Submitted:
19 May 2025
Posted:
20 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
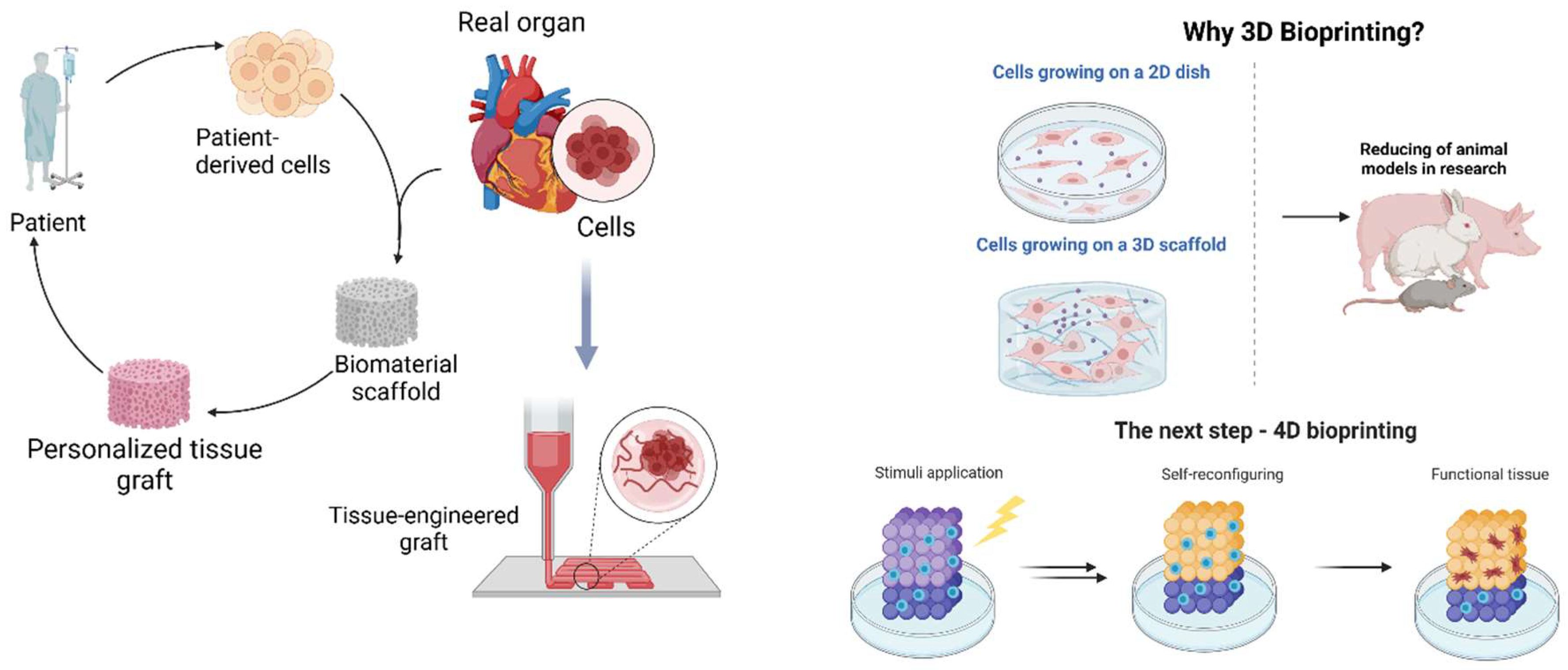
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
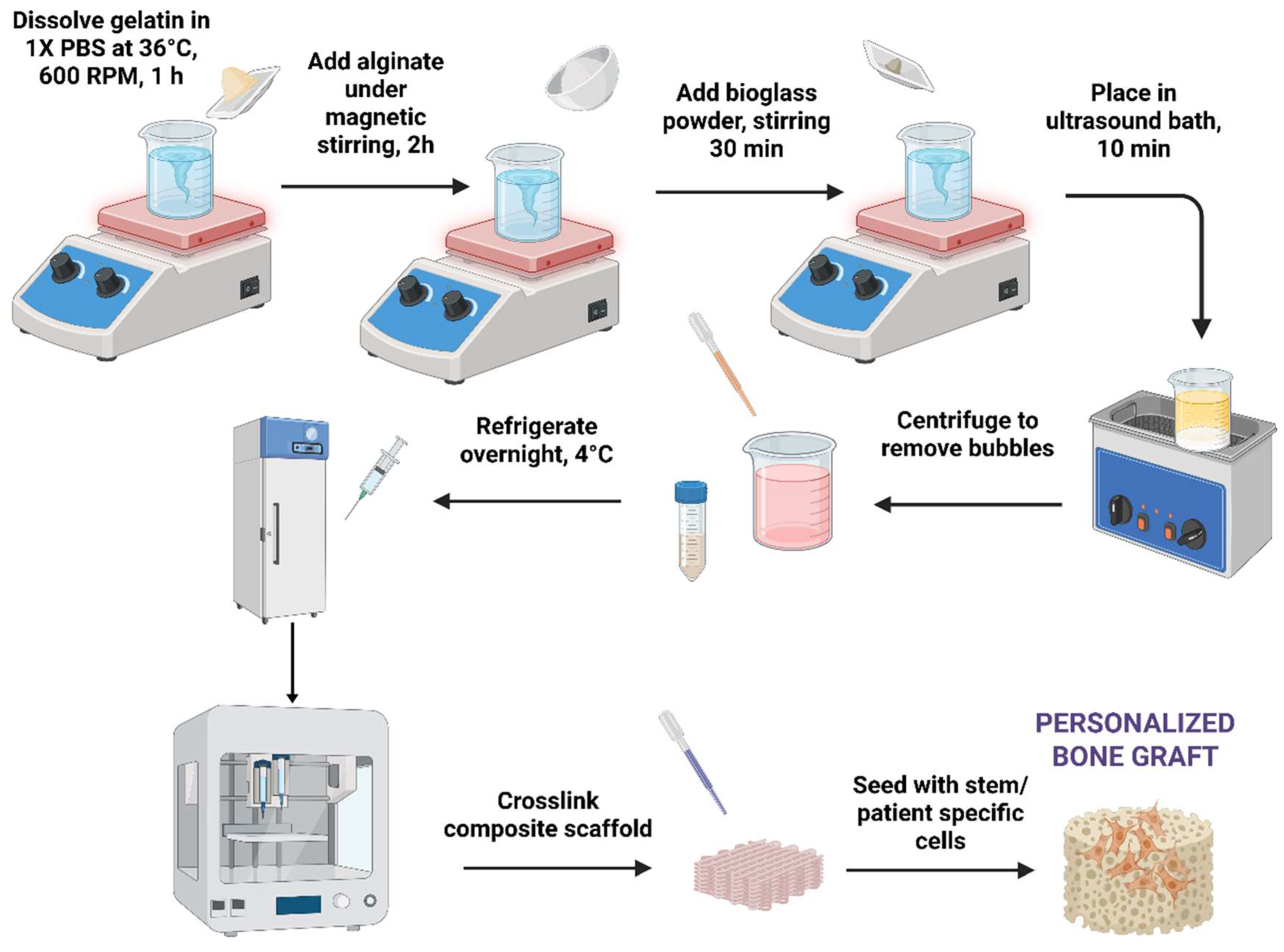
2.2. Hydrogel Synthesis
| Bioglass composition (mol%). | |||||
| 65.0 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 24.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| SiO2 | P2O5 | Na2O | CaO | Ag2O | Eu2O3 |
|
Sample |
Hydrogel composition |
pH |
Pressure (kPa) |
Nozzle diameter |
Printing speed | Layers | Crosslinking time | ||
| Alginate | Gelatin |
Eu-doped BG |
|||||||
| P1 | 3% | 7% | 8 | 25 | 22 G | 20 mm/s | 4 | 5 min | |
| P2 | 7% | 8% | 7 | 135 | |||||
| P3 | 3% | 6% | 0.25% | 8 | 170 | ||||
| P4 | 7% | 8% | 0.50% | 8 | 210 | ||||
| P5 | 7% | 8% | 0.25% | 8 | 225 | ||||
2.3. 3D printing Process
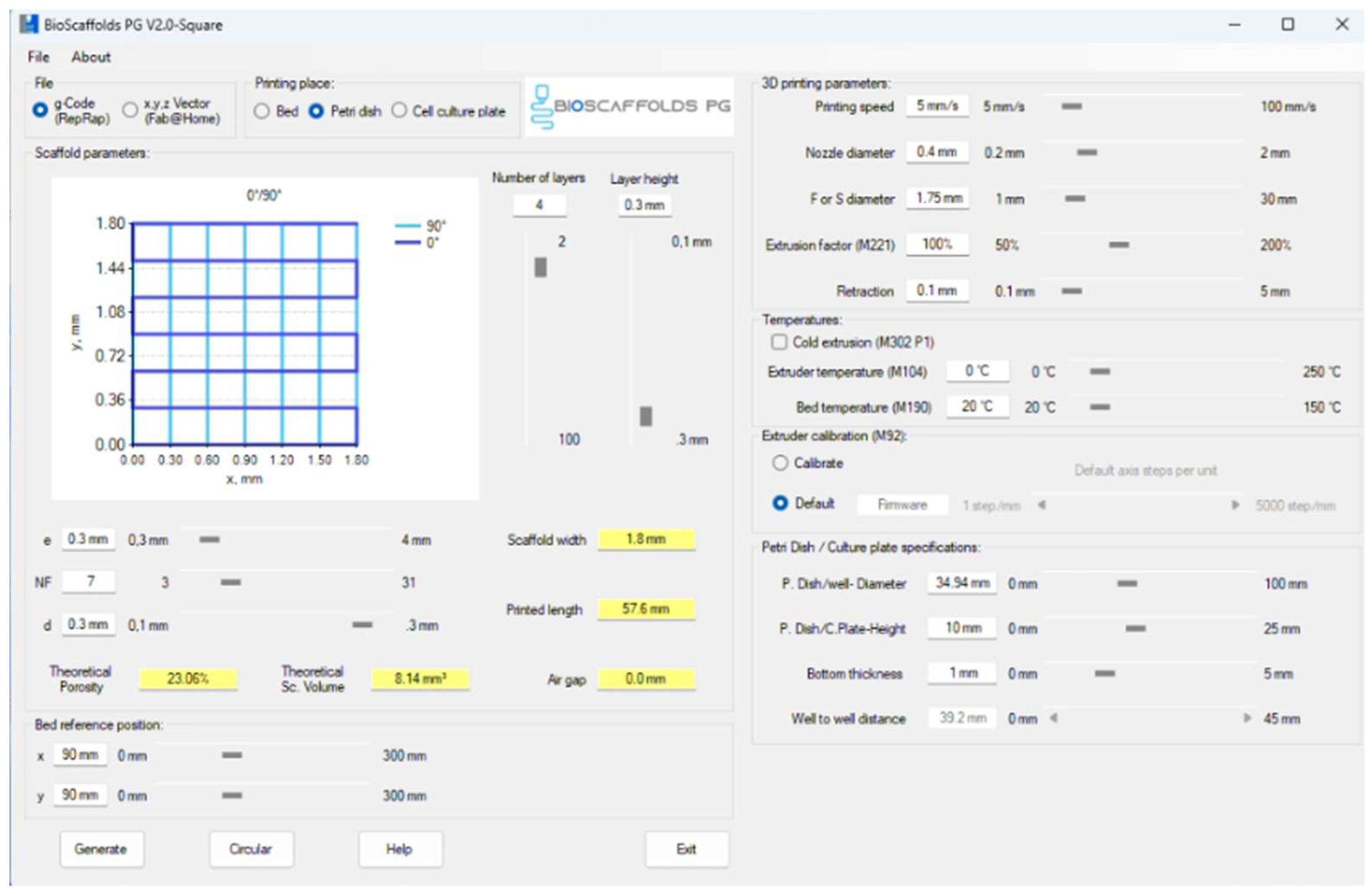
2.4. Characterization Methods
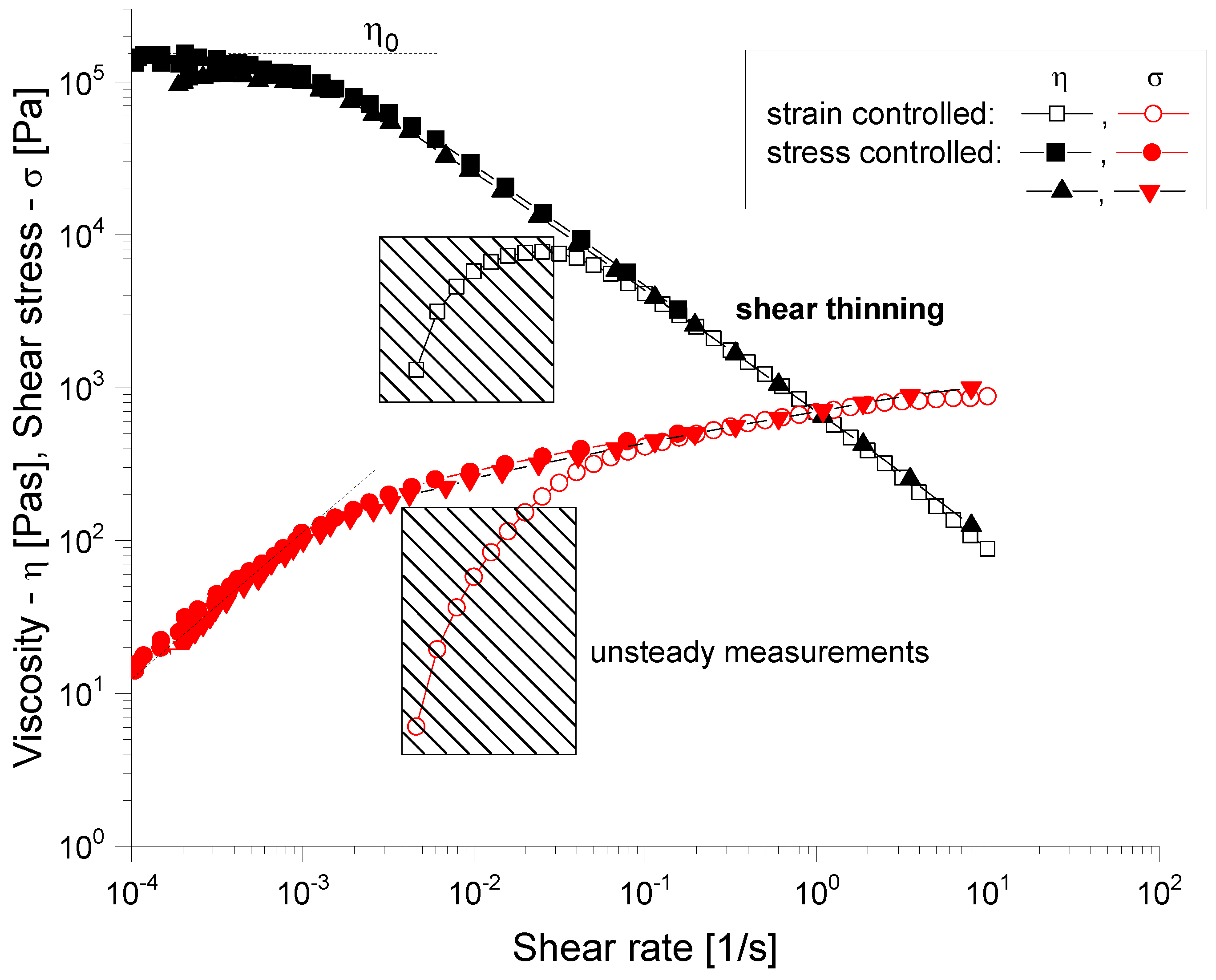
2.4.1. Rheological Evaluation
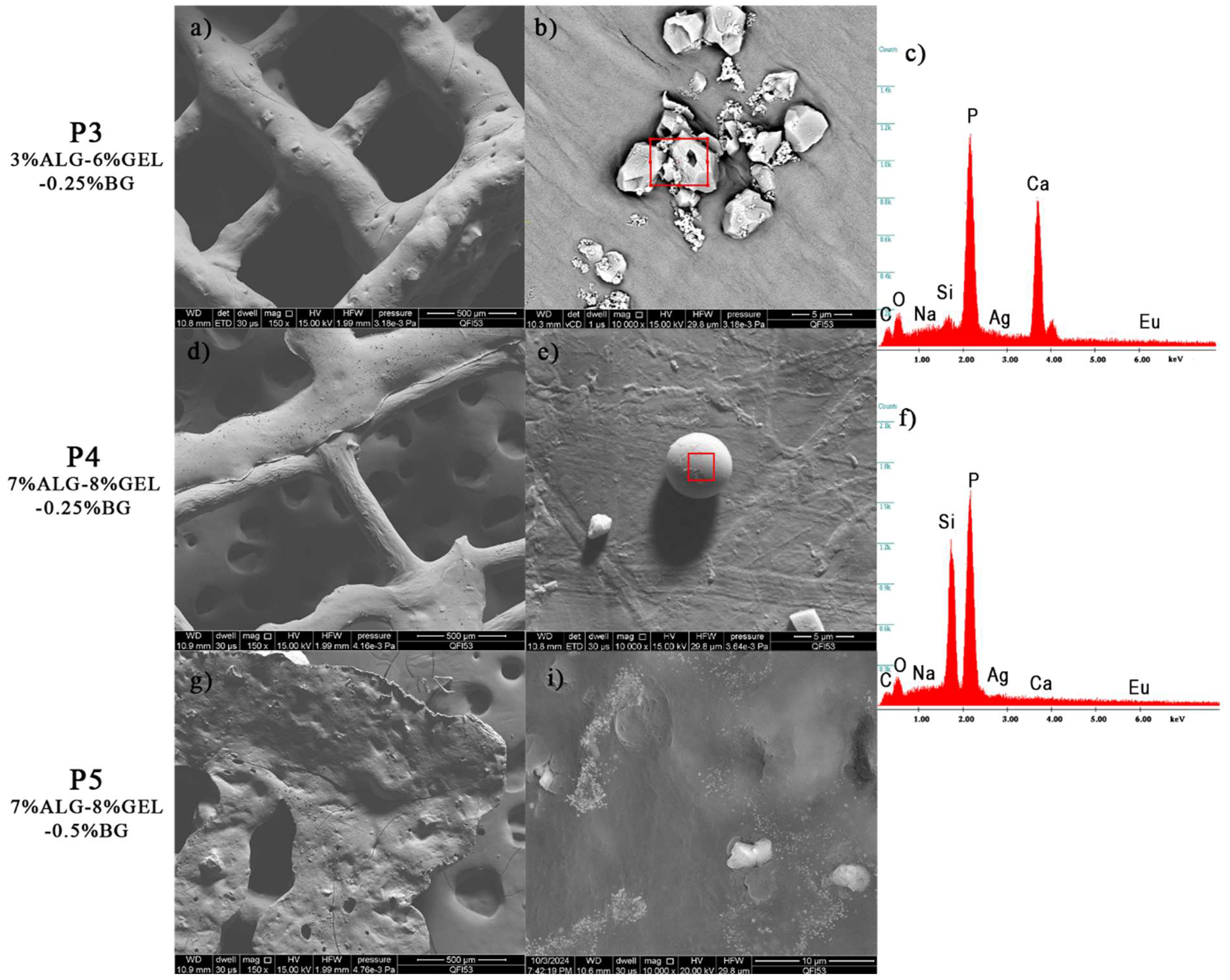
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy
2.4.3. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
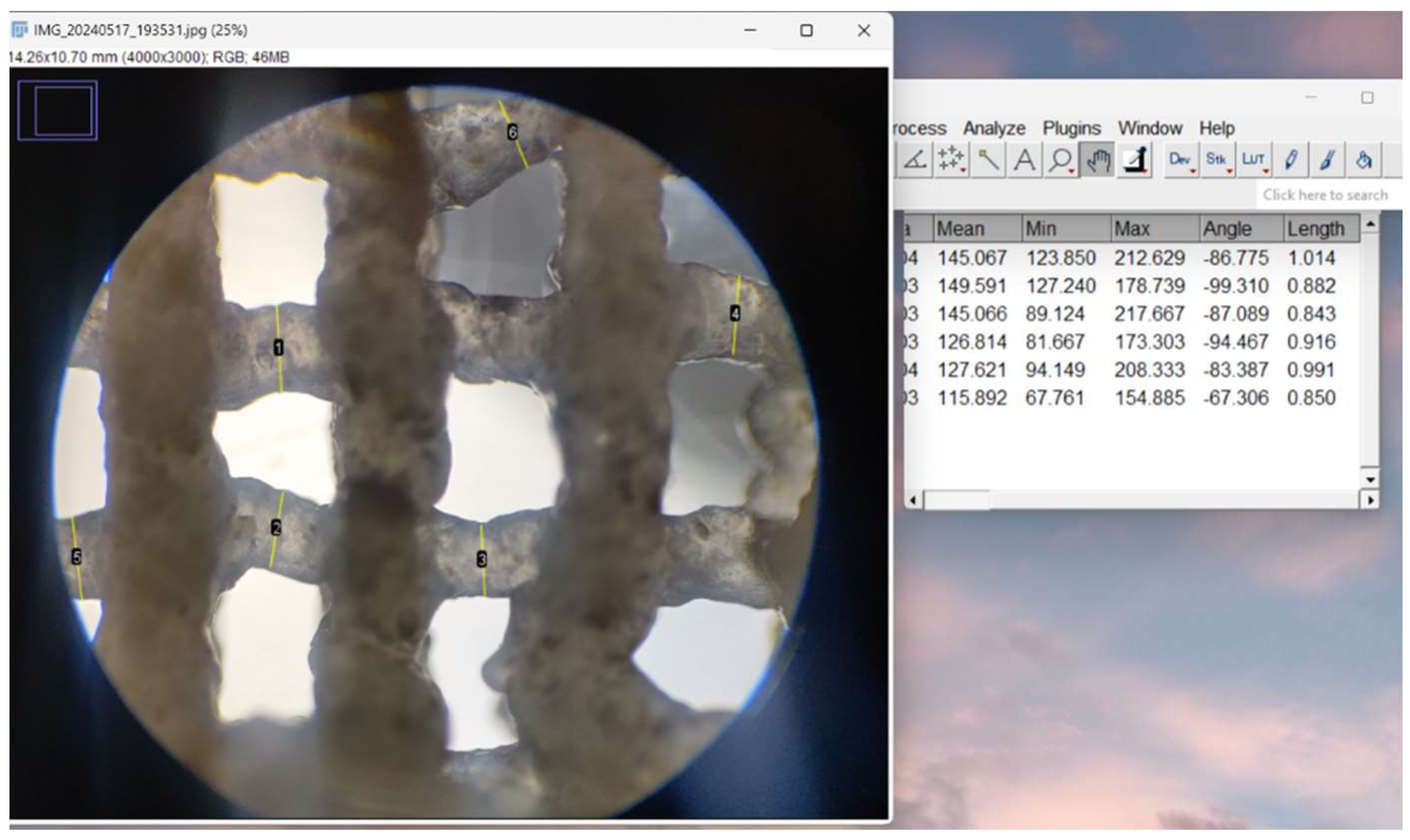
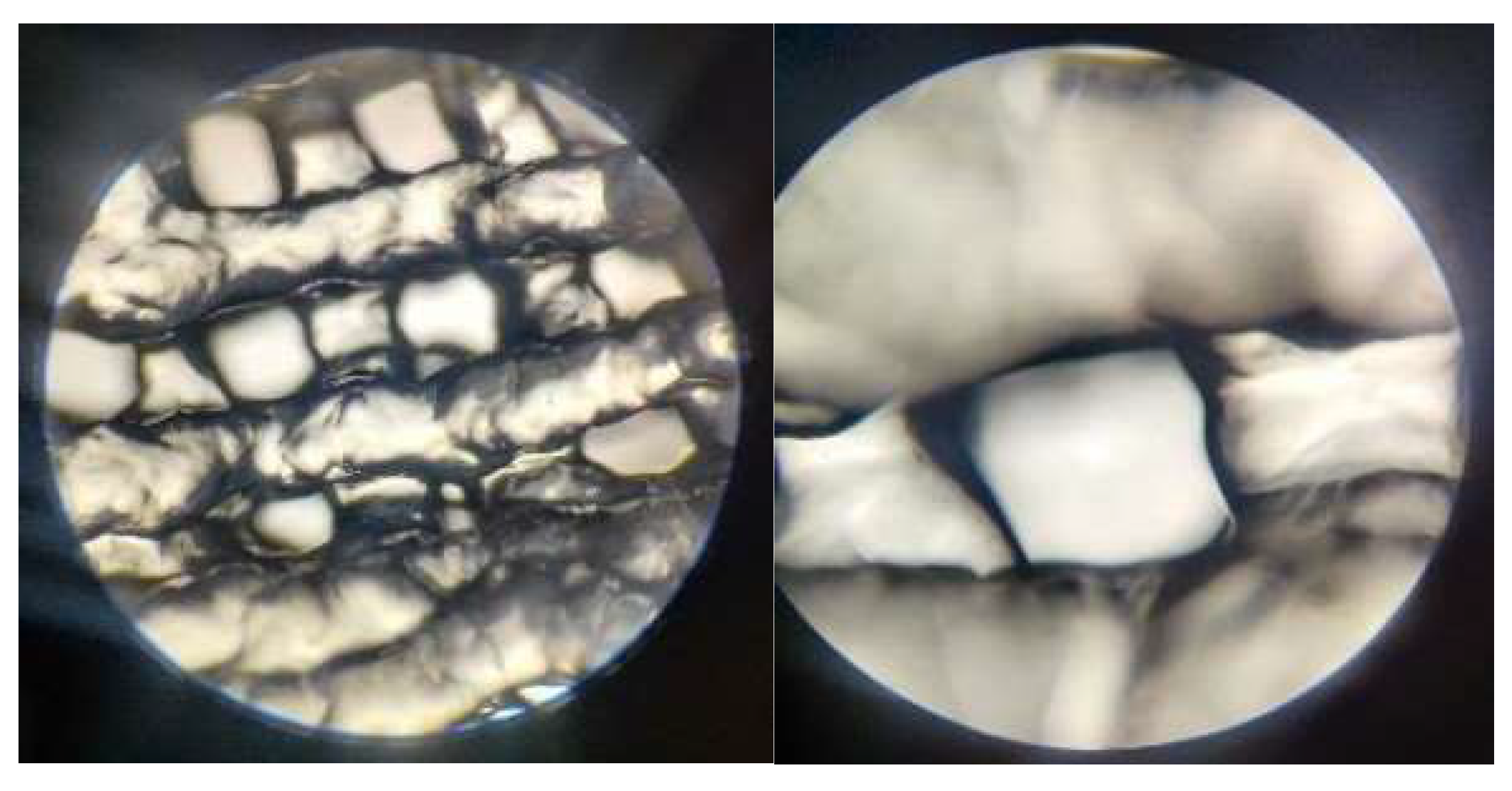
2.4.4. Optical Microscopy – Printing Accuracy
2.4.5. Swelling Degree
2.4.6. Degradation Rate
2.4.7. Porosity Evaluation
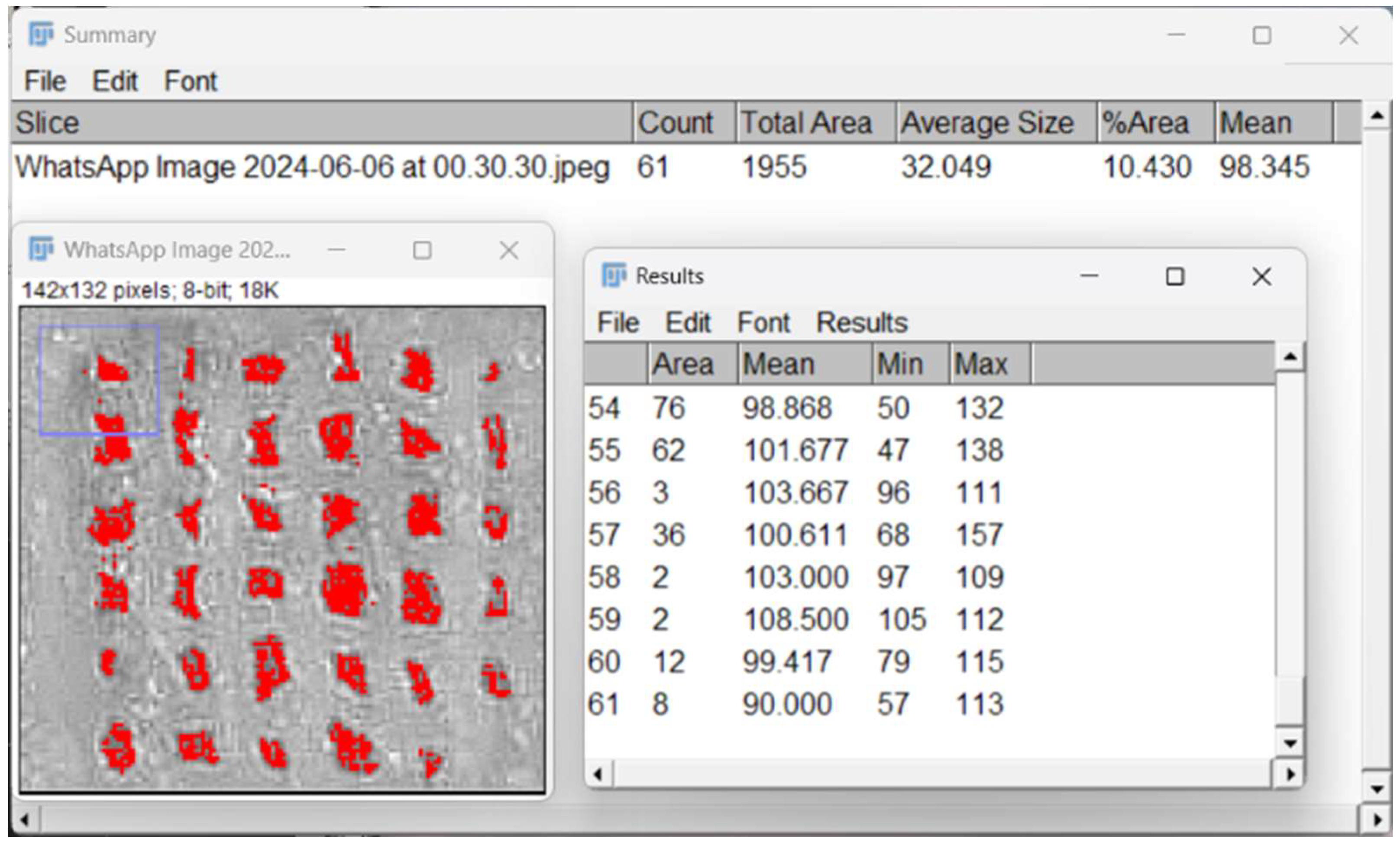
2.4.8. In Vitro Mineralization
| Order | Reagent | Quantities for 100 ml SBF 1.5X |
| #0 | Ultra-pure water | 75 mL |
| #1 | NaCl | 1.1994 g |
| #2 | NaHCO3 | 0.0525 g |
| #3 | KCl | 0.0336 g |
| #4 | K2HPO4・3H2O | 0.0342 g |
| #5 | MgCl2・6H2O | 0.0458 g |
| #6 | 1 kmol/m3 HCl | 6 cm3 |
| #7 | CaCl2 | 0.0417 g |
| #8 | Na2SO4 | 0.0107 g |
| #9 | (CH2OH)3CNH2 | 0.9086 g |
| #10 | 1 kmol/m3 HCl | Appropriate amount for adjusting pH |
