Submitted:
20 April 2025
Posted:
21 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
- Ethical Considerations:- Integrates fairness, bias mitigation, and accountability into Al design.
- Legal Frameworks:- Ensures compliance with laws and regulations protecting rights and privacy.
- Societal Alignment:- Aligns Al systems with societal values and expectations for trustworthiness.
- Implementation Strategies:- Provides practical guidelines for embedding governance throughout the Al lifecycle.
- Challenges and Solutions:- Identifies and addresses key challenges in adopting governance frameworks.
I. Introduction
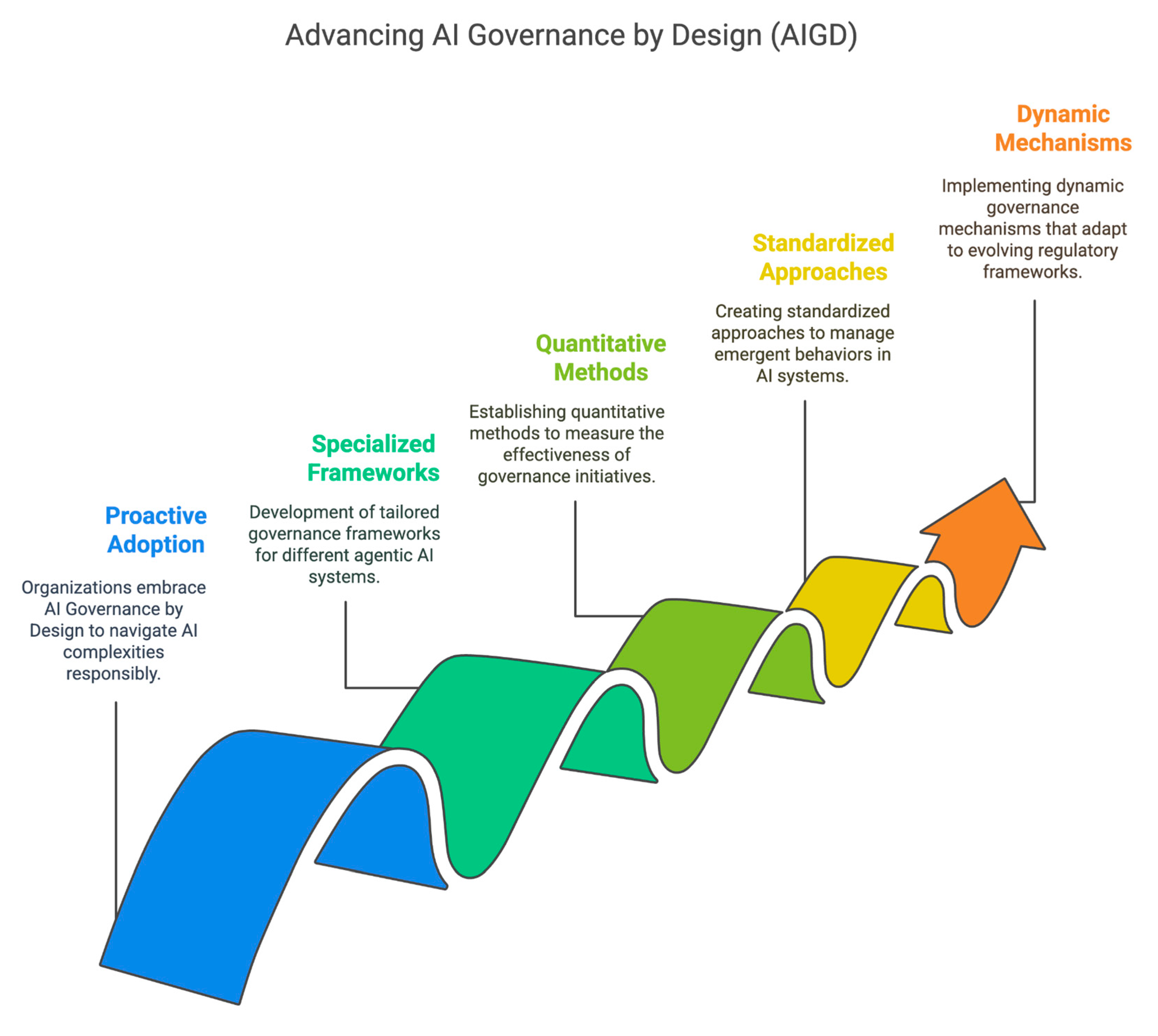
- Presents a comprehensive framework for Al Governance by Design.
- Offers specialized governance considerations for agentic Al systems.
- Provides practical implementation guidelines across the Al lifecycle.
- Analyzes domain-specific governance examples for three types of agentic systems.
- Proposes metrics and methods for assessing governance effectiveness.
II. Understanding Al Governance by Design
A. Limitations of Reactive Governance
- Technological advancement outpaces regulatory frameworks.
- Complex and opaque Al models make post-deployment accountability challenging.
- Reactive measures lead to increased compliance costs and technical debt.
- Post-deployment adjustments can be costly and disruptive to operations.
B. Benefits of a Design-Centric Approach
- Proactively mitigates risks before they manifest in production environments.
