1. Introduction
The 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China (CPC) emphasized the necessity of enhancing legal safeguards for intellectual property rights. The 14th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and the Long-Range Goals Through 2035 position digitalization as a pivotal strategic tool to drive socioeconomic progress, explicitly outlining the framework of the digital economy system for the first time and designating blockchain as one of seven core industries in the digital economy. Amid rapid advancements in information and network technologies, the surge and diversification of intellectual property infringements have posed significant challenges to copyright licensing and complicated the protection of creators' rights. Copyright licensing, which involves granting exclusive or non-exclusive rights to users over copyrighted material, is central to copyright transactions.
Traditionally, digital copyright procedures involve applying for certification through institutions like the China Copyright Protection Center, embedding authenticated digital identifiers into works, and distributing encrypted content in markets (Wang and Sun, 2023). However, the evolution of digital technologies has propelled blockchain-based copyright licensing into a globally debated issue (Li and Lai, 2022). A review of over 394 international publications using keywords such as "blockchain," "intellectual property," and "digital copyright" reveals academic focus on three primary areas, as summarized in
Table 1, which highlights research trends in this field.
Currently, extens Currently, extensive literature indicates that academic research on blockchain and digital copyright remains in its infancy. In the United States, scholars emphasize legal frameworks and technological tools for digital copyright protection, including the use of blockchain and digital watermarking in copyright transactions and content distribution (Magnuson and William J, 2020). European researchers tend to concentrate on legal safeguards and regulatory policies, exploring how copyright law, data protection regulations, and cybersecurity legislation support the growth of the digital publishing sector (Zomaya et al., 2021). International bodies such as WIPO and UNESCO have also undertaken studies in this area, offering global standards and policy guidelines (Bonnet and Teuteberg, 2023). In China, scholars primarily examine the shared challenges in copyright licensing and highlight blockchain's strengths in safeguarding digital copyrights (Abd Ali. et al., 2023). However, studies specifically addressing blockchain-based licensing models are still limited (Li, 2022), with most discussions centering on the technology’s potential in particular use cases within digital copyright.
Nevertheless, the practical implementation of digital rights licensing continues to encounter numerous challenges and dilemmas. One major issue is the ambiguity surrounding the ownership of digital rights. The widespread occurrence of digital copyright infringement, combined with the absence of a standardized rights confirmation system, makes it difficult for parties involved in copyright transactions to determine whether a work is authentic or pirated. Additionally, the processes for authorizing and circulating digital rights licenses lack clarity. Moreover, the high transaction costs and inefficiencies further complicate the process, as parties must invest significant time and resources to locate the rightful owner or an intermediary. This situation creates a conflict between effective copyright licensing and the rapid dissemination of information (Xiong, 2022), ultimately undermining the functioning of the copyright market. To address these issues and enhance both licensing efficiency and information flow, this paper proposes the development of a blockchain-driven copyright licensing model that balances protection with service delivery.
2. Explanation and Features of the Blockchain Concept
Blockchain technology, as a cutting-edge computing paradigm, combines various advanced technologies—such as distributed data storage, peer-to-peer networking, consensus algorithms, and cryptographic methods—to establish a decentralized and trustworthy infrastructure. Its key attributes—decentralization, trust minimization, traceability, and immutability—position it as an effective solution for addressing challenges in digital copyright management. Beyond being a technological breakthrough, blockchain also introduces a novel business framework and redefines production relationships. By leveraging decentralization and smart contracts, it facilitates the emergence of intelligent collaborative systems and decentralized autonomous organizations, thereby enhancing the long-term viability of social enterprises.
2.1. The Concept of Blockchain: Innovative Technologies, Novel Business Models, and New Forms of Production Relations
Blockchain, a composite technology integrating distributed data storage, peer-to-peer transmission, consensus mechanisms, and encryption algorithms, serves as the foundational framework for Bitcoin transactions (Blockchain Whitepaper, 2022). Its defining characteristics—decentralization, immutability, and traceability—position it as an optimal solution for addressing challenges in digital copyright protection. The blockchain system employs multiple interconnected source code components to ensure robust security, particularly within decentralized storage architectures. By utilizing asymmetric encryption and merging trustless protocols with distributed data storage, it guarantees the integrity and reliability of digital rights licensing.
In the realm of copyright, blockchain applications offer mechanisms to verify the originality of intellectual property. First, the technology synthesizes distributed storage, network protocols, encryption, and consensus mechanisms to create a decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof infrastructure (Data Bureau, 2016; Nakamoto, 2022). Second, as an innovative business model, blockchain reduces costs associated with intellectual property registration, verification, and licensing through dedicated management platforms. This shift streamlines digital rights processes, minimizes inefficiencies, and enables marketplaces to leverage technological and legal expertise for smoother transactions and new commercial opportunities (Ren et al., 2024). Third, blockchain’s decentralized architecture and distributed ledger systems redefine production relations by enhancing equity distribution, cost-effectiveness, and operational efficiency in social enterprises. The automation enabled by smart contracts fosters intelligent collaborative organizations (Melanie, 2015), while its governance innovations promote transparency in decision-making and advance decentralized autonomous entities.
2.2. Blockchain Characteristics: Decentralization, Lack of Reliance on Trust, Traceability, and Permanence
The alignment between blockchain technology and digital copyright stems from the seamless incorporation of technical attributes such as decentralization, trustlessness, immutability, and traceability into the copyright licensing framework.
Firstly, decentralization—where data is distributed across equally positioned nodes, each possessing the same level of authority and where no single node controls the stored data—necessitates inter-node competition for data selection (Aoki and Schiff, 2010). Leveraging blockchain's decentralized architecture helps dismantle information silos and facilitates consensus mechanisms for copyright registration and validation. All nodes on the blockchain operate under a unified protocol (Lv, 2019), and any data update requires authorization from other nodes, eliminating the need for third-party trust mechanisms.
Secondly, the trustless nature of blockchain ensures anonymity while supporting data transparency (Chen and Cai, 2020). Through the use of mathematical models and cryptographic algorithms, the system's transparency is maintained. Parties involved in digital rights transactions can rely on publicly available ledgers and shared algorithms to build trust, without needing to disclose or verify personal identity or creditworthiness, nor rely on third-party endorsements.
Thirdly, immutability presents challenges to the “right to erasure” granted by data protection laws (Li, 2023). According to the Cybersecurity Law of the People's Republic of China, individuals have the legal right to request the correction or deletion of personal information. However, once data is recorded on a blockchain, altering or deleting it becomes highly impractical without controlling over half the network nodes (i.e., over 51%). This characteristic may hinder legal entities from fulfilling their data deletion obligations and complicate digital governance.
