Submitted:
14 June 2025
Posted:
16 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Complex Structure Preparation
Molecular Dynamics Simulation Protocol
Analysis of Simulated Structures
Results and Discussion
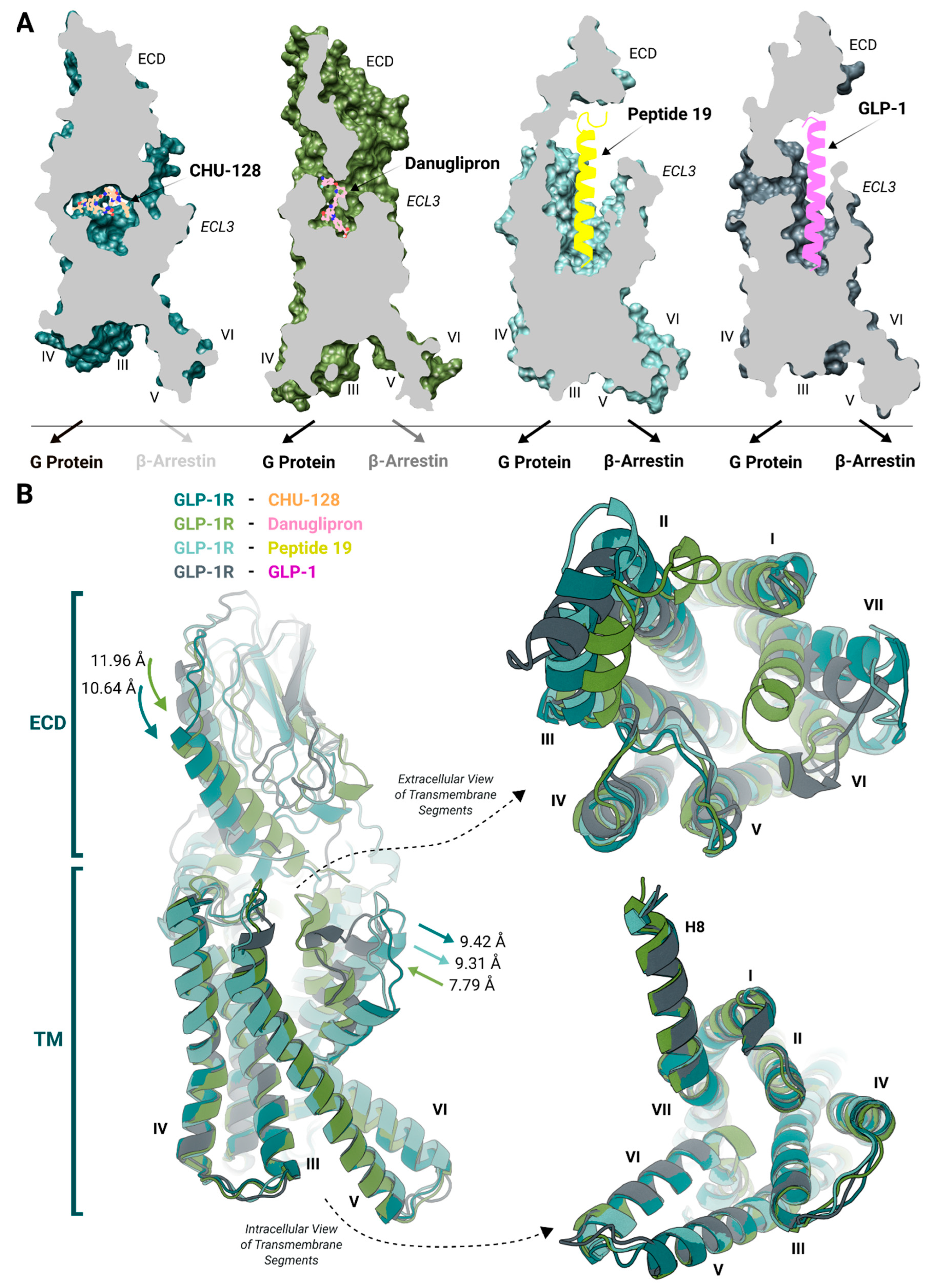
Distinct Binding Mode Led to Unique Signaling
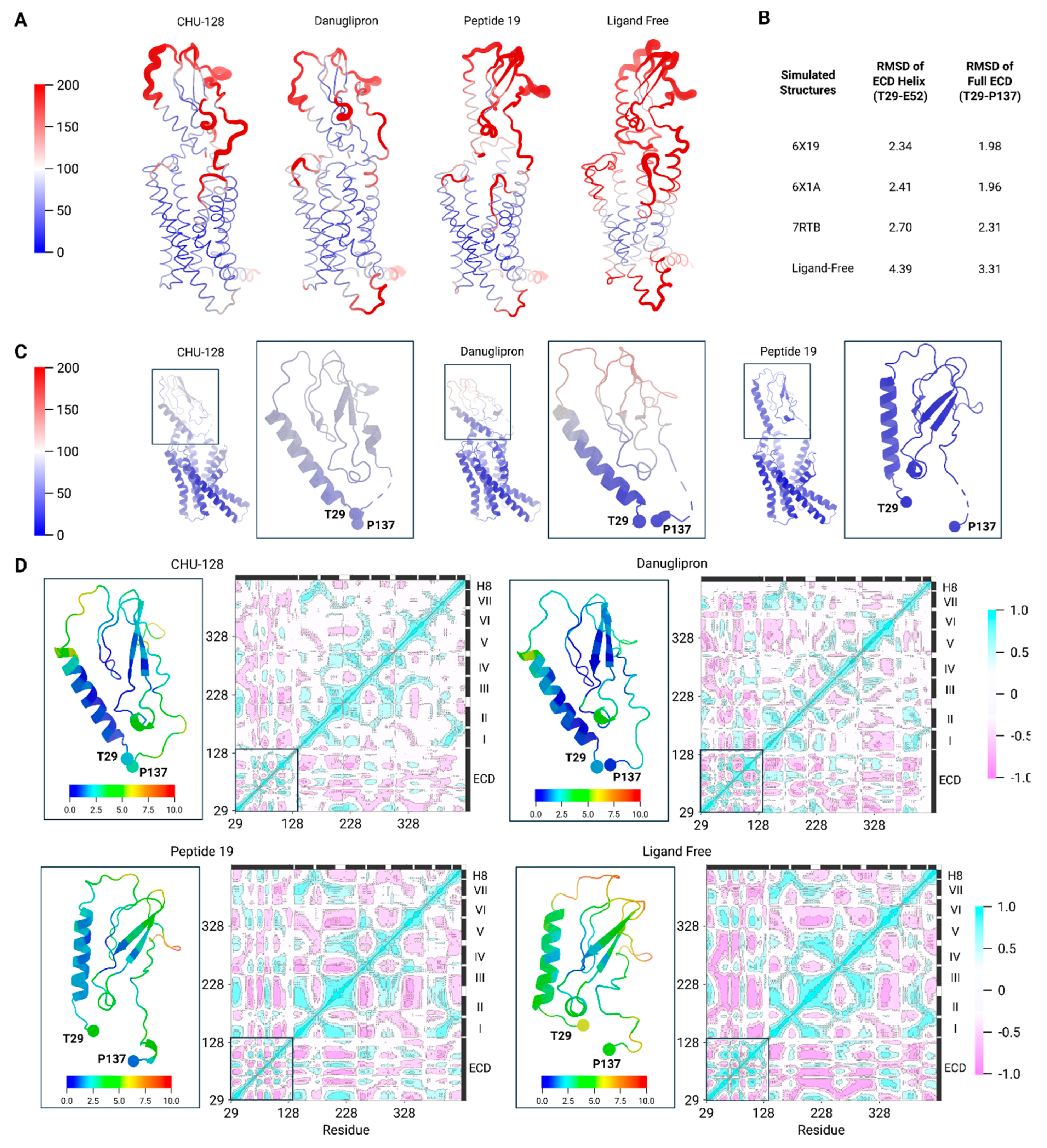
Structural Dynamics of GLP-1R for Ligand-Bound and Ligand-Free Conditions
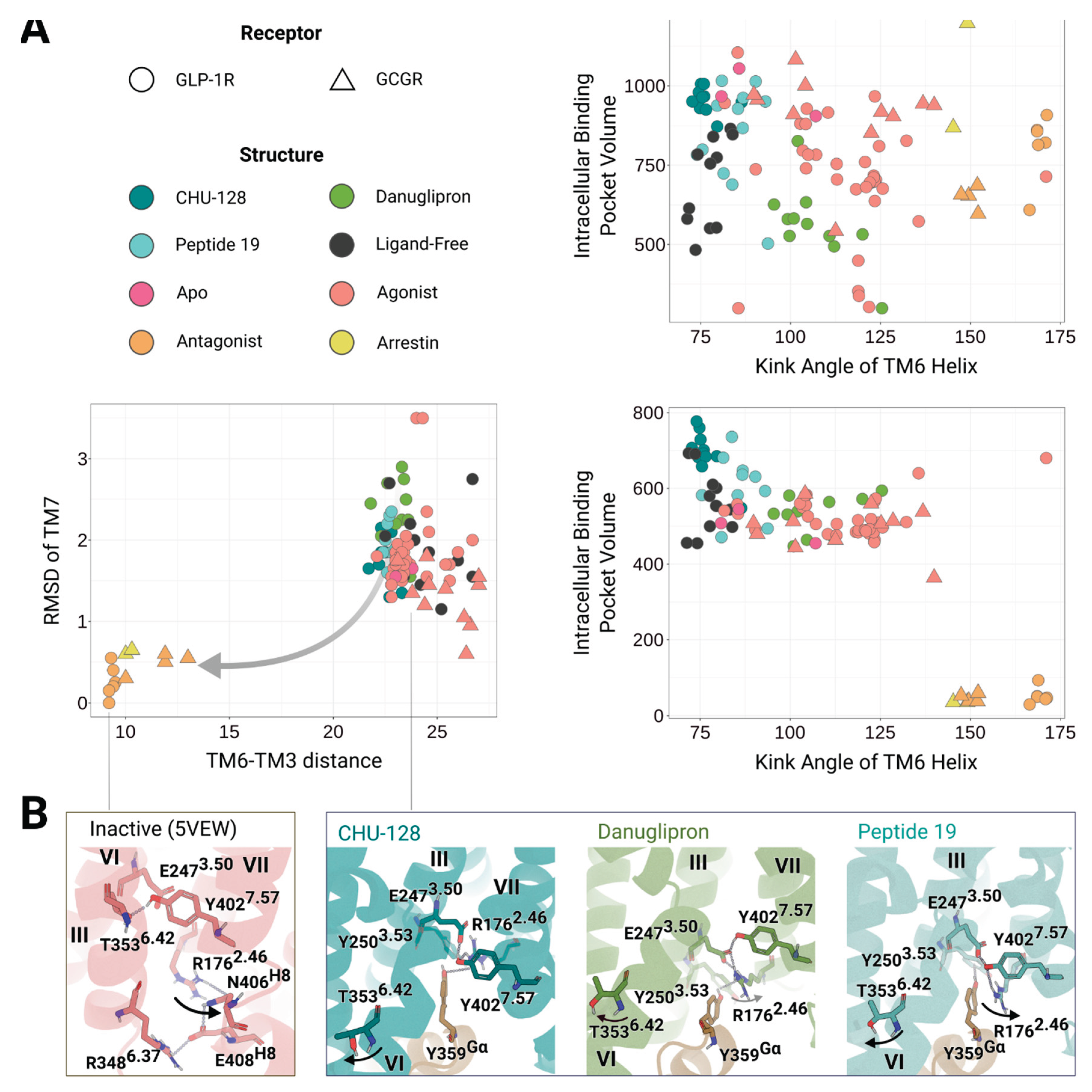
Structural Plasticity of GLP-1R in the Holo State
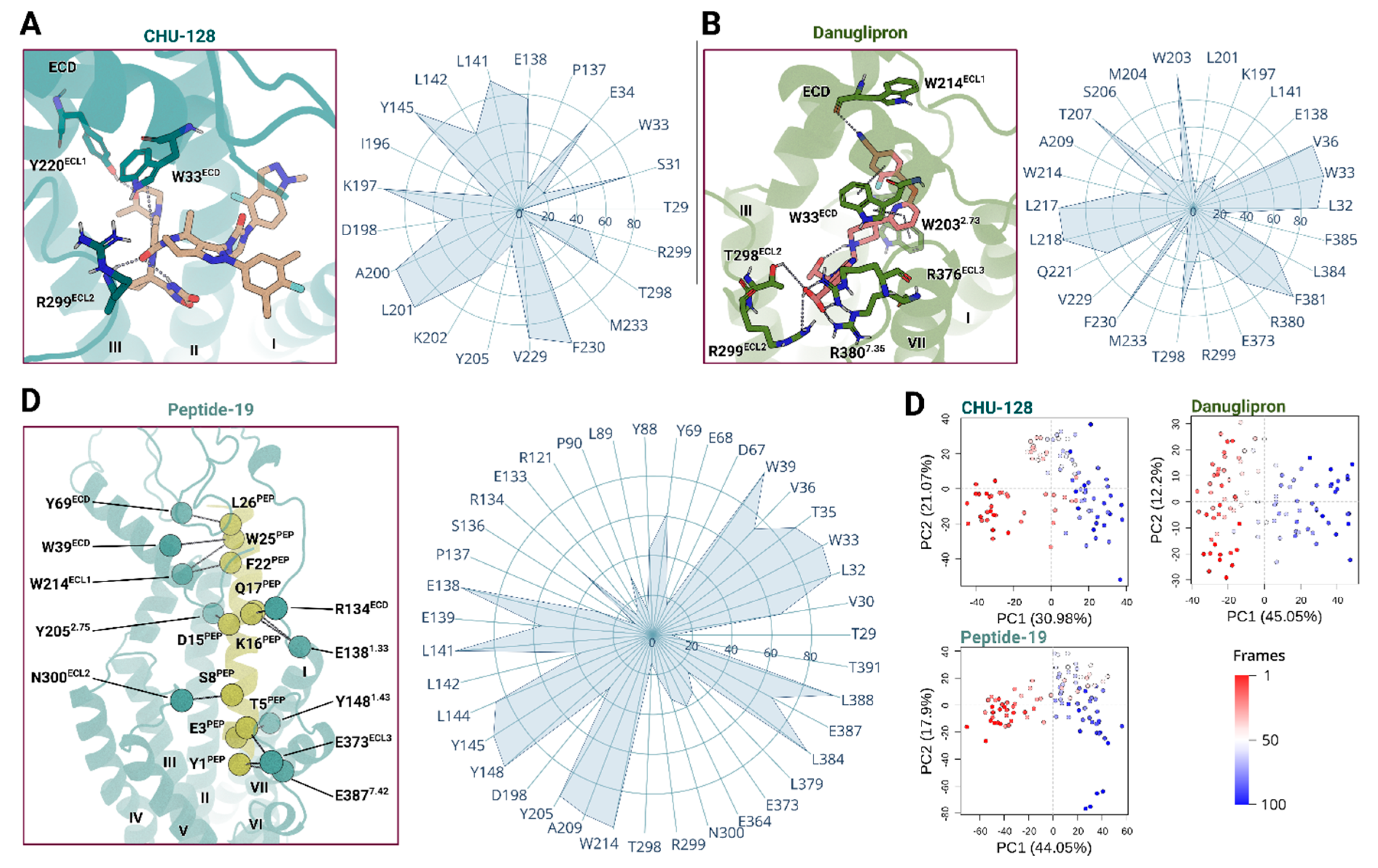
Binding Pocket Variants Upon Danuglipron, CHU-128, and Peptide 19 Binding
Signal Transduction Associated with Distinct Types of Ligand Binding
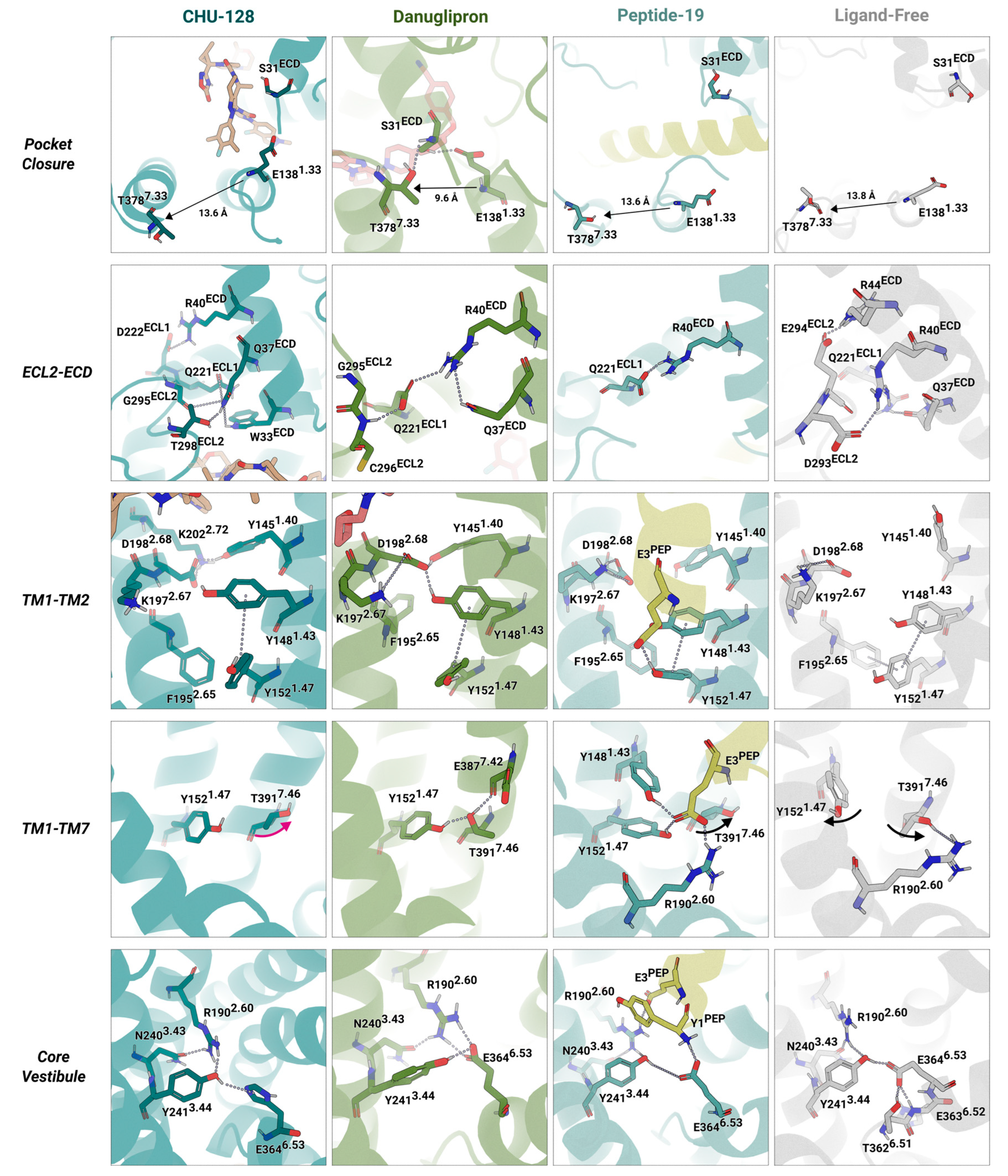
Ligand Recognition and Binding via the Extracellular Domain
Signal Transduction along the Transmembrane Domain
Features of the Intracellular Binding Domain
Biased Agonism and Receptor Signaling Mechanisms
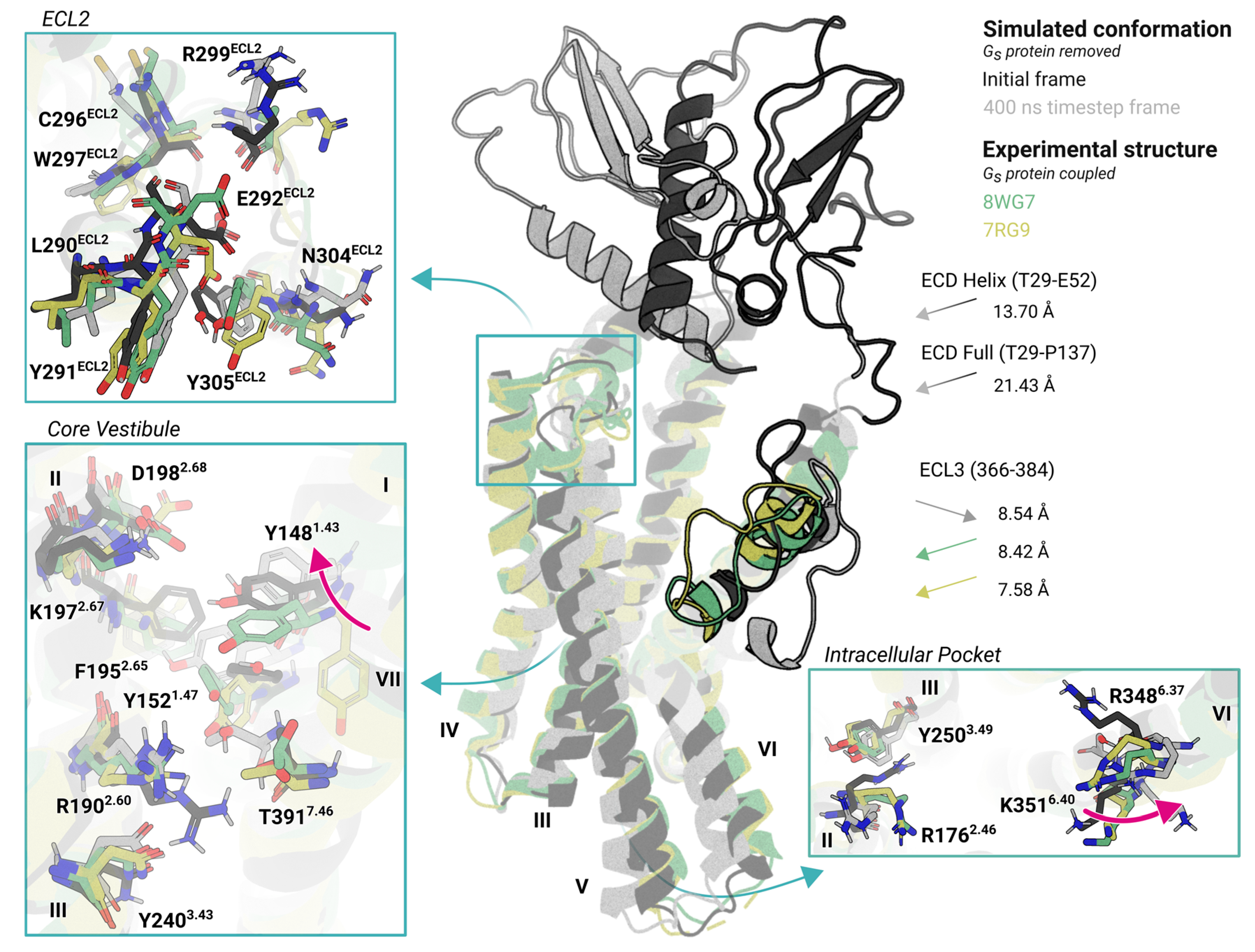
Inferring β-Arrestin-Bound to GLP-1R via Structural Comparison with Related Class B1 GPCRs
Promising Pharmacokinetics of Biased Agonists
Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Notes
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
References
- Hauser, A.S.; Kooistra, A.J.; Munk, C.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Bouvier, M.; Babu, M.M.; Gloriam, D.E. GPCR activation mechanisms across classes and macro/microscales. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2021, 28, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sun, X.; Cui, W.; Xu, M.; Dong, J.; Ekundayo, B.E.; Ni, D.; Rao, Z.; Guo, L.; Stahlberg, H.; et al. Computational drug development for membrane protein targets. Nat Biotechnol 2024, 42, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantakrishnan, S.; Naganathan, A.N. Thermodynamic architecture and conformational plasticity of GPCRs. