Submitted:
20 June 2025
Posted:
23 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Reference Genomes
Genome-Wide Mining of Resistance Gene Analogues
Characterisation of Resistance Gene Analogues
Mining the Protein Sequences of the Cloned Genes
Homolog Identification
Co-Localisation of RLKs and RLPs to Reported Disease Resistance Loci in Brassica Crops
Phylogenetic Analysis
Results
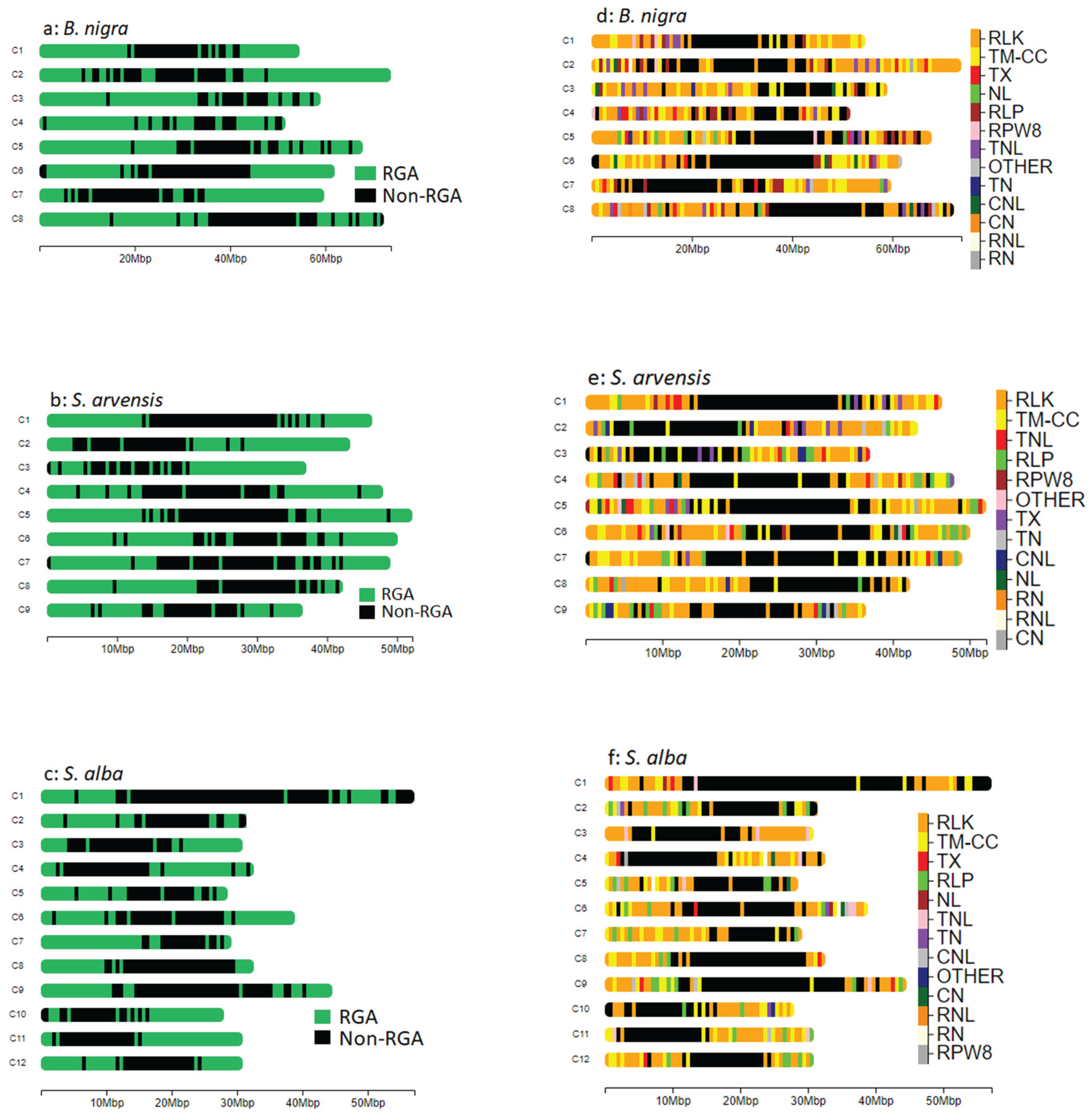
RGAs Identification and Classification
RGA Number and Chromosome Size Relationship
RGAs Distribution and Density
Physical Clustering
RGAs Sequence Pairwise Similarities
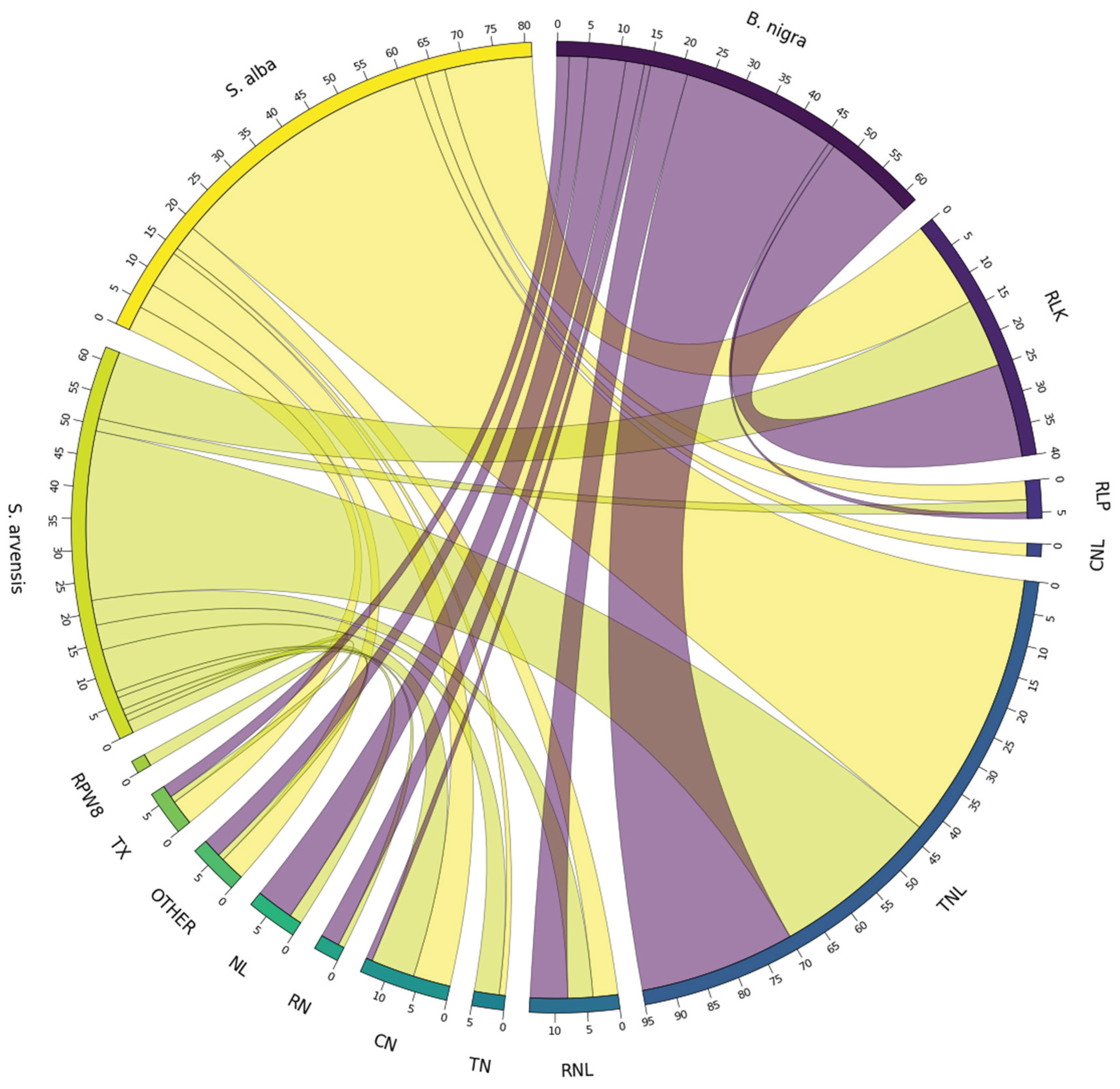
RGA Homolog Identification
Non-RGA Homologues Identification
Co-Localisation of RLKs and RLPs to Reported Disease Resistance Loci
Phylogenetic Analysis
Discussion
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Mohd Saad, N. S., Severn-Ellis, A. A., Pradhan, A., Edwards, D., Batley, J. (2021). Genomics armed with diversity leads the way in Brassica improvement in a changing global environment. Frontiers in Genetics. 12, 600789. [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S. L., Scheben, A., Edwards, D., Spillane, C., Ortiz, R. (2017). Assessing and exploiting functional diversity in germplasm pools to enhance abiotic stress adaptation and yield in cereals and food legumes. Frontiers in Plant Science. 8, 1461. [CrossRef]
- Greer, S. F., Surendran, A., Grant, M., Lillywhite, R. (2023). The current status, challenges, and future perspectives for managing diseases of Brassicas. Frontiers in Microbiology. 14, 1209258. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, I., Dutta, S., Mondal, S., & Mondal, B. (2014). Clubroot disease on Brassica crops in India. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology. 36, 154–160. [CrossRef]
- Barbetti, M. J., Li, C. X., Banga, S. S., Banga, S. K., Singh, D., Sandhu, P. S., Singh, R., Liu, S. Y., You, M. P. (2015). New host resistances in Brassica napus and Brassica juncea from Australia, China and India: key to managing Sclerotinia stem rot (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) without fungicides. Crop Protection. 78, 127–130. [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, C., Kolte, S. J., & Waliyar, F. (2015). Diseases of edible oilseed crops. CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA.