2.4.7. Cell Seeding and LIVE/DEAD Assay
3. Results
3.1. 3D Printing Process
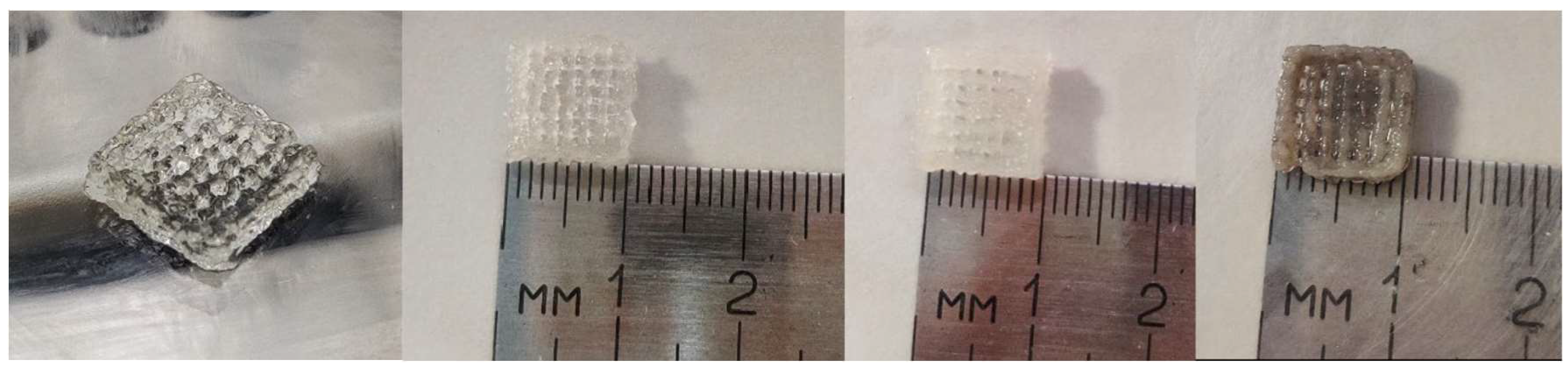
3.2. Characterization Methods
3.2.1. Rheological Evaluation
3.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy
3.2.3. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
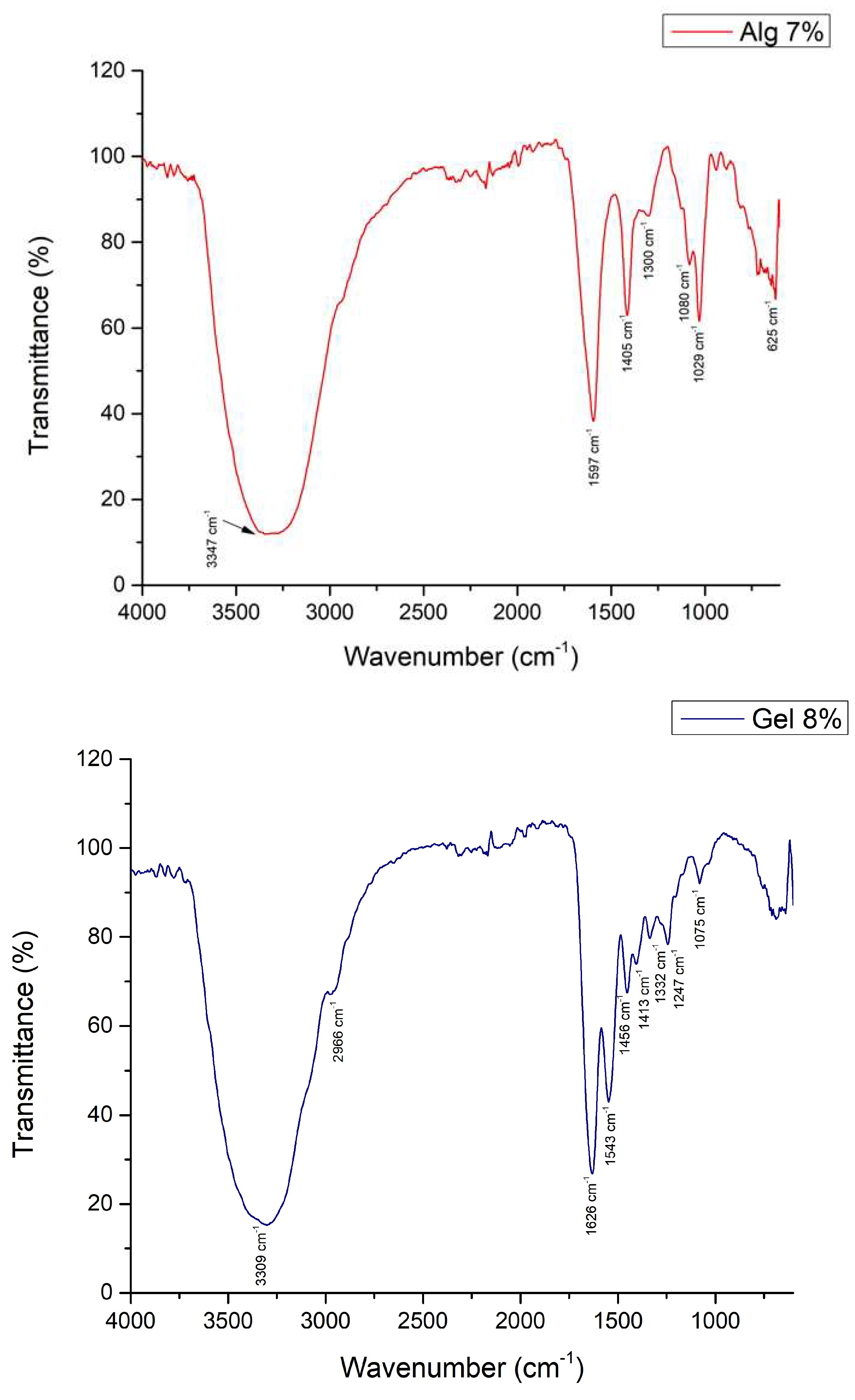
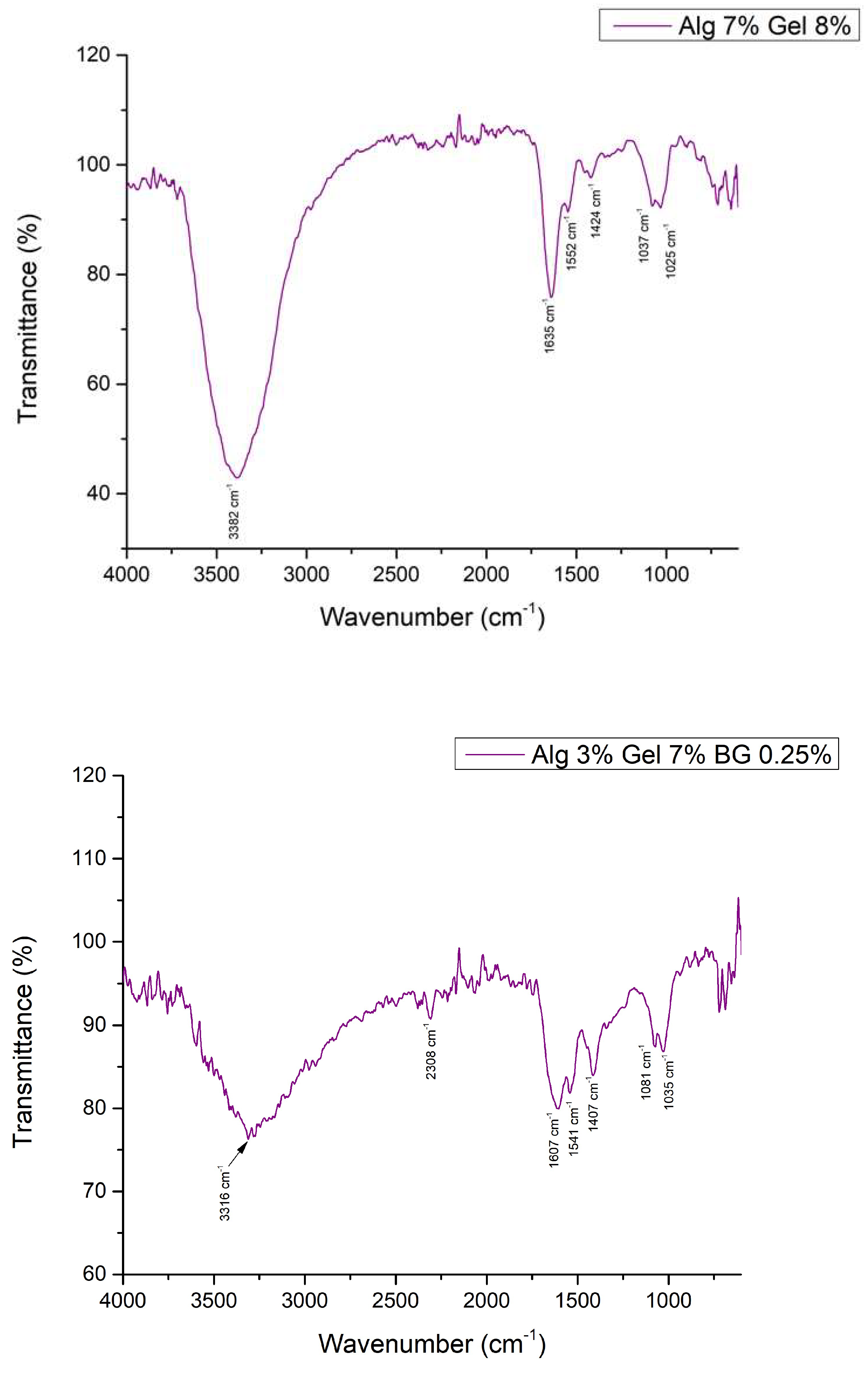
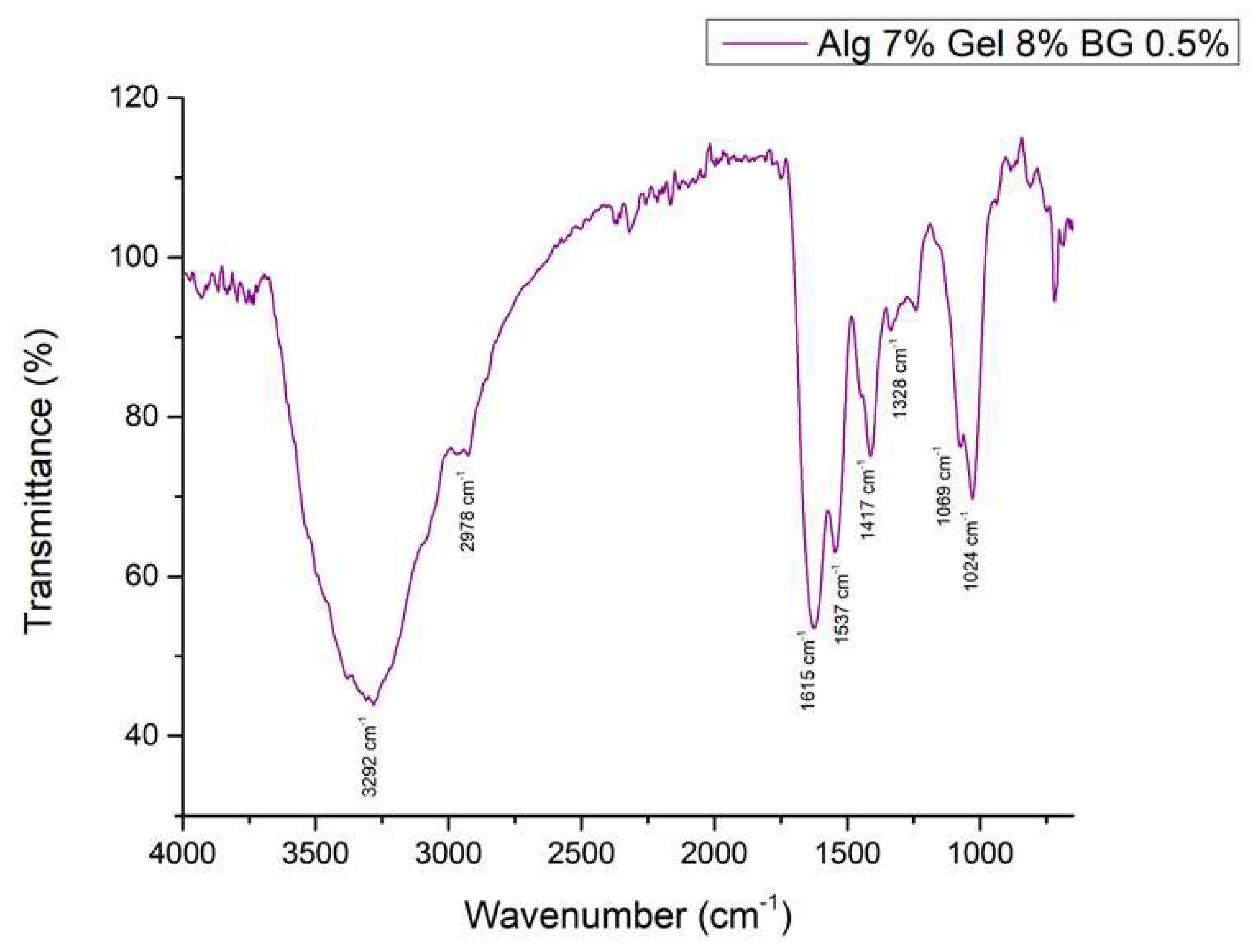
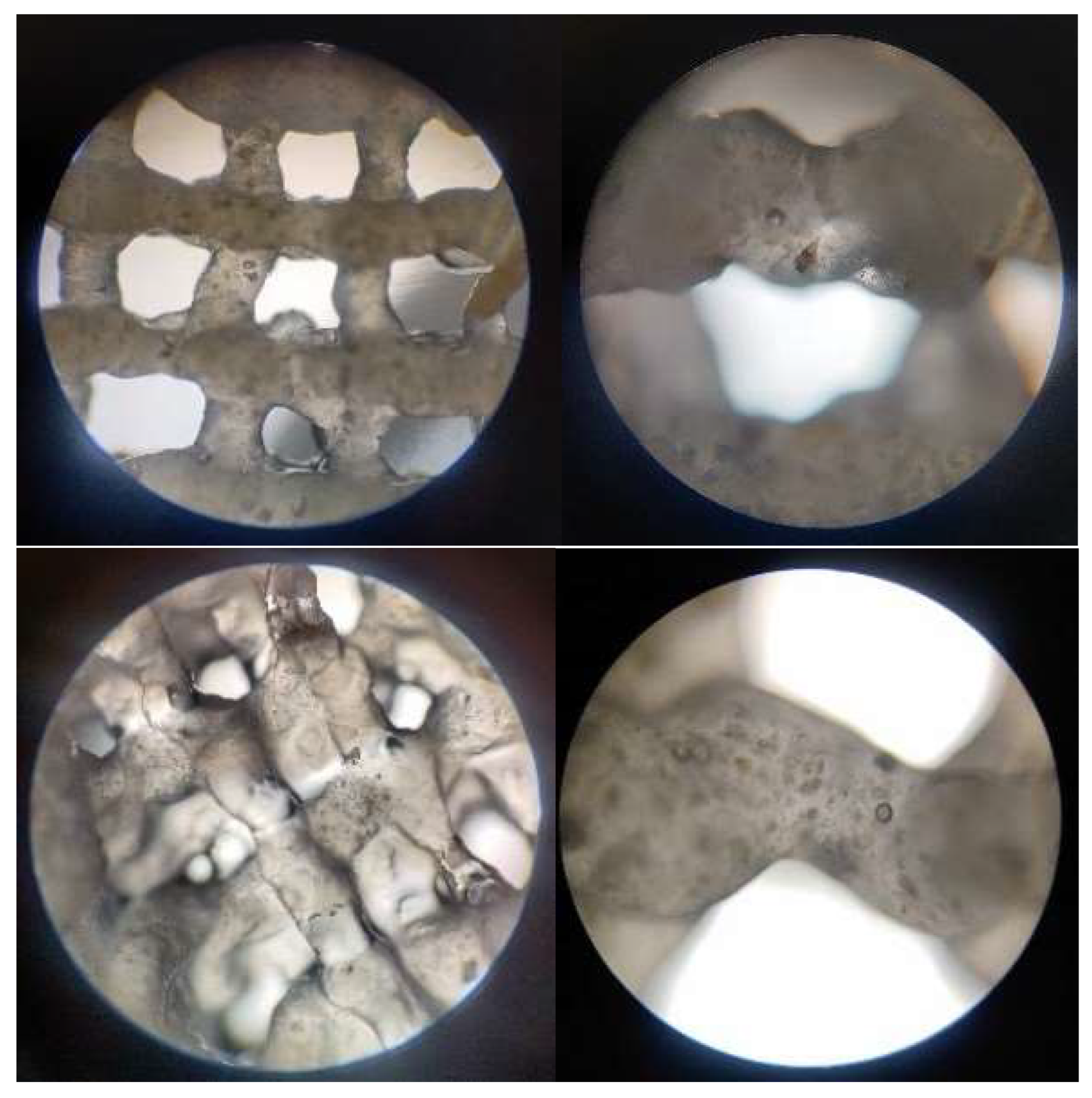
3.2.4. Optical Microscopy – Printing Accuracy
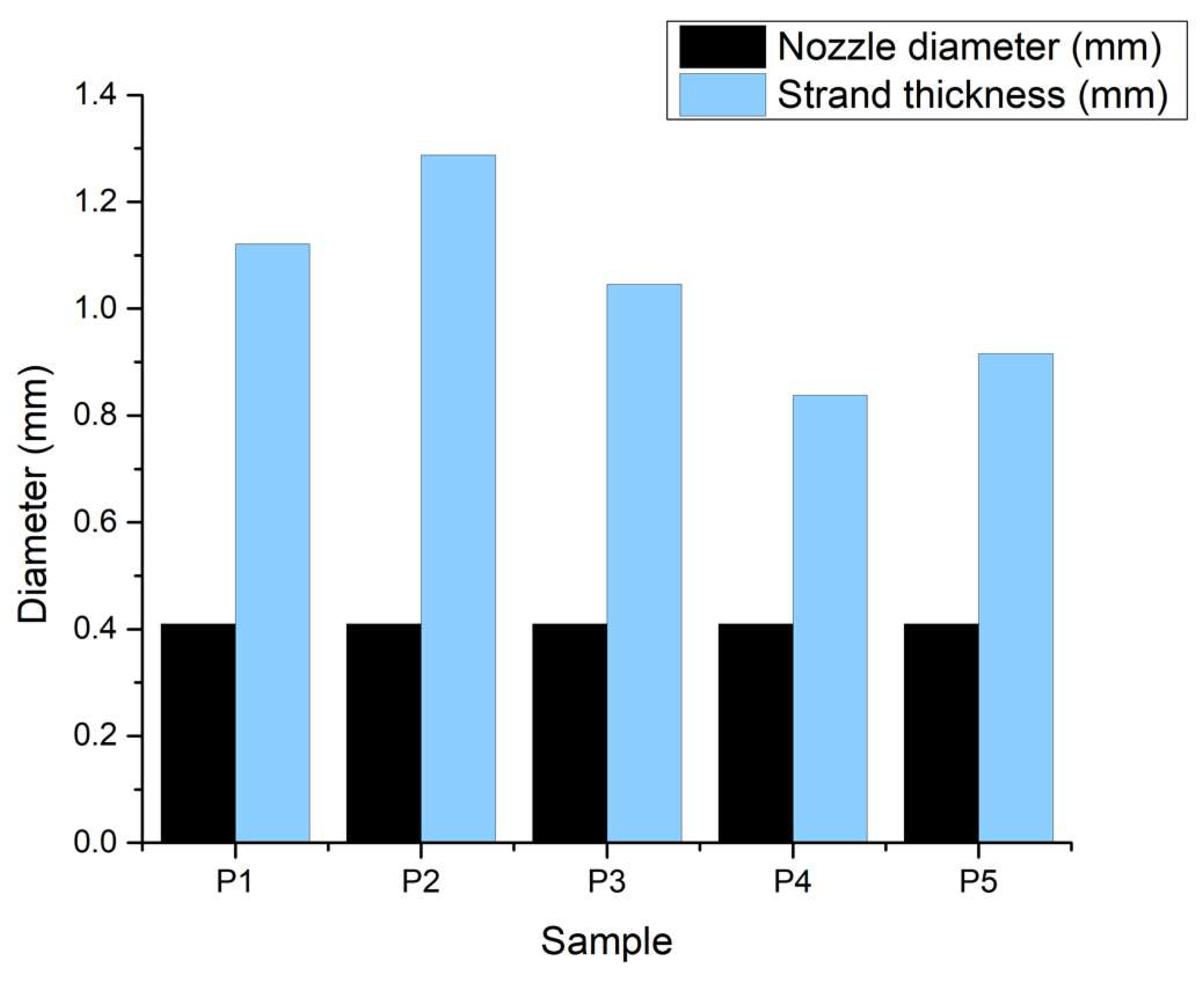
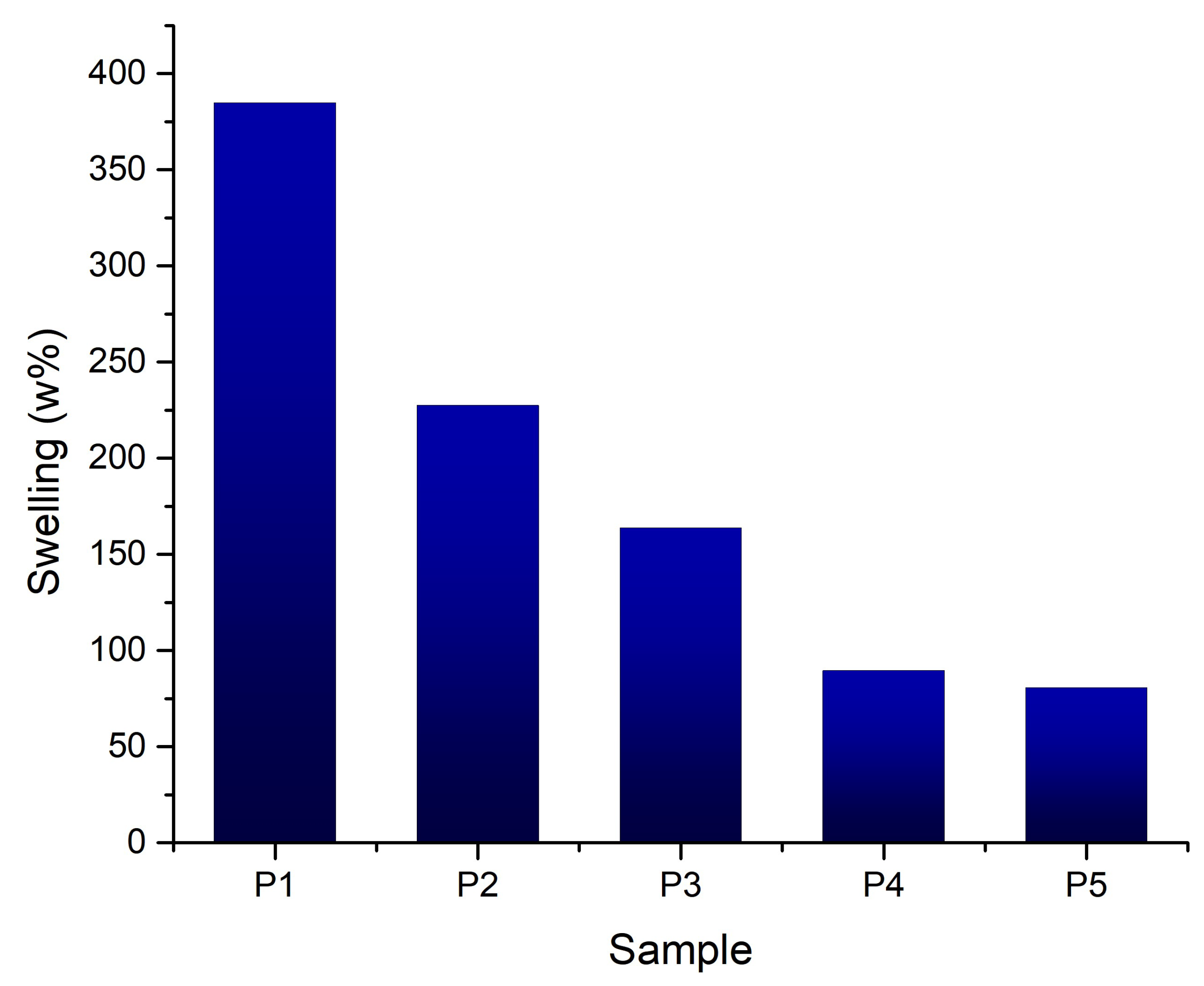
3.2.5. Swelling Degree
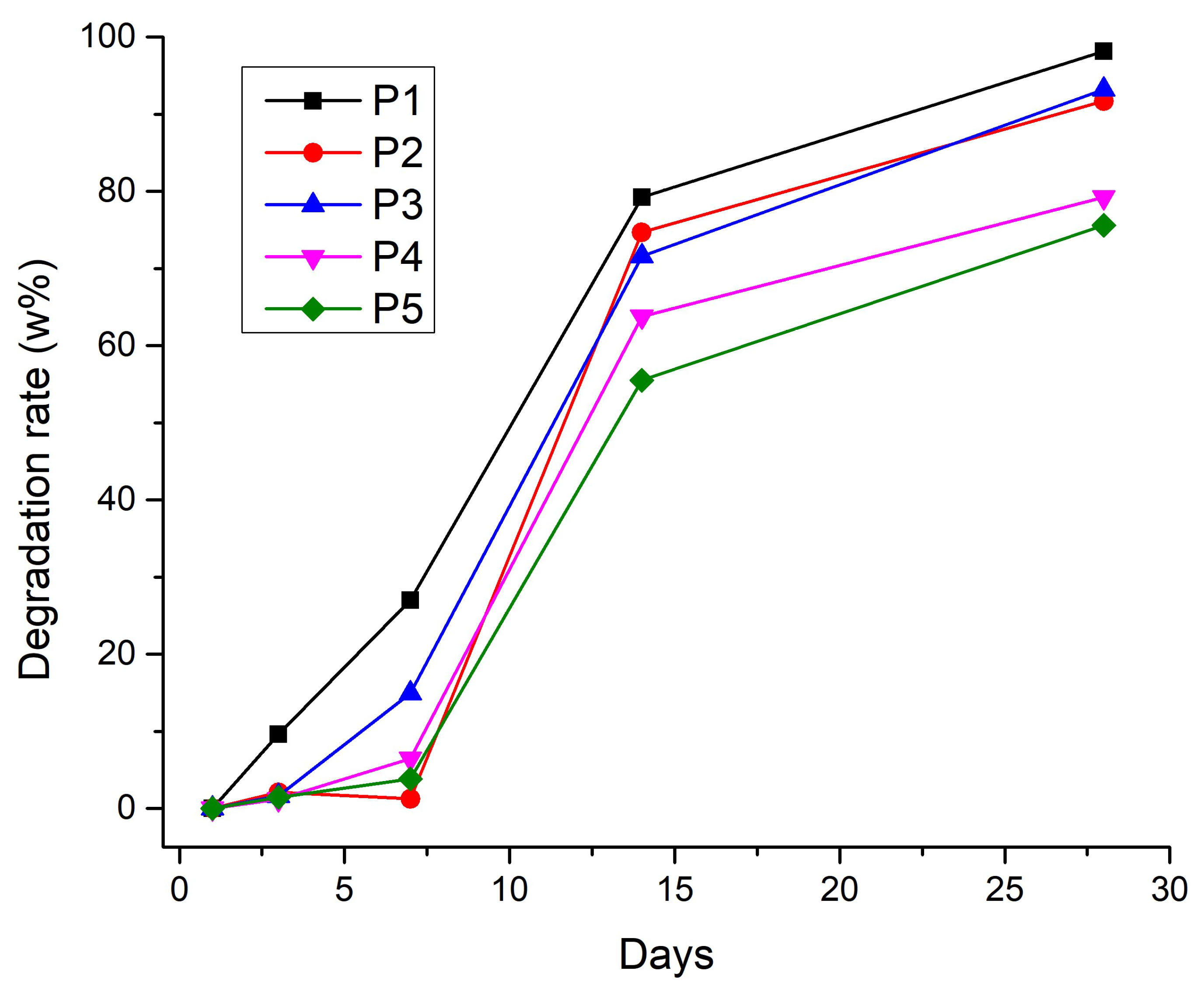
3.2.6. Degradation Rate
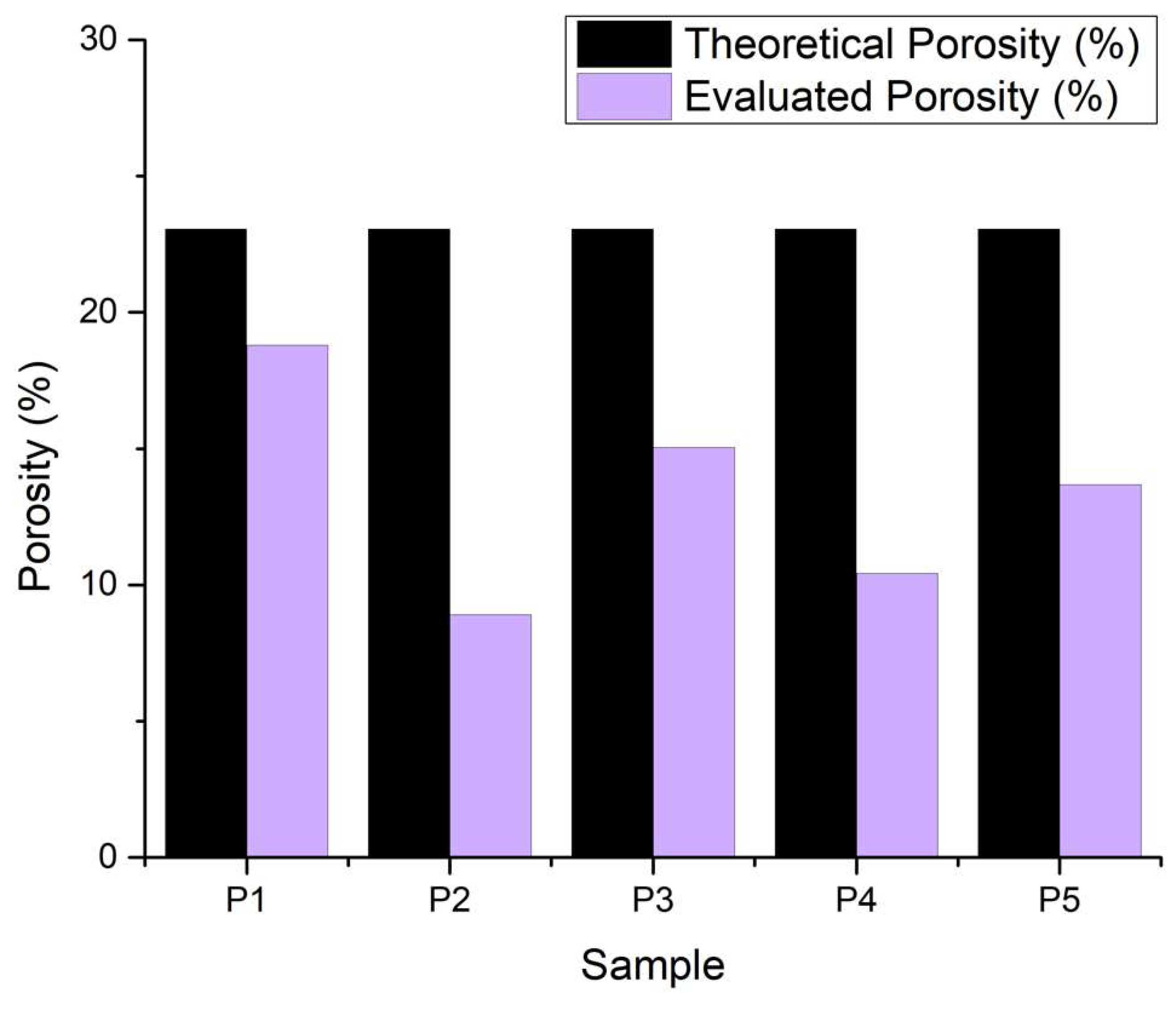
3.2.7. Porosity Evaluation
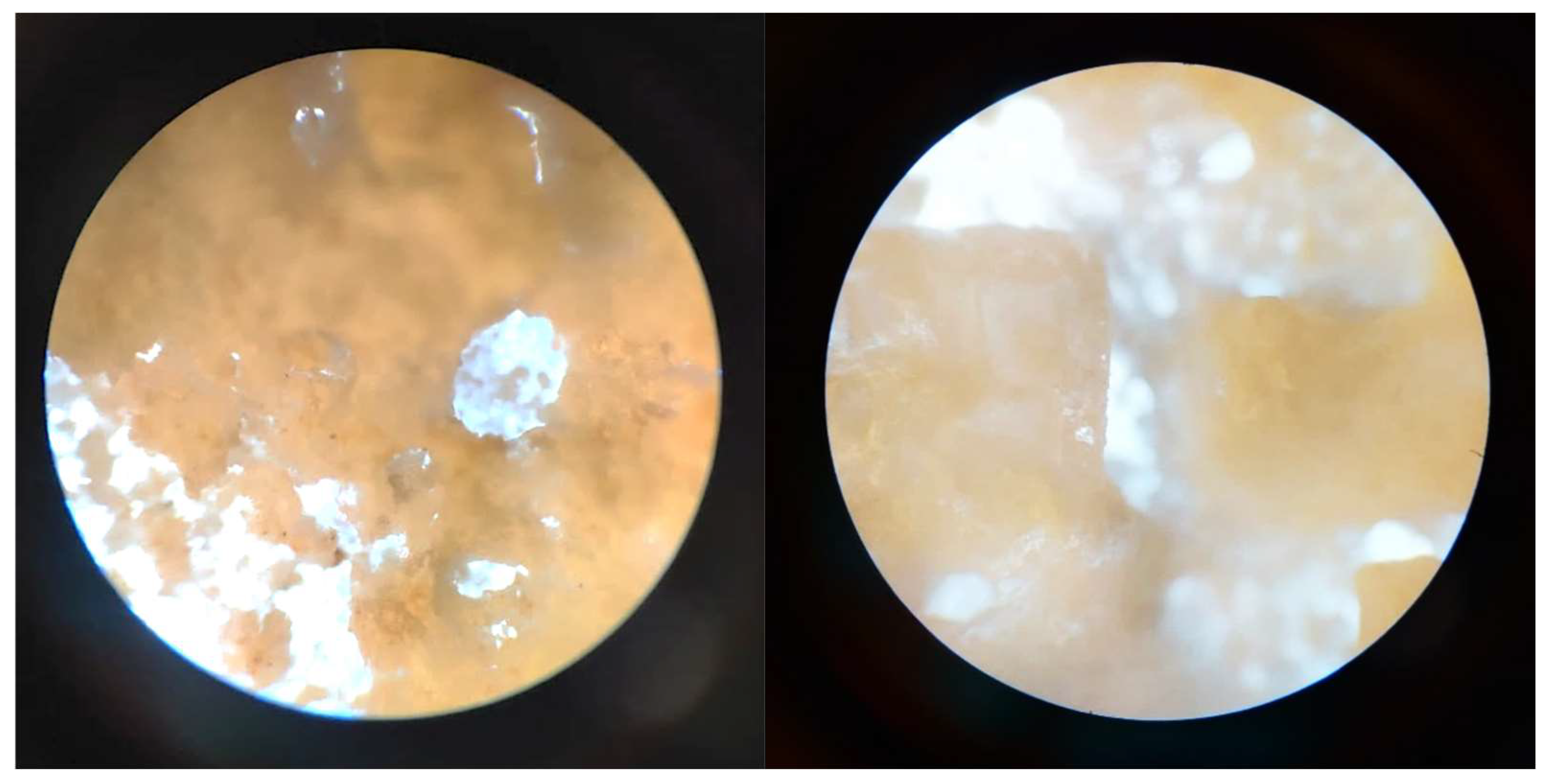
3.2.8. In Vitro Mineralization
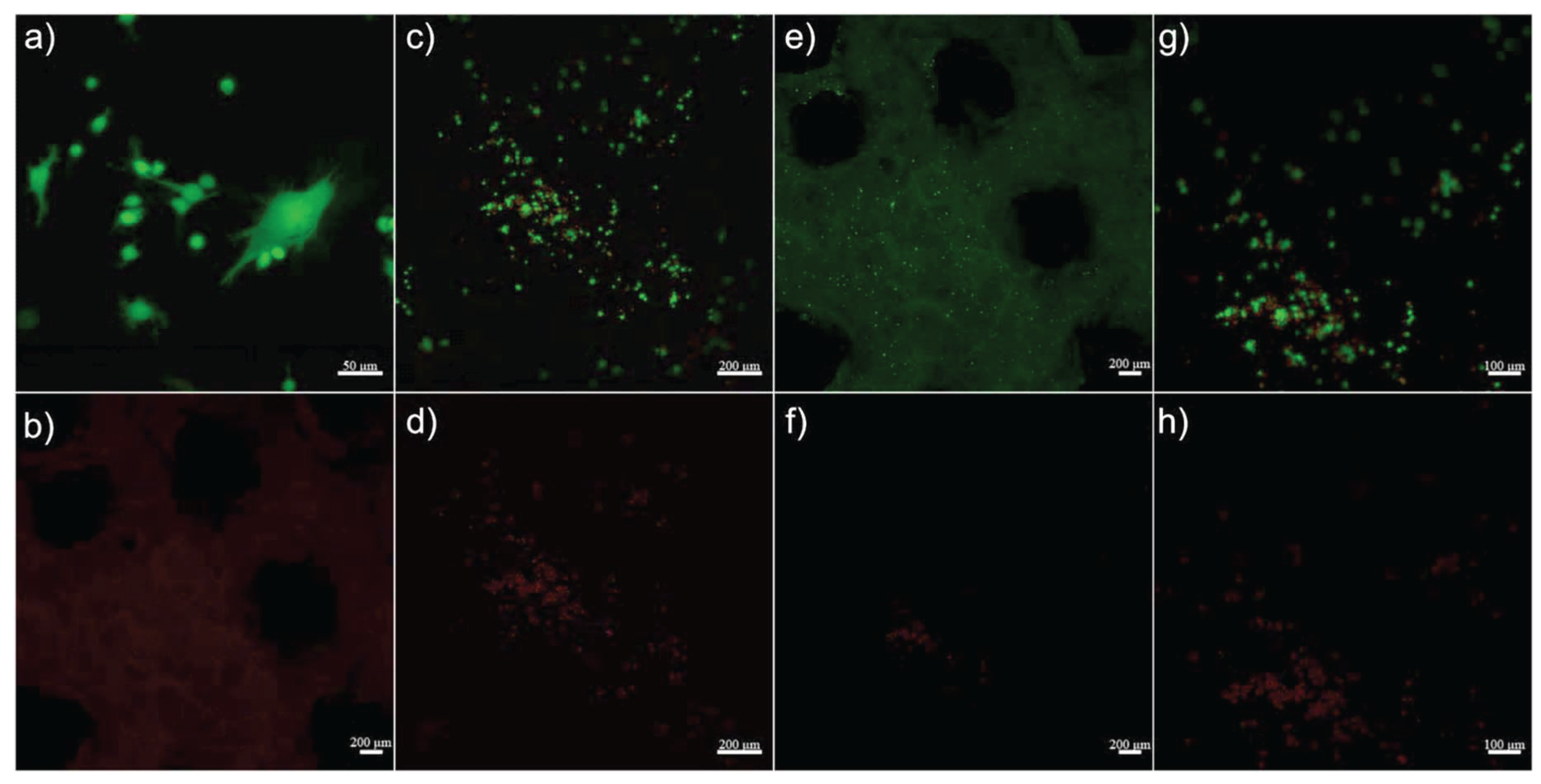
3.2.8. Cell Seeding and LIVE/DEAD Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FTIR | Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy |
| SBF | Simulated body fluid |
| EBB | Extrusion-based bioprinting |
| Alg | alginate |
| Gel | gelatin |
| BG | bioglass |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| hFOB 1.19 | Human fetal osteoblastic cells |
| TEOS | Tetraethyl orthosilicate Si(OC2H5)4 |
| TEP | Triethyl phosphate (C2H5)3PO4 |
| DC | direct current |
| ATR | attenuated total reflection |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| MTT | (3-(4,5-dimethylthazolk-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) |
References
