Submitted:
30 May 2025
Posted:
02 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification, distribution, and renaming of VDAC genes
2.2. Conserved domain, localization, and physico-chemical properties of VDAC proteins
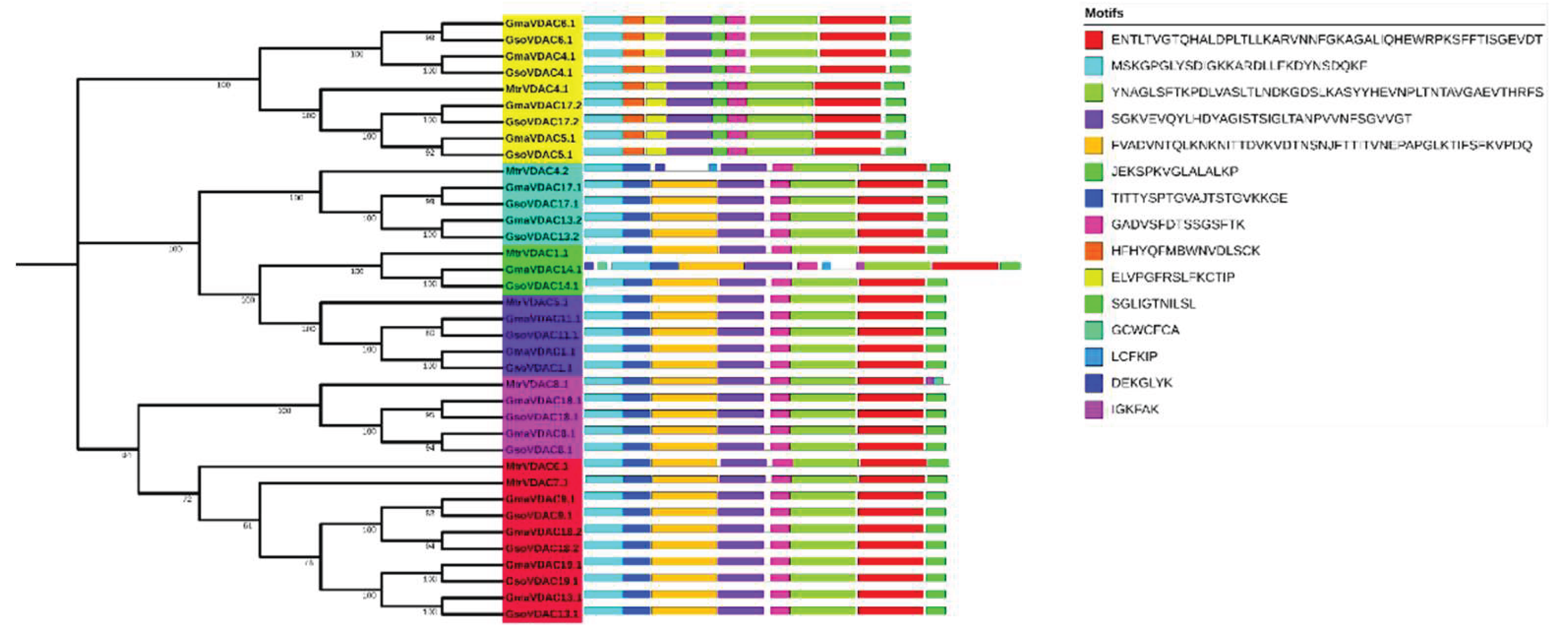
2.3. Classification and phylogenetic analysis
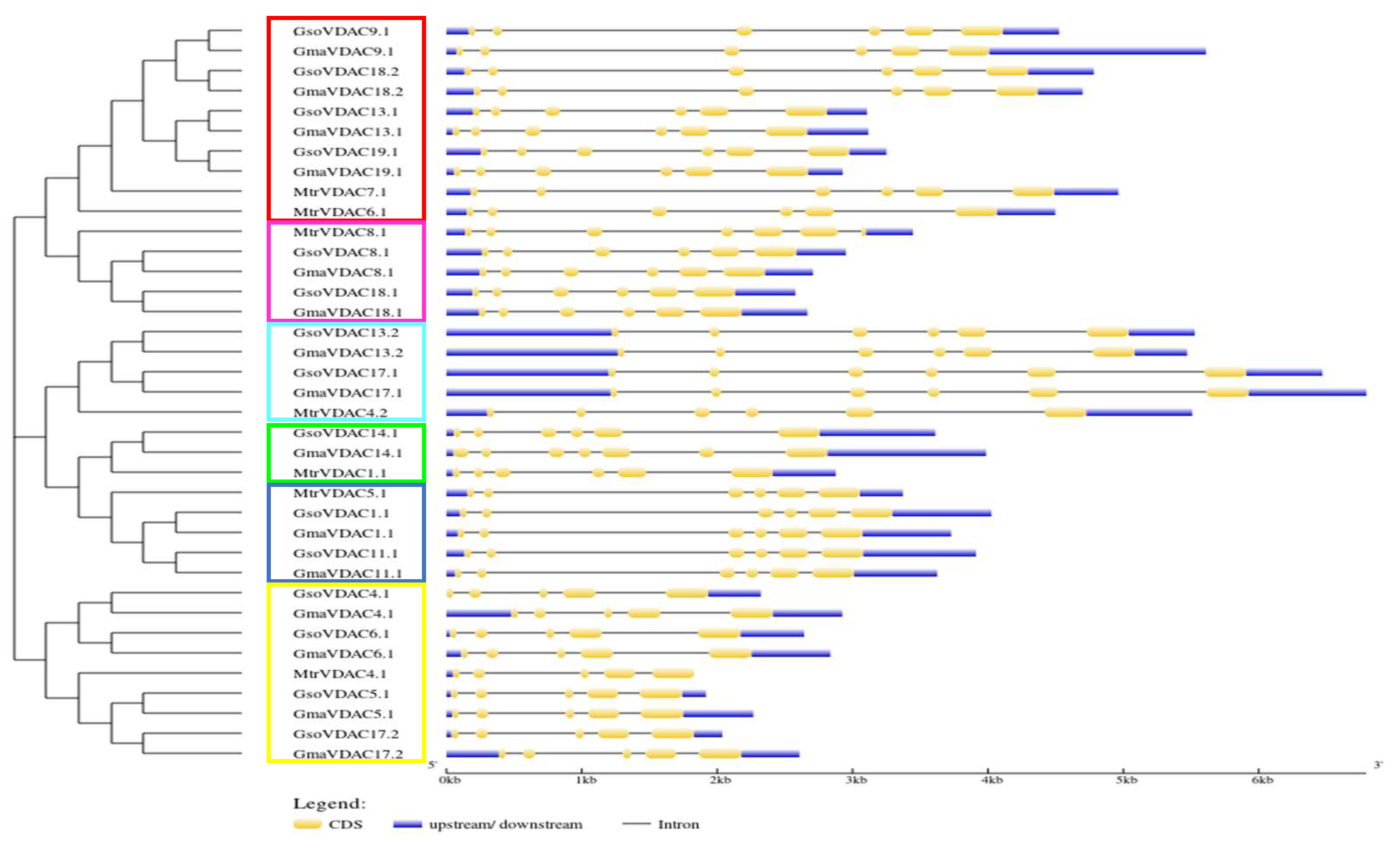
2.4. Conserved motif and gene structure analysis
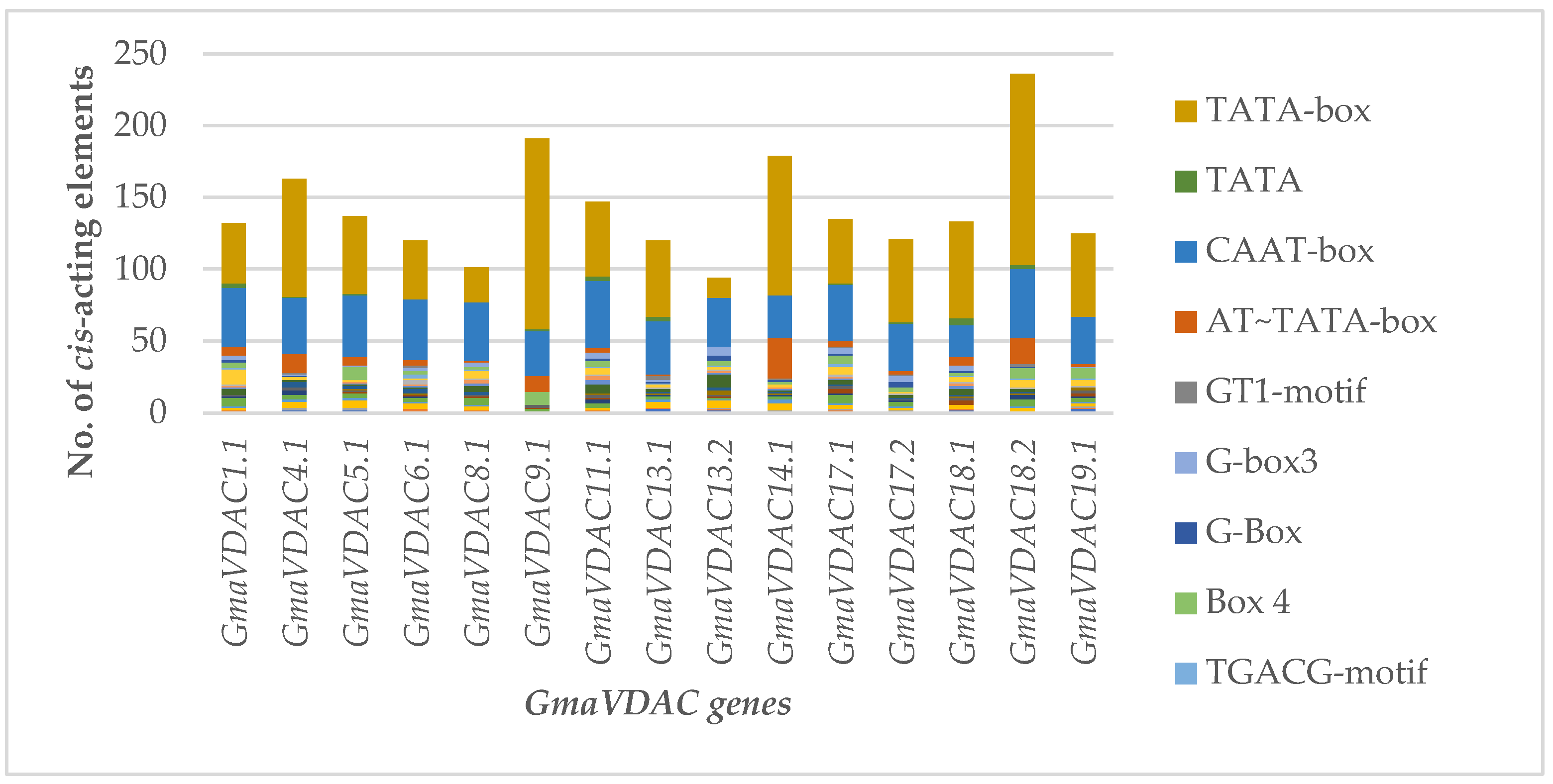
2.5. Identification of cis-acting regulatory elements (CREs) in promoters of GmaVDAC genes
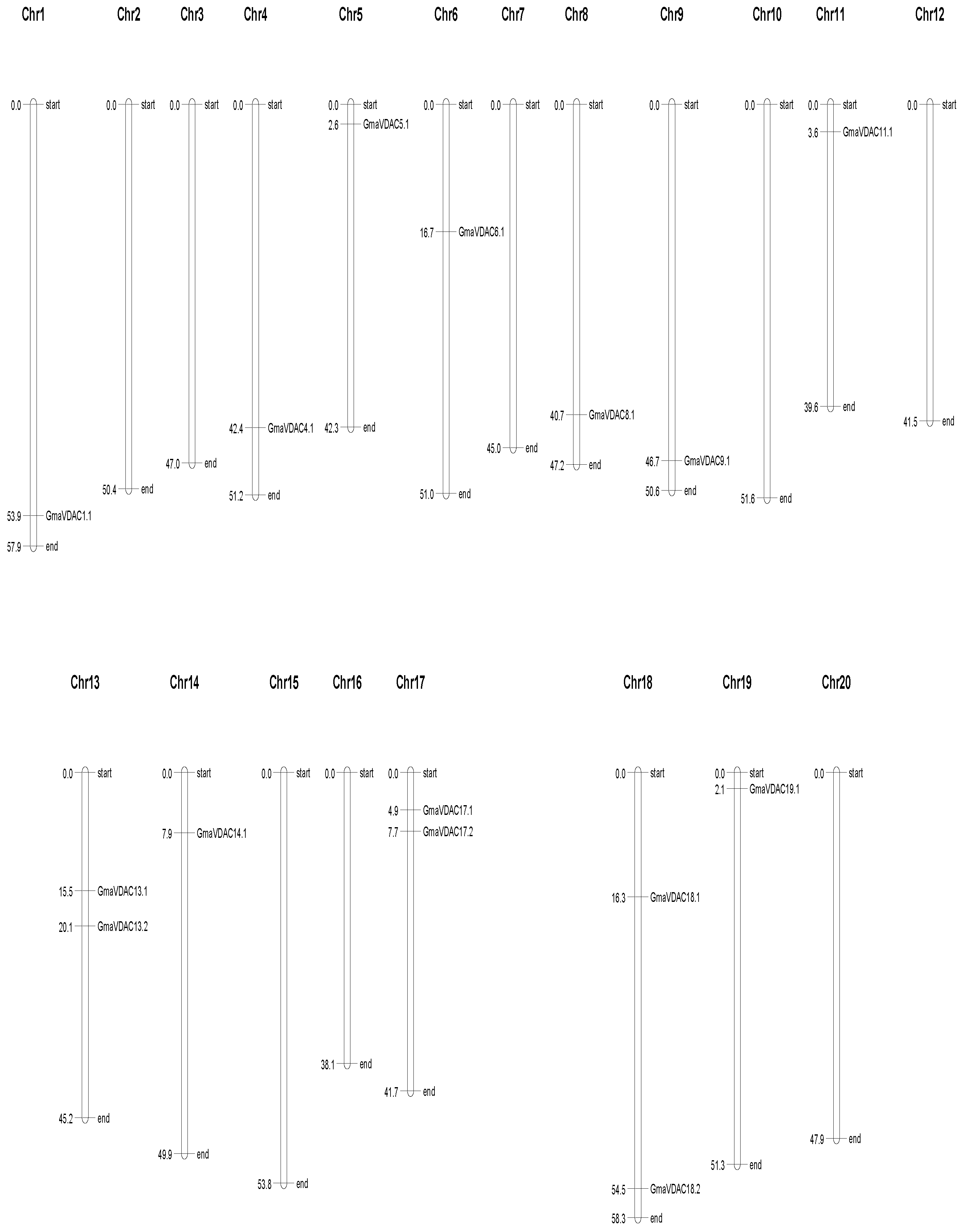
2.7. Gene positions and chromosomal chart
2.8. Synteny analysis