Lastly, traceability is achieved through timestamping technology (Wang and Xiang, 2020). When data is recorded on a blockchain, a unique and unalterable digital signature is generated to mark the exact entry time. A hash value representing the digital rights information is created via cryptographic algorithms and linked sequentially with previous blocks through their hash values. This chronological structuring enhances the credibility of the data. The blockchain’s capacity to comprehensively log and preserve historical data introduces innovative solutions for managing digital copyright licensing (Wang et al., 2022).
3. The Legality of Digital Copyright Licensing Using Blockchain Technology
Digital copyright licensing systems are encountering both significant challenges and promising opportunities in the modern era. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized architecture, offers a transformative model for managing digital rights by dispersing authority and enhancing system resilience. The integration of smart contracts—capable of automatic execution—and the transparent operation of distributed consensus mechanisms substantially boost the efficiency and clarity of copyright transactions. These innovations reduce reliance on centralized intermediaries and address issues related to information asymmetry and trust. Through protocol-driven processes, distributed consensus not only enables accurate account management but also facilitates the execution of smart contracts, including copyright agreements. Collectively, these technological advancements safeguard the interests of both licensors and licensees, lower transaction costs, and foster the sustainable growth of the copyright industry. By leveraging these innovations, blockchain-based copyright licensing systems unlock greater copyright value and incentivize creative endeavors.
3.1. Decentralization Aligns with the Fundamental Purpose of Digital Copyright Licensing
Blockchain’s decentralized architecture enhances system robustness and reliability by dispersing authority, effectively mitigating the risks of targeted attacks and eliminating single points of failure. If one node in the network fails, the overall functionality remains unaffected, thereby ensuring greater system stability. The inherent features of blockchain—such as its distributed ledger—are well-suited for applications including identity verification, rights authentication, and intelligent asset management. Its decentralization also transforms industries related to value exchange by reducing reliance on third-party payment systems.
Digital copyright licensing represents a market-oriented approach to managing copyright assets (Ren, 2022), incentivizing content creation and contributing to the advancement of cultural and social sciences through paid licensing. Blockchain's decentralized framework offers comprehensive support for digital copyright transactions, enabling services such as copyright information queries, value assessment, licensing formats, terms, duration, geographic scope, and pricing. This helps streamline the licensing process, reduce operational costs, enhance service efficiency, and foster a transparent and active copyright licensing ecosystem.
Nevertheless, China's copyright trading market continues to grapple with challenges like information asymmetry, lack of trust, and difficulties in copyright valuation. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and transparent mechanisms, offers effective solutions to these issues (Bykovsky et al., 2023), improving the accuracy of information management, enabling automated revenue distribution, and strengthening the infrastructure of the intellectual property market. Ultimately, this aligns with the fundamental purpose of copyright licensing: to elevate the value of digital rights and stimulate creative output through efficient and reliable mechanisms.
3.2. The Smart Contracts Align with Digital Copyright Licensing Procedures
The smart contracts, which automate contract execution through blockchain technology, offer an efficient, reliable, and equitable solution for digital copyright licensing processes. Their core functionality lies in automatic execution: once predefined conditions are fulfilled, the contract carries out the agreed actions without requiring third-party intervention or oversight. The smart contract code explicitly outlines the terms and conditions of a copyright license and autonomously enforces these terms when conditions are satisfied.
Leveraging blockchain’s decentralized framework, smart contracts facilitate decentralized control and permission management. Copyright licensing processes can be encoded within these smart contracts, which are validated and executed by multiple nodes across the network. This decentralized control mechanism reduces dependence on centralized authorities while fostering a more transparent and equitable copyright licensing environment.
In practice, blockchain-based smart contracts not only accurately record the parties’personal information, licensing conditions, and contractual terms but also automatically manage profit distribution once payment from the copyright licensee is received. Importantly, the use of smart contracts for digital copyright licensing does not alter copyright ownership (Ma and Wang, 2023). Instead, licensees are granted usage rights within the parameters and duration specified by the smart contract. Both parties’ rights and obligations are governed strictly by the terms of the contract, ensuring that licensees cannot exceed the agreed-upon scope without authorization. Usage of the copyrighted work is therefore limited to the defined geographical area and temporal limits.
Overall, blockchain-enabled smart contracts provide a fair, secure, and efficient framework for managing digital copyright licenses. By automating contract enforcement, decentralizing control, and streamlining licensing management, smart contracts protect the interests of both licensors and licensees, mitigate risks, and reduce the likelihood of contractual disputes.
3.3. The Distributed Consensus Mechanism Aligns with the Substantive Interests of Copyright Owners and Users
The divergent priorities of copyright owners and users create a tension between the goals of maximizing licensing efficiency and expanding content dissemination. While copyright holders seek to optimize licensing revenues at minimal cost—primarily aiming to monetize their works in the digital environment—users prioritize broader access and dissemination at the lowest possible expense. Blockchain’s distributed consensus mechanism offers a technological solution that reconciles these conflicting interests by simultaneously enhancing licensing and dissemination efficiency. It facilitates a balance between the rights of various stakeholders and reduces transaction costs without undermining financial incentives.
At its core, a distributed ledger serves as an information-recording system, applicable across payment processing, billing, and computational tasks. It accurately logs the ownership and transactional history of digital assets, with the underlying protocol ensuring the accuracy and consistency of all recorded data. Each block within the blockchain records transactions, and once validated, the block is permanently linked to the chain, ensuring data integrity and traceability.
In the context of copyright revenue distribution, distributed ledger technology presents several key advantages. First, the consensus mechanism allows all participating nodes to reach agreement on critical information without requiring traditional reconciliation procedures. This reduces verification costs, accelerates transaction processing, and lowers royalty fees. Second, the system’s openness, transparency, and traceability enable all participants to access real-time licensing information, fostering a clearer understanding of rights distribution and preventing disputes between licensors and licensees. This transparency significantly improves the governance of copyright licensing.
Moreover, consensus is achieved through agreement among a majority of nodes, and the Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithm ensures system resilience against attacks or misuse. In PoW, nodes that contribute greater computational resources are more likely to gain the right to record transactions. This mechanism not only ensures reliability but also facilitates secure and verifiable record-keeping through randomized problem-solving, a method widely accepted in the blockchain industry.
