Submitted:
14 April 2025
Posted:
14 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
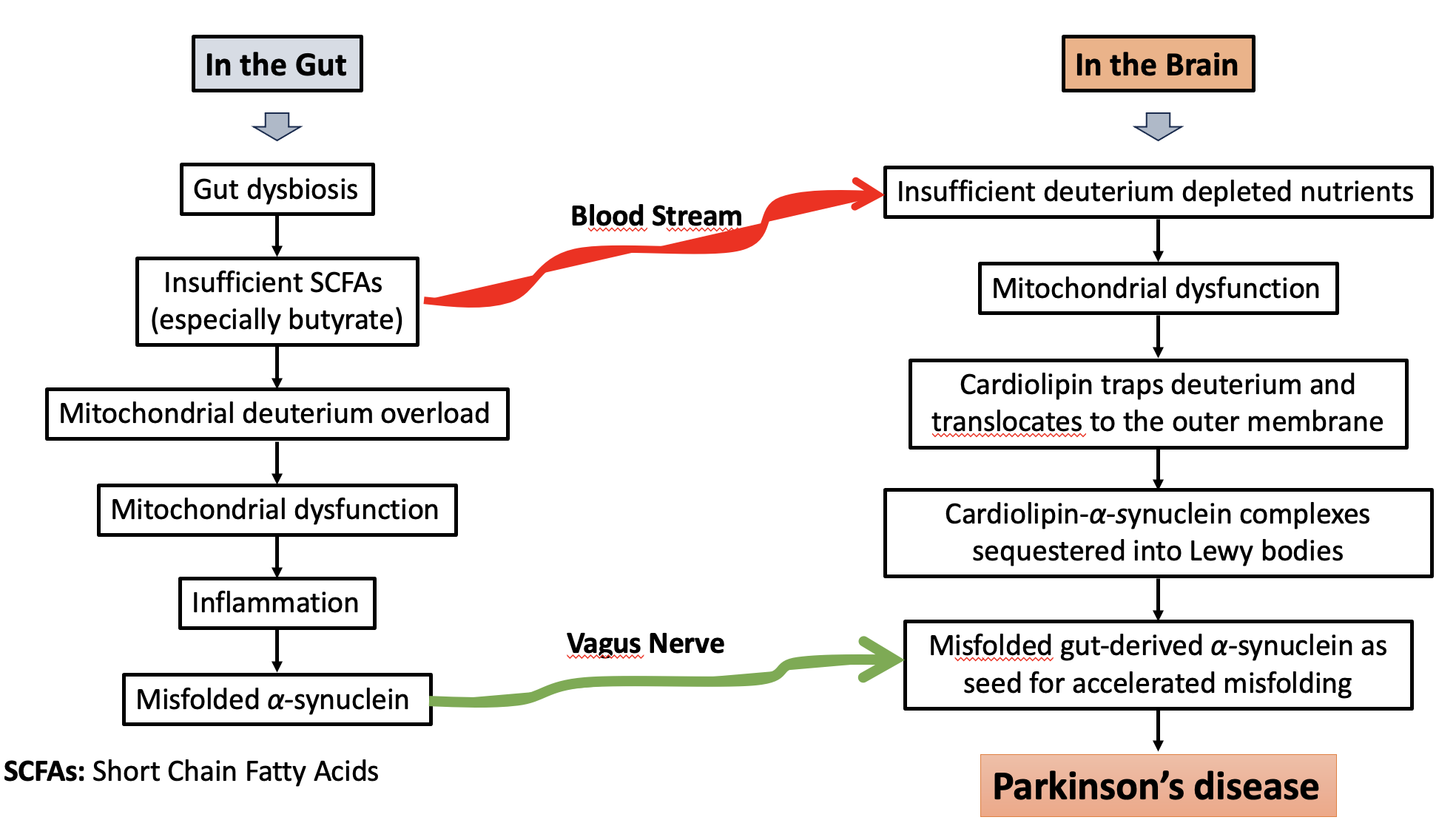
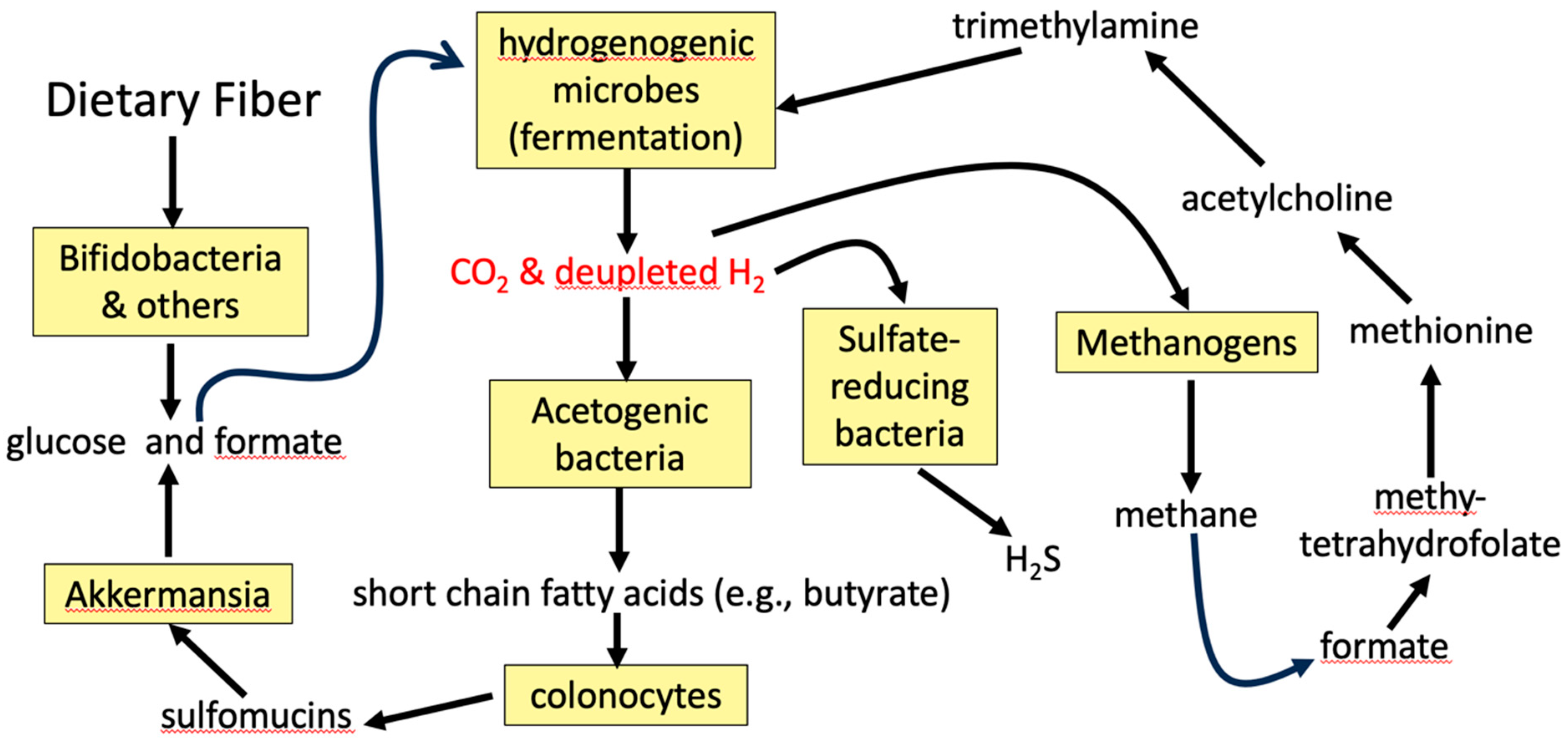
2. Hydrogen Gas Recycling in the Gut and the Competition Among Bacterial Strains
3. The Gut-Brain Axis and the Role of the Gut Microbiome in Human Disease
4. Parkinson’s Disease, Constipation, SIBO, and Methane Gas
5. α-Synuclein, Deuterated PUFAs, Dopamine, and Parkinson’s Disease
6. Cardiolipin and ATP Synthase
7. Cardiolipin, α-Synuclein, Mitochondrial Pore Formation, and Apoptosis
8. Cardiolipin’s Role in Mitophagy is Complex
9. Lewy Bodies and Lipid Deposits
10. The Fine Regulation of Mature Cardiolipin Fatty Acid Content and Parkinson’s Disease
11. Lifestyle Changes to Protect from PD
12. Conclusions
Conflict of Interests
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Abbreviations
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal |
| AA | arachidonic acid |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ALCAT1 | Acyl-coenzyme A:lyso-cardiolipin acyltransferase-1 |
| ATPase | ATP synthase |
| CL | Cardiolipin |
| DDW | deuterium depleted water |
| DHA | docosahexaenoic acid |
| DOPAL | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde |
| Drp1 | dynamin-related protein 1 |
| DβHB | D-β-hydroxybutyrate |
| E coli | Escherichia coli |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| Elovl5 | Elongation of Very Long Chain Fatty Acids 5 |
| FA | fatty acids |
| GSDMD-N | N-terminal fragment of Gasdermin D |
| GSSG | Glutathione disulfide |