- Barbetti, M. J., Li, C. X., You, M. P., Singh, D., Agnihotri, A., Banga, S. K., Sandhu, P. S., Singh, R., & Banga, S. S. (2016). Valuable new leaf or inflorescence resistances ensure improved management of white rust (Albugo candida) in mustard (Brassica juncea) crops. Journal of Phytopathology. 164, 404–411. [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Martinez, D., Addo Nyarko, C. P., Schiessl, S. V., Mason, A. S. (2021). Using wild relatives and related species to build climate resilience in Brassica crops. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 134, 1711–1728. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M. J., Strelkov, S. E., Howard, R. J., & Rahman, H. (2012). Screening of Brassica germplasm for resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae pathotypes prevalent in Canada for broadening diversity in clubroot resistance. Canadian Journal of Plant Science. 92, 501–515. [CrossRef]
- Chu, M., Yu, F., Falk, K. C., Liu, X., Zhang, X., Chang, A., et al. (2013). Identification of the clubroot resistance gene Rpb1 and introgression of the resistance gene into canola breeding lines using a marker-assisted selection approach. Acta Horticulturae. 1005, 599–605. [CrossRef]
- Peng, G., Falk, K. C., Gugel, R. K., Franke, C., Yu, F., James, B., et al. (2014). Sources of resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae (clubroot) pathotypes virulent on canola. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology. 36, 89–99. [CrossRef]
- Chevre, A. M., Eber, F., This, P., Barret, P., Tanguy, X., Brun, H., et al. (1996). Characterization of Brassica nigra chromosomes and of blackleg resistance in B. napus–B. nigra addition lines. Plant Breeding. 115, 113–118. [CrossRef]
- Jones, J. D., Dangl, J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature. 444, 323–329. [CrossRef]
- Sekhwal, M. K., Li, P., Lam, I., Wang, X., Cloutier, S., You, F. M. (2015). Disease resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 16, 19248–19290. [CrossRef]
- Tirnaz, S., Bayer, P., Inturrisi, F., Zhang, F., Yang, H., Dolatabadian, A., et al. (2020). Resistance gene analogs in the Brassicaceae: identification, characterisation, distribution and evolution. Plant Physiology. 184, 909–922. [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, S. T., Coaker, G., Day, B., Staskawicz, B. J. (2006). Host–microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell. 124, 803–814. [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A. J., Wood, A. J., Lightfoot, D. A. (2008). Plant receptor-like serine threonine kinases: roles in signaling and plant defense. Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions. 21, 507–517. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S., Trotochaud, A. E., Clark, S. E. (1999). The Arabidopsis CLAVATA2 gene encodes a receptor-like protein required for the stability of the CLAVATA1 receptor-like kinase. The Plant Cell. 11, 1925–1933. [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, C., Huet, G., Jauneau, A., Camborde, L., Trémousaygue, D., Kraut, A., Zhou, B., Levaillant, M., Adachi, H., Yoshioka, H., et al. (2015). A receptor pair with an integrated decoy converts pathogen disabling of transcription factors to immunity. Cell. 161, 1074–1088. [CrossRef]
- Ravensdale, M., Bernoux, M., Ve, T., Kobe, B., Thrall, P. H., Ellis, J. G., Dodds, P. N. (2012). Intramolecular interaction influences binding of the flax L5 and L6 resistance proteins to their AvrL567 ligands. PLoS Pathogens. 8, e1003004. [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, J. A., Sack, F. D. (2002). Control of stomatal distribution on the Arabidopsis leaf surface. Science. 296, 1697–1700. [CrossRef]
- Cantila, A. Y., Thomas, W. J. W., Bayer, P. E., Edwards, D., & Batley, J. (2024). In silico prediction and analysis of transmembrane-coiled-coil resistance gene analogues in 27 Brassicaceae species. Plant Pathology. 73(1), 115–130. [CrossRef]
- Yang, T., Cai, B., Jia, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, J., King, G. J., Ge, X., & Li, Z. (2023). Sinapis genomes provide insights into whole-genome triplication and divergence patterns within tribe Brassiceae. The Plant Journal. 113(2), 246–261. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., et al. (2016). RGAugury: a pipeline for genome-wide prediction of resistance gene analogs (RGAs) in plants. BMC Genomics. 17, 852. [CrossRef]
- Anand, L., & Rodriguez Lopez, C. M. (2022). ChromoMap: an R package for interactive visualization of multi-omics data and annotation of chromosomes. BMC Bioinformatics. 23(1), 33. [CrossRef]
- Cantila, A. Y., Neik, T. X., Tirnaz, S., Thomas, W. J. W., Bayer, P. E., Edwards, D., & Batley, J. (2022). Mining of cloned disease resistance gene homologs (CDRHs) in Brassica species and Arabidopsis thaliana. Biology. 11(6), 821. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T., Al-Mamun, H. A., Edwards, D., Batley, J., Dolatabadian, A. (2024). Genome-wide identification and prediction of disease resistance genes in Hirschfeldia incana. Agriculture Communications. 2, 3. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J., et al. (2016). The genome sequence of allopolyploid Brassica juncea and analysis of differential homeolog gene expression influencing selection. Nature Genetics. 48, 1225–1232. [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, B., Denoeud, F., Liu, S., Parkin, I. A., Tang, H., Wang, X., Chiquet, J., Belcram, H., Tong, C., Samans, B., et al. (2014). Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science. 345, 950–953. [CrossRef]
