Submitted:
19 April 2025
Posted:
21 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
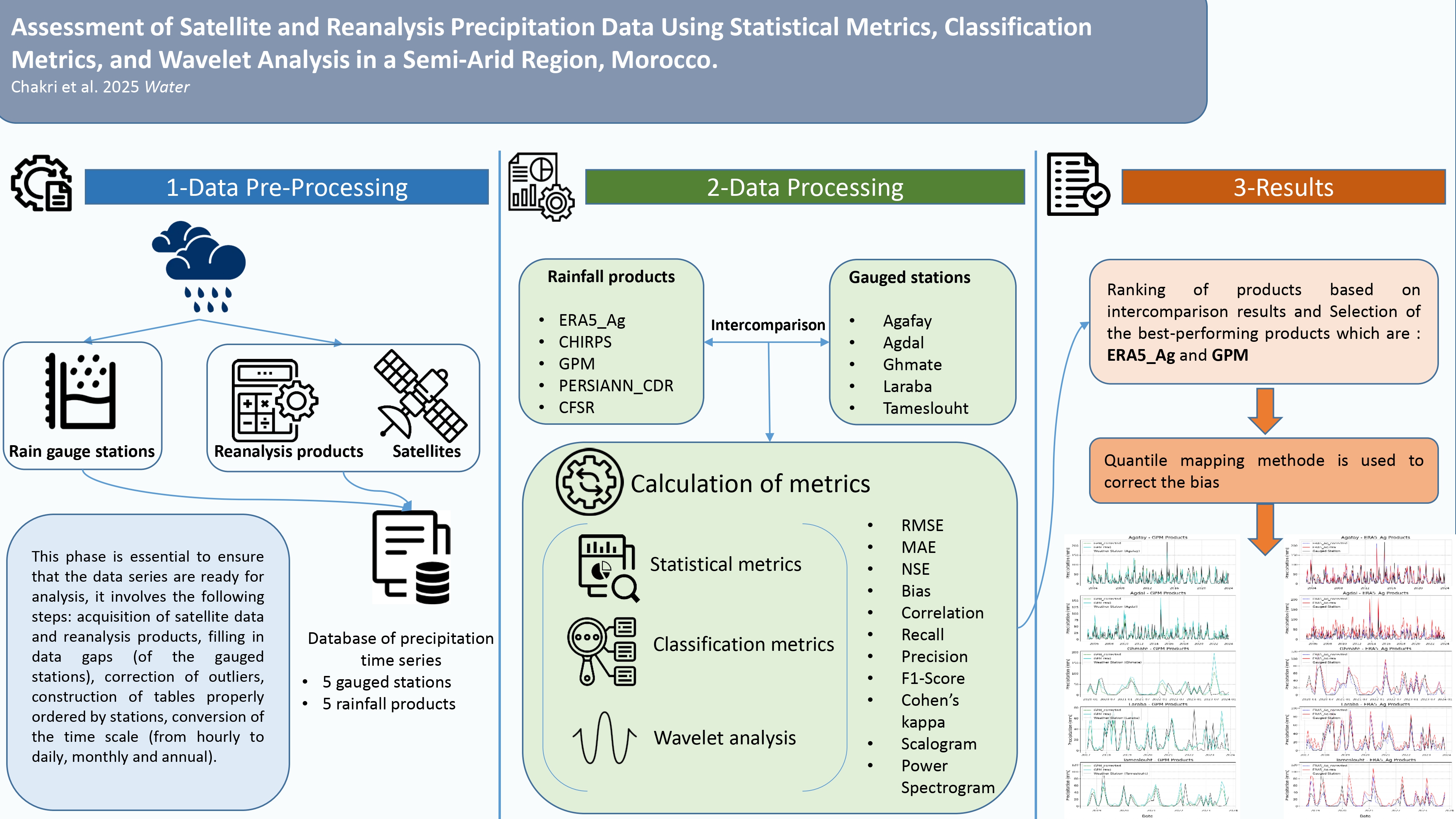
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Characteristics of Rainfall Products and Gauged Stations
3.2. Statistical metrics
3.3. Classification Metrics and Wavelet Analysis
3.4. Application of Quantile Mapping for Bias Correction