- Ensures alignment with ethical and societal values from the outset of development.
- Reduces the likelihood of costly post-deployment adjustments and retrofitting.
- Fosters greater stakeholder trust through demonstrated commitment to responsible practices.
- Creates competitive advantages through enhanced system reliability and user confidence.
III. Core Principles of Al Governance by Design (AIGD)
A. Fairness and Bias Mitigation
B. Transparency and Explainability
C. Accountability and Responsibility
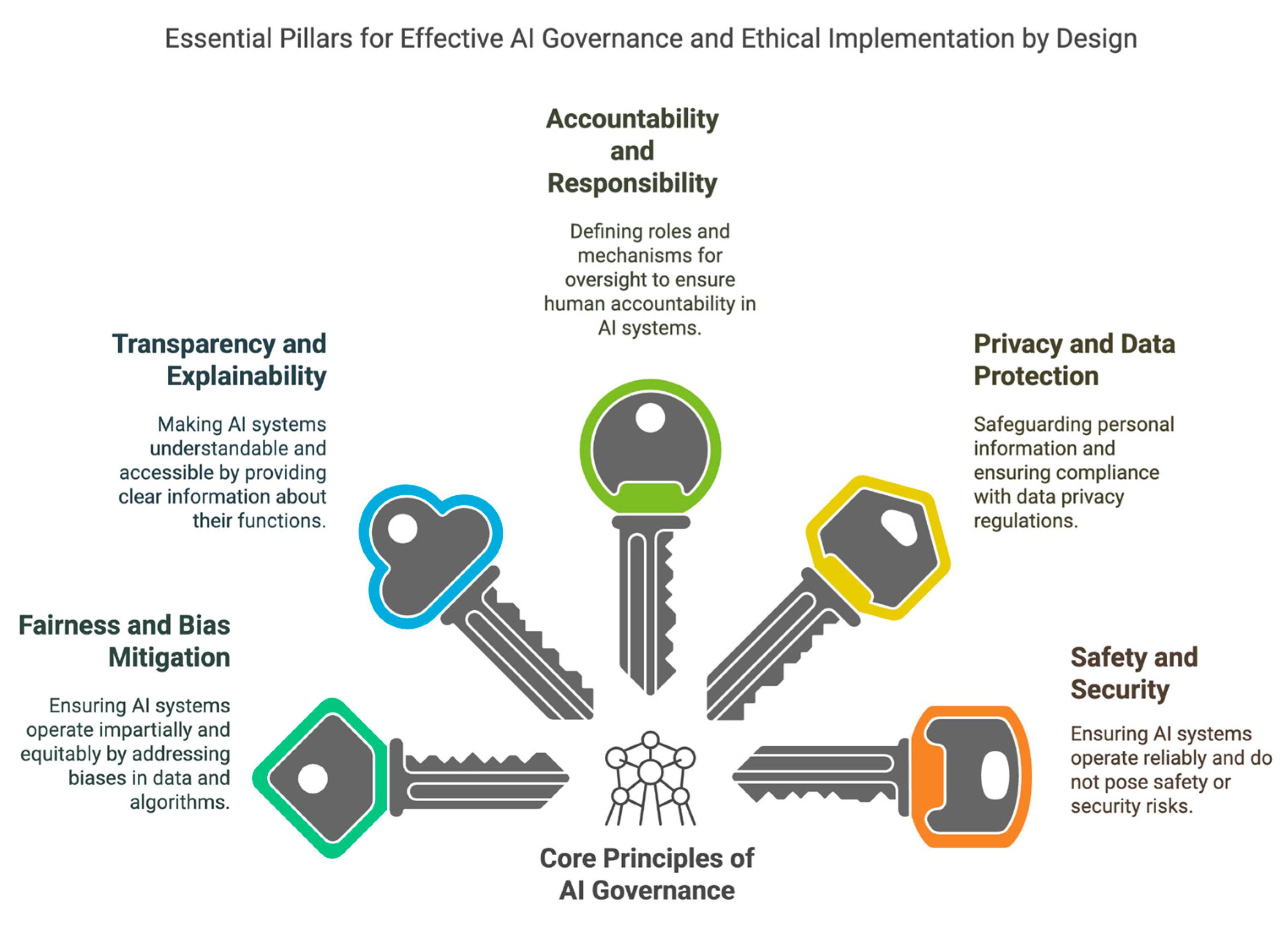
D. Privacy and Data Protection
E. Safety and Security
F. Human Oversight and Control
IV. Al Governance by Design (AIGD) for Agentic Systems
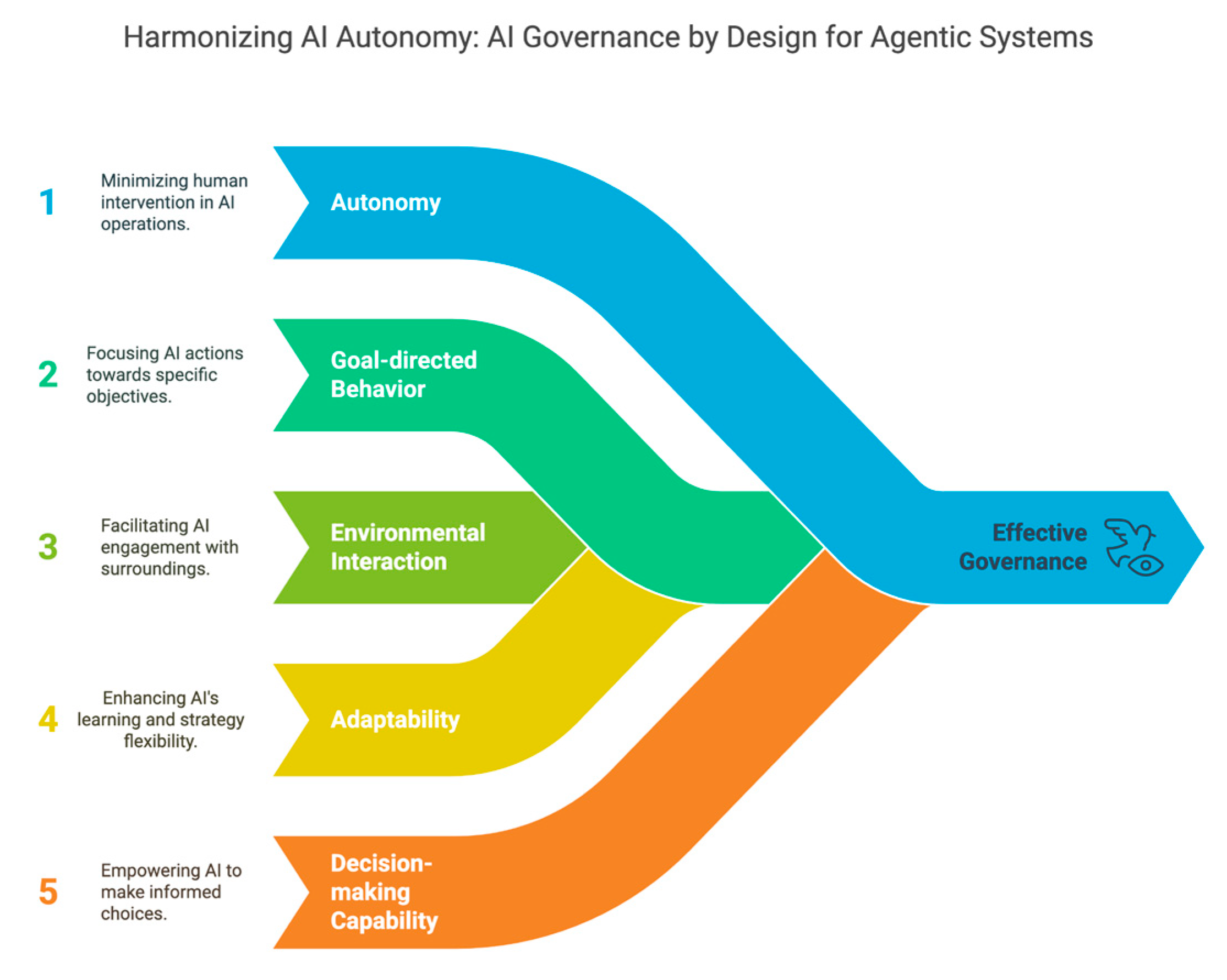
A. Defining Agentic Al Systems
- Autonomy:- Ability to operate with minimal human intervention.
- Goal-directed behavior:- Pursuit of defined objectives.
- Environmental interaction:- Direct engagement with digital or physical environments.
- Adaptability:- Learning and strategy adjustment based on feedback.
- Decision-making capability:- Making choices among alternatives to achieve goals.
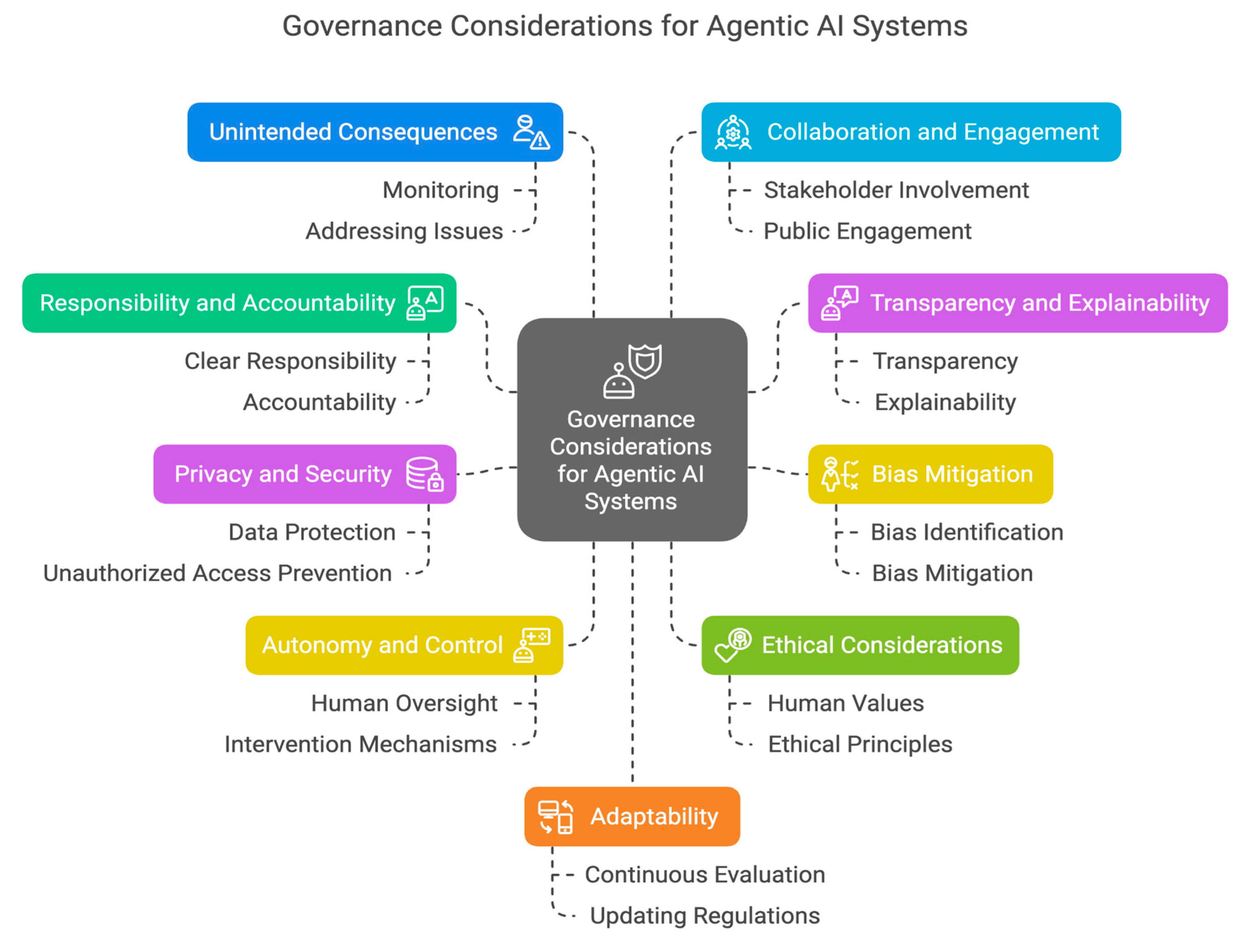
B. Special Governance Considerations for Agentic Al
- Establishing Clear Lines of Responsibility and Accountability:- As agentic AI systems can act autonomously, it is essential to determine who is responsible and accountable for their actions. This includes considering scenarios where the AI system’s actions result in harm or unintended consequences.
