Submitted:
19 May 2025
Posted:
20 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
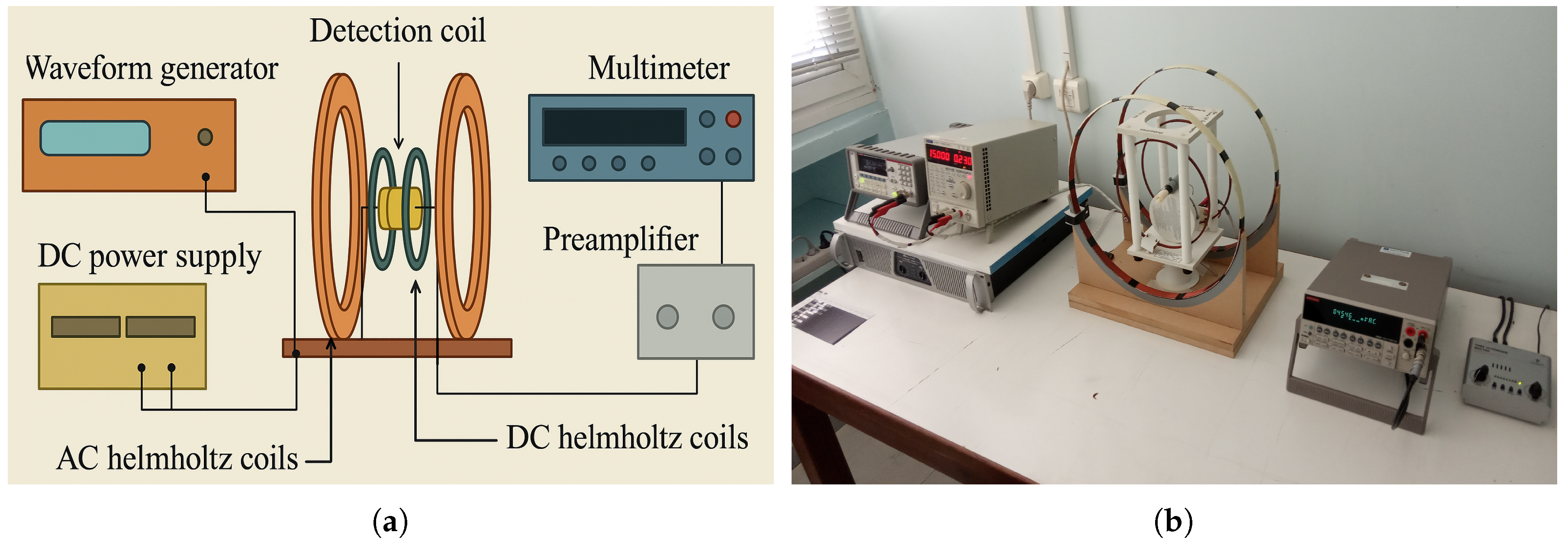
2. Materials and Methods
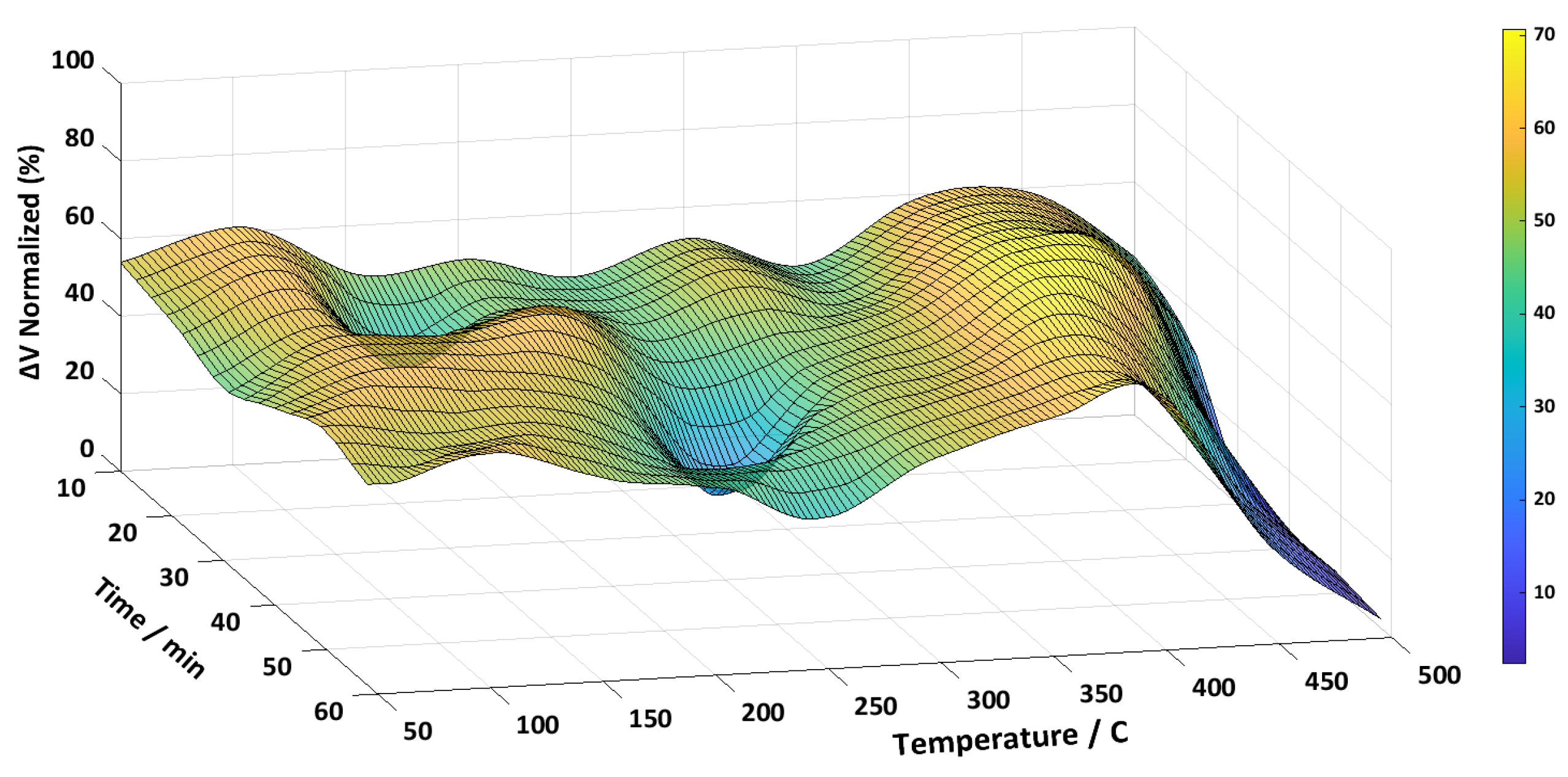
3. Results and Discussion
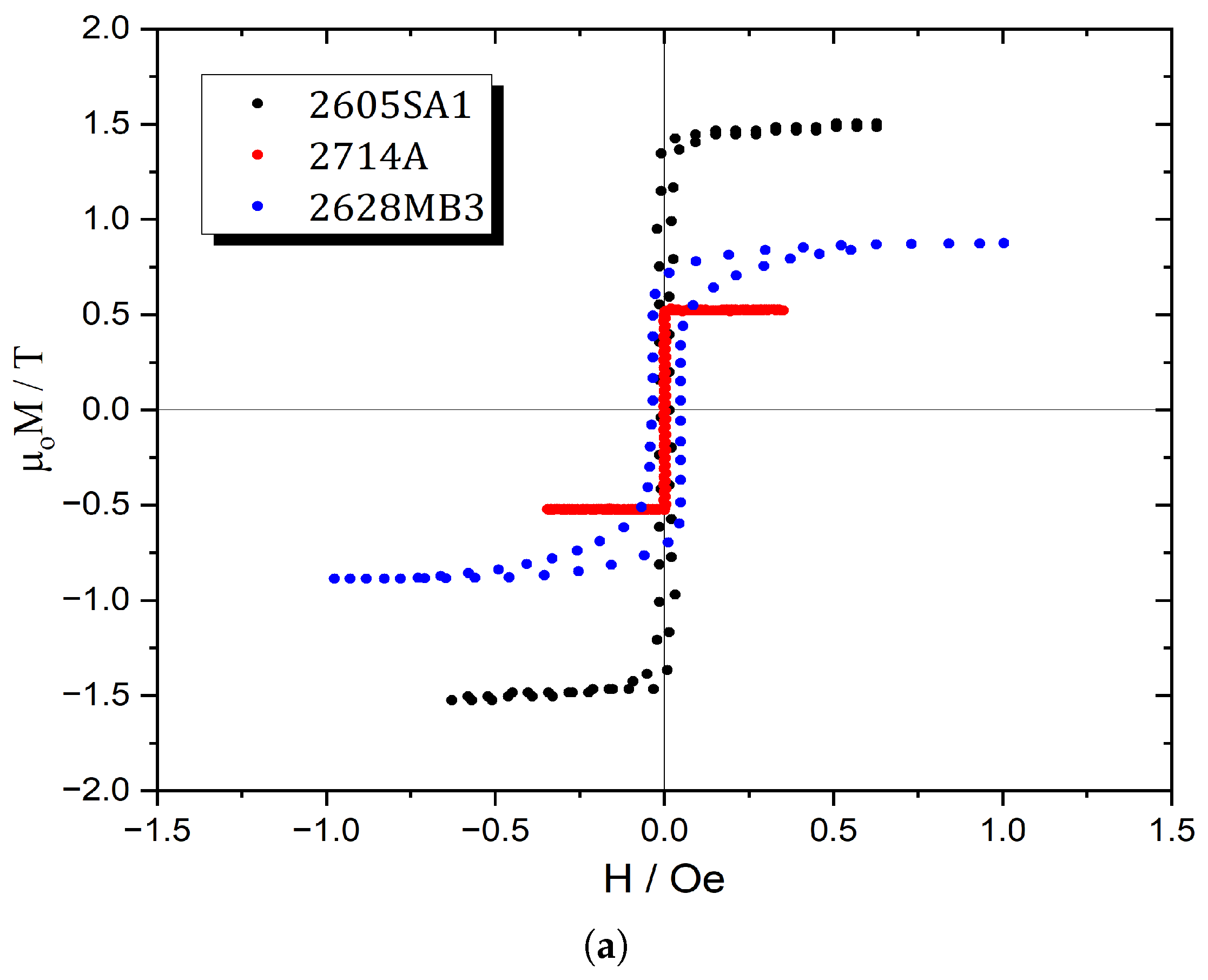
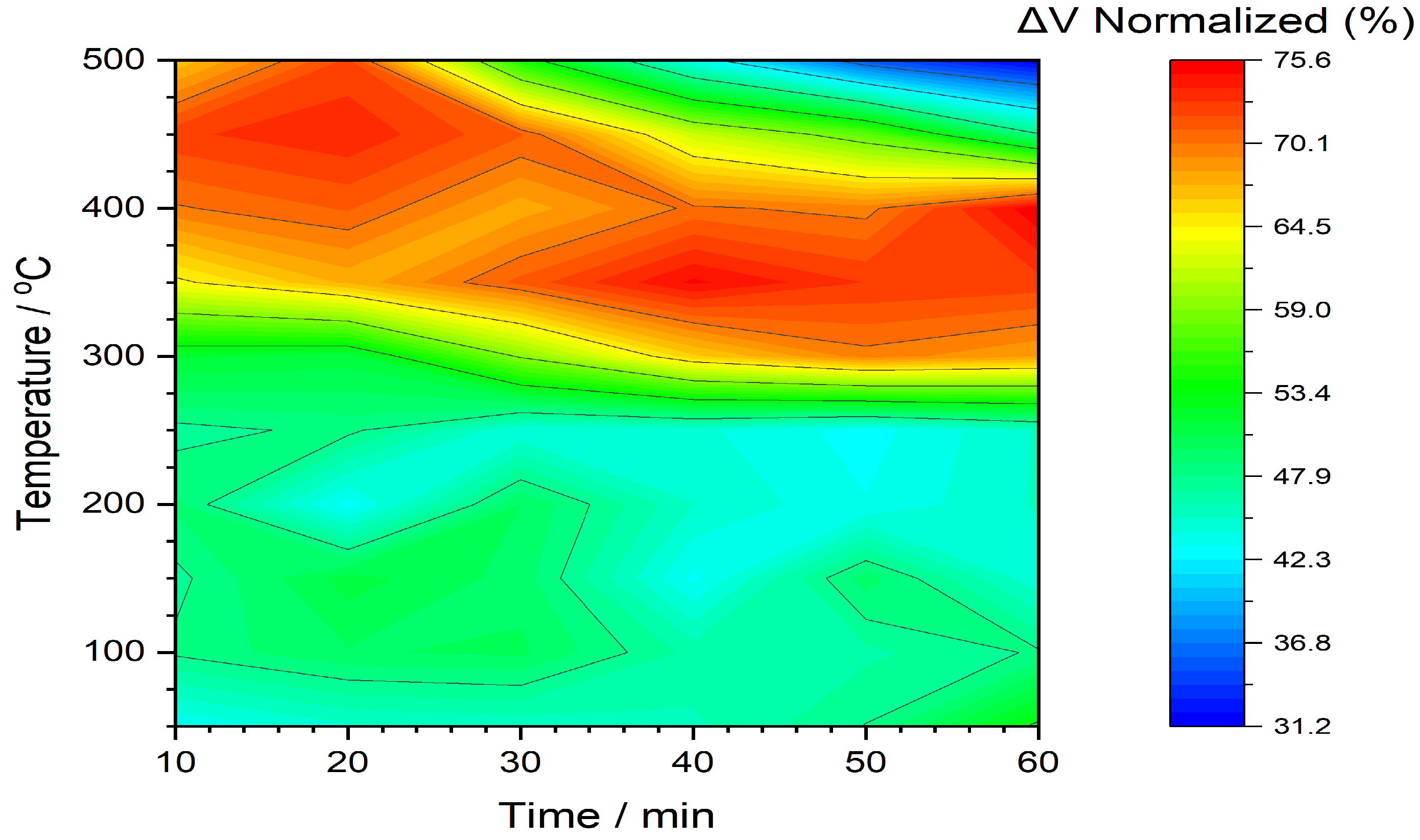
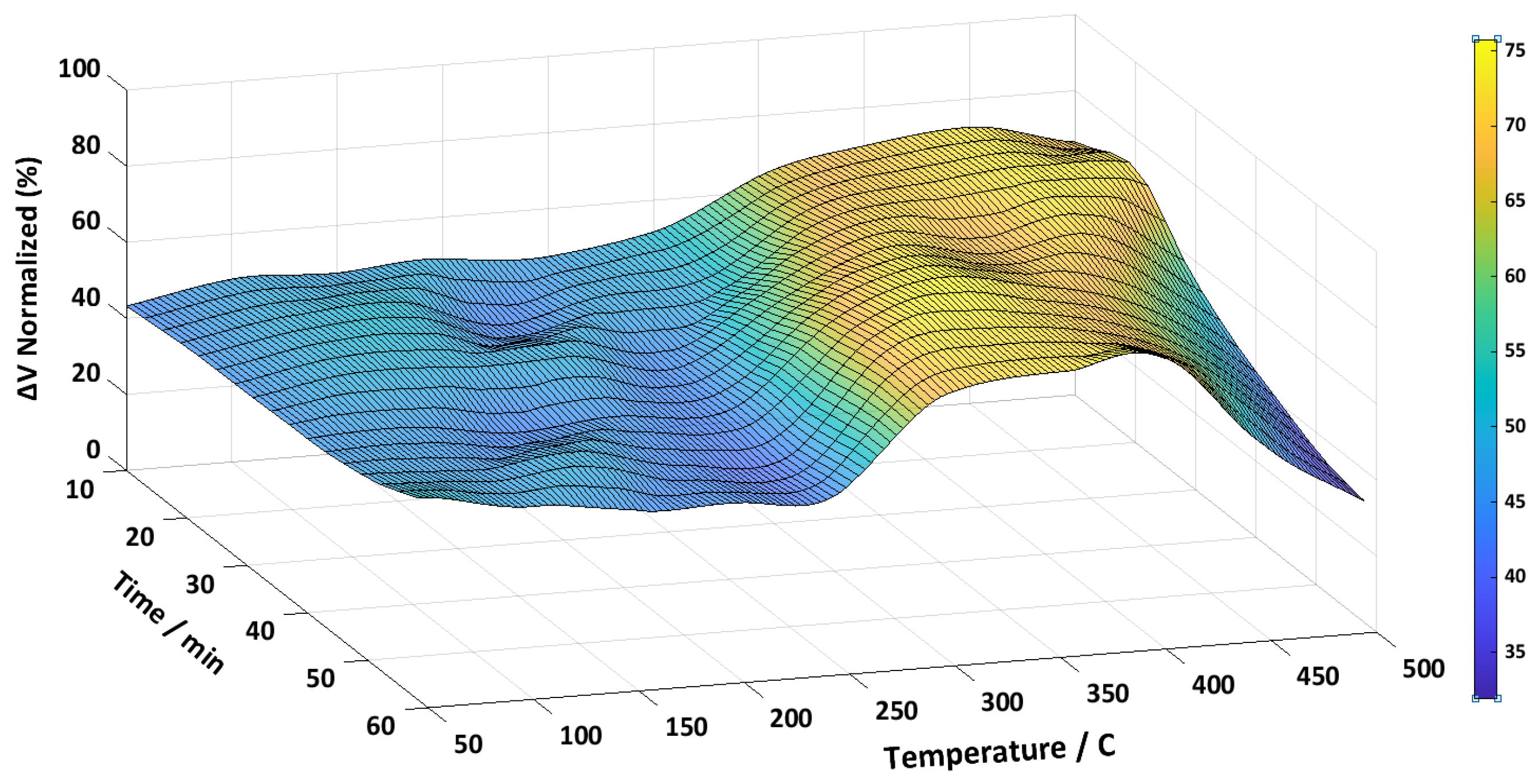
3.1. Metglas 2826MB3
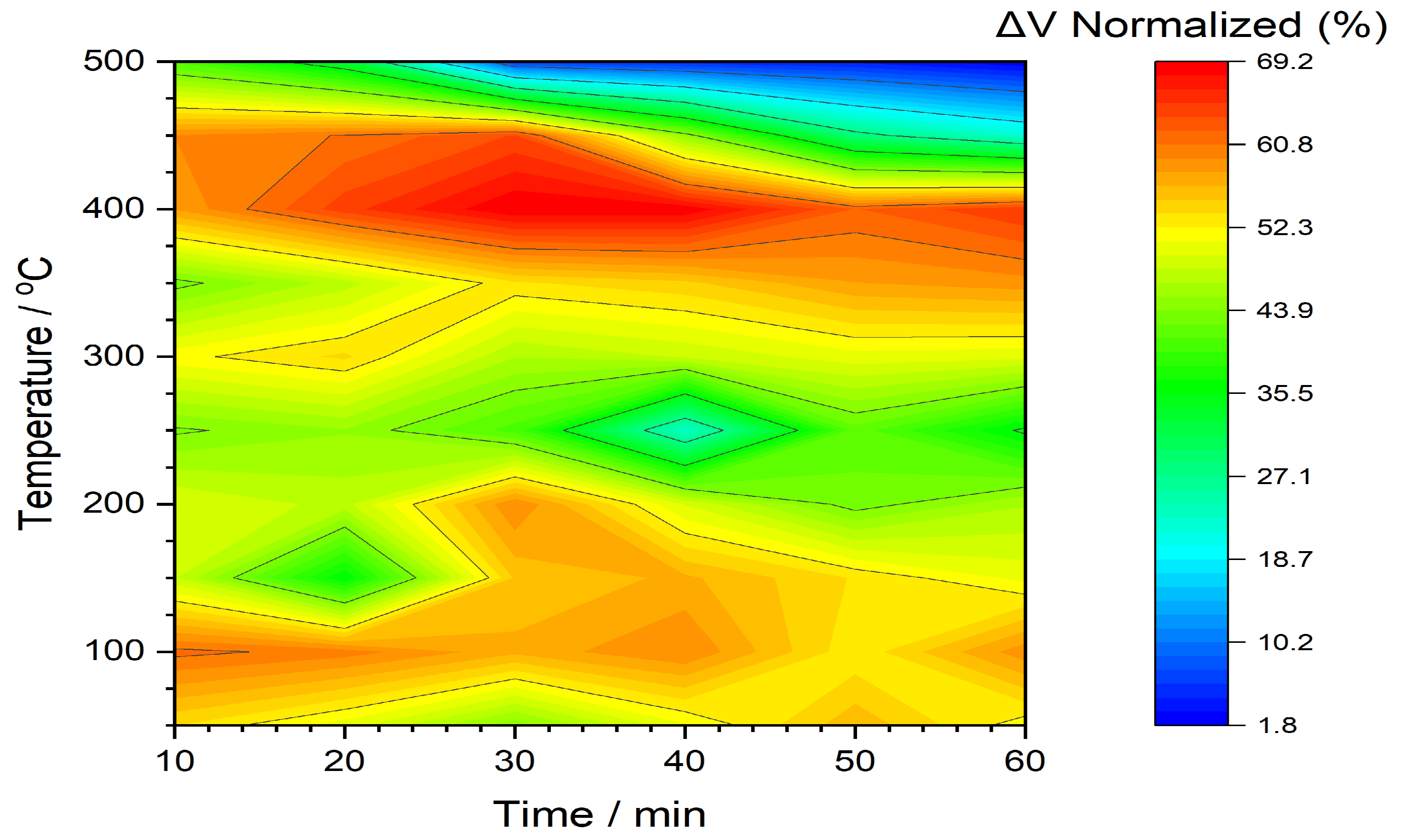
3.2. Metglas 2605SA1
3.3. Metglas 2714A