4. Results
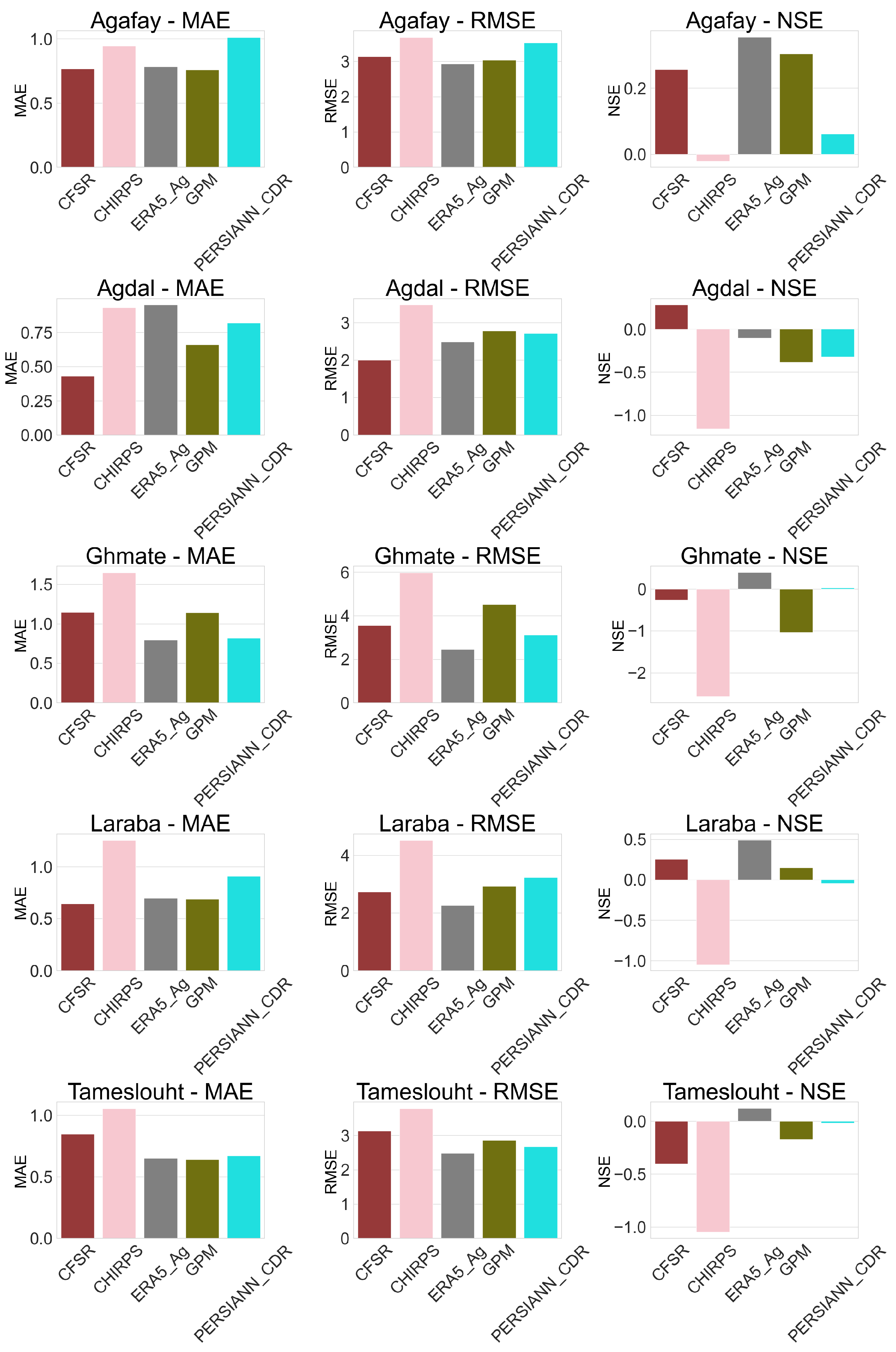
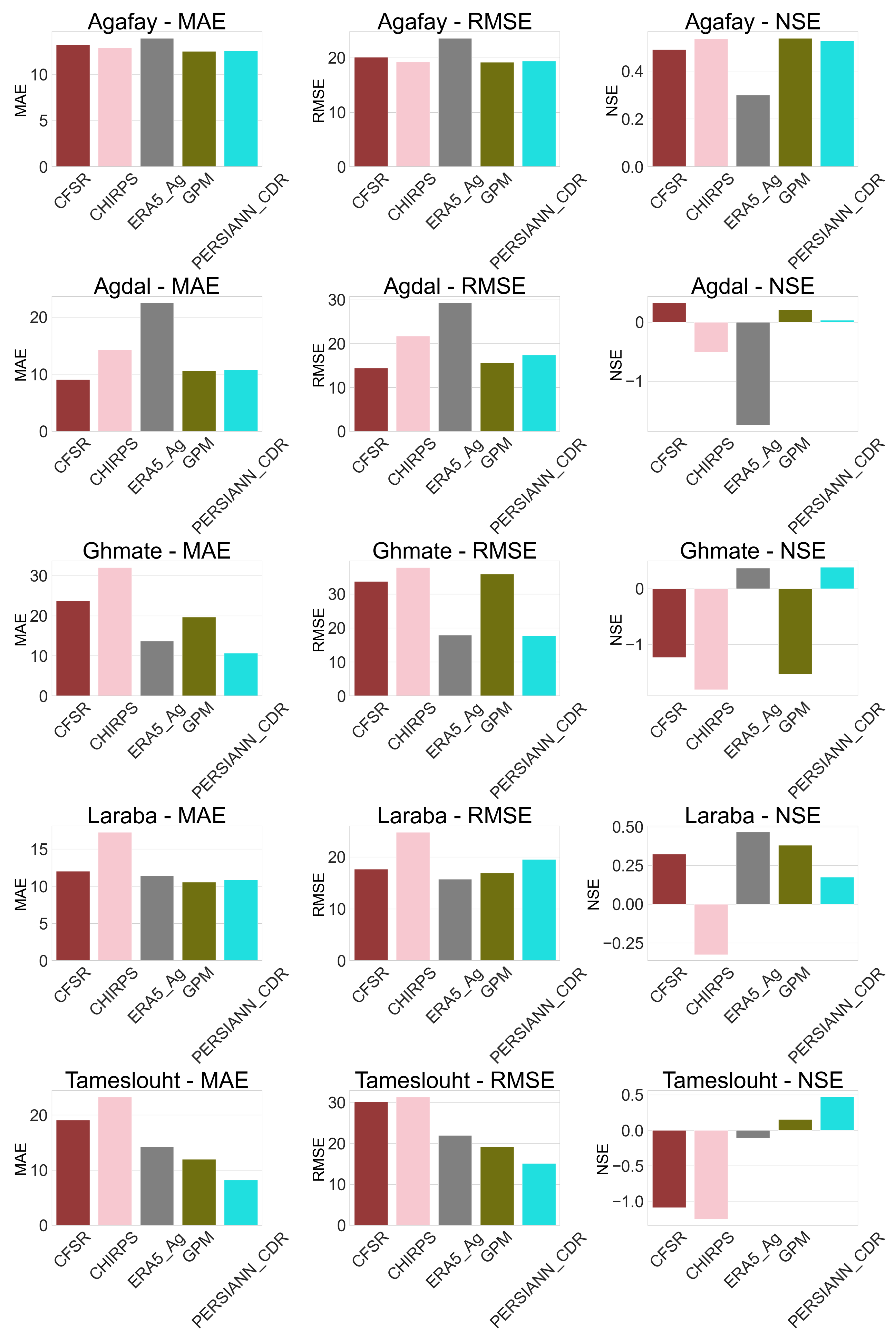
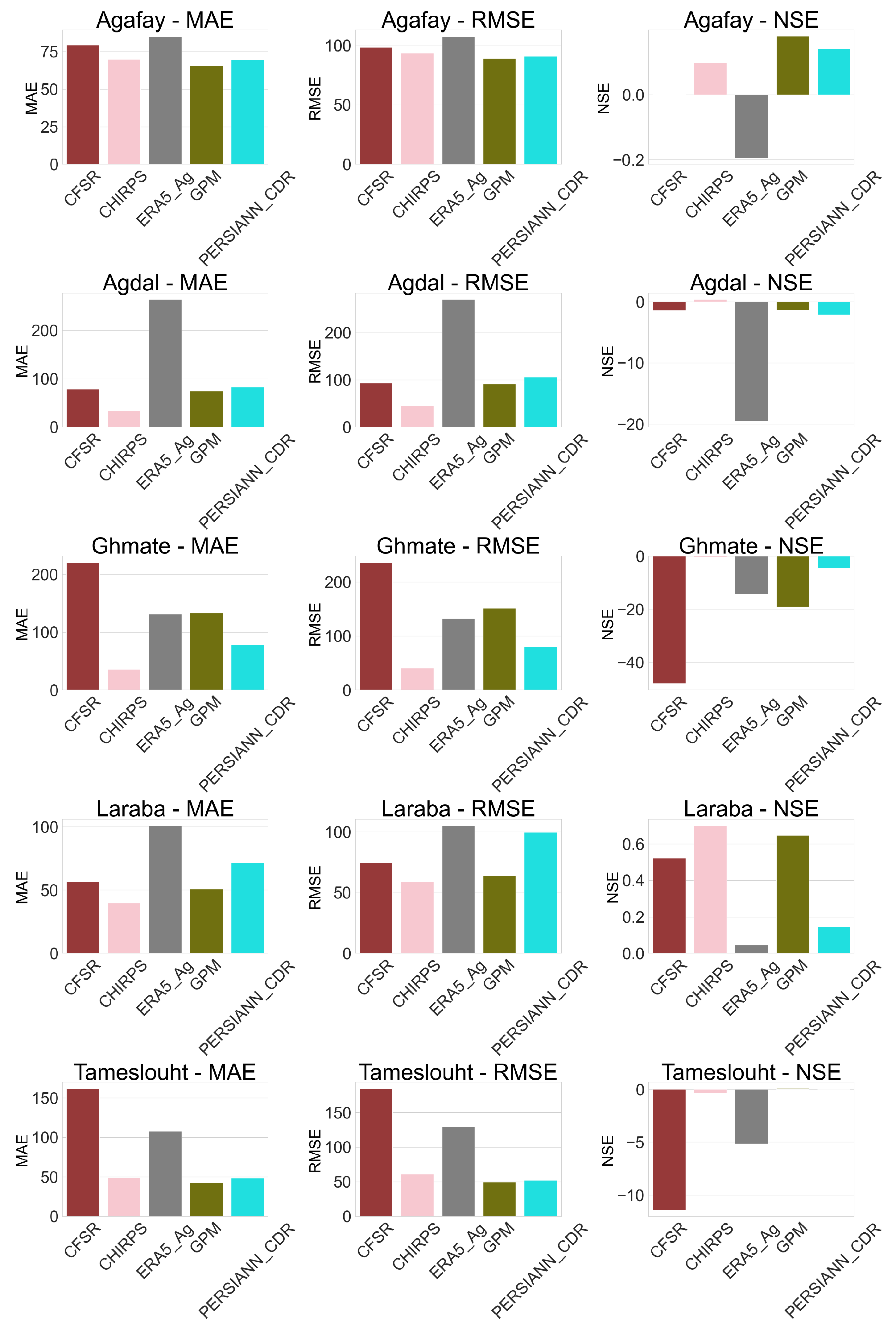
4.1. Application of Statistical Continuous Metric for Raw Data (Daily, Monthly and Annually)
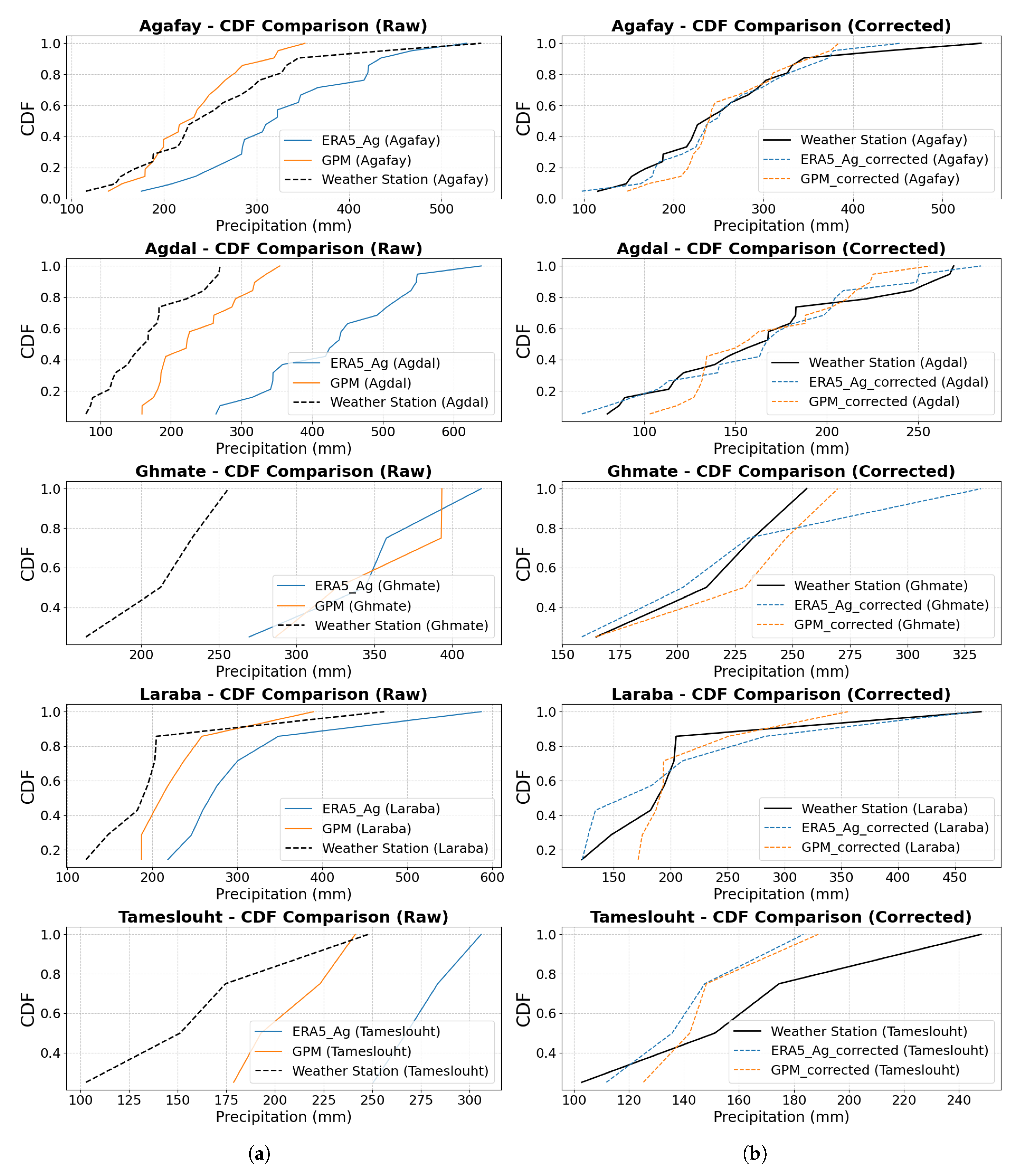
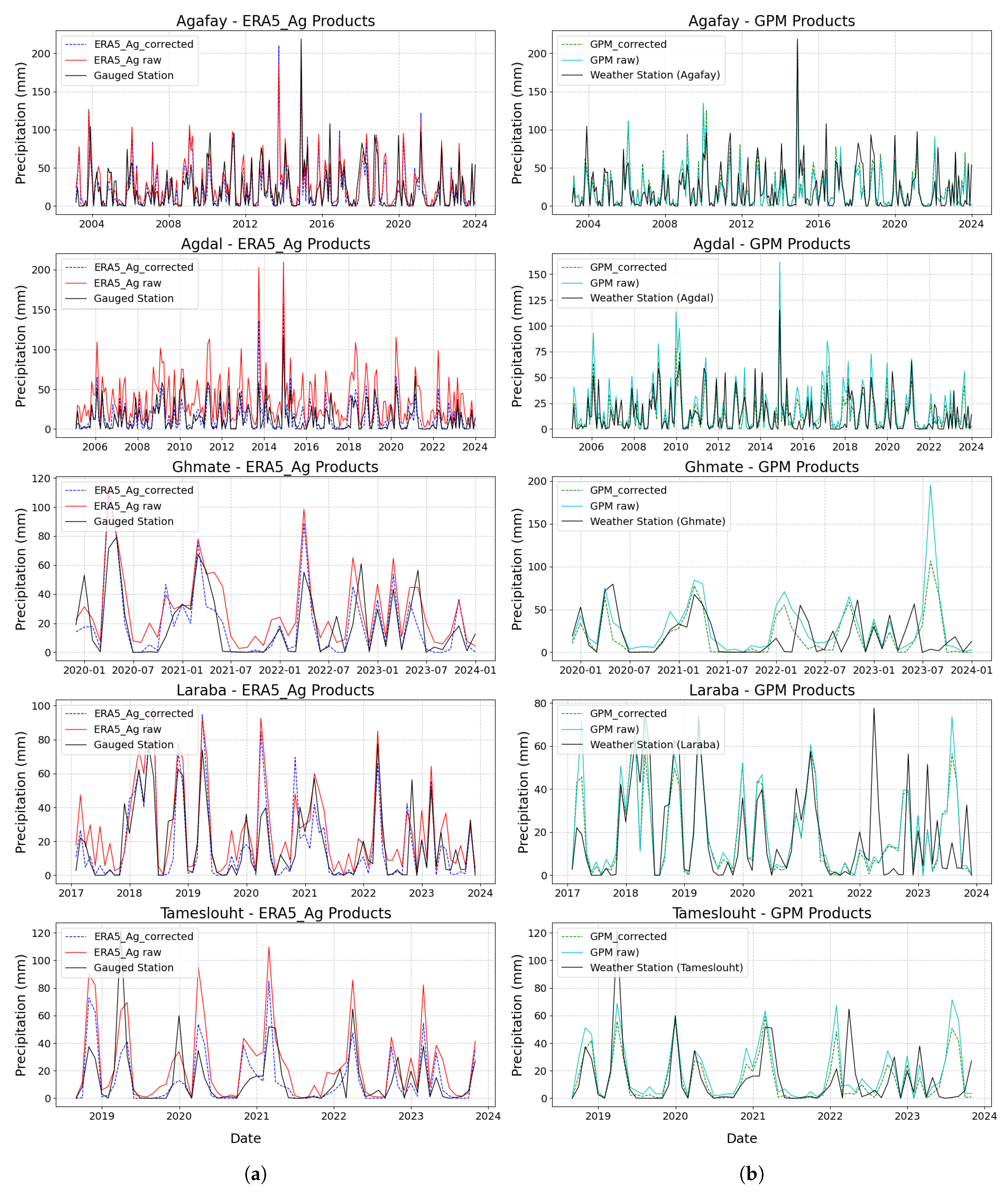
4.2. Evaluation of Bias in Rainfall Products