- Ensuring Transparency and Explainability:- Agentic AI systems should be transparent and explainable, meaning their decision-making processes and actions should be understandable to humans. This is crucial for building trust and enabling effective oversight.
- Mitigating Bias and Discrimination:- Agentic AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate or amplify existing biases and discrimination. It is essential to implement measures to identify and mitigate these biases to ensure fairness and equity.
- Safeguarding Privacy and Security:- Agentic AI systems often process vast amounts of data, including personal and sensitive information. Robust privacy and security measures must be implemented to protect this data and prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
- Balancing Autonomy and Control:- While agentic AI systems are designed to operate autonomously, it is crucial to maintain appropriate levels of human control and oversight. This includes implementing mechanisms for intervention and deactivation when necessary.
- Promoting Human Values and Ethical Considerations:- Agentic AI systems should be designed and operated in alignment with human values and ethical principles. This includes considering the potential impact of AI systems on society and taking steps to minimize harm and maximize benefit.
- Addressing Unintended Consequences and Emergent Behaviors:- Agentic AI systems can exhibit unintended consequences and emergent behaviors that are difficult to predict. It is crucial to monitor AI systems closely and be prepared to address these issues as they arise.
- Fostering Collaboration and Public Engagement:- The development and deployment of agentic AI systems should be a collaborative and inclusive process that involves diverse stakeholders, including the public. This helps ensure that AI systems are aligned with societal needs and values.
- Adapting Governance Frameworks to Technological Advancements:- The field of AI is rapidly evolving, and governance frameworks must be adaptable to keep pace with technological advancements. This includes continuously evaluating and updating regulations and standards to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
- International Collaboration and Standardization:- As AI technologies transcend national borders, international collaboration and standardization are crucial for ensuring consistent and responsible governance practices.
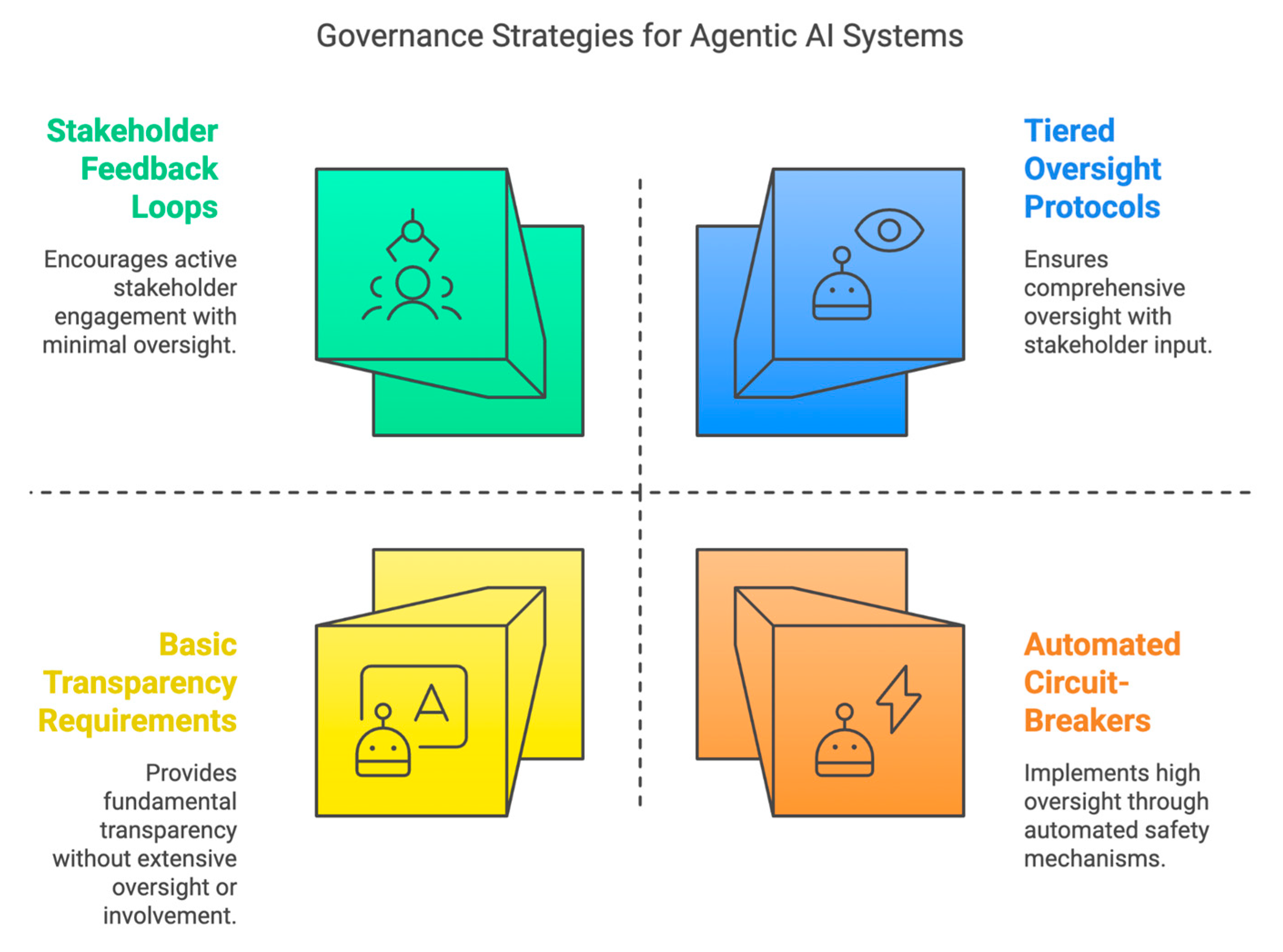
C. Mitigating Actions for Agentic AI Systems
-
Extended Control Mechanisms
- (a)
- Implementation of tiered human oversight protocols based on risk levels.
- (b)
- Establishment of automated circuit-breakers and kill switches.
