Submitted:
02 April 2025
Posted:
02 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
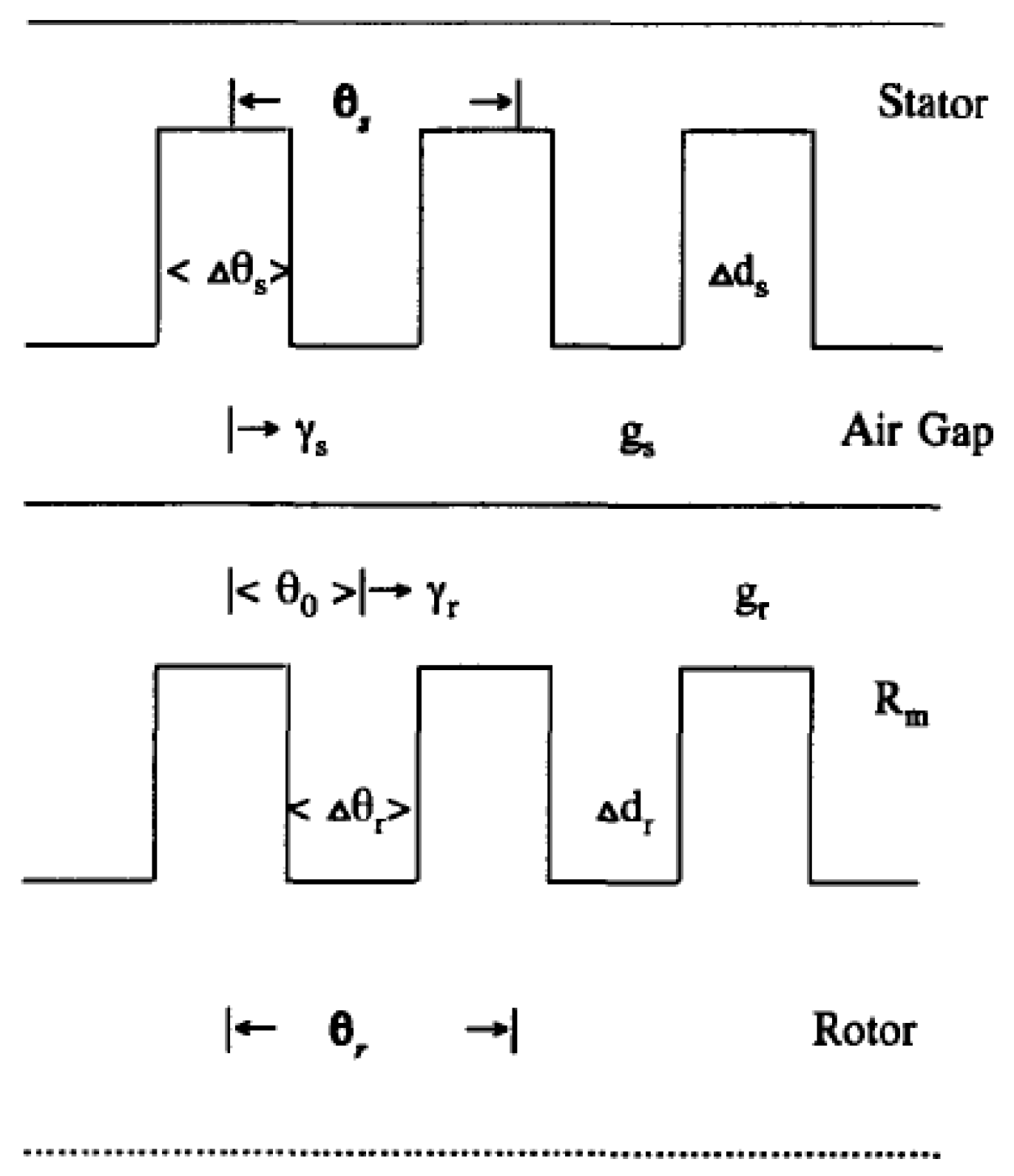
2. Air Gap Permeance