Ultimately, distributed ledger technology allows for precise documentation of the financial arrangements between copyright owners and users (Lai and Li, 2023). It organizes transaction records in chronological order, helping define distinct rights for different parties, and supports an equitable, efficient copyright licensing framework.
4. The Application of Blockchain Technology in Digital Copyright Licensing
In the digital age, blockchain-based copyright licensing offers copyright owners and users a more streamlined, transparent, and secure approach to authorizing and managing intellectual property rights. Unlike traditional copyright registration systems, which typically depend on centralized institutions or third-party entities to authenticate and maintain copyright records, blockchain employs a decentralized architecture to store copyright information across a distributed network. This enables decentralized registration and verification of copyright ownership. Blockchain’s core attributes—immutability and transparency—enhance the security and traceability of copyright data, empowering rights holders to verify their ownership independently, without relying on intermediaries. Furthermore, smart contracts embedded within blockchain systems enable the automation and enforcement of copyright licensing agreements. When licensing contracts are encoded as smart contracts, and relevant licensing terms are recorded on the blockchain, the licensing process becomes self-executing and autonomous. These contracts enforce the allocation of rights according to pre-programmed rules, ensuring that both copyright holders and licensees receive equitable and accurate distributions of rights and benefits. Additionally, blockchain technology facilitates the creation of decentralized licensing marketplaces, where copyright owners and potential licensees can engage in direct transactions. These platforms, underpinned by distributed ledger technology, ensure the transparency and security of all licensing activities. Copyright holders can upload their works to the blockchain, define licensing terms, and make them accessible to potential users. In turn, users can search for and acquire licenses that match their needs directly through the platform. The combination of blockchain’s immutable data structure and the automated execution of smart contracts fosters an environment of transparency, efficiency, and trust in copyright licensing transactions.
4.1. The Significance of Decentralized Registration in Copyright Licensing Certification
Conventional copyright registration systems are typically managed by centralized entities such as copyright agencies or government bodies. However, these systems face several inherent limitations. First, the credibility and authenticity of the registered information rely heavily on the integrity of the central authority. Second, the operation of such systems often demands significant human and material resources, resulting in inefficiencies and high maintenance costs. Third, centralized databases are vulnerable to cyberattacks and data tampering, posing risks to the security and reliability of copyright records.
Blockchain technology introduces a transformative solution by offering a decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger. Through blockchain, copyright holders can register their creations securely, establishing both ownership and creation timestamps (Chu and Yi, 2022). Smart contracts can be employed to automate and validate the registration process, ensuring that the copyright data remains immutable and trustworthy. Essential information—such as the work's details, creation date, and author—can be permanently recorded on the blockchain to establish legal authorship and ownership.
This decentralized model reduces reliance on intermediaries, cuts registration and certification costs, and allows global access to copyright data, thereby promoting the internationalization of copyright protection. Blockchain’s inherent transparency, immutability, and security features significantly reduce the risk of infringement and enhance the enforceability of rights (Cao, 2023). Moreover, by lowering costs, improving accessibility, and fostering stakeholder trust, blockchain presents a more secure, efficient, and credible framework for copyright certification and protection.
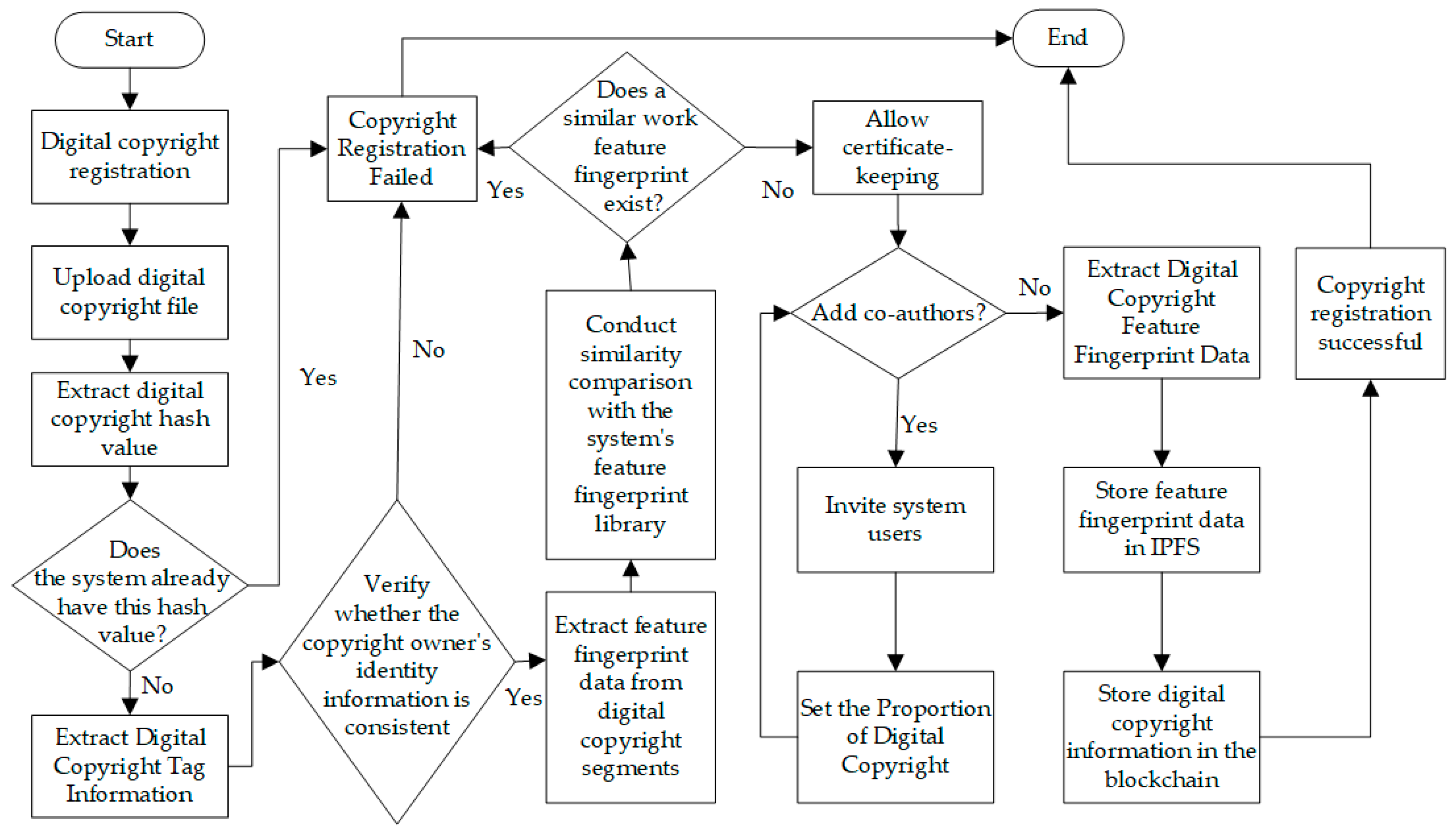
Decentralized systems for copyright registration and certification have the potential to significantly influence a broad spectrum of stakeholders, including content creators, users, copyright management organizations, and judicial authorities. Such systems are expected to reshape the copyright ecosystem in fundamental ways (Qian et al., 2023), particularly by redefining the function of intermediaries and transforming traditional approaches to copyright enforcement. Through the copyright registration and verification module, users can perform various functions—such as registering and confirming ownership of original works, downloading official copyright certificates, and accessing the original work files (see
Figure 1).