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, J.; Shen, S.; Xu, H.E. AlphaFold3 versus experimental structures: assessment of the accuracy in ligand-bound G protein-coupled receptors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2025, 46, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, B.A.; Wong, C.K.; Campbell, J.E.; Hodson, D.J.; Trapp, S.; Drucker, D.J. Revisiting the Complexity of GLP-1 Action from Sites of Synthesis to Receptor Activation. Endocrine Reviews 2021, 42, 101–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes – state-of-the-art. Mol Metab 2020, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Wang, Q.-W.; Yang, X.-Y.; Yang, W.; Li, D.-R.; Jin, J.-Y.; Zhang, H.-C.; Zhang, X.-F. GLP−1 receptor agonists for the treatment of obesity: Role as a promising approach. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1085799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, C.; Zheng, F.; Liu, C.; Tian, X. Therapeutic Potential of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrugno, L.; Deana, C.; Da Porto, A.; Boero, E.; Bellini, V.; Biasucci, D.G.; Bignami, E.G. A narrative review of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists prior to deep sedation or general anesthesia. J Anesth Analg Crit Care 2025, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, C.R.; Andersen, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. How glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists work. Endocr Connect 2021, 10, R200–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Wen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, C.; Xue, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 721135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.P.; Pratley, R.E. GLP-1 Analogs and DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Therapy: Review of Head-to-Head Clinical Trials. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, G.; Gomes Moreira, D.; Richner, M.; Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Ferreira, N.; Jan, A. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Neurodegeneration: Neurovascular Unit in the Spotlight. Cells 2022, 11, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferhatbegović, L.; Mršić, D.; Macić-Džanković, A. The benefits of GLP1 receptors in cardiovascular diseases. Front Clin Diabetes Healthc 2023, 4, 1293926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevola, R.; Epifani, R.; Imbriani, S.; Tortorella, G.; Aprea, C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Marfella, R.; Sasso, F.C. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaïmia, N.; Obeid, J.; Varrault, A.; Sabatier, J.; Broca, C.; Gilon, P.; Costes, S.; Bertrand, G.; Ravier, M.A. GLP-1 and GIP receptors signal through distinct β-arrestin 2-dependent pathways to regulate pancreatic β cell function. Cell Reports 2023, 42, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B. The therapeutic potential of GLP-1 receptor biased agonism. British Journal of Pharmacology 2022, 179, 492–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; McGlone, E.R.; Fang, Z.; Pickford, P.; Corrêa, I.R.; Oishi, A.; Jockers, R.; Inoue, A.; Kumar, S.; Görlitz, F.; et al. Genetic and biased agonist-mediated reductions in β-arrestin recruitment prolong cAMP signaling at glucagon family receptors. J Biol Chem 2020, 296, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, M.; Pickford, P.; Bitsi, S.; Minnion, J.; Ungewiss, J.; Schoeneberg, K.; Rutter, G.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Tomas, A.; Jones, B. Disconnect between signalling potency and in vivo efficacy of pharmacokinetically optimised biased glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Mol Metab 2020, 37, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, Z.; Zou, H.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, R.; Wang, B.; et al. Discovery of ecnoglutide – A novel, long-acting, cAMP-biased glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog. Molecular Metabolism 2023, 75, 101762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzook, A.; Tomas, A.; Jones, B. The Interplay of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Trafficking and Signalling in Pancreatic Beta Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, S.; Khalaila, B.; Stein, N.; Saliba, W.; Zaina, A. Efficacy, adherence and persistence of various glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists: nationwide real-life data. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2024, 26, 4646–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, E.L.; Reddy, S.D.; Kattamuri, L.; Muvva, D.M.; Chozet, L.; Bright, T. Current Insights, Advantages and Challenges of Small Molecule Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists: A Scoping Review. Brown Hospital Medicine 2025, 4, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. GLP-1-based therapies for diabetes, obesity and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Su, H.; Lu, B.; Pang, Z. Research progress of GLP-1RAs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 15, 1483792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, T.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X.; Lu, T.; Jiao, Y. Binding sites and design strategies for small molecule GLP-1R agonists. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2024, 275, 116632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A.; Edmonds, D.J.; Fortin, J.-P.; Kalgutkar, A.S.; Kuzmiski, J.B.; Loria, P.M.; Saxena, A.R.; Bagley, S.W.; Buckeridge, C.; Curto, J.M.; et al. A Small-Molecule Oral Agonist of the Human Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8208–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Sun, B.; Yoshino, H.; Feng, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukazawa, M.; Nagao, S.; Wainscott, D.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Droz, B.A.; et al. Structural basis for GLP-1 receptor activation by LY3502970, an orally active nonpeptide agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 29959–29967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Belousoff, M.J.; Zhao, P.; Kooistra, A.J.; Truong, T.T.; Ang, S.Y.; Underwood, C.R.; Egebjerg, T.; Šenel, P.; Stewart, G.D.; et al. Differential GLP-1R Binding and Activation by Peptide and Non-peptide Agonists. Molecular Cell 2020, 80, 485–500.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.M.; Zhang, X.; Piper, S.J.; Nettleton, T.J.; Vandekolk, T.H.; Langmead, C.J.; Danev, R.; Sexton, P.M.; Wootten, D. Cryo-EM structure of the dual incretin receptor agonist, peptide-19, in complex with the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2021, 578, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Willard, F.S.; Feng, D.