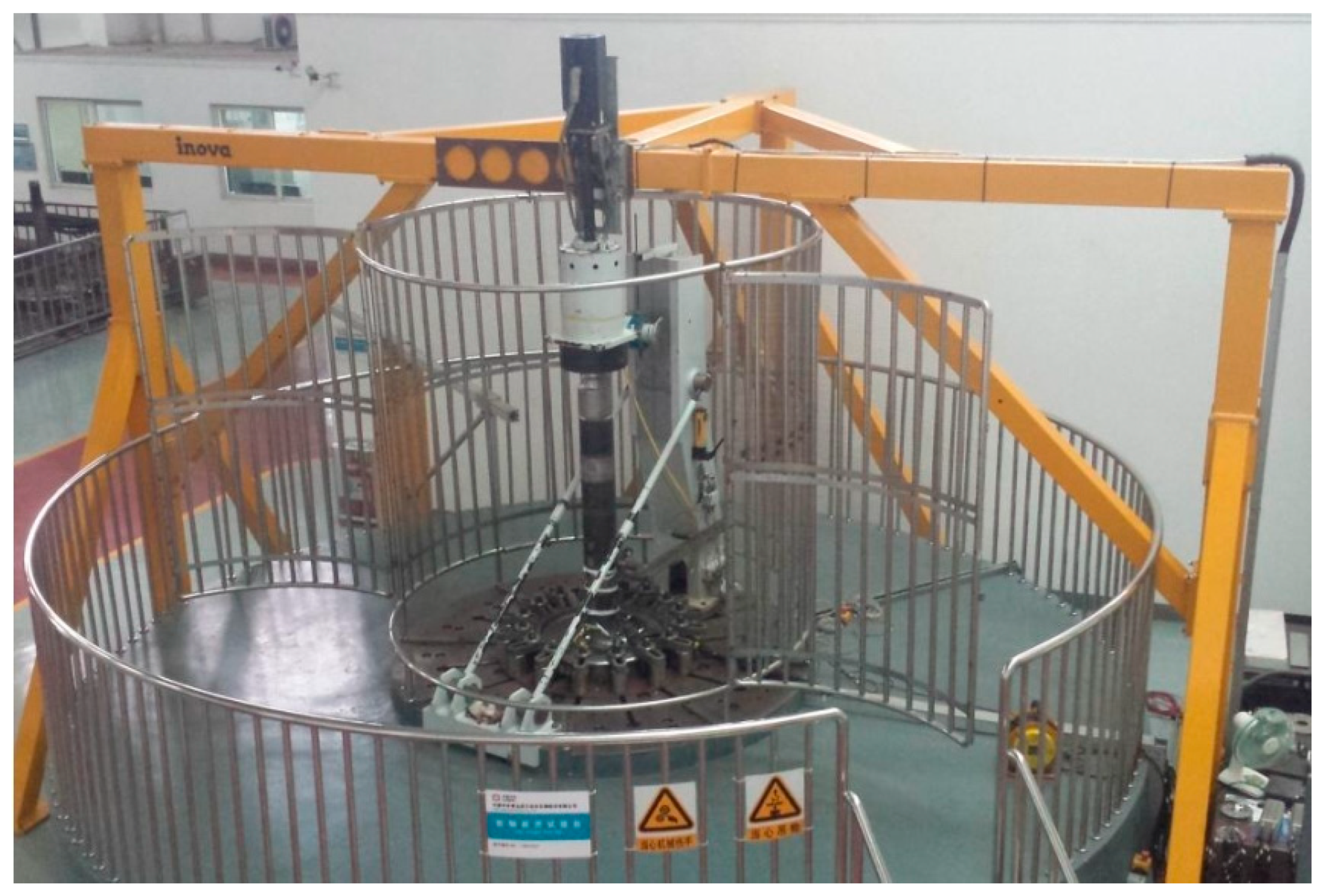
2.1. Test Bench
2.2. Prefabrication of Surface Notches
3. Results
3.1. 1st Round Fatigue Test and Results
3.2. 2nd Round Fatigue Test and Results (Notch Deepened)
3.3. 3rd Round Fatigue Test and Results (Notch Further Deepened)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Two actual axles with circumferential V-shaped notches located 130 mm from the wheel seat—having notch depths of 0.572 mm, and 0.538 mm, and corresponding stress concentration factors of 2.48, and 2.53, respectively—underwent 2 × 107 cycles of fatigue loading. Magnetic particle inspection revealed no cracks along the circumferential notch segments.
