Submitted:
06 May 2025
Posted:
07 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Acquisition
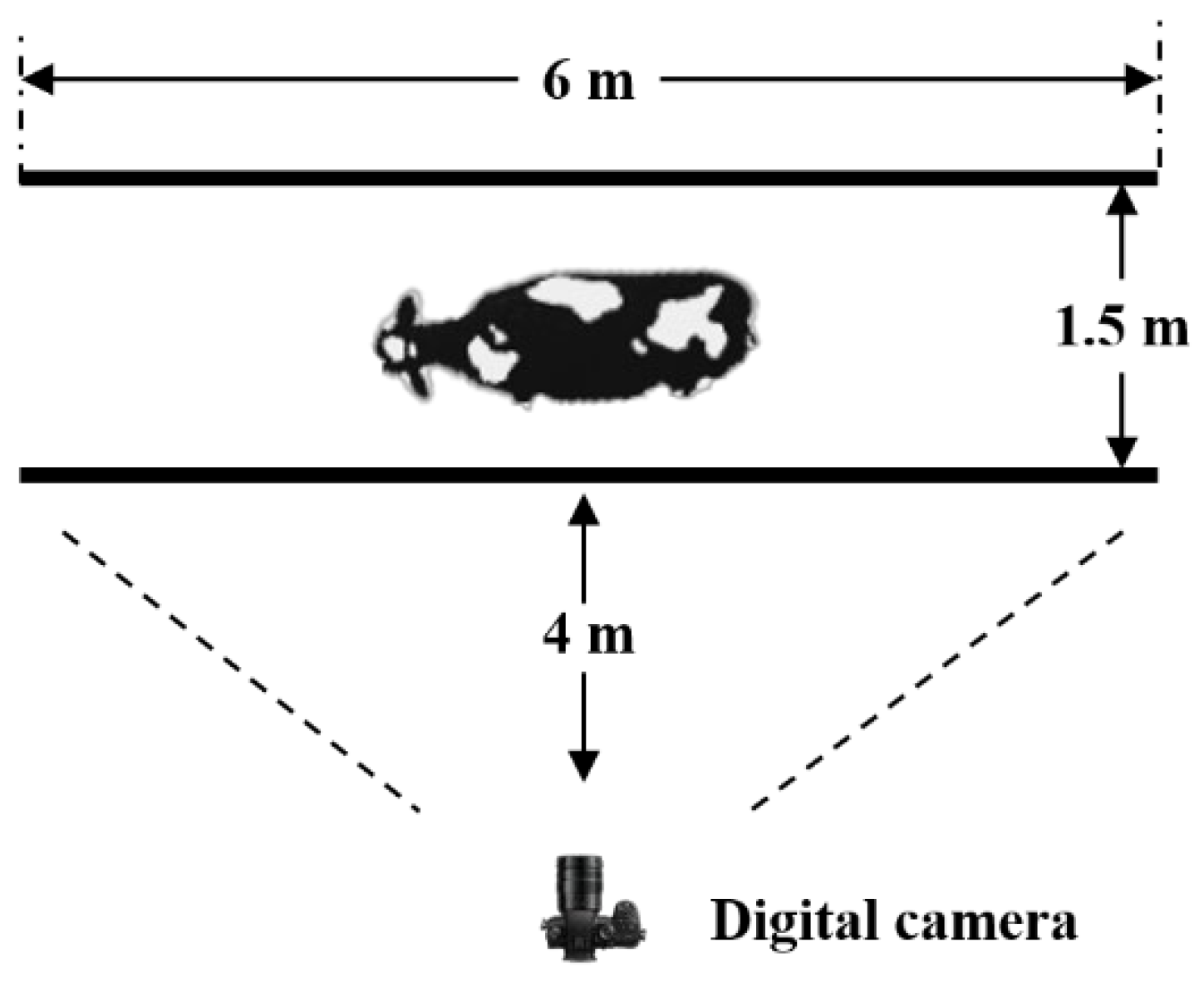
2.2. Methods
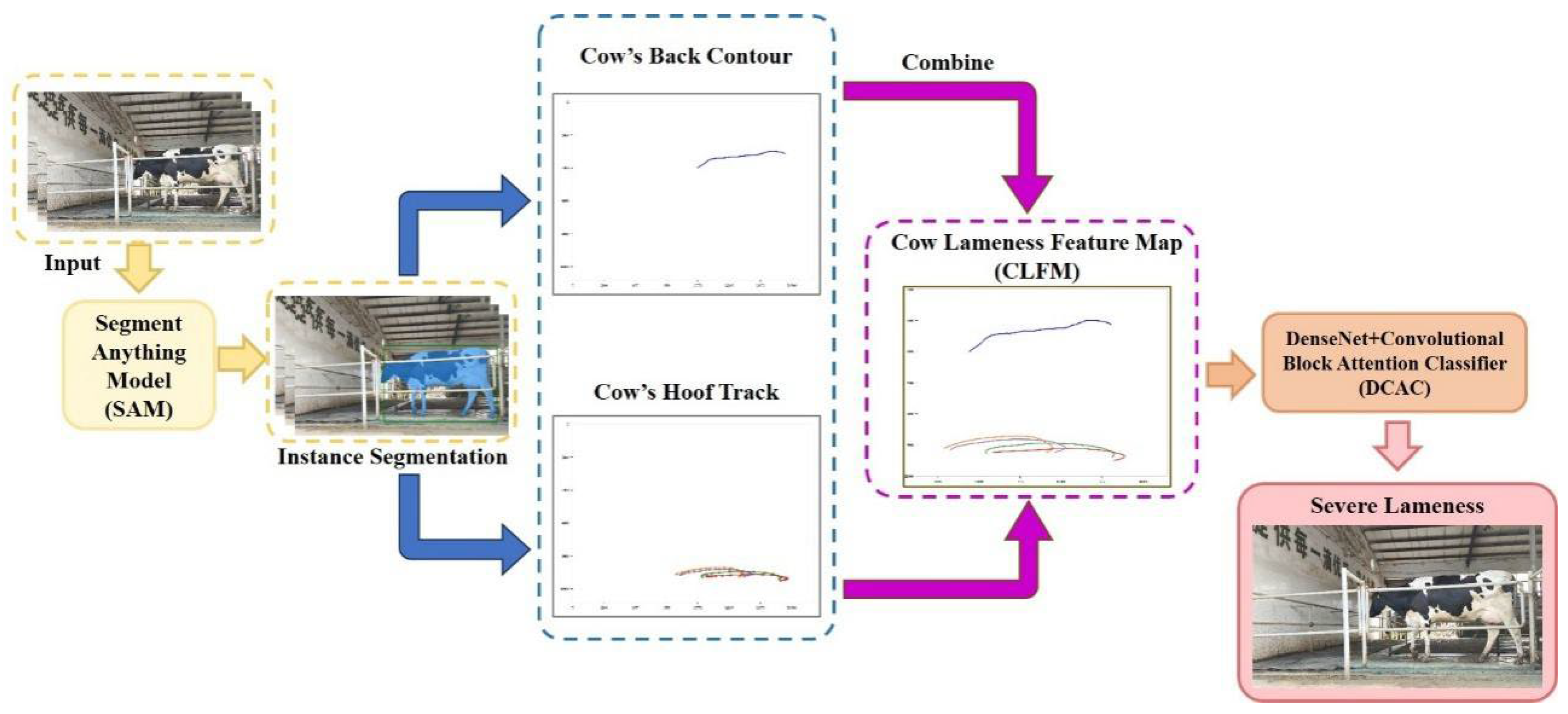
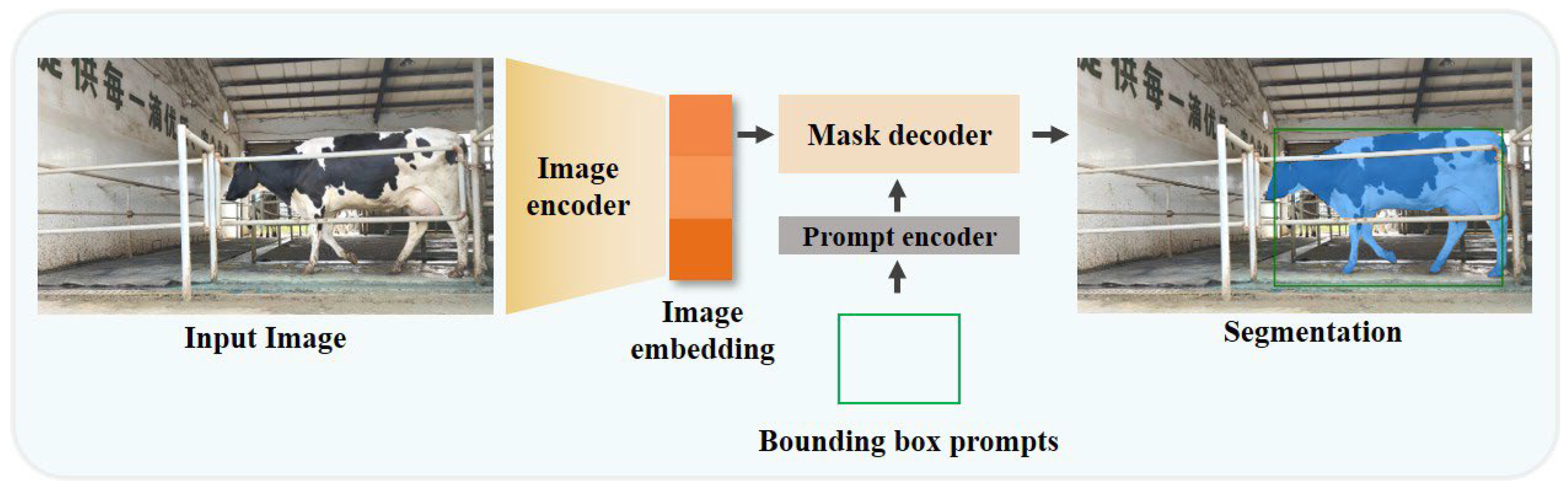
2.2.1. Model Architecture
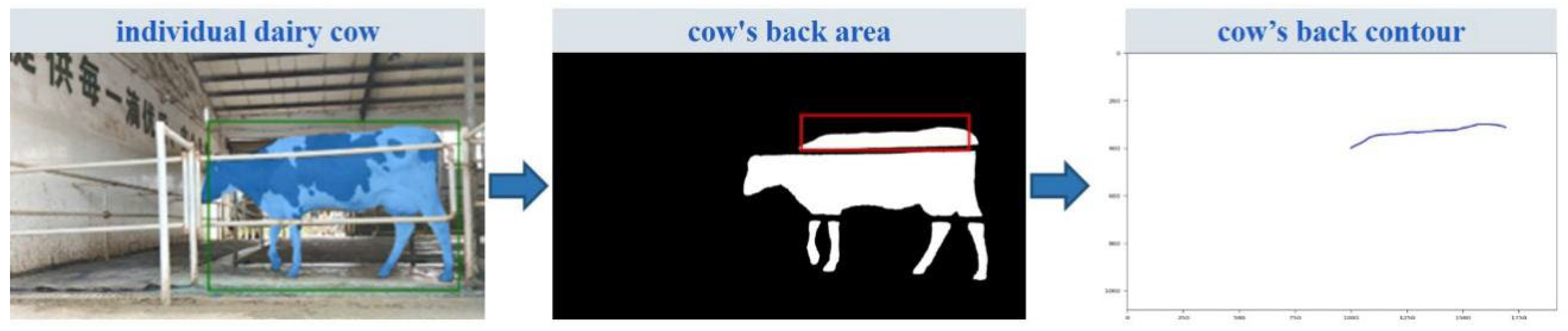
2.2.2. CLFM Model
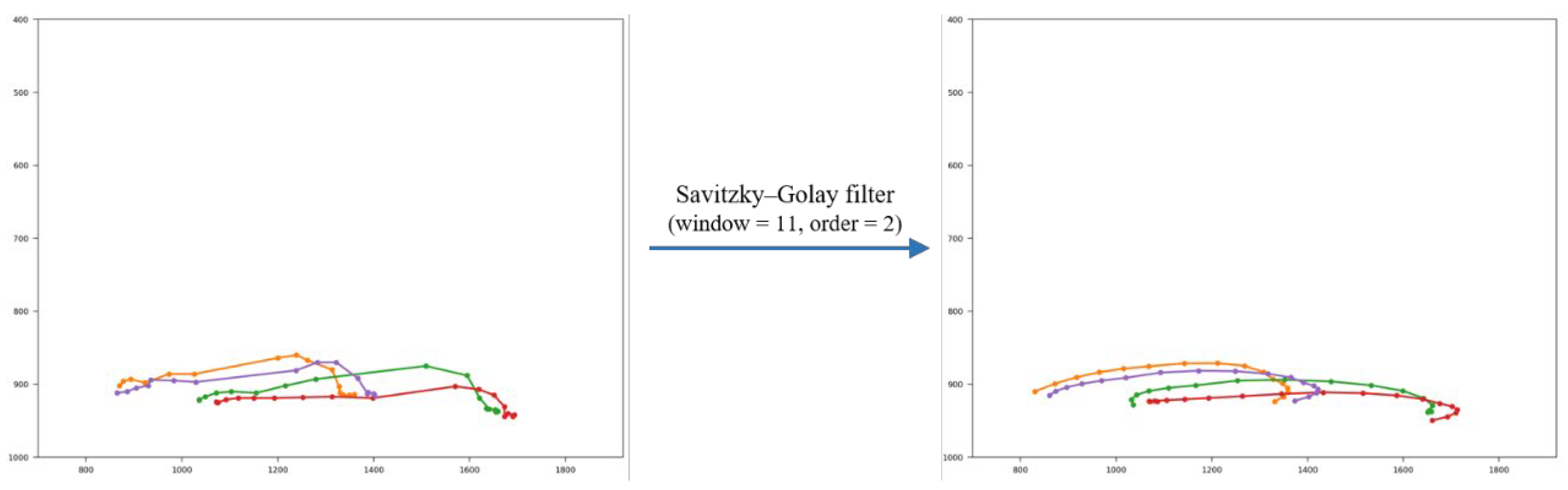


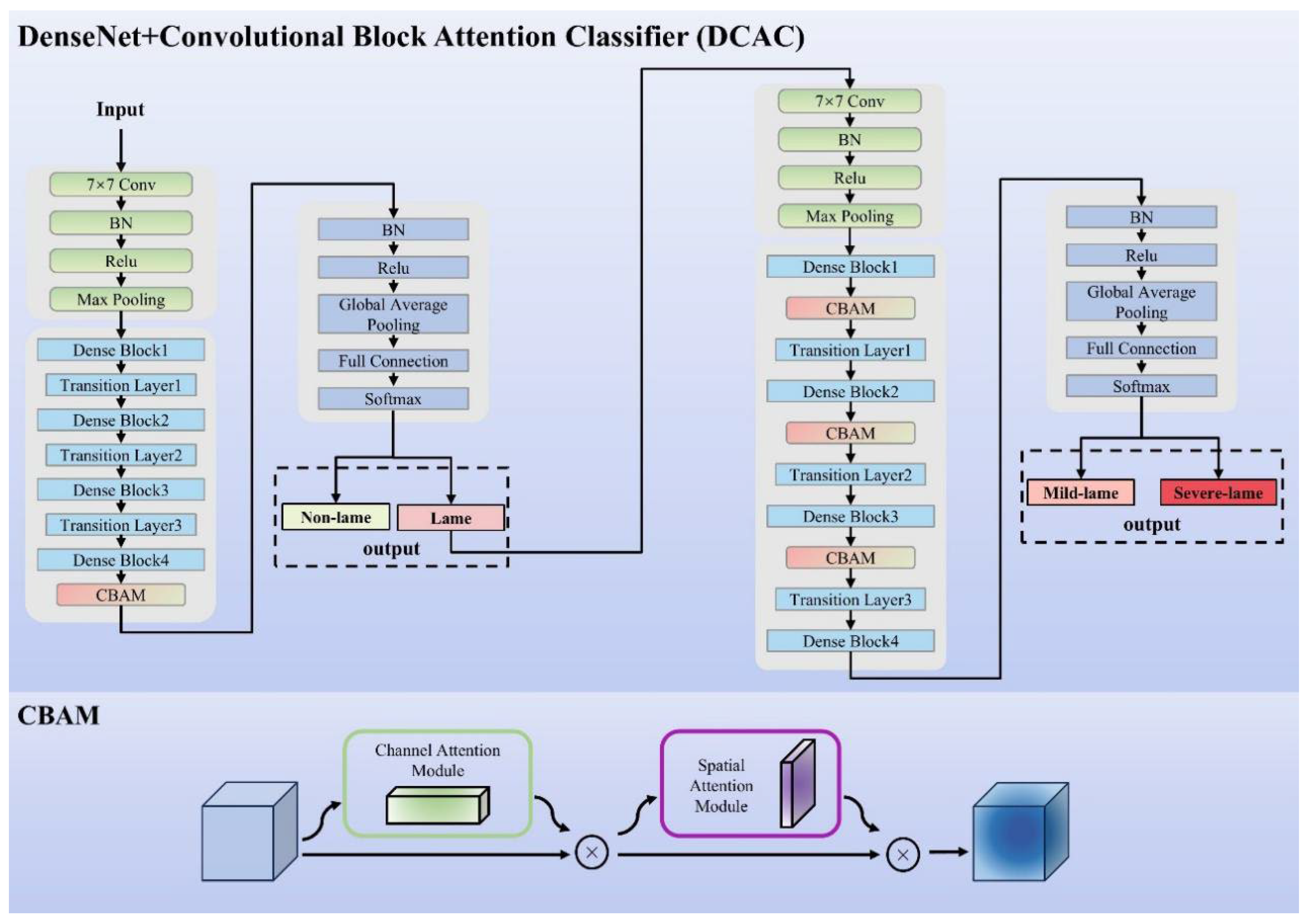
