Submitted:
05 May 2025
Posted:
06 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
- The relationship between TTX and Vibrio bacteria is particularly interesting given the strong correlation between bacterial prevalence, TTX occurrence and warmer climate, as highlighted in previous research [14,40,41,42,43,44,45]. Coastal waters and brackish areas with moderate salinity, typically dominating in Scandinavian marine environments, favors Vibrio populations [46,47,48]. However, high abundance of Vibrio bacteria has also been reported in more saline waters of the Skagerrak Sea, especially in warm summer days [49]. One notable Vibrio outbreak in the Baltic Sea occurred during the warm summer in 2014, when the sea surface temperatures became unusually high [50]. This Vibrio outbreak temporally corresponded with a TTX-positive mussel sample (26 µg/kg) in Scottland (North Sea) [37], assumptively indicating presence of TTX in Swedish marine waters (no samples were tested for TTX presence in Sweden during this period).
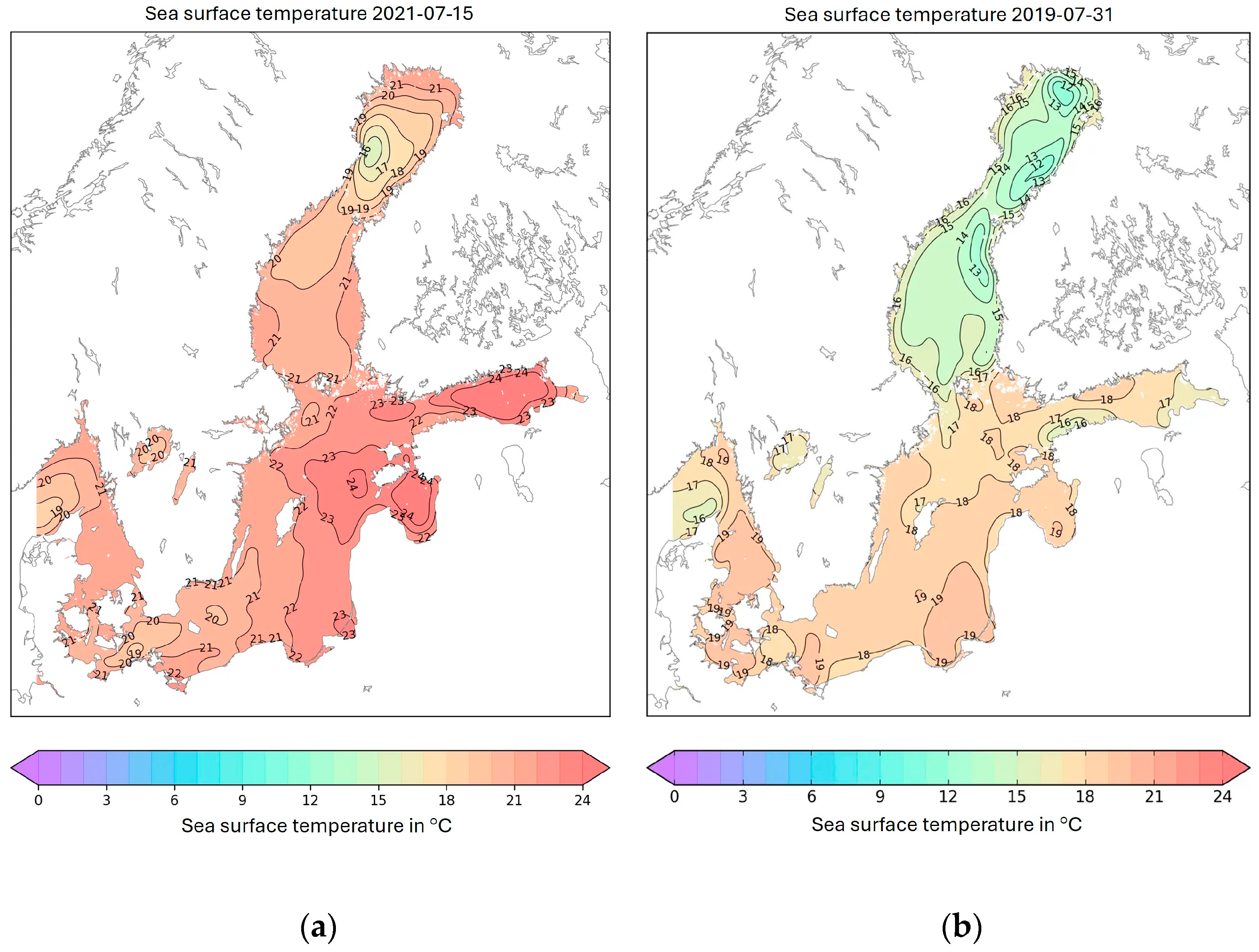
- Furthermore, the assumption of TTX presence in Swedish marine environment is supported with the knowledge that sea surface temperature seems to be one of the ultimate criteria earlier reported for the occurrence of TTX [23,34,37]. The threshold of 15 °C was suggested to indicate a limit above which TTX is more likely to occur in shellfish. Certainly, surface temperatures of the seawater around Sweden can reach well above that threshold during the summer season, as exemplified for the sampling seasons of this study in Figure 4, and the summer of 2014 described above.