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.2. Using Air Gap Permeance for Reluctance Machine Analysis
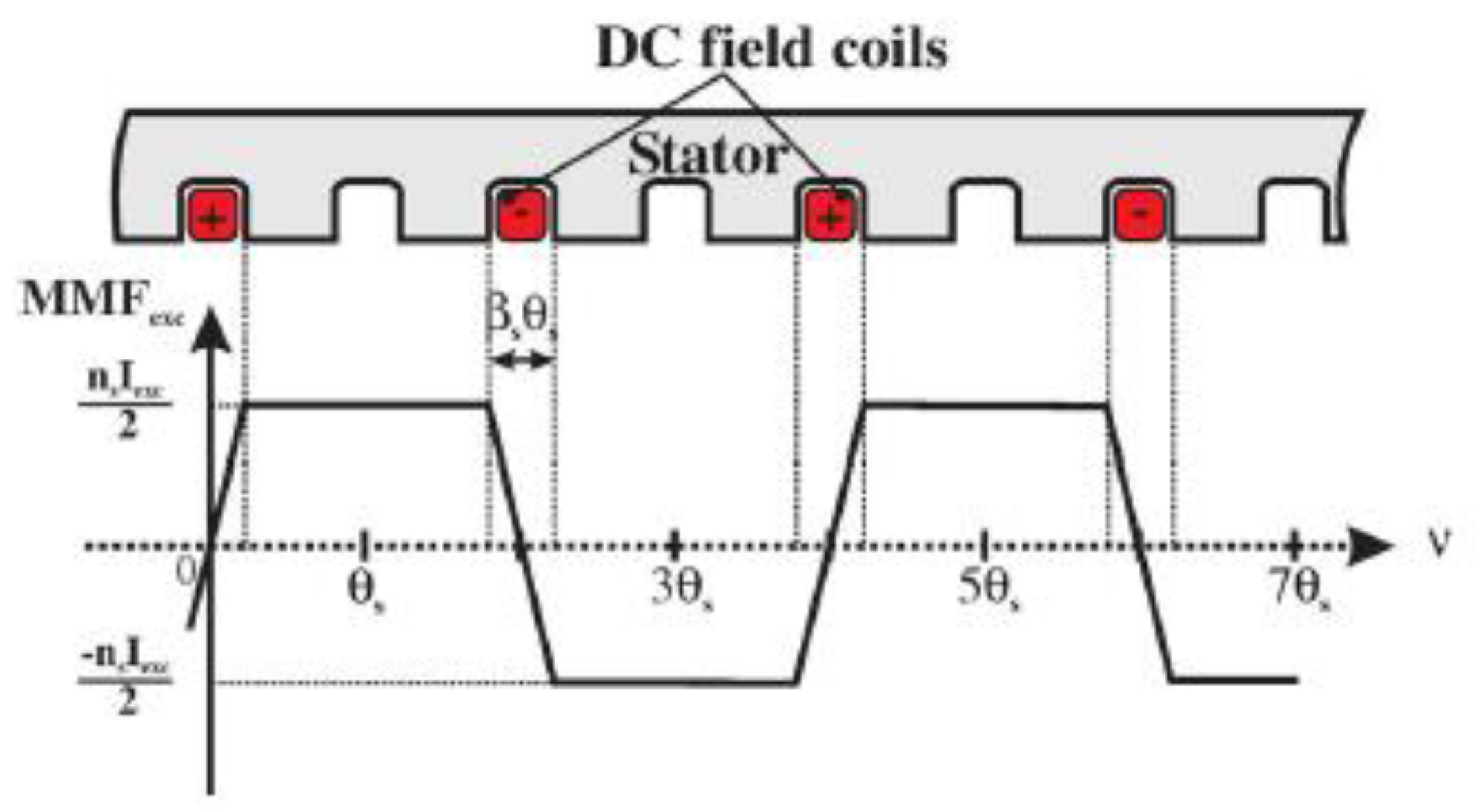
