Submitted:
16 June 2025
Posted:
17 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
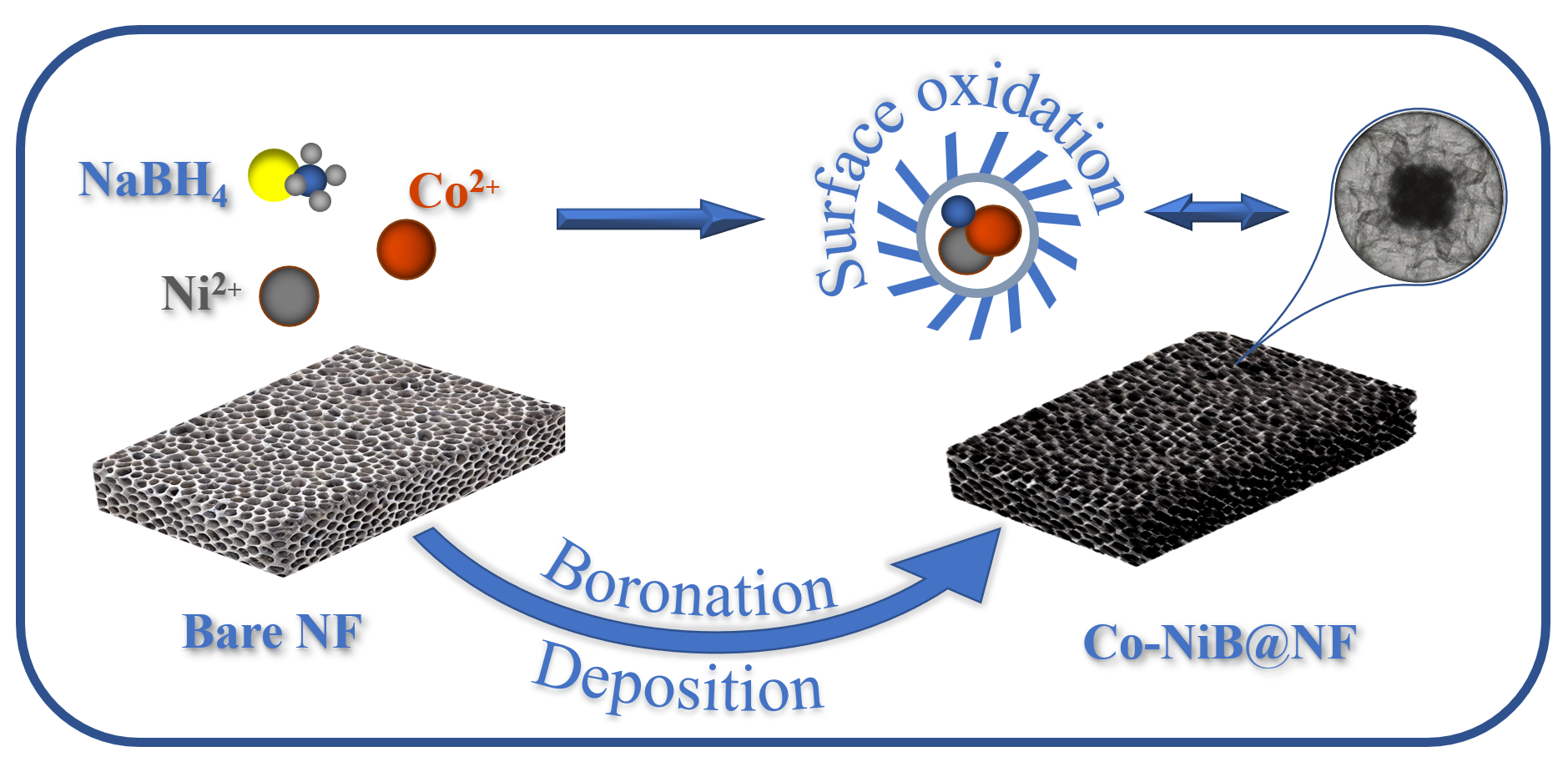
2.1. Preparation of Ni–Co Boride
2.2. Preparation of Ni₉Co₁-LDH@NF
2.3. Catalytic Characterization
2.4. Electrochemical Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
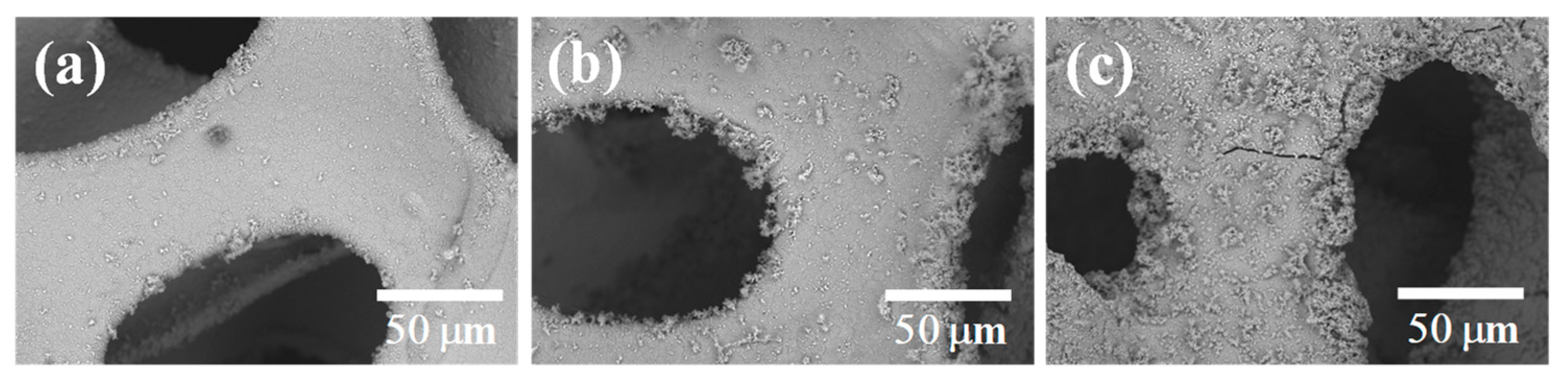
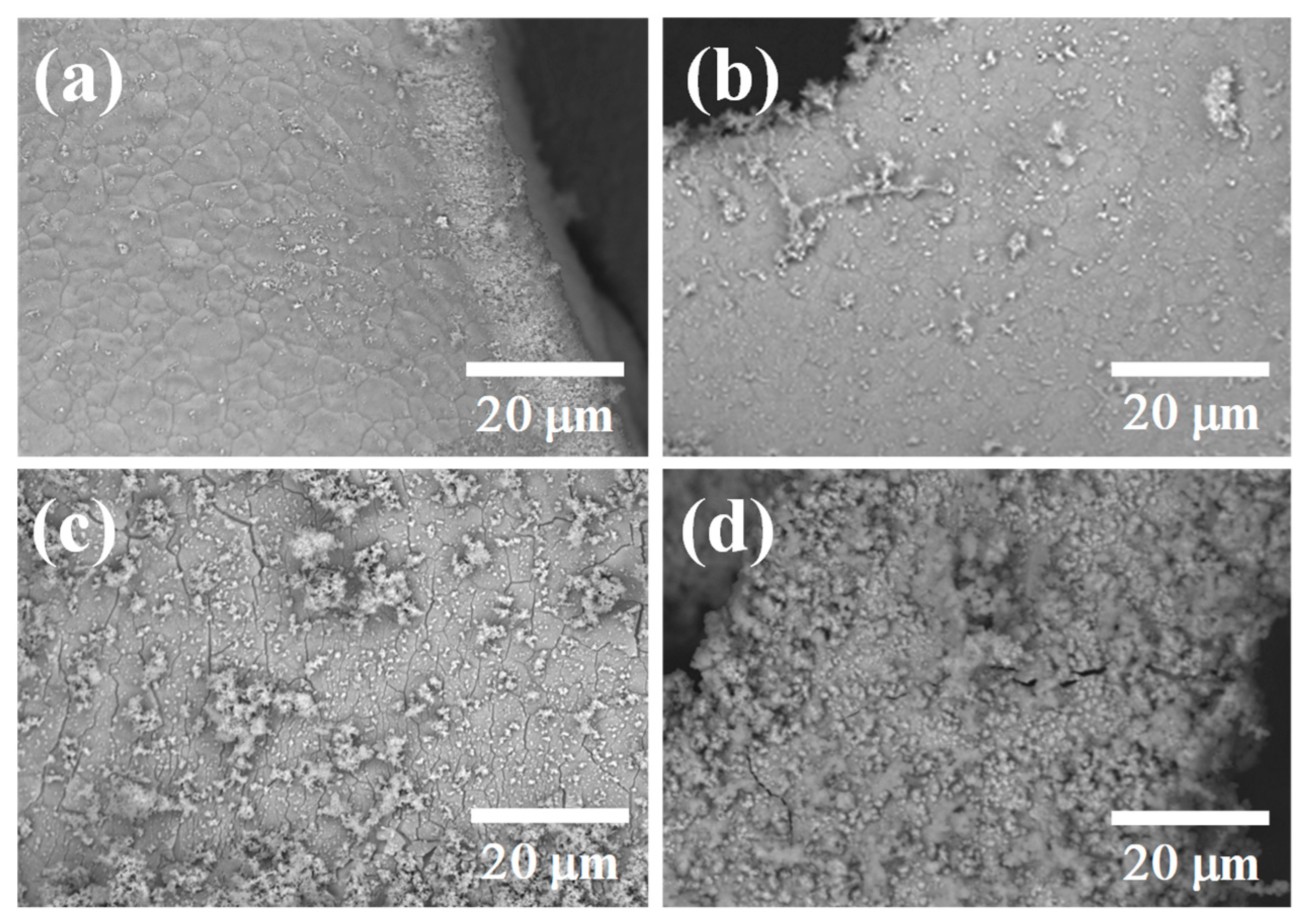
3.1. Morphology and Structure
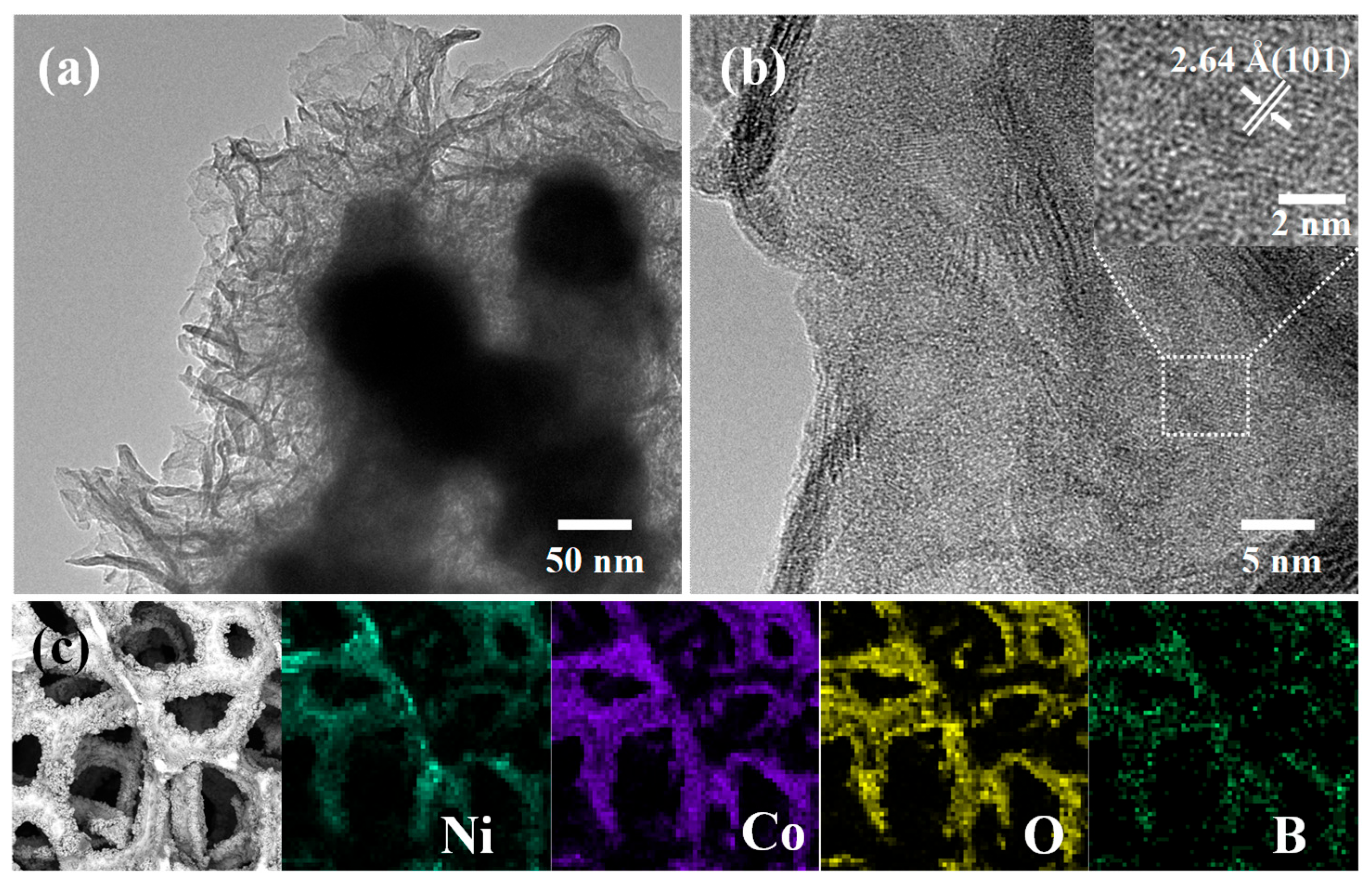
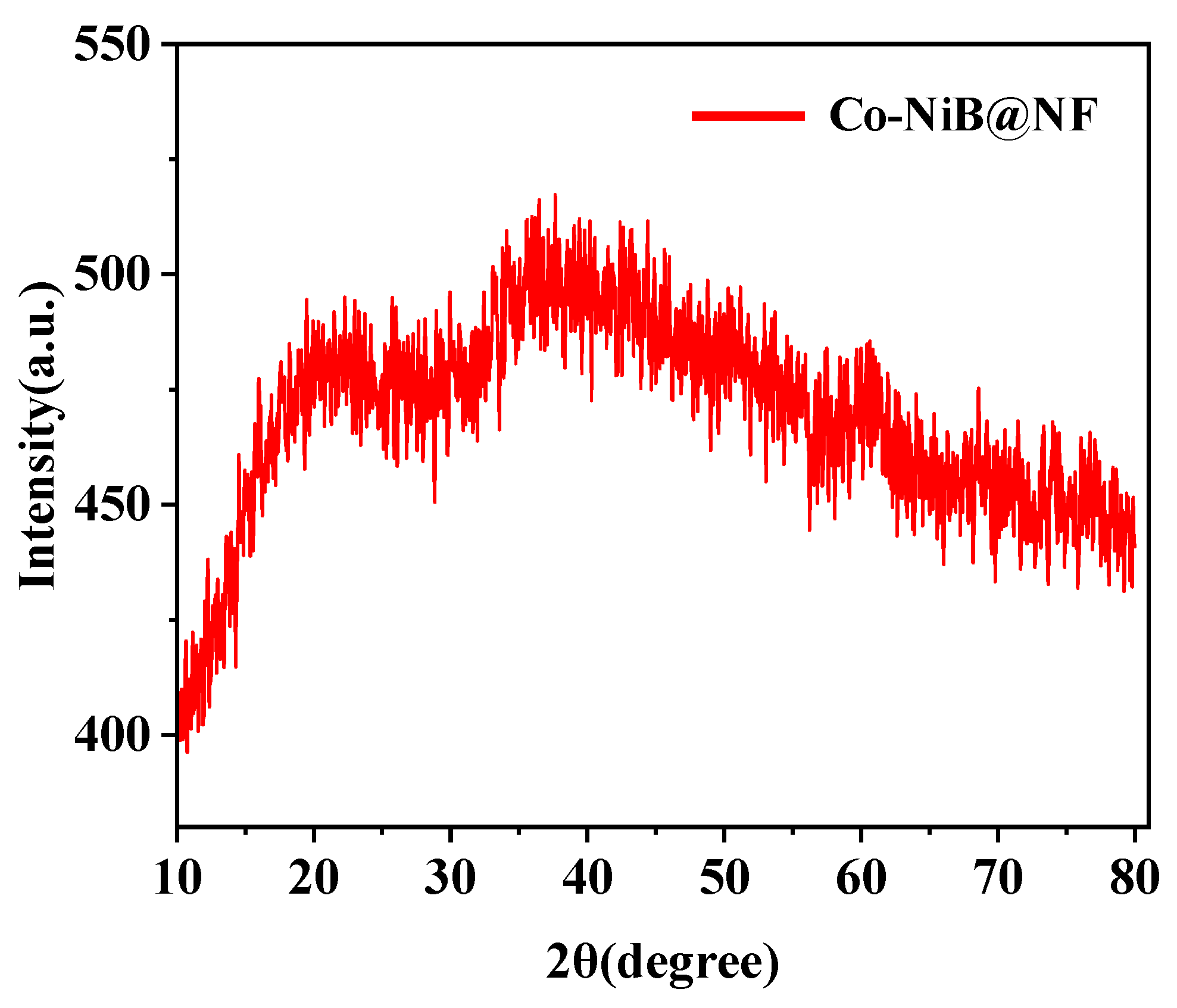
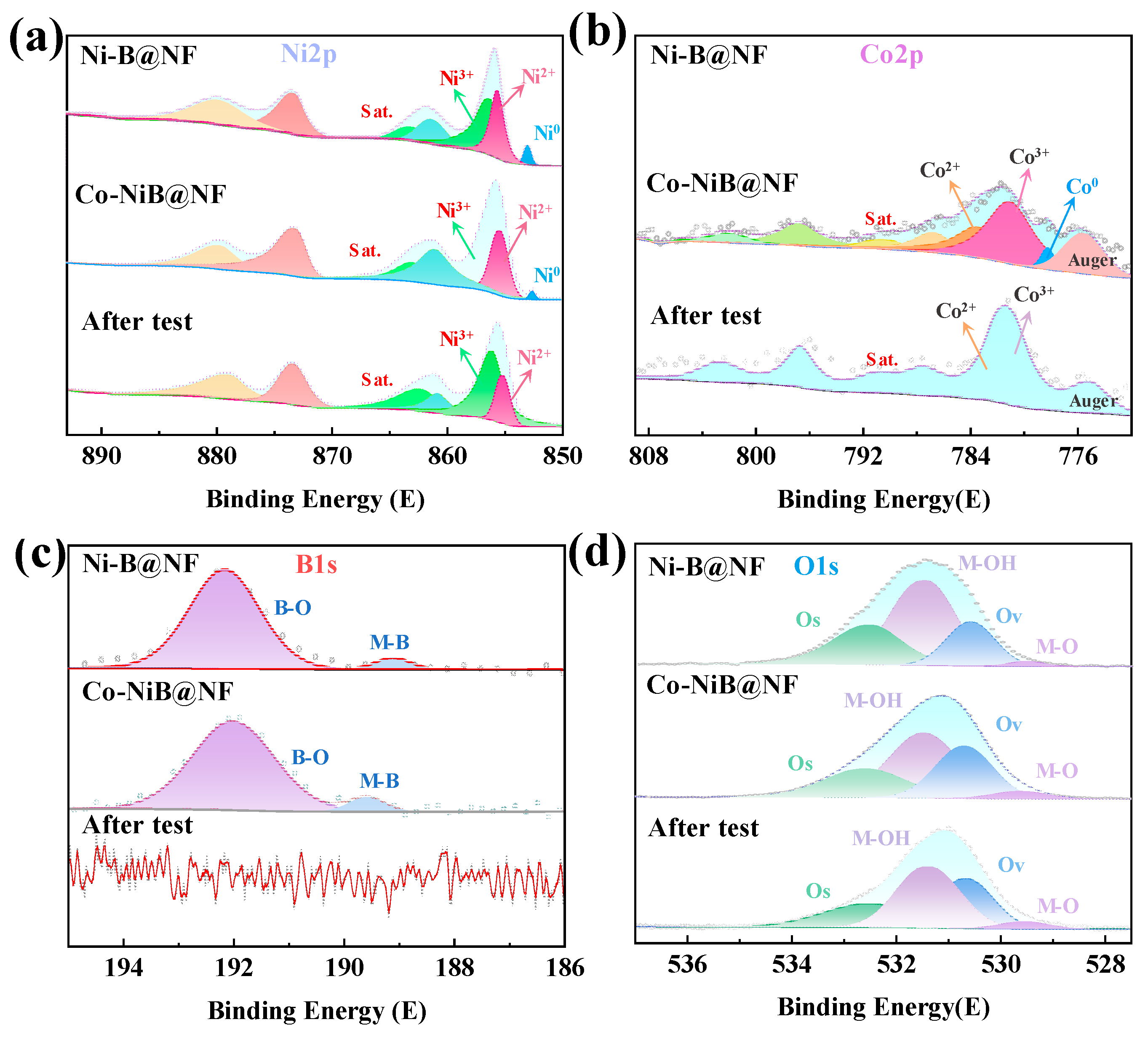
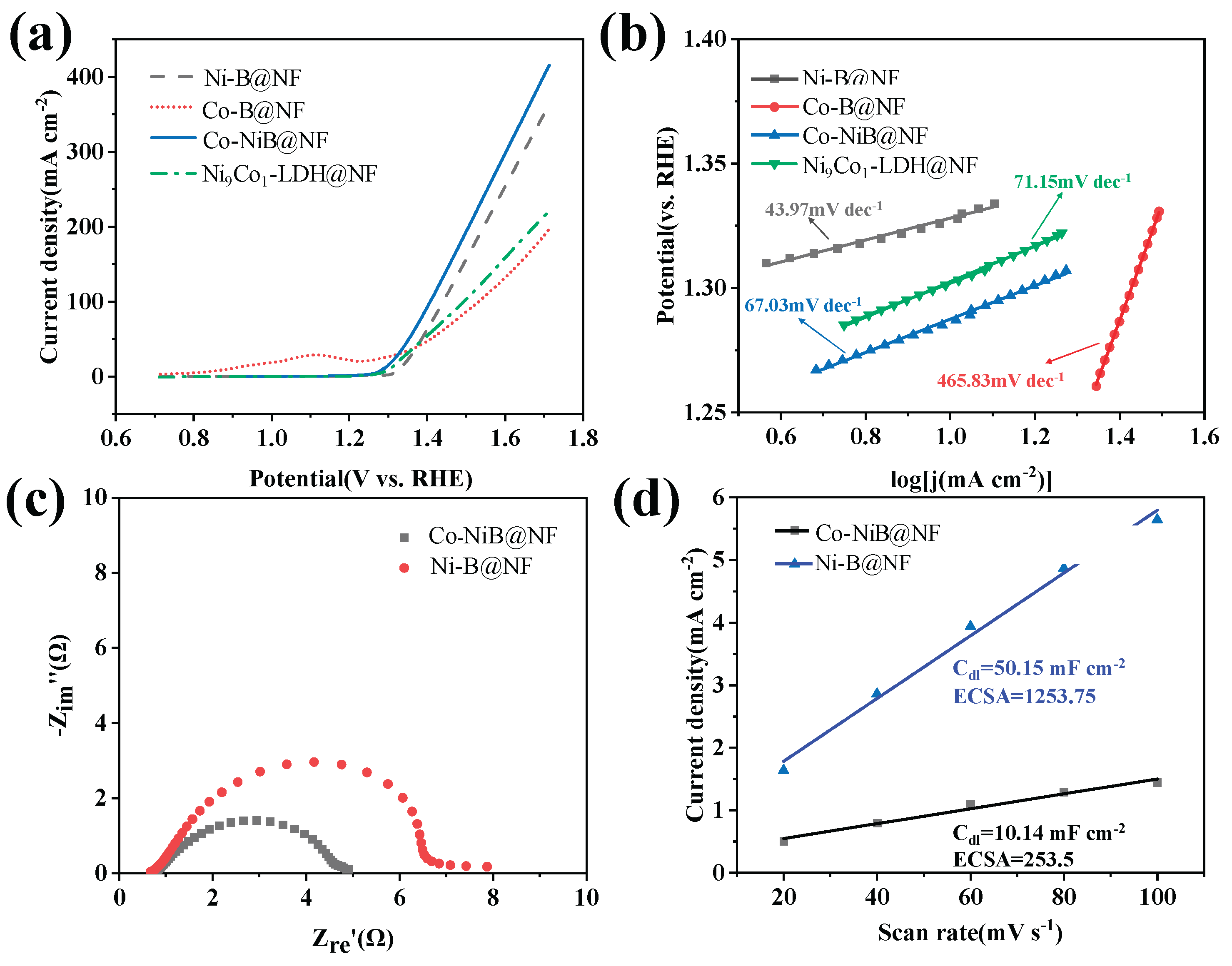
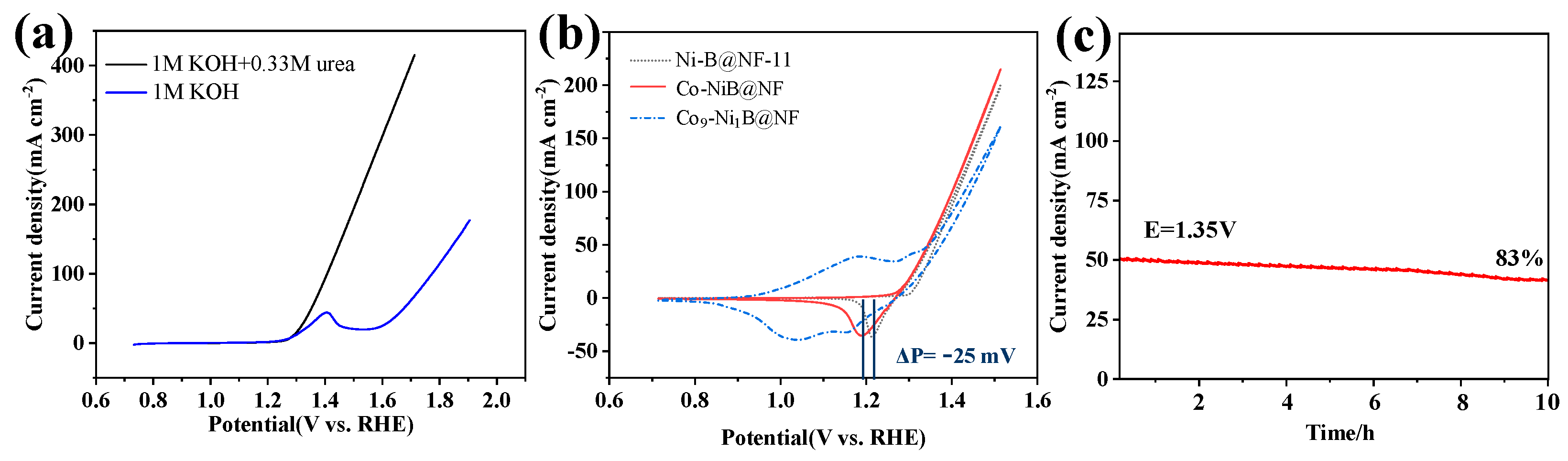
3.2. UOR Performance
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
References