- On Axle H82-6217, the original circumferential V-shaped notch was deepened at eight positions, resulting in notch depths ranging from 0.968 to 1.132 mm and stress concentration factors between 4.12 and 4.84. After 1.02 × 107 cycles of fatigue loading, no cracks were detected at any of the notched arc segments by magnetic particle inspection.
- On Axle H31-6201, eight chordal notches located 15 mm from the wheel seat, with notch depths between 0.709 and 0.906 mm and stress concentration factors from 3.49 to 4.54, were subjected to 2 × 107 fatigue cycles. No cracks were observed at any of the artificially notched arc segments.
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glossary: High-speed rail. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Glossary:High-speed_rail (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- High-speed rail. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High-speed_rail (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Ollivier, G.; Bullock, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, N. High-Speed Railways in China: A Look at Traffic; World bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbst, U.; Klinger, C.; Klingbeil, D. Structural assessment of railway axles - A critical review. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 35, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, T.; Qian, G.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Pan, X.; Du, L.; Liu, X. Effects of inclusion size and stress ratio on the very-high-cycle fatigue behavior of pearlitic steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 142, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.Y.; Liu, G.X.; Yousefian, K.; Jing, G.Q. Track Vertical Stiffness -Value, Measurement Methods, Effective Parameters and Challenges: A review. Transp. Geotech. 2022, 37, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Qian, G.; Wu, S.; Fu, Y.; Hong, Y. Internal crack characteristics in very-high-cycle fatigue of a gradient structured titanium alloy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Duquesnay, D.; Topper, T. Notch fatigue behavior of SAE1045 steel. Int. J. Fatigue 1988, 10, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapetti, M.D.; Tagawa, T.; Miyata, T. Fatigue notch sensitivity of steel blunt-notched specimens. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2002, 25, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verreman, Y.; Limodin, N. Fatigue notch factor and short crack propagation. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2008, 75, 1320–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Sun, C.; Liu, X.; Hong, Y. Very-high-cycle fatigue behavior of a structural steel with and without induced surface defects. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 93, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagoda, T.; Bilous, P.; Blacha, L. Investigation on the effect of geometric and structural notch on the fatigue notch factor in steel welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 101, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Dong, Y.; Mu, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Fatigue limit prediction of cracked and notched specimens related to grain size. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 177, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Cho, S.S. Correlation between fretting and plain fatigue using fatigue damage gradient. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2014, 28, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zuo, Z.; Qin, W. A fretting related damage parameter for fretting fatigue life prediction. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 73, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Teng, Z.; Khan, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Effect of fretting damage on characteristics of high strength bearing steel up to very high cycle fatigue. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 217, 106526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ping, X.; Zeng, X.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Q.; Ying, S.; Hu, T. Fretting fatigue experiment and simulation of WC-12Co coating taking into account the wear effects. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 441, 128555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavuto, A.; Martarelli, M.; Pandarese, G.; Revel, G.M.; Tomasini, E.P. Experimental investigation by Laser Ultrasonics for train wheelset flaw detection. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1149, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.; Alahakoon, S.; Spiryagin, M.; Cole, C. Rail foot flaw detection based on a laser induced ultrasonic guided wave method. Measurement 2019, 148, 106922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Ni, Y.Q.; Wang, X. Real-time defect detection of high-speed train wheels by using Bayesian forecasting and dynamic model. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 139, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Su, H.; Sun, C.; Hong, Y. The behavior of crack initiation and early growth in high-cycle and very-high-cycle fatigue regimes for a titanium alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 115, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Hong, Y. High-cycle and very-high-cycle fatigue behaviour of a titanium alloy with equiaxed microstructure under different mean stresses. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2019, 42, 1950–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Su, H.; Liu, X.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale fatigue failure features of titanium alloys with equiaxed or bimodal microstructures from low-cycle to very-high-cycle loading numbers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 890, 145906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13261; Railway applications - Wheelsets and bogies - Axles - Product requirements. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2023.