| H2S | hydrogen sulfide |
| His50 | Histidine-50 |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| IBS | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| KIE | kinetic isotope effect |
| LA | Linoleic acid |
| LB | Lewy bodies |
| LIPA | light-induced protein aggregation |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| MASH | metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| MPTP | 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine |
| NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| OA | oleic acid |
| PD | Parkinson's disease |
| PUFAs | polyunsaturated fatty acids |
| SCFAs | short chain fatty acids |
| SIBO | small intestinal bacterial overgrowth |
| acetyl-CoA | acetyl coenzyme A |
| deupleted | deuterium depleted |
| α-syn | α-synuclein |
References
- Liddle RA. Parkinson's disease from the gut. Brain Res. 2018;1693(Pt B):201-206. [CrossRef]
- Henrich MT, Oertel WH, Surmeier DJ, Geibl FF. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease - a key disease hallmark with therapeutic potential. Mol Neurodegener. 2023;18(1):83. [CrossRef]
- Olgun A. Biological effects of deuteronation: ATP synthase as an example. Theor Biol Med Model. 2007;4:9. [CrossRef]
- Pryde SE, Duncan SH, Hold GL, Stewart CS, Flint HJ. The microbiology of butyrate formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002;217(2):133-9. [CrossRef]
- Krichevsky MI, Friedman I, Newell MF, Sisler FD. Deuterium fractionation during molecular hydrogen formation in marine pseudomonad. J Biol Chem. 1961;236:252-5.