- V. Siracusa, G. Maimone, and V. Antonelli, “State-of-Art of Standard and Innovative Materials Used in Cranioplasty,” Polymers 2021, Vol. 13, Page 1452, vol. 13, no. 9, p. 1452, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Wei, J. X. Ma, L. Xu, X. S. Gu, and X. L. Ma, “Biodegradable materials for bone defect repair,” Military Medical Research, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1–25, 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Mandrycky, Z. Wang, K. Kim, and D. H. Kim, “3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues,” Biotechnol Adv, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 422–434, Jul. 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Hasan et al., “Advances in osteobiologic materials for bone substitutes,” J Tissue Eng Regen Med, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 1448–1468, 2018. [CrossRef]
- L. Cheng et al., “3D Printing of Micro- and Nanoscale Bone Substitutes: A Review on Technical and Translational Perspectives,” International Journal of Nanomedicine, vol. 16, p. 4289, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Konka, J. Buxadera-Palomero, M. Espanol, and M. P. Ginebra, “3D printing of hierarchical porous biomimetic hydroxyapatite scaffolds: Adding concavities to the convex filaments,” Acta Biomater, vol. 134, pp. 744–759, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. Matai, G. Kaur, A. Seyedsalehi, A. McClinton, and C. T. Laurencin, “Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering,” Biomaterials, vol. 226, p. 119536, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Farshidfar, S. Iravani, and R. S. Varma, “Alginate-Based Biomaterials in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine,” Marine Drugs 2023, Vol. 21, Page 189, vol. 21, no. 3, p. 189, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. U. Arif, M. Y. Khalid, A. Zolfagharian, and M. Bodaghi, “4D bioprinting of smart polymers for biomedical applications: recent progress, challenges, and future perspectives,” React Funct