1. Introduction
Planck-scale constants such as ℏ, , and appear across quantum mechanics, relativity, and field theory as natural units that demarcate physical limits. While these constants define scales of action, length, and energy, their physical origin remains abstract. In most frameworks, —the Planck energy—is introduced dimensionally, as a derived combination of fundamental constants. Yet its interpretation often remains speculative: is it a maximum energy? A threshold for quantum gravity? A boundary where classical theory breaks down?
Quantum Substrate Dynamics (QSD) [
1] provides a structural framework in which Planck energy arises not from dimensional analysis alone, but from the causal and geometric constraints of a coherence-bound substrate. In QSD, energy is not an independent quantity, but the measurable consequence of coherent offload within a Lorentz-invariant medium. Coherence structures—mass-phase configurations—can only persist, move, or interact if they remain recoverable within bounded regions of the substrate. These regions are defined by the coherence envelope
, which governs the minimal support volume for causally valid structure.
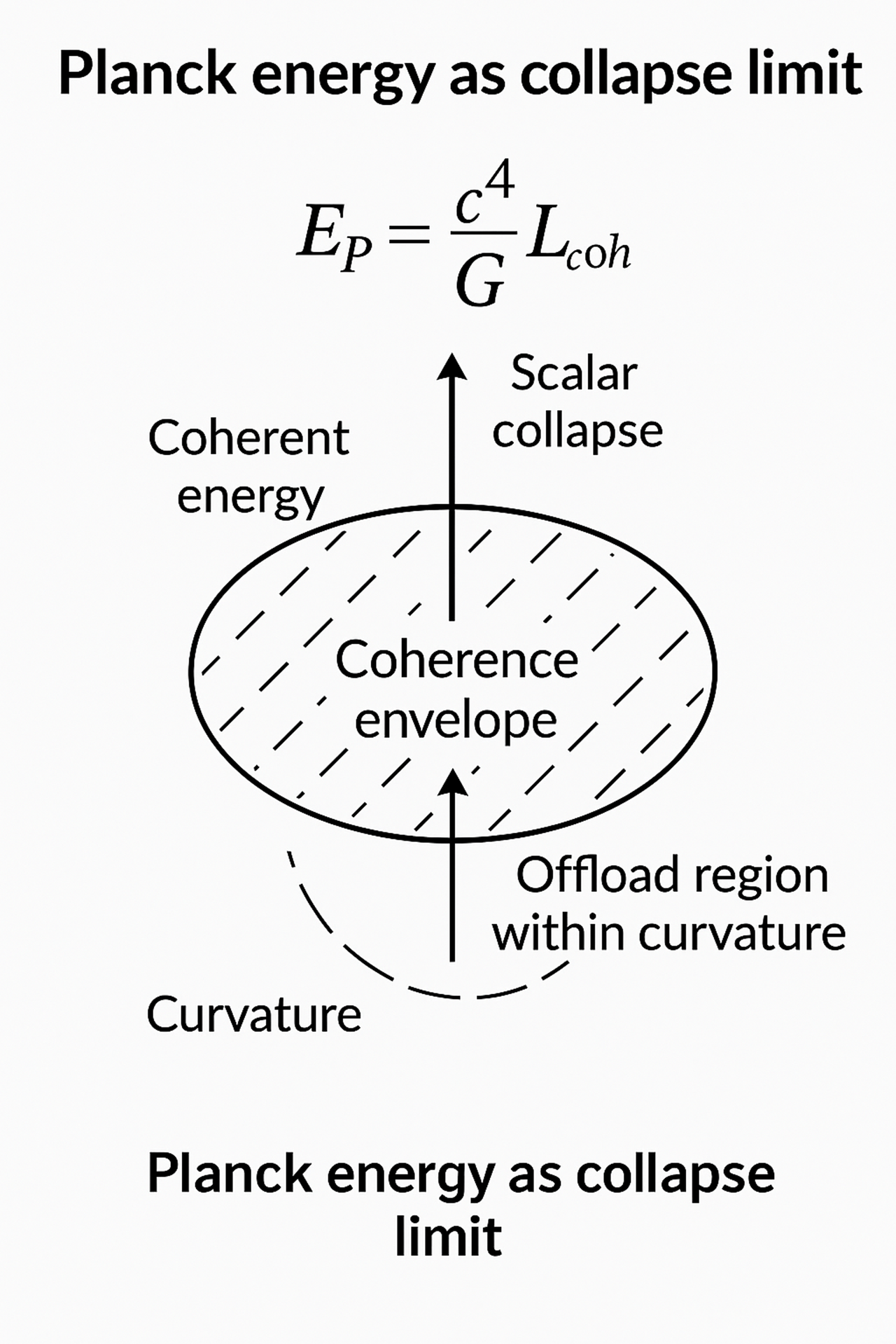
In this context, Planck energy is reinterpreted as the structural collapse limit: the maximum coherent energy density that the substrate can support within a single coherence envelope before scalar collapse becomes inevitable. The expression
is not a theoretical maximum in the abstract, but a physical saturation threshold—the point at which internal curvature and tension exceed the substrate’s ability to maintain phase-locked structure. Beyond this limit, coherent mass-phase configurations cannot persist and must offload energy into the surrounding substrate, resulting in emission, decay, or geometric disintegration.