- Greene BL, Wu CH, McTernan PM, Adams MW, Dyer RB. Proton-coupled electron transfer dynamics in the catalytic mechanism of a [NiFe]-hydrogenase. J Am Chem Soc. 2015; 137(13): 45584566. [CrossRef]
- Walker AW, Duncan SH, McWilliam Leitch EC, Child MW, Flint HJ. pH and peptide supply can radically alter bacterial populations and short-chain fatty acid ratios within microbial communities from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005;71(7):3692-700. [CrossRef]
- Anderson FL, Coffey MM, Berwin BL, Havrda MC. Inflammasomes: An emerging mechanism translating environmental toxicant exposure into neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol Sci. 2018;166(1):3-15. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen SS, Ingerslev LR, Olsen M, Prause M, Billestrup N. Butyrate functions as a histone deacetylase inhibitor to protect pancreatic beta cells from IL-1-induced dysfunction. FEBS J. 2024;291(3):566-583. [CrossRef]
- Folkerts J, Redegeld F, Folkerts G, Blokhuis B, van den Berg MPM, de Bruijn MJW, et al. Butyrate inhibits human mast cell activation via epigenetic regulation of FcRI-mediated signaling. Allergy. 2020;75(8):1966-1978. [CrossRef]
- Rinne JO, Anichtchik OV, Eriksson KS, Kaslin J, Tuomisto L, Kalimo H, et al. Increased brain histamine levels in Parkinson’s disease but not in multiple system atrophy. J Neurochem. 2002;81(5):954-60. [CrossRef]
- Przedborski S, Tieu K, Perier C, Vila M. MPTP as a mitochondrial neurotoxic model of Parkinson’s disease. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2004;36(4):375-9. [CrossRef]
- Tieu K, Perier C, Caspersen C, Teismann P, Wu DC, Yan SD, et al. D-beta-hydroxybutyrate rescues mitochondrial respiration and mitigates features of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(6):892-901. [CrossRef]
- Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. 1997;388(6645):839-40. [CrossRef]
- Xu L, Pu J. Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: from pathogenetic dysfunction to potential clinical application. Parkinsons Dis. 2016; 2016: 1720621. [CrossRef]
- Sampson TR, Debelius JW, Thron T, Janssen S, Shastri GG, Ilhan ZE, et al. Gut microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell. 2016;167(6):1469-1480.e12. [CrossRef]
- Wang T, Leibrock N, Plugge CM, Smidt H, Zoetendal EG. In vitro interactions between Blautia hydrogenotrophica, Desulfovibrio piger and Methanobrevibacter smithii under hydrogenotrophic conditions. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(2):2261784. [CrossRef]
- Cornick S, Tawiah A, Chadee K. Roles and regulation of the mucus barrier in the gut. Tissue Barriers. 2015;3(1-2):e982426. [CrossRef]
- Kang X, Ploner A, Wang Y, Ludvigsson JF, Williams DM, Pedersen NL, et al. Genetic overlap between Parkinson’s disease and inflammatory bowel disease. Brain Commun. 2023;5(1):fcad002. [CrossRef]
- Nishiwaki H, Ito M, Hamaguchi T, Maeda T, Kashihara K, Tsuboi Y, et al. Short chain fatty acids-producing and mucin-degrading intestinal bacteria predict the progression of early Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022;8(1):65. [CrossRef]
- Ijssennagger N, van der Meer R, van Mil SWC. Sulfide as a mucus barrier-breaker in inflammatory bowel disease? Trends Mol Med. 2016;22(3):190-199. [CrossRef]
- Singh SB, Carroll-Portillo A, Lin HC. Desulfovibrio in the gut: The enemy within? Microorganisms. 2023;11(7):1772. [CrossRef]
- Murros KE, Huynh VA, Takala TM, Saris PEJ. Desulfovibrio bacteria Are associated with Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:652617. [CrossRef]
- Murros KE. Hydrogen sulfide produced by gut bacteria may induce Parkinson’s disease. Cells. 2022;11(6):978. [CrossRef]
- Bhatia M. Role of hydrogen sulfide in the pathology of inflammation. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:159680. [CrossRef]
- Huynh VA, Takala TM, Murros KE, Diwedi B, Saris PEJ. Desulfovibrio bacteria enhance alpha-synuclein aggregation in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Parkinson’s disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1181315. [CrossRef]
- Kendall AI. Some observations on the study of the intestinal bacteria. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1909; 6(6): 499-507. https://tinyurl.com/3enn9vb8.