Polym, vol. 179, p. 105374, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Ma, W. Wu, Y. Wei, L. Ren, S. Lin, and J. Wu, “Biomimetic gelatin/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/nano-hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering,” Mater Des, vol. 207, p. 109865, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Mccoy, C. Jungreuthmayer, and F. J. O’Brien, “Influence of flow rate and scaffold pore size on cell behavior during mechanical stimulation in a flow perfusion bioreactor,” Biotechnology and Bioengineering, vol. 109, no. 6, pp. 1583–1594, Jun. 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Vijayavenkataraman, W. C. Yan, W. F. Lu, C. H. Wang, and J. Y. H. Fuh, “3D bioprinting of tissues and organs for regenerative medicine,” Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, vol. 132, pp. 296–332, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. Reina-Romo, I. Papantoniou, V. Bloemen, and L. Geris, Computational design of tissue engineering scaffolds. Elsevier Ltd, 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. Fairag, D. H. Rosenzweig, J. L. Ramirez-Garcialuna, M. H. Weber, and L. Haglund, “Three-Dimensional Printed Polylactic Acid Scaffolds Promote Bone-like Matrix Deposition in Vitro,” ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, vol. 11, no. 17, pp. 15306–15315, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- G. G. dos Santos et al., “4th Generation Biomaterials Based on PVDF-Hydroxyapatite Composites Produced by Electrospinning: Processing and Characterization,” Polymers 2022, Vol. 14, Page 4190, vol. 14, no. 19, p. 4190, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. ; Liu et al., “Recent Advances in Decellularized Matrix-Derived Materials for Bioink and 3D Bioprinting,” Gels 