This paper develops the structural interpretation of as a collapse threshold within QSD. We derive its form from first principles, link it to the previously established coherence envelope, and explore its role in governing the limits of mass stability, waveform persistence, and energetic containment. The reinterpretation of Planck energy as a causal boundary—rather than a speculative frontier—grounds it within a physical model of coherence, recovery, and structural failure. The result is a testable, geometrically constrained, and causally meaningful explanation for one of the most fundamental constants in modern physics.
While this work introduces a novel substrate-based framework, it acknowledges the long-standing efforts to understand collapse, coherence, and the role of physical constants in both classical and quantum contexts. The behavior of quantized emission from saturating wave envelopes has been explored in nonlinear optical systems [
8], and decoherence has been widely discussed as a mechanism for classical emergence from quantum substrates [
9]. The philosophical and dimensional status of constants such as
ℏ and
G continues to evolve across multiple theoretical frameworks [
10]. The present formulation does not directly rely on these treatments, but recognizes them as part of the broader effort to contextualize quantization, coherence, and physical law.
2. Materials and Methods
This manuscript was developed through a combination of theoretical derivation, substrate conservation modeling, and coherence-structured analysis. The expression for Planck energy was formulated by the author using first-principles substrate dynamics, with all mathematical relationships derived to preserve causal consistency, empirical falsifiability, and structural compatibility with both relativistic constraints and quantized behavior.
In support of the editorial process, generative AI tools—specifically OpenAI’s ChatGPT (version GPT-4o, 2025)—were used to assist in:
Generating illustrative figures based on the author’s conceptual framework, with iterative refinement to ensure fidelity to the substrate-based dynamics of the model,
Researching, validating, and cross-referencing related scientific concepts to improve accuracy, contextual alignment, and clarity,
Summarizing and formatting externally sourced material already selected by the author.
No original theoretical contributions were generated by the AI system; all scientific claims, hypotheses, derivations, and interpretations were authored and reviewed by the human researcher. The use of ChatGPT is disclosed in alignment with journal policy for transparency in the writing process.
3. Discussion
3.1. The Collapse Threshold as a Physical Limit
In the standard view of high-energy physics, Planck energy
is regarded as a symbolic upper bound—an extrapolated scale at which quantum and gravitational effects are presumed to unify, often without a clearly defined physical mechanism. Within the Quantum Substrate Dynamics (QSD) framework, however, this threshold gains a specific structural meaning: it is the
maximum coherent energy supportable by a single substrate envelope before rupture occurs.
This expression is not speculative; it follows directly from substrate conservation and geometry. It reflects a physical saturation point: the total energy that a coherence envelope of size can carry before its internal phase structure exceeds the substrate’s curvature compliance. In this model, collapse does not occur because of mathematical singularities or undefined field behavior—it occurs because the substrate can no longer reconfigure fast enough to maintain coherence under the load.
This yield behavior is not continuous or reversible. Once the threshold is surpassed:
The envelope destabilizes,
Scalar pacing is broken,
Energy is offloaded either as quantized emission (e.g., radiation) or as structural rupture (e.g., TIGB or gravitational-wave precursor).
Unlike in general relativity, where black hole collapse leads to undefined conditions hidden behind event horizons, QSD provides a mechanism for observable collapse precursors and coherent emission boundaries. Collapse is not an abstract divergence—it is a phase response to substrate saturation. The system fails not because of infinite density, but because the region can no longer store coherence structure within the allowed pacing cycle. Scalar recovery is outmatched by the energy stored in the transverse envelope.
The collapse threshold thus represents a causal limit on the substrate’s capacity to maintain phase continuity, not a fundamental breakdown of theory. It defines a point beyond which no internal structure can remain stable without reorganizing or offloading. This offload may be serial (burst emissions), layered (rebound shells), or catastrophic (coherence fracture), depending on the local topology and pacing gradients.
As such, the Planck energy in QSD is no longer a dimensional construct—it is a directly interpretable physical limit tied to geometric, causal, and recoverable substrate behavior. It is falsifiable through collapse structure, spectral emission patterns, and the presence of quantized ejection events at known energy densities.
3.2. Toward a Mathematical Formalism for Collapse Dynamics
The preceding sections have shown that Planck energy in QSD represents the maximum energy that a coherence envelope of size can sustain before rupture, defined by the saturation of scalar pacing and transverse energy support. To model the dynamic behavior of this collapse more formally, we now outline a minimal mathematical framework that captures the essential features of envelope evolution near the collapse limit.
3.2.1. Envelope Energy Evolution
Let
denote the local coherence tension density in a region of the substrate.
1 The total energy contained within a coherence envelope of spatial extent
is then:
where
V is the coherence-supporting volume at time
t. As transverse energy is injected or accumulated into the region,
increases and approaches a maximum supportable value
set by the structural yield threshold:
This provides a dynamic criterion: when the local energy density exceeds this threshold, the envelope is no longer recoverable and will yield.
3.2.2. Collapse Condition and Recovery Lag
The scalar pacing constraint defines a recovery interval:
A collapse event is triggered when the energy injection or internal reconfiguration rate exceeds the recoverable pacing of the scalar mode:
This defines a local collapse rate ceiling: any process that delivers energy faster than this limit must result in scalar rupture or yield.
3.2.3. Envelope Instability Growth
We may define an instability field
which evolves under coherence strain. Its dynamics obey a driven nonlinear diffusion equation of the form:
where:
is a coherence diffusivity constant (analogous to how fast phase stress propagates),
couples local energy density to rupture likelihood,
models substrate damping or recovery.