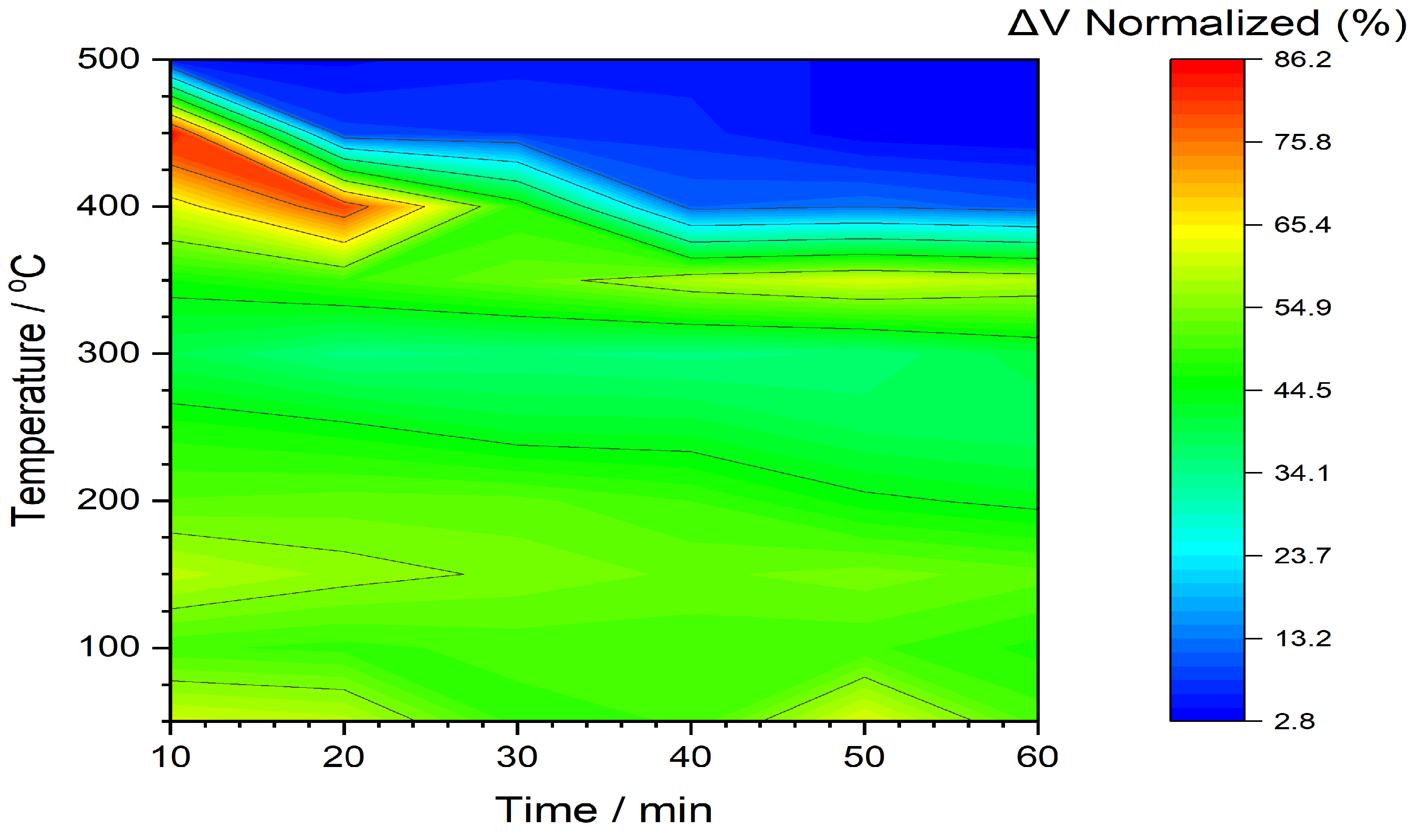
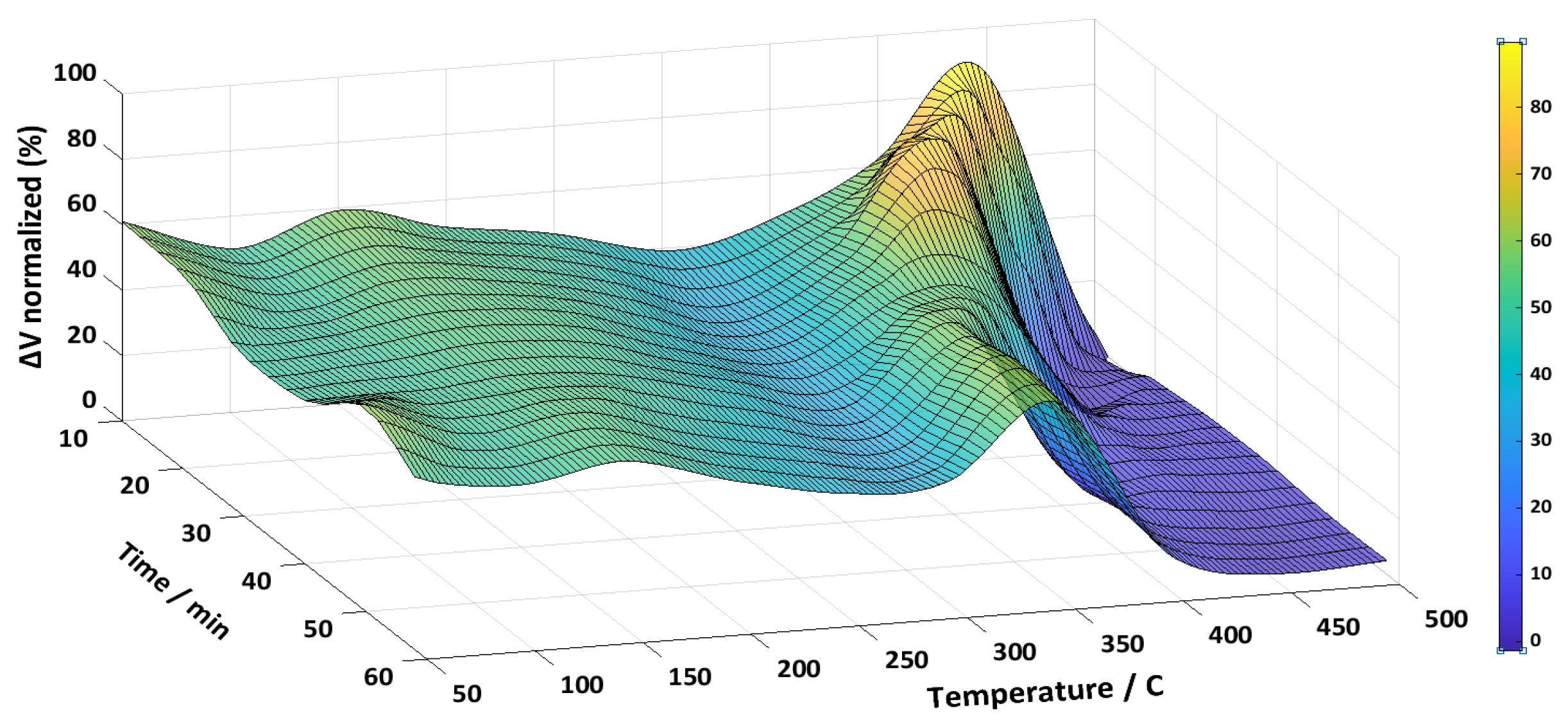
3.4. Reported benefits of thermal annealing in literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goumiri, S.; Yahiaoui, S.; Djahel, S. Smart Mobility in Smart Cities: Emerging challenges, recent advances and future directions. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems 2025, 29, 81–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Aye, L.; Ngo, T.D.; Zhou, J. Performance evaluation of low-cost air quality sensors: A review. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 818, 151769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainurin, S.N.; Wan Ismail, W.Z.; Mahamud, S.N.I.; Ismail, I.; Jamaludin, J.; Ariffin, K.N.Z.; Wan Ahmad Kamil, W.M. Advancements in monitoring water quality based on various sensing methods: a systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 14080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshami, A.; Ali, E.; Elsayed, M.; Eltoukhy, A.E.; Zayed, T. IoT Innovations in Sustainable Water and Wastewater Management and Water Quality Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review of Advancements, Implications, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sishodia, R.P.; Ray, R.L.; Singh, S.K. Applications of remote sensing in precision agriculture: A review. Remote sensing 2020, 12, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, S.; Kefale, H.; Gelaye, Y. Application of precision agriculture technologies for sustainable crop production and environmental sustainability: A systematic review. The Scientific World Journal 2024, 2024, 2126734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tat, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ngo, D.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J. A programmable magnetoelastic sensor array for self-powered human–machine interface. Applied Physics Reviews 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, S.; Karipott, S.S.; Guldberg, R.E.; Ong, K.G. Magnetoelastic sensors for real-time tracking of cell growth. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 2021, 118, 2380–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, D. Magnetostriction and magnetoelasticity. Handbook of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 2020, pp. 1–45.