2023, Vol. 9, Page 195, vol. 9, no. 3, p. 195, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. E. Brennan Fournet, F. A. Azaman, S. Gunbay, Y. Y. Chen, and D. M. Devine, “Orthopaedic 3D Printing in Orthopaedic Medicine,” Polymer-Based Additive Manufacturing, pp. 121–142, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Y. Hann et al., “Dual 3D printing for vascularized bone tissue regeneration,” Acta Biomater, vol. 123, pp. 263–274, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Bhargav, V. Sanjairaj, V. Rosa, L. W. Feng, and J. Fuh YH, “Applications of additive manufacturing in dentistry: A review,” Jul. 01, 2018, John Wiley and Sons Inc. [CrossRef]
- A. L. Jardini, M. A. Larosa, A. Kaasi, and P. Kharmandayan, “Additive Manufacturing in Medicine,” in Encyclopedia of Smart Materials, Elsevier, 2021, pp. 300–320. [CrossRef]
- Ž. P. Kačarević et al., “An Introduction to 3D Bioprinting: Possibilities, Challenges and Future Aspects,” Materials 2018, Vol. 11, Page 2199, vol. 11, no. 11, p. 2199, Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- W. L. Ng, A. Chan, Y. S. Ong, and C. K. Chua, “Deep learning for fabrication and maturation of 3D bioprinted tissues and organs,” Jul. 02, 2020, Taylor and Francis Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Z. Gu, J. Fu, H. Lin, and Y. He, “Development of 3D bioprinting: From printing methods to biomedical applications,” Sep. 01, 2020, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. [CrossRef]
- I. T. Ozbolat, W. Peng, and V. Ozbolat, “Application areas of 3D bioprinting,” Drug Discovery Today, vol. 21, no. 8, pp. 1257–1271, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Dikyol, M. Altunbek, P. Bartolo, and B. Koc, “Multimaterial bioprinting approaches and their implementations for vascular and