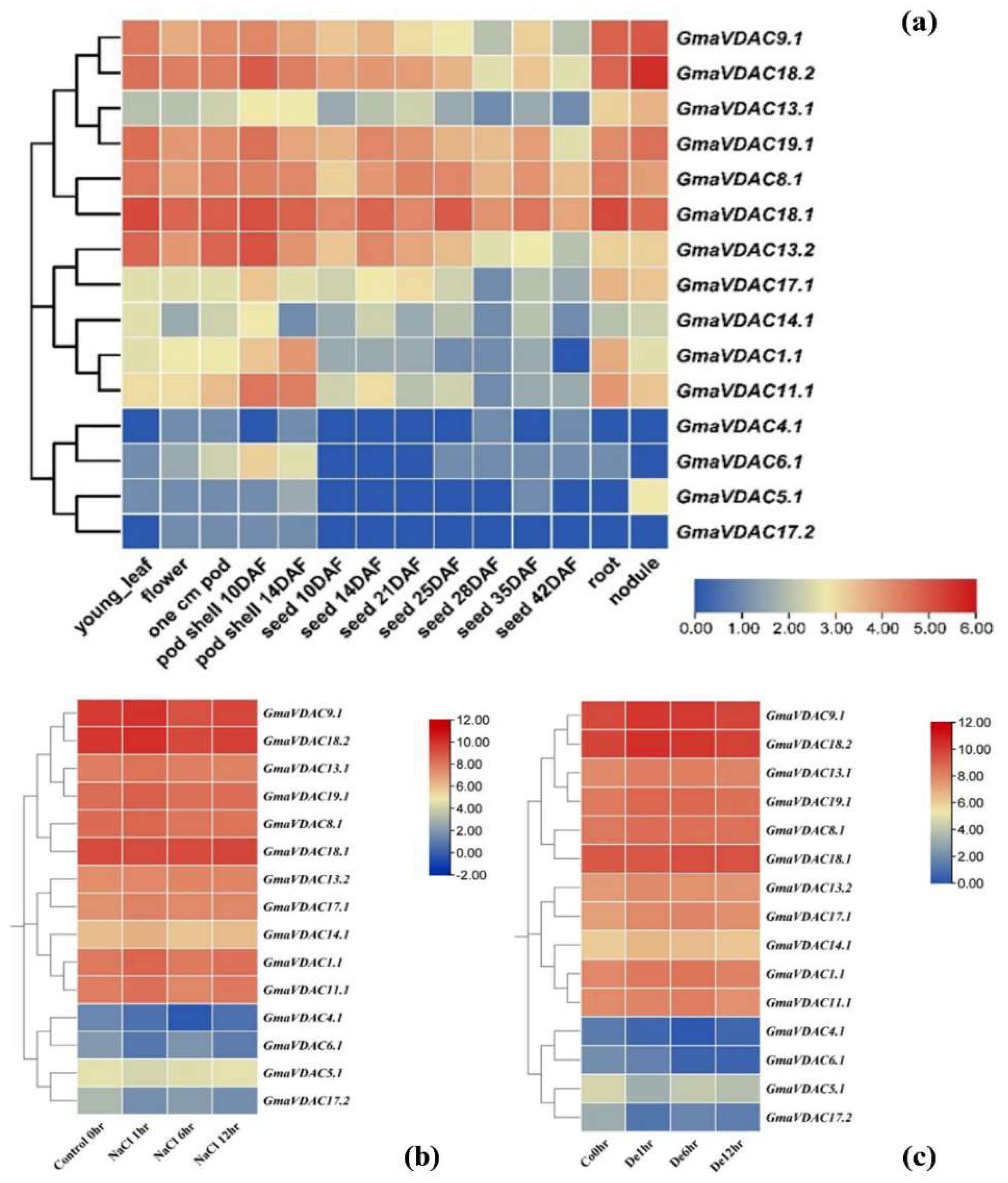
2.9. Expression pattern analysis of GmaVDAC genes
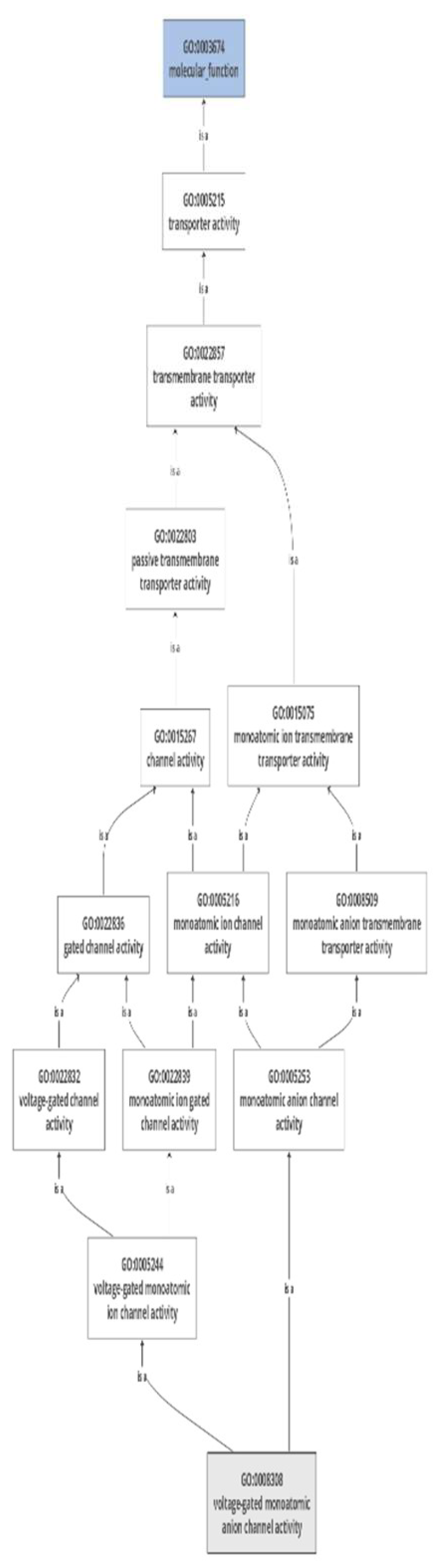
2.10. Gene ontology analysis
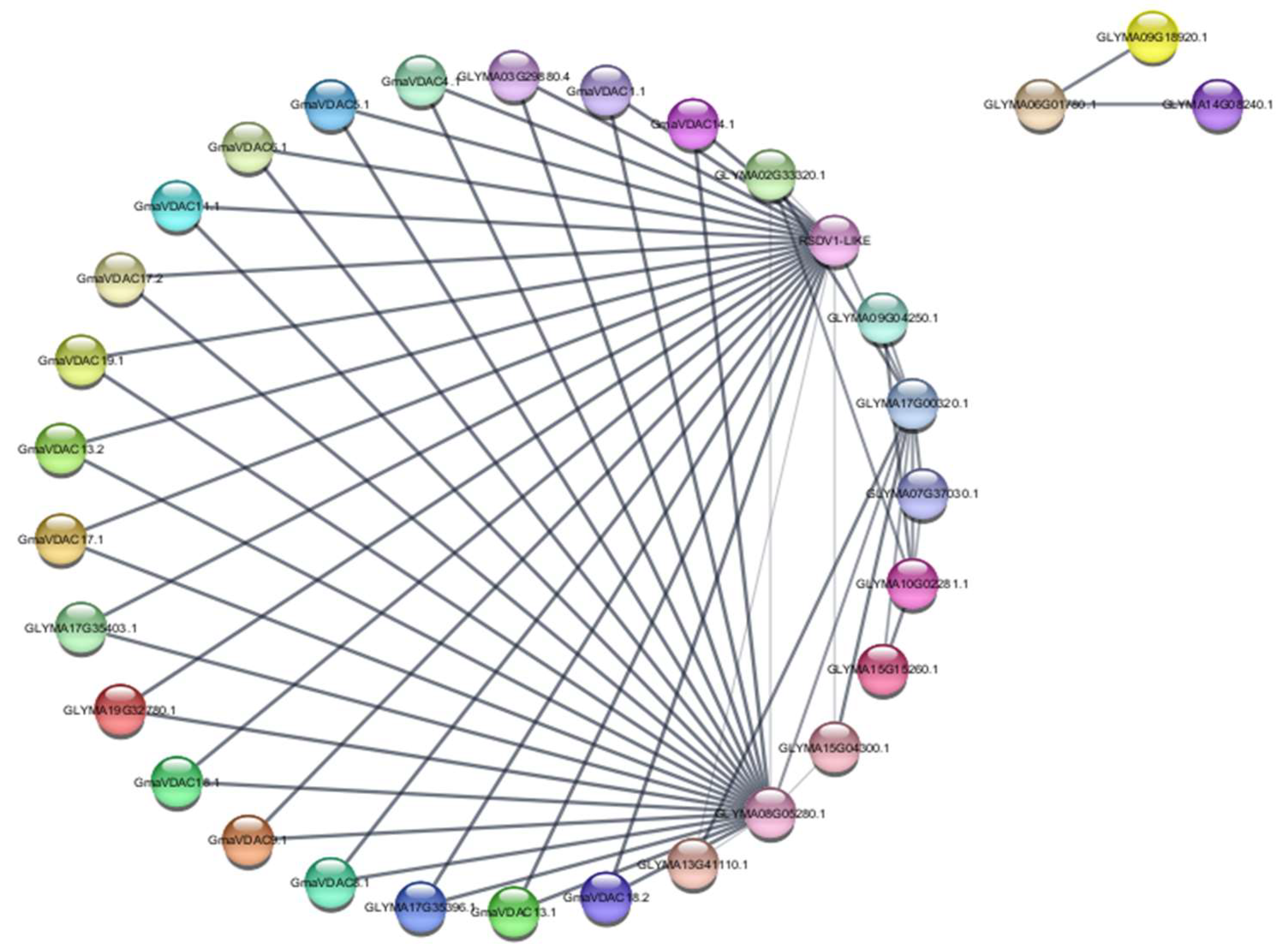
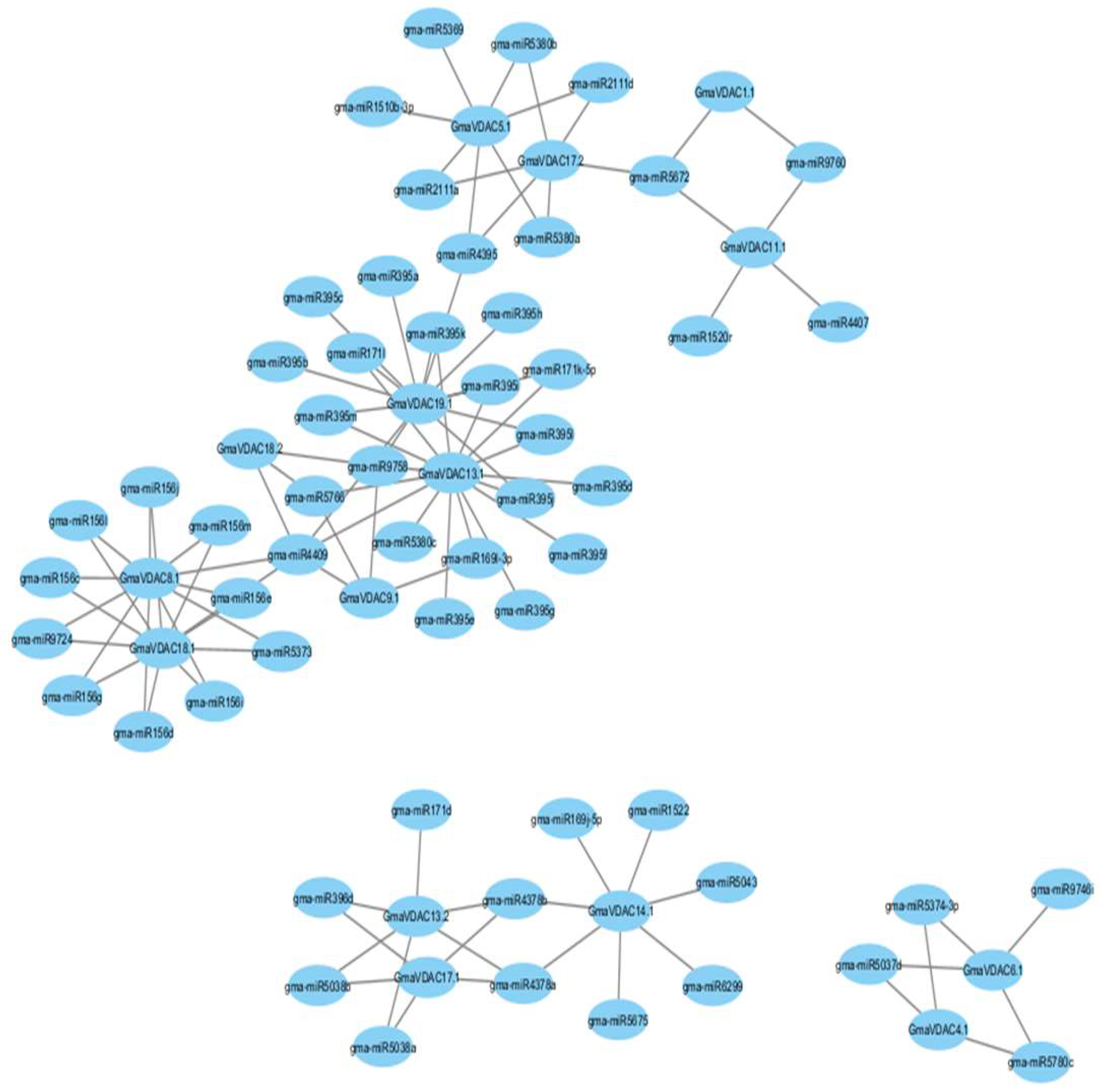
2.11. Protein interactions network and microRNA targets prediction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of VDAC genes and retrieval of sequences
4.2. Conserved domain, subcellular localization and physico-chemical properties
4.3. Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) and phylogenetic relationship
4.4. Gene structure prediction and motif analysis
4.5. Cis-regulatory elements (CREs) and Chromosomal distribution