2.2.3. DCAC Model
3. Results
3.1. Extraction of Hoof
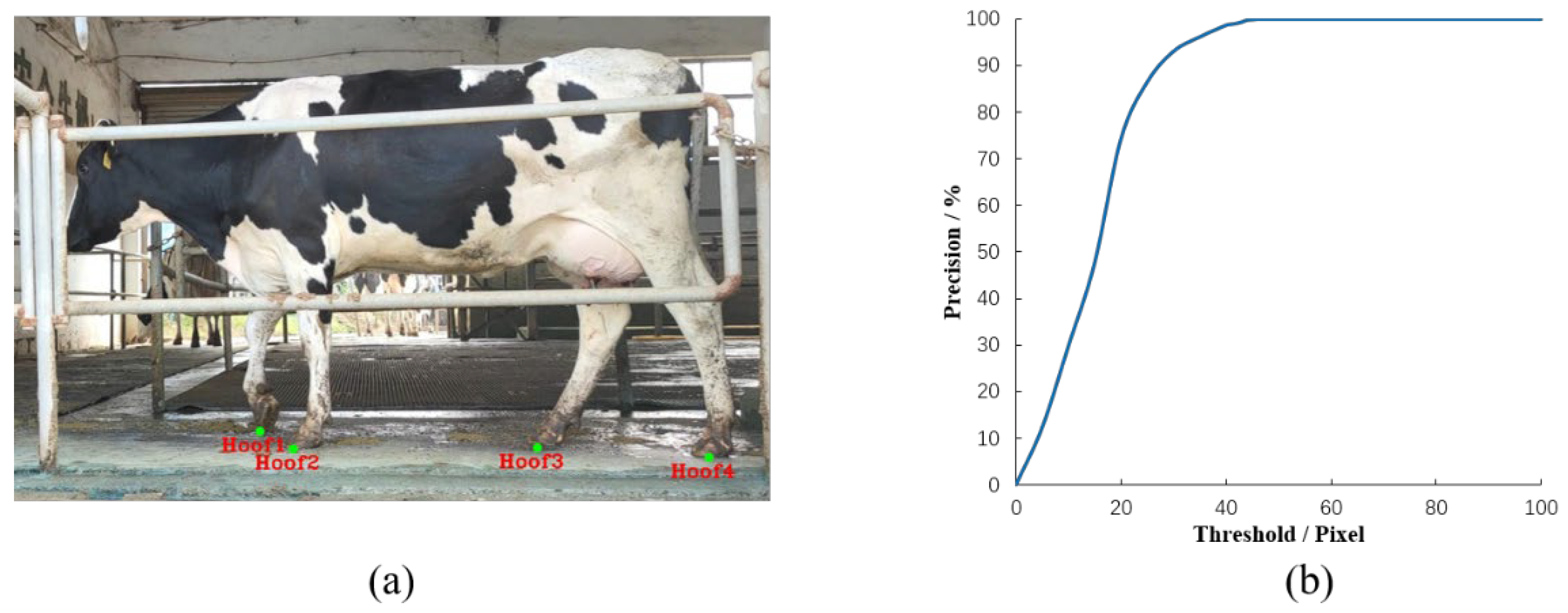
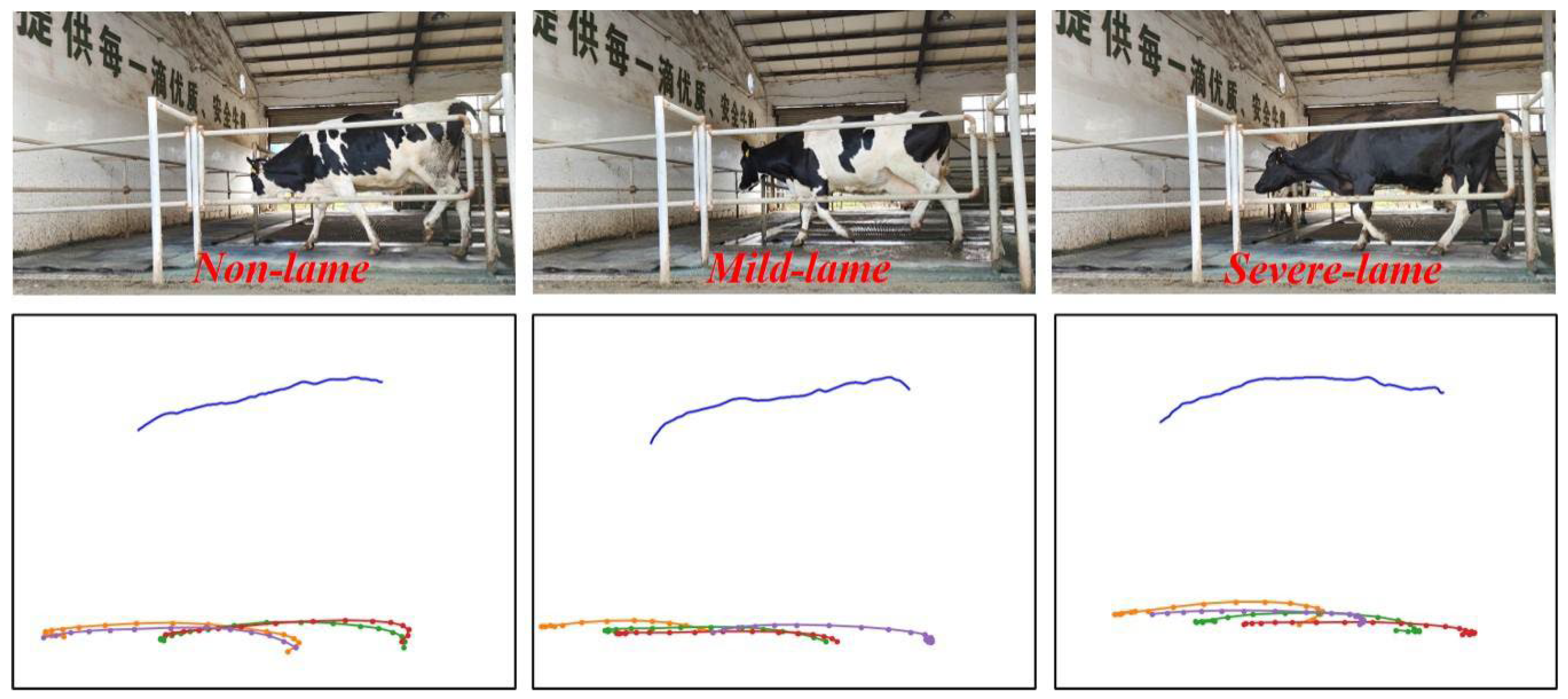
3.2. Detection Results
4. Discussion
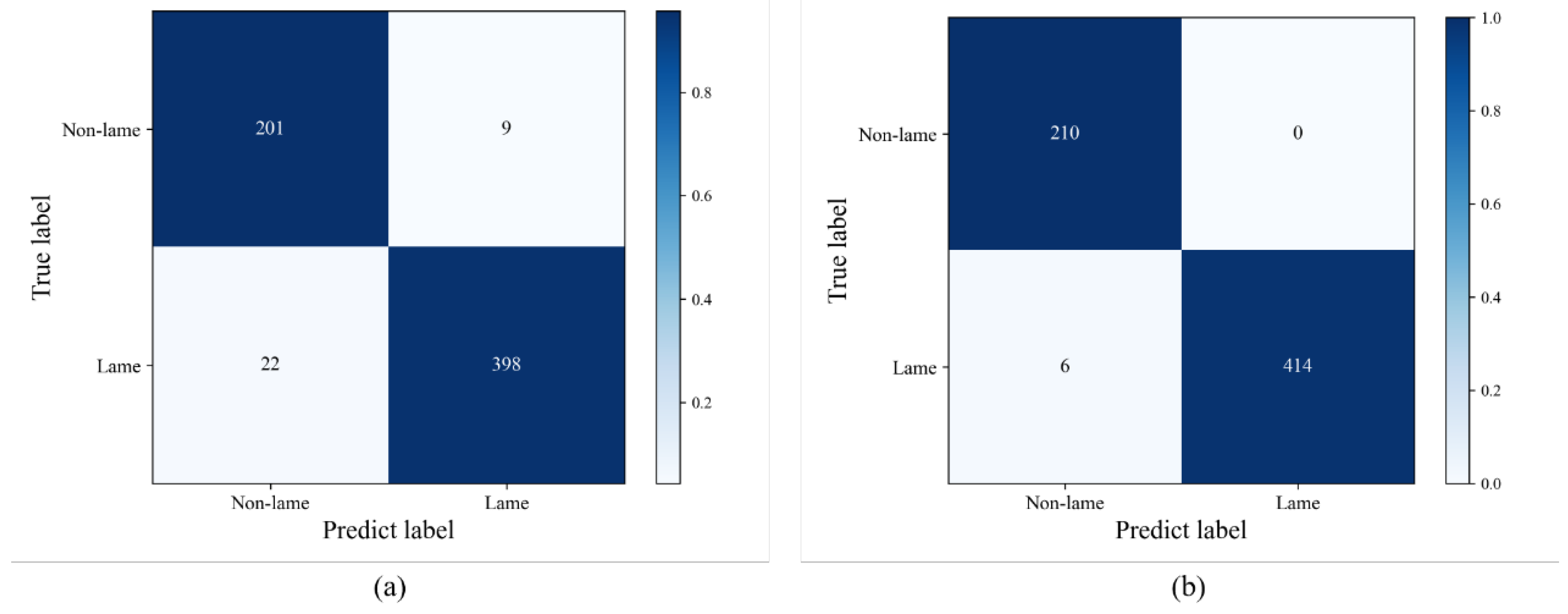
| Locomotion scores | Algorithm classification | Total | Sensitivity (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score 1 | Score 2 | Score 3 | |||||