- Parkin, I. A. P., et al. (2014). Transcriptome and methylome profiling reveals relics of genome dominance in the mesopolyploid Brassica oleracea. Genome Biology. 15, R77. [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I., & Bork, P. (2021). Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Research. 49, W293–W296. [CrossRef]
- Bayer, P. E., Golicz, A. A., Tirnaz, S., Chan, C. K. K., Edwards, D., Batley, J. (2019). Variation in abundance of predicted resistance genes in the Brassica oleracea pangenome. Plant Biotechnology Journal. 17, 789–800. [CrossRef]
- Inturrisi, F., Bayer, P. E., Cantila, A. Y., et al. (2022). In silico integration of disease resistance QTL, genes and markers with the Brassica juncea physical map. Molecular Breeding. 42, 37. [CrossRef]
- Shiu, S. H., & Bleecker, A. B. (2003). Expansion of the receptor-like kinase/Pelle gene family and receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology. 132, 530–543. [CrossRef]
- Meyers, B. C., Kozik, A., Griego, A., Kuang, H., & Michelmore, R. W. (2003). Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 15, 809–834. [CrossRef]
- Shiu, S. H., Karlowski, W. M., Pan, R., Tzeng, Y. H., Mayer, K. F., & Li, W. H. (2004). Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell. 16, 1220–1234. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T., Wang, Y., Chen, J. Q., Araki, H., Jing, Z., Jiang, K., Shen, J., & Tian, D. (2004). Genome-wide identification of NBS genes in japonica rice reveals significant expansion of divergent non-TIR NBS-LRR genes. Molecular Genetics and Genomics. 271, 402–415. [CrossRef]
- Fritz-Laylin, L. K., Krishnamurthy, N., Tör, M., Sjölander, K. V., Jones, J. D. (2005). Phylogenomic analysis of the receptor-like proteins of rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology. 138, 611–623. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Wei, W., Feng, J., Luo, H., Pi, M., Liu, Z., Kang, C. (2018a). Genome re-annotation of the wild strawberry Fragaria vesca using extensive Illumina- and SMRT-based RNA-seq datasets. DNA Research. 25, 61–70. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H., Bayer, P. E., Tirnaz, S., Edwards, D., Batley, J. (2020). Genome-wide identification and evolution of receptor-like kinases (RLKs) and receptor-like proteins (RLPs) in Brassica juncea. Biology (Basel). 10, 17. [CrossRef]
- Larkan, N. J., Ma, L., Haddadi, P., Buchwaldt, M., Parkin, I. A. P., Djavaheri, M., Borhan, M. H. (2020). The Brassica napus wall-associated kinase-like (WAKL) gene Rlm9 provides race-specific blackleg resistance. The Plant Journal. 104, 892–900. [CrossRef]
- McHale, L., Tan, X., Koehl, P., Michelmore, R. W. (2006). Plant NBS-LRR proteins: Adaptable guards. Genome Biology. 7, 212. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., Salman, A., Guo, C., Yu, J., Cao, S., Gao, X., Li, W., Li, H., Guo, Y. (2018b). Identification and characterization of LRR-RLK family genes in potato reveal their involvement in peptide signaling of cell fate decisions and biotic/abiotic stress responses. Cells. 7, 120. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N., Rai, K. M., Balasubramanian, V. K., Upadhyay, S. K., Luo, H., Mendu, V. (2018). Genome-wide identification and characterization of LRR-RLKs reveal functional conservation of the SIF subfamily in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). BMC Plant Biology. 18, 185. [CrossRef]
- Shumayla, Sharma, S., Kumar, R., Mendu, V., Singh, K., Upadhyay, S. K. (2016). Genomic dissection and expression profiling revealed functional divergence in Triticum aestivum leucine rich repeat receptor like kinases (TaLRRKs). Frontiers in Plant Science. 7, 1374. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X., Wang, G. L. (2011). Genome-wide identification, characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the rice LRR-kinases. PLoS ONE. 6, e16079. [CrossRef]
- Tomé, F., Nägele, T., Adamo, M., Garg, A., Marco-Llorca, C., Nukarinen, E., Pedrotti, L., Peviani, A., Simeunovic, A., Tatkiewicz, A., et al. (2014). The low energy signaling network. Frontiers in Plant Science. 5, 353. [CrossRef]
- Narusaka, M., Shirasu, K., Noutoshi, Y., Kubo, Y., Shiraishi, T., Iwabuchi, M., et al. (2009). RRS1 and RPS4 provide a dual resistance-gene system against fungal and bacterial pathogens. The Plant Journal. 60, 218–226. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B., Liu, M., Wang, Y., Yuan, W., Zhang, H. (2022). Plant NLRs: Evolving with pathogen effectors and engineerable to improve resistance. Frontiers in Microbiology. 13, 1018504. [CrossRef]
- Blommaert, J. (2020). Genome size evolution: Towards new model systems for old questions. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 287, 20201441. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H., Giordano, F., Ning, Z. (2016). Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencing and genome assembly. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics. 14, 265–279. [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R. L., Jockusch, E. L. (2018). Jumping genomic gigantism. Nature Ecology & Evolution. 2, 1687–1688.
- Shen, C.-H. (2019). Chapter 5 – The Genome. In: Shen, C.-H. (Ed.), Diagnostic Molecular Biology. Academic Press, pp. 117–141.