- (c)
- Regular testing of intervention capabilities under varied conditions.
-
Agency-Specific Transparency Requirements
- (a)
- Clear disclosure of system boundaries and capabilities.
- (b)
- Explicit communication of the degree of autonomy in decision-making.
- (c)
- Logging of agentic decisions and their rationales.
-
Behavioral Monitoring and Drift Detection
- (a)
- Continuous monitoring for unexpected emergent behaviors.
- (b)
- Detection of goal misalignment or strategy drift.
- (c)
- Regular validation against initial specifications and intentions.
-
Stakeholder Participation in Governance
- (a)
- Inclusion of end-users in governance design processes.
- (b)
- Regular feedback loops with affected communities.
- (c)
- Multi-disciplinary input on agency parameters and limits.
V. Framework for Implementation Across the Al Lifecycle
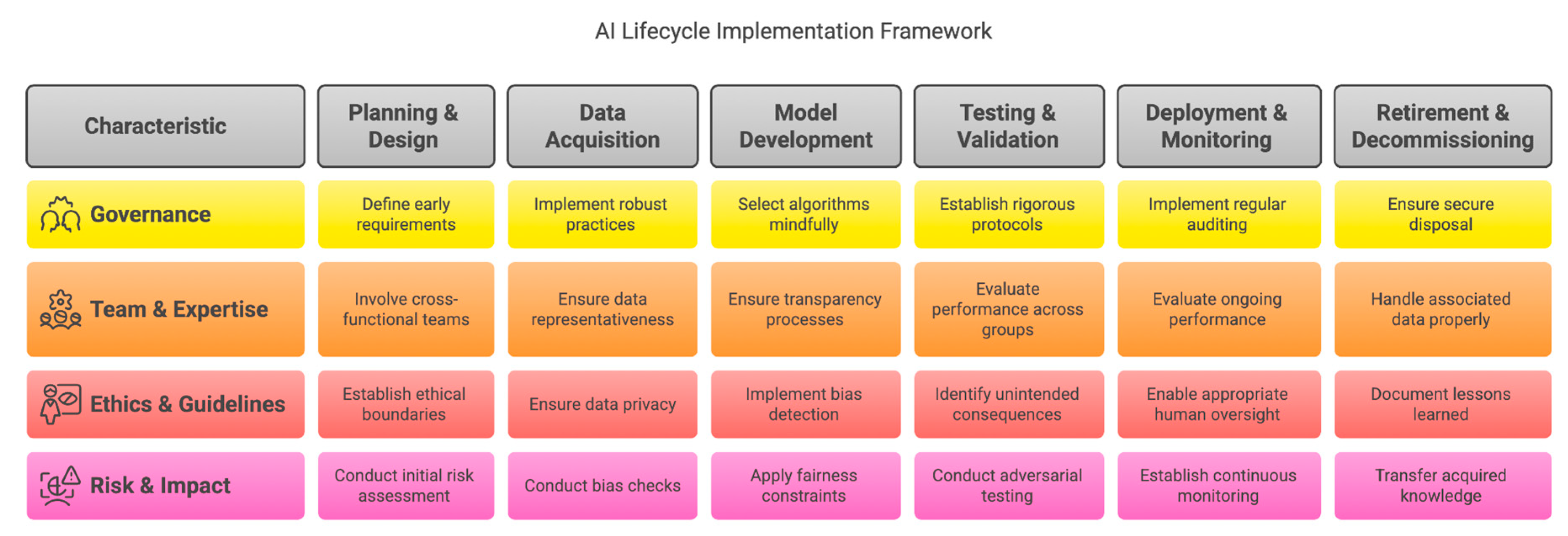
A. Planning and Design Phase
- Define governance requirements early in the project lifecycle.
- Involve cross-functional teams with diverse expertise.
- Establish ethical guidelines and boundaries.
- Conduct initial risk assessment and impact analysis.
B. Data Acquisition and Preparation
- Implement robust data governance practices13.
- Ensure data quality, privacy, and representativeness.
- Conduct bias checks and mitigation strategies.
- Document data provenance and transformations.
C. Model Development and Training
- Select algorithms with governance considerations in mind.
- Implement bias detection and mitigation techniques6,7.
- Ensure transparency in model development processes8,9.
- Apply fairness constraints during optimization.
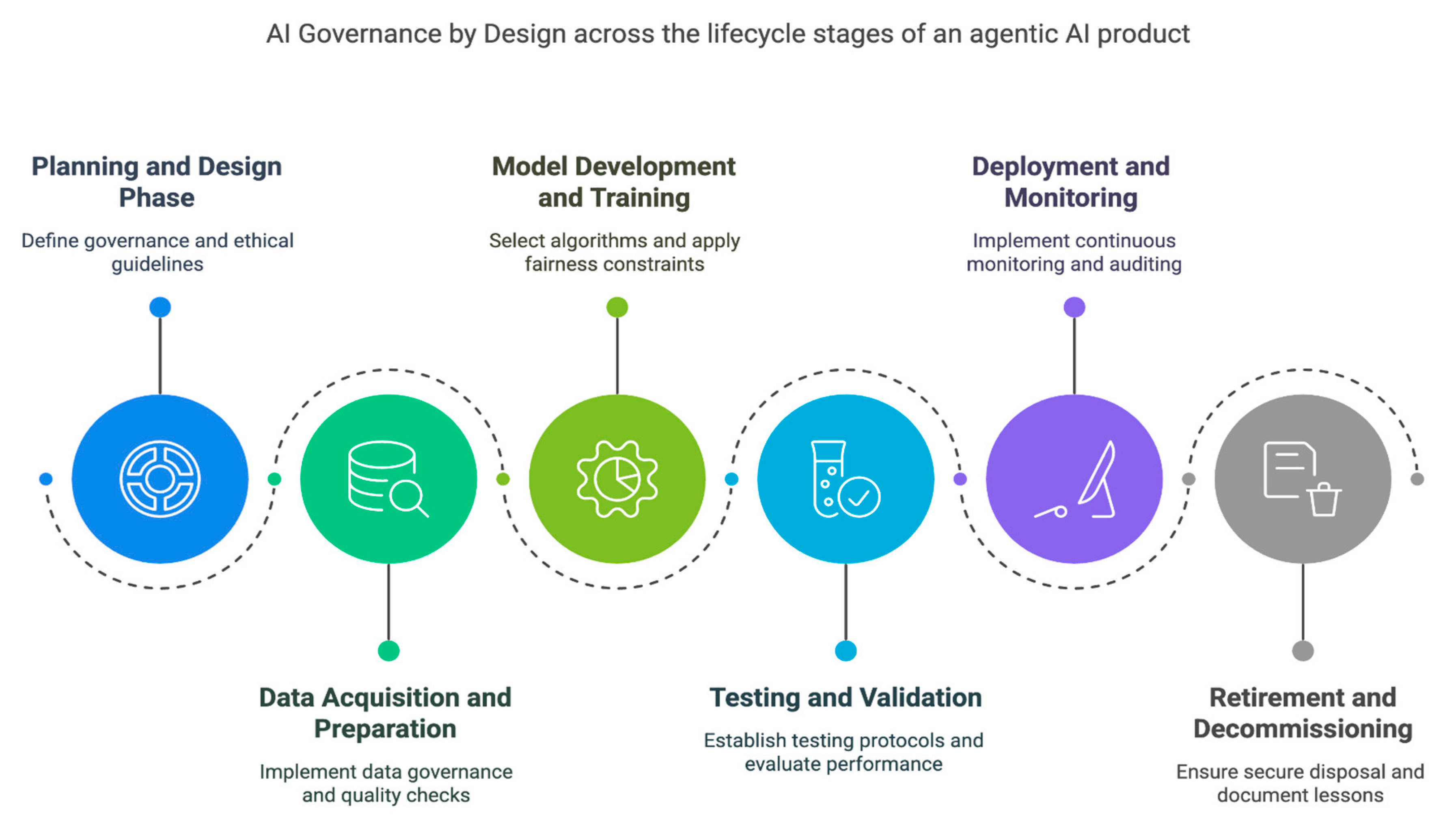
D. Testing and Validation
- Establish rigorous testing protocols for safety, reliability, and fairness.