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Chen, Q.; Vieth, M.; Ho, J.D.; Showalter, A.D.; Stutsman, C.; Ding, L.; et al. Structural determinants of dual incretin receptor agonism by tirzepatide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2022, 119, e2116506119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Z.; Zhao, F.; Li, Y.; Luo, G.; Mai, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Cai, X.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Molecular features of the ligand-free GLP-1R, GCGR and GIPR in complex with Gs proteins. Cell Discov 2024, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, M. Signaling profiles in HEK 293T cells co-expressing GLP-1 and GIP receptors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2022, 43, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.R.; Frias, J.P.; Brown, L.S.; Gorman, D.N.; Vasas, S.; Tsamandouras, N.; Birnbaum, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Small Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Danuglipron for Glycemic Control Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Network Open 2023, 6, e2314493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 2016, 54, 5.6–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release Notes - Release 2024-4. Available online: https://www.schrodinger.com/life-science/download/release-notes/ (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Park, S.; Choi, Y.K.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder: Past, Current, and Future Developments and Applications. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2023, 19, 2161–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, D370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemkul, J.A. From Proteins to Perturbed Hamiltonians: A Suite of Tutorials for the GROMACS-2018 Molecular Simulation Package [Article v1.0]. Living Journal of Computational Molecular Science 2019, 1, 5068–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud-Agrawal, N.; Denning, E.J.; Woolf, T.B.; Beckstein, O. MDAnalysis: A toolkit for the analysis of molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2011, 32, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, B.J.; Skjærven, L.; Yao, X.