- Gebhardt, C., Valkonen, J. P. (2001). Organization of genes controlling disease resistance in the potato genome. Annual Review of Phytopathology. 39, 79–102. [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R., Ponce, O., Ramirez, M., Mostajo, N., Orjeda, G. (2012). Genome-wide identification and mapping of NBS-encoding resistance genes in Solanum tuberosum group Phureja. PLoS ONE. 7, e34775. [CrossRef]
- Ameline-Torregrosa, C., Wang, B. B., O’Bleness, M. S., Deshpande, S., Zhu, H., Roe, B., Young, N. D., Cannon, S. B. (2008). Identification and characterization of nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in the model plant Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiology. 146, 5–21. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J., Tehrim, S., Zhang, F., Tong, C., Huang, J., Cheng, X., Dong, C., Zhou, Y., Qin, R., Hua, W., et al. (2014). Genome-wide comparative analysis of NBS-encoding genes between Brassica species and Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics. 15, 3. [CrossRef]
- Golicz, A. A., Bayer, P. E., Barker, G. C., Edger, P. P., Kim, H., Martinez, P. A., Chan, C. K. K., Severn-Ellis, A., McCombie, W. R., Parkin, I. A., et al. (2016). The pangenome of an agronomically important crop plant Brassica oleracea. Nature Communications. 7, 13390. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. M., Shao, Z. Q., Wang, Q., Hang, Y. Y., Xue, J. Y., Wang, B., Chen, J. Q. (2016). Uncovering the dynamic evolution of nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes in Brassicaceae. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology. 58, 165–177. [CrossRef]
- Dolatabadian, A., Bayer, P. E., Tirnaz, S., Hurgobin, B., Edwards, D., Batley, J. (2020). Characterisation of disease resistance genes in the Brassica napus pangenome reveals significant structural variation. Plant Biotechnology Journal. 18, 969–982. [CrossRef]
- Alamery, S., Tirnaz, S., Bayer, P., Tollenaere, R., Chaloub, B., Edwards, D., Batley, J. (2018). Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis of NBS-LRR resistance genes in Brassica napus. Crop and Pasture Science. 69, 72. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y., Chhapekar, S. S., Lu, L., Oh, S., Singh, S., Kim, C. S., Kim, S., et al. (2021). Genome-wide identification and characterization of NBS-encoding genes in Raphanus sativus L. and their roles related to Fusarium oxysporum resistance. BMC Plant Biology. 21, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, H., Katagiri, S., Kanamori, H., Mukai, Y., Sasaki, T., Matsumoto, T., Wu, J. (2020). Evolutionary dynamics and impacts of chromosome regions carrying R-gene clusters in rice. Scientific Reports. 10, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Perochon, A., Benbow, H. R., Ślęczka-Brady, K., Malla, K. B., & Doohan, F. M. (2021). Analysis of the chromosomal clustering of Fusarium-responsive wheat genes uncovers new players in the defense against head blight disease. Scientific Reports. 11, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- van Wersch, S., & Li, X. (2019). Stronger when together: clustering of plant NLR disease resistance genes. Trends in Plant Science. 24(8), 688–699.
- Hulbert, S. H., Webb, C. A., Smith, S. M., & Sun, Q. (2001). Resistance gene complexes: evolution and utilization. Annual Review of Phytopathology. 39, 285–312. [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, A. C., Fonseca, F. C. D. A., Cotta, M. G., Alves, G. S. C., Miller, R. N. G. (2019). Plant NLR receptor proteins and their potential in the development of durable genetic resistance to biotic stresses. Biotechnology Research and Innovation. 3, 80–94. [CrossRef]
- Sanseverino, W., et al. (2013). PRGdb 2.0: towards a community-based database model for the analysis of R-genes in plants. Nucleic Acids Research. 41, D1167–D1171. [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, K. S., & Michelmore, R. W. (2009). Arabidopsis thaliana genes encoding defense signaling and recognition proteins exhibit contrasting evolutionary dynamics. Genetics. 181(2), 671–684. [CrossRef]
- Song, X., et al. (2021). Brassica carinata genome characterization clarifies U’s triangle model of evolution and polyploidy in Brassica. Plant Physiology. 186, 388–406. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M. S., Takahashi, H., Miyazaki, A., Hamamoto, H., Yamaguchi, I., Kusano, T., Shah, J. (2004). Up-regulation of Arabidopsis thaliana NHL10 in the hypersensitive response to cucumber mosaic virus infection and in senescing leaves is controlled by signalling pathways that differ in salicylate involvement. Planta. 218, 740–750. [CrossRef]
- Tang, D., Wang, G., & Zhou, J. M. (2017). Receptor kinases in plant-pathogen interactions: More than pattern recognition. The Plant Cell. 29(4), 618–637. [CrossRef]
- Dodds, P. N., Chen, J., Outram, M. A., & et al. (2024). Pathogen perception and signaling in plant immunity. The Plant Cell. [CrossRef]
- Kibby, E. M., Conte, A. N., Burroughs, A. M., Nagy, T. A., Vargas, J. A., Whalen, L. A., Aravind, L., Whiteley, A. T. (2023). Bacterial NLR-related proteins protect against phage. Cell. 186, 2410–2424. [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, Z., Wu, C.-h., Ding, P. (2021). A comparative overview of the intracellular guardians of plants and animals: NLRs in innate immunity and beyond. Annual Review of Plant Biology. 72, 155–184. [CrossRef]
- Kourelis, J., Sakai, T., Adachi, H., Kamoun, S. (2021). RefPlantNLR is a comprehensive collection of experimentally validated plant disease resistance proteins from the NLR family. PLoS Biology. 19, e3001124. [CrossRef]
- Meyers, B., Dickerman, A., Michelmore, R., Sivaramakrishnan, S., Sobral, B., Young, N. (1999). Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. The Plant Journal. 20, 317–332. [CrossRef]
- Larkan, N. J., Lydiate, D. J., Parkin, I. A. P., Nelson, M. N., Epp, D. J., Cowling, W. A., Rimmer, S. R., Borhan, M. H. (2013). The Brassica napus blackleg resistance gene LepR3 encodes a receptor-like protein triggered by the Leptosphaeria maculans effector AVRLM1. New Phytologist. 197, 595–605. [CrossRef]
- Larkan, N. J., Ma, L., Borhan, M. H. (2015). The Brassica napus receptor-like protein RLM2 is encoded by a second allele of the LepR3/Rlm2 blackleg resistance locus. Plant Biotechnology Journal. 13, n/a. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L., Borhan, M. H. (2015). The receptor-like kinase SOBIR1 interacts with Brassica napus LepR3 and is required for Leptosphaeria maculans AvrLm1-triggered immunity. Frontiers in Plant Science. 6, 933. [CrossRef]
- Boutrot, F., Zipfel, C. (2017). Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Annual Review of Phytopathology. 55, 257–286. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., VandenLangenberg, K., Wehner, T. C., Weng, Y. (2014). QTLs for downy mildew resistance and their association with LRR-RLK/RLP resistance gene homologs in cucumber. Cucurbitaceae 2014, Michigan, USA.