- Evaluate performance across various scenarios and user groups.
- Identify unintended consequences or biases.
- Conduct adversarial testing of governance controls.
E. Deployment and Monitoring
- Establish continuous monitoring mechanisms.
- Implement regular auditing procedures.
- Evaluate ongoing performance and compliance.
- Enable appropriate human oversight.
F. Retirement and Decommissioning
- Ensure secure and ethical disposal of Al models.
- Properly handle associated data in accordance with regulations.
- Document lessons learned for future implementations.
VI. Case Studies:- Al Governance by Design for Agentic Systems
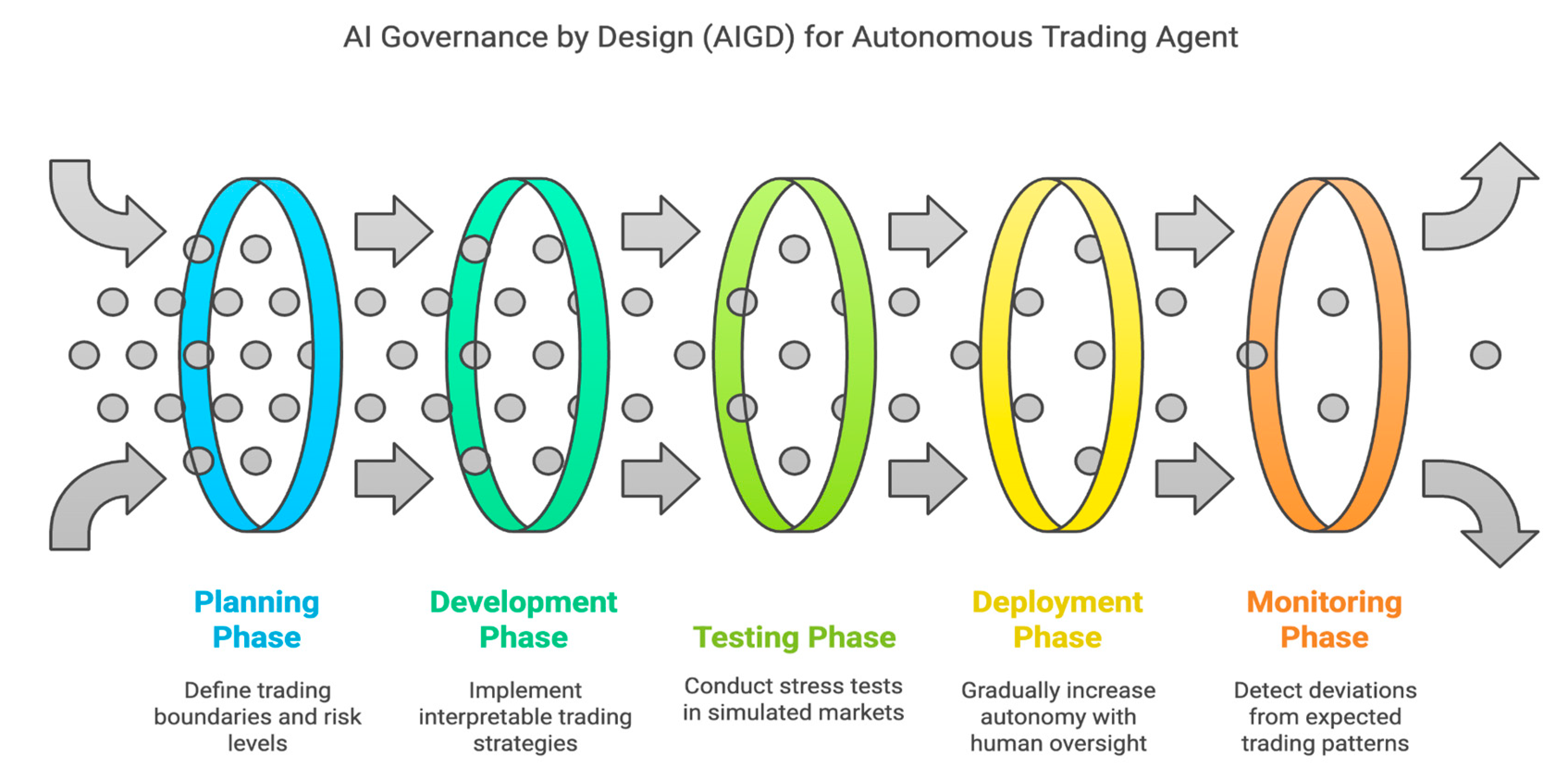
A. Autonomous Financial Trading Agent
-
Governance Design Elements:-
- (a)
- Planning Phase:- Define clear boundaries for trading amounts, risk levels, and asset classes.
- (b)
- Development Phase:- Implement interpretable strategies with clear decision trees.
- (c)
- Testing Phase:- Run stress tests in simulated market conditions including market crashes.
- (d)
- Deployment Phase:- Start with human-in-the-loop approval for trades, gradually increasing autonomy.
- (e)
- Monitoring Phase:- Implement real-time drift detection if trading patterns deviate from expected parameters.
-
Agentic Safeguards:-
- (a)
- Maximum trade size limits that dynamically adjust based on market volatility.
- (b)
- Behavioral fingerprinting to detect unusual trading patterns.
- (c)
- Daily risk exposure reports with mandatory human review.
- (d)
- Multi-level authentication for changing trading parameters.
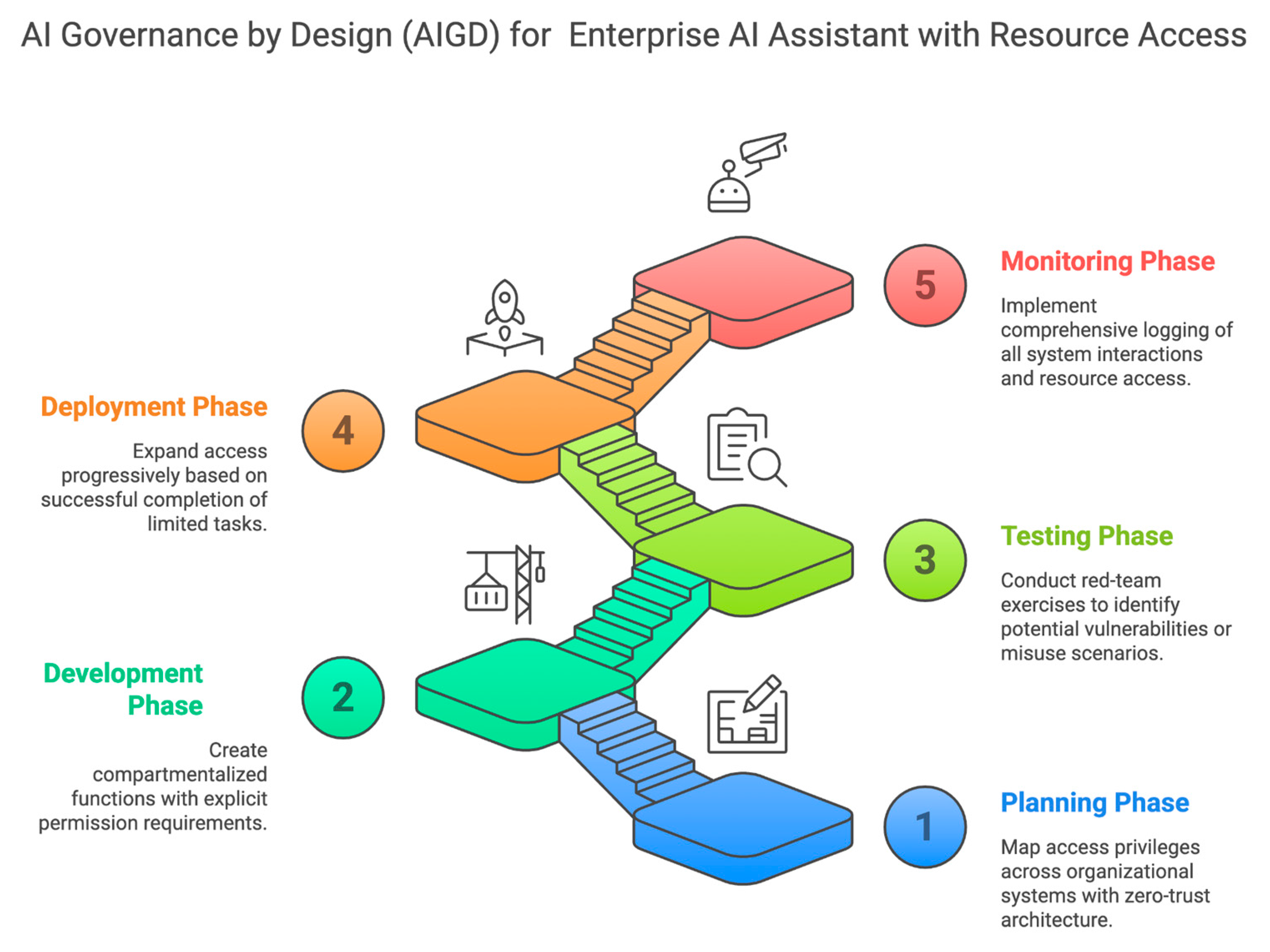
B. Enterprise Al Assistant with Resource Access
-
Governance Design Elements:-
- (a)
- Planning Phase:- Map access privileges across organizational systems with zero-trust architecture.