- Oliveira, A. M.; Beswick, R. R.; Yan, Y. A Green Hydrogen Economy for a Renewable Energy Society. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2021, 33, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, B.; Huang, W.; Li, J. Promotion Effects of Pr-Doped CeO2·H2O to Pt Catalysts toward Alcohol Electrooxidation Reaction. Mater. Lett. 2023, 349, 134796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. K.; Rajavelu, K.; Montag, M.; et al. Advances in Catalytic Electrooxidation of Urea: A Review. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zou, X. Intermetallic Borides: Structures, Synthesis and Applications in Electrocatalysis. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 2248–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quílez-Bermejo, J.; García-Dalí, S.; Karthik, R.; et al. Zinc Doping Enhances the Electrocatalytic Properties of Cobalt Borides for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 901395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shao, Q.; Huang, X. Amorphous Oxide Nanostructures for Advanced Electrocatalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 3943–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. High-Performance Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysis by Boronized Metal Sheets with Self-Functionalized Surfaces. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dong, J.; Yang, X.; et al. Hydrogelator as Growth-Controlling Agent for Enhancing the Catalytic Activity of NiB Amorphous Alloy Catalyst. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 7861–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Jagadeesan, S. N.; Zhang, L.; et al. Enhanced Urea Oxidation Electrocatalytic Activity by Synergistic Cobalt and Nickel Mixed Oxides. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2023, 15, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, J.; et al. First Principles Study on High-Efficient Overall Water Splitting by Anchoring Cobalt Boride with Transition Metal Atoms. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 53, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhou, K.; Xie, M.; et al. Self-Supported Nickel Iron Selenide@Nickel Cobalt Boride Core-Shell Nanosheets Electrode for Asymmetric Supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 447, 137495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamadar, A. S.; Sutar, R. B.; Patil, S.; et al. Attaining High-Rate Hydrogen Evolution via SILAR Deposited Bimetallic Nickel Cobalt Boride Electrode: Exploring the Influence of Ni to Co Ratio. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 85, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Cao, G.; Chen, Z.; et al. Cobalt Nickel Boride as an Active Electrocatalyst for Water Splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 12379–12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagurunathan, A. T.; Seenivasan, S.; Kavinkumar, T.; et al. Phosphorus Doping of Nickel–Cobalt Boride to Produce a Metal–Metalloid–Nonmetal Electrocatalyst for Improved Overall Water Splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 4643–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, B.; Yu, T.; et al. Insights into Correlation among Surface-Structure-Activity of Cobalt-Derived Pre-Catalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, R.; Zou, H.; et al. Amorphous Iron-Doped Nickel Boride with Facilitated Structural Reconstruction and Dual Active Sites for Efficient Urea Electrooxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qin, H.; Ye, Z.; et al. Interconnected Mn-Doped Ni(OH)2 Nanosheet Layer for Bifunctional Urea Oxidation and Hydrogen Evolution: The Relation between Current Drop and Urea Concentration during the Long-Term Operation. ACS ES&T Eng. 2022, 2, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, M.; Shetti, R. S.; Mathi, S.; et al. Ni-Tethered MoS2: In-Situ Fast Reduction Synthesis as an Ultra-Durable and Highly Active Electrocatalyst for Water Splitting and Urea Oxidation. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 26, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Ru-Doped 3D Porous Ni3N Sphere as Efficient Bi-Functional Electrocatalysts toward Urea Assisted Water-Splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 25081–25089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sun, M.; Wu, S.; et al. Oxygen-Incorporated NiMoP Nanotube Arrays as Efficient Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for Urea-Assisted Energy-Saving Hydrogen Production in Alkaline Electrolyte. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Hollow NiMo-Based Nitride Heterojunction with Super-Hydrophilic/Aerophobic Surface for Efficient Urea-Assisted Hydrogen Production. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 95, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zou, W.; Qiu, S.; et al. Active Site Tailoring of Ni-Based Coordination Polymers for High-Efficiency Dual-Functional HER and UOR Catalysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2310155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Material/substrate | Electrolyt | Potential (V vs. RHE) @ (mA cm-2) | Reference |
| Co-NiB@NF | 1MKOH+0.33M urea | 1.29@10 | This work |
| aFe-NiB | 1MKOH+0.5M urea | 1.29@10 | [16] |
| Mn-Ni(OH)2/CP | 1MKOH+0.33M urea | 1.33@10 | [17] |
| NiMoS2/NF | 1MKOH+0.33M urea | 1.39@10 | [18] |
| Ru-Ni3N@NC | 1MKOH+0.33M urea | 1.36@10 | [19] |
| O-NiMoP/NF | 1MKOH+0.5M urea | 1.41@100 | [20] |
| Ni/NiMoN | 1MKOH+0.5M urea | 1.39@100 | [21] |
| W-NT@NF-3 | 1MKOH+0.33M urea | 1.43@100 | [22] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