- Stotz, H. U., et al. (2018). Genomic evidence for genes encoding leucine-rich repeat receptors linked to resistance against the eukaryotic extra- and intracellular Brassica napus pathogens Leptosphaeria maculans and Plasmodiophora brassicae. PLoS One. 13, e0198201. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J., et al. (2015). Genome-wide SNP identification and QTL mapping for black rot resistance in cabbage. BMC Plant Biology. 15, 32. [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, M. J., et al. (2020a). In silico characterization and expression of disease-resistance-related genes within the collinear region of Brassica napus blackleg resistant locus LepR1 in B. oleracea. Journal of General Plant Pathology. 86, 442–456. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.R., Ferdous, M.J., Park, J. I., Robin, A.H.K., Natarajan, S., Jung, H.-J. et al. (2020). In-silico identification and differential expression of putative disease resistance-related genes within the collinear region of Brassica napus blackleg resistance locus LepR2′ in Brassica oleracea. Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology. 61, 879–890. [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, M. J., et al. (2020b). In-silico identification and differential expressions of LepR4-syntenic disease resistance-related domain containing genes against blackleg causal fungus Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica oleracea. Gene Reports. 19, 100598. [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, M. J., et al. (2019). Inheritance pattern and molecular markers for resistance to blackleg disease in cabbage. Plants. 8, 583. [CrossRef]
- Chang, A., et al. (2019). Clubroot resistance gene Rcr6 in Brassica nigra resides in a genomic region homologous to chromosome A08 in B. rapa. BMC Plant Biology. 19, 224. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H., et al. (2021). Candidate Rlm6 resistance genes against Leptosphaeria maculans identified through a genome-wide association study in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 134, 2035–2050. [CrossRef]
- Raman, H., et al. (2021). The Rlm13 gene, a new player of Brassica napus–Leptosphaeria maculans interaction maps on chromosome C03 in canola. Frontiers in Plant Science. 12, 564604. [CrossRef]
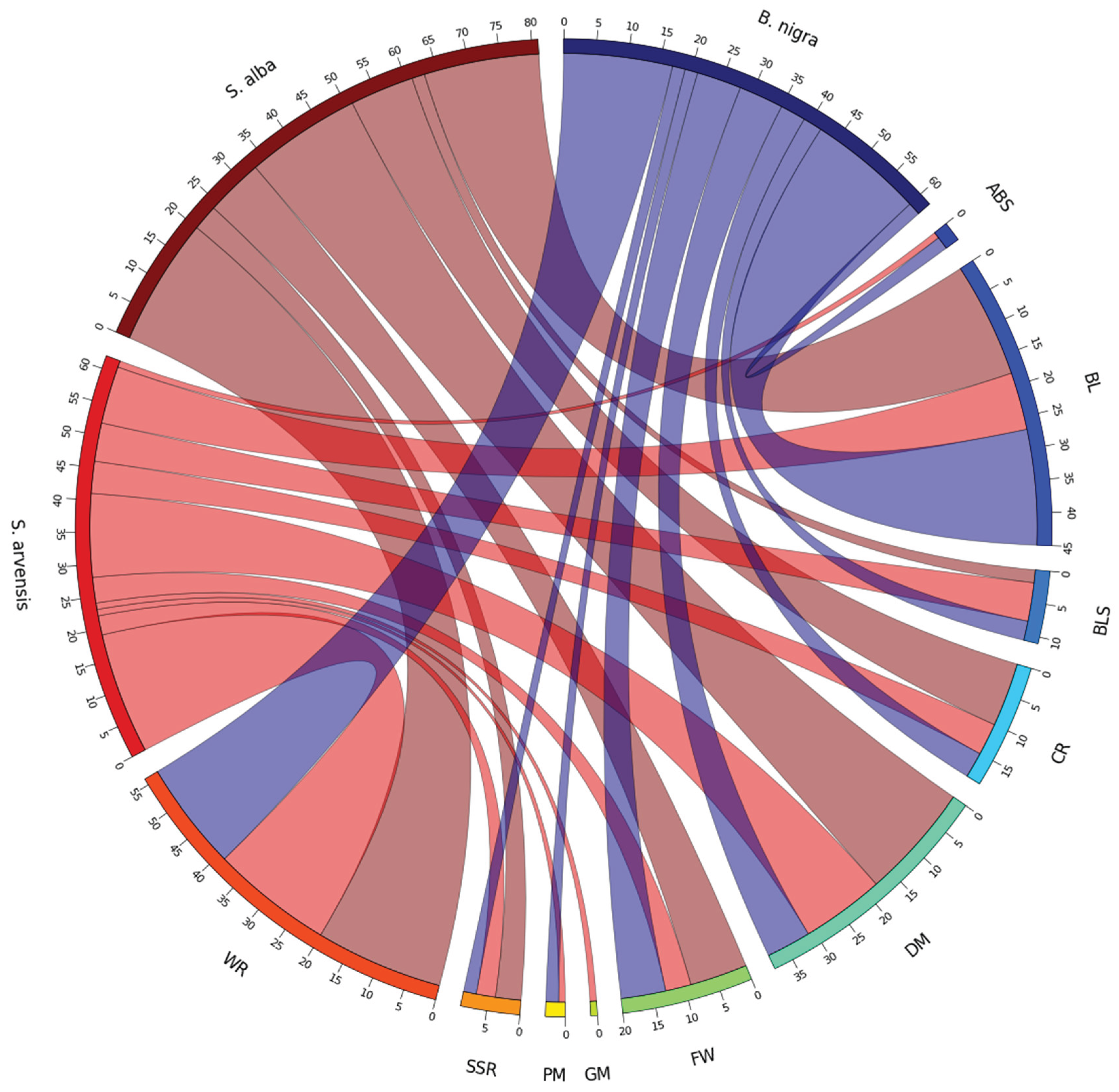
| QTL | Species | Disease | Chromosome (QTL coordinates) | Reference |
| A7 | Bna | BL | A08 (9,926,520–14,644,781) | [84] |
| A8.dy09 | Bna | BL | A08 (9,514,104–15,735,553) | |
| A9.dy05 | Bna | BL | A09 (5,371,869–20,078,473) | |
| C6.dy13 | Bna | BL | C06 (13,138,327–20,245,793) | |
| C8 | Bna | BL | C08 (23,938,650–35,120,753) | |
| CRQTL-GN_2 | Bna | CR | C03 (1,185,066–2,835,468) | |
| Dw12 | Bna | SSR | C02 (3,710,868–6,707,092) | |
| Dw16 | Bna | SSR | C06 (28,554,990–35,465,622) | |
| Dw3 | Bna | SSR | A03 (15,547,362–16,064,878) | |
| LepR1 | Bna | BL | A02 (11,756,829–18,651,329) | |
| LRA9-1 | Bna | SSR | A09 (22,050,676–23,688,607) | |
| LRA9-2 | Bna | SSR | A09 (22,050,676–22,586,868) | |
| LRC5 | Bna | SSR | C04 (3,065,391–7,930,616) | |
| qFR10-1 | Bna | SSR | C02 (1,027,454–3,174,971) | |
| qFR10-2 | Bna | SSR | C02 (1,099,275–6,816,020) | |
| qFR11-1 | Bna | SSR | A09 (29,166,099–29,361,292) | |
| qFR11-3 | Bna | SSR | C02 (1,027,454–3,174,971) | |
| qSR10-1 | Bna | SSR | A02 (1,610,851–7,705,833) | |
| qSR10-2 | Bna | SSR | A03 (3,131,828–6,786,833) | |
| qSR10-3 | Bna | SSR | C02 (1,027,454–3,953,336) | |
| qSR11-1 | Bna | SSR | A09 (27,128,147–28,071,597) | |
| qSR11-2 | Bna | SSR | C02 (1027454–3,953,336) | |
| Rlm3 | Bna | BL | A07 (15,120,000–16,290,000) | |
| SCR-C6 | Bna | CR | C06 (25,090,000–26,220,000) | |