- (b)
- Development Phase:- Create compartmentalized functions with explicit permission requirements.
- (c)
- Testing Phase:- Red-team exercises to identify potential vulnerabilities or misuse scenarios.
- (d)
- Deployment Phase:- Progressive access expansion based on successful completion of limited tasks.
- (e)
- Monitoring Phase:- Comprehensive logging of all system interactions and resource access.
-
Agentic Safeguards:-
- (a)
- Task-specific access provisioning with automatic expiration.
- (b)
- Natural language processing to detect potentially harmful instructions.
- (c)
- Regular auditing of interaction logs for anomalous patterns.
- (d)
- Contextual authentication based on task sensitivity.
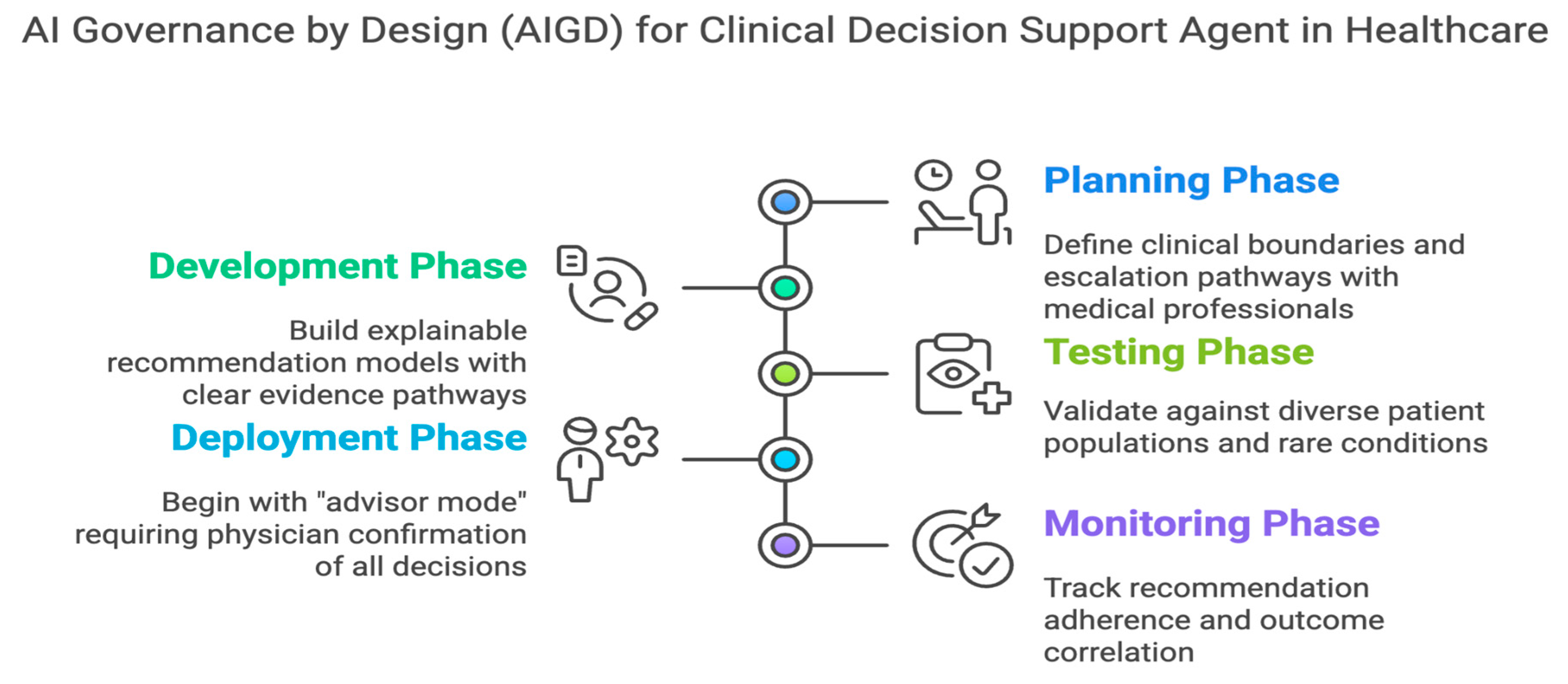
C. Clinical Decision Support Agent in Healthcare
-
Governance Design Elements:-
- (a)
- Planning Phase:- Define clinical boundaries and escalation pathways with medical professionals.
- (b)
- Development Phase:- Build explainable recommendation models with clear evidence pathways.
- (c)
- Testing Phase:- Validate against diverse patient populations and rare conditions.
- (d)
- Deployment Phase:- Begin with "advisor mode" requiring physician confirmation of all decisions.
- (e)
- Monitoring Phase:- Track recommendation adherence and outcome correlation.
-
Agentic Safeguards:-
- (a)
- Mandatory uncertainty disclosure when confidence levels fall below thresholds.
- (b)
- Automated detection of potential diagnosis biases across demographic groups.
- (c)
- Scheduled recalibration based on latest medical literature.
- (d)
- Dual validation requirements for high-risk recommendations.