vascularized tissues,” Bioprinting, vol. 24, no. May, p. e00159, 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. C. Simcock, S. C. Shelmerdine, D. Langan, G. Anna, N. J. Sebire, and O. J. Arthurs, “Micro-CT yields high image quality in human fetal post-mortem imaging despite maceration,” BMC Medical Imaging, vol. 21, no. 1, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Fahimipour et al., “3D printed TCP-based scaffold incorporating VEGF-loaded PLGA microspheres for craniofacial tissue engineering,” Dental Materials, vol. 33, no. 11, pp. 1205–1216, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- I. Gorroñogoitia, U. Urtaza, A. Zubiarrain-Laserna, A. Alonso-Varona, and A. M. Zaldua, “A Study of the Printability of Alginate-Based Bioinks by 3D Bioprinting for Articular Cartilage Tissue Engineering,” Polymers, vol. 14, no. 2, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. S. Gungor-Ozkerim, I. Inci, Y. S. Zhang, A. Khademhosseini, and M. R. Dokmeci, “Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: an overview,” Biomater Sci, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 915–946, May 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Schwab, R. Levato, M. D’Este, S. Piluso, D. Eglin, and J. Malda, “Printability and Shape Fidelity of Bioinks in 3D Bioprinting,” Chem Rev, vol. 120, no. 19, pp. 11028–11055, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. C. Hernández-González, L. Téllez-Jurado, and L. M. Rodríguez-Lorenzo, “Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: A review,” Feb. 01, 2020, Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- A. Tariq, S. A. Bhawani, K. M. Alotaibi, and A. Moheman, “Smart biopolymers and their applications,” Smart Polymer Nanocomposites: Biomedical and Environmental Applications, pp. 