-Q. The Bio3D packages for structural bioinformatics. Protein Science 2021, 30, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Conte, A.; Camagni, G.F.; Clementel, D.; Minervini, G.; Monzon, A.M.; Ferrari, C.; Piovesan, D.; Tosatto, S.C.E. RING 4.0: faster residue interaction networks with novel interaction types across over 35,000 different chemical structures. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, W306–W312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.R.; Sørensen, J.; Hensley, N.; Wong, C.; Zhu, C.; Perison, T.; Amaro, R.E. POVME 3.0: Software for Mapping Binding Pocket Flexibility. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 4584–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-L.; Khoshouei, M.; Glukhova, A.; Furness, S.G.B.; Zhao, P.; Clydesdale, L.; Koole, C.; Truong, T.T.; Thal, D.M.; Lei, S.; et al. Phase-plate cryo-EM structure of a biased agonist-bound human GLP-1 receptor–Gs complex. Nature 2018, 555, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingler, L.M.; Elgeti, M.; Hilger, D.; Latorraca, N.R.; Lerch, M.T.; Staus, D.P.; Dror, R.O.; Kobilka, B.K.; Hubbell, W.L.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Angiotensin Analogs with Divergent Bias Stabilize Distinct Receptor Conformations. Cell 2019, 176, 468–478.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, D.; Reynolds, C.A.; Smith, K.J.; Mobarec, J.C.; Koole, C.; Savage, E.E.; Pabreja, K.; Simms, J.; Sridhar, R.; Furness, S.G.B.; et al. The Extracellular Surface of the GLP-1 Receptor Is a Molecular Trigger for Biased Agonism. Cell 2016, 165, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Implications of ligand-receptor binding kinetics on GLP-1R signalling. Biochemical Pharmacology 2022, 199, 114985. [CrossRef]