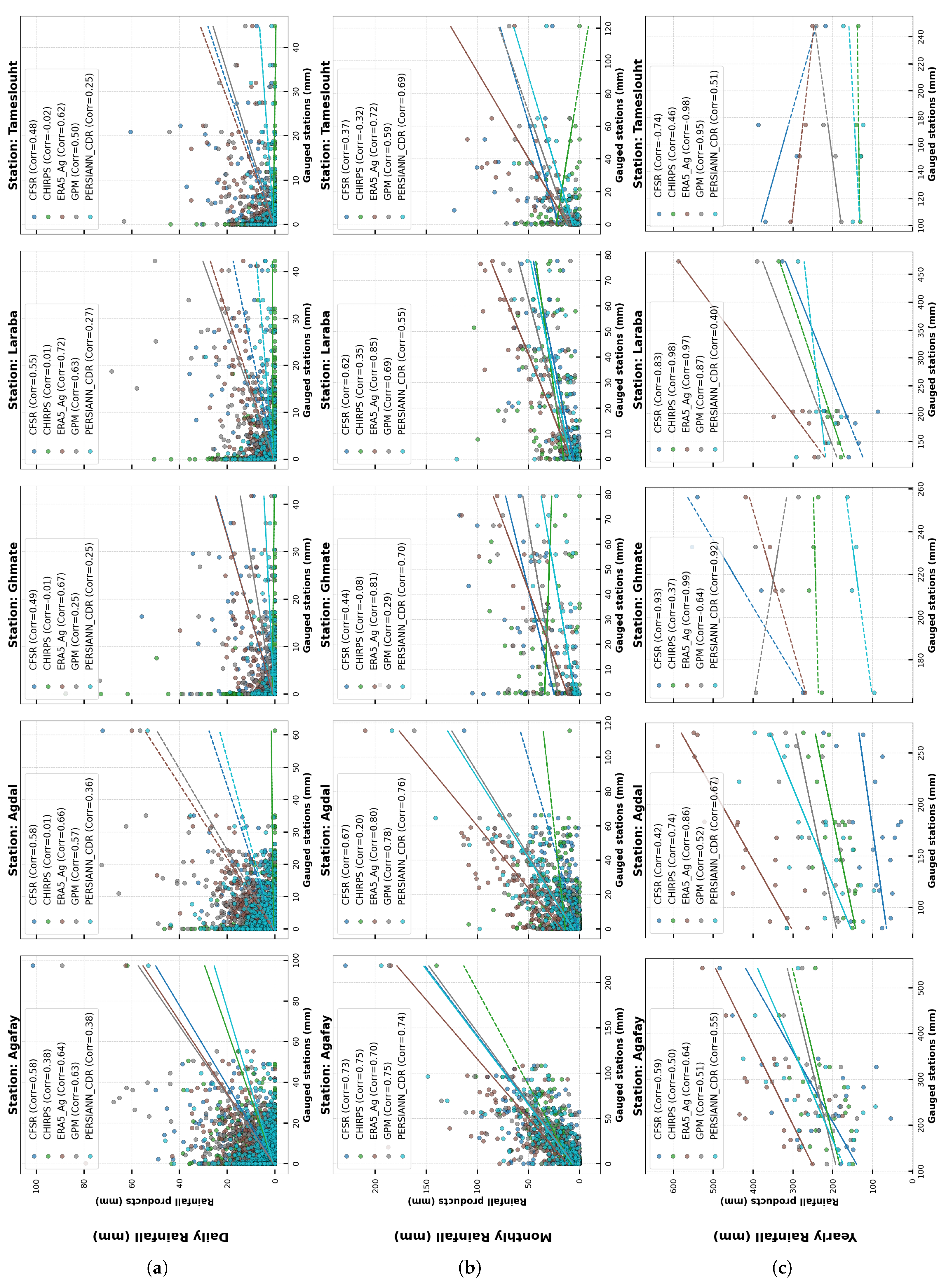
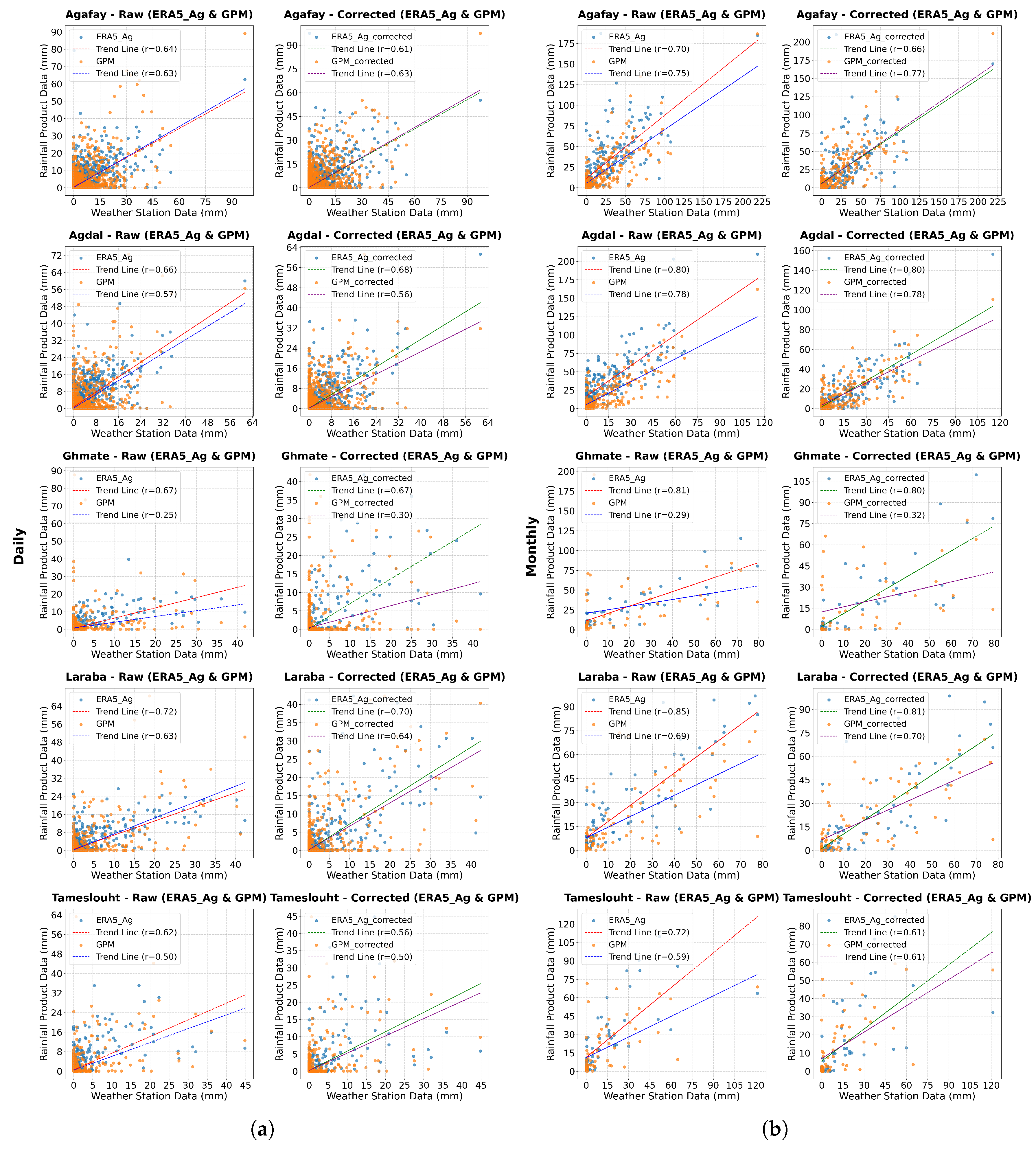
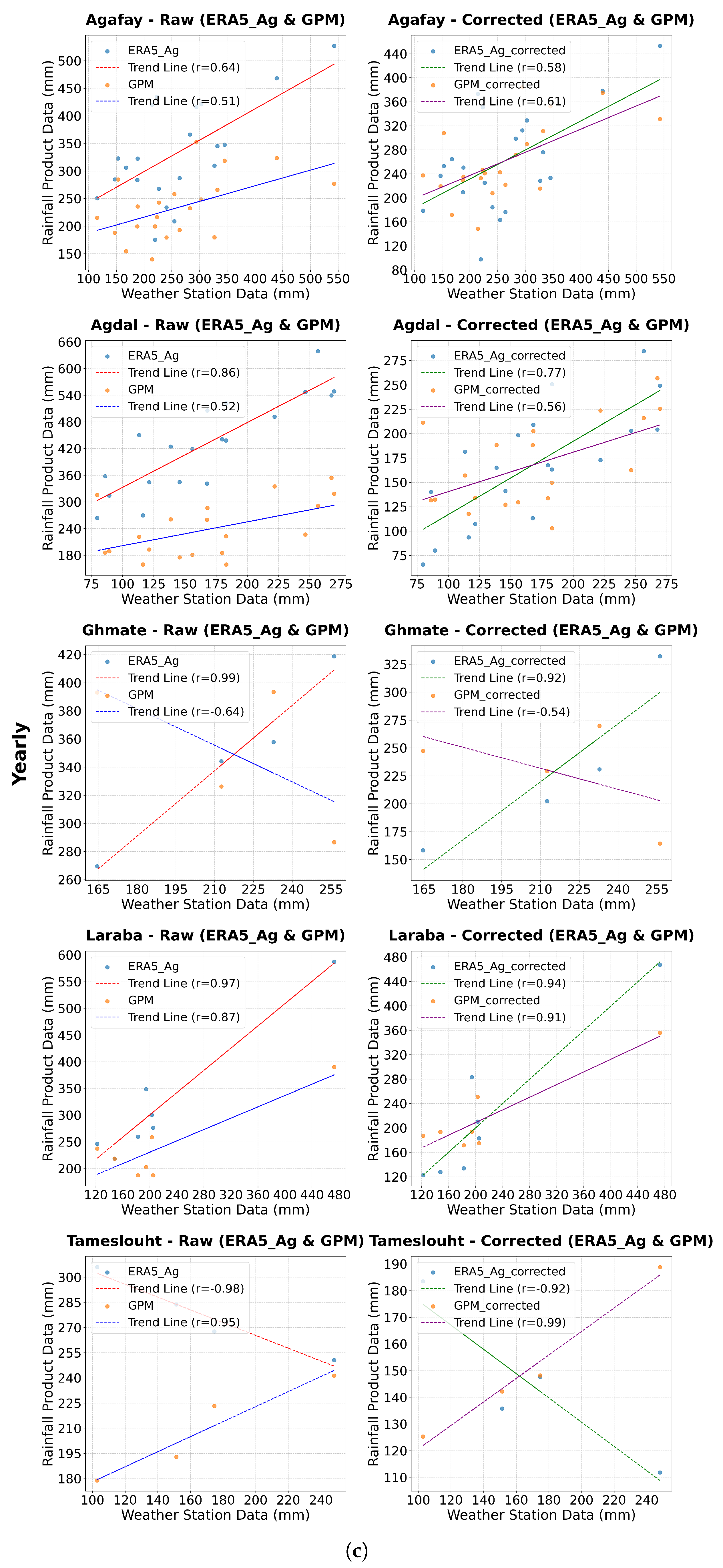
4.3. Correlation Analysis of Rainfall Product Performance
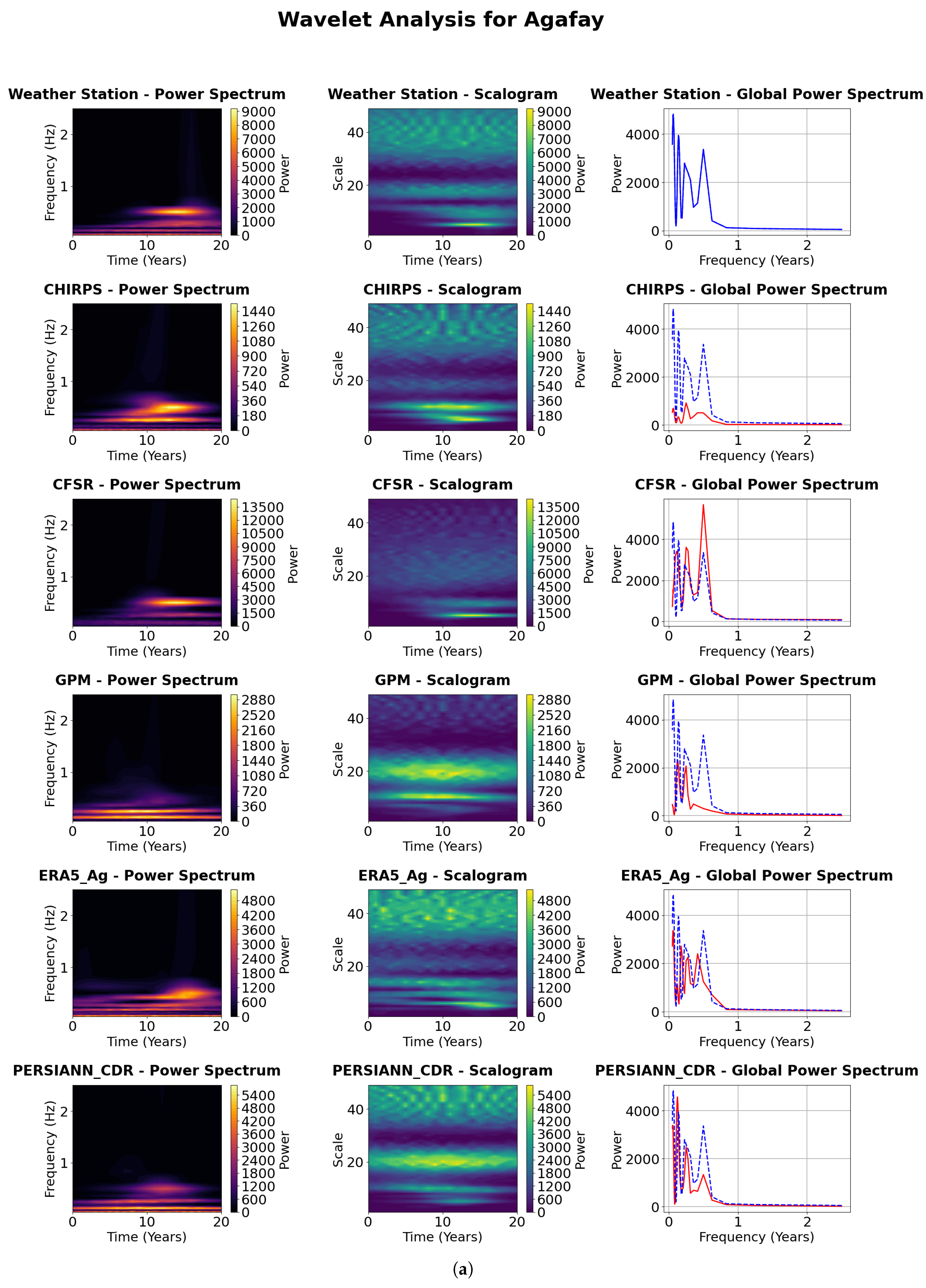
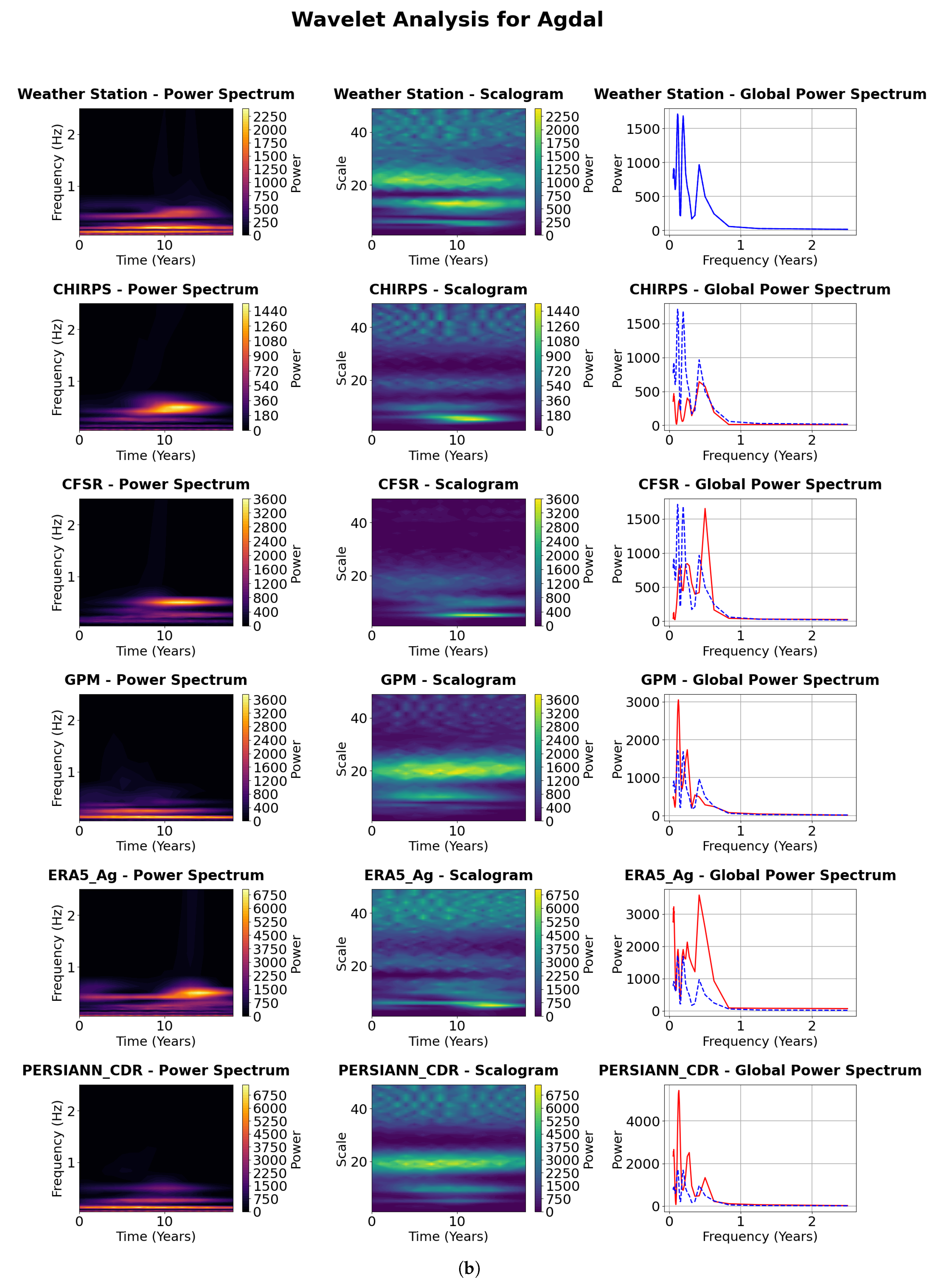
4.4. Wavelet Approach to Temporal and Extreme Event Analysis