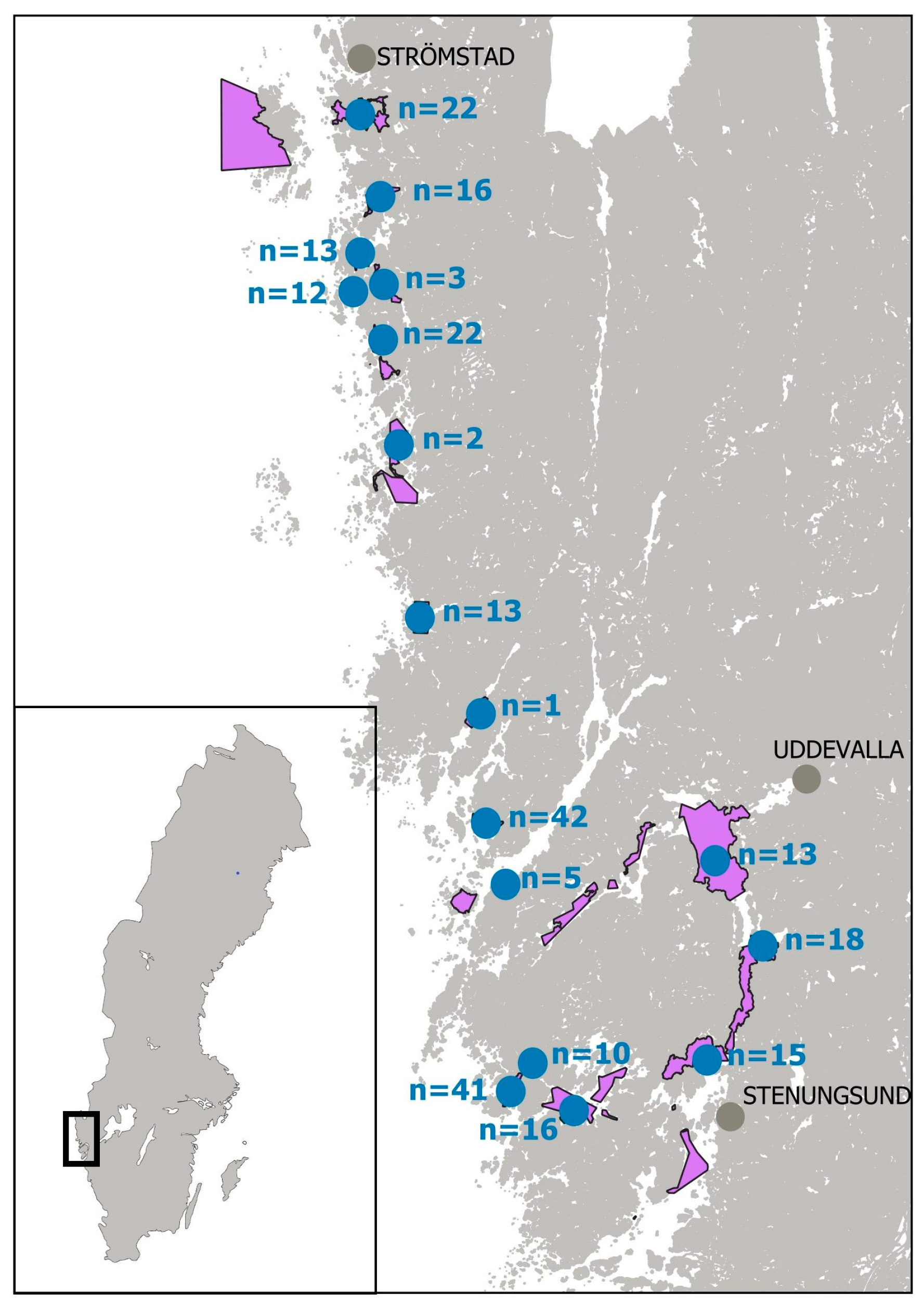
- Introduction of invasive species, like the pufferfish or the spread of the invasive ribbon worm Cephalotrix simula to southern and northern Europe in the last decade, are strongly associated with the occurrence of TTX in European marine waters [21,55,56,57]. To the best of our knowledge, the latest biodiversity survey concerning nemerteans along the Swedish west coast was conducted in 2007 [58]. Various nemertean species have been studied in Sweden since then [59] but the occurrence of C. simula has not been reported yet. It is, however, reasonable to assume that the species could have become introduced into Swedish marine waters. One of the main vectors for the introduction of marine invasive species globally is ballast water of ships by which aquatic organisms are transported to new environments. Aspects on its constantly increasing impact on the existing ecosystems have been addressed elsewhere [60,61,62,63]. A majority of Sweden’s blue mussel production is located within 60 km north of the Port of Gothenburg, which is the largest port in Scandinavia.
- With the above outlined conditions 1) – 3) one could suggest that there is no major difference in the general conditions for TTX occurrence in the marine environment, compared to previous reports on TTX presence in northern Europe, which supports our hypothesis while the results of this screening study could not confirm it.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Standards, Reagents and Chemicals
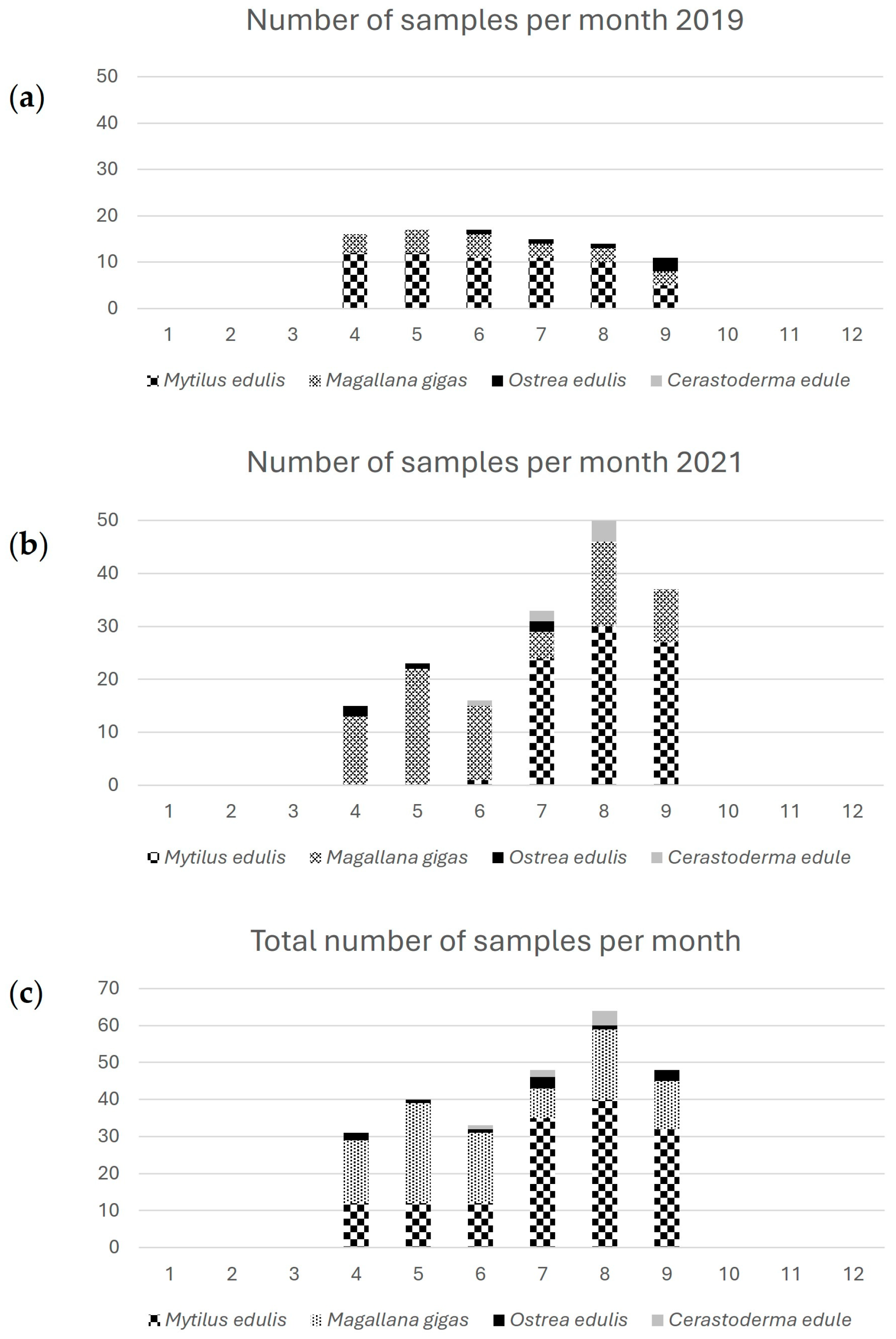
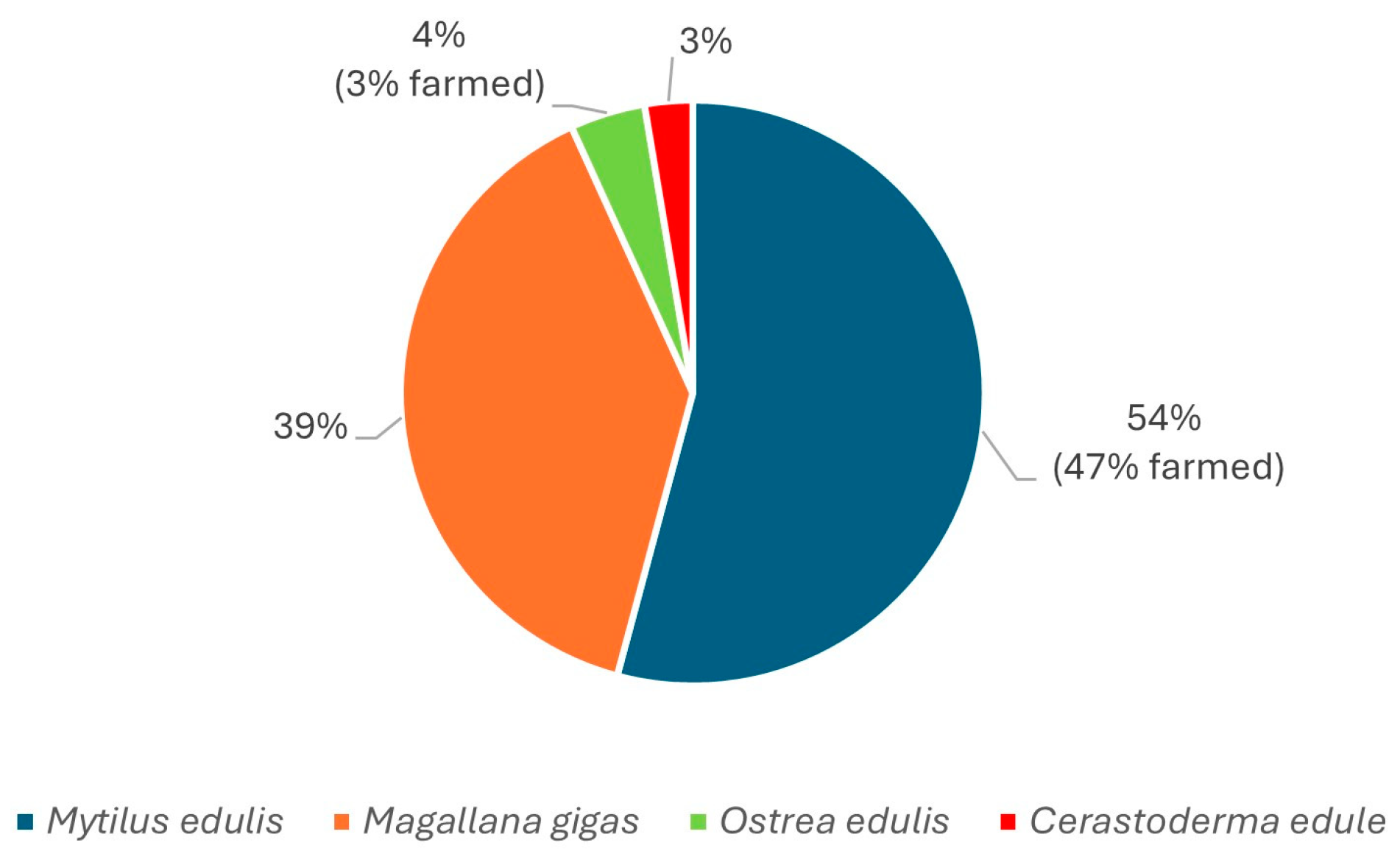
3.2. Sampling and Sample Preparation
3.3. Screening Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guardone, L.; Maneschi, A.; Meucci, V.; Gasperetti, L.; Nucera, D.; Armani, A. A Global Retrospective Study on Human Cases of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) Poisoning after Seafood Consumption. Food Reviews International 2019, 36, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, F.R.; Nazmul Ahasan, H.A.; Mamunur Rashid, A.K.; Al Mamun, A.; Khaliduzzaman, S.M. Tetrodotoxin poisoning: a clinical analysis, role of neostigmine and short-term outcome of 53 cases. Singapore Med J 2007, 48, 830–833. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.J.; Ha, K.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Mok, J.S.; Son, K.T.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, J.H. Paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) and tetrodotoxin (TTX) of Korean pufferfish. Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 2021, 24, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bane, V.; Lehane, M.; Dikshit, M.; O'Riordan, A.; Furey, A. Tetrodotoxin: chemistry, toxicity, source, distribution and detection. Toxins (Basel) 2014, 6, 693–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.I.; Magarlamov, T.Y. An Overview of the Anatomical Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Animals. Toxins 2022, 14, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, R.; Kalaitzis, J.A.; Neilan, B.A. On the origins and biosynthesis of tetrodotoxin. Aquat Toxicol 2011, 104, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P.; Gokbulut, C.; Kosker, A.R.; Campàs, M.; Ozogul, F. An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Marine Drugs 2022, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, G.M.; Lechner, M.; Fontes, A.; Kats, L.B.; Eisthen, H.L.; Shaffer, H.B. From Poison to Promise: The Evolution of Tetrodotoxin and Its Potential as a Therapeutic. Toxins 2021, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiao, K.; Cui, R.; Xu, M.; Cai, S.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Z. Tetrodotoxin: The State-of-the-Art Progress in Characterization, Detection, Biosynthesis, and Transport Enrichment. Marine Drugs 2024, 22, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin--distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Gilhen, J.; Russell, R.W.; Krysko, K.L.; Melaun, C.; Kurz, A.; Kauferstein, S.; Kordis, D.; Mebs, D. Variability of tetrodotoxin and of its analogues in the red-spotted newt, Notophthalmus viridescens (Amphibia: Urodela: Salamandridae). Toxicon 2012, 59, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malykin, G.V.; Velansky, P.V.; Magarlamov, T.Y. Levels and Profile of Tetrodotoxins in Spawning Cephalothrix mokievskii (Palaeonemertea, Nemertea): Assessing the Potential Toxic Pressure on Marine Ecosystems. Toxins (Basel) 2025, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varini, C.; Manganelli, M.; Scardala, S.; Antonelli, P.; Losasso, C.; Testai, E. An Update of Tetrodotoxins Toxicity and Risk Assessment Associated to Contaminated Seafood Consumption in Europe: A Systematic Review. Toxins 2025, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheepa, V.; Vasconcelos, V. Microbial diversity associated with tetrodotoxin production in marine organisms. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2013, 36, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magarlamov, T.Y.; Melnikova, D.I.; Chernyshev, A.V. Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria: Detection, Distribution and Migration of the Toxin in Aquatic Systems. Toxins 2017, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Powell, A.; Schofield, A.; Lees, D.N.; Baker-Austin, C. Detection of the pufferfish toxin tetrodotoxin in European bivalves, England, 2013 to 2014. Euro Surveill 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.D.; Higgins, C.; Higman, W.; Hungerford, J. Potential Threats Posed by Tetrodotoxins in UK Waters: Examination of Detection Methodology Used in Their Control. Mar Drugs 2015, 13, 7357–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xie, L.; Xia, G.; Zhang, J.; Nie, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R. A new tetrodotoxin-producing actinomycete, Nocardiopsis dassonvillei, isolated from the ovaries of puffer fish Fugu rubripes. Toxicon 2005, 45, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlamis, A.; Katikou, P.; Rodriguez, I.; Rey, V.; Alfonso, A.; Papazachariou, A.; Zacharaki, T.; Botana, A.M.; Botana, L.M. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Greek Shellfish by UPLC-MS/MS Potentially Linked to the Presence of the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 1779–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Sato, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Ogata, T. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in Alexandrium tamarense, a causative dinoflagellate of paralytic shellfish poisoning. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Fenwick, D.; Powell, A.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Ford, C.; Hatfield, R.G.; Santos, A.; Martinez-Urtaza, J.; Bean, T.P.; Baker-Austin, C. , et al. New Invasive Nemertean Species (Cephalothrix Simula) in England with High Levels of Tetrodotoxin and a Microbiome Linked to Toxin Metabolism. Mar Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Hatfield, R.G.; Walker, D.I.; Hooper, C.; Alewijnse, S.; Baker-Austin, C.; Turner, A.D.; Ritchie, J.M. Investigating Non-Native Ribbon Worm Cephalothrix simula as a Potential Source of Tetrodotoxin in British Bivalve Shellfish. Mar Drugs 2024, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Teixeira Alves, M.; Triñanes, J.A.; Martinez-Urtaza, J.; Haverson, D.; Bradley, K.; Baker-Austin, C.; Huggett, J.F.; Stewart, G.; Ritchie, J.M. , et al. Sea temperature influences accumulation of tetrodotoxin in British bivalve shellfish. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 885, 163905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Gago-Martínez, A. Emerging Marine Biotoxins. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hort, V.; Arnich, N.; Guérin, T.; Lavison-Bompard, G.; Nicolas, M. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Bivalves and Gastropods from the French Mainland Coasts. Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réveillon, D.; Savar, V.; Schaefer, E.; Chevé, J.; Halm-Lemeille, M.-P.; Hervio-Heath, D.; Travers, M.-A.; Abadie, E.; Rolland, J.-L.; Hess, P. Tetrodotoxins in French Bivalve Mollusks—Analytical Methodology, Environmental Dynamics and Screening of Bacterial Strain Collections. Toxins 2021, 13, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Vale, C.; Alfonso, C.; Vale, P.; Tellez, A.; Botana, L.M. First toxicity report of tetrodotoxin and 5,6,11-trideoxyTTX in the trumpet shell Charonia lampas lampas in Europe. Anal Chem 2008, 80, 5622–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ortega, J.F.; Santos, J.M.M.-d.l.; Herrera-Gutiérrez, M.E.; Fernández-Sánchez, V.; Loureo, P.R.; Rancaño, A.A.; Téllez-Andrade, A. Seafood Intoxication by Tetrodotoxin: First Case in Europe. The Journal of Emergency Medicine 2010, 39, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.R.; Giráldez, J.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Leão, J.M.; Pinto, E.; Soliño, L.; Gago-Martínez, A. High Levels of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) in Trumpet Shell Charonia lampas from the Portuguese Coast. Toxins (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, O.; Ünal, V.; Ceyhan, T.; Bilecenoglu, M. First confirmed record of Lagocephalus sceleratus(Gmelin, 1789) in the Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Fish Biology 2005, 66, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulman, A.; Abd Rabou, A.F.N.; Al Mabruk, S.; Bariche, M.; Bilecenoğlu, M.; Demirel, N.; Galil, B.S.; Hüseyinoğlu, M.F.; Jimenez, C.; Hadjioannou, L. , et al. Assessment of Human Health Impacts from Invasive Pufferfish (Attacks, Poisonings and Fatalities) across the Eastern Mediterranean. Biology 2024, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Souissi, J.; Rifi, M.; Ghanem, R.; Ghozzi, L.; Boughedir, W.; Azzurro, E. Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) expands through the African coasts towards the Western Mediterranean Sea: a call for awareness. Management of Biological Invasions 2014, 5, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific opinion on the risks for public health related to the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and TTX analogues in marine bivalves and gastropods. EFSA J. 2017, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Gerssen, A.; Bovee, T.H.F.; Klijnstra, M.D.; Poelman, M.; Portier, L.; Hoogenboom, R. First Report on the Occurrence of Tetrodotoxins in Bivalve Mollusks in The Netherlands. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P. Public Health Risks Associated with Tetrodotoxin and Its Analogues in European Waters: Recent Advances after The EFSA Scientific Opinion. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessy, L.; Boundy, M.J.; Smith, K.F.; Harwood, D.T.; Hawes, I.; Wood, S.A. Tetrodotoxin in marine bivalves and edible gastropods: A mini-review. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Coates, L.; Bickerstaff, L.; Milligan, S.; O'Neill, A.; Faulkner, D.; McEneny, H.; Baker-Austin, C.; Lees, D.N. , et al. Detection of Tetrodotoxin Shellfish Poisoning (TSP) Toxins and Causative Factors in Bivalve Molluscs from the UK. Mar Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, I.; Alfonso, A.; Alonso, E.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Roel, M.; Vlamis, A.; Katikou, P.; Jackson, S.A.; Menon, M.L.; Dobson, A. , et al. The association of bacterial C9-based TTX-like compounds with Prorocentrum minimum opens new uncertainties about shellfish seafood safety. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 40880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patria, F.P.; Pekar, H.; Zuberovic-Muratovic, A. Multi-Toxin Quantitative Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxins in Bivalve Mollusks with Ultra-Performance Hydrophilic Interaction LC-MS/MS-An In-House Validation Study. Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Jeon, J.K.; Arakawa, O.; Sugita, H.; Deguchi, Y.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin and anhydrotetrodotoxin in Vibrio sp. isolated from the intestines of a xanthid crab, Atergatis floridus. J Biochem 1986, 99, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, J.M.; Lozano-Leon, A.; Giráldez, J.; Vilariño, Ó.; Gago-Martínez, A. Preliminary Results on the Evaluation of the Occurrence of Tetrodotoxin Associated to Marine Vibrio spp. in Bivalves from the Galician Rias (Northwest of Spain). Mar Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchiocchi, S.; Campacci, D.; Siracusa, M.; Dubbini, A.; Accoroni, S.; Romagnoli, T.; Campanelli, A.; Griffoni, F.; Tavoloni, T.; Gorbi, S. , et al. A Hotspot of TTX Contamination in the Adriatic Sea: Study on the Origin and Causative Factors. Mar Drugs 2022, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchiocchi, S.; Campacci, D.; Siracusa, M.; Dubbini, A.; Leoni, F.; Tavoloni, T.; Accoroni, S.; Gorbi, S.; Giuliani, M.E.; Stramenga, A. , et al. Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related? Mar Drugs 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernroth, B.E.; Baden, S.P. Alteration of host-pathogen interactions in the wake of climate change - Increasing risk for shellfish associated infections? Environ Res 2018, 161, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Brettar, I.; Pezzati, E.; Reid, P.C.; Colwell, R.R.; Höfle, M.G.; Pruzzo, C. Long-term effects of ocean warming on the prokaryotic community: evidence from the vibrios. The ISME Journal 2011, 6, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyraitė, G.; Kataržytė, M.; Bučas, M.; Kalvaitienė, G.; Kube, S.; Herlemann, D.P.; Pansch, C.; Andersson, A.F.; Pitkanen, T.; Hokajärvi, A.M. , et al. Epidemiological and environmental investigation of the 'big four' Vibrio species, 1994 to 2021: a Baltic Sea retrospective study. Euro Surveill 2024, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.L.; Farid, A.F.; Dalsgaard, I. Occurrence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus in marine and estuarine bathing areas in Danish coast. Zentralblatt fur Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie und Hygiene. 1. Abt. Originale B, Hygiene 1981, 173, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Gjerde, J.; Böe, B. Isolation and characterization of Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus from the Norwegian coastal environment. Acta Vet Scand 1981, 22, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Johansson, M.; Bertilsson, S. Environmental Influences on <i>Vibrio</i> Populations in Northern Temperate and Boreal Coastal Waters (Baltic and Skagerrak Seas). Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2006, 72, 6004–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Austin, C.; Trinanes, J.A.; Salmenlinna, S.; Löfdahl, M.; Siitonen, A.; Taylor, N.G.; Martinez-Urtaza, J. Heat Wave-Associated Vibriosis, Sweden and Finland, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis 2016, 22, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute (SMHI). Available online: https://www.smhi.se/klimat/klimatet-da-och-nu/manadens-vader-och-vatten-i-sverige/manadens-vader-och-vatten-i-sverige/2019-07-05-juni-2019---normala-observationer (accessed on 5th March 2025).
- Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute (SMHI). Available online: https://www.smhi.se/klimat/klimatet-da-och-nu/manadens-vader-och-vatten-i-sverige/manadens-vader-och-vatten-i-sverige/2021-08-09-juli-2021---sma-variationer-under-hogtrycksbetonad-julimanad (accessed on 5th March 2025).
- Albretsen, J.; Aure, J.; Sætre, R.; Danielssen, D.S. Climatic variability in the Skagerrak and coastal waters of Norway. ICES Journal of Marine Science 2011, 69, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutheil, C.; Meier, H.E.M.; Gröger, M.; Börgel, F. Warming of Baltic Sea water masses since 1850. Climate Dynamics 2023, 61, 1311–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajihara, H.; Sun, S.C.; Chernyshev, A.V.; Chen, H.X.; Ito, K.; Asakawa, M.; Maslakova, S.A.; Norenburg, J.L.; Strand, M.; Sundberg, P.; et al. Taxonomic identity of a tetrodotoxin-accumulating ribbon-worm Cephalothrix simula (Nemertea: Palaeonemertea): a species artificially introduced from the Pacific to Europe. Zoolog Sci 2013, 30, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álvarez, F.Á.; Machordom, A. DNA barcoding reveals a cryptic nemertean invasion in Atlantic and Mediterranean waters. Helgoland Marine Research 2013, 67, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faasse, M.; Turbeville, J.M. The first record of the north-west Pacific nemertean Cephalothrix simula in northern Europe. Marine Biodiversity Records 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, P.; Gibson, R.; Strand, M. Swedish nemerteans (phylum Nemertea), with description of a new hoplonemertean genus and species. Journal of Natural History 2007, 41, 2287–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, M.; Hedström, M.; Seth, H.; McEvoy, E.G.; Jacobsson, E.; Göransson, U.; Andersson, H.S.; Sundberg, P. The Bacterial (Vibrio alginolyticus) Production of Tetrodotoxin in the Ribbon Worm Lineus longissimus-Just a False Positive? Mar Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, K. Marine bioinvasion prevention : understanding ballast water transportation conditions and the development of effective treatment systems. PhD Thesis, Newcastle University, School of Marine Science and Technology, 2011. doi: http://theses.ncl.ac.uk/jspui/handle/10443/1246. [Google Scholar]
- Flagella, M.M.; Abdulla, A.A. Ship ballast water as a main vector of marine introductions in the Mediterranean Sea. WMU Journal of Maritime Affairs 2005, 4, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.W.; Carlton, J.T.; Carlton, D.A.; Geller, J.B. Ballast water as a vector for tintinnid transport. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 1997, 149, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagenkopp Lohan, K.M.; Darling, J.A.; Ruiz, G.M. International shipping as a potent vector for spreading marine parasites. Diversity and Distributions 2022, 28, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P.; Vlamis, A. Tetrodotoxins: recent advances in analysis methods and prevalence in European waters. Current Opinion in Food Science 2017, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Turner, A.D.; Baker-Austin, C.; Huggett, J.F.; Ritchie, J.M. Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Pacific Oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Mar Drugs 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boundy, M.J.; Biessy, L.; Roughan, B.; Nicolas, J.; Harwood, D.T. Survey of Tetrodotoxin in New Zealand Bivalve Molluscan Shellfish over a 16-Month Period. Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).