Submitted:
15 June 2025
Posted:
17 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
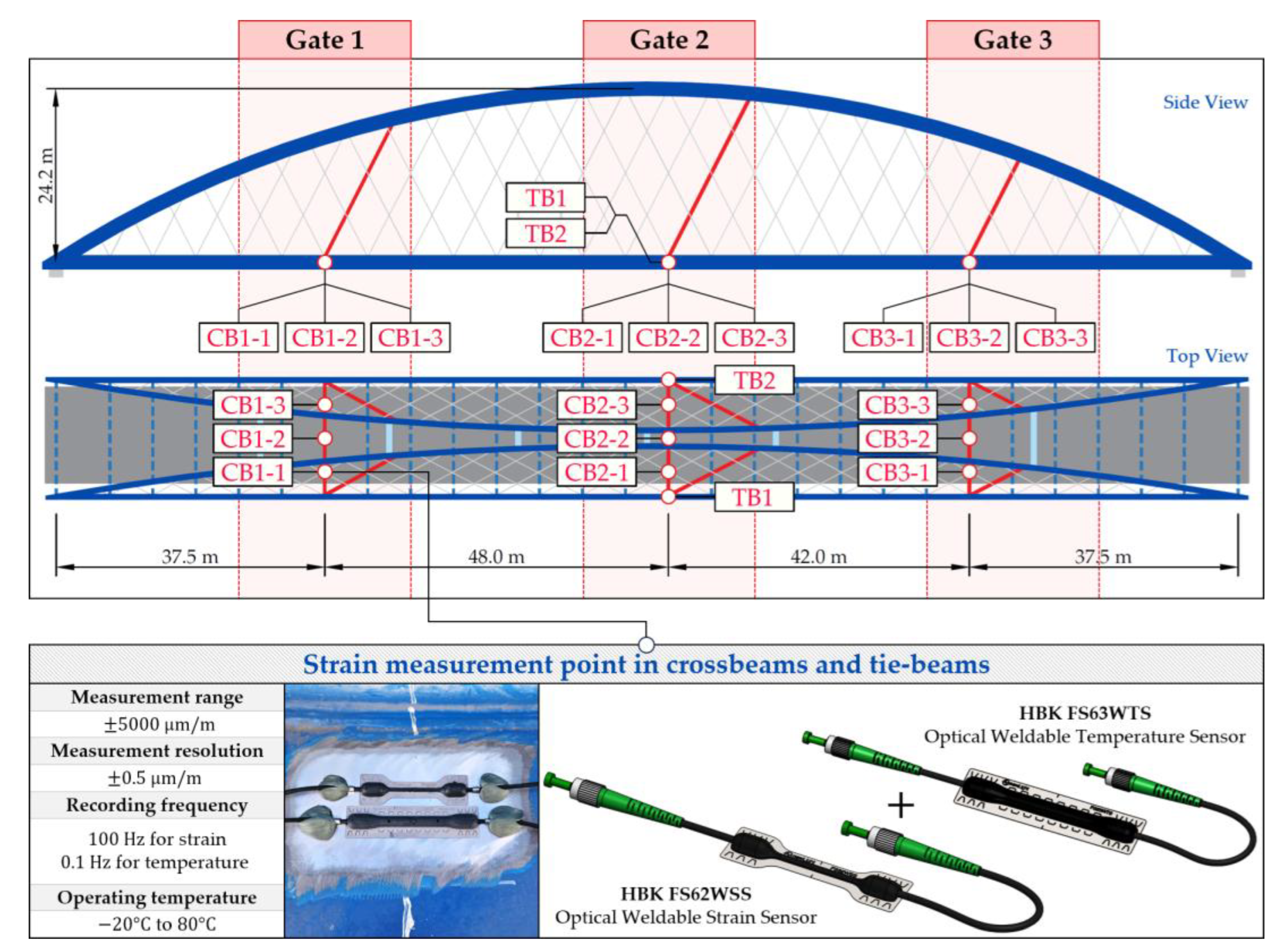
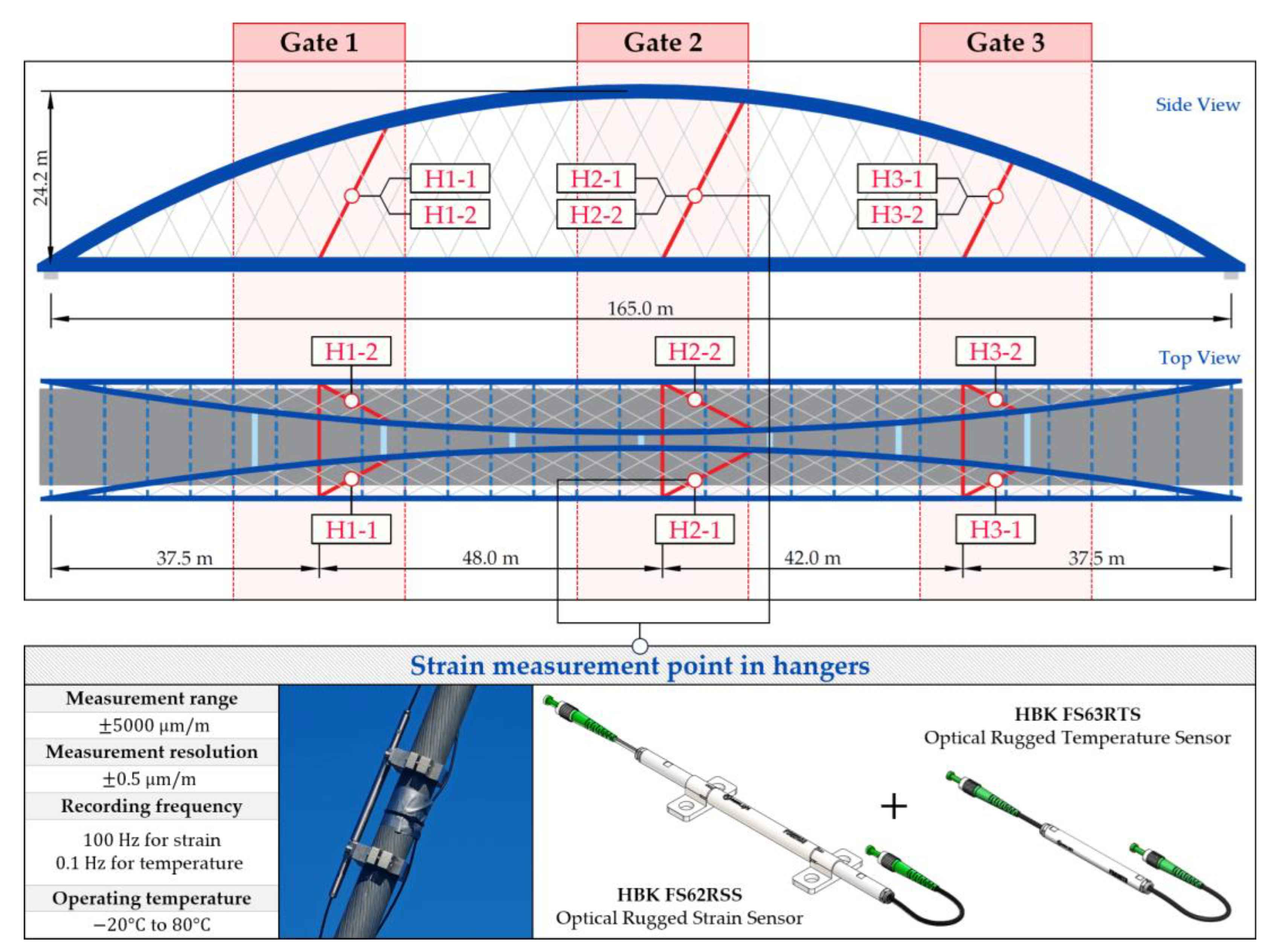
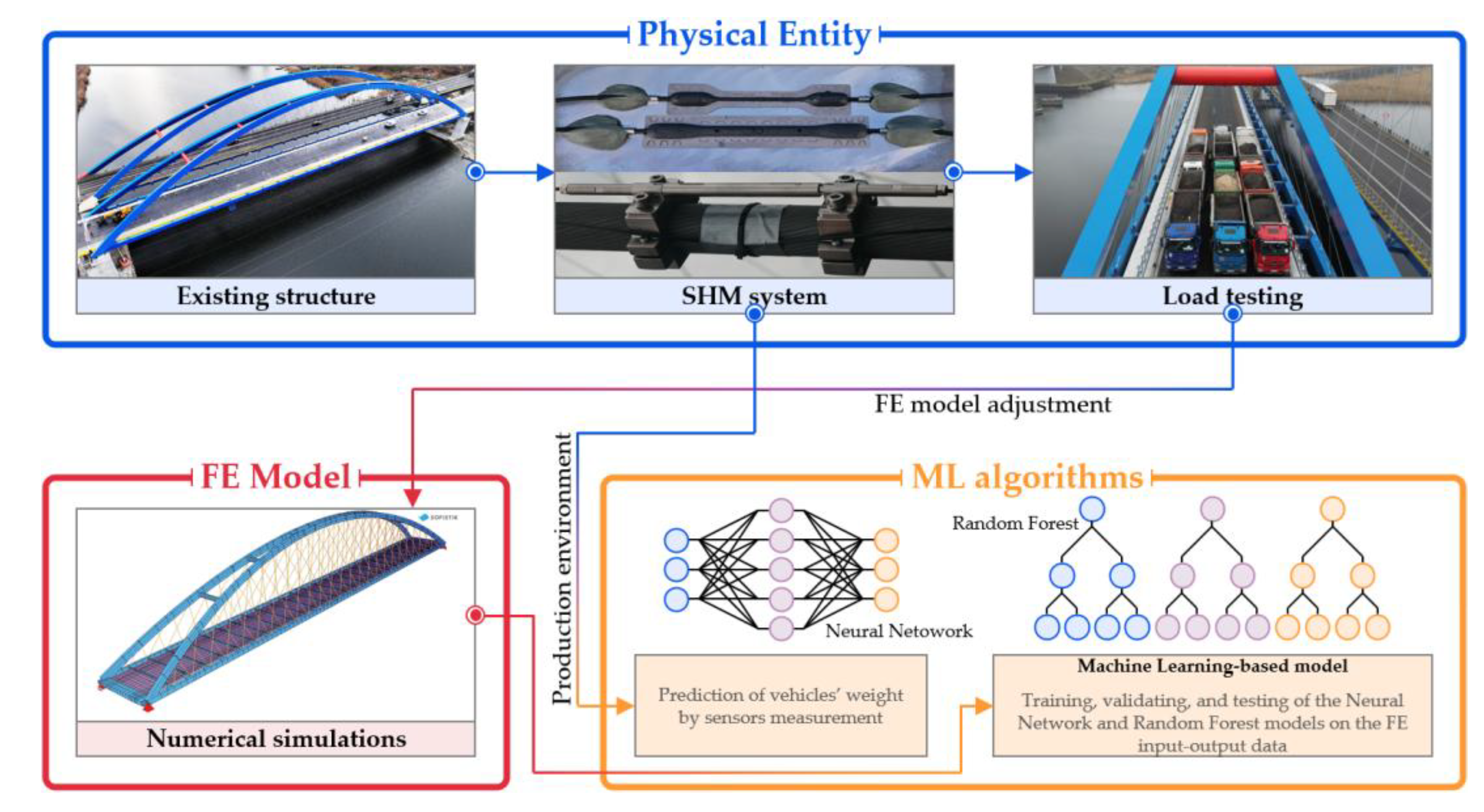
2.1. Bridge and SHM System Overview
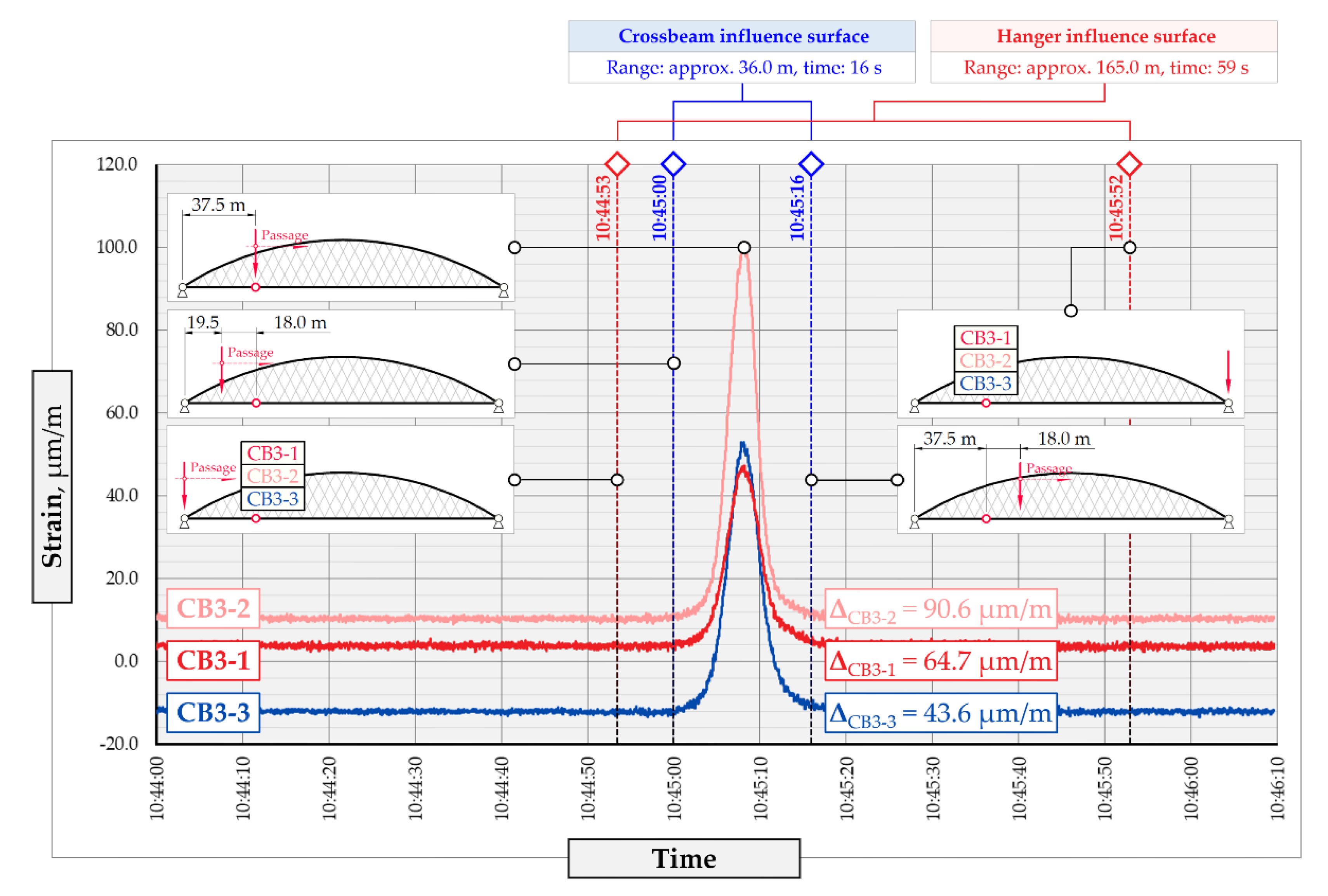
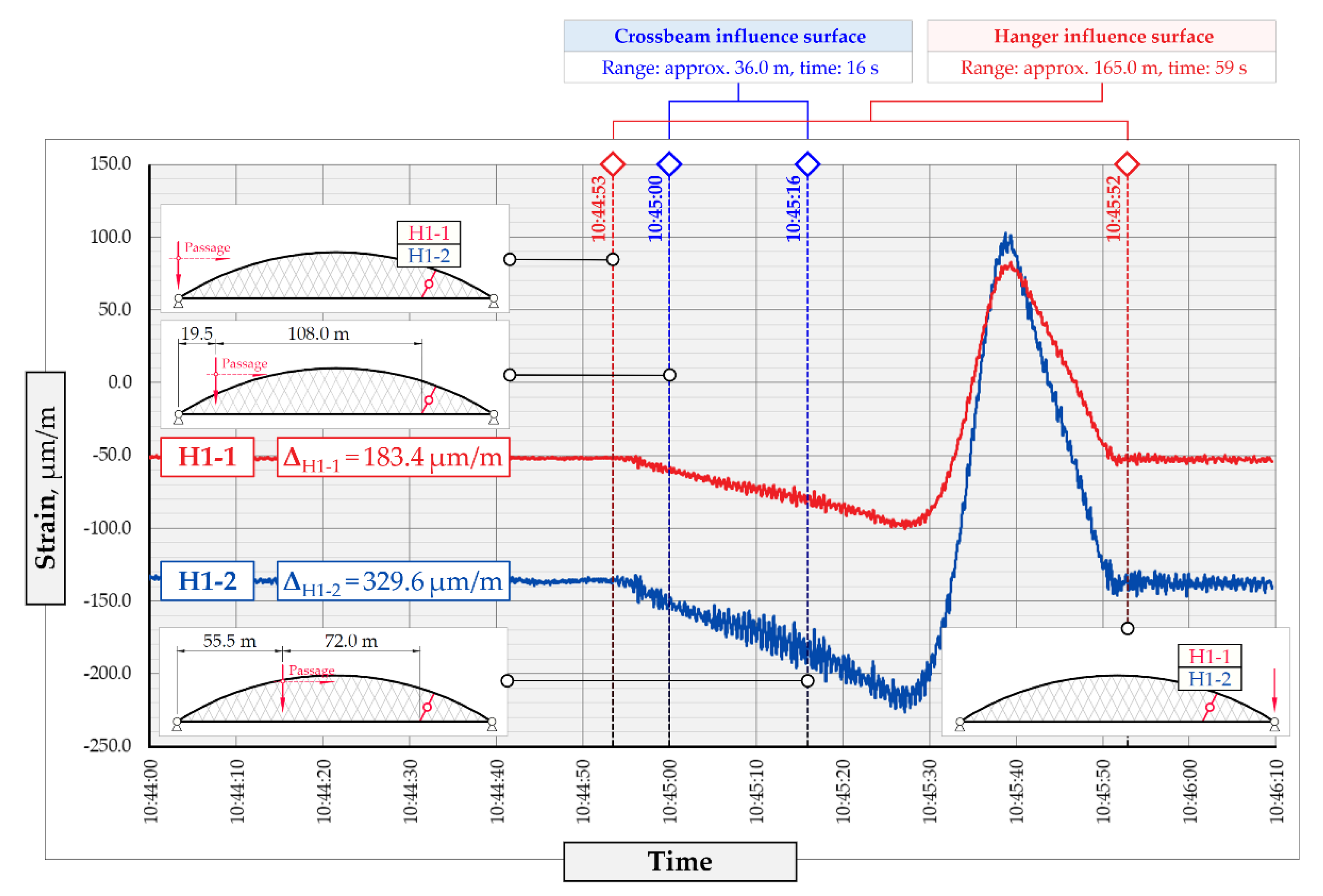
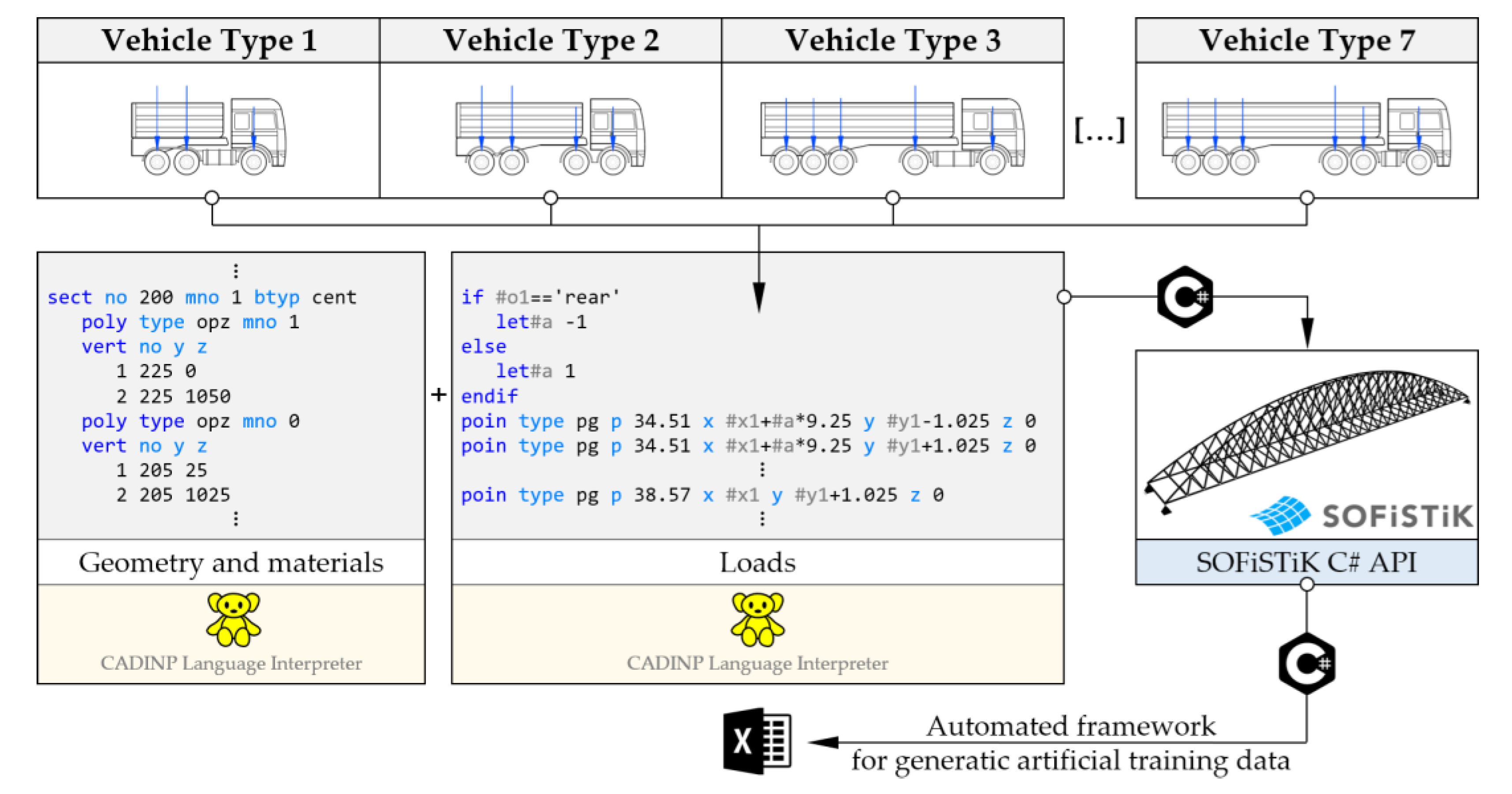
2.2. Load Testing and Physics-Informed BWIM Design
2.3. Dataset and Machine Learning Algorithms
3. Results
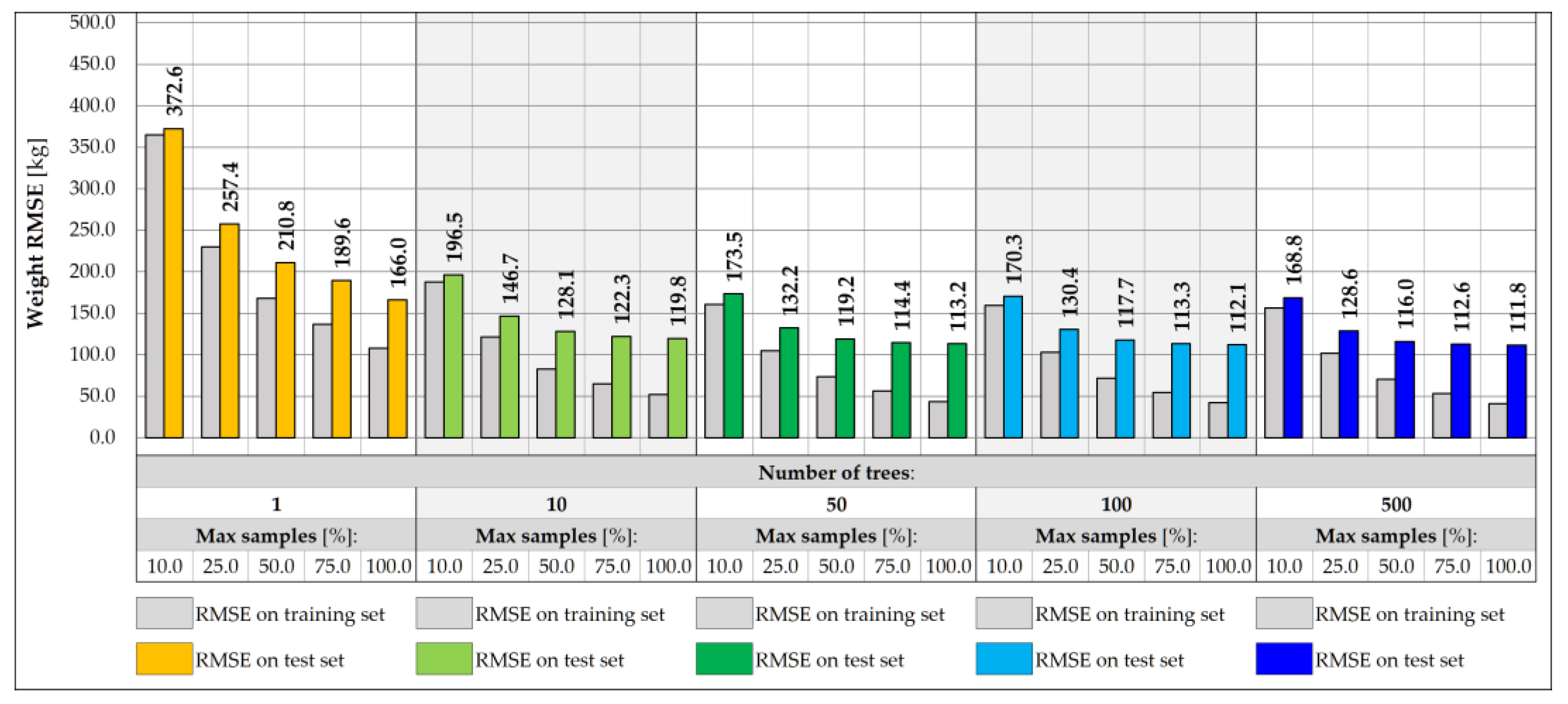
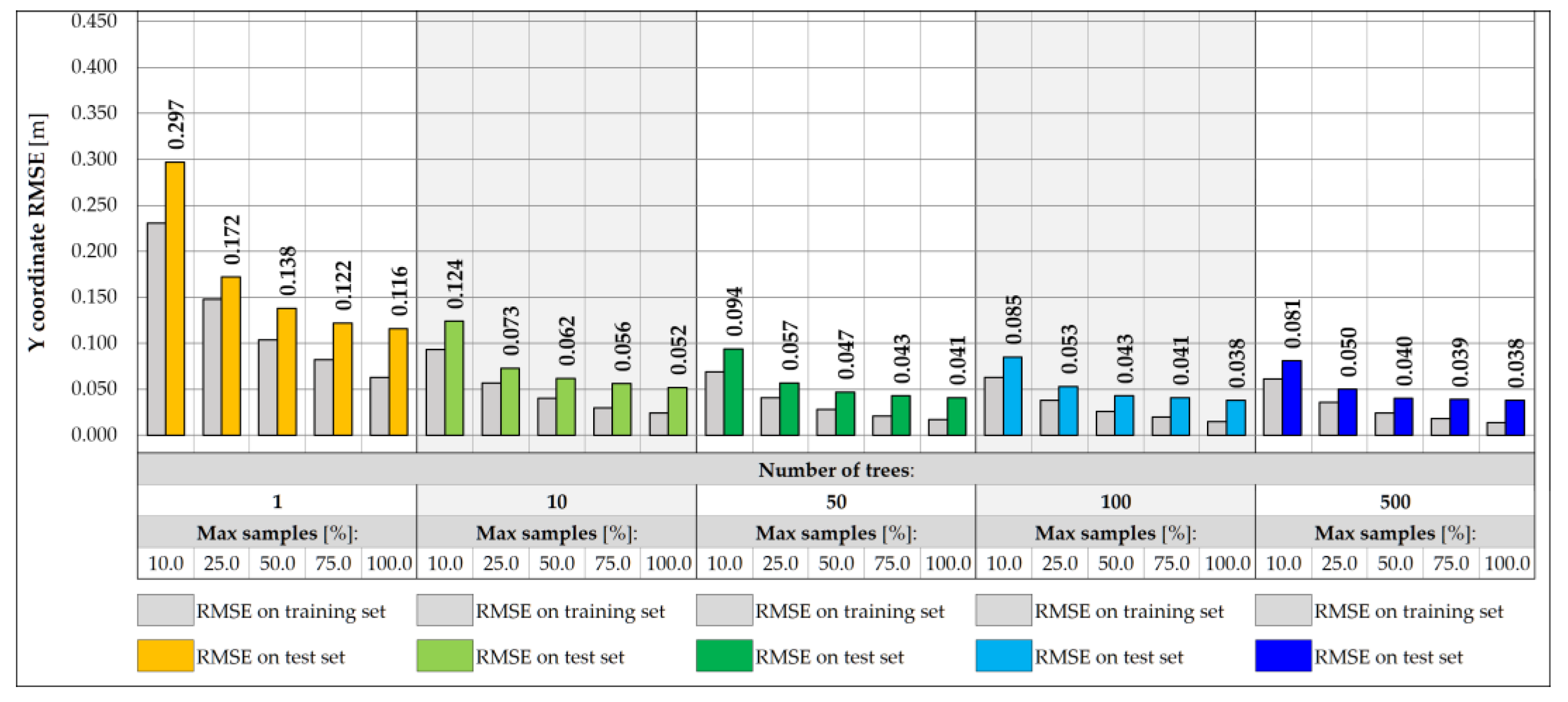
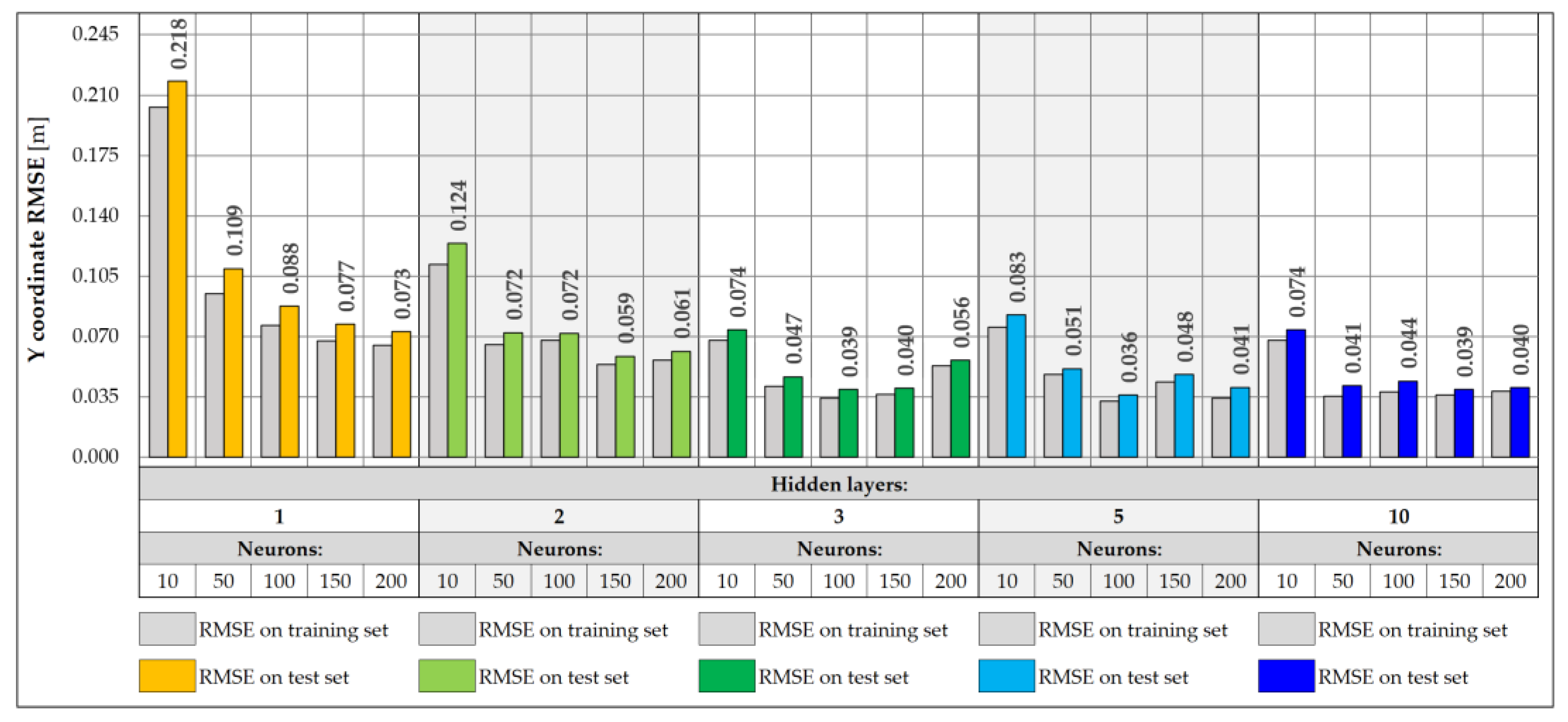
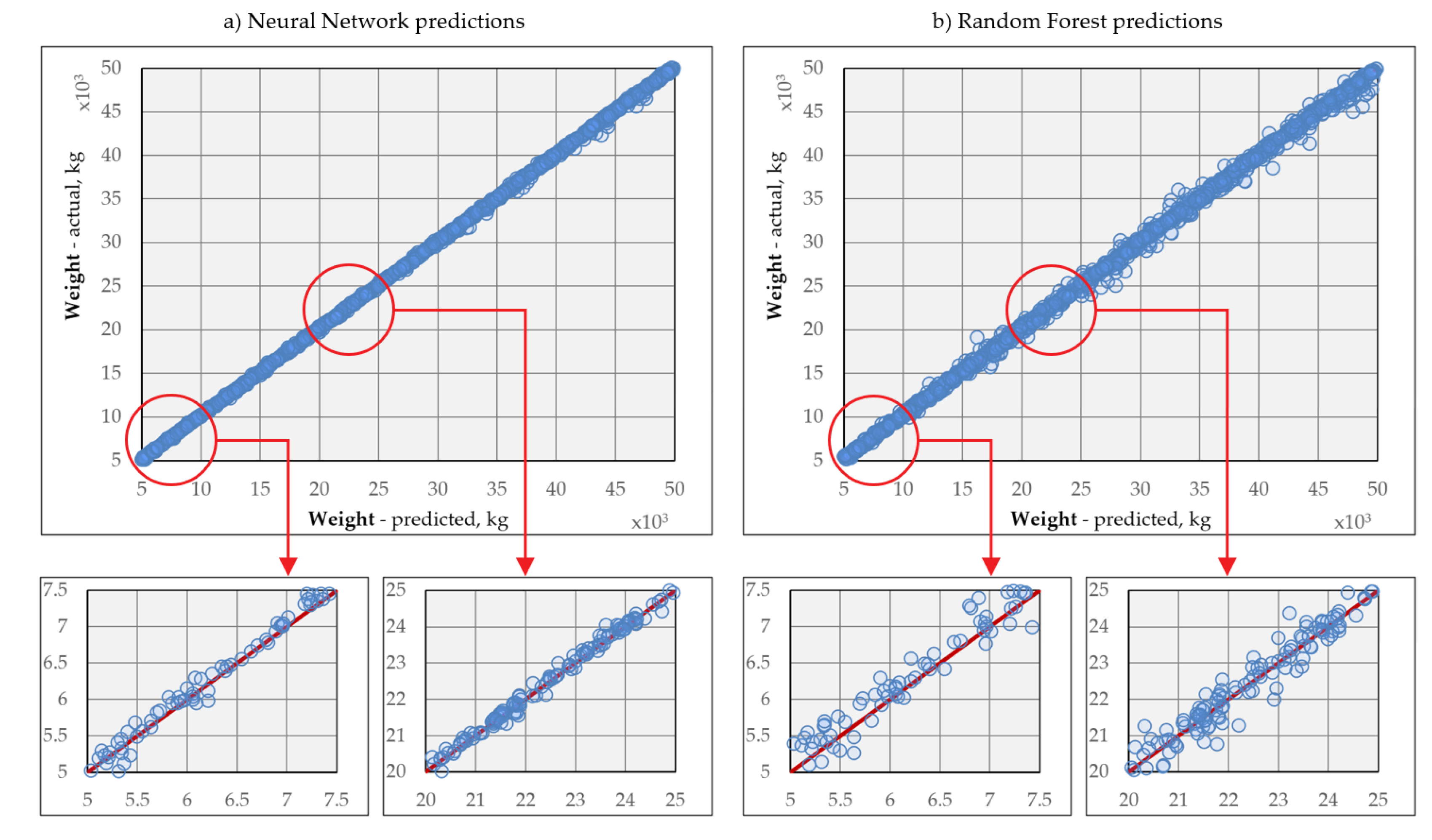
3.1. Random Forest-Based Predictive Models
3.2. Neural Network-Based Predictive Models
4. Measurement Uncertainties
4.1. Criterion of Correct Prediction
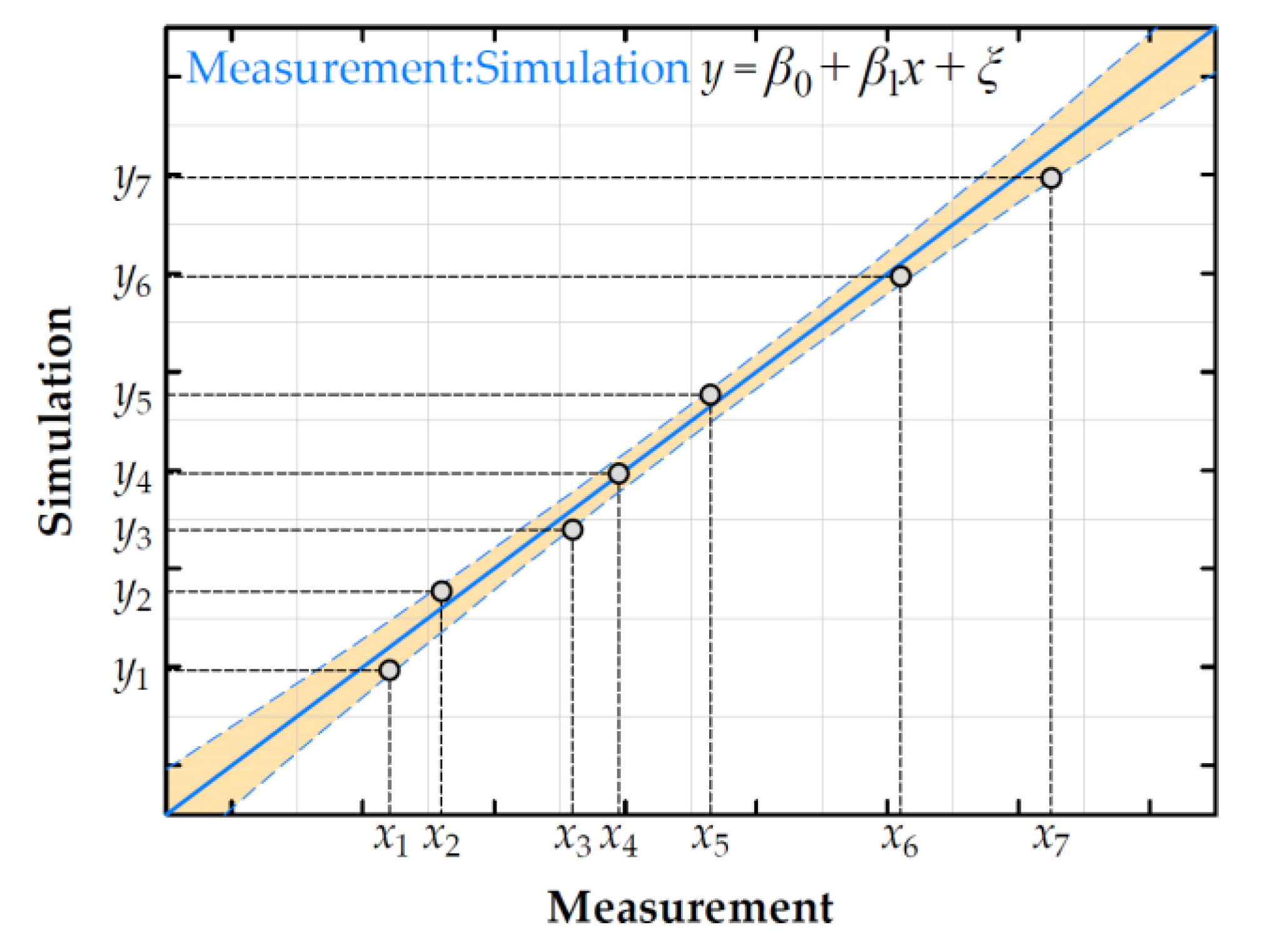
4.2. Regression Model to Estimate Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pozo, F.; Tibaduiza, D.A.; Vidal, Y. Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring and Condition Monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, D.; Martin-Candilejo, A.; Cueto-Felgueroso, L.; Santillán, D. Use of Fiber-Optic Sensors to Monitor Concrete Dams: Recent Breakthroughs and New Opportunities. Structures 2024, 67, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Messerer, D.; Herbers, M.; Speck, K.; Laukner, J.; Gläser, C.; Jesse, F.; Marx, S. Monitoring of a Prestressed Bridge Girder with Integrated Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors. Procedia Structural Integrity 2024, 64, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-J.; Zhu, H.-H.; Wu, H.-Y.; Zhu, B.; Shi, B. Experimental Investigation on Pipe-Soil Interaction Due to Ground Subsidence via High-Resolution Fiber Optic Sensing. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2022, 127, 104586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, T. Deformation Monitoring of Ultra-Deep Foundation Excavation Using Distributed Fiber Optic Sensors. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 2021, 861, 072057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, I.; Zubia, J.; Durana, G.; Aldabaldetreku, G.; Illarramendi, M.; Villatoro, J. Optical Fiber Sensors for Aircraft Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 15494–15519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, C.; Manandhar, A.; Kiesel, P.; Raghavan, A. Monitoring the Strain Evolution of Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes Using an Optical Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor. Energy Technology 2016, 4, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Takeda, S.; Hisada, S.; Ogasawara, T. Detection of Matrix Cracks in Composite Laminates Using Embedded Fiber-Optic Distributed Strain Sensing. Sens Actuators A Phys 2024, 380, 116039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, P. Improving