- Schijve, J. Fatigue of Structures and Materials, 2nd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Ji, Z.; Zhu, M.; Ma, W.; Gao, S.; Xu, M. Notch-insensitive, tough and self-healing conductive bacterial cellulose nanocomposite hydrogel for flexible wearable strain sensor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, W.; Deng, J.; Yu, M.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, J. Hydrogen-induced delayed fracture behavior of notched 316L austenitic stainless steel: Role of grain refinement. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 166, 108880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, S. Assessment of structural materials containing notch-type defects: A comprehensive validation of the FAD-TCD methodology on metallic and non-metallic materials. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2024, 133, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, L.; Díaz, A.; Rodriguez-Aparicio, R.; Mayoral, N.; Cuesta, I.I.; Alegre, J.M. Notch sensitivity analysis of a 2205 duplex stainless steel in a gaseous hydrogen environment. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2024, 134, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Long, Z.; Cui, Y.; You, L. Strengthening effects of indentation notches on metallic glasses and their sensitivity to stress triaxiality. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2024, 645, 123187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minerva, G.; Awd, M.; Koch, A.; Walther, F.; Beretta, S. Transferability of anomaly data to fatigue properties of PBF-LB AlSi10Mg parts with different volumes. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 195, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Irfan, S.; Maleki, E.; Lee, S.; Liu, J.P.; Shao, S.; Shamsaei, N. Determining critical surface features affecting fatigue behavior of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 197, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Lim, H.J.; Sohn, H. Reference-free remaining fatigue life prediction for notched aluminum 6061-T6 plates without preliminary fatigue tests. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 229, 112569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jha, J.S.; Mishra, S.K.; Tandaiya, P. Effect of notch root radius on apparent fracture toughness of Ti6Al4V alloy: experiments and simulations. Int. J. Fract. 2025, 249, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussahra, M.S.N.; Madani, K.; Benyettou, M.; Harmel, M.W.; Aminallah, S.; Zouggar, K.; Campilho, R.D.S.G. Novel patch shape for the repair of inclined cracks in DH 36 steel structures: Numerical analysis. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Sun, C.; Hong, Y. Fatigue crack growth behavior in gradient microstructure of hardened surface layer for an axle steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 700, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Hu, F.; Xu, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Ao, N.; Su, Y.; Shobu, T.; Wu, S. Gradient residual stress and fatigue life prediction of induction hardened carbon steel S38C axles: Experiment and simulation. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 185, 108336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Qin, T.; Ao, N.; Su, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, P.; Parker, J.D.; Shinohara, T.; Chen, J.; Wu, S. Gradient residual strain determination of surface impacted railway S38C axles by neutron Bragg-edge transmission imaging. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 306, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Qin, T.; Su, Y.; He, L.; Ao, N.; Parker, J.D.; Shinohara, T.; Wu, S. Residual stress relaxation of railway gradient S38C steel during fatigue crack growth by neutron imaging and diffraction. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 193, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M. Analysis and research of fretting damage on wheel/rd2 axle interface; Dissertation/Thesis. Chengdu, China, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010.
- Murakami, Y. Metal Fatigue: Effect of Small Defects and Nonmetallic Inclusions; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zerbst, U.; Beretta, S.; Köhler, G.; Lawton, A.; Vormwald, M.; Beier, H.T.; Klinger, C.; Cerny, I.; Rudlin, J.; Heckel, T.; Klingbeil, D. Safe life and damage tolerance aspects of railway axles - A review. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2013, 98, 214–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Song, Q.; Zhou, L.; Pan, X. Characteristic of interior crack initiation and early growth for high cycle and very high cycle fatigue of a martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 758, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Pan, X.; Hong, Y. Further investigation on microstructure refinement of internal crack initiation region in VHCF regime of high-strength steels. Frattura ed Integrità Strutturale 2019, 13(49), 1-11.