| Score 1 | 210 | 0 | 0 | 210 | 100 | ||
| Score 2 | 6 | 175 | 29 | 210 | 83.33 | ||
| Score 3 | 0 | 33 | 177 | 210 | 84.29 | ||
| Specificity (%) | 98.57 | 92.14 | 93.10 | ||||
| Algorithm | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AdaBoost [18] | 77.90 | - | - |
| SVM-R [17] | 80.07 | 76.78 | 81.15 |
| Logistic Regression [39] | 87.30 | 88.80 | 85.7 |
| Our | 92.80 | 89.21 | 94.60 |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Džermeikaitė, K.; Krištolaitytė, J.; Anskienė, L.; Šertvytytė, G.; Lembovičiūtė, G.; Arlauskaitė, S.; Girdauskaitė, A.; Rutkauskas, A.; Baumgartner, W.; Antanaitis, R. Effects of Lameness on Milk Yield, Milk Quality Indicators, and Rumination Behaviour in Dairy Cows. Agriculture 2025, 15, 286. [CrossRef]
- McLennan, K.M. Why Pain Is Still a Welfare Issue for Farm Animals, and How Facial Expression Could Be the Answer. Agriculture 2018, 8, 127. [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.B. Changes in limb loading with lameness for a number of friesian cattle. Br. Vet. J. 1989, 145, 28-38. [CrossRef]
- Van Nuffel, A.; Zwertvaegher, I.; Pluym, L.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Thorup, V. M.; Pastell, M.; Sonck, B.; Saeys, W. Lameness detection in dairy cows: Part 1. How to distinguish between non-lame and lame cows based on differences in locomotion or behavior. Animals 2015, 5, 838-860. [CrossRef]
- Greenough, P. R.; MacCallum, F. J.; Weaver, A. D. Lameness in Cattle. In Lameness in Cattle, 2nd ed.; Wright (Scientechnica): Bristol, UK, 1981.