Once a work's copyright information is recorded on the blockchain, it serves as credible and verifiable evidence of ownership. The system employs a three-tiered verification process to assess the originality of submitted works. First, it examines the content hash of the file to determine whether the work has already been registered, thereby preventing duplicate submissions. Second, it conducts a preliminary assessment by comparing metadata—such as the creator’s name, date of creation, and copyright statement—with the identity of the uploading user. While this tag information provides useful context, it can be altered and thus cannot alone serve as definitive proof of originality. To enhance verification, the system also utilizes the Shazam algorithm to extract feature fingerprint data from segments of the work and compares it against an internal fingerprint database. These fingerprints—unique digital signatures used to identify multimedia content such as audio and video files—enable the system to detect similarities and prevent the re-registration of substantially similar content (Zhang et al., 2021). This layered verification approach not only safeguards the rights of copyright owners but also supports greater transparency and fairness in the creative process. Nonetheless, as digital technologies evolve, copyright protection systems must continuously adapt to new challenges. Integrating blockchain technology further strengthens the immutability and visibility of copyright data, offering a more robust foundation for copyright enforcement. Altogether, these three verification stages ensure both the originality of creative works and the prevention of redundant registrations.
Blockchain technology enhances the security of copyright data and minimizes the risk of infringement through advanced cryptographic methods and a decentralized storage framework. As Wang et al. (2023) note, blockchain employs cryptographic algorithms to encrypt copyright-related information and distribute it across numerous nodes within the network. This significantly raises the threshold for unauthorized alterations and enhances overall data integrity. The decentralized architecture ensures that no single point of failure exists, thereby reducing vulnerabilities to cyberattacks and data loss. Moreover, blockchain’s inherent transparency contributes to lowering the incidence of copyright violations. All transactions and records are permanently recorded on a public ledger, enabling open verification and audit by any party. This level of transparency improves the traceability and clarity of digital rights ownership, making infringements more detectable and less likely. Copyright holders can rely on immutable timestamps and verifiable transaction histories as authoritative proof of ownership, thereby strengthening their ability to enforce rights. Additionally, the immutability of blockchain ensures that once copyright data is recorded, it remains permanently preserved and immune to unauthorized deletion or modification. This creates a reliable evidentiary basis for protecting copyright and diminishes the possibility of infringers altering or erasing ownership records.
4.2. Allocation and Management of Copyright Licensing Rights and Interests via Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology is transforming the conventional approach to copyright licensing. Traditionally, once a copyright license is granted, the copyright holder often loses oversight of how the work is used, making it difficult to monitor and enforce rights. In contrast, the integration of blockchain and smart contracts introduces a novel and effective solution to this challenge. As a decentralized and distributed ledger system, blockchain enables secure and efficient documentation and verification of digital transactions. Smart contracts, which automatically execute contractual terms (Li et al., 2024), complement this infrastructure by facilitating transparent and enforceable rights management. In this model, copyright holders can embed licensing terms and usage permissions directly into smart contracts. When a work is licensed, all associated transaction data is immutably recorded on the blockchain. This allows rights holders to track how, when, and where their content is being used in real time. Such a transparent and traceable framework significantly enhances the ability to detect unauthorized use and respond with appropriate legal measures. Ultimately, the convergence of blockchain and smart contracts offers a streamlined, equitable, and secure method for managing copyright licensing, empowering creators to retain control over their works while reducing the risk of infringement.
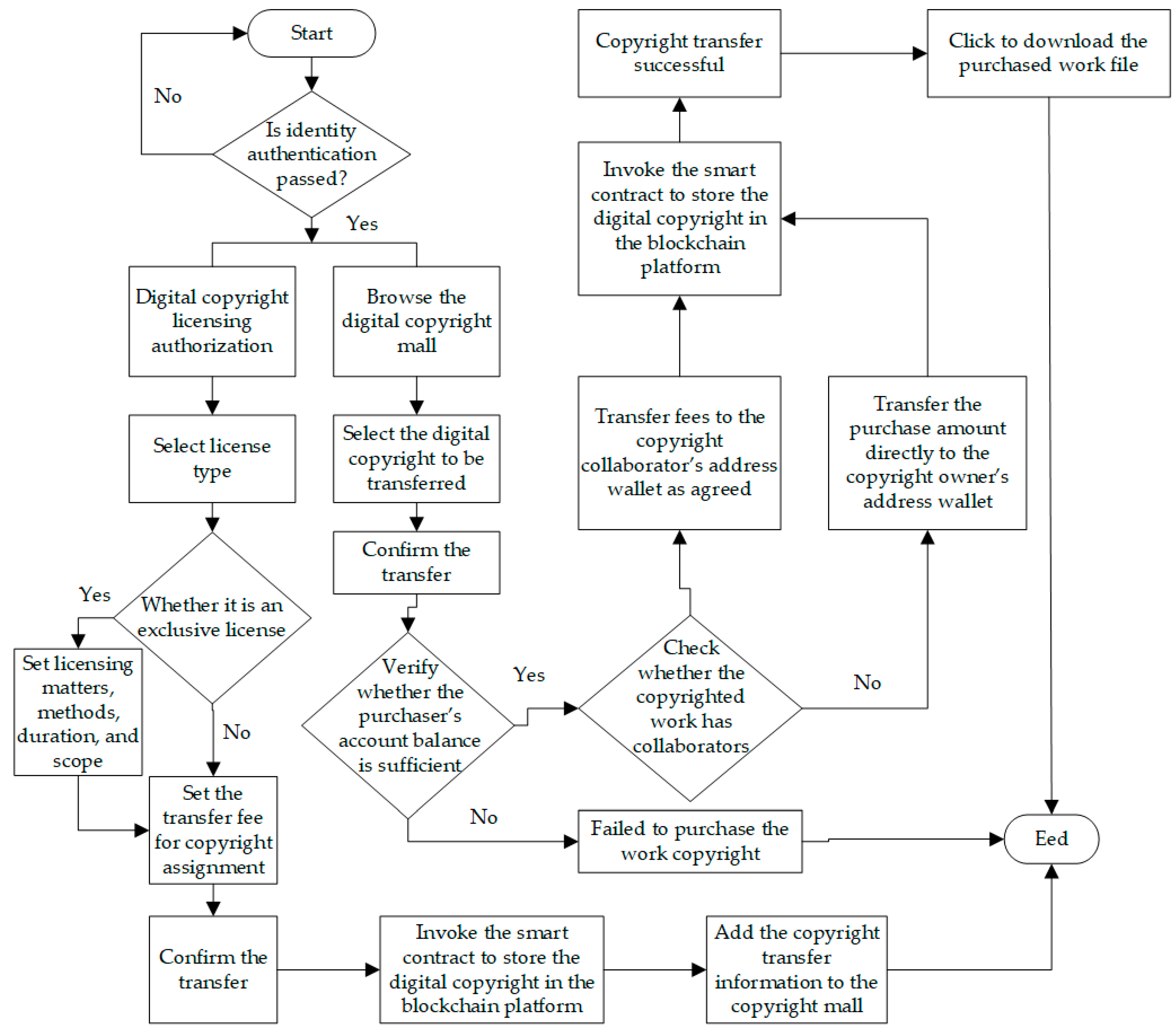
The smart contracts are specifically designed to enable the automated allocation of copyright-related interests. Within the Digital Rights Licensing Smart Contract Process Module, these contracts facilitate the seamless transfer of copyright ownership and usage rights between users (see