VII. Key Challenges in Implementation
A. Expertise and Skills Gap
B. Complex Regulatory Landscape
C. Balancing Innovation and Compliance
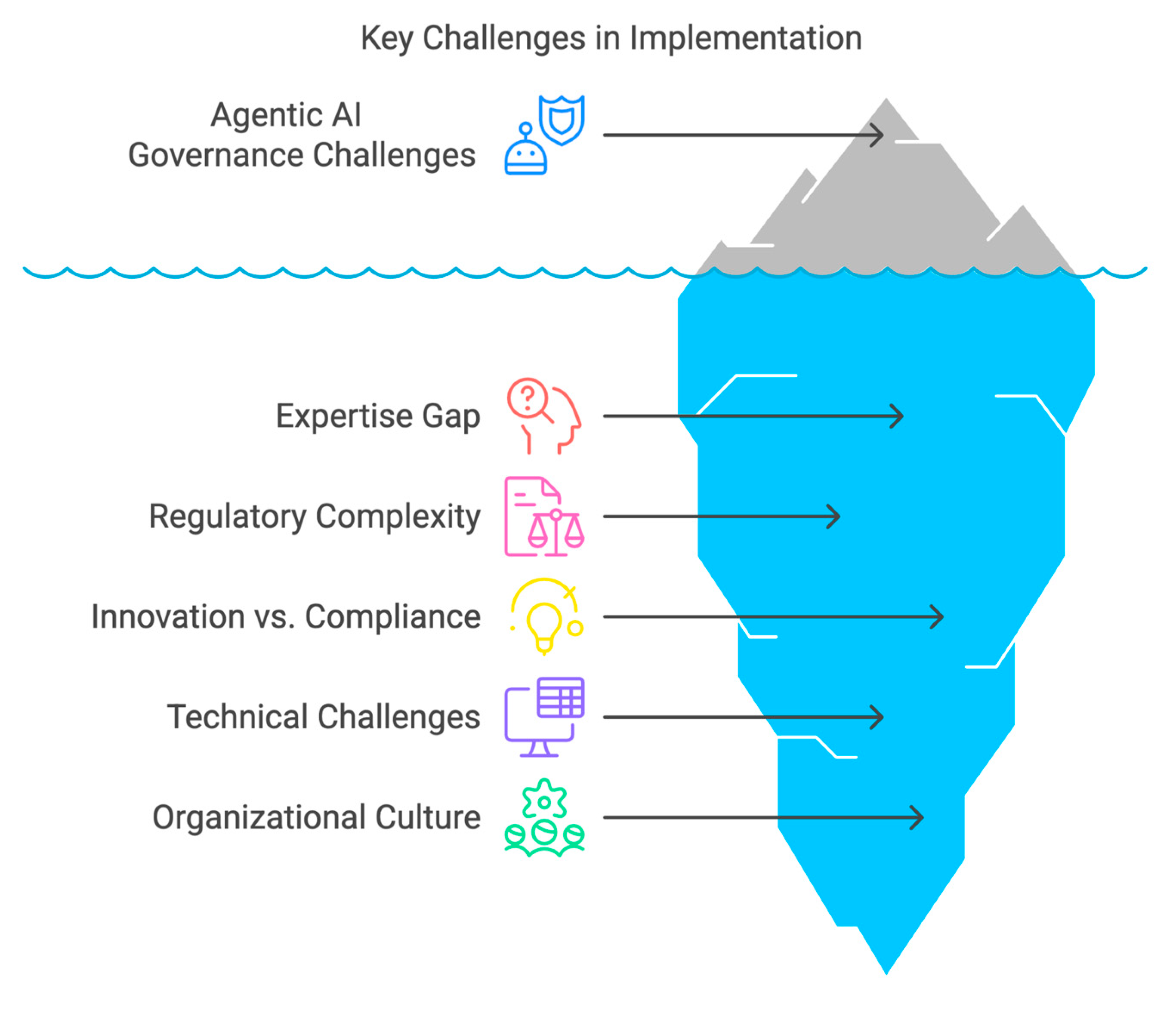
D. Technical Challenges
- Algorithmic bias detection in complex, adaptive systems [6, 7].
- Transparency and explainability for advanced machine learning models [8,9}.
- Effective drift detection for systems that learn continuously.
- Reliable failsafe mechanisms that don’t impede legitimate operations.
E. Organizational and Cultural Factors
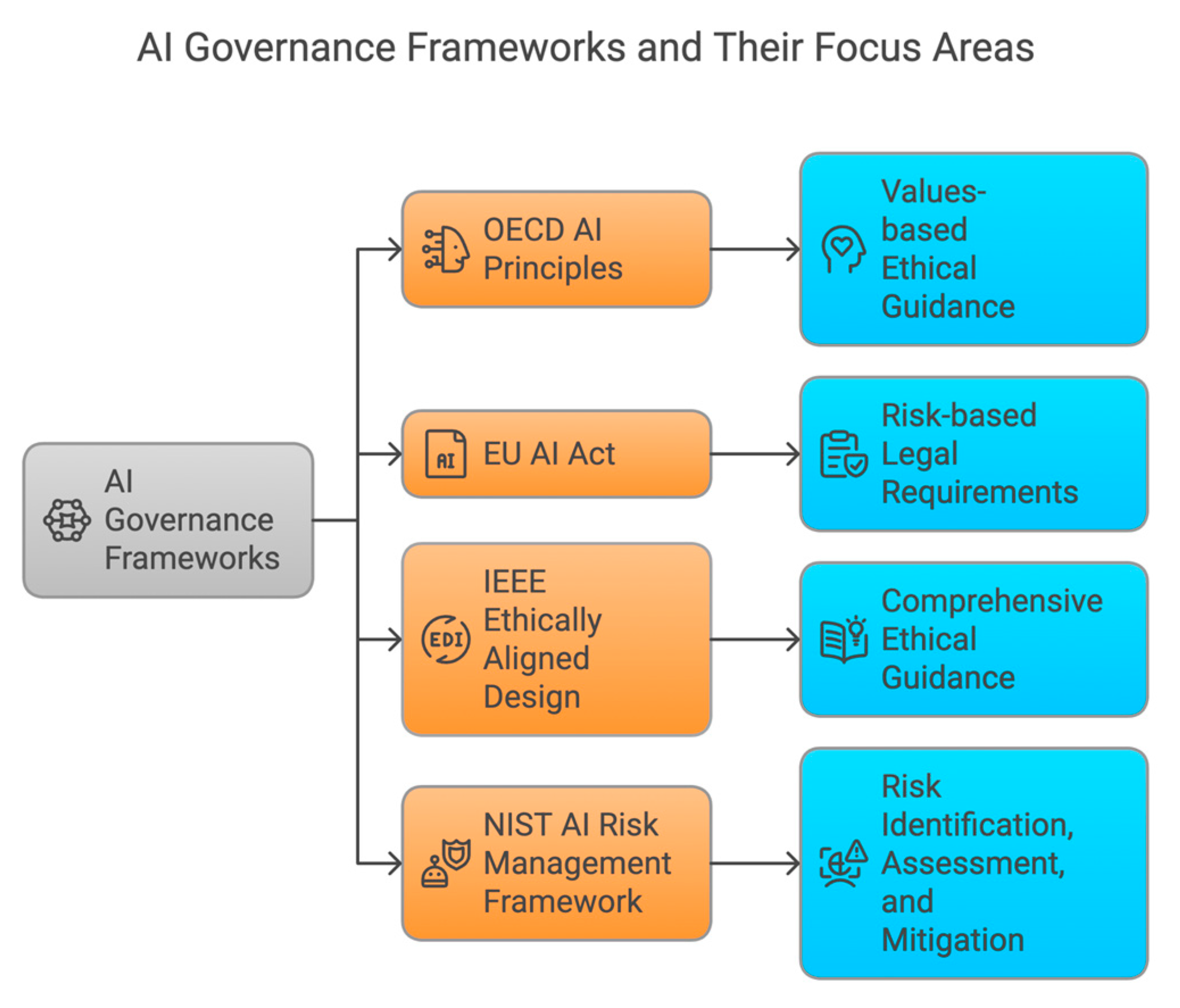
VIII. Comparative Analysis of Established Frameworks
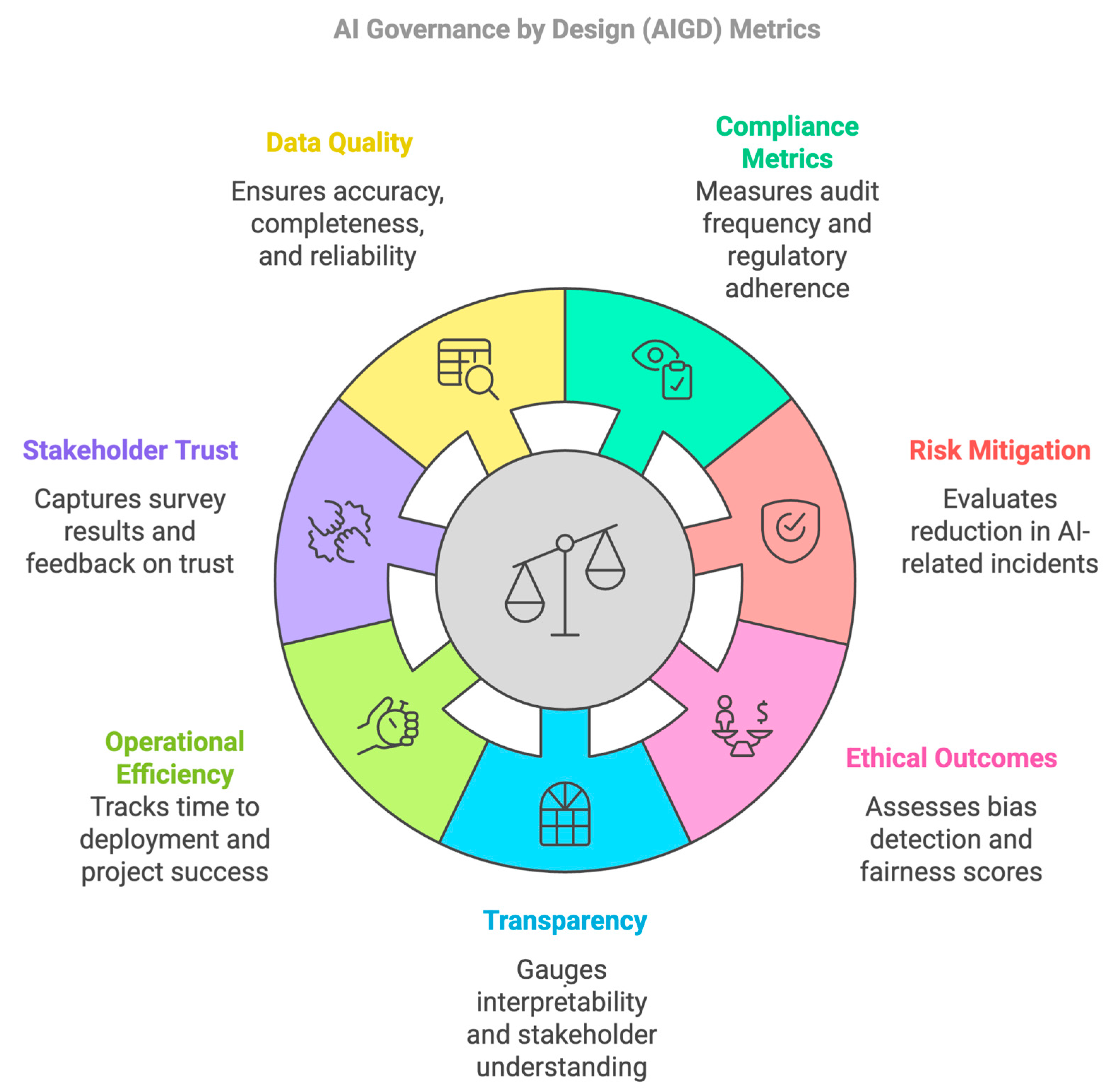
IX. Measuring Effectiveness of Governance Initiatives
- Compliance Metrics:- Audit frequency, regulatory violations, certification status.
- Risk Mitigation:- Reduction in Al-related incidents and security breaches.
- Ethical Outcomes:- Bias detection rates, fairness scores across demographic groups.
- Transparency:- Interpretability scores, stakeholder comprehension measures.
- Operational Efficiency:- Time to deployment, project success rates, governance overhead.
- Stakeholder Trust:- Survey results, feedback analysis, adoption metrics.
- Data Quality:- Accuracy, completeness, and reliability metrics.
X. Conclusion and Future Work
Acknowledgments
References
- Artificial Intelligence Governance & Alignment with Enterprise Governance, Medium, Mar. 2025. https://transcend.io/blog/enterprise-ai-governance.
- "Governance by Design: Embedding Compliance and Ethics in Al Development," AIGN, Mar. 2025. https://aign.global/ai-governance-consulting/patrick-upmann/governance-by-design-embedding-compliance-and-ethics-in-ai-development/.
- "The Algorithmic Problem in Artificial Intelligence Governance," United Nations University, Mar. 2025. https://unu.edu/article/algorithmic-problem-artificial-intelligence-governance.
- "Dynamic Al governance: A recipe for crafting trustworthy Al," Deloitte, Mar. 2025. https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/public-sector/static-to-dynamic-ai-governance.html.
- "Looking beyond compliance: The wide-ranging costs of not implementing Al governance," IBM, Mar. 2025. https://repository.law.miami.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1454&context=umblr.
- "What Is Algorithmic Bias?, IBM, Mar. 2025. https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/algorithmic-bias#:~:text=Algorithmic%20bias%20occurs%20when%20systematic,socioeconomic%2C%20racial%20and%20gender%20biases.
- "Combating Algorithmic Bias: Solutions to Al Development to Achieve Social Justice," Trends Research, Mar. 2025. https://trendsresearch.org/insight/combating-algorithmic-bias-solutions-to-ai-development-to-achieve-social-justice/.