- Aziz Q, Thompson DG. Brain-gut axis in health and disease. Gastroenterology. 1998;114(3):559-78. [CrossRef]
- Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS, et al. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science. 2006;312(5778):1355-9. [CrossRef]
- Lu S, Zhao Q, Guan Y, Sun Z, Li W, Guo S, et al. The communication mechanism of the gut-brain axis and its effect on central nervous system diseases: A systematic review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;178:117207. [CrossRef]
- He Y, Wang K, Su N, Yuan C, Zhang N, Hu X, et al. Microbiota-gut-brain axis in health and neurological disease: Interactions between gut microbiota and the nervous system. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(18):e70099. [CrossRef]
- Phillips RJ, Walter GC, Wilder SL, Baronowsky EA, Powley TL. Alpha-synuclein-immunopositive myenteric neurons and vagal preganglionic terminals: autonomic pathway implicated in Parkinson’s disease? Neuroscience. 2008;153(3):733-50. [CrossRef]
- Pan-Montojo F, Schwarz M, Winkler C, Arnhold M, O'Sullivan GA, Pal A, et al. Environmental toxins trigger Parkinson’s disease-like progression via increased alpha-synuclein release from enteric neurons in mice. Sci Rep. 2012; 2: 898. [CrossRef]
- Ahn EH, Kang SS, Liu X, Chen G, Zhang Z, Chandrasekharan B, et al. Initiation of Parkinson's disease from gut to brain by δ-secretase. Cell Res. 2020;30(1):70-87. [CrossRef]
- Kim C, Lv G, Lee J, Jung BC, Masuda-Suzukake M, Hong C-S, et al. Exposure to bacterial endotoxin generates a distinct strain of α-synuclein fibril. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 30891. [CrossRef]
- Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24(2):197-211. [CrossRef]
- Shameli A, Xiao W, Zheng Y, Shyu S, Sumodi J, Meyerson HJ, et al. A critical role for alpha-synuclein in development and function of T lymphocytes. Immunobiology. 2016;221(2):333-40. [CrossRef]
- Alam MM, Yang D, Li XQ, Liu J, Back TC, Trivett A, et al. Alpha-synuclein, the culprit in Parkinson disease, is required for normal immune function. Cell Rep. 2022;38(2):110090. [CrossRef]
- Karikari AA, McFleder RL, Ribechini E, Blum R, Bruttel V, Knorr S, et al. Neurodegeneration by α-synuclein-specific T cells in AAV-A53T-α-synuclein Parkinson's disease mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;101:194-210. [CrossRef]
- Sampson TR, Challis C, Jain N, Moiseyenko A, Ladinsky MS, Shastri GG, et al. A gut bacterial amyloid promotes α-synuclein aggregation and motor impairment in mice. Elife. 2020;9:e53111. [CrossRef]
- Romano S, Savva GM, Bedarf JR, Charles IG, Hildebrand F, Narbad A. Meta-analysis of the Parkinson’s disease gut microbiome suggests alterations linked to intestinal inflammation. npj Parkinsons Dis. 2021; 7: 27. [CrossRef]
- Unger MM, Spiegel J, Dillmann KU, Grundmann D, Philippeit H, Brmann J, et al. Short chain fatty acids and gut microbiota differ between patients with Parkinson’s disease and age-matched controls. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016;32:66-72. [CrossRef]
- Tan AH, Chong CW, Lim SY, Yap IKS, Teh CSJ, Loke MF, et al. Gut microbial ecosystem in Parkinson disease: New clinicobiological insights from multi-omics. Ann Neurol. 2021;89(3):546-559. [CrossRef]
- Aho VTE, Houser MC, Pereira PAB, Chang J, Rudi K, Paulin L, et al. Relationships of gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, inflammation, and the gut barrier in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2021;16(1):6. [CrossRef]
- Chen SJ, Chen CC, Liao HY, Lin YT, Wu YW, Liou JM, et al. Association of fecal and plasma levels of short-chain fatty acids with gut microbiota and clinical severity in patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2022;98(8):e848-e858. [CrossRef]
- Salvi PS, Cowles RA. Butyrate and the intestinal epithelium: modulation of proliferation and inflammation in homeostasis and disease. Cells. 2021;10(7):1775. [CrossRef]
- Elford JD, Becht N, Garssen J, Kraneveld AD, Perez-Pardo P. Buty and the beast: the complex role of butyrate in Parkinson’s disease. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1388401. [CrossRef]
- Yu QJ, Yu SY, Zuo LJ, Lian TH, Hu Y, Wang RD, et al. Parkinson disease with constipation: clinical features and relevant factors. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):567. [CrossRef]
- Dănău A, Dumitrescu L, Lefter A, Tulbă D, Popescu BO. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth as potential therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11663. [CrossRef]
- Tansel A, Levinthal DJ. Understanding Our tests: Hydrogen-methane breath testing to diagnose small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2023;14(4):e00567. [CrossRef]
- Kunkel D, Basseri RJ, Makhani MD, Chong K, Chang C, Pimentel M. Methane on breath testing is associated with constipation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56(6):1612-8. [CrossRef]