Figure 2). They can define the proportion of entitlements among stakeholders and execute distributions automatically based on predetermined rules, thus minimizing manual intervention and promoting equitable rights allocation. Additionally, smart contracts offer flexibility in determining the basis for distribution—whether linked to sales metrics, usage frequency, or other criteria—ensuring alignment with the specific interests of involved parties. This automated distribution process not only streamlines operations but also enhances transparency and ensures fairness in the allocation of rights and profits. The immutable and decentralized architecture of blockchain, combined with the autonomous nature of smart contracts, significantly bolsters the integrity and credibility of copyright governance. Contract execution relies on the collective validation of multiple nodes within the blockchain network, eliminating the influence of a centralized authority and safeguarding the impartiality of contract enforcement. All copyright data and related transaction records are securely recorded on the blockchain, forming an immutable ledger that cannot be altered or erased (Miao, 2023). This protects copyright information from manipulation and strengthens the overall security of rights management. In sum, the adoption of a blockchain-based licensing framework leads to a copyright management system that is not only efficient and transparent but also automated and highly secure—contributing to the prevention of unauthorized use and fostering a more trustworthy and equitable rights distribution environment.
Smart contracts offer notable benefits in enhancing the transparency and verifiability of copyright licensing procedures. By recording copyright data and transaction histories on the blockchain, they establish a tamper-resistant distributed ledger that guarantees the authenticity and reliability of licensing activities. These contracts can be programmed with clearly defined rules and eligibility requirements that users must meet to obtain licensing rights (Huang et al., 2023), effectively curbing unauthorized usage and abuse of copyright-protected content. Utilizing the decentralized characteristics of blockchain, smart contracts create a shared and verifiable database where copyright information and related records are accessible to all stakeholders. In contrast to conventional systems—often managed by intermediaries or centralized authorities and prone to information imbalance and trust issues—smart contract frameworks ensure that licensing details are stored transparently on the blockchain, allowing for open review and verification. Additionally, smart contracts support the configuration of licensing parameters such as fees, usage duration, and permitted scope (Wu, 2024), enabling intelligent execution of copyright agreements. These contracts are self-enforcing and remain unchanged until triggered, ensuring secure and consistent execution of licensing terms. Once conditions are met, smart contracts can automatically perform functions like royalty payments or usage monitoring.
4.3. Authorization in an Immutable Copyright Licensing Marketplace
A blockchain-enabled digital copyright licensing marketplace refers to a decentralized trading platform developed with blockchain technology, designed to facilitate the exchange of copyright licenses. This system allows for secure, transparent, and streamlined transactions through the use of smart contracts, thereby offering a reliable environment for both copyright holders and licensees. Within such a marketplace, copyright owners can grant or transfer usage rights to users in a decentralized manner. Leveraging the distributed ledger capabilities of blockchain, the platform ensures the transparency and traceability of all copyright transactions (Chen et al., 2023). By recording licensing data and transaction logs on an immutable ledger, blockchain technology guarantees the integrity and authenticity of copyright-related information. This immutability significantly reduces the risk of data manipulation or forgery, as all parties involved can independently access and verify the stored records—establishing a foundation of trust for all transactions. Smart contracts further enhance the marketplace by automating the allocation of rights and benefits within each licensing agreement. These contracts are programmed with predefined conditions, and once those are fulfilled, the corresponding benefits are distributed automatically. This automation not only minimizes the potential for human error and disputes during the transaction process (Xu et al., 2022), but also increases the overall efficiency and precision of licensing operations. Moreover, smart contracts can ensure equitable distribution of rights based on agreed-upon parameters such as usage scope, time limits, and other relevant criteria.