Collapse onset occurs when
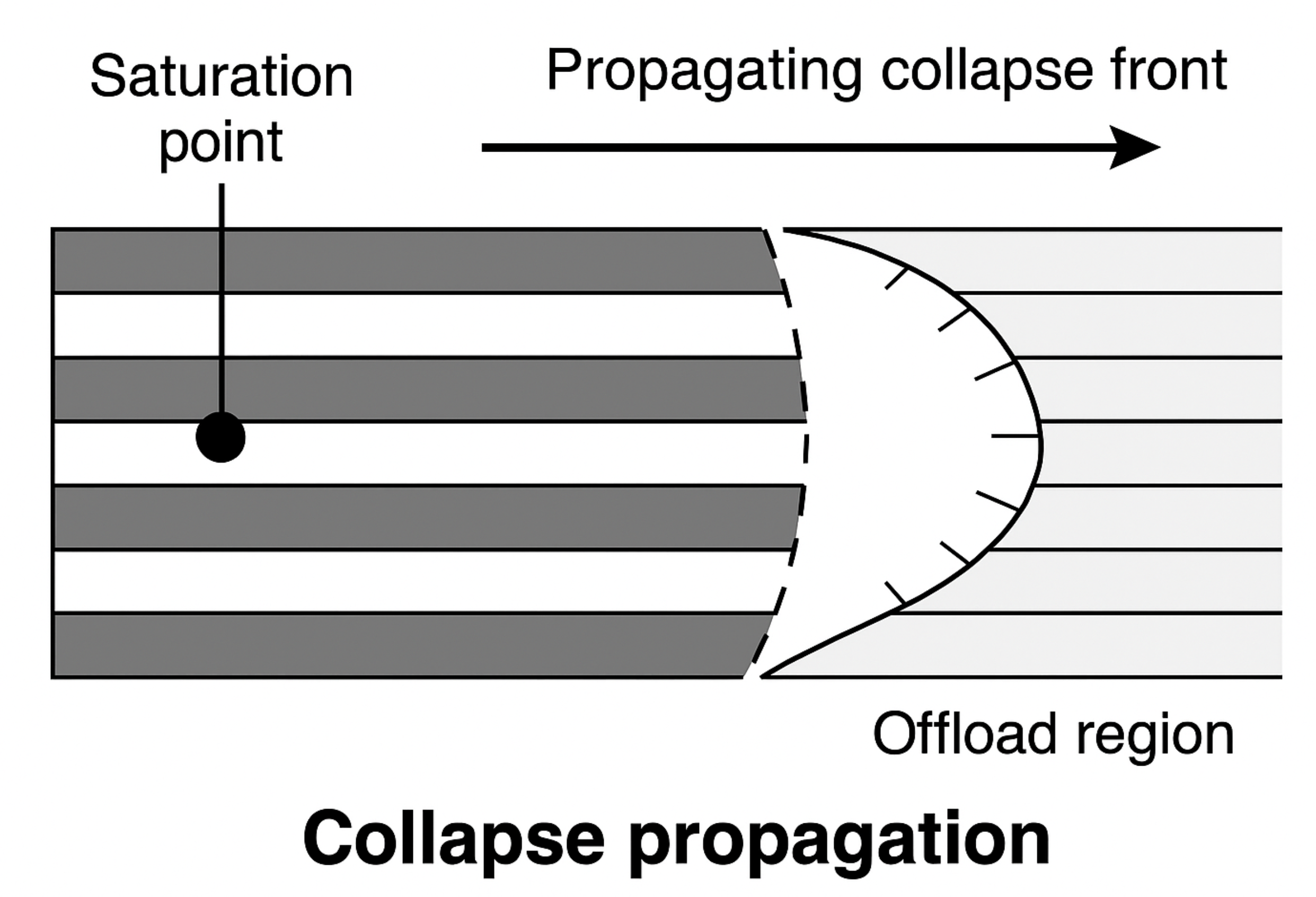
, corresponding to a coherence fracture front that propagates through the envelope. Once rupture is triggered locally, the collapse front propagates causally through the envelope as a scalar phase discontinuity. This front expands outward from the saturation point, limited by the scalar recovery speed
, and reshapes the coherence configuration as it passes. This resembles domain wall rupture in condensed matter systems or mode-locked pulse fronts in optical media. The spatial spread is not instantaneous, but layered and structured, allowing partial offload in concentric or asymmetric bursts depending on local curvature, see
Figure 1.
3.2.4. Post-Rupture Recovery and Memory Effects
Whether rupture originates at the outer boundary of a coherence envelope or within its interior, the affected substrate region enters a scalar recovery phase. During this interval, no new coherent mass-phase structure can form until local phase alignment is restored. The recovery timescale is bounded below by the scalar pacing limit:
but full structural reset may require multiple cycles depending on rupture intensity, envelope topology, and residual tension gradients.
We model the local recovery state with a coherence restoration function
, normalized such that
represents a ruptured region and
represents full recovery of local substrate coherence. A simple first-order temporal model can be written as:
where:
is the characteristic recovery time, typically ,
is a damping or inhibition term representing lingering scalar strain or residual interference from prior collapse.
In the absence of secondary rupture or active inhibition (
), the solution approaches exponential recovery:
indicating that even after causal pacing permits substrate reuse, full structural coherence is only asymptotically restored. In systems with partial rupture or nonlinear recoil,
may remain non-zero for extended intervals, delaying envelope reuse.
Because the coherence substrate is causal and continuous, the rupture location—whether at the core, shell, or mid-envelope—only determines the geometry of the recovery front, not its physics. The recovery field evolves locally, ensuring that both surface-triggered and interior-origin collapse obey the same pacing and memory constraints.