the Durability of the Optical Fiber Sensor Based on Strain Transfer Analysis. Optical Fiber Technology 2018, 42, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonina, S.N.; Kazanskiy, N.L.; Butt, M.A. Optical Fibre-Based Sensors—An Assessment of Current Innovations. Biosensors 2023, 13, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tarawneh, M.; Huang, Y.; Lu, P.; Bridgelall, R. Weigh-In-Motion System in Flexible Pavements Using Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors Part A: Concept. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2020, 21, 5136–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara De Maeijer, P.; Luyckx, G.; Vuye, C.; Voet, E.; Van den bergh, W.; Vanlanduit, S.; Braspenninckx, J.; Stevens, N.; De Wolf, J. Fiber Optics Sensors in Asphalt Pavement: State-of-the-Art Review. Infrastructures 2019, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujon, M.; Dai, F. Application of Weigh-in-Motion Technologies for Pavement and Bridge Response Monitoring: State-of-the-Art Review. Autom Constr 2021, 130, 103844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Podolsky, J.; Huang, Y.; Lu, P. Assessing Vehicle Wandering Effects on the Accuracy of Weigh-in-Motion Measurement Based on In-Pavement Fiber Bragg Sensors through a Hybrid Sensor-Camera System. Sensors 2023, 23, 8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pau, A.; Vestroni, F. Weigh-in-motion of Train Loads Based on Measurements of Rail Strains. Struct Control Health Monit 2021, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintão, B.; Mosleh, A.; Vale, C.; Montenegro, P.; Costa, P. Development and Validation of a Weigh-in-Motion Methodology for Railway Tracks. Sensors 2022, 22, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharenko, M.; Frøseth, G.T.; Rönnquist, A. Train Classification Using a Weigh-in-Motion System and Associated Algorithms to Determine Fatigue Loads. Sensors 2022, 22, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Roy, K. Application of Bridge Weigh-in-Motion System in Bridge Health Monitoring: A State-of-the-Art Review. Struct Health Monit 2023, 22, 4194–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekič, D.; Kosič, M.; Kalin, J.; Žnidarič, A.; Anžlin, A. Challenges of Implementing Bridge Weigh-in-Motion on a Century-Old Steel-Riveted Railway Bridge. In Bridge Maintenance, Safety, Management, Digitalization and Sustainability; CRC Press: London, 2024; pp. 1429–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Breccolotti, M.; Natalicchi, M. Bridge Damage Detection Through Combined Quasi-Static Influence Lines and Weigh-in-Motion Devices. International Journal of Civil Engineering 2022, 20, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajializadeh, D.; Žnidarič, A.; Kalin, J.; OBrien, E.J. Development and Testing of a Railway Bridge Weigh-in-Motion System. