Submitted:
26 May 2025
Posted:
28 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Measurement and Entropy in Isolated Quantum Systems
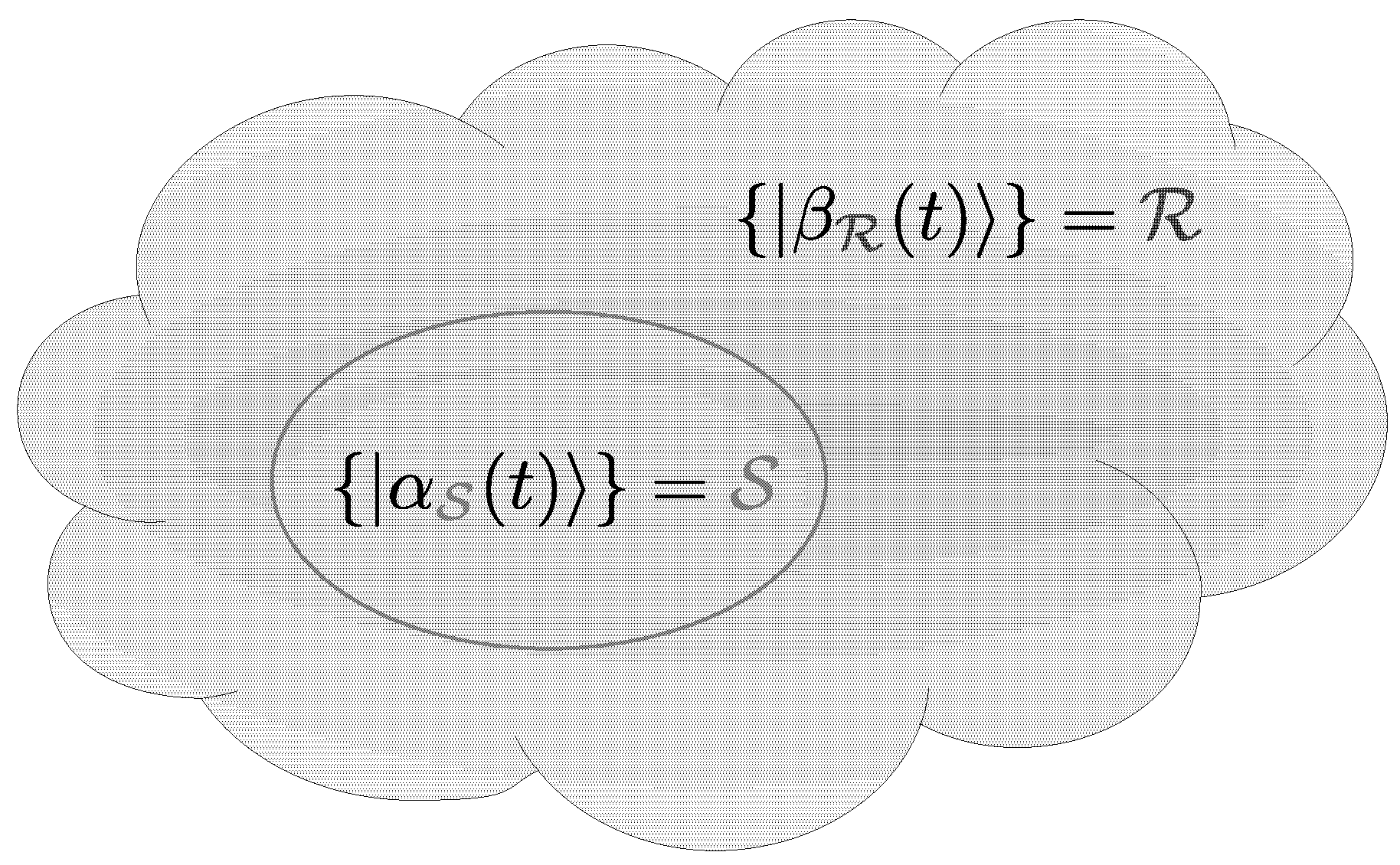
3. Model and Time-Evolution Method
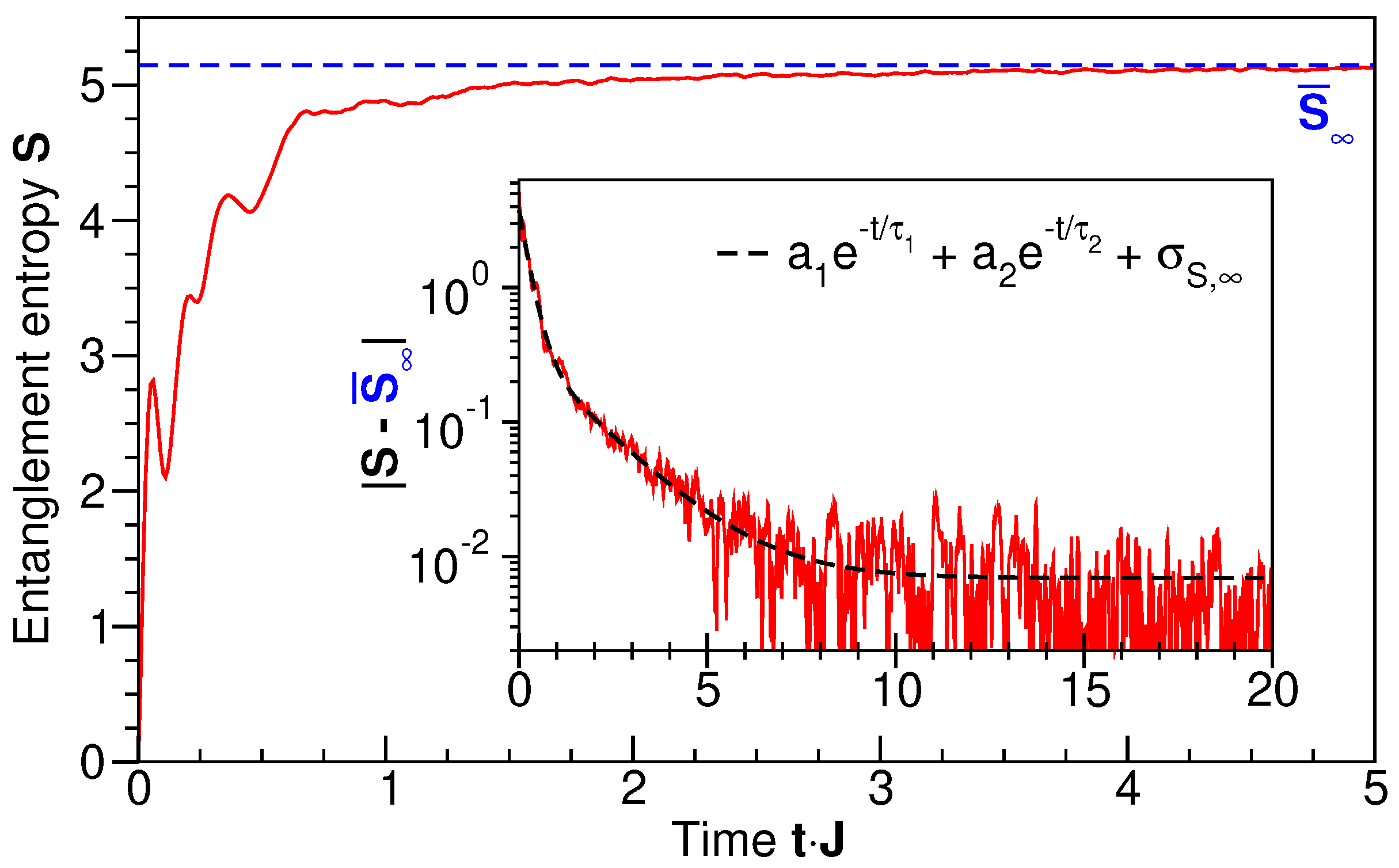
4. Entanglement Entropy
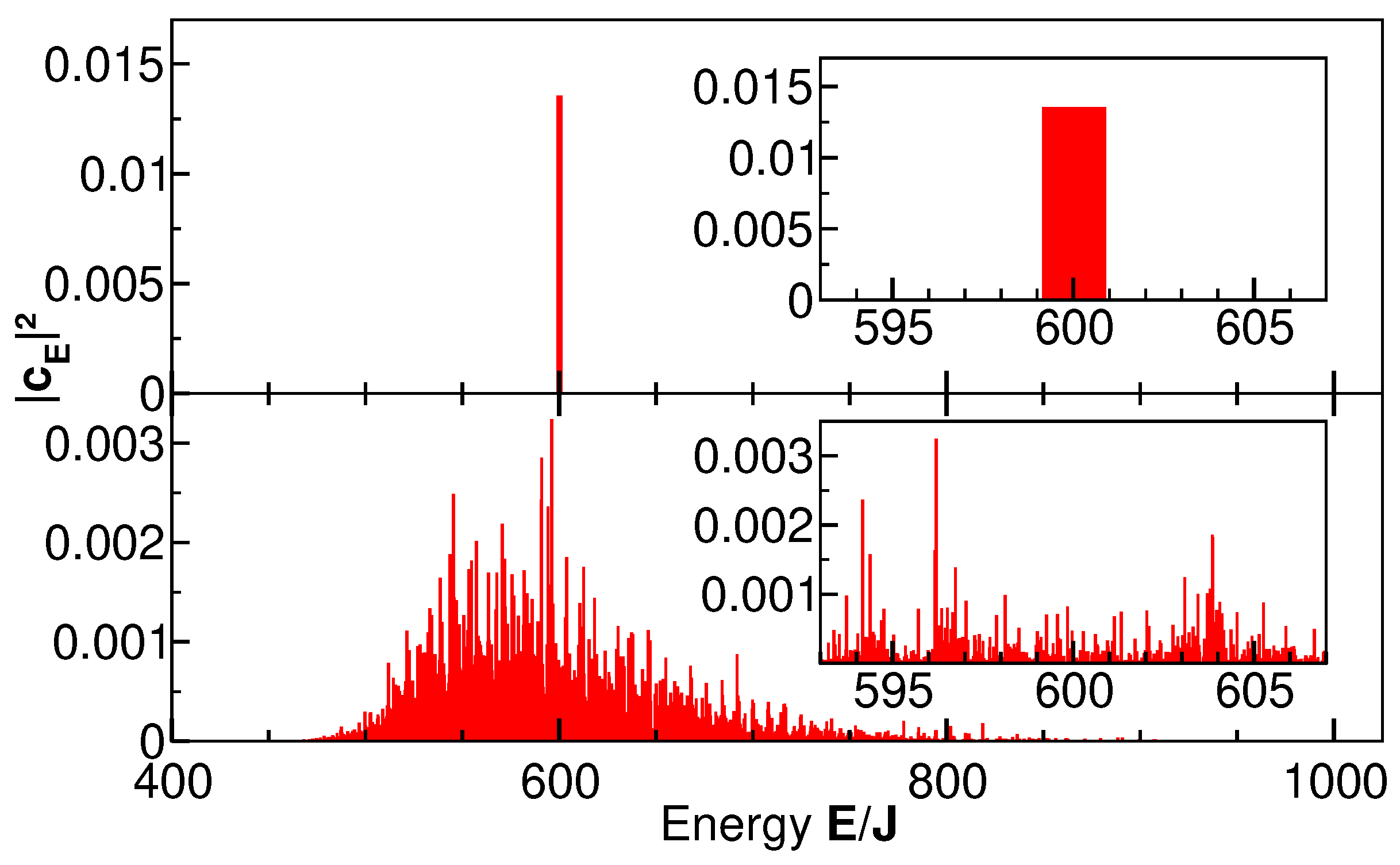
4.1. Broad energy spectrum
4.2. Narrow Energy Spectrum
5. Thermalization Dynamics of Local Occupation Numbers and Spectra
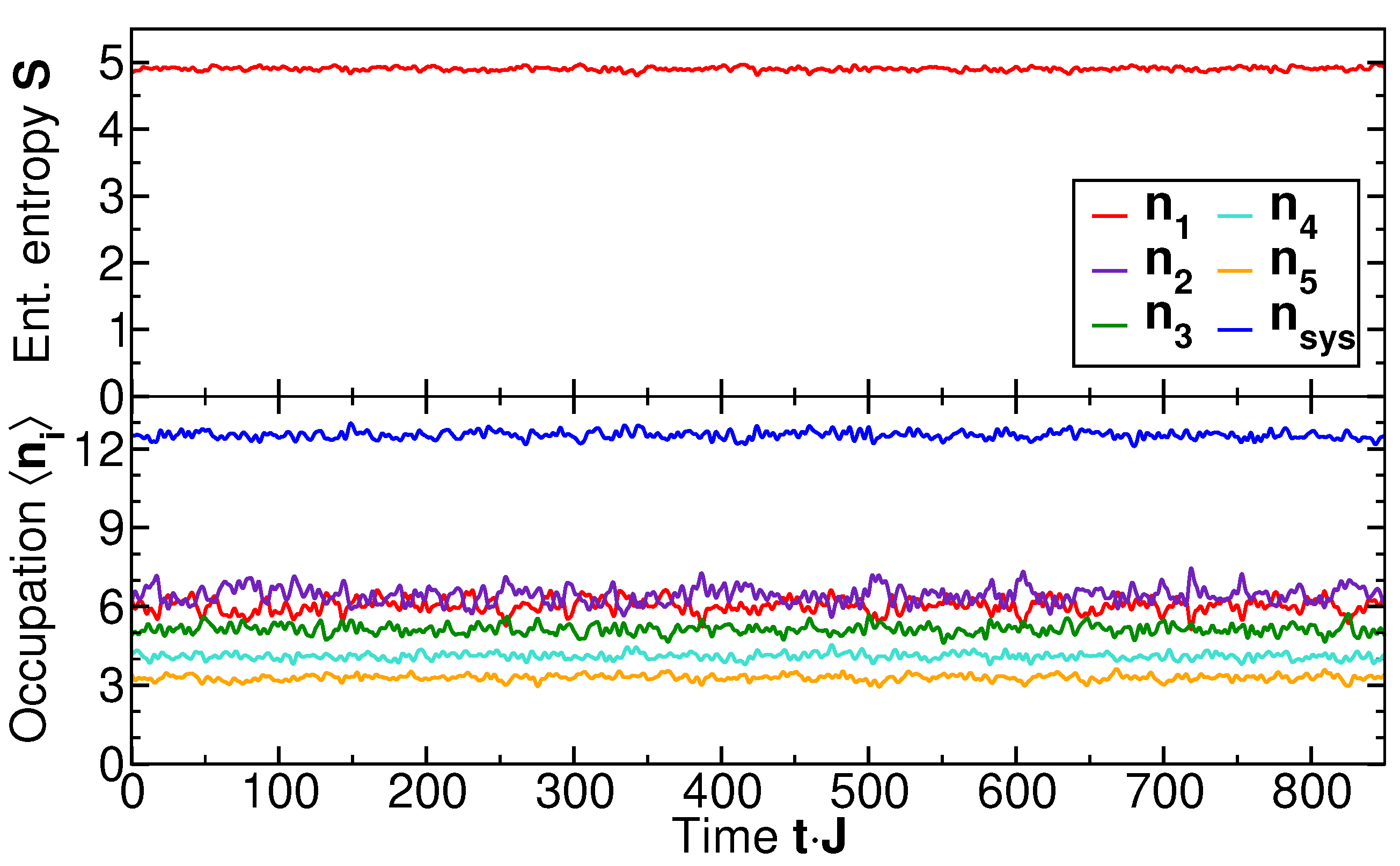
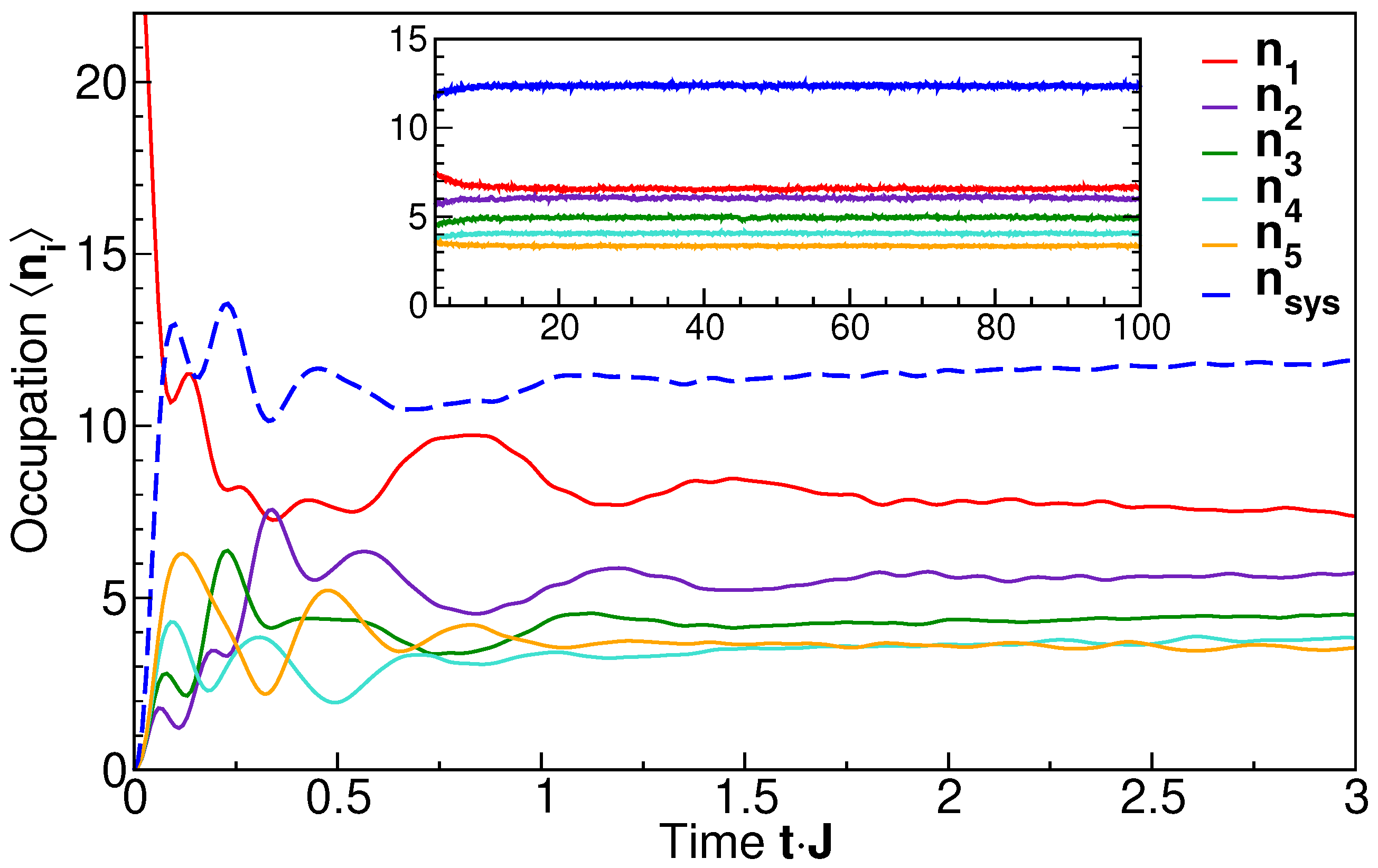
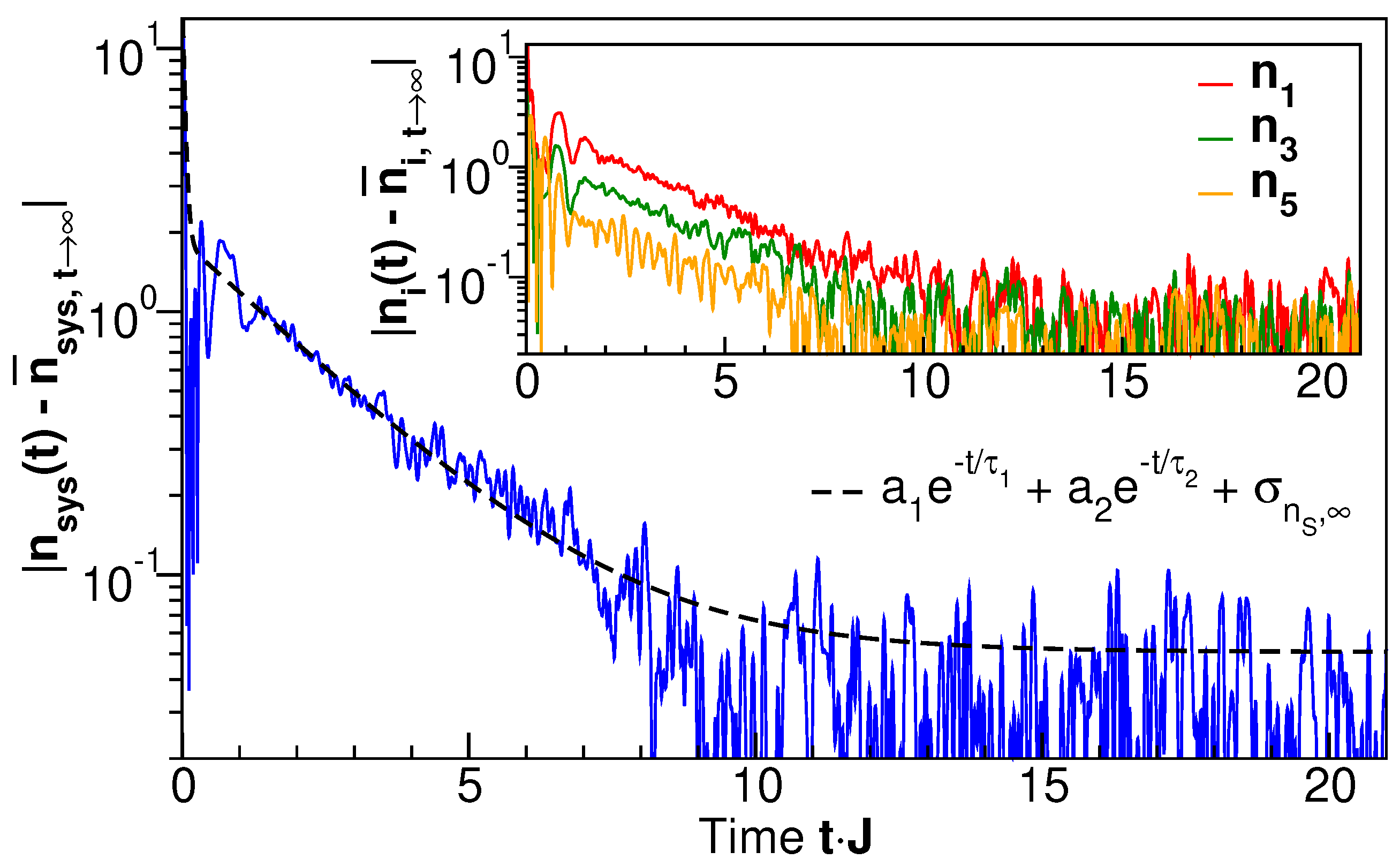
5.1. Thermalization Dynamics of Local Occupation Numbers