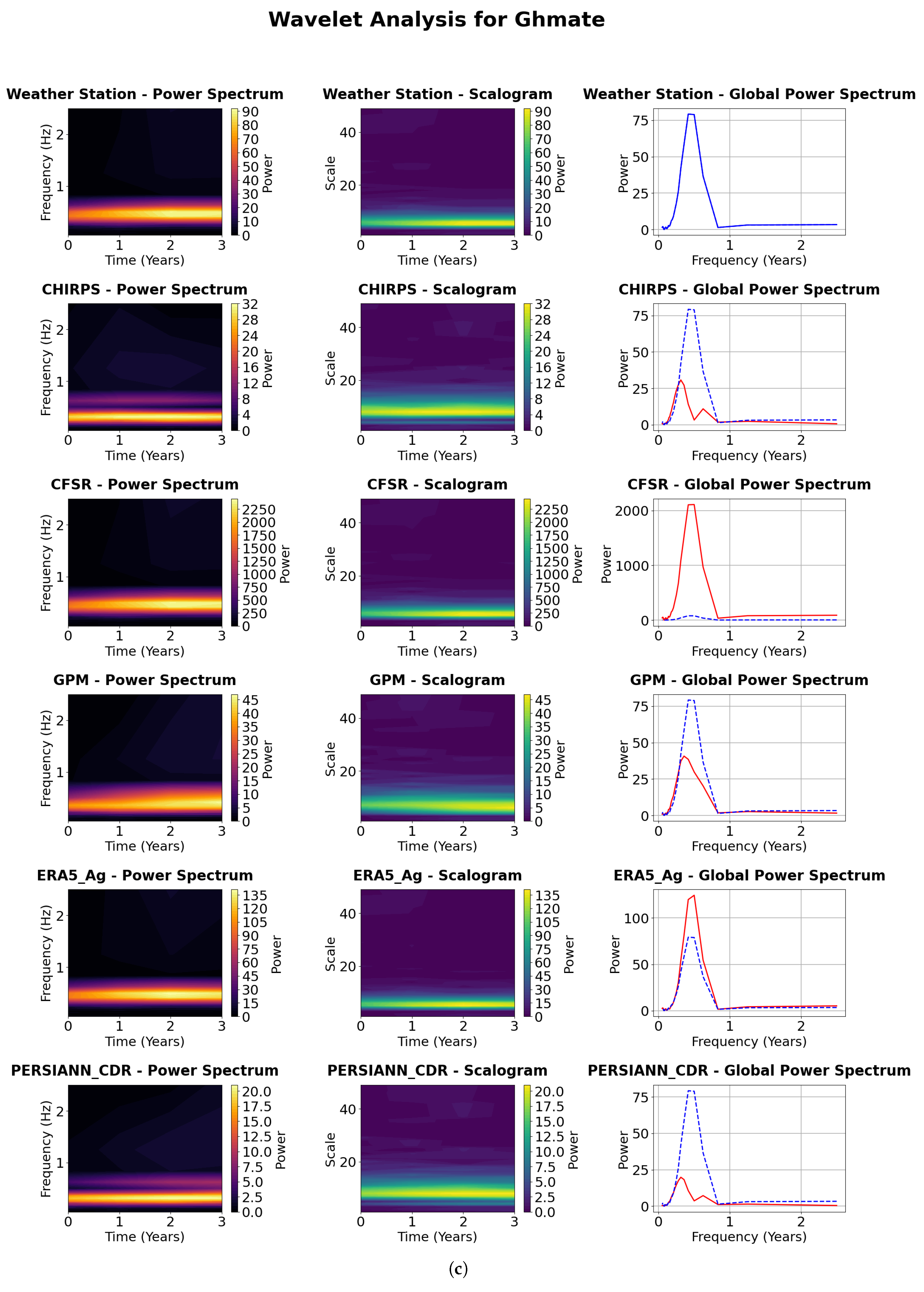
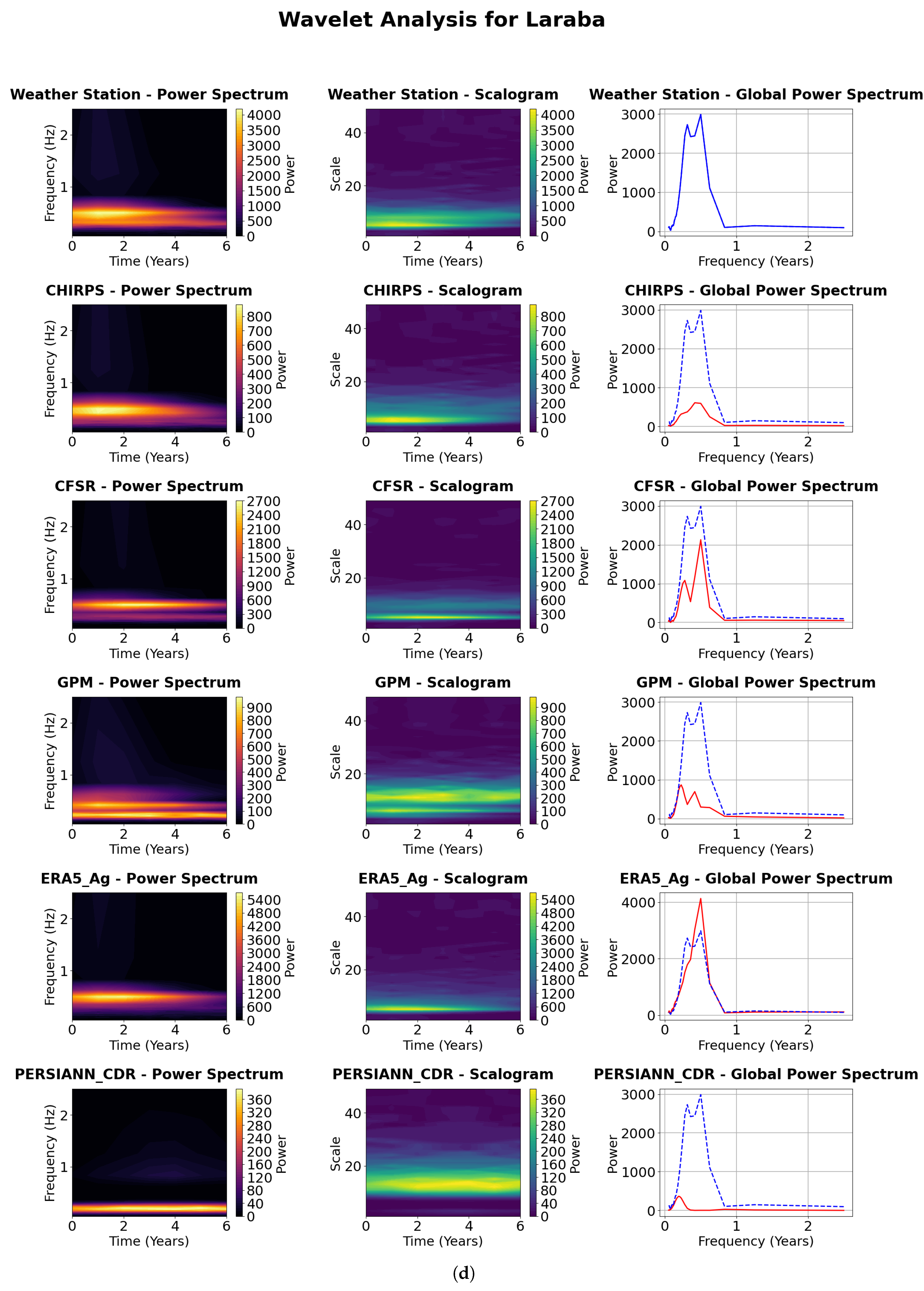
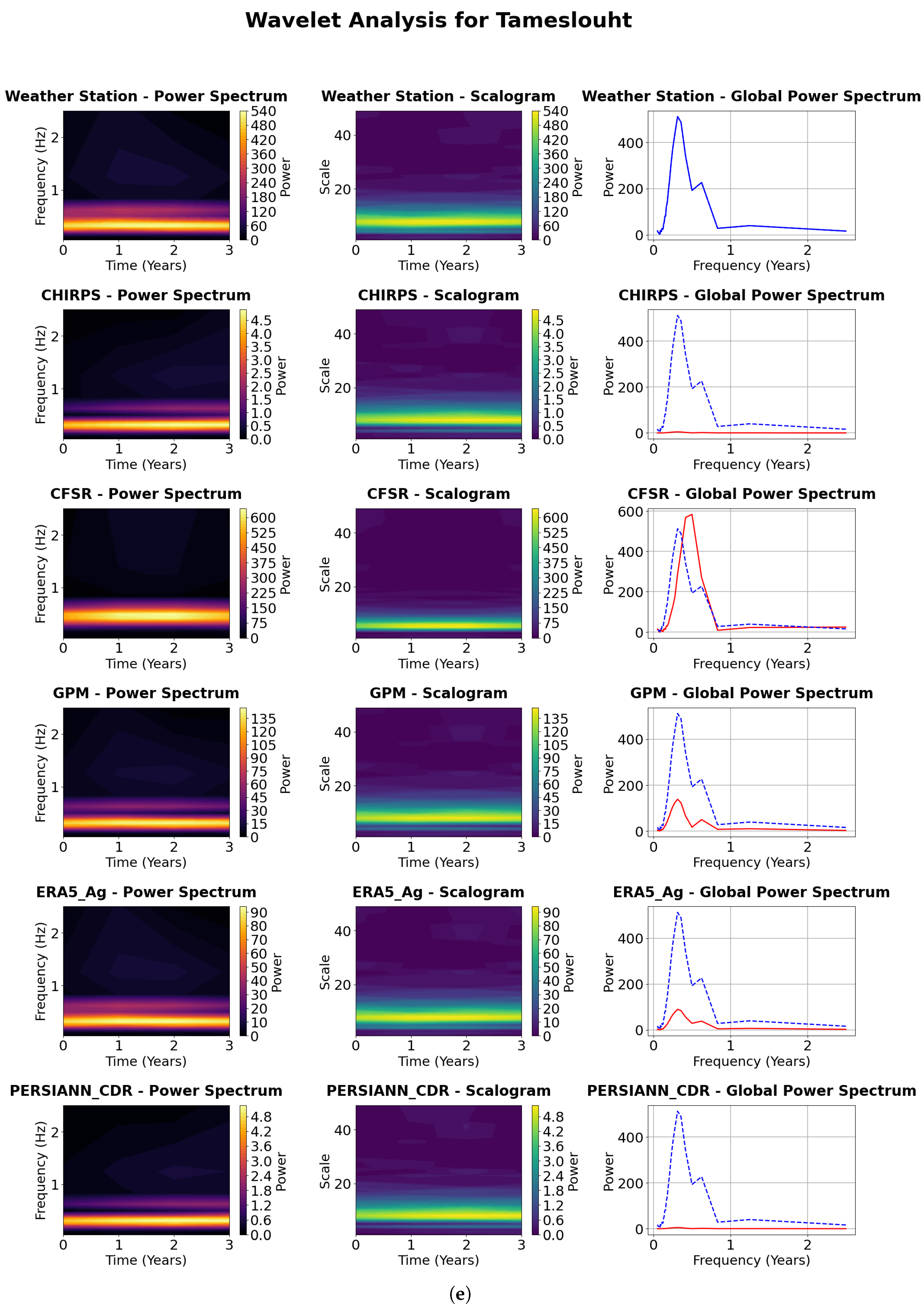
4.4.1. Visualization of the Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT)
4.4.2. Power Spectrum Analysis
4.4.3. Scalograms Analysis
4.4.4. Global Power Spectrum Analysis
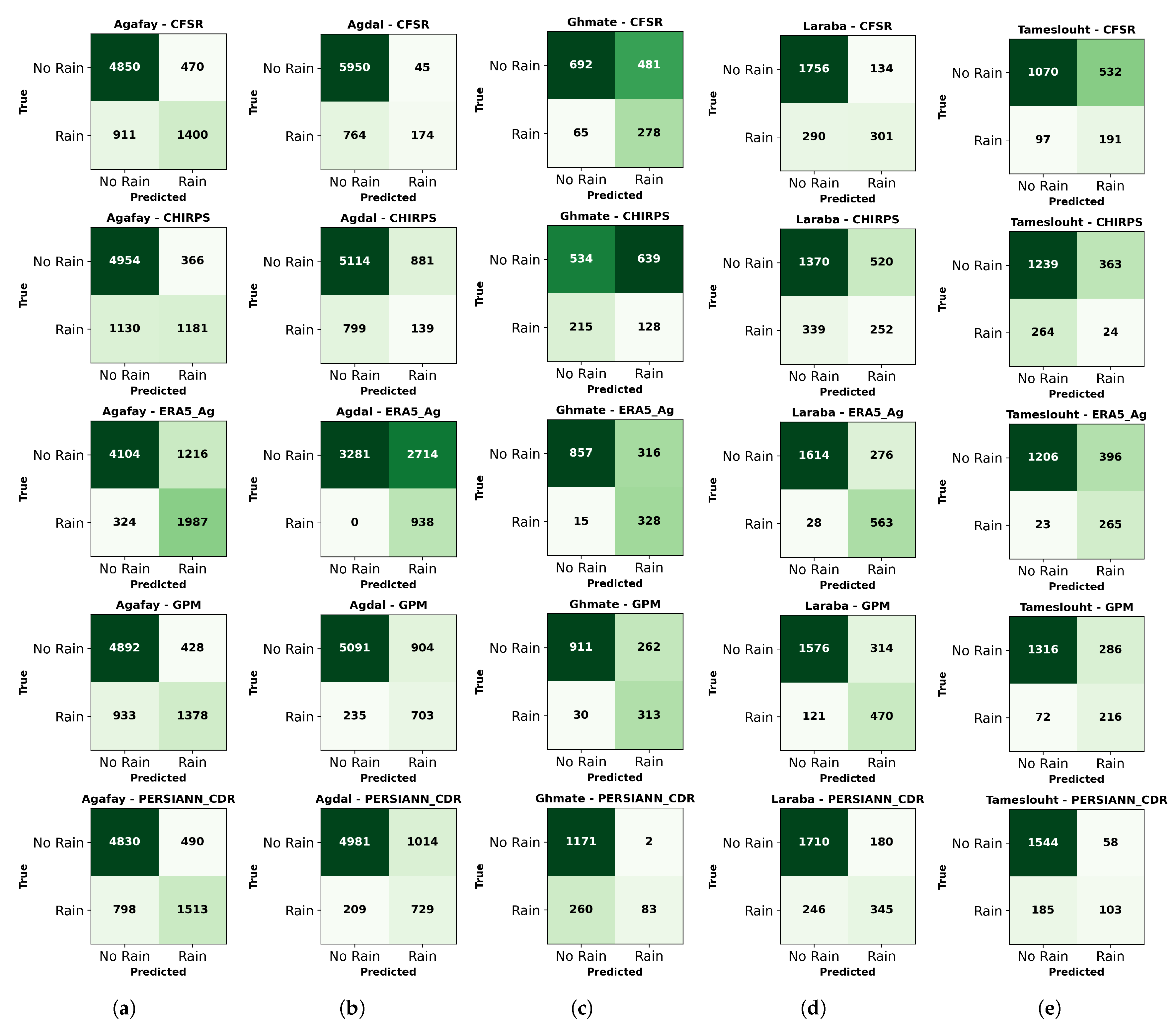