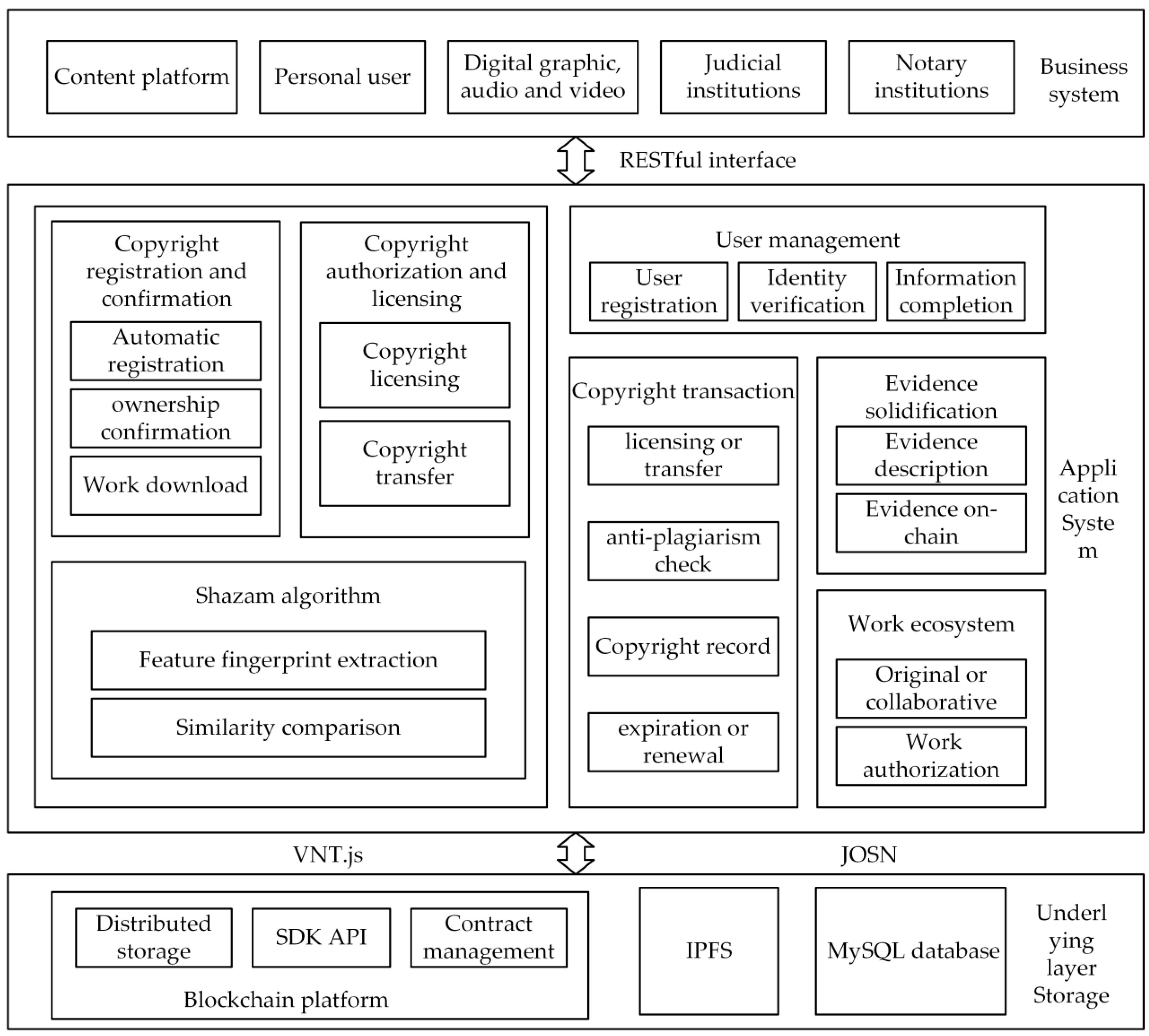
The architecture of the blockchain-based digital rights licensing model (
Figure 3) is structured around three core components.
Firstly, the foundational data storage system integrates a blockchain platform, IPFS (InterPlanetary File System), and a standalone database storage engine. Each of these components offers distinct advantages and limitations. When data is recorded on the blockchain, it benefits from tamper resistance and full traceability, making it suitable for use as admissible legal evidence. However, due to the gas fees associated with public blockchains—representing the cost of performing operations in cryptocurrency—only essential information is typically stored directly on-chain. To address this limitation, the model combines blockchain with IPFS technology, forming a hybrid solution for copyright management. While blockchain ensures the integrity and timestamping of copyright metadata, IPFS is utilized to store large-scale work files, maintaining consistency and synchronization between the metadata and content. Smart contracts are employed to automate copyright transactions, while IPFS archives the associated transaction records to guarantee transparency and traceability. The use of cryptographic hashes and timestamps on the blockchain strengthens the evidentiary value of stored records, and IPFS preserves the original file data to support data authenticity and completeness. However, it is important to acknowledge potential privacy concerns: individuals with knowledge of address hashes may be able to access the linked content, thus posing risks to data confidentiality. While the combination of blockchain and IPFS offers notable improvements in efficiency, transparency, and security for copyright governance, it necessitates the implementation of robust privacy protection measures to mitigate data exposure risks. Lastly, in contrast to the decentralized solutions, user-generated work files are also stored locally, with their file paths recorded in a MySQL database. This approach enhances file access speed, although it offers comparatively weaker security protections.
Secondly, within the digital rights licensing framework, the application layer serves as the intermediary between the foundational data storage systems and the operational business modules. This component is primarily responsible for executing the system's business logic. The back-end system is composed of both smart contract-driven and non-smart contract elements, each playing a pivotal role in upholding and enforcing copyright protections. In smart contract systems, several key functionalities are implemented. User management ensures proper authentication and access control, facilitating secure copyright transactions and the establishment of evidentiary records. The core module for copyright registration safeguards creators’ intellectual property rights, while the transaction module enables users to engage in secure and transparent exchanges of copyrights. The evidence preservation function maintains data integrity and timestamping, thereby providing robust legal support. Additionally, ecosystem contracts—such as those for authorization management and revenue distribution—introduce operational flexibility. A critical feature of this system is the infringement monitoring module, which is specifically designed to identify and track unauthorized usage of copyrighted content. This module plays an essential role in detecting potential infringements and initiating protective measures for rights holders. Central to this capability is the integration of the Shazam algorithm, a fingerprinting technology that can analyze and identify copyrighted works, thereby supporting infringement detection and verification processes. The effectiveness of both copyright registration and infringement detection relies heavily on this algorithm, which enhances the system’s ability to provide credible evidence and enforce intellectual property rights. Collectively, these components ensure the integrity and efficiency of the digital rights licensing system and support the broader objectives of copyright protection.
Finally, in the digital copyright licensing model, the business system encompasses a range of stakeholders, including content platforms, individual users, producers of digital images, audio, and video, as well as judicial and notary institutions. This component serves a crucial function by offering a user-friendly interface through which rights holders and users can conduct key operations such as copyright registration, licensing, evidence preservation, and infringement monitoring. This accessible interface facilitates the protection of intellectual property while enhancing the transparency and traceability of copyright transactions. It allows rights holders to easily register their works and assert their legal entitlements. The licensing module enables flexible authorization of copyrighted content, with smart contracts automatically executing licensing agreements to guarantee secure and transparent transactions. Moreover, the evidence solidification function utilizes blockchain to record timestamps and cryptographic hashes, thereby offering verifiable and tamper-proof proof of ownership. By integrating these functionalities into an intuitive and efficient interface, the business system enhances the overall effectiveness, security, and accountability of digital rights management, ensuring that copyright enforcement and licensing processes are carried out smoothly and reliably.