| Sll14a | Bna | SSR | C04 (396,764–9,418,160) | |
| Sll14b | Bna | SSR | C04 (11,691,778–28,720,453) | |
| Sll2 | Bna | SSR | A02 (32458–3,454,175) | |
| SRA1 | Bna | SSR | A01 (12,444,829–19,857,639) | |
| SRA2-1 | Bna | SSR | A02 (16,670,964–20,474,897) | |
| SRA2-2 | Bna | SSR | A02 (21,084,362–24,719,312) | |
| SRA6 | Bna | SSR | A06 (20,965,425–23,324,273) | |
| SRA8 | Bna | SSR | A08 (7,467,851–8,338,138) | |
| SRA9-1 | Bna | SSR | A09 (22,586,748–26,573,318) | |
| SRC6-1 | Bna | SSR | C06 (30,278,840–34,585,422) | |
| SRC6-2 | Bna | SSR | C06 (30,278,840–34,585,422) | |
| SRC7 | Bna | SSR | C07 (29,634,609–31,761,057) | |
| TS A09 | Bna | BL | A09 (24,341,296–25,991,630) | |
| AcB1-A4.1 | Bju | WR | A04 (9,446,467–11,808,704) | [33] |
| AcB1-A5.1 | Bju | WR | A05 (3,795,221–6,894,070) | |
| AcB1-A5.1 | Bju | WR | B06 (4,226,533–7,156,115) | |
| BjCHI1 | Bju | HR | A03 (9,353,574–21,355,565) | |
| LMJR1 | Bju | BL | B03 (498,805–10,675,185) | |
| LMJR2 | Bju | BL | B08 (1–21,282,056) | |
| PhR2 | Bju | BL | A08 (21,485,767–24,843,799) | |
| PhR2 | Bju | BL | B03 (1,554,162–4,778,538) | |
| BRQTL-C1_1 | Bol | BR | C01 (14,884,502–16,579,946) | [85] |
| BRQTL-C1_2 | Bol | BR | C01 (18,227,386–37,119,290) | |
| BRQTL-C3 | Bol | BR | C03 (19,714,632–22,846,644) | |
| BRQTL-C6 | Bol | BR | C06 (7,423,787–10,466,894) | |
| LepR1 | Bol | BL | C02 (23,420,917–39,667,823) | [86] |
| LepR2 | Bol | BL | C09 (36,661,274–41,215,564) | [87] |
| LepR4 | Bol | BL | C03 (35,912,191–49,368,477) | [88] |
| Rlm1 | Bol | BL | C06 (20,455,085–36,165,661) | [89] |
| Rcr6 | Bni | CR | B03 (6,100,000–6,600,000) | [90] |
| Rlm6 | Bju | BL | A07 (28,140,000–28,631,000) | [91] |
| Rlm6 | Bju | BL | B04 (19,804,000–22,303,000) | |
| Rlm13 | Bna | BL | C03 (2,573,230–5,711,418) | [92] |
| Species | Position (Mbp) | RLK | LRR-RLK | LysM-RLK | Other receptor | RLP | LRR-RLP | LysM-RLP | Other receptor | TM-CC | TNL | CNL | RNL | TX | TN | NL | RN | CN | OTHER | RPW8 | Total | RGA/Mbp |
| B. nigra | Chr01 (54.73) | 74 | 28 | 4 | 42 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 131 | 2.39 |
| Chr02 (73.74) | 147 | 57 | 0 | 90 | 23 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 53 | 20 | 6 | 3 | 16 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 293 | 3.97 | |
| Chr03 (59.02) | 117 | 44 | 0 | 73 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 22 | 8 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 230 | 3.89 | |
| Chr04 (51.41) | 87 | 38 | 1 | 48 | 28 | 27 | 1 | 0 | 30 | 35 | 13 | 0 | 23 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 237 | 4.60 | |
| Chr05 (67.89) | 132 | 47 | 0 | 85 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 0 | 29 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 12 | 6 | 11 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 237 | 3.49 | |
| Chr06 (61.87) | 83 | 37 | 0 | 46 | 22 | 22 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 154 | 2.48 | |
| Chr07 (59.87) | 61 | 33 | 1 | 27 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 128 | 2.13 | |
| Chr08 (71.98) | 118 | 39 | 0 | 79 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 19 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 203 | 2.82 | |
| Contig 005 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 013 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 032 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 041 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 048 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 067 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 158 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 193 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 296 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 323 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 353 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Total | 821 | 325 | 6 | 490 | 164 | 162 | 2 | 0 | 272 | 119 | 37 | 9 | 71 | 30 | 37 | 9 | 15 | 30 | 11 | 1625 | ||