- Tan AH, Mahadeva S, Thalha AM, Gibson PR, Kiew CK, Yeat CM, et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014;20(5):535-40. [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli M, Bonazzi P, Scarpellini E, Bendia E, Lauritano EC, Fasano A, et al. Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2011;26(5):889-92. [CrossRef]
- Li Z, Liang H, Hu Y , Lu L, Zheng C, Fan Y, et al. Gut bacterial profiles in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(1):140-157. [CrossRef]
- Miquel S, Martín R, Rossi O, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, Chatel JM, Sokol H, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013;16(3):255-61. [CrossRef]
- Gandhi A, Shah A, Jones MP, Koloski N, Talley NJ, Morrison M, et al. Methane positive small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes. 2021;13(1):1933313. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Mao B, Gu J, Wu J, Cui S, Wang G, et al. Blautia -- a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes. 2021;13(1):1-21. [CrossRef]
- Dudzik CG, Walter ED, Millhauser GL. Coordination features and affinity of the Cu+ site in the α-synuclein protein of Parkinson’s disease. Biochemistry. 2011;50(11):1771-7. [CrossRef]
- Farzadfard A, Pedersen JN, Meisl G, Somavarapu AK, Alam P, Goksyr L, et al. The C-terminal tail of α-synuclein protects against aggregate replication but is critical for oligomerization. Commun Biol. 2022;5(1):123. [CrossRef]
- Chen C, Turnbull DM, Reeve AK. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease - cause or consequence? Biology (Basel). 2019;8(2):38. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Kaushik S, Massey AC, Mazzulli J, Mosharov EV, et al. Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(2):777-88. [CrossRef]
- Burke WJ, Li SW, Williams EA, Nonneman R, Zahm DS. 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde is the toxic dopamine metabolite in vivo: implications for Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Brain Res. 2003;989(2):205-13. [CrossRef]
- Fivenson EM, Lautrup S, Sun N, Scheibye-Knudsen M, Stevnsner T, Nilsen H, et al. Mitophagy in neurodegeneration and aging. Neurochem Int. 2017;109:202-209. [CrossRef]
- Palikaras K, Lionaki E, Tavernarakis N. Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(9):1013-1022. [CrossRef]
- Shchepinov MS, Roginsky VA, Brenna JT, Molinari RJ, To R, Tsui H, et al. Chapter 31 - Deuterium protection of polyunsaturated fatty acids against lipid peroxidation: a novel approach to mitigating mitochondrial neurological diseases. Watson RR, De Meester F, Eds. Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Brain and Neurological Health, Academic Press 2014; 373-383.
- Raefsky SM, Furman R, Milne G, Pollock E, Axelsen P, Mattson MP, et al. Deuterated polyunsaturated fatty acids reduce brain lipid peroxidation and hippocampal amyloid beta-peptide levels, without discernable behavioral effects in an APP/PS1 mutant transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2018;66:165176. https://doi. org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.02.024.
- Beal MF, Chiluwal J, Calingasan NY, Milne GL, Shchepinov MS, Tapias V. Isotope-reinforced polyunsaturated fatty acids improve Parkinson’s disease-like phenotype in rats overexpressing α-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020;8(1):220. [CrossRef]
- Navratil AR, Shchepinov MS, Dennis EA. Lipidomics reveals dramatic physiological kinetic isotope effects during the enzymatic oxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids ex vivo. J Am Chem Soc. 2018; 140(1): 235-243. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Zhao T, Li J, Xia M, Li Y, Wang X, et al. Oxidative stress and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE): implications in the pathogenesis and treatment of aging-related diseases. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:2233906. [CrossRef]
- Seneff S, Nigh G, Kyriakopoulos A. Is deuterium sequestering by reactive carbon atoms an important biological mechanism to reduce deuterium content in biological water? Preprints. Jan 25, 2025. [CrossRef]
- Xiang W, Menges S, Schlachetzki JC, Meixner H, Hoffmann AC, Schltzer-Schrehardt U, Becker CM, Winkler J, Klucken J. Posttranslational modification and mutation of histidine 50 trigger alpha synuclein aggregation and toxicity. Mol Neurodegener. 2015;10:8. [CrossRef]
- Sardar Sinha M, Villamil Giraldo AM, Öllinger K, Hallbeck M, Civitelli L. Lipid vesicles affect the aggregation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified α-synuclein oligomers. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(9 Pt B):3060-3068. [CrossRef]
- Bae EJ, Ho DH, Park E, Jung JW, Cho K, Hong JH, et al. Lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal promotes seeding-capable oligomer formation and cell-to-cell transfer of α-synuclein. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18(7):770-83. [CrossRef]
- Chi YC, Armstrong GS, Jones DN, Eisenmesser EZ, Liu CW. Residue histidine 50 plays a key role in protecting α-synuclein from aggregation at physiological pH. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(22):15474-81. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura R, Tomizawa I, Iwai A, Ikeda T, Hirayama K, Chiu YW, et al. Photo-oxygenation of histidine residue inhibits α-synuclein aggregation. FASEB J. 2023;37(12):e23311. [CrossRef]