Importantly, the substrate retains partial memory of prior coherence geometry during this process. This memory may manifest as structural bias for future envelope formation, preferred symmetry axes, or altered rupture thresholds in subsequent offload events. These effects resemble residual topologies in post-collapse domain realignment, and may explain observable coherence imprinting in burst emissions or collapse echoes.
3.2.5. Emission Profile and Envelope Offload
Once rupture begins, energy is released in quantized bursts, structured by the coherence geometry of the mass-phase knot. The offload power can be approximated as:
where
is a normalized burst profile shaped by envelope asymmetry and scalar delay gradients, and
accounts for partial rupture or phased re-emission.
This function determines the observable signature of the event: its rise time, spectral distribution, and recurrence behavior.
3.2.6. Summary and Future Directions
This formalism is not yet a complete set of QSD field equations, but it demonstrates how core substrate variables—energy density, pacing speed, coherence diffusivity, and structural geometry—can be coupled to model collapse and offload dynamics. Extensions of this model may include:
Nonlinear recovery gating with temporal hysteresis,
Geometric dependence of under envelope deformation,
Tensorial modeling of phase stress and directional rupture propagation.
Ultimately, this framework aims to replace singularity-based collapse models with a structurally recoverable, quantized, and falsifiable description of mass-phase envelope failure under coherent substrate limits.
3.3. Explicit Treatment of Quantization
The coherence envelope length plays a central role in determining the energy capacity, pacing constraints, and collapse behavior of mass-phase structures in QSD. While previous sections have treated as a continuous variable to establish general saturation dynamics, the substrate’s structural properties suggest that only a discrete set of envelope configurations are physically stable. This leads naturally to a form of geometric mass quantization.
3.3.1. Quantized Envelope Modes
In a conserved coherence substrate, the envelope must maintain:
- (1)
Internal phase symmetry,
- (2)
Sufficient scalar pacing to prevent rupture,
- (3)
Boundary continuity across wavefronts.
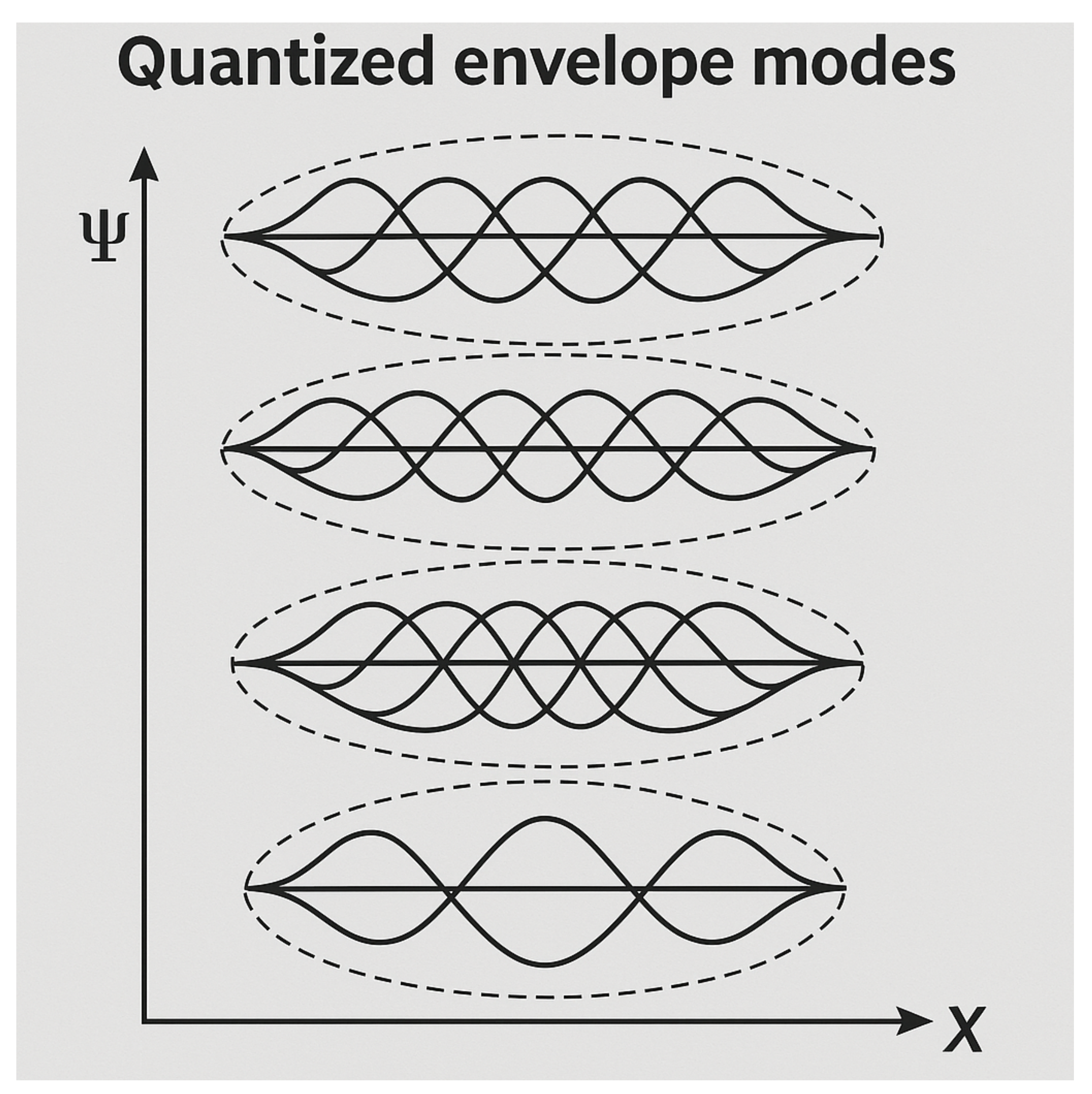
These conditions constrain the allowed spatial forms of stable coherence envelopes to standing-wave-like structures that satisfy both geometric closure and causal pacing. As a result, only certain values of support persistent, phase-locked mass-phase configurations.