Distinct from conventional copyright licensing frameworks, the blockchain-based licensing marketplace emphasizes decentralization and operates without reliance on intermediaries. Participants are empowered to independently register copyrights, manage associated information, and carry out transactions directly via the blockchain, thereby lowering both the barriers to entry and the overall costs associated with copyright management. This decentralized structure fosters a more equitable and inclusive marketplace by mitigating issues of information asymmetry and the potential for centralized abuse of power. The inherent immutability of blockchain technology ensures that licensing activities remain transparent and traceable (Wu, 2020). Copyright holders can monitor the usage of their works within digital environments in real time, facilitating the early detection of infringements and enabling prompt legal recourse, thereby enhancing both the credibility and enforceability of copyright governance. Furthermore, the blockchain-enabled marketplace transcends traditional geographic and sectoral boundaries, allowing for truly global participation in copyright transactions. This broader reach significantly expands the potential for diverse and cross-border trading opportunities. The technology also supports fine-grained segmentation of copyright ownership, enabling flexible and tailored licensing arrangements to meet the varied needs of different stakeholders. In essence, the blockchain-based licensing ecosystem introduces transformative mechanisms to copyright management by combining the transparency of blockchain, the automation of smart contracts, and the decentralized nature of the platform. It offers a more efficient, equitable, and trustworthy environment for both copyright owners and users, thereby advancing the digital rights industry and elevating the standards of rights management.
5. Countermeasures for Using Blockchain Technology to Improve the Efficiency of Copyright Licensing
Blockchain technology has significantly transformed the copyright licensing model, offering a solution to the challenges of balancing copyright protection and the efficiency of information dissemination in the digital age. Its decentralized, immutable, and traceable nature presents a new approach to copyright licensing. First, blockchain serves as a decentralized database, allowing for the registration and authentication of copyright information through a distributed network, ensuring both the permanence and transparency of the data. This enables copyright holders to easily prove ownership without relying on third-party verification bodies. Moreover, blockchain’s smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically enforce the distribution of rights, ensuring fairness in stake allocation. Blockchain also facilitates the creation of a decentralized, transparent, and secure marketplace for digital copyright transactions. The combination of blockchain's immutability, the automated enforcement of smart contracts, and its distributed consensus model fosters a more efficient, transparent, and secure digital copyright licensing framework, offering unprecedented opportunities for managing copyright in the digital age. Nevertheless, the implementation of blockchain technology in copyright licensing still faces several challenges—technical, legal, and social—that require further exploration and research. While digital technology presents new hurdles for traditional legal frameworks, it also invigorates them, necessitating an adaptive approach to integrate new technologies. This shift will help rebuild the copyright licensing system, ensuring a balance between the rights of copyright holders and public interest. By fully embracing and leveraging blockchain technology, we can promote the growth of the digital economy and support sustainable societal advancement.
First, leveraging the decentralized nature of blockchain technology can enhance the transparency and security of digital rights licensing. Traditional copyright registration and licensing systems heavily rely on centralized authorities, which not only increase the risk of data manipulation but also create a single point of failure. If these centralized bodies experience security breaches or attacks, the entire system's stability and reliability are at risk. In contrast, blockchain technology, with its distributed ledger system, offers unparalleled protection for copyright data. Each copyright record is encrypted and stored across multiple network nodes, ensuring the information remains tamper-proof. Furthermore, the blockchain’s timestamp feature provides an accurate record of when each work was created or modified, making copyright ownership clear and traceable. This reduces the likelihood of copyright disputes and minimizes the risk of infringement. Statistics indicate that since blockchain technology has been applied to copyright management, the number of copyright disputes has decreased by approximately 20%. This highlights blockchain's significant potential to enhance the efficiency of copyright management, offering creators a more reliable and effective platform for copyright protection (Copyright Society of China, 2023). As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play an increasingly vital role in digital rights management, further fostering innovation and progress in copyright protection.
Second, by utilizing smart contracts in the digital rights licensing process, the licensing procedure can be streamlined, enhancing automation and building greater trust. Smart contracts automatically enforce the terms of the copyright license agreements, such as royalty payments, permission distribution, and management, without the need for manual intervention. This significantly reduces transaction costs and increases the efficiency of the licensing process. Furthermore, smart contracts offer unmatched transparency and verifiability in copyright transactions, which not only fosters trust between buyers and sellers but also revitalizes the growth of the copyright market. These improvements benefit both copyright holders and users, replacing the cumbersome manual processes of traditional models with a more efficient automated system, making copyright transactions smoother and more efficient. Simultaneously, transparent transaction records enhance security for market participants, reducing the likelihood of disputes and contributing to the stability and growth of the copyright market. Thus, the adoption of smart contracts is becoming an essential component of digital copyright, paving the way for the industry's future development.
Third, the blockchain-based digital copyright licensing model fosters the diverse growth of the copyright ecosystem. By introducing a decentralized system for copyright registration and certification, the barriers to registering copyrights are significantly lowered, allowing more creators to protect their original works in a more accessible and efficient manner. This change not only benefits a wider range of artists and creators but also revitalizes the creative industry as a whole. Blockchain technology goes beyond just copyright registration; it also creates a more open, transparent, and fair market environment for copyright transactions. This technological feature reduces intermediaries, simplifies the complex processes involved in copyright circulation, and encourages more efficient allocation and movement of copyright resources. Additionally, blockchain ensures the security and traceability of every transaction, boosting trust among participants. Furthermore, the blockchain-based model not only safeguards creators' rights but also stimulates the innovation potential of the cultural industry. It dismantles many of the barriers present in traditional copyright systems, offers emerging artists opportunities to showcase their work, and promotes the exchange and integration of diverse types of artwork. As a result, this new model is gradually creating a healthier and more dynamic cultural industry ecosystem, laying a solid foundation for the future growth and development of culture.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization,L.L. and Y.Q.; Software, L.L.; Formal analysis, L.L.; Investigation, L.L.; Writing – original draft, L.L. and Y.Q.; Writing – review & editing, L.L. and Y.Q.; Supervision, Y.Q. Funding acquisition, L.L. and Y.Q.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funds
This research was funded by the National Social Science Fund of China, grant number 24FFXB056;the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China,grant number 72374176;the Research Project of Zhejiang Provincial Department of Education of China,grant number Y202455057; and the Project of Zhejiang Law Society of China,grant number2024NC38.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of in-terest.