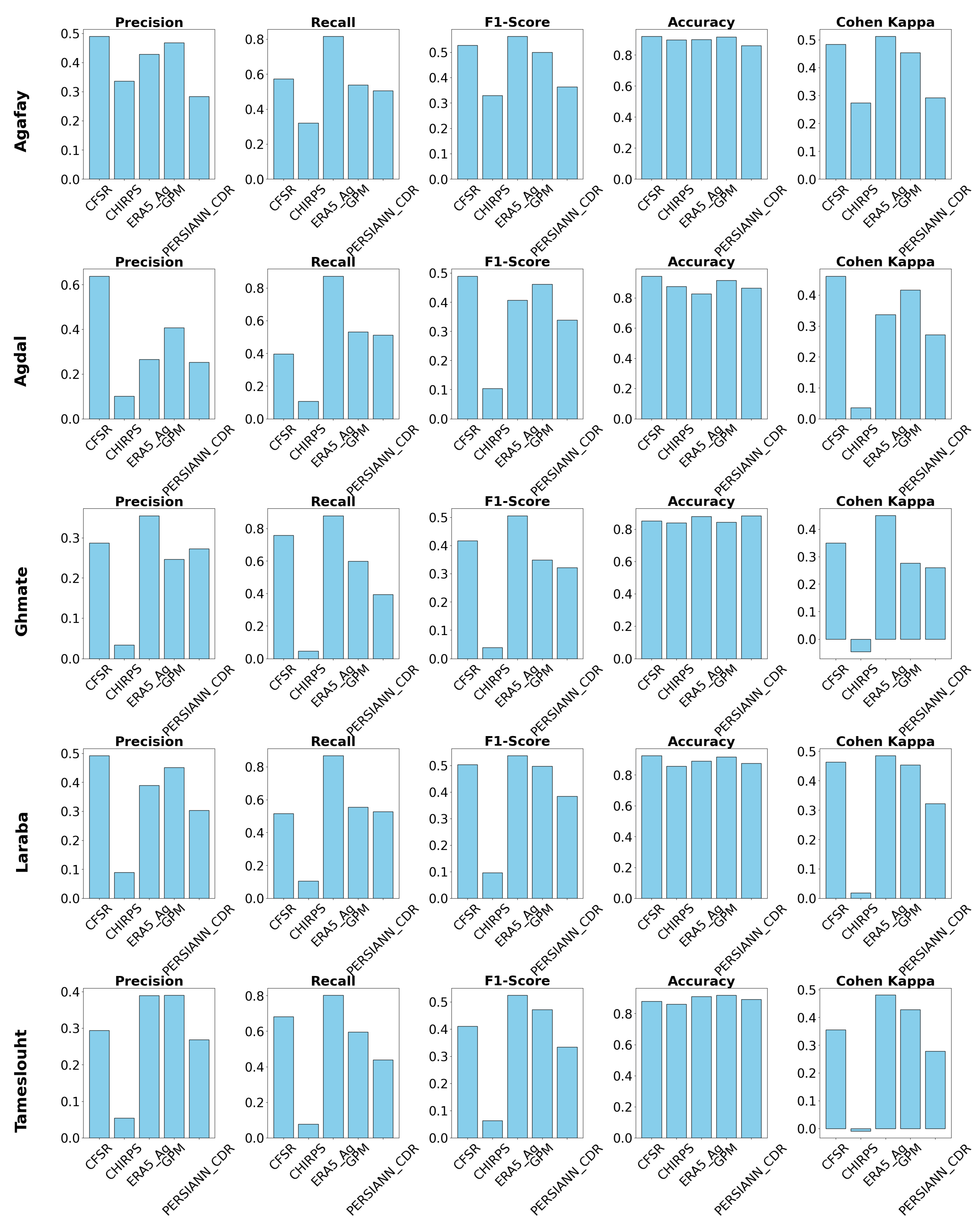
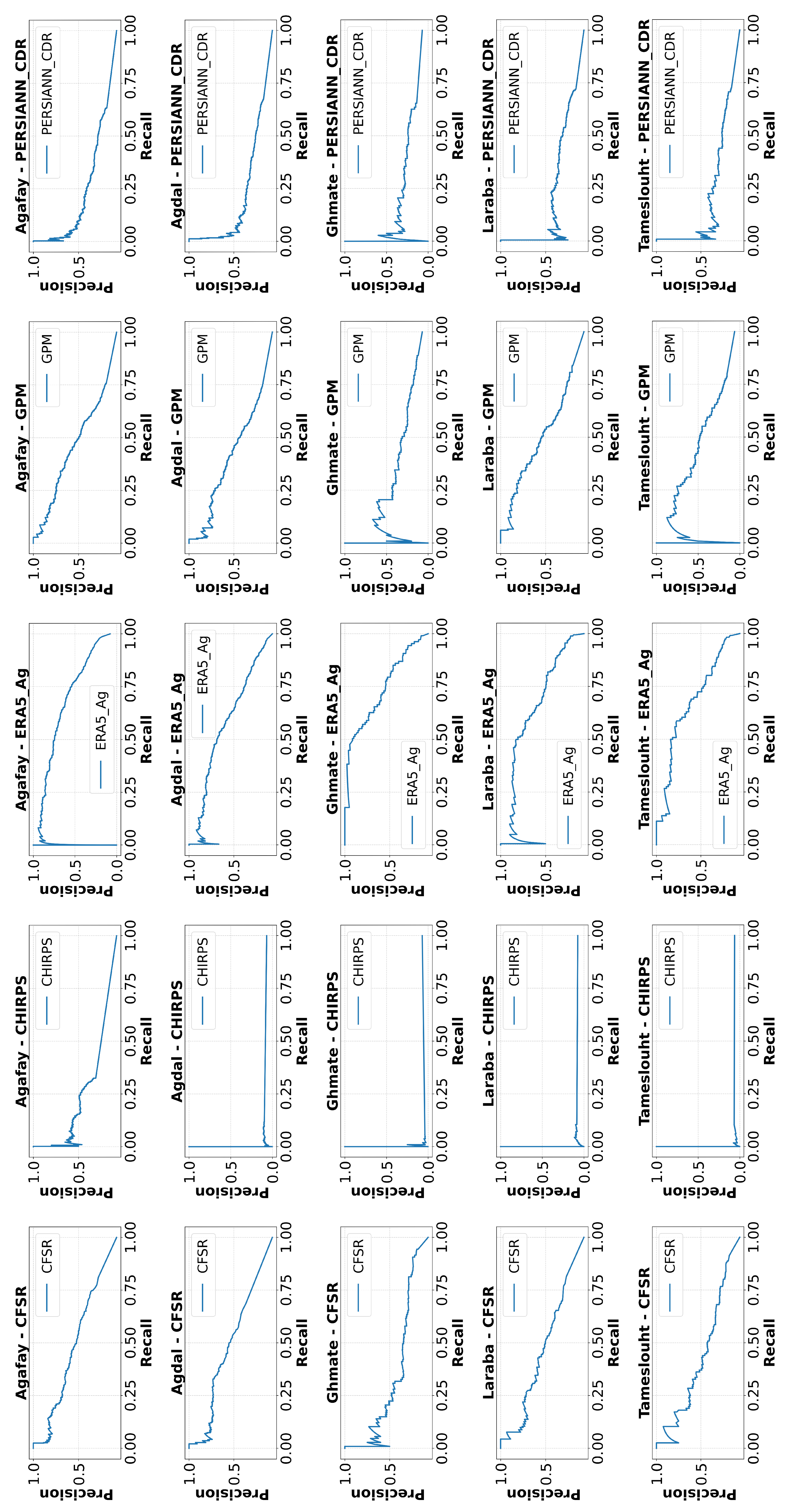
4.5. Classification Metrics Analysis
- Products with Balanced Performance : The GPM and PERSIANN_CDR products demonstrate relatively stable curves across several stations, notably Agafay, Agdal, and Laraba. This stability indicates their ability to balance precision and recall effectively.