145–167, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. N. Smith et al., “The microscopic distribution of hydrophilic polymers in interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs) of medical grade silicone,” Polymer, vol. 224, p. 123671, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Suarato, R. Bertorelli, and A. Athanassiou, “Borrowing from nature: Biopolymers and biocomposites as smart wound care materials,” Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, vol. 6, no. OCT, p. 137, Oct. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, N. Joshi, A. Jayakrishnan, and R. Banerjee, “Self-crosslinked oxidized alginate/gelatin hydrogel as injectable, adhesive biomimetic scaffolds for cartilage regeneration,” Acta Biomaterialia, vol. 10, no. 8, pp. 3650–3663, 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. Hajikhani, F. Scocozza, M. Conti, M. Marino, F. Auricchio, and P. Wriggers, “Experimental characterization and computational modeling of hydrogel cross-linking for bioprinting applications,” International Journal of Artificial Organs, vol. 42, no. 10, pp. 548–557, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Chen, L. Liu, J. Pan, J. Mei, C. Li, and Y. Zheng, “Biomimetic composite scaffold of hydroxyapatite/gelatin-chitosan core-shell nanofibers for bone tissue engineering,” Materials Science and Engineering: C, vol. 97, pp. 325–335, Apr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Shuaib, D. Motan, P. Bhattacharya, A. McNabb, T. M. Skerry, and D. Lacroix, “Heterogeneity in The Mechanical Properties of Integrins Determines Mechanotransduction Dynamics in Bone Osteoblasts,” Scientific Reports 2019 9:1, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 1–14, Sep. 2019. [CrossRef]