References
- Abd Ali S M. et al(2023). “Redactable blockchain: comprehensive review, mechanisms, challenges, open issues and future research directions” Security and Privacy in Blockchains and the IoT II. [CrossRef]
- Aoki R., Schiff A(2010).“Intellectual property clearinghouses:the effects of reduced transaction costs in licensing” Information Economics & Policy. [CrossRef]
- Bonnet S., Teuteberg F(2023). “Impact of blockchain and distributed ledger technology for the management of the intellectual property life cycle: a multiple case study analysis ”, Computers in Industry. [CrossRef]
- Lv N,J.“Blockchain 4.0”,Journal of Systems Science,2019 27(1):65-67.
- Bonnet S., Teuteberg F(2023). “Impact of blockchain and distributed ledger technology for the management of the intellectual property life cycle: a multiple case study analysis ”, Computers in Industry. [CrossRef]
- Blockchain whitepaper(2022). http://www.caict.ac.cn/kxyj/qwfb/bps/202212/P020230105572446062995.pdf.
- Bykovsky, Y.A., Vasiliev, A.N(2023),“Data verification in the agent, combining blockchain and quantum keys by means of multiple-valued logic”.Applied System Innovation. [CrossRef]
- Chen F, Cai Z,D.“Trust Construction and Social Adjustment of Blockchain Technology Socialization”. Studies in Science of Science. [CrossRef]
- Chu,M, Yi,J,M(2022),“NFT copyright works trading: legal risks and the way to "break the game”,Editor's Friend. [CrossRef]
- Cao S,R(2023).“The normative effect and practical optimization of blockchain smart legal contracts: From the perspective of alleviating the dilemma of traditional smart contracts”,Technology and Law(Chinese and English). [CrossRef]
- Chen,L,Y,Ma,X,F,He,J, et al(2023).“Privacy authorization method of blockchain smart contract based on TrustZone”.Journal of Computer Applications.
- Copyright Society of China(2023).“Report on the use of new technologies in the field of copyright” https://www.ncac.gov.cn/xxfb/ywxx/202302/t20230228_863980.html.
- Chen,L,Y,Ma,X,F, He,J et al(2023).“Privacy authorization method of blockchain smart contract based on TrustZone”.Journal of Computer Applications.
- Data Bureau(2016).“Ministry of Industry and Information Technology: 2016 White Paper on China's Blockchain Technology and Application Development”.
- Huang,J,R,Liu,B,X,Zhang,L,et al(2023).“Decentralized anonymous identity authentication model based on smart contract and non-fungible token”,Computer Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Lai,L,N, Li Y,M(2023).“Blockchain empowerment: enterprise intellectual property protection under the paradigm of networked open innovation”Science and Technology Management Research.
- Li R,H., “Hierarchical and Nested Governance Model of Digital Copyright Law under Blockchain: Theoretical Logic and Implementation Path ”. Journal of Publishing and Distribution Research. [CrossRef]
- Li Z,S(2023).“Research on UGC copyright protection based on blockchain technology”.Network Security Technology and Application.
- Li,Y,M,Lai,L,N.(2022)“The dilemma and the way out of the whole chain protection of digital copyright in the context of blockchain”.Science and Technology Management Research.
- Li,Q,X,Ma C,Y,Xie,L,et al(2024).“Mechanism and Strategy of Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chain Value Creation: An Economic Analysis under Quality Information Asymmetry Management World”.
- Miao,Z,Y(2023),“On the Application and Regulation of Blockchain Technology——Starting from theCase of Tencent v. Lao Gan Ma”Journal of Chongqing University(Social Sciences),Vol.
- Magnuson, William J(2020). “Blockchain democracy: technology, law and the rule of the crowd.”Cambridge University Press.
- Melanie S(2015)..“Blockchain: Blueprint for a new economy” O'Reilly Media, Inc.
- Ma Z,G, Wang X,Q(2023).“Construction of Metaverse NFT Mapping Rights”,Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University(Social Sciences). [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto S(2019).“Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system”.https://bitcoin.org/en/bitcoin-paper.
- Qian,H,Zheng,Z,H, Rong,B,J,et al(2023).“RPFT:High-efficiency consensus algorithm based on PoW”.Journal of Chinese Computer Systems. [CrossRef]
- Ren,R,J, Gui,Y,C, Pu D,M.(2024)“Research on New Content Production under AIGC and Blockchain Service Network Architecture” Journal of Publication and Distribution Research. [CrossRef]
- Ren A,Q,(2022)“The dilemma and breakthrough of collective copyright management in China under blockchain technology” Journal of Publishing and Distribution Research. [CrossRef]
- Wang,L, Xiang,J,G,“Construction of real-time audit framework based on blockchain technology”Finance and Accounting Communication. [CrossRef]
- Wang,Y, Sheng,X, Xue,X,Q(2022).“Research on Blockchain Technology and Internet Financial Risk Prevention and Control Path”,Studies in Science of Science. [CrossRef]
- Wang J,Y,,Wang,T, Yuan,W,L, et al(2023).“A review of the development process of distributed ledger technology”.Computer Application Research. [CrossRef]
- Wu,Y(2024).“Digital Business Environment: China Issues and the Path of Rule of Law” Northern Law Science. [CrossRef]
- Wu,Y(2020).“On the private law structure of smart contracts”.Jurist. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., Sun, Y.. (2023),“Research on the infringement governance of online music under the mode of short video copyright sharing: Based on the transaction cost theory”,Journal of Beijing Union University(Humanities and Social Sciences), Vol.21 No.1,p.62-71.
- Xu,C,Y,Chen,Y,Q,Wang,H,J(2022).“The impact of diversified development on the level of enterprise risk-takingj under the empowerment of blockchain——Based on the perspective of the digital economy era”.China Soft Science.
- Xiong Q(2022).“Geomatics of Wuhan University(Philosophy and Social Science)”. [CrossRef]
- Zhang,G,C, Tang,H,Y, Chen,J,H, et al(2021).“Blockchain-based Digital Music Copyright Management System” . Journal of Computer Applications.
- Zomaya A Y., et al(2021). “Circuit copyright blockchain: blockchain-based homomorphic encryption for IP circuit protection” IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).