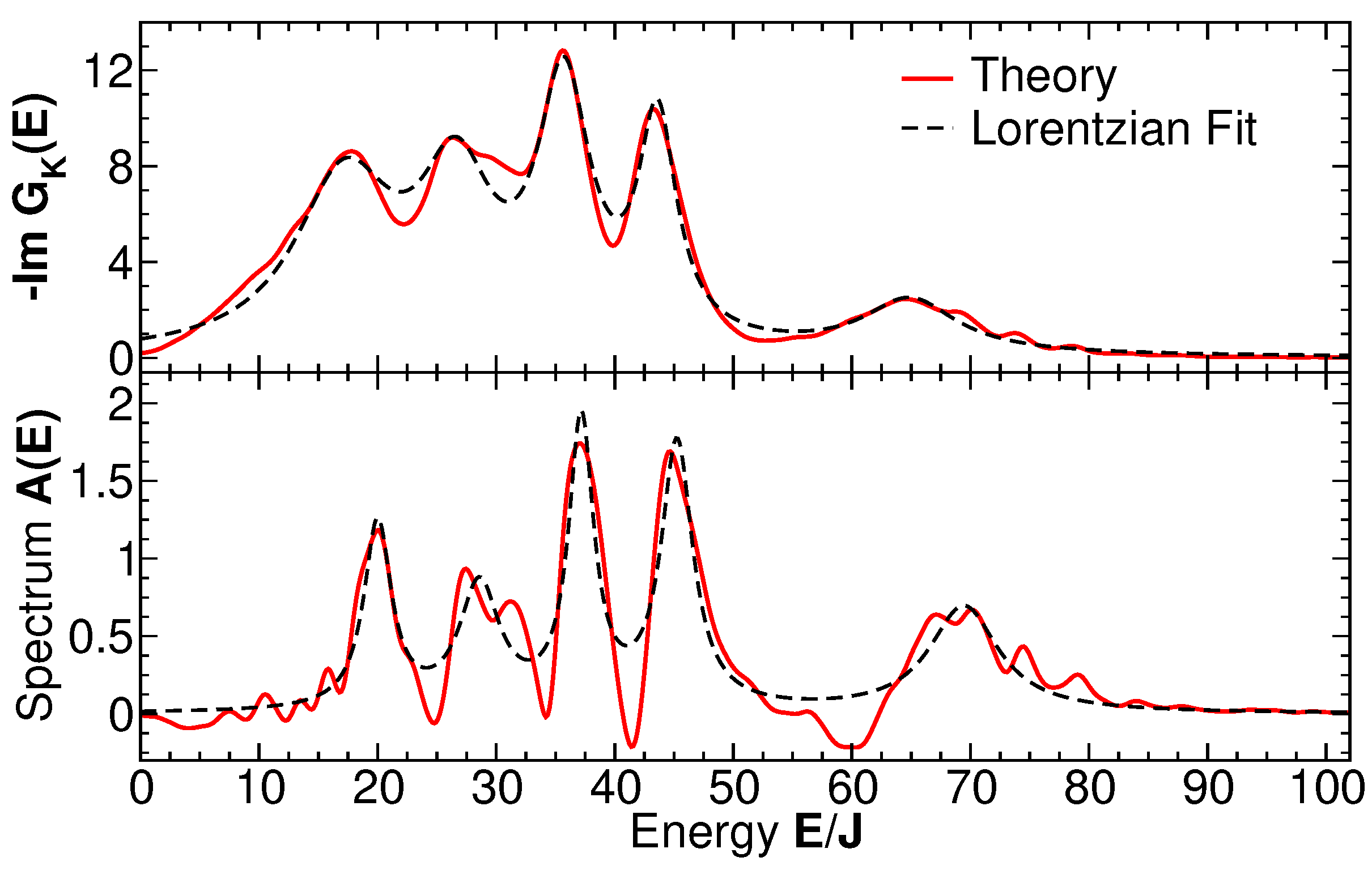
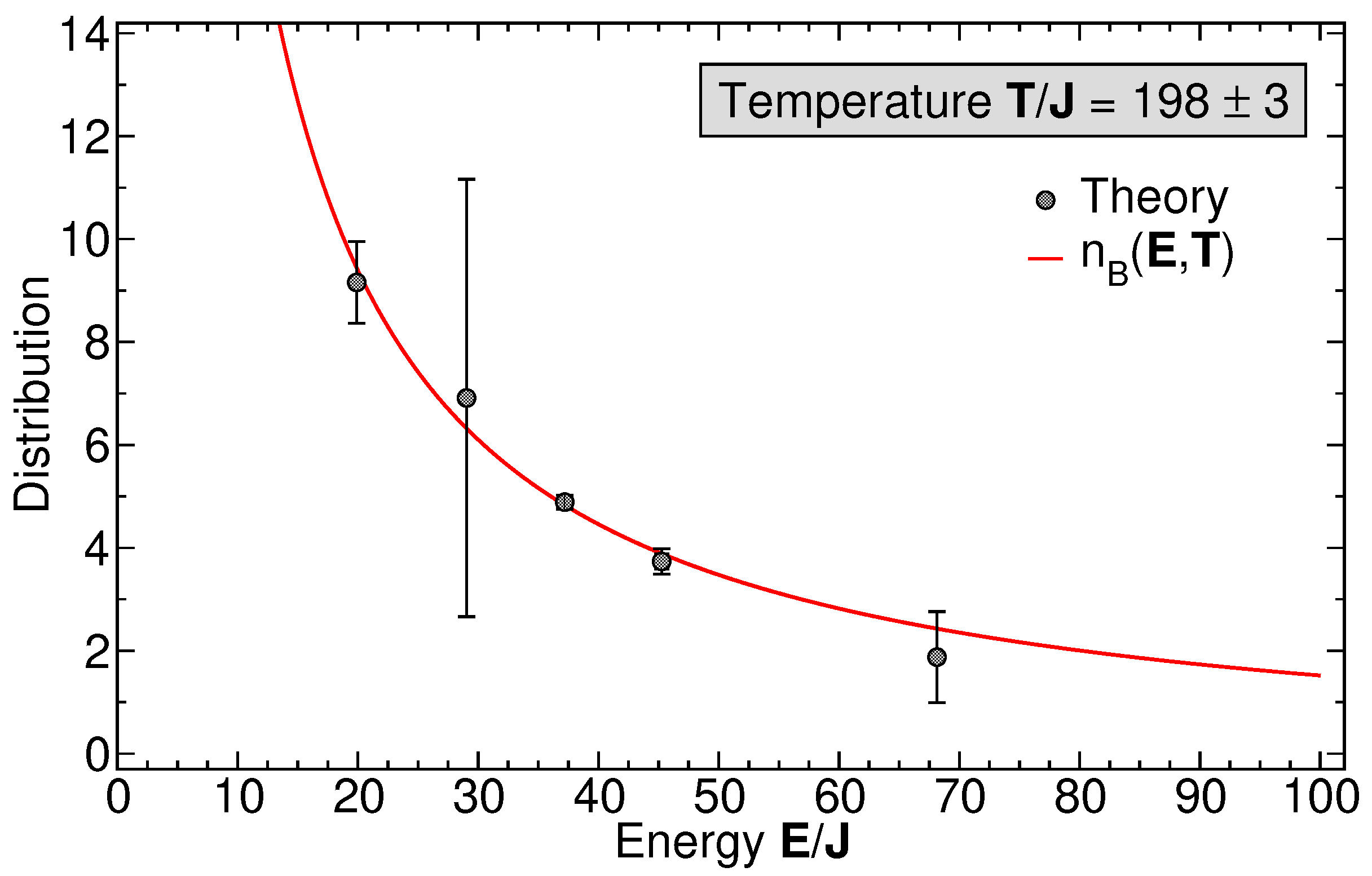
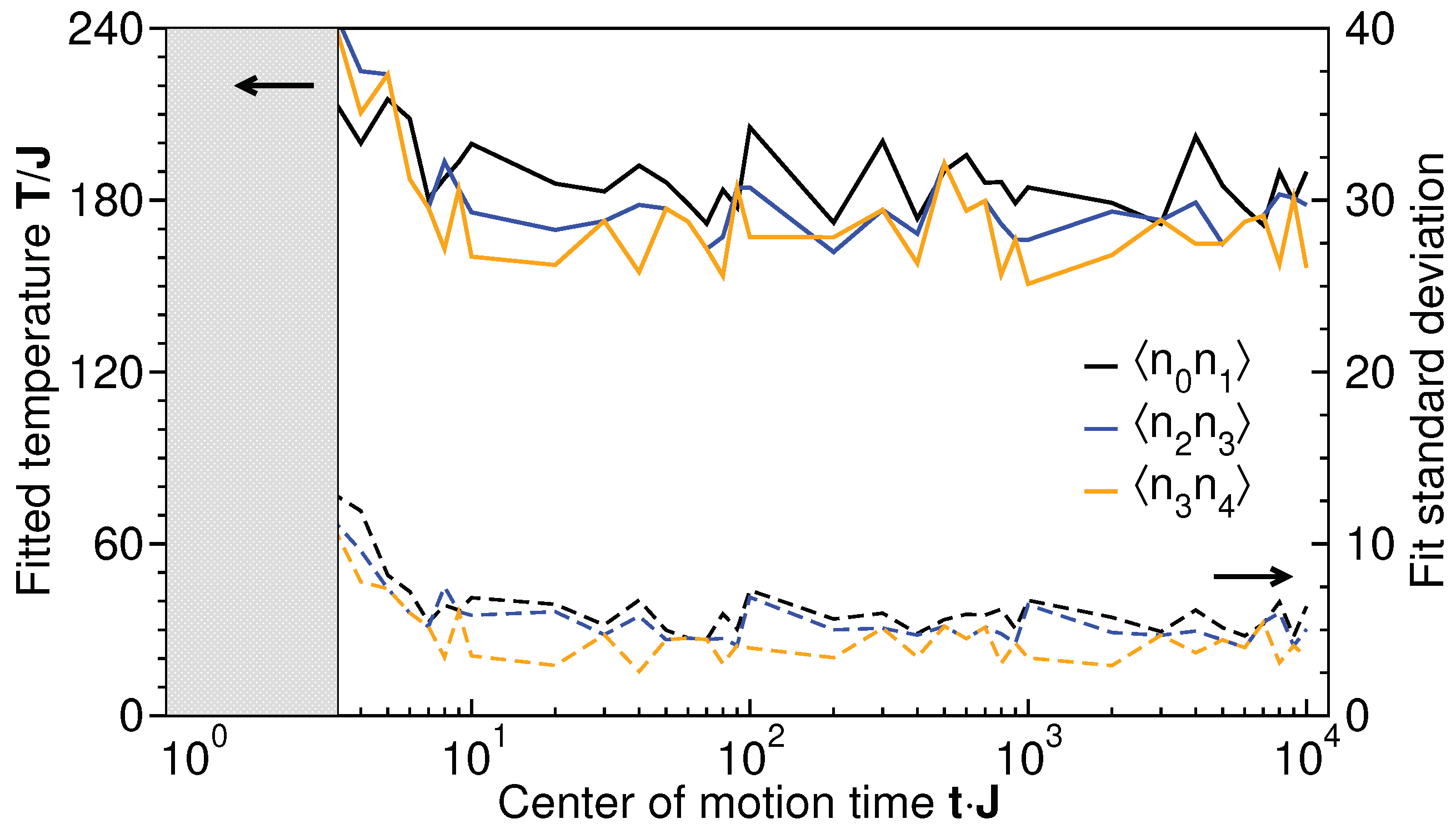
5.2. Long-Time Thermalization of Local Spectra
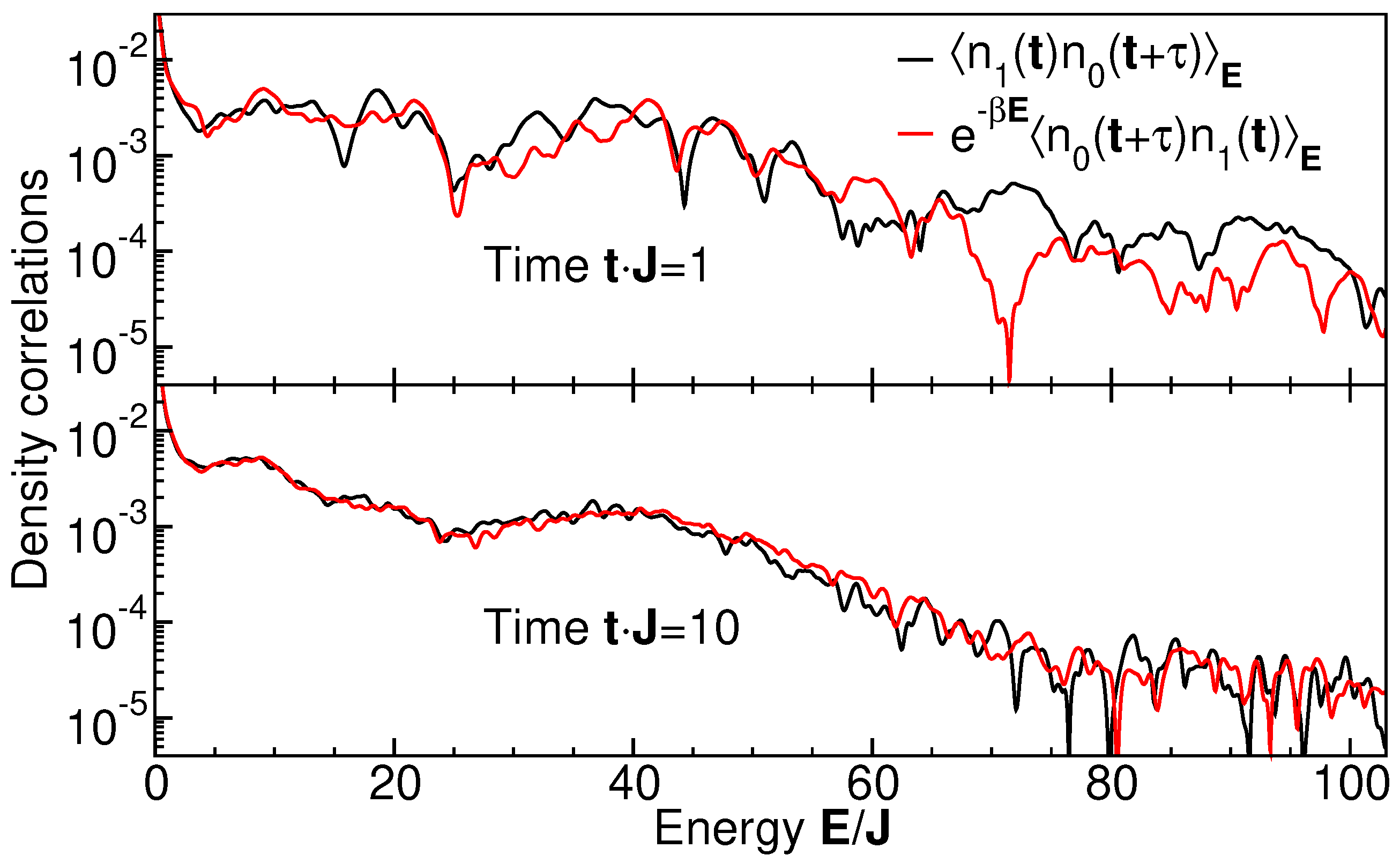
6. Thermal Behavior of Non-Local Density Correlations
7. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ETH | Eigenstatet thermalization hypothesis |
| DBG | Dynamical (heat) bath generation |
| FDT | Fluctuation-dissipation theorem |
| GOE | Gaussian orthogonal ensemble |
| COM | Center of motion |
References
- Deutsch, J.M. Quantum statistical mechanics in a closed system. Physical Review A 1991, 43, 