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.-J.; Song, K.-Y.; Choi, C.; Na, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S. Real-Time Distributed Strain Monitoring of a Railway Bridge during Train Passage by Using a Distributed Optical Fiber Sensor Based on Brillouin Optical Correlation Domain Analysis. J Sens 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, R.; Ribeiro, D.; Matos, L.; Mosleh, A.; Calçada, R. Bridge Weigh-in-Motion System for the Identification of Train Loads Using Fiber-Optic Technology. Structures 2021, 30, 1056–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Sui, Q.; Jia, L.; Jiang, M. Load Identification of High-Speed Train Crossbeam Based on Bayesian Finite Element Model Updating and Load-Strain Linear Superposition Algorithm. IEEE Sens J 2023, 23, 13489–13498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Dutta, S.; Kurup, P.; Yu, T.; Wang, X. A Review of Railway Infrastructure Monitoring Using Fiber Optic Sensors. Sens Actuators A Phys 2020, 303, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Abdulhakeem, S.; Fang, C.; Han, T.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Faisal, Y. A New Wayside Method for Measuring and Evaluating Wheel-Rail Contact Forces and Positions. Measurement 2020, 166, 108244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sharan, P.; Alodhayb, A.N.; Alrebdi, T.A.; Upadhyaya, A.M. Design and Development of Wagon Load Monitoring System Using Fibre Bragg Grating Sensor. Optical Fiber Technology 2025, 90, 104149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martincek, I.; Kacik, D.; Horak, J. Interferometric Optical Fiber Sensor for Monitoring of Dynamic Railway Traffic. Opt Laser Technol 2021, 140, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Yang, Z.; Liang, X.; Yang, R.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q.; Luo, W. Experimental Study on Wayside Monitoring Method of Train Dynamic Load Based on Strain of Ballastless Track Slab. Constr Build Mater 2023, 394, 132084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sharan, P.; Saara, K. Optomechanical Behaviour of Optical Sensor for Measurement of Wagon Weight at Different Speeds of the Train. Journal of Optics 2023, 52, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, N.S.; Blanc, J.; Hornych, P.; Bouveret, B.; Carroget, J.; Le feuvre, Y. Continuous Strain Monitoring of an Instrumented Pavement Section. International Journal of Pavement Engineering 2019, 20, 1435–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.W.; Singh, R.R.; Wang, H. Impact of Surface Roughness, Speed, and Sensor Configuration on Weigh-in-Motion (WIM) System Accuracy. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Fu, K.; Lin, M. Tire–Pavement Contact-Aware Weight Estimation for Multi-Sensor WIM Systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Jung, Y.W.; Utebayeva, A.; Kamaliyeva, Z.; Collins, N.; Sarbassov, D.; Sagin, J.; Amanzhlova, R. High-Performance High-Speed WIM For Sustainable Road Load Monitoring Using GIS Technology. Transport Problems 2021, 16, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, F. Applications of Optical Fiber Sensor in Pavement Engineering: A Review. Constr Build Mater 2023, 400, 132713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Y.; Pan, Y. Deep Learning Based Vehicle Detection and Classification Methodology Using Strain Sensors under Bridge Deck. Sensors 2020, 20, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Rocheti, E.; Moreira Bacurau, R. Weigh-in-Motion Systems Review: Methods for Axle and Gross Vehicle Weight Estimation. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 134822–134836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; He, W.; Yu, Y.; Cai, C.S. Equivalent Shear Force Method for Detecting the Speed and Axles of Moving Vehicles on Bridges. Journal of Bridge Engineering 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tan, C.; OBrien, E.J.; Uddin, N.; Zhang, B. Wavelet-Based Optimum Identification of Vehicle Axles Using Bridge Measurements. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, H.; Uddin, N.; Guo, H.; Yan, B. An Extended Bridge Weigh-in-Motion System without Vehicular Axles and Speed Detectors Using Nonnegative LASSO Regularization. Journal of Bridge Engineering 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Z.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhao, M.X.; Zhong, Q.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, T. Performance of Bridge Weigh-in-Motion Methods Considering Environmental Temperature Field Effect. Structures 2025, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Z.; Zhong, Q.-M.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Yang, G.; Feng, D.-C. Evaluation of Performance of Bridge Weigh-in-Motion Methods Considering Spatial Variability of Bridge Properties. ASCE ASME J Risk Uncertain Eng Syst A Civ Eng 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinen, S.K.; Lopez, R.H.; Miguel, L.F.F. A Shear-Force-Based Bridge Weigh-in Motion Approach for Simple Supported Structures. Structures 2024, 70, 107607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamandala, S.; Sai Prasad, R.L.N.; Pancharathi, R.K.; Pavan, V.D.R.; Kishore, P. Study on Bridge Weigh in Motion (BWIM) System for Measuring the Vehicle Parameters Based on Strain Measurement Using FBG Sensors. Optical Fiber Technology 2021, 61, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, X.; Wu, G. A Bridge Weigh-in-Motion Method of Motorway Bridges Considering Random Traffic Flow Based on Long-Gauge Fibre Bragg Grating Sensors. Measurement 2021, 186, 110081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.T.A.; Morgese, M.; Taylor, T.; Ansari, F. Method and Application for Influence-Line-Free Distributed Detection of Gross Vehicle Weights in Bridges. Structures 2025, 73, 108298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskoui, E.A.; Taylor, T.; Ansari, F. Method and Sensor for Monitoring Weight of Trucks in Motion Based on Bridge Girder End Rotations. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering 2020, 16, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Xie, Y.M. Conceptual Design of Long Span Steel-UHPC Composite Network Arch Bridge. Eng Struct 2023, 277, 115434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mucci, V.M.; Cardellicchio, A.; Ruggieri, S.; Nettis, A.; Renò, V.; Uva, G. Artificial Intelligence in Structural Health Management of Existing Bridges. Autom Constr 2024, 167, 105719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayane, I.; Leander, J.; Karoumi, R. An Unsupervised Machine Learning Approach for Real-Time Damage Detection in Bridges. Eng Struct 2024, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Cao, Z.; Sun, H.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, L. Transfer Learning for Structure Damage Detection of Bridges through Dynamic Distribution Adaptation. Structures 2024, 67, 106972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xin, J.; Tang, Q.; Hu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J. Explainable Machine Learning Model for Load-Deformation Correlation in Long-Span Suspension Bridges Using XGBoost-SHAP. Developments in the Built Environment 2024, 20, 100569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, A.; Reyes-Aldasoro, C.C. Dynamic Analysis of the Effects of Vehicle Movement over Bridges Observed with CCTV Images. Eng Struct 2024, 317, 118653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.T.; Keenan, M.; Nguyen, A.; Ghazvineh, S.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Manalo, A. A Supervised Machine Learning Approach for Structural Overload Classification in Railway Bridges Using Weigh-in-Motion Data. Structures 2025, 71, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosso, M.; Vasconcelos, K.L.; Ho, L.L.; Bernucci, L.L.B. Use of Regression Trees to Predict Overweight Trucks from Historical Weigh-in-Motion Data. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering 2020, 7, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yang, J.; Luo, X. Quick Weighing of Passing Vehicles Using the Transfer-Learning-Enhanced Convolutional Neural Network. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 139, 2507–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Xia, Y.; Sun, S.; Sun, L. Integrating Bridge Influence Surface and Computer Vision for Bridge Weigh-in-motion in Complicated Traffic Scenarios. Struct Control Health Monit 2022, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HBK – Hottinger Brüel & Kjær HBM FiberSensing: Optical Measurement Solutions – Brochure; Vilar do Pinheiro, Portugal, 2025.