- Sherer TB, Richardson JR, Testa CM, Seo BB, Panov AV, Yagi T, et al. Mechanism of toxicity of pesticides acting at complex I: relevance to environmental etiologies of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem. 2007;100(6):1469-79. [CrossRef]
- Cole NB, Dieuliis D, Leo P, Mitchell DC, Nussbaum RL. Mitochondrial translocation of alpha-synuclein is promoted by intracellular acidification. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(10):2076-89. [CrossRef]
- Miller SM, Klinman JP. Magnitude of intrinsic isotope effects in the dopamine beta-monooxygenase reaction. Biochemistry. 1983;22(13):3091-6. PMID: 6882738. [CrossRef]
- May JM, Cobb CE, Mendiratta S, Hill KE, Burk RF. Reduction of the ascorbyl free radical to ascorbate by thioredoxin reductase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(36):23039-45. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Edmondson DE. 2H kinetic isotope effects and pH dependence of catalysis as mechanistic probes of rat monoamine oxidase A: comparisons with the human enzyme. Biochemistry. 2011;50(35):7710-7. [CrossRef]
- Cohen G, Farooqui R, Kesler N. Parkinson disease: a new link between monoamine oxidase and mitochondrial electron flow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(10):4890-4. [CrossRef]
- Thase ME. The role of monoamine oxidase inhibitors in depression treatment guidelines. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73 Suppl 1:10-6. [CrossRef]
- Strekalova T, Evans M, Chernopiatko A, Couch Y, Costa-Nunes J, Cespuglio, R, et al. Deuterium content of water increases depression susceptibility: the potential role of a serotonin-related mechanism. Behav Brain Res. 2015; 277: 2370244. [CrossRef]
- Gillman PK. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, opioid analgesics and serotonin toxicity.Br J Anaesth. 2005;95(4):434-41. [CrossRef]
- Chicco AJ, Sparagna GC. Role of cardiolipin alterations in mitochondrial dysfunction and disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292(1):C33-44. [CrossRef]
- Acehan D, Malhotra A, Xu Y, Ren M, Stokes DL, Schlame M. Cardiolipin affects the supramolecular organization of ATP synthase in mitochondria. Biophys J. 2011; 100:21842192. [CrossRef]
- Eble KS, Coleman WB, Hantgan RR, Cunningham CC. Tightly associated cardiolipin in the bovine heart mitochondrial ATP synthase as analyzed by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(32):19434-40.
- Spikes TE, Montgomery MG, Walker JE. Structure of the dimeric ATP synthase from bovine mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(38):23519-23526. [CrossRef]
- Garcia Fernandez M, Troiano L, Moretti L, Nasi M, Pinti M, Salvioli S, et al. arly changes in intramitochondrial cardiolipin distribution during apoptosis. Cell Growth Differ. 2002;13(9):449-55.
- Kim TH, Zhao Y, Ding WX, Shin JN, He X, Seo YW, et al. Bid-cardiolipin interaction at mitochondrial contact site contributes to mitochondrial cristae reorganization and cytochrome C release. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15(7):3061-72. [CrossRef]
- Ellis CE, Murphy EJ, Mitchell DC, Golovko MY, Scaglia F, Barcel-Coblijn GC, et al. Mitochondrial lipid abnormality and electron transport chain impairment in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(22):10190-201. [CrossRef]
- Mühleip A, McComas SE, Amunts A. Structure of a mitochondrial ATP synthase with bound native cardiolipin. Elife. 2019;8:e51179. [CrossRef]
- Tang Y, Wu J, Sun X, Tan S, Li W, Yin S, et al. Cardiolipin oxidized by ROS from complex II acts as a target of gasdermin D to drive mitochondrial pore and heart dysfunction in endotoxemia. Cell Rep. 2024;43(5):114237. Erratum in: Cell Rep. 2025;44(3):115395. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115395. [CrossRef]
- Ghio S, Camilleri A, Caruana M, Ruf VC, Schmidt F, Leonov A, et al. Cardiolipin promotes pore-forming activity of alpha-synuclein oligomers in mitochondrial membranes. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10(8):3815-3829. [CrossRef]
- Ryan T, Bamm VV, Stykel MG, Coackley CL, Humphries KM, Jamieson-Williams R, et al. Cardiolipin exposure on the outer mitochondrial membrane modulates α-synuclein. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):817. [CrossRef]
- Gilmozzi V, Gentile G, Castelo Rueda MP, Hicks AA, Pramstaller PP, Zanon A, et al. Interaction of alpha-synuclein with lipids: mitochondrial cardiolipin as a critical player in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:578993. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura K, Nemani VM, Azarbal F, Skibinski G, Levy JM, Egami K, et al. Direct membrane association drives mitochondrial fission by the Parkinson disease-associated protein alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(23):20710-26. [CrossRef]
- Devi L, Raghavendran V, Prabhu BM, Avadhani NG, Anandatheerthavarada HK. Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(14):9089-100. [CrossRef]