We denote these quantized envelope modes as:
where
is the minimum coherence length scale supported by the substrate (often set by the structural Planck length), and
defines the envelope mode number.
Each quantized
defines a distinct energy limit:
This relationship suggests that different particle or mass states correspond to stable coherence configurations occupying distinct envelopes, each with its own energy support, pacing interval, and rupture threshold.
These allowable envelope configurations are visualized in
Figure 2, which shows discrete standing-wave modes constrained within the same coherence boundary
. Only these quantized modes can persist as recoverable mass-phase structures within the substrate.
3.3.2. Implications for Mass and Energy Discreteness
Mass in QSD is not a pointlike quantity but a persistent, structured phase configuration within a coherence volume. Quantization of therefore implies quantization of:
Supported energy values (mass–energy equivalence),
Recovery pacing (Planck time variants),
Emission thresholds (burst energy spectra),
Stability domains (permitted particle geometries).
This creates a discrete lattice of allowed structural mass states. Unstable or non-permitted values either fail to form, decay into lower modes, or offload energy until a stable envelope configuration is reached.
3.3.3. Observational and Experimental Relevance
Quantization of introduces a testable structure to the spectrum of mass and energy. If each stable matter state corresponds to a quantized coherence envelope, we expect:
Mass thresholds and cutoffs at regular geometric intervals,
Spectral emission features during collapse events tied to envelope mode transitions,
A finite spectrum of stable phase knots matching observed particle states.
This provides a mechanism to explain why only certain mass values occur in nature and why high-energy events emit in structured, quantized bursts.
3.3.4. Summary
In QSD, is not a continuously tunable parameter but a geometrically constrained and causally gated structure. Only discrete envelope modes can maintain phase coherence under recoverable substrate conditions. This leads naturally to mass quantization as a geometric effect, offering a substrate-level explanation for particle spectra, energy levels, and coherent emission thresholds.
3.4. Structural Origins of G: Compliance, Not Constant
In classical physics, Newton’s gravitational constant G is treated as a fixed coupling parameter—a universal scaling factor inserted into the gravitational law without explanation of its physical origin. Within the QSD framework, however, G is revealed to be a compliance factor of the substrate: a structural property that reflects how easily the substrate yields to curvature imposed by local phase tension.
This reinterpretation is rooted in the structural derivation of Planck’s constant
ℏ from substrate geometry. In QSD,
ℏ emerges from the offload structure of a coherence envelope, governed by modal propagation speeds and coherence size:
Rearranging, we obtain a structural expression for
G:
Here, is the transverse coherence propagation speed (governing spatial energy transfer), is the scalar recovery speed, which governs how fast the substrate resets its internal coherence after an energy offload or collapse event. It sets the minimum interval between successive energy transfers within a coherence envelope. , is the coherence support length, and ℏ is the minimum offload unit—a structural action quantum. This shows that G is not a fixed coupling inserted externally, but a derived ratio from internal substrate properties.
This has several critical implications:
Geometric dependence: G scales with , the coherence area. In compact, saturated systems (e.g., near black hole cores), compresses, leading to a reduced effective G—i.e., tighter curvature compliance.
Causal pacing control: The recovery speed limits how fast the substrate can support scalar reconfiguration. Slower pacing increases the apparent compliance, modulating G in time-dependent systems.
Modal embedding: The transverse propagation speed governs how rapidly coherence tension spreads spatially, and appears raised to the fourth power—highlighting its dominant role in determining gravitational stiffness.
This expression also explains why G appears constant under typical conditions: in most systems, , , and remain approximately stable across moderate curvature regimes. However, QSD predicts that G will vary across extreme curvature gradients, such as in neutron stars, galactic halos, or high-strain merger zones.
Furthermore, G acts analogously to an elastic modulus in material science—a measure of how much phase curvature the substrate tolerates per unit energy tension. Systems with higher phase gradient curvature (strong coherence strain) experience a “stiffer” substrate, corresponding to a lower effective G.
This structural derivation also aligns with the Planck energy expression in QSD:
Substituting the above expression for
G yields:
This confirms that gravitational coupling, quantum action, and the energy saturation limit are all structurally linked by substrate coherence rules. The same coherence envelope geometry that sets the offload quantum
ℏ also governs gravitational stiffness and collapse energy thresholds. There is no circularity—only a triangulated conservation relationship embedded in substrate dynamics, see Figure
Section 3.4.
[scale=4] (A) at (0.5, 1); (B) at (0, 0); (C) at (1, 0);
[thick] (A) – (B) – (C) – cycle;
t (0.5, 0.5) Coherence Length;
above=2pt] at (A) ; below left=1pt] at (B) ; below right=1pt] at (C) ;
In this view, gravity is not a force transmitted through spacetime, but the observable result of local substrate compliance under phase tension. G is not constant—it is a field- and structure-dependent parameter defined by causal pacing, coherence geometry, and energy offload rate. This perspective leads naturally to predictions of G-variation across space and scale, potentially detectable in astrophysical systems, merger dynamics, or even engineered coherence media.