- Products with Variable Performance : The ERA5_Ag product exhibits variability depending on the station. For example, at Ghmate, the curve shows better stability; however, at Tameslouht, precision decreases rapidly as recall increases.
- Products with Limitations : The CHIRPS and CFSR products display very steep curves for most stations, with precision dropping quickly. This trend indicates a challenge in maintaining a good balance between precision and recall.
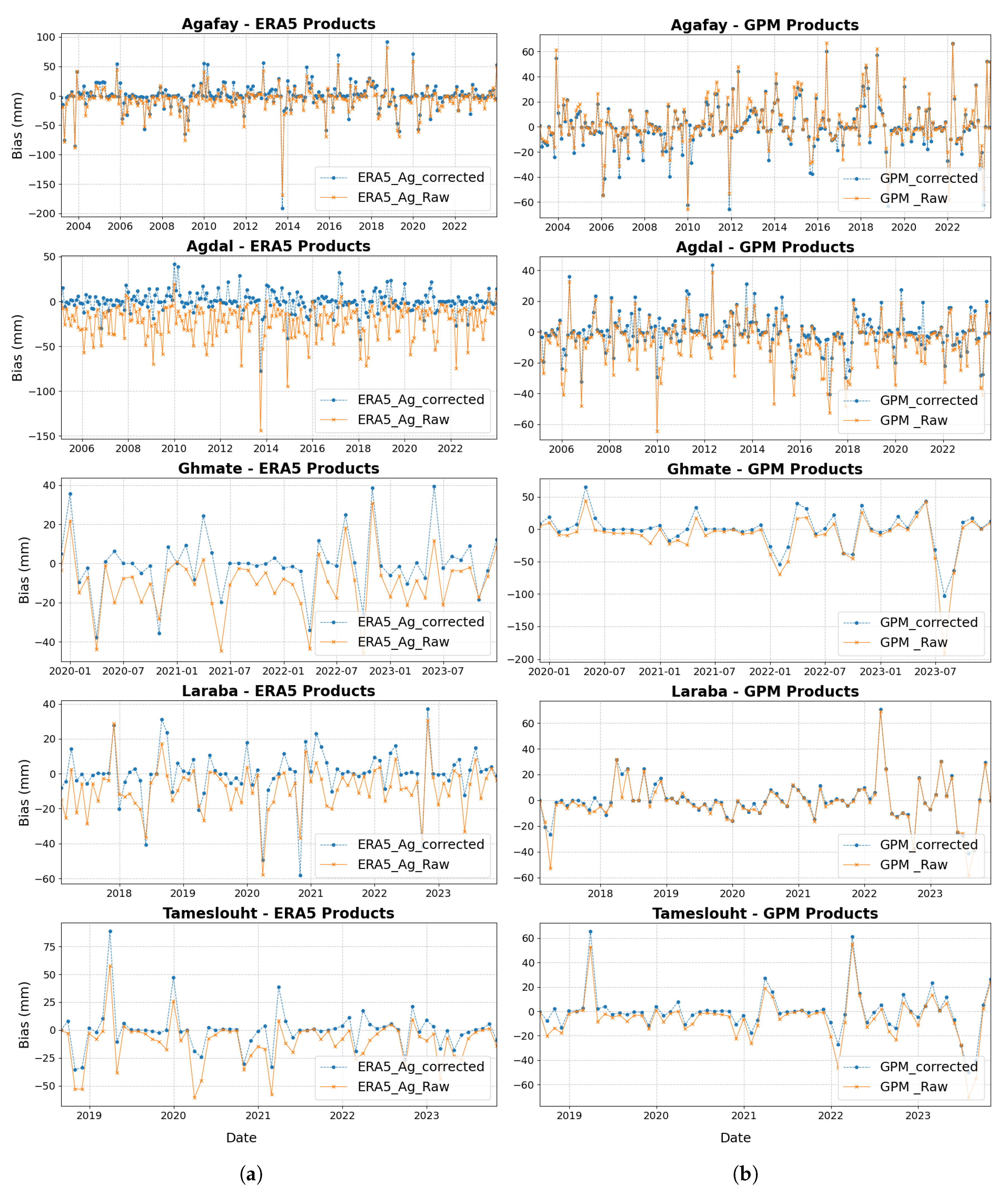
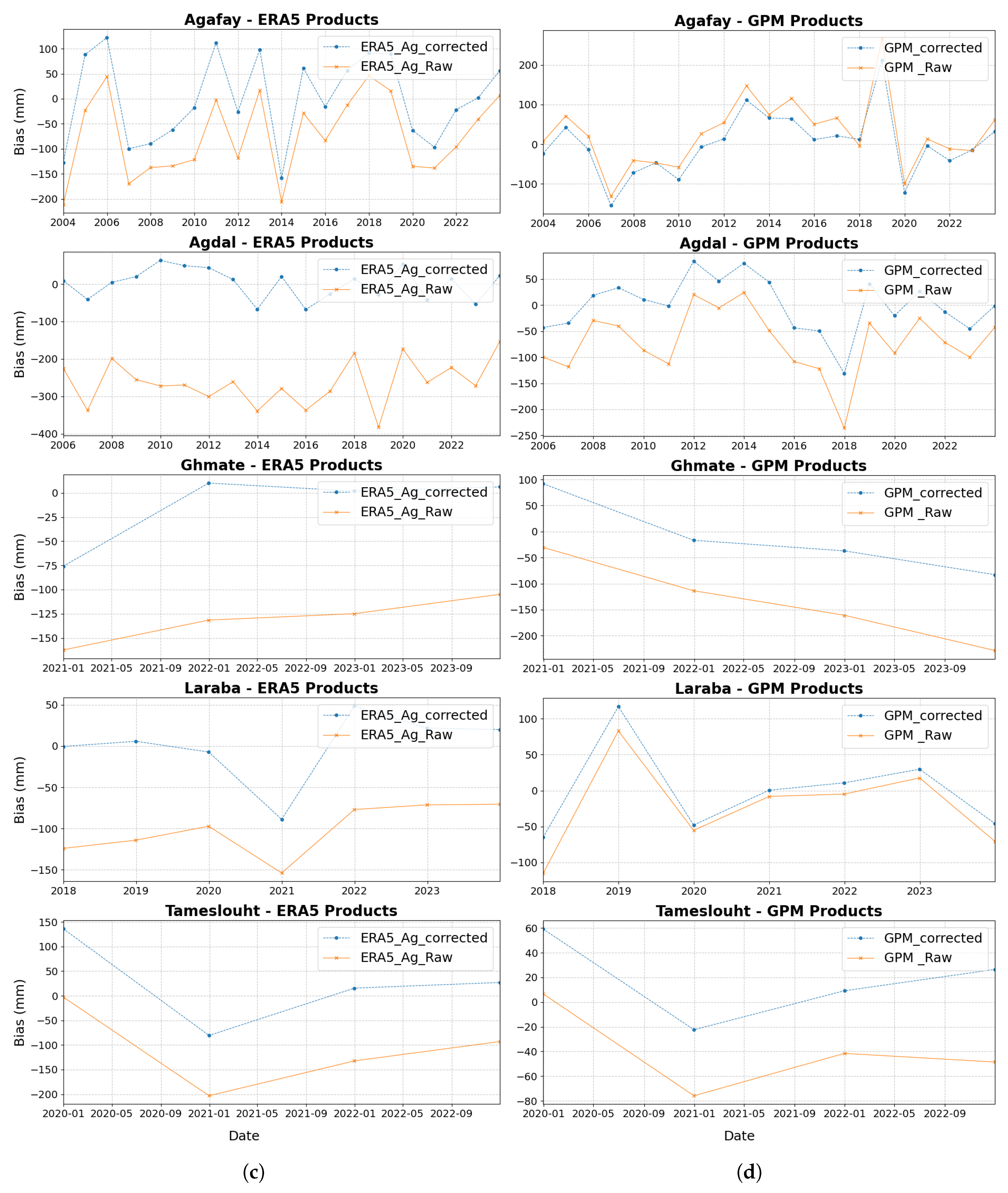
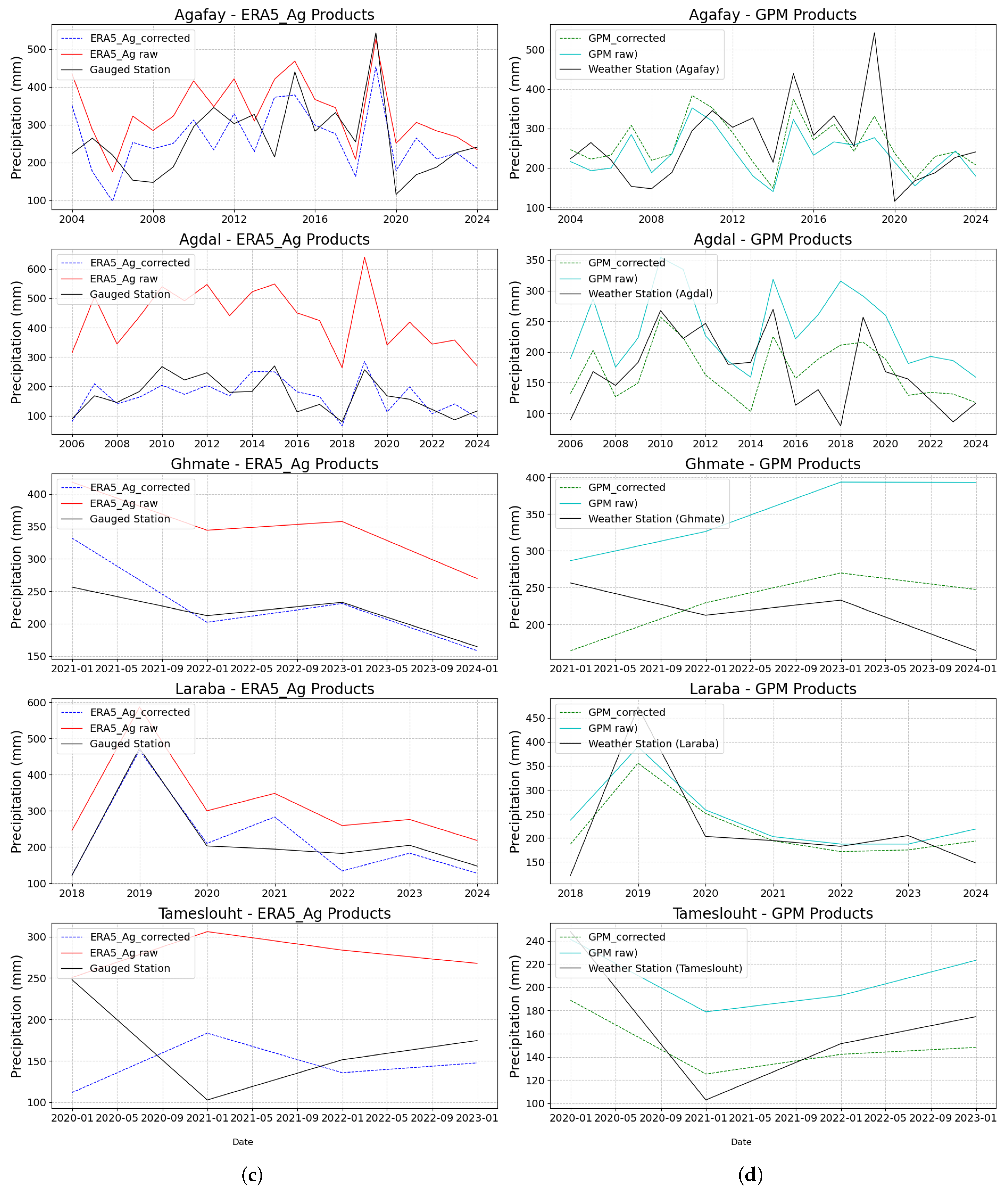
4.6. Application of Bias Correction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrett, E. The Estimation of Monthly Rainfall from Satellite Data. Monthly Weather Review 1970, 98, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.; Martin, D. The Use of Satellite Data in Rainfall Monitoring; Academic Press, 1981.