- Pan, X.; Xu, S.; Qian, G.; Nikitin, A.; Shanyavskiy, A.; Palin-Luc, T.; Hong, Y. The mechanism of internal fatigue-crack initiation and early growth in a titanium alloy with lamellar and equiaxed microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 798, 140110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zheng, L.; Hong, Y. Microstructure refinement and grain size distribution in crack initiation region of very-high-cycle fatigue regime for high-strength alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Jian, Z.; Qian, Y.; Pan, X.; Ma, X.; Hong, Y. Very-high-cycle fatigue behavior of AlSi10Mg manufactured by selective laser melting: Effect of build orientation and mean stress. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 138, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Qian, G.; Hong, Y. Nanograin formation in dimple ridges due to local severe-plastic-deformation during ductile fracture. Scr. Mater. 2021, 194, 11363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Pan, X.; Qian, G.; Zheng, L.; Hong, Y. Crack initiation mechanisms under two stress ratios up to very-high-cycle fatigue regime for a selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 149, 106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, S. The fatigue behaviors of a medium-carbon pearlitic wheel-steel with elongated sulfides in high-cycle and very-high-cycle regimes. Materials 2021, 14(15), 4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Du, L.; Qian, G.; Hong, Y. Microstructure features induced by fatigue crack initiation up to very-high-cycle regime for an additively manufactured aluminium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 173, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Xu, S.; Nikitin, A.; Shanyavskiy, A.; Palin-Luc, T.; Hong, Y. Crack initiation induced nanograins and facets of a titanium alloy with lamellar and equiaxed microstructure in very-high-cycle fatigue. Mater. Lett. 2024, 357, 135769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Pan, X.; Hong, Y. New insights into microstructure refinement in crack initiation region of very-high-cycle fatigue for SLM Ti-6Al-4V via precession electron diffraction. Materialia 2024, 33, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Pan, X.; Su, T.; Long, X.; Liu, B.; Tang, Q.; Ren, X.; Sun, C.; Qian, G.; et al. A new probabilistic control volume scheme to interpret specimen size effect on