- Samourgkanidis, G. Experimental study and characterization of magnetoelastic ribbons as vibration sensors and their application for the identification of cracks in cantilever beams through the dynamic behavior of the beam. PhD thesis, Πανεπιστη´μιo Πατρω´ν. Σχoλη´ Πoλυτεχνικη´. Tμη´μα Xημικω´ν Mηχανικω´ν. Toμε´ας …, 202.
- Köster, U.; Herold, U. Crystallization of metallic glasses. Glassy Metals I: Ionic Structure, Electronic Transport, and Crystallization 2005, pp. 225–259.
- Suryanarayana, C. In situ mechanical crystallization of amorphous alloys. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2023, 961, 171032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, A.M.; Ignakhin, V.; Lugovskaya, L.; Osaulenko, R.; Sekirin, I. Crystallization kinetics and magnetostriction properties of amorphous Fe80-xCoxP14B6 metallic glasses. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 2020, 512, 166972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fan, J.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Wang, A.; Li, S.; Liu, J. Low-Loss Soft Magnetic Materials and Their Application in Power Conversion: Progress and Perspective. Energies 2025, 18, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehalia, V.; Walia, G.; Bhalla, D. Analysing the reduction of no-load losses in distribution transformers on the usage of amorphous alloy. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing, Vol. 2900. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, A.; Terada, H.; Nagata, T.; Kurita, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Fukui, K.; Azuma, D.; Hasegawa, R. Development of distribution transformer based on new amorphous metals. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2009). IET; 2009; p. 0474. [Google Scholar]
- Turutin, A.V.; Vidal, J.V.; Kubasov, I.V.; Kislyuk, A.M.; Malinkovich, M.D.; Parkhomenko, Y.N.; Kobeleva, S.P.; Kholkin, A.L.; Sobolev, N.A. Low-frequency magnetic sensing by magnetoelectric metglas/bidomain LiNbO3 long bars. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 2018, 51, 214001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichurin, M.; Petrov, R.; Sokolov, O.; Leontiev, V.; Kuts, V.; Kiselev, D.; Wang, Y. Magnetoelectric magnetic field sensors: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, H.; Spano, M. Theory and application of highly magnetoelastic Metglas 2605SC. Journal of Applied Physics 1982, 53, 8092–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, E.; DeMoyer, R.; Vranish, J. A new Metglas sensor. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 1986, pp. 166–170.
- Jen, S.; Liu, C.; Lin, H.; Chou, S. Frequency dependence of the magnetostrictive phenomenon in Metglas® 2605SA1 ribbon: A minor-loop case. AIP Advances 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzoudis, D.; Baimpos, T.; Samourgkanidis, G. A New Method for the Measurement of the Diffusion Coefficient of Adsorbed Vapors in Thin Zeolite Films, Based on Magnetoelastic Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baimpos, T.; Gora, L.; Nikolakis, V.; Kouzoudis, D. Selective detection of hazardous VOCs using zeolite/Metglas composite sensors. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 2012, 186, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baimpos, T.; Tsukala, V.; Nikolakis, V.; Kouzoudis, D. A modified method for the calculation of the humidity adsorption stresses inside zeolite films using magnetoelastic sensors. Sensor Letters 2012, 10, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samourgkanidis, G.; Nikolaou, P.; Gkovosdis-Louvaris, A.; Sakellis, E.; Blana, I.; Topoglidis, E. Hemin-Modified SnO2/Metglas Electrodes for the Simultaneous Electrochemical and Magnetoelastic Sensing of H2O2. Coatings 2018, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagasti, A.; Bouropoulos, N.; Kouzoudis, D.; Panagiotopoulos, A.; Topoglidis, E.; Gutiérrez, J. Nanostructured ZnO in a metglas/ZnO/hemoglobin modified electrode to detect the oxidation of the hemoglobin simultaneously by cyclic voltammetry and magnetoelastic resonance. Materials 2017, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samourgkanidis, G.; Kouzoudis, D. Magnetoelastic ribbons as vibration sensors for real-time health monitoring of rotating metal beams. Sensors 2021, 21, 8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouzoudis, D.; Samourgkanidis, G.; Tapeinos, C.I. Contactless Detection of Natural Bending Frequencies using Embedded Metallic-Glass Ribbons inside Plastic Beams made of 3-D Printing. Recent Progress in Materials 2021, 3, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapeinos, C.I.; Kamitsou, M.D.; Dassios, K.G.; Kouzoudis, D.; Christogerou, A.; Samourgkanidis, G. Contactless and Vibration-Based Damage Detection in Rectangular Cement Beams Using Magnetoelastic Ribbon Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samourgkanidis, G.; Kouzoudis, D. A pattern matching identification method of cracks on cantilever beams through their bending modes measured by magnetoelastic sensors. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics 2019, 103, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samourgkanidis, G.; Kouzoudis, D. Experimental detection by magnetoelastic sensors and computational analysis with finite elements, of the bending modes of a cantilever beam with minor damage. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 2018, 276, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagasti, A.; Palomares, V.; Porro, J.M.; Orúe, I.; Sánchez-Ilárduya, M.B.; Lopes, A.C.; Gutiérrez, J. Magnetic, magnetoelastic and corrosion resistant properties of (Fe–Ni)-based metallic glasses for structural health monitoring applications. Materials 2019, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samourgkanidis, G.; Kouzoudis, D. Characterization of magnetoelastic ribbons as vibration sensors based on the measured natural frequencies of a cantilever beam. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 2020, 301, 111711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.C.; Islam, M.R.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, H.Y. State-of-the-art technologies for development of high frequency transformers with advanced magnetic materials. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity 2018, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhamad, M.; Elleau, C.; Mazaleyrat, F.; Guillaume, C.; Jarry, B. Short-circuit withstand tests of metglas 2605SA1-based amorphous distribution transformers. IEEE transactions on magnetics 2011, 47, 4489–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z. Ultra sensitive magnetic sensors integrating the giant magnetoelectric effect with advanced microelectronics; The Pennsylvania State University, 2011.