In summary, QSD removes G from the list of unexplained constants. It becomes a measurable expression of coherence field geometry—a compliance metric of a conserved, phase-structured universe.
3.5. Planck Energy and Scalar Recovery Limits
In the Quantum Substrate Dynamics (QSD) framework, Planck energy does not emerge from dimensional analysis or quantum gravity heuristics—it represents the maximum energy that a coherence envelope can sustain without rupture, determined by the causal structure of scalar recovery. This limit arises from the interplay between transverse energy support and the timing constraints imposed by the substrate’s scalar mode.
The scalar recovery speed
governs how rapidly the substrate can reset a coherence region after an offload event. This timing constraint defines the minimum period required between coherent energy transfers in the same region. When combined with the envelope geometry
, this sets a causal limit on energy pacing:
This is the physical interpretation of Planck time in QSD: it is the
minimum coherence recovery interval permitted by the substrate at full saturation. The Planck energy is then the maximum amount of energy that can be coherently supported and released within this interval, subject to the offload throughput imposed by the transverse mode:
This relationship confirms that is not merely a high-energy boundary but a pacing ceiling—the point beyond which energy cannot be stored and released in a single coherence cycle without disrupting the causal integrity of the substrate. Once this threshold is crossed, the substrate cannot recover fast enough to maintain coherence, leading to rupture, emission, or scalar cascade.
Importantly, this view links Planck energy directly to quantization: energy becomes discretized because the substrate enforces temporal separation between offload events. The Planck interval is the causal enforcement of this separation, not a mathematical artifact. The scalar recovery speed thus determines not only collapse limits but also the coherence-driven basis for energy quantization.
In this context, the existence of defines a hard ceiling on causal energy throughput. No process—astrophysical or engineered—can release more than into a single coherence region without violating the structural constraints of the substrate. This makes a falsifiable and physically testable limit, rather than a theoretical curiosity.
3.6. Planck Energy and Coherence Geometry
The QSD expression for Planck energy,
establishes a direct relationship between the maximum coherent energy and the geometric structure of the mass-phase envelope. In this formulation,
is not merely a dimensional placeholder—it represents the physical coherence support scale that defines the spatial extent over which transverse energy can be maintained without violating scalar pacing. As such, the energy capacity of a mass-phase structure is explicitly geometry-bound.
This insight reframes the origin of mass stability. A mass-phase knot can only persist if its internal waveform configuration fits within a coherence envelope that supports the tension geometry required to maintain causal offload pacing. If the structure is too compact (i.e., is too small), transverse energy accumulation exceeds recoverable coherence, resulting in rupture. If the structure is too diffuse, scalar recovery becomes inefficient, and the mass-phase loses internal symmetry and coherence, leading to instability or decay.
Therefore, represents not only a maximum energy threshold but also an upper bound on the geometric density of mass-phase configurations. This creates a well-defined phase space for allowable mass structures:
Stable mass arises only when coherence geometry supports internal waveform symmetry within a bounded envelope.
Masses that exceed must emit energy or reconfigure to remain coherent.
Masses below a critical threshold may lack the internal tension necessary to maintain coherent phase alignment, leading to dispersal or failure to form.
This framework provides a structural mechanism for known mass thresholds in astrophysical and particle-scale systems. It offers a geometric explanation for the upper mass limits of stars, the instability of supermassive neutron cores, and the exclusion of high-energy bound states beyond collapse thresholds.
Moreover, this coherence-based interpretation implies that the energy signature of any emission event will encode the geometry of the underlying phase st
3.7. Connecting with Particle Physics
While this paper does not attempt to reproduce the Standard Model mass spectrum, it introduces a structurally grounded mechanism that may underlie mass quantization and discrete emission behavior in particle-scale systems. In QSD, stable mass-phase configurations are supported within coherence envelopes of quantized spatial extent, defined by the relation:
where
is the minimum allowable coherence support length set by substrate constraints. Each envelope mode
has an associated Planck energy ceiling:
defining the maximum energy that can be stored coherently in that envelope before rupture or offload occurs. If collapse is triggered, the emitted energy is constrained not only by
, but by the internal coherence mode of the structure.
We define a discrete energy emission condition:
where:
n is the internal coherence mode number,
is the scalar recovery speed,
is the effective offload frequency of that mode.
This relation implies that:
Emission occurs in quantized energy packets tied to internal envelope modes,
Only specific values are supported per domain,
There is a maximum , set by envelope saturation.
Mass quantization in this framework arises naturally: only envelopes that satisfy both geometric support and scalar pacing can maintain stable mass-phase structure. Others will rupture or decay into lower-mode configurations.
This model suggests a physically motivated path to mass discreteness, independent of symmetry-group postulates. Energy quanta arise from substrate pacing and offload structure, not field operators. Although QSD does not yet map these envelope modes to known particle masses, this framework offers a causal, falsifiable mechanism for:
In this context, particle-like behavior becomes a manifestation of coherent substrate geometry—an emergent structure bounded by Planck-scale causality and substrate compliance. Future work will explore specific envelope solutions and their correspondence to observed particle mass states.
3.8. Experimental and Observational Windows
The QSD interpretation of Planck energy as a structural collapse threshold enables a range of falsifiable predictions that distinguish it from both classical gravitational theory and quantum field models. Because corresponds to the maximum energy supportable within a coherence envelope of size , its saturation should produce distinct, observable signatures across astrophysical and possibly laboratory regimes.