| S. arvensis | Chr01 (46.40) | 75 | 23 | 2 | 50 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 129 | 2.78 |
| Chr02 (43.41) | 124 | 45 | 1 | 78 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 38 | 14 | 4 | 1 | 13 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 222 | 5.11 | |
| Chr03 (37.28) | 65 | 28 | 1 | 36 | 23 | 23 | 0 | 0 | 26 | 11 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 147 | 3.51 | |
| Chr04 (47.78) | 91 | 34 | 0 | 57 | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 26 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 182 | 3.80 | |
| Chr05 (52.17) | 68 | 35 | 0 | 33 | 16 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 39 | 9 | 5 | 28 | 7 | 15 | 1 | 13 | 3 | 1 | 236 | 4.52 | |
| Chr06 (49.85) | 125 | 39 | 0 | 86 | 27 | 26 | 1 | 0 | 33 | 14 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 220 | 4.41 | |
| Chr07 (49.15) | 86 | 38 | 0 | 48 | 16 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 3 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 162 | 3.29 | |
| Chr08 (42.09) | 104 | 33 | 1 | 70 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 8 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 174 | 4.13 | |
| Chr09 (36.73) | 80 | 25 | 0 | 55 | 20 | 19 | 1 | 0 | 25 | 7 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 150 | 4.08 | |
| Contig 357 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 358 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 452 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Total | 818 | 300 | 5 | 513 | 155 | 153 | 2 | 0 | 266 | 132 | 41 | 8 | 69 | 39 | 33 | 8 | 22 | 22 | 12 | 1625 | ||
| S. alba | Chr01 (57.15) | 55 | 19 | 2 | 34 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 86 | 1.50 |
| Chr02 (31.68) | 55 | 28 | 1 | 26 | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 35 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 108 | 3.40 | |
| Chr03 (31.00) | 78 | 21 | 0 | 57 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 101 | 3.25 | |
| Chr04 (32.85) | 62 | 31 | 0 | 31 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 128 | 3.89 | |
| Chr05 (28.50) | 60 | 20 | 1 | 39 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 12 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 94 | 3.29 | |
| Chr06 (38.87) | 60 | 22 | 1 | 37 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 111 | 2.85 | |
| Chr07 (29.24) | 65 | 27 | 0 | 38 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 107 | 3.65 | |
| Chr08 (32.51) | 48 | 19 | 1 | 28 | 14 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 16 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 2.76 | |
| Chr09 (44.42) | 79 | 31 | 0 | 48 | 13 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 18 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 124 | 2.79 | |
| Chr10 (28.29) | 60 | 24 | 0 | 36 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 108 | 3.81 | |
| Chr11 (30.85) | 48 | 23 | 0 | 25 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 89 | 2.88 | |
| Chr12 (30.69) | 62 | 22 | 0 | 40 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 3.25 | |
| Contig 191 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 373 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Contig 456 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | |
| Total | 734 | 287 | 6 | 441 | 104 | 101 | 3 | 0 | 247 | 47 | 15 | 4 | 37 | 13 | 14 | 7 | 11 | 8 | 8 | 1249 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