- Ebert, E.; Manton, M.; Arkin, P.; Allam, R.; Holpin, G.; Gruber, A. Results from the GPCP Algorithm Intercomparison Program (AIP). Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 1996, 77, 2875–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.; Manton, M. Performance of Satellite Rainfall Estimation Algorithms during TOGA COARE. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 1998, 55, 1537–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P. Global Precipitation: A 17 Year Monthly Analysis Based on Gauge Observations, Satellite Estimates, and Numerical Model Outputs. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 1997, 78, 2539–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphugwi, M.; Blamey, R.; Reason, C. Rainfall Characteristics over the Congo Air Boundary Region in Southern Africa: A Comparison of Station and Gridded Rainfall Products. Atmospheric Research 2024, 311, 107718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobard, R.; Gosset, M.; Menzel, P.; et al. Comparing Satellite and Surface Rainfall Products over West Africa at Meteorologically Relevant Scales during the AMMA Campaign Using Error Estimates. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology 2010, 49, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romilly, T.; Gebremichael, M. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates over Ethiopian River Basins. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2011, 15, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaddor, I.; Belaroui, A.; al, e. Hydrological Simulation (Rainfall Runoff) of Kalaya Watershed (Tangier, Morocco) Using Geo Spatial Tools. ResearchGate 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qadem, A.; Belaroui, A.; al, e. Contribution a l etude Hydroclimatique d un Bassin Versant Montagnard Semi Aride?: Cas Du Bassin Versant de Zloul, Moyen Atlas. ResearchGate 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux, V.; Hajhouji, Y.; al, e.; Dimopoulos, Y.; Dezetter, A.; al, e. Modelisation de La Relation Pluie Debit a l aide Des Reseaux de Neurones Artificiels. ResearchGate 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Taia, S.; Belaroui, A.; al, e. Modelisation de l hydrologie et de l erosion Du Bassin Versant de l Oued Beht. ResearchGate 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.; Knapp, K.; Cecil, D.; Nelson, B.; Prat, O. PERSIANN CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multi Satellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Rowland, J.; Romero, B.; Husak, G.; Michaelsen, J.; Verdin, J. The Climate Hazards Infrared Precipitation with Stations a New Environmental Record for Monitoring Extremes. Scientific Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horanyi, A.; Munoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Stocker, E.; Bolvin, D.; Nelkin, E.; Tan, J. GPM IMERG Final Precipitation L3 Half Hourly 0. 1 Degree x 0.1 Degree V06 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; al, e. Impact of Topography and Climate on the Performance of Satellite Based Rainfall Estimates in Mountainous Regions. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, J.; Hsu, K.; al, e. Evaluation of Satellite Based Rainfall Estimates over Diverse Climatological Regions. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2011, 12, 767–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; al, e. Assessing the Impact of Different Reanalysis Products on Rainfall Estimates in Arid and Semi Arid Regions. Journal of Climate 2018, 31, 8915–8934. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.; al, e. Performance of the TRMM Based Multi Satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) in Assessing Rainfall in Africa. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2015, 19, 4975–4992. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, R.; al, e. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Precipitation Estimates from Satellite Based Products and Ground Stations in Tropical and Subtropical Regions. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2014, 15, 2177–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Er Raki, S.; Le Page, M.; Hanich, L.; Fakir, Y.; Merlin, O.; Mangiarotti, S.; Gascoin, S.; Ezzahar, J.; et al. Remote Sensing of Water Resources in Semi Arid Mediterranean Areas: The Joint International Laboratory TREMA. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2015, 36, 4879–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Haile, A.; Tian, Y.; Joyce, R. Evaluation of the High Resolution CMORPH Satellite Rainfall Product Using Dense Rain Gauge Observations and Radar Based Estimates. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2012, 13, 1784–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.; Janowiak, J.; Kidd, C. Comparison of Near Real Time Precipitation Estimates from Satellite Observations and Numerical Models. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2007, 88, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.C.; Roan, J. Retrievals for the Rainfall Rate over Land Using Special Sensor Microwave Imager Data during Tropical Cyclones: Comparisons of Scattering Index, Regression, and Support Vector Regression. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2012, 13, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapiano, M.; Arkin, P. An Intercomparison and Validation of High Resolution Satellite Precipitation Estimates with 3 Hourly Gauge Data. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2009, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; UENO, K.; NAKAMURA, K. Comparison of Satellite Precipitation Products with Rain Gauge Data for the Khumb Region, Nepal Himalayas. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan. Ser. II 2011, 89, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakachen, W.; Raksapatcharawong, M.; Seto, S. Performance Evaluation of Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) Products over the Chaophraya River Basin, Thailand. Hydrological Research Letters 2014, 8, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palharini, R.; Vila, D.; Rodrigues, D.; Palharini, R.; Mattos, E.; Pedra, G. Assessment of Extreme Rainfall Estimates from Satellite Based: Regional Analysis. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 2021, 23, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Heap, A. A Review of Comparative Studies of Spatial Interpolation Methods in Environmental Sciences: Performance and Impact Factors. Ecological Informatics 2011, 6, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Hu, J.; Gebregiorgis, A.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X. Inter Comparison of High Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products over Central Asia. Remote Sensing 2015, 7, 7181–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geelani, S.; Abbas, S.; Umar, M.; Usman, M.; Yousfani, I. Validation of Satellite Based Gridded Rainfall Products with Station Data over Major Cities in Punjab. Int J Innov Sci Technol.
- Tsuzuki, K.; Nakamura, S.; Tebakari, T.; Yoshimi, K. Proposal of a New Rainfall Product Using Modified Weather Radar Data Published by the Thai Meteorological Department and Its Application: A Case Study in Thailand. Hydrological Research Letters 2025, 19, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; et al. Remote Sensing of Drought: Progress, Challenges and Opportunities. Reviews of Geophysics 2015, 53, 452–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.; et al. Global Scale Evaluation of 22 Precipitation Datasets Using Gauge Observations and Hydrological Modeling. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2017, 21, 6201–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) or Mean Absolute Error (MAE)? Atmospheric Environment 2014, 90, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; et al. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi Global, Multiyear, Combined Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Duc, P.; Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Phan Van, T.; Pham Thanh, H. Application of Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) Network for Seasonal Prediction of Monthly Rainfall across Vietnam. Earth Science Informatics 2024, 17, 3925–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, W.; Tan, G.; Alriah, M.; Elameen, A. Evaluation and Correction Analysis of the Regional Rainfall Simulation by CMIP6 over Sudan. Geographica Pannonica 2024, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkirane, M.; Amazirh, A.; Laftouhi, N.E.; Khabba, S.; Chehbouni, A. Assessment of GPM Satellite Precipitation Performance after Bias Correction, for Hydrological Modeling in a Semi Arid Watershed (High Atlas Mountain, Morocco). Atmosphere 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, L.; Bremnes, J.; Haugen, J.; Engen Skaugen, T. Statistical Downscaling and Bias Correction of Climate Model Outputs. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2012, 16, 3383–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panofsky, H.; Brier, G. Some Applications of Statistics to Meteorology; Pennsylvania State University Press, 1968.
- Themebl, M.; Gobiet, A.; Leuprecht, A. Empirical Statistical Downscaling and Error Correction of Daily Precipitation from Regional Climate Models. International Journal of Climatology 2011, 31, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elair, C.; Rkha Chaham, K.; Hadri, A. Assessment of Drought Variability in the Marrakech Safi Region (Morocco) at Different Time Scales Using GIS and Remote Sensing. Water Supply 2023, 23, 4592–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaida, J.; Witam, O.; Ibnoussina, M.; Delmaki, A.; Benkirane, M. Contribution of Remote Sensing and GIS to Analysis of the Risk of Flooding in the Zat Basin (High Atlas Morocco). Natural Hazards 2021, 108, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaba, M.; El Khalki, E.; Saidi, M.; Alam, J. Estimation of Flood Discharge in Ungauged Basin Using GPM IMERG Satellite Based Precipitation Dataset in a Moroccan Arid Zone. Earth Systems and Environment 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eini, M.; Rahmati, A.; Piniewski, M. Hydrological Application and Accuracy Evaluation of PERSIANN Satellite Based Precipitation Estimates over a Humid Continental Climate Catchment. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachdane, M.; El Khalki, E.; Saidi, M.; Tramblay, Y. Evaluation of GPM IMERG Products and ERA5 Reanalysis for Flood Modeling in a Semi Arid Watershed 2022.
- Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Duan, Z. Hydrologic Evaluation of TRMM and GPM IMERG Satellite Based Precipitation in a Humid Basin of China. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Xuan, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y. Evaluation and Hydrological Application of Precipitation Estimates Derived from PERSIANN CDR, TRMM 3B42V7, and NCEP CFSR over Humid Regions in China. Hydrological Processes 2016, 30, 3061–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, W.; Brocca, L.; Rigon, R. Comparative Evaluation of Different Satellite Rainfall Estimation Products and Bias Correction in the Upper Blue Nile (UBN) Basin. Atmospheric Research. [CrossRef]
- Gebremicael, T.; Deitch, M.; Gancel, H.; Croteau, A.; Haile, G.; Beyene, A.; Kumar, L. Satellite Based Rainfall Estimates Evaluation Using a Parsimonious Hydrological Model in the Complex Climate and Topography of the Nile River Catchments. Atmospheric Research 2022, 266, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.; Li, L.; Jun, K. Evaluation of Multi Satellite Precipitation Products for Streamflow Simulations: A Case Study for the Han River Basin in the Korean Peninsula, East Asia. Water 2018, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.; Arsenault, R. Evaluation of the ERA5 Reanalysis as a Potential Reference Dataset for Hydrological Modelling over North America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, F.; Barbosa, H.; Penaloza Murillo, M.; Moreno, M.; Farias, A. Intercomparison of Improved Satellite Rainfall Estimation with CHIRPS Gridded Product and Rain Gauge Data over Venezuela. Atmosfera 2016, 29, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khalki, E.; Tramblay, Y.; Saidi, M.; Ahmed, M.; Chehbouni, A. Hydrological Assessment of Different Satellite Precipitation Products in Semi Arid Basins in Morocco. Frontiers in Water 2023, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, A.; Igmoullan, B.; Namous, M.; El Bouazzaoui, I.; Ait Brahim, Y.; El Khalki, E.; Saidi, M. Evaluation of PERSIANN CCS CDR, ERA5, and SM2RAIN ASCAT Rainfall Products for Rainfall and Drought Assessment in a Semi Arid Watershed, Morocco. Journal of Water and Climate Change 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, M.; Alam, J. Rainfall Frequency Analysis Using Assessed and Corrected Satellite Precipitation Products in Moroccan Arid Areas. The Case of Tensift Watershed. Earth Systems and Environment 2022, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Salih, W.; Epule, T.; Chehbouni, A.; El Khalki, E. Assessment of Satellite Precipitation Products during Extreme Events in a Semiarid Region 2023.
- Jaffar, O.; Hadri, A.; El Khalki, E.; Ait Naceur, K.; Saidi, M.; Tramblay, Y.; Chehbouni, A. Assessment of Hydrological Model Performance in Morocco in Relation to Model Structure and Catchment Characteristics. Journal of Hydrology Regional Studies 2024, 54, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saouabe, T.; Ait Naceur, K.; El Khalki, E.; Hadri, A.; Saidi, M. GPM IMERG Product: A New Way to Assess the Climate Change Impact on Water Resources in a Moroccan Semi Arid Basin. Journal of Water and Climate Change 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, J. Element Analysis: A Wavelet Based Method for Analysing Time Localized Events in Noisy Time Series. Proceedings of the Royal Society A 2017, 473, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobach, H.; Tropea, C.; Cordier, L.; Bonnet, J.; Delville, J.; Lewalle, J.; Farge, M.; Schneider, K.; Adrian, R. , C.; Yarin, A.; Foss, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007; p. 1337 1398.Processing. In Springer Handbook of Experimental Fluid Mechanics; Tropea, C., Yarin, A., Foss, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamrane, Z.; Turki, I.; Laignel, B.; Mahe, G.; Laftouhi, N.E. Characterization of the Interannual Variability of Precipitation and Streamflow in Tensift and Ksob Basins (Morocco) and Links with the NAO. Atmosphere 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiah, W.; Johnson, R.; Muthoni, F.; Mengistu, G.; Amekudzi, L.; Kwabena, O.; Kizito, F. Bias Correction and Spatial Disaggregation of Satellite Based Data for the Detection of Rainfall Seasonality Indices. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, D.; Kumar, D.; Amarjyothi, K.; Saha, U. Bias Correction of Satellite Precipitation Estimates Using Mumbai MESONET Observations: A Random Forest Approach. Atmospheric Research 2025, 315, 107858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouazzaoui, I.; Ait Brahim, Y.; Amazirh, A.; Bougadir, B. Projections of Future Droughts in Morocco: Key Insights from Bias Corrected Med CORDEX Simulations in the Haouz Region. Earth Systems and Environment 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habitou, N.; Morabbi, A.; Ouazar, D.; Bouziane, A.; Hasnaoui, M.; Sabri, H. CHIRPS Precipitation Open Data for Drought Monitoring: Application to the Tensift Basin, Morocco. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2020, 14. [Google Scholar]
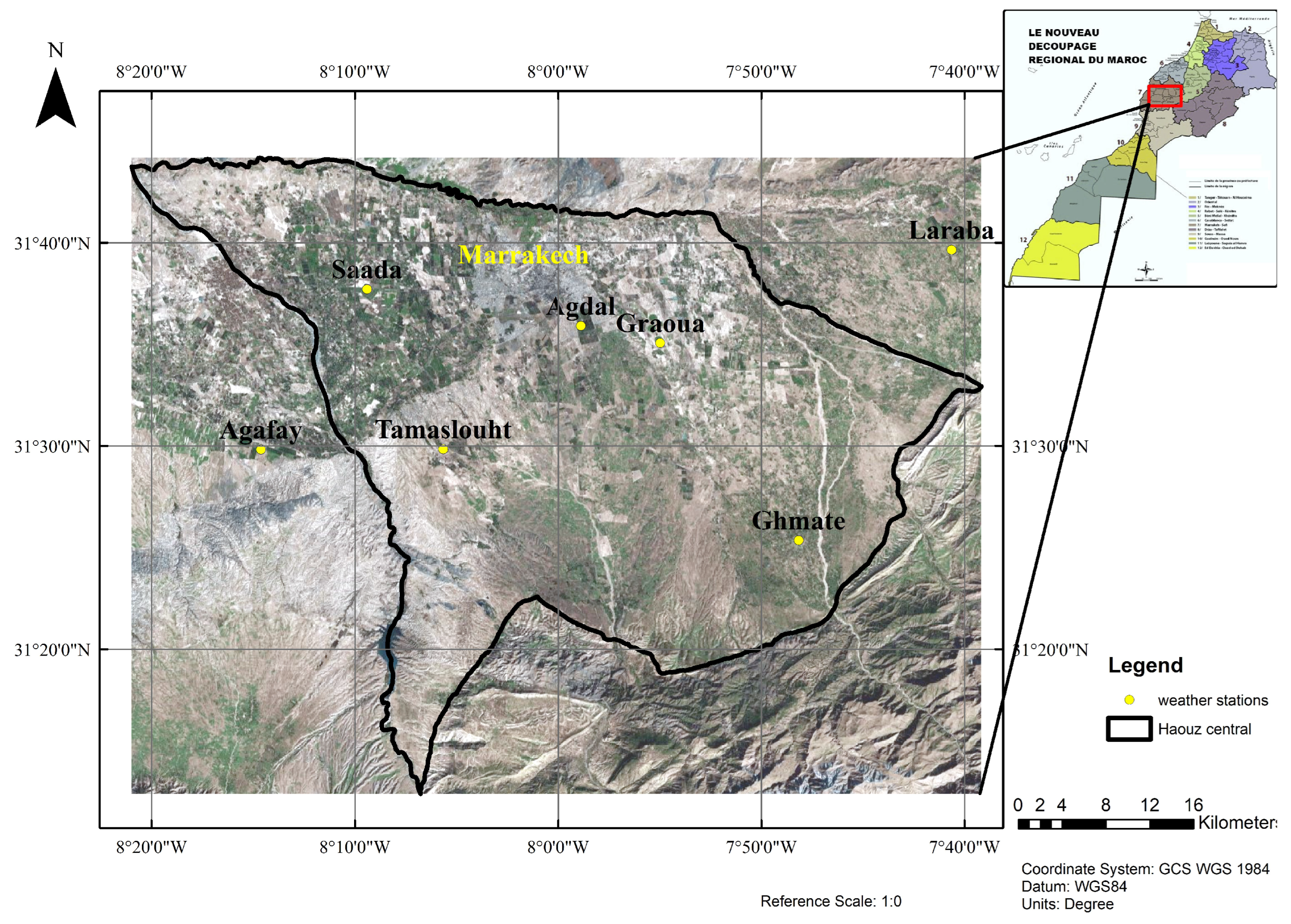
| Station | X | Y | Altitude (m) | First Start-up Date | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agafay | -8.24378 | 31.49711 | 479 | 2003-Present | 30 min |
| Agdal | -7.98143 | 31.59856 | 506 | 2004-Present | 30 min |
| Graoua | -7.91641 | 31.58444 | 523 | 2003-Present | 30 min |
| Ghmate | -7.80290 | 31.42273 | 761 | 2019-Present | 30 min |
| Laraba | -7.67748 | 31.66089 | 782 | 2017-Present | 30 min |
| Saada | -8.15673 | 31.62859 | 415 | 2022-Present | 30 min |
| Tameslouht | -8.09430 | 31.49745 | 554 | 2018-Present | 30 min |
| Product | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Time Span | Data Source | Coverage | Access Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHIRPS | 0.05° ( 5 km) | Daily, Monthly | 1981–present | Infrared satellite + gauge-based corrections | Global (50°S–50°N) | https://www.chc.ucsb.edu/data/chirps |
| ERA5-Ag | 9 km ( 0.08°) | Hourly, Daily | 1950–present | ECMWF reanalysis | Global | https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/ |
| GPM | 0.1° ( 10 km) | Half-hourly, Daily | 2000–present | Multi-satellite + gauge correction | Global (60°S–60°N) | https://gpm.nasa.gov/data/directory |
| PERSIANN-CDR | 0.25° ( 25 km) | Daily | 1983–present | Infrared-based with machine learning corrections | Global (60°S–60°N) | https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/climate-data-records/precipitation-persiann |
| CFSR | 0.2° ( 20 km) | Hourly, Daily | 1979–2010 (Replaced by CFSv2) | NOAA NCEP Reanalysis | Global | https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds093.0/ |
| Metrics | Formulas | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE | Lower RMSE values indicate better model performance,while higher values indicate larger errors. | |
| MAE | A lower MAE indicates a better fit,while a higher MAE suggests a less accurate model. | |
| NSE | An NSE of 1 indicates perfect prediction. | |
| Bias | A bias close to 0 is ideal. | |
| Pearson Correlation | A value of 1 indicates perfect correlation. |
| Estimated : Rainy | Estimated : Not rainy | |
|---|---|---|
| Observed : Rainy | True Positives (TP) | False Negatives (FN) |
| Observed : not rainy | False Positives (FP) | True Negatives (TN) |
| Metrics | Formule |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | |
| Precision | |
| Recall | |
| F1-Score | |
| Cohen’s Kappa |
| Parameter | Value used | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelet type | Cmor1-2.5 | Complex Morlet wavelet with parameters 1, 2.5 |
| Sampling period | Time step set to 1 year (data is annual). | |
| Wavelet scales | np.arange(1, 50) | Range of scales used for the Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT). |
| Associated frequencies | Freqs (computed by PyWavelets) | Frequencies corresponding to the scales. |
| Detrending | Detrend(data) | Removal of the linear trend from the time series. |
| Gauged station | CFSR | CHIRPS | ERA5_Ag | GPM | PERSIANN_CDR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | M | A | M | A | M | A | M | A | M | |
| Agafay | -2.25 | -26.93 | -3.59 | -42.95 | 5.98 | 71.48 | -2.28 | -27.27 | -1.28 | -15.42 |
| Agdal | -5.92 | -71.06 | 2.12 | 25.42 | 21.98 | 263.77 | 5.83 | 69.97 | 6.66 | 80.03 |
| Ghmate | 16.89 | 168.91 | 13.04 | 130.49 | 9.79 | 97.91 | 10.04 | 100.40 | -7.13 | -71.33 |
| Laraba | -3.54 | -41.99 | 3.16 | 37.52 | 8.25 | 97.84 | 1.76 | 20.88 | -0.70 | -8.36 |
| Tameslouht | 12.97 | 136.25 | 5.49 | 57.72 | 10.63 | 111.71 | 5.19 | 54.54 | -0.70 | -7.38 |
| Station | CFSR | CHIRPS | ERA5_Ag | GPM | PERSIANN_CDR | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | M | Y | D | M | Y | D | M | Y | D | M | Y | D | M | Y | |
| Agafay | 0.58 | 0.73 | 0.59 | 0.38 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.64 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 0.38 | 0.74 | 0.55 |
| Agdal | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 0.20 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.57 | 0.78 | 0.52 | 0.36 | 0.76 | 0.67 |
| Ghmate | 0.49 | 0.44 | 0.93 | -0.01 | -0.08 | 0.37 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 0.99 | 0.25 | 0.29 | -0.64 | 0.25 | 0.70 | 0.92 |
| Laraba | 0.55 | 0.62 | 0.83 | 0.01 | 0.35 | 0.98 | 0.72 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.27 | 0.55 | 0.40 |
| Tameslouht | 0.48 | 0.37 | -0.74 | -0.02 | -0.32 | 0.46 | 0.62 | 0.72 | -0.98 | 0.50 | 0.59 | 0.95 | 0.25 | 0.69 | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