- Dadsena S, Cuevas Arenas R, Vieira G, Brodesser S, Melo MN, Garca-Sez AJ. Lipid unsaturation promotes BAX and BAK pore activity during apoptosis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):4700. [CrossRef]
- Wang C, Youle RJ. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:95-118. [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti SS, Sunder VS, Kaur U, Bala S, Sharma P, Kiran M, et al. Identifying the mechanisms of α-synuclein-mediated cytotoxicity in Parkinsons disease: new insights from a bioinformatics-based approach. Future Neurol. 2020; 15(3): FNL49. [CrossRef]
- Panov A, Dikalov S, Shalbuyeva N, Taylor G, Sherer T, Greenamyre JT. Rotenone model of Parkinson disease: multiple brain mitochondria dysfunctions after short term systemic rotenone intoxication. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(51):42026-35. [CrossRef]
- Chu CT, Ji J, Dagda RK, Jiang JF, Tyurina YY, Kapralov AA, et al. Cardiolipin externalization to the outer mitochondrial membrane acts as an elimination signal for mitophagy in neuronal cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(10):1197-1205. [CrossRef]
- Lurette O, Martín-Jiménez R, Khan M, Sheta R, Jean S, Schofield M, et al. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein disrupts mitochondrial metabolism and induce mitophagy via cardiolipin externalization. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(11):729. [CrossRef]
- Martín-Jiménez R, Lurette O, Hebert-Chatelain E. Alpha-synuclein aggregates trigger cardiolipin externalization and mitophagy, Autophagy Reports. 2024; 3:1: 2314361. [CrossRef]
- Chu CT, Bayr H, Kagan VE. LC3 binds externalized cardiolipin on injured mitochondria to signal mitophagy in neurons: implications for Parkinson disease. Autophagy. 2014;10(2):376-8. [CrossRef]
- Bayati A, Ayoubi R, Aguila A, Zorca CE, Deyab, G, Han C, et al. Modeling Parkinson’s disease pathology in human dopaminergic neurons by sequential exposure to α-synuclein fibrils and proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Neurosci. 2024; 27: 2401-2416. [CrossRef]
- Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Pistolese M, Di Venosa N, Federici A, Ruggiero FM. Decrease in mitochondrial complex I activity in ischemic/reperfused rat heart: involvement of reactive oxygen species and cardiolipin. Circ Res. 2004;94(1):53-9. [CrossRef]
- Vives-Bauza C, Zhou C, Huang Y, Cui M, de Vries RL, Kim J, et al. PINK1-dependent recruitment of Parkin to mitochondria in mitophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(1):378-83. [CrossRef]
- Song C, Zhang J, Qi S, Liu Z, Zhang X, Zheng Y, et al. Cardiolipin remodeling by ALCAT1 links mitochondrial dysfunction to Parkinson’s diseases. Aging Cell. 2019;18(3):e12941. [CrossRef]
- Mahajan M, Bharambe N, Shang Y, Lu B, Mandal A, Madan Mohan P, et al. NMR identification of a conserved Drp1 cardiolipin-binding motif essential for stress-induced mitochondrial fission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(29):e2023079118. [CrossRef]
- Buhlman L, Damiano M, Bertolin G, Ferrando-Miguel R, Lombs A, Brice A, et al. Functional interplay between Parkin and Drp1 in mitochondrial fission and clearance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1843(9):2012-26. [CrossRef]
- Vouilloz A, Bourgeois T, Diedisheim M, Pilot T, Jalil A, Le Guern N, et al. Impaired unsaturated fatty acid elongation alters mitochondrial function and accelerates metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis progression. Metabolism. 2025;162:156051. [CrossRef]
- Erskine D, Koss D, Korolchuk VI, Outeiro TF, Attems J, McKeith I. Lipids, lysosomes and mitochondria: insights into Lewy body formation from rare monogenic disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2021;141(4):511-526. [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradian SH, Lewis AJ, Genoud C, Hench J, Moors TE, Navarro PP, et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22(7):1099-1109. [CrossRef]
- Fanning S, Selkoe D, Dettmer U. Parkinson’s disease: proteinopathy or lipidopathy? NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2020;6:3. [CrossRef]
- Perrin RJ, Woods WS, Clayton DF, George JM. Exposure to long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids triggers rapid multimerization of synucleins. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(45):41958-62. [CrossRef]
- Hatton C, Reeve A, Lax NZ, Blain A, Ng YS, El-Agnaf O, et al. Complex I reductions in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Lewy body dementia: the role of Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020;8(1):103. [CrossRef]
- Schlame M. Cardiolipin synthesis for the assembly of bacterial and mitochondrial membranes. J Lipid Res. 2008;49(8):1607-20. [CrossRef]
- Alashmali SM, Lin L, Trépanier MO, Cisbani G, Bazinet RP. The effects of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid deprivation on the inflammatory gene response to lipopolysaccharide in the mouse hippocampus. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):237. [CrossRef]