3. Magnetic Potentials
3.1. Theoretical Background of Magnetic Potentials
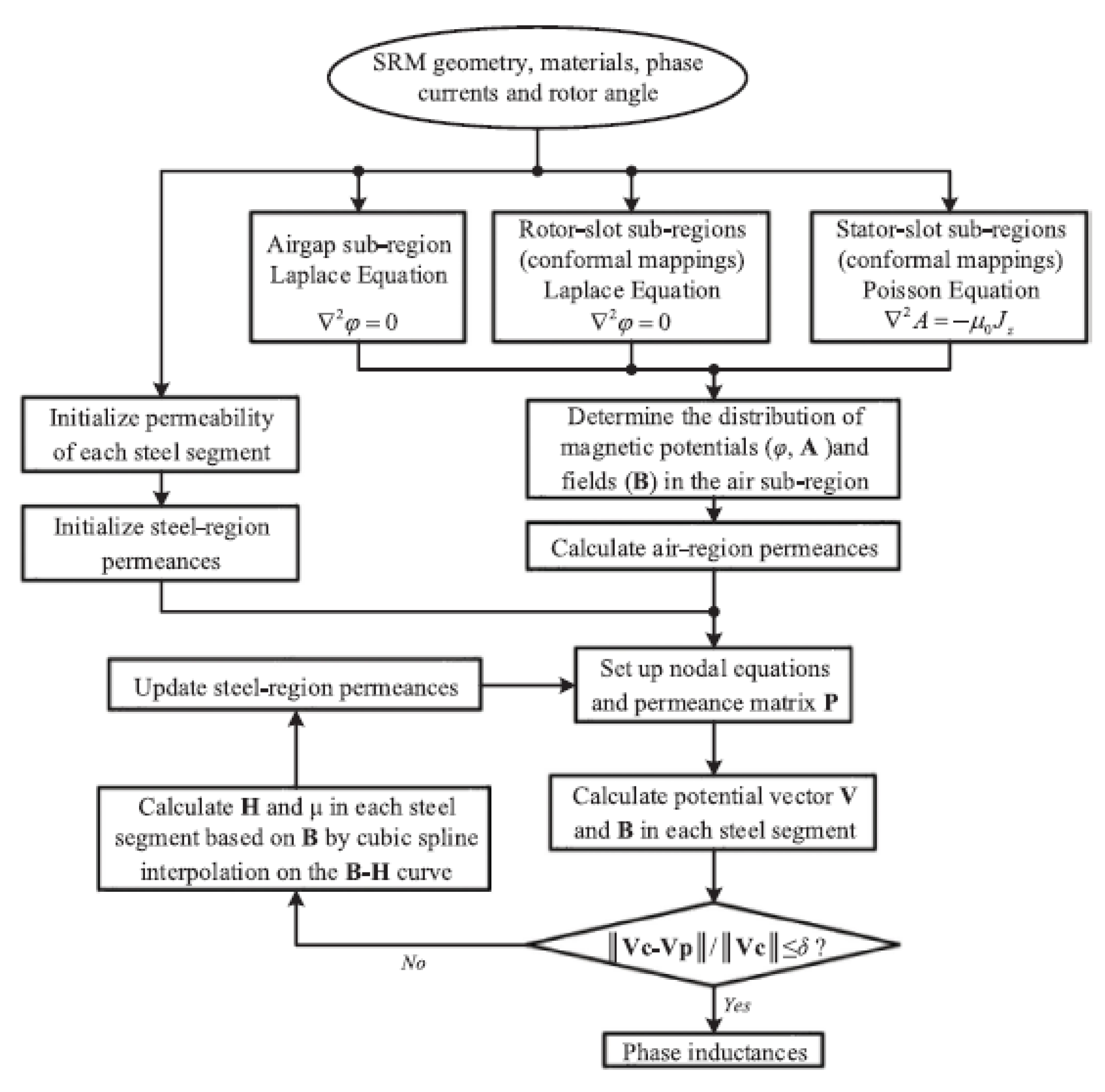
3.2. Applying Magnetic Potentials to Reluctance Motors