fatigue life of additively manufactured titanium alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 183, 108262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Hong, Y. High-cycle and very-high-cycle fatigue of an additively manufactured aluminium alloy under axial cycling at ultrasonic and conventional frequencies. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 185, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Fu, R.; Du, L.; Pan, X. Research viewpoint on performance enhancement for very-high-cycle fatigue of Ti-6Al-4V alloys via laser-based powder bed fusion. Crystals 2024, 14(9), 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Chang, Y.; Pan, X.; Qian, G.; Hong, Y. Numerical simulation of crack surface contacting behavior with stress-induced martensitic phase transformation in very-high-cycle fatigue regime. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 198, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Tao, Z.; Long, X. Extraordinary specimen-size effect on long-life fatigue of additively manufactured AlSi10Mg. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 301, 110524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Kok, Y.; Tan, Y.J.; Descoins, M.; Mangelinck, D.; Tor, S.B.; Leong, K.F.; Chua, C.K. Graded microstructure and mechanical properties of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 2015, 97, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.K.; Ding, H.H.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, Q.Y.; Guo, J.; Zhu, M.H. Investigation on microstructure and wear characteristic of laser cladding Fe-based alloy on wheel/rail materials. Wear 2015, 330, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Jian, Z.; Pan, X.; Berto, F. In-situ investigation on fatigue behaviors of Ti-6Al-4V manufactured by selective laser melting. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 133, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Jia, Q.; Li, J.; Chong, K.; Du, L.; Pan, X.; Chang, C. Mechanical properties and parameter optimization of TC4 alloy by additive manufacturing. China Surf. Eng. 2022, 35, 215–223. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Badoniya, P.; Srivastava, M.; Jain, P.K.; Rathee, S. A state-of-the-art review on metal additive manufacturing: Milestones, trends, challenges and perspectives. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2024, 46, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Pan, S.