- Schlageter-Tello, A.; Bokkers, E.A.; Groot Koerkamp, P.W.; Van Hertem, T.; Viazzi, S.; Romanini, C.E.; Halachmi, I.; Bahr, C.; Berckmans, D.; Lokhorst, K. . Relation between observed locomotion traits and locomotion score in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci 2015, 98, 8623-8633. [CrossRef]
- Van Nuffel, A.; Zwertvaegher, I.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Pastell, M.; Thorup, V.M.; Bahr, C.; Sonck, B.; Saeys, W. Lameness Detection in Dairy Cows: Part 2. Use of Sensors to Automatically Register Changes in Locomotion or Behavior. Animals 2015, 5, 861-885. [CrossRef]
- Pastell, M.; Hanninen, L.; de Passillé, A.M.; Rushen, J. Measures of weight distribution of dairy cows to detect lameness and the presence of hoof lesions. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 954-960. [CrossRef]
- Poikalainen, V.; Praks, J.; Kokin, E.; Aland, A.; Veemäe, I.; Peets, S.; Ahokas, J.; Pastell, M.; Hautala, M.; Berckmans, D.; et al. Elaboration of basic methods for automatic analysis of cows’ gait. Agron. Res. 2010, 8, 216-225.
- Maertens, W.; Vangeyte, J.; Baert, J.; Jantuan, A.; Mertens, K.C.; De Campeneere, S.; Pluk, A.; Opsomer, G.; Van Weyenberg, S.; Van Nuffel, A. Development of a real time cow gait tracking and analysing tool to assess lameness using a pressure sensitive walkway: The GAITWISE system. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 110, 29-39. [CrossRef]
- Pastell, M.; Tiusanen, J.; Hakojärvi, M.; Hänninen, L. A wireless accelerometer system with wavelet analysis for assessing lameness in cattle. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 104, 545-551. [CrossRef]
- Mandel, R.; Harazy, H.; Gygax, L.; Nicol, C.J.; Ben-David, A.; Whay, H.R.; Klement, E. Detection of lameness in dairy cows using a grooming device. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1511-1517. [CrossRef]
- Alsaaod, M.; Fadul, M.; Steiner, A. Automatic lameness detection in cattle. Vet. J. 2019, 246, 35-44. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, K.; Fan, H.; He, Z. Real-Time Cattle Pose Estimation Based on Improved RTMPose. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1938. [CrossRef]
- Viazzi, S.; Bahr, C.; Van Hertem, T.; Schlageter-Tello, A.; Romanini, C.E.B.; Halachmi, I.; Lokhorst, C.; Berckmans, D. Comparison of a three-dimensional and two-dimensional camera system for automated measurement of back posture in dairy cows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 100, 139-147. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Bewley, J.M.; He, D.; Jin, X. Automatic lameness detection in dairy cattle based on leg swing analysis with an image processing technique. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 148, 226-236. [CrossRef]
- Russello, H.; van der Tol, R.; Holzhauer, M.; van Henten, E.J.; Kootstra, G. Video-based automatic lameness detection of dairy cows using pose estimation and multiple locomotion traits. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 223, 12. [CrossRef]
- Myint, B.B.; Onizuka, T.; Tin, P.; Aikawa, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Zin, T.T. Development of a real-time cattle lameness detection system using a single side-view camera. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Song, H.B.; He, D.J. Lameness detection of dairy cows based on a double normal background statistical model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 158, 140-149. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A. C.; Moore, D. A.; Vanegas, J.; Wenz, J. R. Association of abnormal hind-limb postures and back arch with gait abnormality in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci, 2014, 97, 2178–2185. [CrossRef]
- Flower, F.C.; Weary, D.M. Gait assessment in dairy cattle. Animal 2009, 3, 87-95. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Y.; Leroy, T.; Vranken, E.; Maertens, W.; Sonck, B.; Berckmans, D. Automatic detection of lameness in dairy cattle - Vision-based trackway analysis in cow’s locomotion. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 64, 39-44. [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.H.; Wu, Q.; Yin, X.Q.; Jiang, B.; Wang, H.; He, D.J.; Song, H.B. Lameness detection of dairy cows based on the YOLOv3 deep learning algorithm and a relative step size characteristic vector. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 189, 150-163. [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, G. Accurate detection of lameness in dairy cattle with computer vision: A new and individualized detection strategy based on the analysis of the supporting phase. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10628-10638. [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, S.D.; Li, Q.; Liu, G. Dimension-reduced spatiotemporal network for lameness detection in dairy cows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 10. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Si, Y.S.; Chu, M.Y.; Liu, N.; Kang, X.; Liu, G. A novel lameness detection method for dairy cows based on temporal gait and spatial post features. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 13. [CrossRef]
- Bahr, C.; Leroy, T.; Song, X.; Vranken, E.; Maertens, W.; Vangeyte, J.; Van Nuffel, A.; Sonck, B.; Berckmans, D. Automatic detection of lameness in dairy cattle–analyzing image parameters related to lameness. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, Reno, NV, USA; 31 August–4 September 2009; Livestock Environment VIII: Iguassu Falls, 592 Brazil, 2009.