4.6. Gene duplications and syntenic analysis
4.7. Protein interactions network and microRNA targets prediction
4.8. Gene ontology analysis
4.8. Expression pattern of GmaVDAC genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Ran, Y. Progresses, Challenges, and Prospects of Genome Editing in Soybean (Glycine Max). Front Plant Sci 2020, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, M.; Aleem, S.; Sharif, I.; Wu, Z.; Aleem, M.; Tahir, A.; Atif, R.M.; Cheema, H.M.N.; Shakeel, A.; Lei, S.; et al. Characterization of SOD and GPX Gene Families in the Soybeans in Response to Drought and Salinity Stresses. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostovtseva, T.K.; Bezrukov, S.M.; Hoogerheide, D.P.; Kmita, H.; Messina, A.A. Regulation of Mitochondrial Respiration by VDAC Is Enhanced by Membrane-Bound Inhibitors with Disordered Polyanionic C-Terminal Domains. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Yu, Y.; Song, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X. Characterization of the Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel (VDAC) Gene Family in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) and Its Potential Mechanism in Response to Drought and Salinity Stresses. Gene 2022, 809, 146031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, H.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, C.; Fan, H.; Li, D.; Dong, L.; et al. Draft Genome of the Wheat A-Genome Progenitor Triticum Urartu. Nature 2013, 496, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.P.; Buzhynskyy, N.; Prima, V.; Sturgis, J.N.; Scheuring, S. Supramolecular Assembly of VDAC in Native Mitochondrial Outer Membranes. J Mol Biol 2007, 369, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshan-Barmatz, V.; Shteinfer-Kuzmine, A.; Verma, A. VDAC1 at the Intersection of Cell Metabolism, Apoptosis, and Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusano, T.; Tateda, C.; Takahashi, Y.; Berberich, T. Voltage-Dependent Anion Channels: Their Roles in Plant Defense and Cell Death. Plant Cell Rep 2009, 28, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidani, H.; Grobys, D.; Léonetti, M.; Kmita, H.; Homblé, F. Towards Understanding of Plant Mitochondrial VDAC Proteins : An Overview of Bean (Phaseolus Vulgaris) VDAC Proteins. 4, 62. [CrossRef]
- Mei Yang, Xinhang Duan, Zhaoyu Wang, Hang Yin, Junrui Zang, Kai Zhu, Y. W. and P.Z. Overexpression of a Voltage-Dependent Anion-Selective Channel (VDAC) Protein-Encoding Gene, MsVDAC, from Medicago Sativa Confers Cold and Drought Tolerance to Transgenic Tobacco. 2021, 12, 1706.