3.8.1. Astrophysical Collapse Events
High-energy astrophysical phenomena provide natural laboratories for testing coherence rupture behavior. Events such as gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), fast radio bursts (FRBs), and certain types of core-collapse supernovae are characterized by sharp, structured energy release consistent with QSD’s predicted offload behavior.
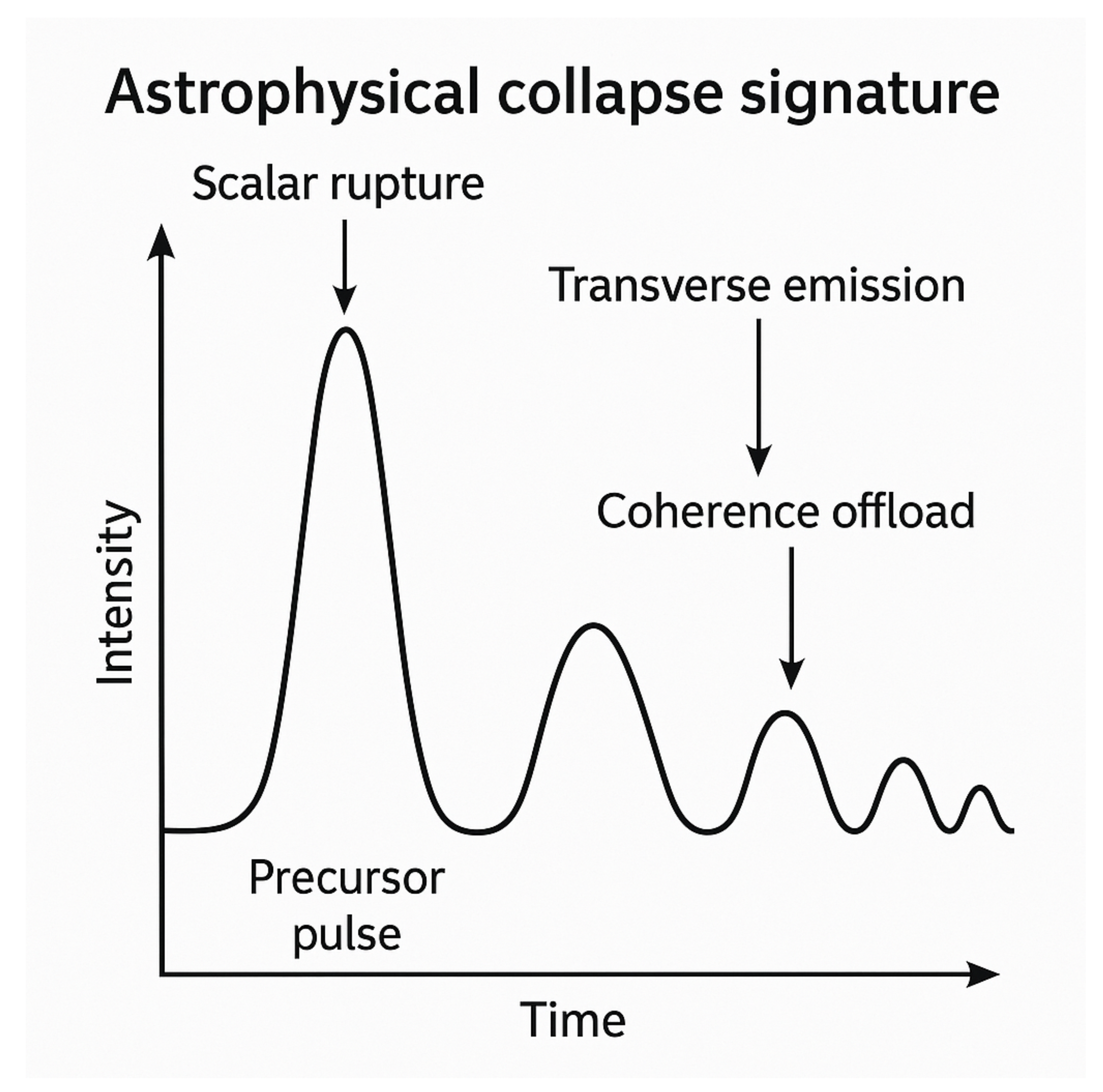
In particular, the following signatures are consistent with coherence envelope failure:
Quantized or layered burst emissions, indicating serial or radial offload from a collapsing envelope.
Scalar precursor pulses that precede photon release, consistent with scalar mode pacing breaking before transverse rupture.
High-energy terminal events with energy approaching or exceeding known neutron star mass limits, suggesting trench saturation or TIGB-class (trench-induced gamma burst) collapse.
These events should not be smooth or continuous, as predicted by general relativity, but structured and phase-encoded, with time-resolved features that reflect internal symmetry failure and quantized reconfiguration. QSD further predicts that these emissions will reflect the coherence geometry of the collapsing envelope, encoding symmetry, compression mode, and scalar pacing in the burst profile, see
Figure 3.
3.8.2. Black Hole Precursors and Merger Frustration
In black hole mergers or near-horizon regimes, QSD predicts coherence trench saturation may lead to merger frustration or scalar offload before full event horizon formation. This opens the possibility for:
Pre-merger emissions that do not align with general relativity’s predictions.
Nonlinear delay or recoil patterns in ringdown waveforms, indicating temporary trench collapse or offload buffering.