- Krumm, B.; Roth, B.L. A Structural Understanding of Class B GPCR Selectivity and Activation Revealed. Structure 2020, 28, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Clydesdale, L.; Dai, A.; Cai, X.; Feng, Y.; Yang, D.; Liang, Y.-L.; Koole, C.; Zhao, P.; Coudrat, T.; et al. Two distinct domains of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor control peptide-mediated biased agonism. J Biol Chem 2018, 293, 9370–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oqua, A.I.; Chao, K.; Eid, L.E.; Casteller, L.; Miguéns, A.; Barg, S.; Jones, B.; Serna, J.B. de la; Rouse, S.L.; Tomas, A. Molecular mapping and functional validation of GLP-1R cholesterol binding sites in pancreatic beta cells. eLife 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, Q.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Shang, S.; An, X.; Yao, X. Investigation of ECD conformational transition mechanism of GLP-1R by molecular dynamics simulations and Markov state model. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 8470–8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, W.; Sun, X.; Zhong, W.; Yuan, D.; et al. Structural insights into the activation of GLP-1R by a small molecule agonist. Cell Res 2020, 30, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardella, T.J.; Vilardaga, J.-P. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCIII. The parathyroid hormone receptors--family B G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol Rev 2015, 67, 310–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T. Conserved 2nd Residue of Helix 8 of GPCR May Confer the Subclass-Characteristic and Distinct Roles through a Rapid Initial Interaction with Specific G Proteins. IJMS 2019, 20, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Aradhyam, G.K. Divergent roles of DRY and NPxxY motifs in selective activation of downstream signalling by the apelin receptor. Biochem J 2024, 481, 1707–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, F.K.; Akasaka, H.; Shihoya, W.; Nureki, O. Cryo-EM structure of the endothelin-1-ETB-Gi complex. eLife 2023, 12, e85821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Maruszko, K.; Kim, S.-K.; Yang, M.Y.; Vo, A.-D.P.; Goddard, W.A.I. Structure and Molecular Mechanism of Signaling for the Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Bound to Gs Protein and Exendin-P5 Biased Agonist. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 20422–20431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Eid, L.; Reynolds, C.A.; Tomas, A. ; Ben Jones Biased agonism and polymorphic variation at the GLP-1 receptor: Implications for the development of personalised therapeutics. Pharmacological Research 2022, 184, 106411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Buenaventura, T.; Kanda, N.; Chabosseau, P.; Owen, B.M.; Scott, R.; Goldin, R.; Angkathunyakul, N.; Corrêa Jr, I.R.; Bosco, D.; et al. Targeting GLP-1 receptor trafficking to improve agonist efficacy. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deganutti, G.; Liang, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.; Khoshouei, M.; Clydesdale, L.; Belousoff, M.J.; Venugopal, H.; Truong, T.T.; Glukhova, A.; Keller, A.N.; et al. Dynamics of GLP-1R peptide agonist engagement are correlated with kinetics of G protein activation. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, D.; Kumar, K.K.; Hu, H.; Pedersen, M.F.; O’Brien, E.S.; Giehm, L.; Jennings, C.; Eskici, G.; Inoue, A.; Lerch, M.; et al. Structural insights into differences in G protein activation by family A and family B GPCRs. Science 2020, 369, eaba3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compounds | Danuglipron | CHU-128 | Peptide 19 |
| Chemical structure | 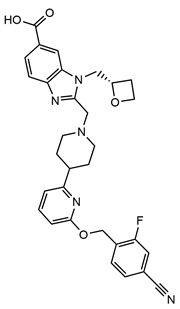 |
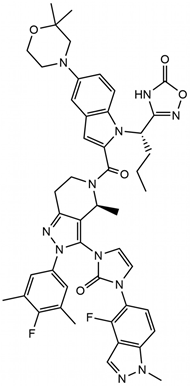 |
 |
| Molecular mass | 555.6 g/mol | 883.96 g/mol | 4064 g/mol |
| Ligand type | Small Molecule | Small Molecule | 38-residue Peptide |
| Activity type | Balanced | G protein biased | Balanced |
| Binding site | Orthosteric | Orthosteric | Orthosteric |
| PDB | Simulation time (ns) | Resolution (Å) | Activity State | Ligand | Ligand Type | Downstream Protein |
| 6X1A | 3x500 | 2.50 | Active | Danuglipron | Balanced agonist | Gs |
| 6X19 | 3x500 | 2.10 | Active | CHU-128 | Biased agonist | Gs |
| 7RTB | 3x500 | 2.14 | Active | Peptide 19 | Balanced agonist | Gs |
| 7RTB | 3x500 | 2.14 | Ligand-Free | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