- "Al on Trial: Navigating Explainability and Transparency," Tech For Good Institute, Mar. 2025. https://techforgoodinstitute.org/blog/expert-opinion/ai-on-trial-navigating-explainability-and-transparency/.
- "Addressing Transparency & Explainability When Using Al Under Global Standards," Mayer Brown, Mar. 2025. https://www.mayerbrown.com/-/media/files/perspectives-events/publications/2024/01/addressing-transparency-and-explainability-when-using-ai-under-global-standards.pdf%3Frev=8f001eca513240968f1aea81b4516757.
- "Al Governance Framework: Accountability & Consumer Rights, Dialzara, Mar. 2025. https://dialzara.com/blog/ai-governance-framework-accountability-and-consumer-rights/.
- "What is Al Governance?," Palo Alto Networks, Mar. 2025. <https://www.paloaltonetworks.ca/cyberpedia/ai-governance#:~:text=AI%20governance%20encompasses%20the%20policies,and%20maintenance%20of%20AI%20systems.>.
- "The growing data privacy concerns with Al: What you need to know," DataGuard, Mar. 2025. https://www.dataguard.com/blog/growing-data-privacy-concerns-ai/.
- "Data Governance for Al: Challenges & Best Practices," Atlan, Mar. 2025. https://atlan.com/know/data-governance/for-ai/.
- "9 Principles of an Al Governance Framework," Duality Tech, Mar. 2025. https://dualitytech.com/blog/ai-governance-framework/.
- "Principles For Enterprise Al Governance," Forbes, Mar. 2025. https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2024/12/17/why-leaders-should-follow-principles-based-ai-governance/.
- "What is Responsible Al," Microsoft Learn, Mar. 2025. https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cloud-adoption-framework/organize/responsible-ai.
- "What Is Al ethics? The role of ethics in Al," SAP, Mar. 2025. https://www.sap.com/resources/what-is-ai-ethics#:~:text=AI%20ethics%20helps%20ensure%20that,and%20the%20potential%20societal%20impacts.
- "Al Plans Hampered By Lack Of Skills, Governance Challenges," Silicon UK, Mar. 2025. https://www.silicon.co.uk/e-innovation/ai-plans-hampered-by-lack-of-skills-governance-challenges-573946.
- "What is Al Compliance and Why It Matters For Businesses," Tevora, Mar. 2025. https://www.tevora.com/resource/what-is-ai-compliance/.
- "Keys to fostering Al Governance that creates Business Value," Plain Concepts, Mar. 2025. https://www.plainconcepts.com/ai-governance/.
- "Resistance to Al: Governance and Cultural Challenges," Allganize’s Al, Mar. 2025. https://www.allganize.ai/en/blog/resistance-to-ai-governance-and-cultural-challenges.
- "A User Guide for Responsible Generative AI Governance"Vector Institute, Mar. 2025. https://res-ai.ca/.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