- Desai, M.K.; Mishra, R.N.; Verma, D.; Nair, S.; Sopory, S.K.; Reddy, M.K. Structural and Functional Analysis of a Salt Stress Inducible Gene Encoding Voltage Dependent Anion Channel (VDAC) from Pearl Millet (Pennisetum Glaucum). Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2006, 44, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, Y.P.; Cheng, G.; Liu, X.Q.; Xia, C.J.; Luo, F.Y.; Wang, C.T. Genomic Survey and Gene Expression Analysis of the VDAC Gene Family in Rice. Genetics and Molecular Research 2015, 14, 15683–15696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Yue, Z.; Hu, Q.; Chen, Y. . Liu, J. Genomic Insights into Salt Adaptation in a Desert Poplar. Nat Commun 2013, 4, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severin, A.J.; Cannon, S.B.; Graham, M.M.; Grant, D.; Shoemaker, R.C. Changes in Twelve Homoeologous Genomic Regions in Soybean Following Three Rounds of Polyploidy. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yin, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, J.; Jia, J.; Huo, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, R.; Gong, H. Transcriptomic Dynamics Provide an Insight into the Mechanism for Silicon-Mediated Alleviation of Salt Stress in Cucumber Plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2019, 174, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandrey, M.; Trevaskis, B.; Brewin, N.; M. K., U. Molecular and Cell Biology of a Family of Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel Porins in Lotus Japonicus. Plant Physiol 2004, 134, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateda, C.; Watanabe, K.; Kusano, T. Molecular and Genetic Characterization of the Gene Family Encoding the Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 2011, 62, 4773–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, D.W.S.; Peloquin, S.J. Breeding Value of 2n Pollen (Diplandroids) in Tetraploid x Diploid Crosses in Potatoes. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 1975, 46, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Bhatt, V.; Rana, N.; Shivaraj, S.M. Advances of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Technologies to Enhance the Biofortifications in Crops. Advances in Agri-Food Biotechnology. [CrossRef]
- Magadum, S.; Banerjee, U.; Murugan, P.; Gangapur, D.; Ravikesavan, R. Gene Duplication as a Major Force in Evolution. J Genet 2013, 92, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Han, G.; Gene, S.Z.-; 2015, U. Systematic Analysis of Maize Class III Peroxidase Gene Family Reveals a Conserved Subfamily Involved in Abiotic Stress Response. Gene 2015, 566, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Conery, J.S. The Evolutionary Fate and Consequences of Duplicate Genes. Science (1979) 2000, 290, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Anderson, J.B.; Derbyshire, M.K.; DeWeese-Scott, C. ., Bryant, S.H. CDD: A Conserved Domain Database for Interactive Domain Family Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 35, D237–D240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.M.; Nam, D. WegoLoc: Accurate Prediction of Protein Subcellular Localization Using Weighted Gene Ontology Terms. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1028–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. The Proteomics Protocols Handbook 2005, 1, 571–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol Biol Evol 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An Upgraded Gene Feature Visualization Server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and Analyzing DNA and Protein Sequence Motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 2006, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE: A Database of Plant Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements and a Portal to Tools for in Silico Analysis of Promoter Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the Graphical Presentation of Linkage Maps and QTLs. Journal of heredity 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A Toolkit for Detection and Evolutionary Analysis of Gene Synteny and Collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, B. HIV Signature and Sequence Variation Analysis. Computational analysis of HIV molecular sequences 2000, 4, 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, P.X. PsRNATarget: A Plant Small RNA Target Analysis Server (2017 Release). Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, W49–W54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING V11: Protein–Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Morris, J.H.; Demchak, B.; Bader, G.D. Biological Network Exploration with Cytoscape 3. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics 2014, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S. Blast2GO: A Comprehensive Suite for Functional Analysis in Plant Genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 2008, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Du, H.; Liu, Y.; Ni, L.; Wang, Z.; Liang, C.; Tian, Z. Update Soybean Zhonghuang 13 Genome to a Golden Reference. Sci China Life Sci 2019, 62, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belamkar, V.; Weeks, N.T.; Bharti, A.K.; Farmer, A.D.; Graham, M.A.; Cannon, S.B. Comprehensive Characterization and RNA-Seq Profiling of the HD-Zip Transcription Factor Family in Soybean (Glycine Max) during Dehydration and Salt Stress. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
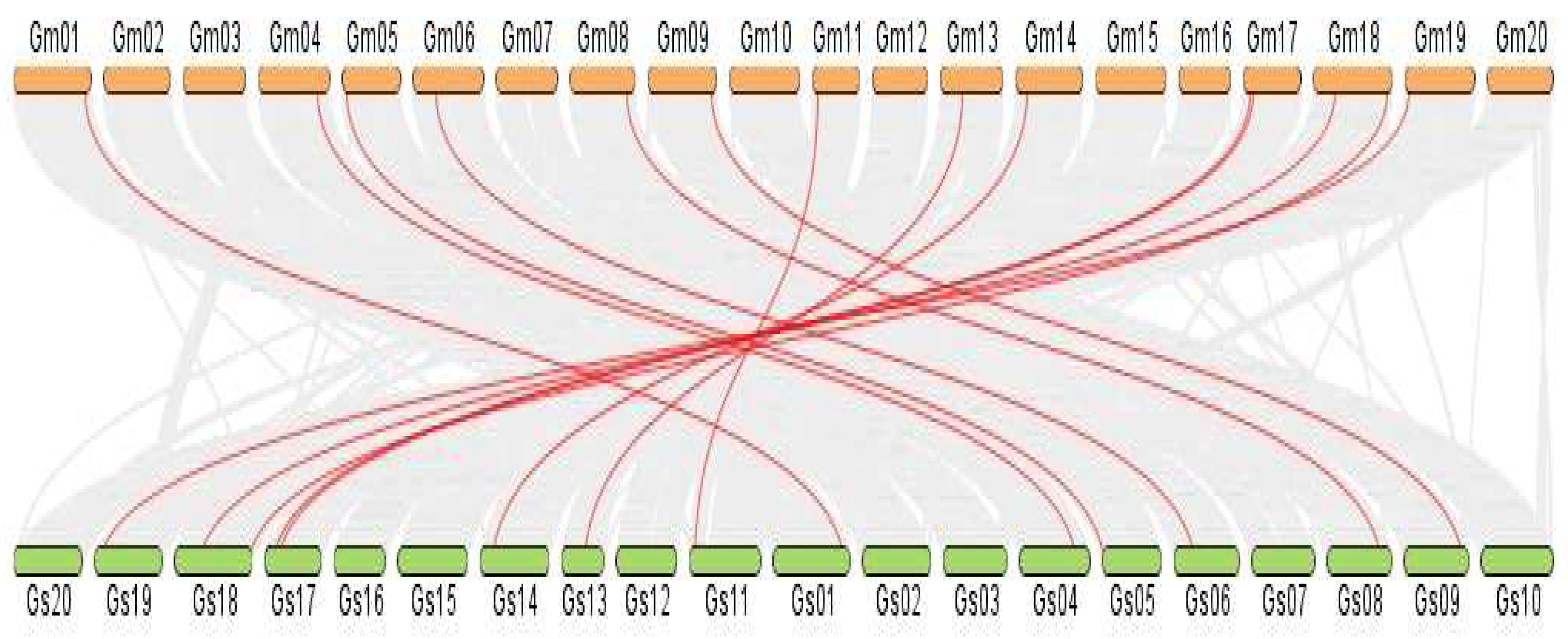
| Duplicated pair | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | Duplicate type | Selection type | T (Mya) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GmaVDAC1.1/GmaVDAC11.1 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.18 | Segmental | Purifying | 6.10 |
| GmaVDAC4.1/GmaVDAC6.1 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.21 | Segmental | Purifying | 11.39 |
| GmaVDAC5.1/GmaVDAC17.2 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.23 | Segmental | Purifying | 7.02 |
| GmaVDAC8.1/GmaVDAC18.1 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.06 | Segmental | Purifying | 11.31 |
| GmaVDAC9.1/GmaVDAC18.2 | 0.005 | 0.06 | 0.08 | Segmental | Purifying | 5.16 |
| GmaVDAC13.1/GmaVDAC19.1 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.12 | Segmental | Purifying | 12.51 |
| GmaVDAC13.2/GmaVDAC17.1 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.18 | Segmental | Purifying | 8.75 |
| Sr. No. | Crop | Botanical name | Database link |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Adzuki bean | Vigna angularis | https://legacy.legumeinfo.org/ |
| 2. | Arabidopsis | Arabidopsis thaliana | https://www.arabidopsis.org/ |
| 3. | Barrel clover | Medicago truncatula | https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/ |
| 4. | Birdsfoot trefoil | Lotus japonicus | https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/ |
| 5. | Chickpea | Cicer arietinum | https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/ |
| 6. | Common bean | Phaseolus vulgaris | https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/ |
| 7. | Cowpea | Vigna unguiculata | https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/ |
| 8. | Cultivated soybean | Glycine max | https://www.soybase.org/ |
| 9. | Mungbean | Vigna radiata | https://legacy.legumeinfo.org/ |
| 10. | Narrow leaf lupin | Lupinus angustifolius | https://legacy.legumeinfo.org/ |
| 11. | Pea | Pisum sativum | https://legacy.legumeinfo.org/ |
| 12. | Peanut | Arachis hypogaea | https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/ |
| 13. | Pigeon pea | Cajanus cajan | https://legacy.legumeinfo.org/ |
| 14. | Wild soybean | Glycine soja | https://www.soybase.org/ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