- Teufelberger-Redaelli. Cable System (FLC). Technical Product Data; Cologno Monzese: Milan, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nowoświat, A.; Olechowska, M. Experimental Validation of the Model of Reverberation Time Prediction in a Room. Buildings 2022, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


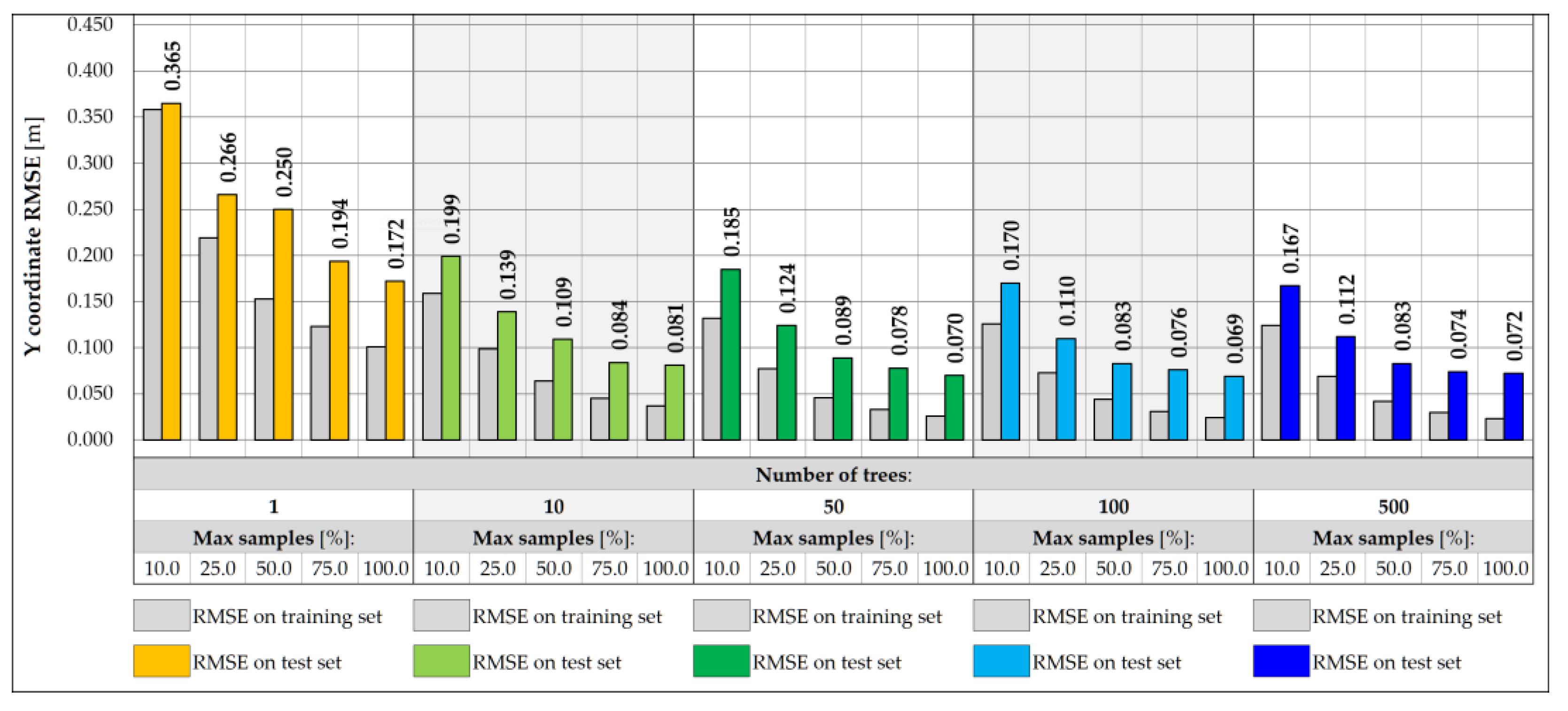
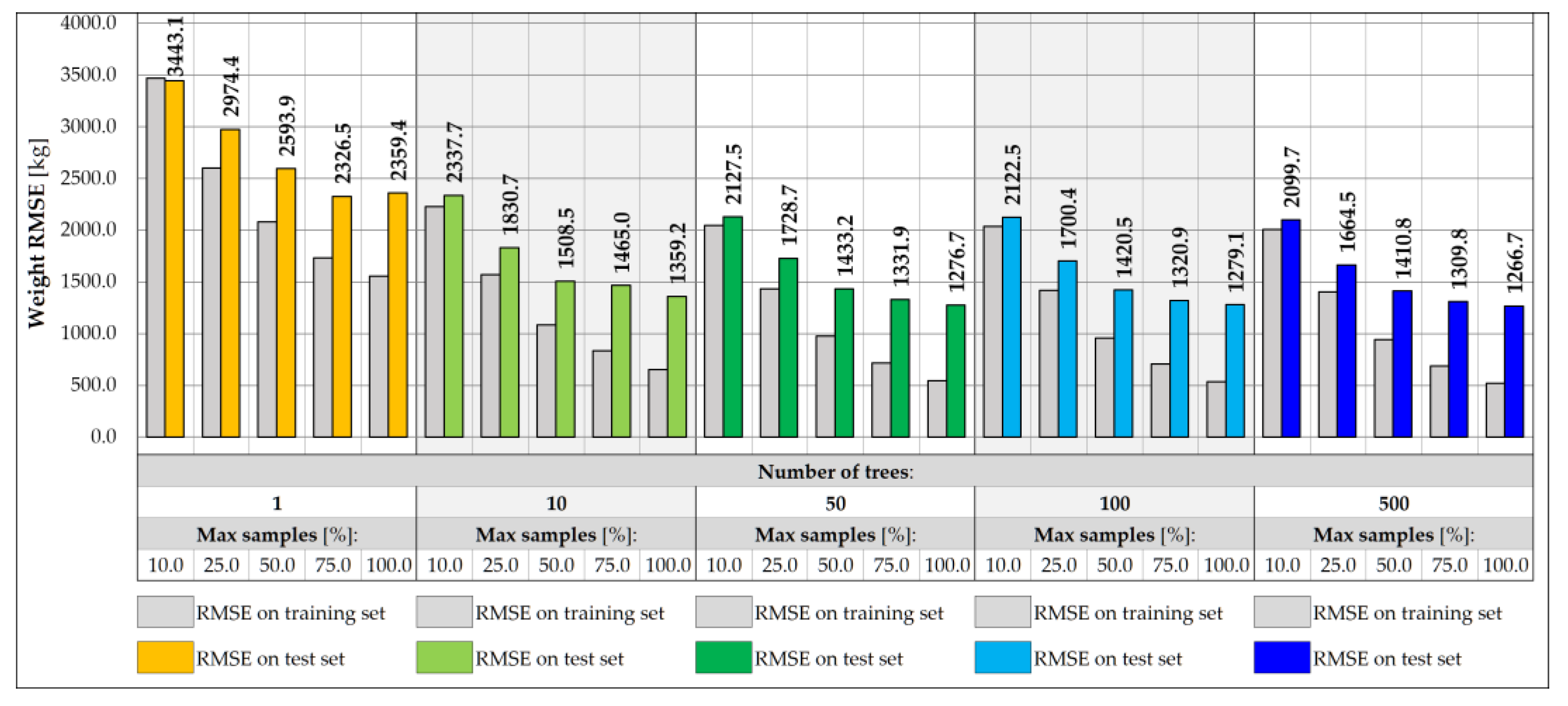
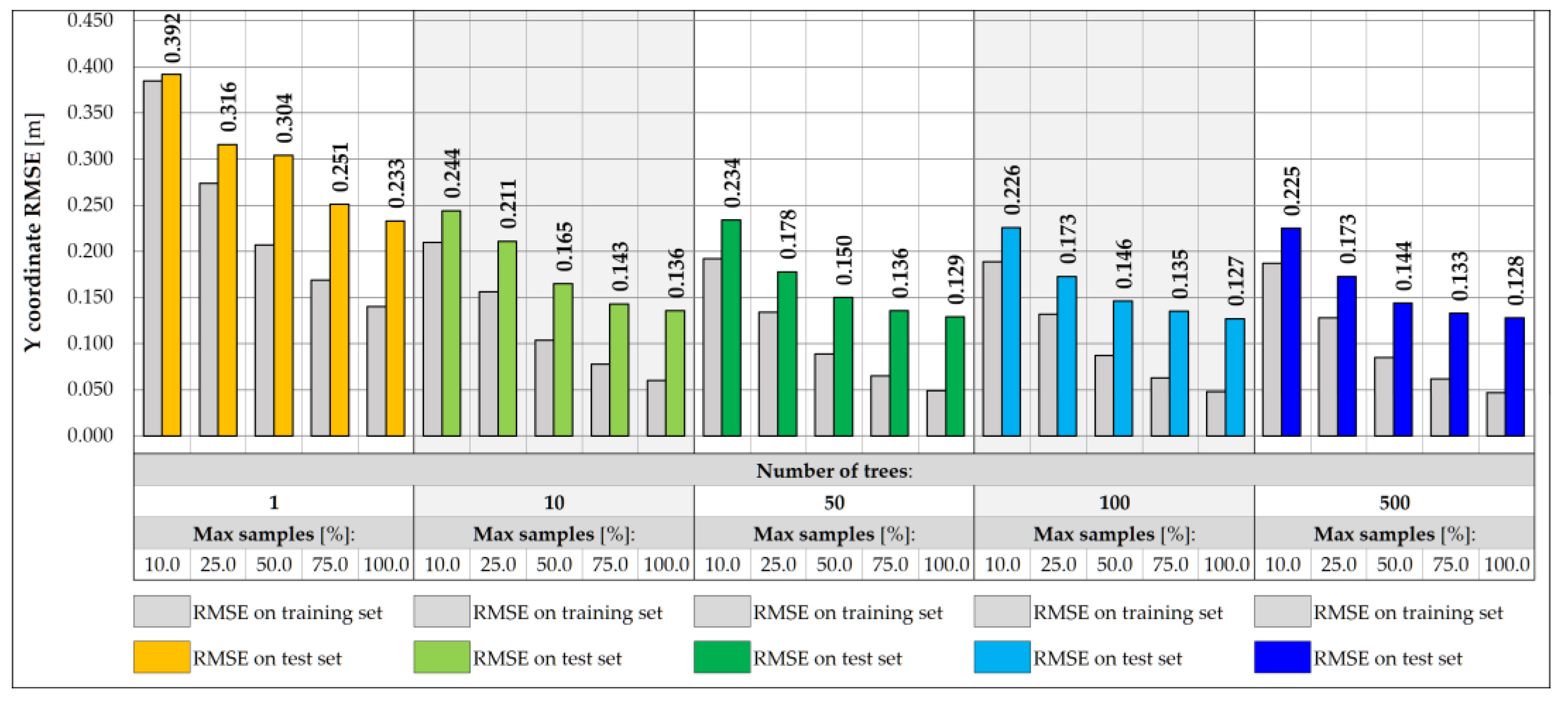
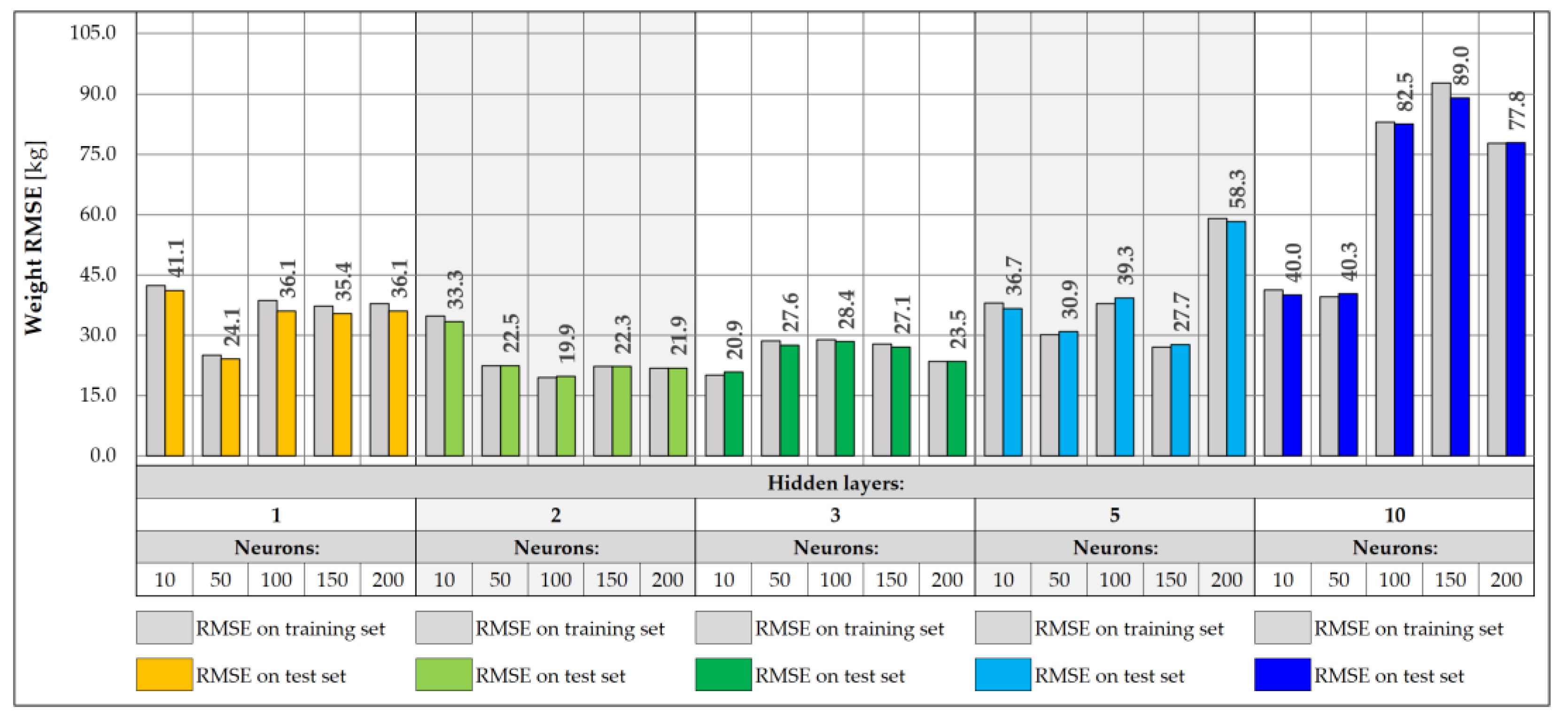
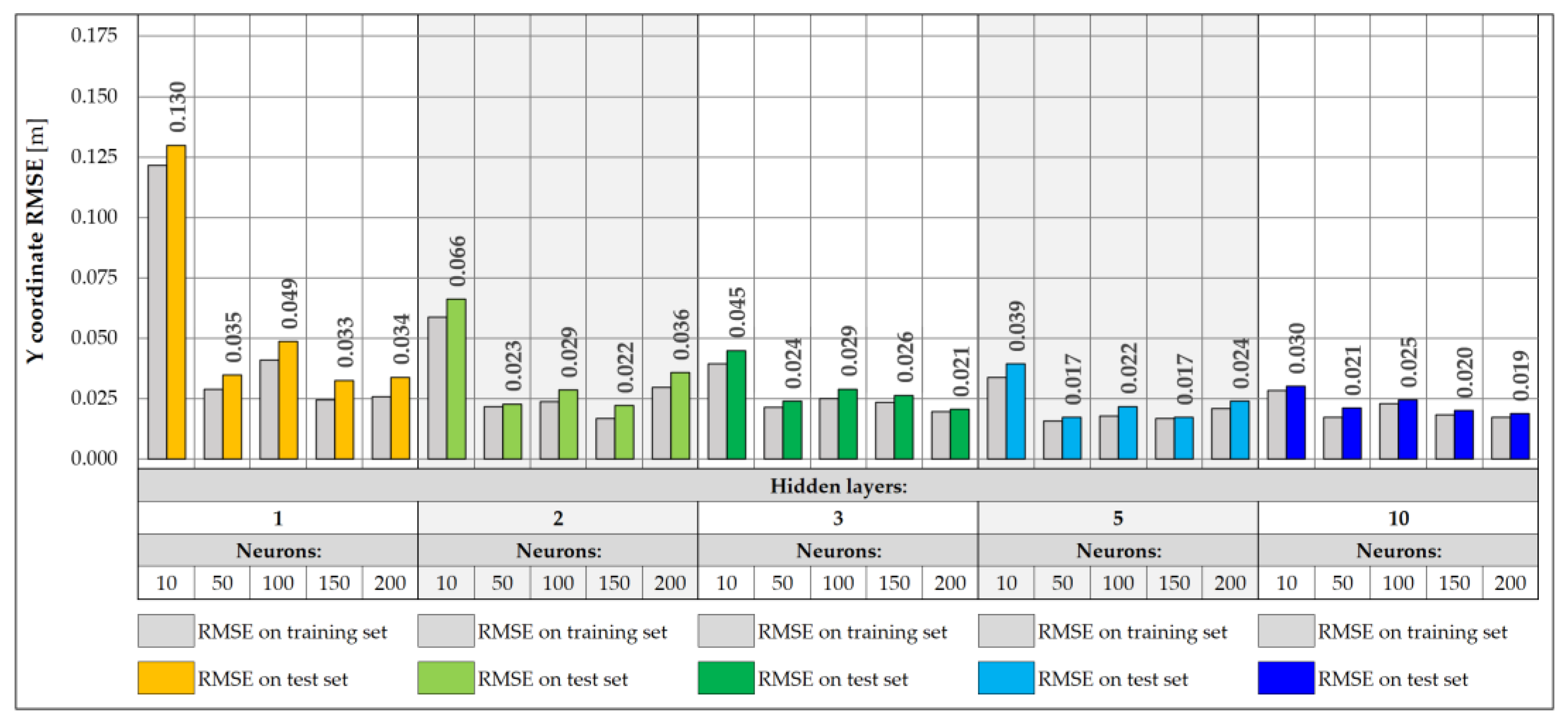
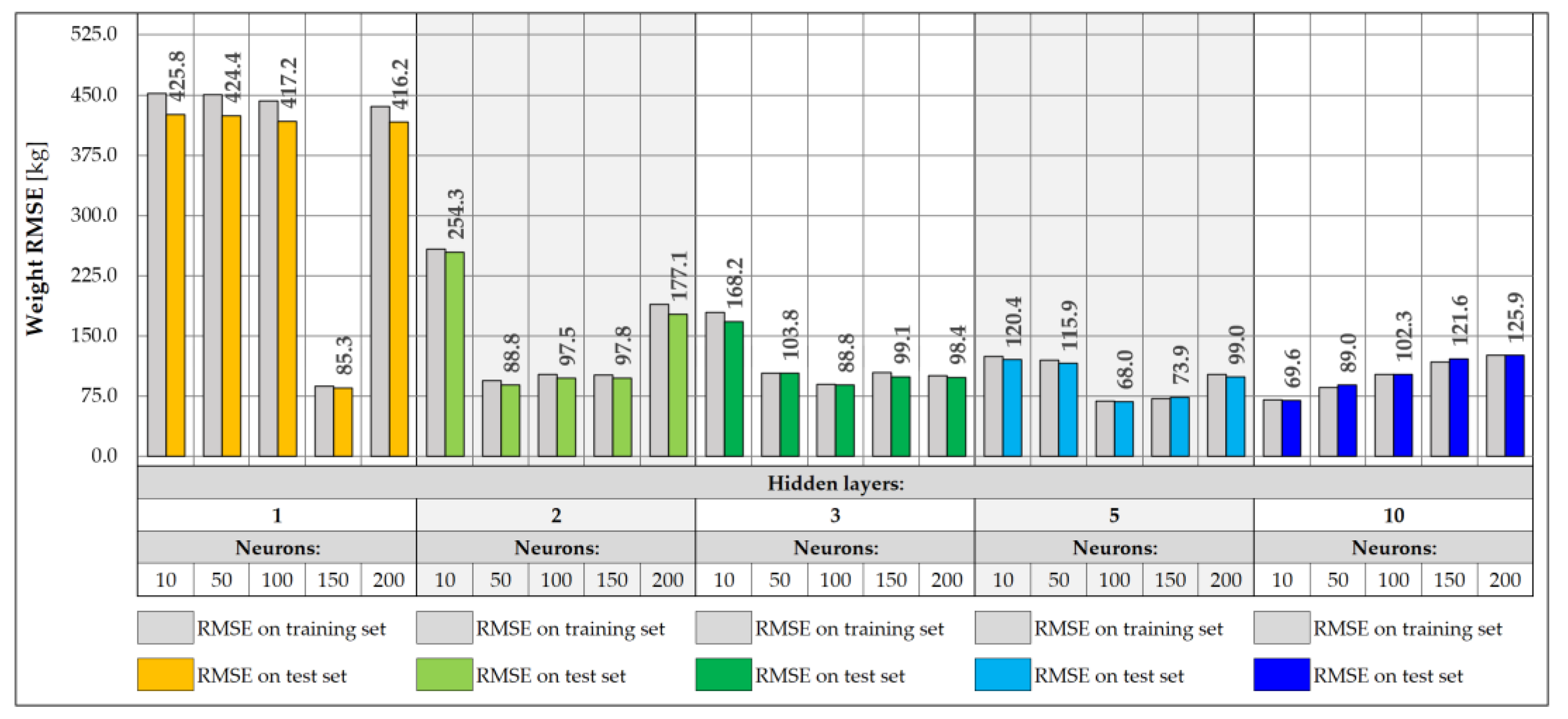
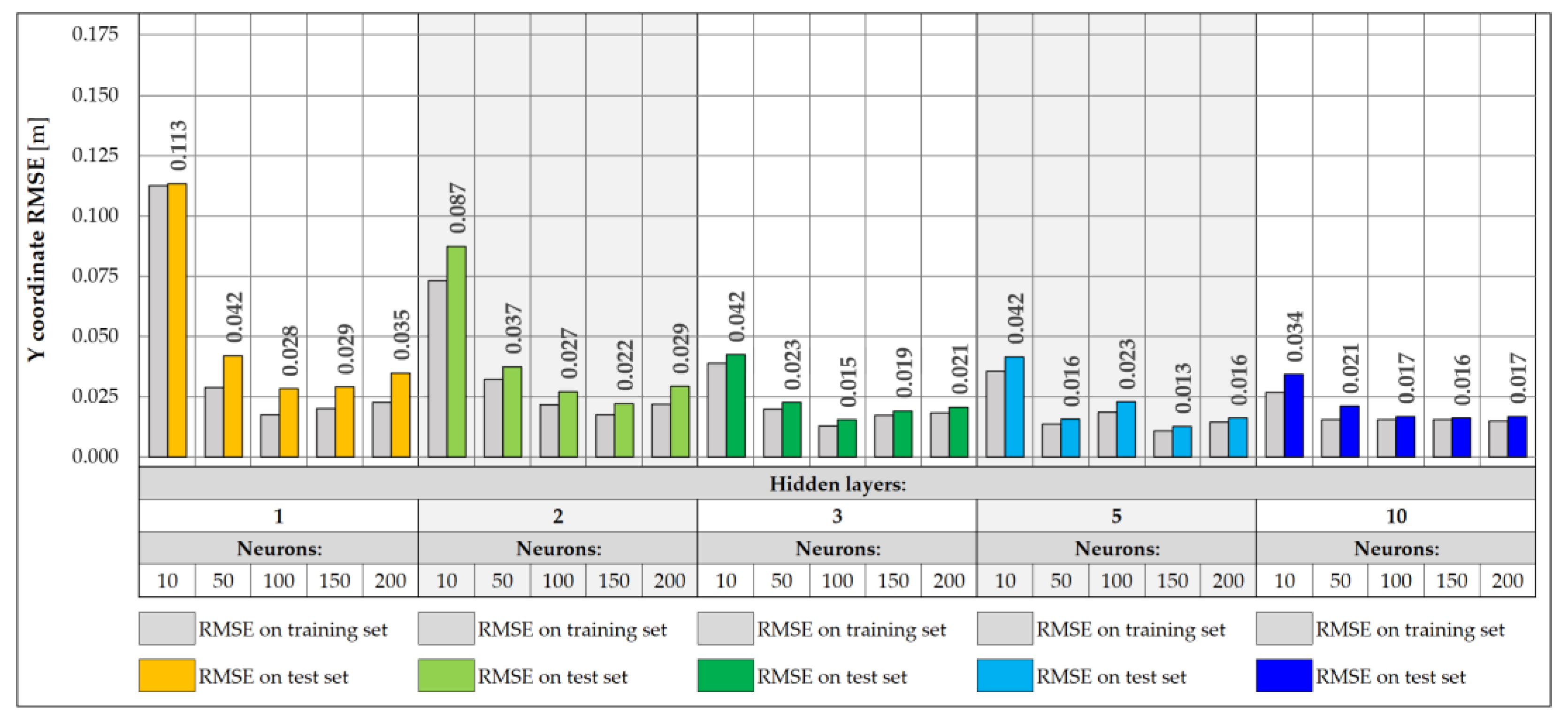
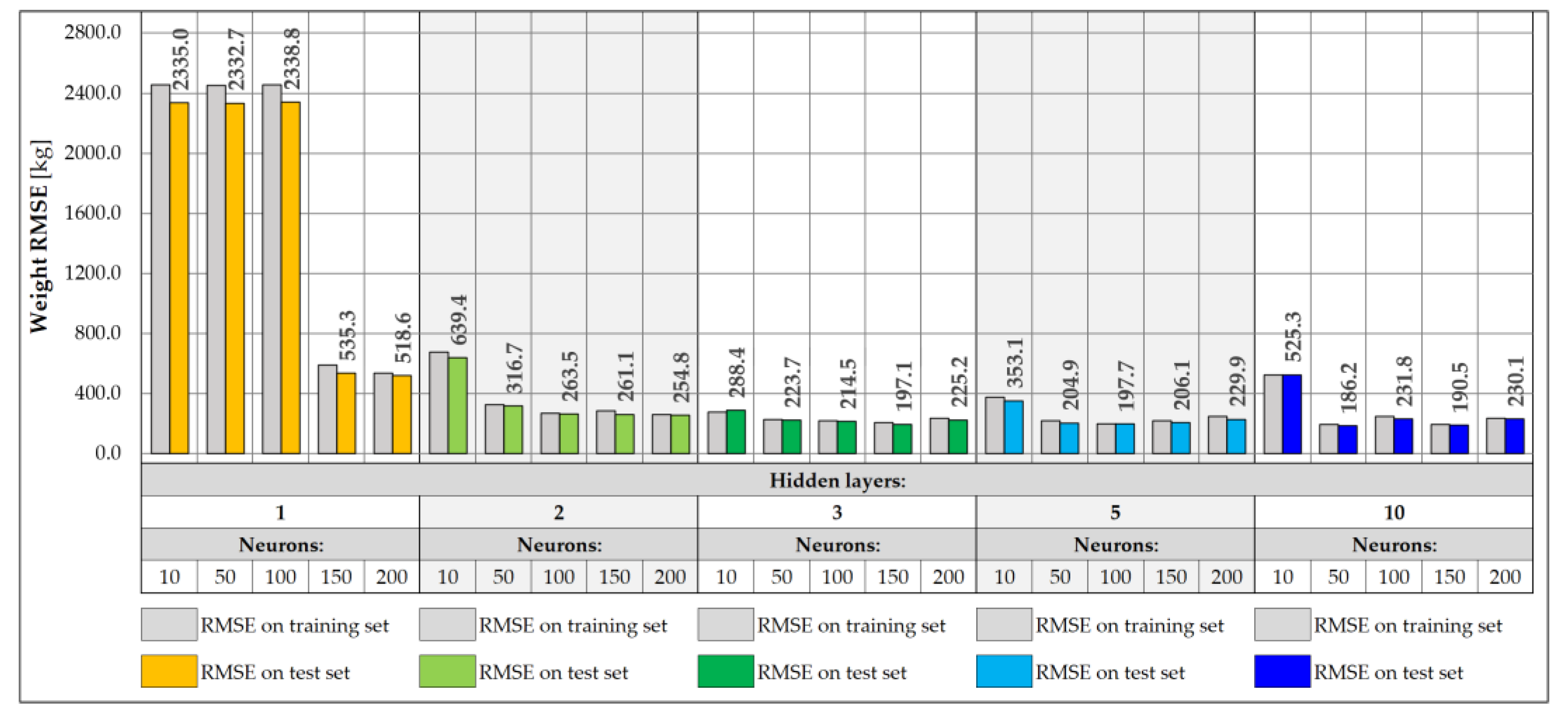
|
Random Forest Regression: Total weight estimation number of trees: 500, max samples: 100.0% | |||
| Training set size | Training time 1 [s] | RMSE [kg] | |
| Training set | Test set | ||
| 4 800 | 5.5 | 518.1 | 1 266.7 |
| 12 000 | 14.4 | 356.8 | 883.4 |
| 24 000 | 33.1 | 271.9 | 674.1 |
| 48 000 | 73.2 | 197.7 | 509.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