- Poursaberi, A.; Bahr, C.; Pluk, A.; Van Nuffel, A.; Berckmans, D. Real-time automatic lameness detection based on back posture extraction in dairy cattle: Shape analysis of cow with image processing techniques. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 74, 110-119. [CrossRef]
- Viazzi, S.; Bahr, C.; Schlageter-Tello, A.; Van Hertem, T.; Romanini, C.E.B.; Pluk, A.; Halachmi, I.; Lokhorst, C.; Berckmans, D. Analysis of individual classification of lameness using automatic measurement of back posture in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 257-266. [CrossRef]
- Piette, D.; Norton, T.; Exadaktylos, V.; Berckmans, D. Individualised automated lameness detection in dairy cows and the impact of historical window length on algorithm performance. Animal 2020, 14, 409-417. [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Liang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, G. Accuracy of Detecting Degrees of Lameness in Individual Dairy Cattle Within a Herd Using Single and Multiple Changes in Behavior and Gait. Animals 2025, 15, 1144. [CrossRef]
- Annelies, V, N.; Ingrid, Z.; Liesbet, P. Lameness Detection in Dairy Cows: Part 1. How to Distinguish between Non-Lame and Lame Cows Based on Differences in Locomotion or Behavior. Animals. 2015, 5, 838-860.
- Haladjian, J.; Hodaie, Z.; Nüske, S.; Brügge, B. Gait Anomaly Detection in Dairy Cattle. The Fourth International Conference on Animal-Computer Interaction, Milton Keynes, UK, 21–23 November 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8.
- Gardenier, J.; Underwood, J.; Clark, C. Object Detection for Cattle Gait Tracking. The 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2206–2213.
- Van Nuffel, A.; Vangeyte, J.; Mertens, K. C.; Pluym, L.; De Campeneere, S.; Saeys, W.; Opsomer, G.; Van Weyenberg, S. Exploration of measurement variation of gait variables for early lameness detection in cattle using the GAITWISE. Livest. Sci. 2013, 156 88–95. [CrossRef]
- VanNuffel, A..; Sprenger, M..; Tuyttens, F.A.M..; Maertens, W. Cowgait scores and kinematic gait data: Can people see gait irregularities? Anim.Welf. 2009, 18, 433–439. [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.Z.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L., Xiao, T.T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y.; Dolla’r, P.; Girshick, R. Segment Anything. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023, pp. 3992-4003.
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627-1639. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., 2023. Research on Automatic Lameness Detection Method of Dairy Cows Based on Machine Learning. Mechanical engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang. MA Thesis.
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qin, L.; Yue, S.; Zeng, P. Cows’ legs tracking and lameness detection in dairy cattle using video analysis and Siamese neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107618. [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, Z.J.; Liu, X.W.; Chu, M.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Kang, X.; Liu, G. Lameness detection system for dairy cows based on instance segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 249, 123775. [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning Spatiotemporal Features with 3D Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7-13 December 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 4489–4497.
- Tran, D.; Wang, H.; Torresani, L.; Ray, J.; LeCun, Y.; Paluri, M. A Closer Look at Spatiotemporal Convolutions for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-22 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 6450–6459.
- Adair, S.; Baus, M.; Belknap, J.; Bell, R.; Boero, M.; Bussy, C.; Cardenas, F.; Casey, T.; Castro, J.; Davis, W. Response to letter to the editor: Do we have to redefine lameness in the era of quantitative gait analysis. Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 415–417. [CrossRef]
| Score | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The cow walks with a level-back posture. The gait is normal. No signs of head bob when the cow is walking. |
| 2 | In most cases, the back is arched when the cow is walking. The gait might be slightly uneven and the cow may walk with short strides. In most cases, there are no signs of head bob when walking. |
| 3 | The back is visibly arched when the cow is walking. The cow is obviously lame on 1 or more legs. The cow is unable, unwilling, or very reluctant to bear weight on the affected leg. In most cases, head bob will be evident when walking. |
| Classification model | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet121 | 95.08 | 95.71 | 94.76 |
| DCAC | 99.05 | 100 | 98.57 |
| Classification model | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DenseNet121 | 88.99 | 83.49 | 91.75 |
| DCAC | 92.80 | 89.21 | 94.60 |
| Algorithm | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3 + LSTM [23] | 97.00 | - | - |
| Siam-AM + SVM [40] | 94.73 | 96.21 | 95.14 |
| C3D [42] | 75.68 | 81.08 | 70.27 |
| R3D [43] | 74.32 | 70.27 | 78.38 |
| R2Plus1D [43] | 67.57 | 75.68 | 59.46 |
| SOLOv2+SVM [41] | 98.65 | 100 | 97.30 |
| Our | 99.05 | 100 | 98.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