2046–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srednicki, M. Chaos and quantum thermalization. Physical Review E 1994, 50, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigol, M.; Dunjko, V.; Olshanii, M. Thermalization and its mechanism for generic isolated quantum systems. Nature 2008, 452, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessio, L.; Kafri, Y.; Polkovnikov, A.; Rigol, M. From quantum chaos and eigenstate thermalization to statistical mechanics and thermodynamics. Advances in Physics 2016, 65, 239–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigol, M. Breakdown of Thermalization in Finite One-Dimensional Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozsgay, B. Failure of the generalized eigenstate thermalization hypothesis in integrable models with multiple particle species. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment 2014, 2014, P09026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posazhennikova, A.; Trujillo-Martinez, M.; Kroha, J. Thermalization of Isolated Bose-Einstein Condensates by Dynamical Heat Bath Generation. Annalen der Physik 2017, 1700124, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, S. Why ETH? On thermalization and locality. arXiv 2025, arXiv:arXiv:2502.04784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posazhennikova, A.; Trujillo-Martinez, M.; Kroha, J. Inflationary Quasiparticle Creation and Thermalization Dynamics in Coupled Bose-Einstein Condensates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 225304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, S.; Lebowitz, J.L.; Tumulka, R.; Zanghì, N. Canonical Typicality. Physical Review Letters 2006, 96, 050403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurek, W.H. Pointer basis of quantum apparatus: Into what mixture does the wave packet collapse? Physical Review D 1981, 24, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, W.H. Environment-induced superselection rules. Physical Review D 1982, 26, 1862–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, W.H. Decoherence, einselection, and the quantum origins of the classical. Reviews of Modern Physics 2003, 75, 715–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milburn, G.J. Intrinsic decoherence in quantum mechanics. Physical Review A 1991, 44, 5401–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.P.; Adlam, E.; Masanes, L.; Wiebe, N. Thermalization and Canonical Typicality in Translation-Invariant Quantum Lattice Systems. Comm. Math. Phys. 2015, 340, 499–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollath, C.; Läuchli, A.M.; Altman, E. Quench Dynamics and Nonequilibrium Phase Diagram of the Bose-Hubbard Model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 180601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oganesyan, V.; Huse, D.A. Localization of interacting fermions at high temperature. Physical Review B 2007, 75, 155111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atas, Y.Y.; Bogomolny, E.; Giraud, O.; Roux, G. Distribution of the Ratio of Consecutive Level Spacings in Random Matrix Ensembles. Physical Review Letters 2013, 110, 084101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, H.; Lieb, E.H. Entropy inequalities. Communications in Mathematical Physics 1970, 18, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammer, J. Quantum field theory of non-equilibrium states, 1. paperback ed ed.; Cambridge Univ. Press: Cambridge, 2011. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | Sufficiently complex means that the Hilbert space dimension is large, and the Hilbert space does not factorize into disjoint sectors by the system dynamics. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