- Kolano, R.; Kolano-Burian, A.; Krykowski, K.; Hetmańczyk, J.; Hreczka, M.; Polak, M.; Szynowski, J. Amorphous soft magnetic core for the stator of the high-speed PMBLDC motor with half-open slots. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 2016, 52, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austrin, L.; Figueroa-Karlstrom, E.; Engdahl, G. Evaluation of switching losses in magnetic amplifiers as an alternative to IGBT switching technologies. In Proceedings of the 2008 4th IET Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives. IET; 2008; pp. 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Quach, H.P.; Chui, T.C. Low temperature magnetic properties of Metglas 2714A and its potential use as core material for EMI filters. Cryogenics 2004, 44, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, V.S.; Le, M.; Quang, V.P. Fluxgate-based displacement sensor design. Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism 2023, 36, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadogan, J.; Campbell, S.; Jing, J.; Foley, C.; Kater, P.; Mai, Y. Annealing embrittlement of Fe78Si9B13 (METGLAS-2605S2). Hyperfine Interactions 2014, 226, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Chen, Z.; Di, W.; Fang, B.; Luo, H. Enhancement magnetoelectric effect in Metglas-Fe by annealing. Applied Physics A 2021, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Yim, S.H.; Son, D. Effects of Annealing Temperature on Amorphous CoFeCrBSi Alloys for Flux-gate Magnetometers. Journal of Magnetics 2021, 26, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Zhuang, X.; Yan, B.; Zhu, W.; Dolabdjian, C.; Fang, G. Magnetomechanical properties of Fe-Si-B and Fe-Co-Si-B metallic glasses by various annealing temperatures for actuation applications. Sensors 2022, 23, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Wei, R.; Chen, C.; Li, F. Improving the B s and soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous ribbons by manipulating the surface crystallization behavior. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2021, 32, 21206–21212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palneedi, H.; Patil, D.R.; Priya, S.; Woo, K.; Ye, J.; Woo, Y.M.; Hwang, Y.S.; Hwang, G.T.; Park, J.H.; Ryu, J. Intense Pulsed Light Thermal Treatment of Pb (Zr, Ti) O3/Metglas Heterostructured Films Resulting in Extreme Magnetoelectric Coupling of over 20 V cm- 1 Oe- 1. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2303553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samourgkanidis, G.; Varvatsoulis, K.; Kouzoudis, D. The Effect of the Thermal Annealing Process to the Sensing Performance of Magnetoelastic Ribbon Materials. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, J.D. Magnetomechanical properties of amorphous metals. physica status solidi (a) 1982, 70, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Properties | 2628MB3 | 2605SA1 | 2714A |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base material | Fe-Ni | Fe | Co |
| Density (g / cm3) | 7.90 | 7.18 | 7.59 |
| Saturation Induction (T) | 0.88 | 1.56 | 0.57 |
| Saturation Magnetostriction (ppm) | 12 | 27 | < 0.5 |
| Curie Temperature (C) | 353 | 395 | 225 |
| Crystallization Temperature (C) | 410 | 510 | 550 |
| Ref. | Alloy | OAS (C-min) | Property | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [41] | Fe78Si9B13 (Metglas 2605S2) | 360 - 5 | In-plane magnetic texture | 27.2 % |
| [42] | Mn-PMNT/FeBSiC | 360 - 5 | Piezomagnetic coefficient | 36.8 % |
| [43] | Co67Fe3Cr3B12Si15 | 350 - 60 | Noise level | 108.3 % |
| [44] | FeCoSiB (Vitrovac 7600) | 390 - 20 | Coupling factor | 23 % |
| FeSiB (Metglas 2605SA1) | 440 - 20 | // | 73 % | |
| [45] | Fe74.89Cr3.04Ni1.23Co0.11Mn0.47Cu0.02Mo0.01C0.11P0.12Si9B11 | 523 - 10 | Magnetic permeability | 136.8 % |
| Fe78.32Mn0.49Cu0.02Mo0.01C0.12P0.13Si9.41B11.5 | 521 - 10 | Core losses | 50 % | |
| [46] | Pb(Zr,Ti)O3/FeSiB (PZT/Metglas 2605SA1) | 300 - 2 | Magnetoelectric coupling | ≈1000 % |
| CW | Fe37Ni42Mo4B17 (Metglas 2826MB3) | 457 - 22 | Magnetic signal | 75.8 % |
| FeSiB (Metglas 2605SA1) | 412 - 31 | // | 70 % | |
| Co66Fe4Ni1B14Si15 (Metglas 2714A) | 442 - 9 | // | 86.8 % |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