- Flønes IH, Tzoulis C. Mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction - a hallmark pathology of idiopathic Parkinson's disease? Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:874596. [CrossRef]
- Burtscher J, Syed MMK, Keller MA, Lashuel HA, Millet GP. Fatal attraction - The role of hypoxia when alpha-synuclein gets intimate with mitochondria. Neurobiol Aging. 2021;107:128-141. [CrossRef]
- Fanning S, Haque A, Imberdis T, Baru V, Barrasa MI, Nuber S, et al. Lipidomic analysis of α-synuclein neurotoxicity identifies stearoyl CoA desaturase as a target for Parkinson treatment. Mol Cell. 2019;73(5):1001-1014.e8. [CrossRef]
- Lee HJ, Mayette J, Rapoport SI, Bazinet RP. Selective remodeling of cardiolipin fatty acids in the aged rat heart. Lipids Health Dis. 2006;5:2. [CrossRef]
- Bobela W, Aebischer P, Schneider BL. Alpha-synuclein as a mediator in the interplay between aging and Parkinson's disease. Biomolecules. 2015;5(4):2675-700. [CrossRef]
- Kudo Y, Nakamura K, Tsuzuki H, Hirota K, Kawai M, Takaya D, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid enhances the treatment efficacy for castration-resistant prostate cancer by inhibiting autophagy through Atg4B inhibition. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024;760:110135. [CrossRef]
- Hou X, Watzlawik JO, Fiesel FC, Springer W. Autophagy in Parkinson’s disease. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(8):2651-2672. [CrossRef]
- Taha AY. Linoleic acid-good or bad for the brain? NPJ Sci Food. 2020;4:1. Erratum in: NPJ Sci Food. 2020;4:6. doi: 10.1038/s41538-020-0066-4. [CrossRef]
- Van Q, Liu J, Lu B, Feingold KR, Shi Y, Lee RM, et al. Phospholipid scramblase-3 regulates cardiolipin de novo biosynthesis and its resynthesis in growing HeLa cells. Biochem J. 2007;401(1):103-9. PMID: 16939411; PMCID: PMC1698660. [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Adiv S, Amer-Sarsour F, Berdichevsky Y, Boxer E, Goldstein O, Gana-Weisz M, et al. TMEM16F regulates pathologic α-synuclein secretion and spread in cellular and mouse models of Parkinson's disease. Aging Cell. 2025;24(2):e14387. [CrossRef]
- Manganelli V, Capozzi A, Recalchi S, Riitano G, Mattei V, Longo A, et al. The role of cardiolipin as a scaffold mitochondrial phospholipid in autophagosome formation: In vitro evidence. Biomolecules. 2021;11(2):222. [CrossRef]
- De Franceschi G, Frare E, Pivato M, Relini A, Penco A, Greggio E, et al. Structural and morphological characterization of aggregated species of -synuclein induced by docosahexaenoic acid. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(25):22262-74. [CrossRef]
- Deng K, Wang L, Nguyen SM, Shrubsole MJ, Cai Q, Lipworth L, et al. A dietary pattern promoting gut sulfur metabolism is associated with increased mortality and altered circulating metabolites in low-income American adults. eBioMedicine 2025; 115: 105690. [CrossRef]
- Répás Z, Győri Z, Buzás-Bereczki O, Boros LG. The biological effects of deuterium present in food. Discover Food. 2025; 5:57.
- Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Testa CM, Seo BB, Richardson JR, Kim JH, et al. Mechanism of toxicity in rotenone models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci. 2003;23(34):10756-64. [CrossRef]
- Anderson T, Merrill AK, Eckard ML, Marvin E, Conrad K, Welle K, Oberdrster G, Sobolewski M, Cory-Slechta DA. Paraquat inhalation, a translationally relevant route of exposure: disposition to the brain and male-specific olfactory impairment in mice. Toxicol Sci. 2021;180(1):175-185. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Qin D, Yang H, Wang W, Xiao J, Zhou L, Fu H. Neuroprotective effects of deuterium-depleted water (DDW) against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in differentiated PC12 cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(5):1034-1044. [CrossRef]
- Oosterhof TH, Darweesh SKL, Bloem BR, de Vries NM. Considerations on how to prevent Parkinson’s disease through exercise. J Parkinsons Dis. 2024;14(s2):S395-S406. [CrossRef]
- Janssen Daalen JM, Schootemeijer S, Richard E, Darweesh SKL, Bloem BR. Lifestyle Interventions for the prevention of Parkinson disease: A recipe for action. Neurology. 2022;99(7 Suppl 1):42-51. [CrossRef]
- Matta Reddy A, Iqbal M, Chopra H, Urmi S, Junapudi S, Bibi S, Kumar Gupta S, Nirmala Pangi V, Singh I, Abdel-Daim MM. Pivotal role of vitamin D in mitochondrial health, cardiac function, and human reproduction. EXCLI J. 2022;21:967-990. [CrossRef]
- Hu L, Shi Y, Zou X, Lai Z, Lin F, Cai G, Liu X. Association of time spent outdoors with the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A prospective cohort study of 329,359 participants. BMC Neurol. 2024;24(1):10. [CrossRef]

| Phospholipid | Classification | # bis-allylic carbons | 4 months | 12 months | 24 months |
| Oleic acid | 18:1n-9 | 0 | 279 | 291 | 347 |
| Linoleic acid | 18:2n-6 | 1 | 5525 | 6025 | 3965 |
| Arachidonic acid | 20:4n-6 | 3 | 79 | 140 | 178 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid | 22:6n-3 | 5 | 104 | 230 | 307 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