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; He, X.; Pan, X. Anisotropic tensile behavior and fracture characteristics of an additively manufactured nickel alloy without and with a heat treatment of solution aging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 927, 148015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

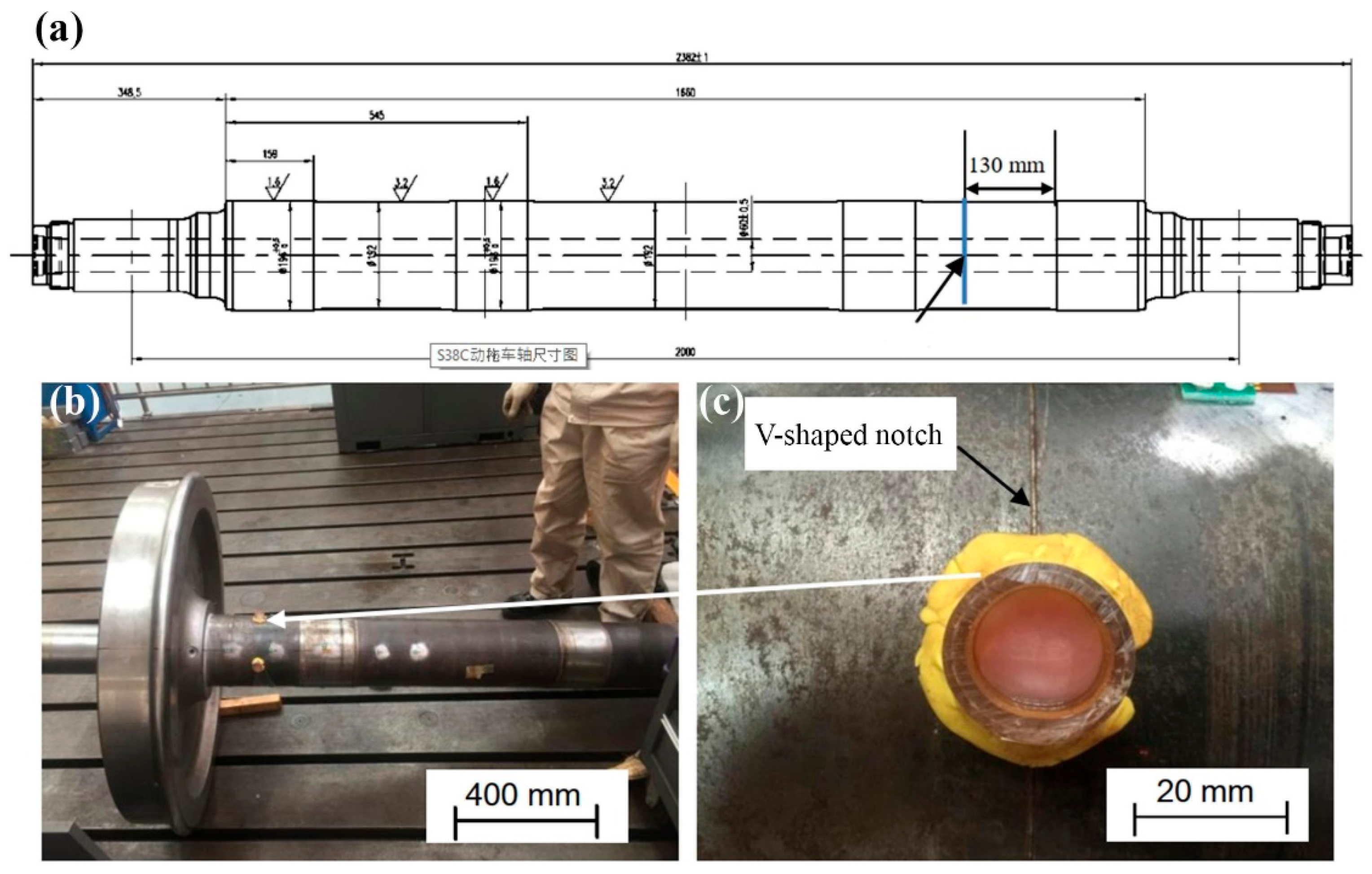
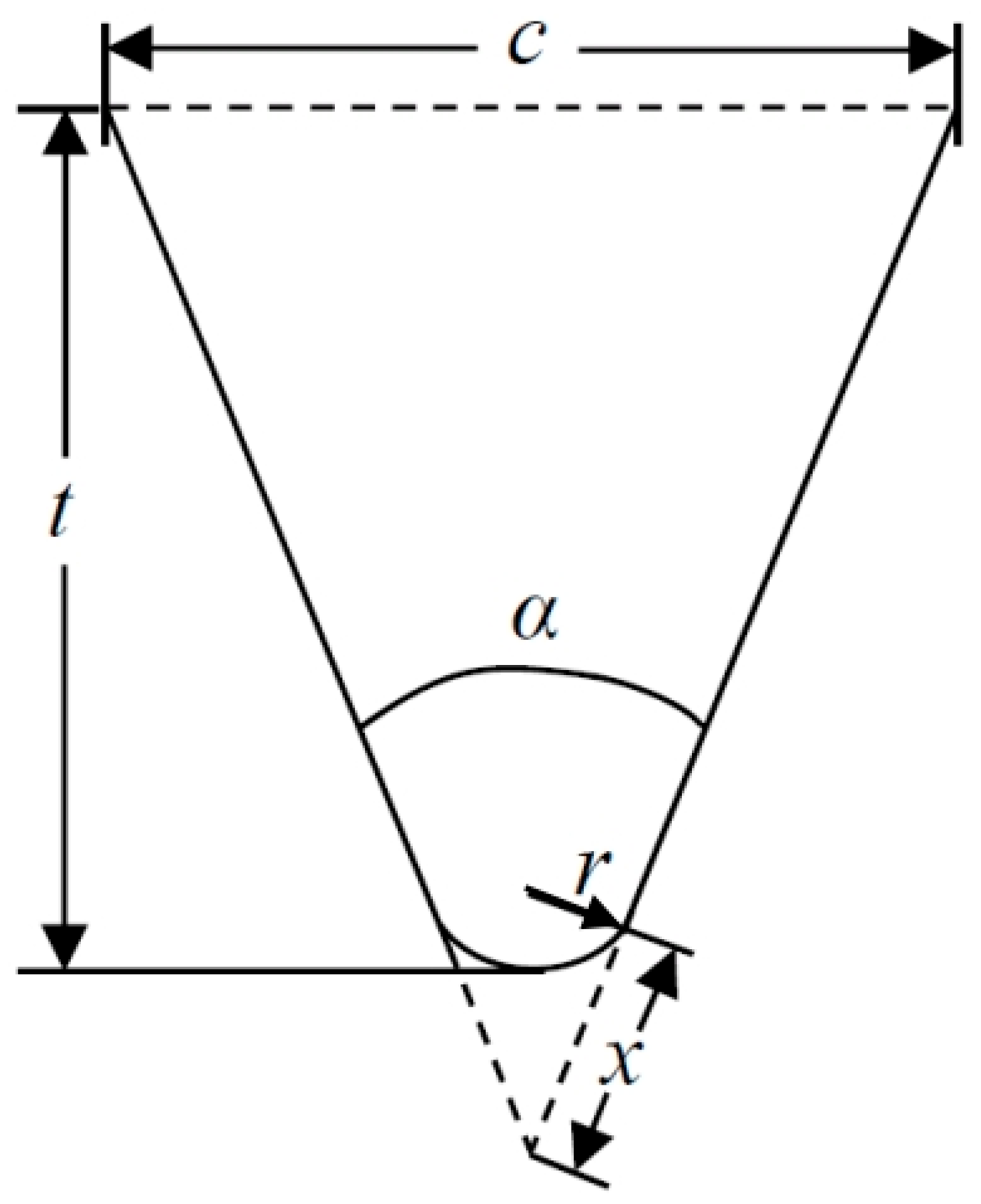
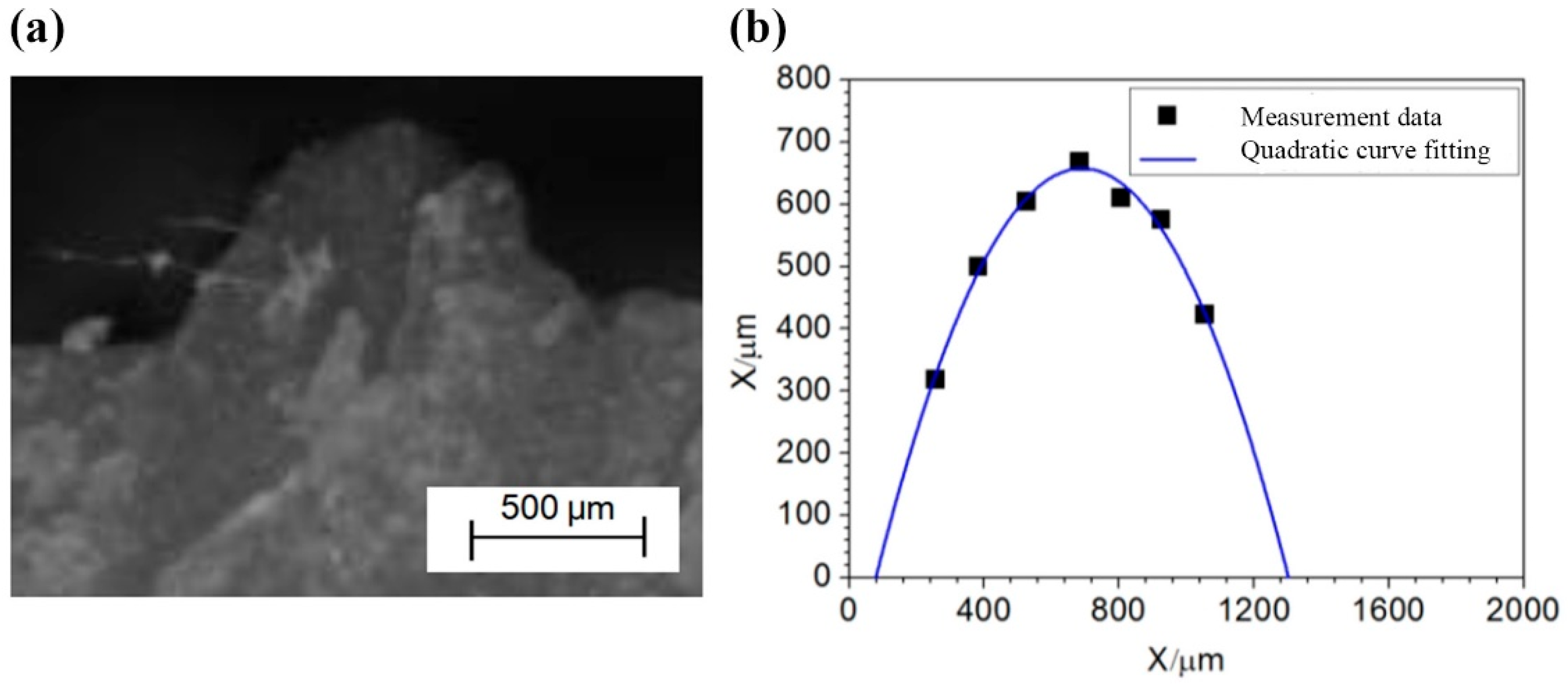
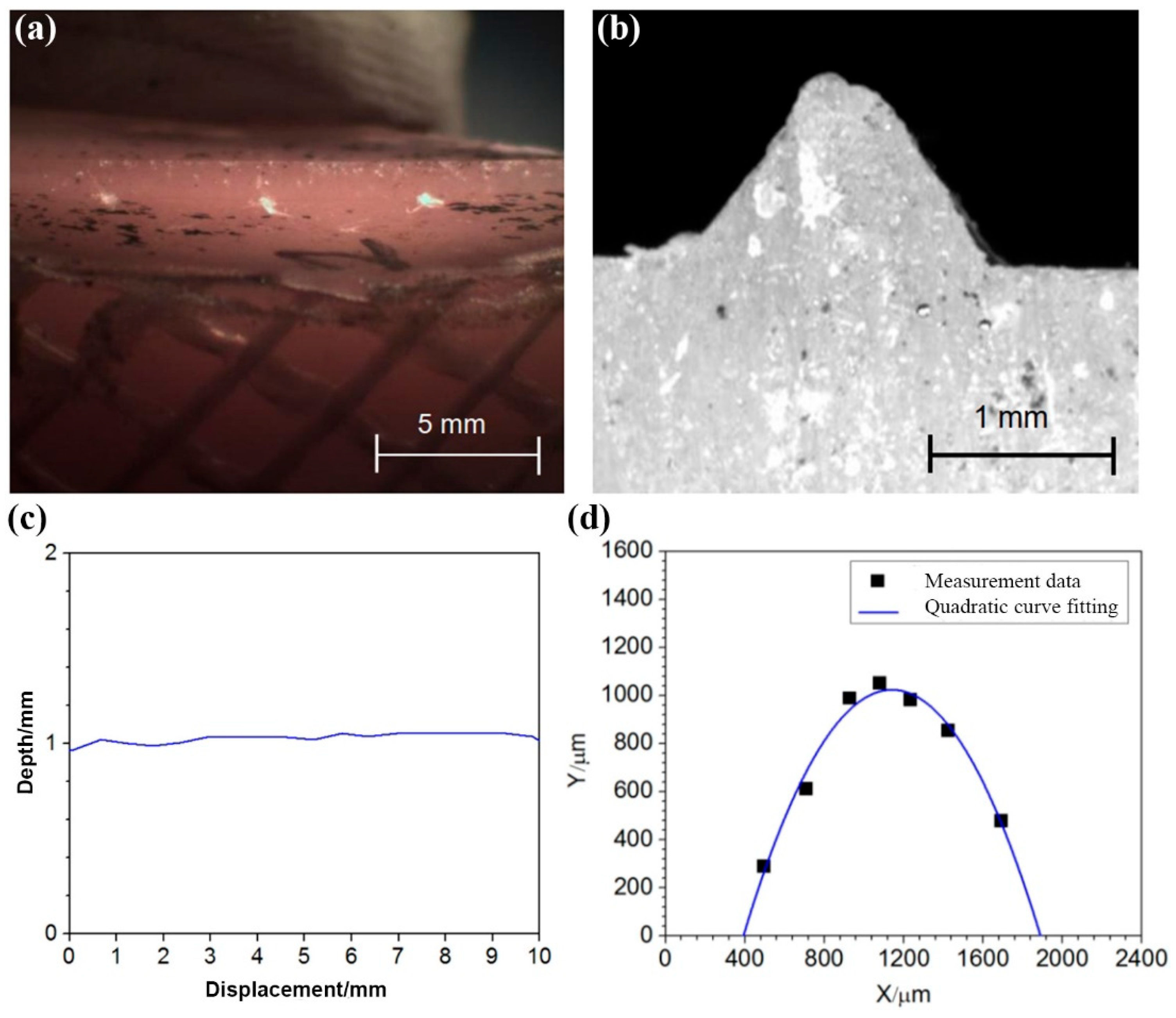
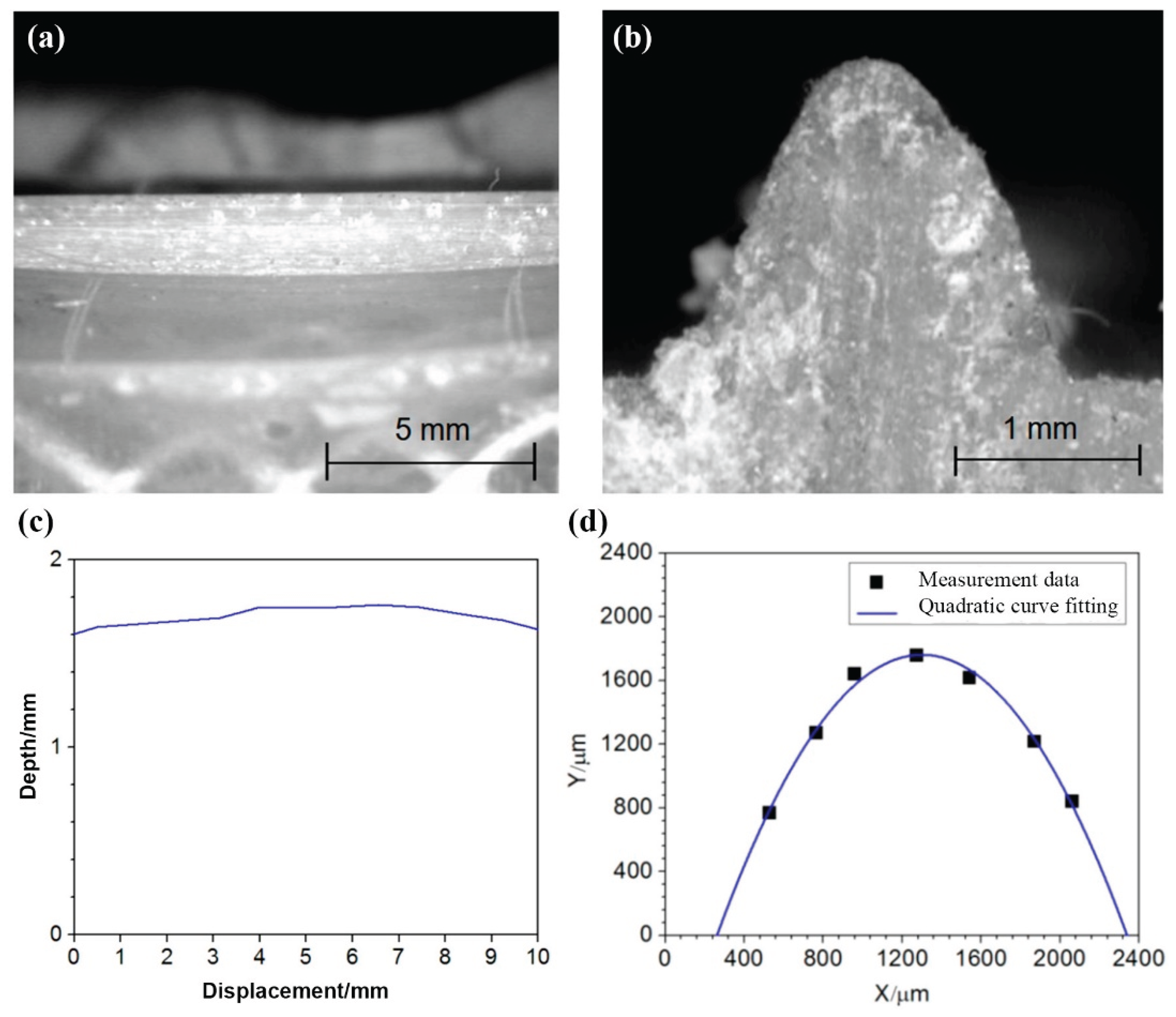
| Axle number | Notch opening angle | Notch depth/mm | Curvature radius at the notch base | SCF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H82-6217 | 88.6° | 0.572 | 0.389 | 2.48 |
| H31-6201 | 86.0° | 0.538 | 0.355 | 2.53 |
| Axle number | Loading/MPa | Number of cycles | Test result description |
|---|---|---|---|
| H82-6217 | Axle body 136 | 1×107 | No cracks detected (low-load preliminary test) |
| Axle body 240 | 1×107 | No cracks detected | |
| 1×107 | No cracks detected | ||
| H31-6201 | Axle body 240 | 1×107 | No cracks detected |
| 1×107 | No cracks detected |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