Energy dissipation without apparent mass loss, consistent with scalar yield that does not couple to external observers in the electromagnetic domain.
Precision gravitational wave observation (e.g., from LIGO, Virgo, or future missions) offers an avenue for testing these predictions through waveform analysis and comparison with classical merger models.
3.8.3. Laboratory-Scale Analogues
Though the full Planck-scale collapse process is not reachable in current experimental systems, analog coherence structures may offer indirect paths toward testing substrate behavior:
Nonlinear laser compression in structured media may allow coherence envelope saturation and rupture analogues in photonic systems.
Superfluid or BEC phase collapse, especially in toroidal geometries, may mimic scalar gating, recovery lag, and quantized offload behavior.
Fracture dynamics in tensioned lattices may serve as classical substrate analogs, especially when coupled with phase-controlled energy loading.
QSD predicts that in all such systems, there will be a coherence saturation limit beyond which energy cannot be supported in a single domain without triggering a quantized release or phase reset. Identifying such behavior in engineered systems may offer a proof-of-concept for structured yield and coherence threshold mechanics.
3.8.4. Summary
Together, these observational and experimental windows offer testable avenues for distinguishing QSD’s structural interpretation of Planck energy from traditional models. In each case, the critical prediction is that collapse and emission are not continuous—but quantized, structured, and geometrically constrained. Planck energy becomes, not an abstract boundary, but a concrete and falsifiable limit in the causal substrate dynamics of mass, radiation, and collapse.
3.9. Reinterpreting Planck Units Structurally
In conventional physics, Planck units—length, time, and energy—are derived through dimensional analysis, combining fundamental constants ℏ, G, and c into quantities with units of space, time, and energy. These values are often interpreted as heuristic thresholds beyond which classical theories fail, but their physical origin remains undefined. In QSD, these units acquire clear structural interpretations grounded in the substrate’s causal and geometric constraints.
3.9.1. Planck Length as Coherence Support Radius
In QSD, the Planck length is not a minimum position scale or a quantum of spacetime. It is the characteristic length scale of a fully saturated coherence envelope, below which the substrate cannot maintain stable phase alignment. This coherence length defines the minimal spatial region within which a mass-phase knot can form and persist. Structures smaller than cannot sustain transverse tension under recoverable scalar pacing and therefore fail to stabilize.
3.9.2. Planck Time as Scalar Recovery Interval
Planck time
is traditionally viewed as the smallest meaningful unit of time. In QSD, it has a causal and functional role:
This is the minimum time required for scalar recovery to reset a coherence envelope of length . It represents the substrate’s gating interval: the shortest duration between energy offload events that preserves causal coherence. No energy structure can cycle faster than this interval without disrupting the substrate’s phase continuity. This pacing constraint enforces quantization as a structural necessity.
3.9.3. Planck Energy as Collapse Limit
As developed in earlier sections, Planck energy is interpreted in QSD as the maximum energy that can be coherently stored in a region of size
before rupture occurs:
This expression confirms that is not merely a boundary for theoretical breakdown, but a structural yield threshold—the energy limit imposed by substrate geometry and offload pacing. It marks the point at which the envelope can no longer maintain internal waveform symmetry under recoverable conditions.
3.9.4. Unification Through Substrate Behavior
In total, QSD unifies the Planck units as expressions of causal substrate behavior:
sets the spatial coherence limit.
sets the temporal pacing limit.
sets the energetic support limit.
Each unit reflects the boundary at which the substrate can no longer maintain coherence—not an abstract boundary of knowledge, but a concrete physical limit rooted in geometry, phase stability, and recovery time. These units become falsifiable expressions of causal structure, not theoretical artifacts.
This reinterpretation transforms Planck units from dimensional thresholds into physically meaningful expressions of substrate architecture. They are no longer symbolic placeholders for unknown physics—they are derived limits on what coherent structure can exist within a conserved and causally gated field.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we have reinterpreted Planck energy not as a heuristic boundary derived from dimensional analysis, but as a physically grounded collapse limit arising from the structure of a conserved coherence substrate. Within the Quantum Substrate Dynamics (QSD) framework, defines the maximum energy that can be stably supported within a localized coherence envelope of size before rupture or offload becomes compulsory. This reinterpretation provides a testable and causally constrained mechanism for quantization, collapse, and emission.
We derived
as a function of the transverse coherence propagation rate
, the scalar recovery rate
, the curvature compliance
G, and the coherence envelope geometry:
This expression reveals that Planck energy is not a fixed threshold but a contextual structural limit that varies with coherence geometry and pacing capacity. It marks the point beyond which the substrate can no longer maintain phase stability, leading to scalar emission, rebound structuring, or coherence fracture. Collapse is reframed as a substrate-driven yield event, not a singularity in geometry.
We further showed that this saturation point is deeply linked to the physical interpretations of Planck time and length, unifying all Planck-scale quantities as causal consequences of substrate behavior. In this view, quantization arises from scalar pacing constraints, and energy is limited by the recoverable coherence support of a finite region. These insights lead to falsifiable predictions for burst structure, emission spectra, and rupture thresholds in astrophysical and possibly laboratory systems.
By grounding Planck energy in substrate mechanics, QSD replaces abstract constants with structural causality. The Planck scale becomes the active boundary of coherent structure, not a symbolic boundary of theory. This interpretation provides a foundation for modeling collapse, mass stability, and high-energy emission using causal geometry rather than singular extrapolation. As such, it offers a concrete, testable path forward in understanding both the limits and origins of quantized energy in the physical universe.