- G. Kaur, O. P. Pandey, K. Singh, D. Homa, B. Scott, and G. Pickrell, “A review of bioactive glasses: Their structure, properties, fabrication and apatite formation,” J Biomed Mater Res A, vol. 102, no. 1, pp. 254–274, 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. N. Trandaș et al., “Properties of europium and silver doped bioglass thin films obtained by two deposition methods: Biointerfaces for bioinert implants,” Mater Chem Phys, vol. 309, p. 128396, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Qian, L. Zhang, X. Liu, S. Wu, S. Peng, and C. Shuai, “Silver-doped bioglass modified scaffolds: A sustained antibacterial efficacy,” Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications, vol. 129, Oct. 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Unal, C. Tasar, and B. Ercan, “Fabrication and in vitro characterization of antibacterial magneto-luminescent core-shell bioactive glass nanoparticles,” Ceram Int, vol. 49, no. 12, pp. 20118–20126, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Wu et al., “The biological functions of europium-containing biomaterials: A systematic review,” Mater Today Bio, vol. 19, p. 100595, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Flores-Jacobo, · Ena, A. Aguilar-Reyes, · Carlos, and A. León-Patiño, “Effect of Dopants on the Physical, Mechanical, and Biological Properties of Porous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering,” Biomedical Materials & Devices 2022, vol. 1, pp. 1–22, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Kokubo and H. Takadama, “How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity?,” Biomaterials, vol. 27, no. 15, pp. 2907–2915, 2006. [CrossRef]
- Q. Facts and E. Em, “LIVE/DEAD ® Viability/Cytotoxicity Kit *for mammalian cells*,” 2005.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