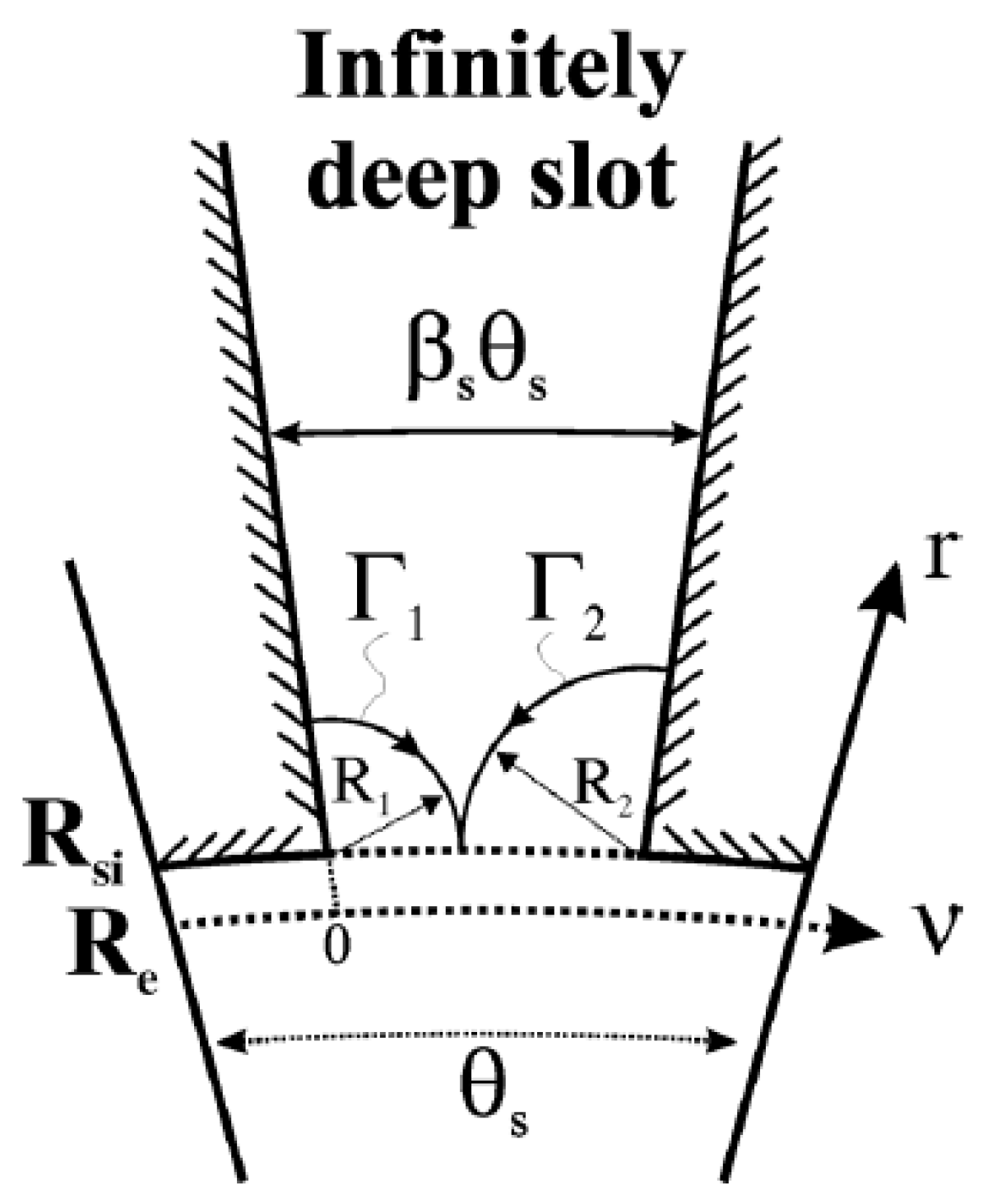
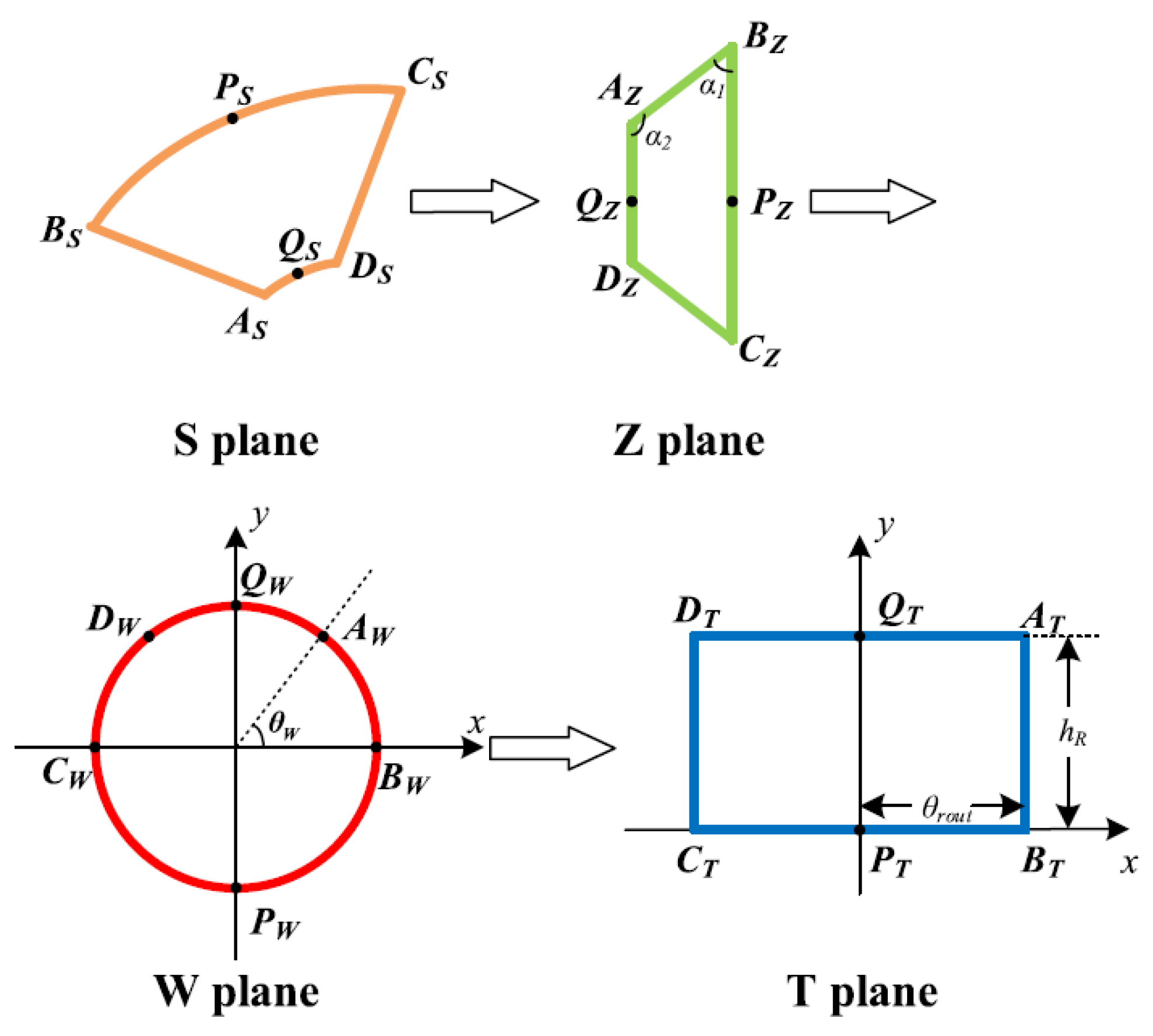
4. Conformal Mapping
4.1. Theoretical Background of Conformal Mapping
4.2. Conformal Mapping in Reluctance Motor Analysis
6. Summary of Major Techniques
7. Other Techniques Used in Reluctance Motor Research
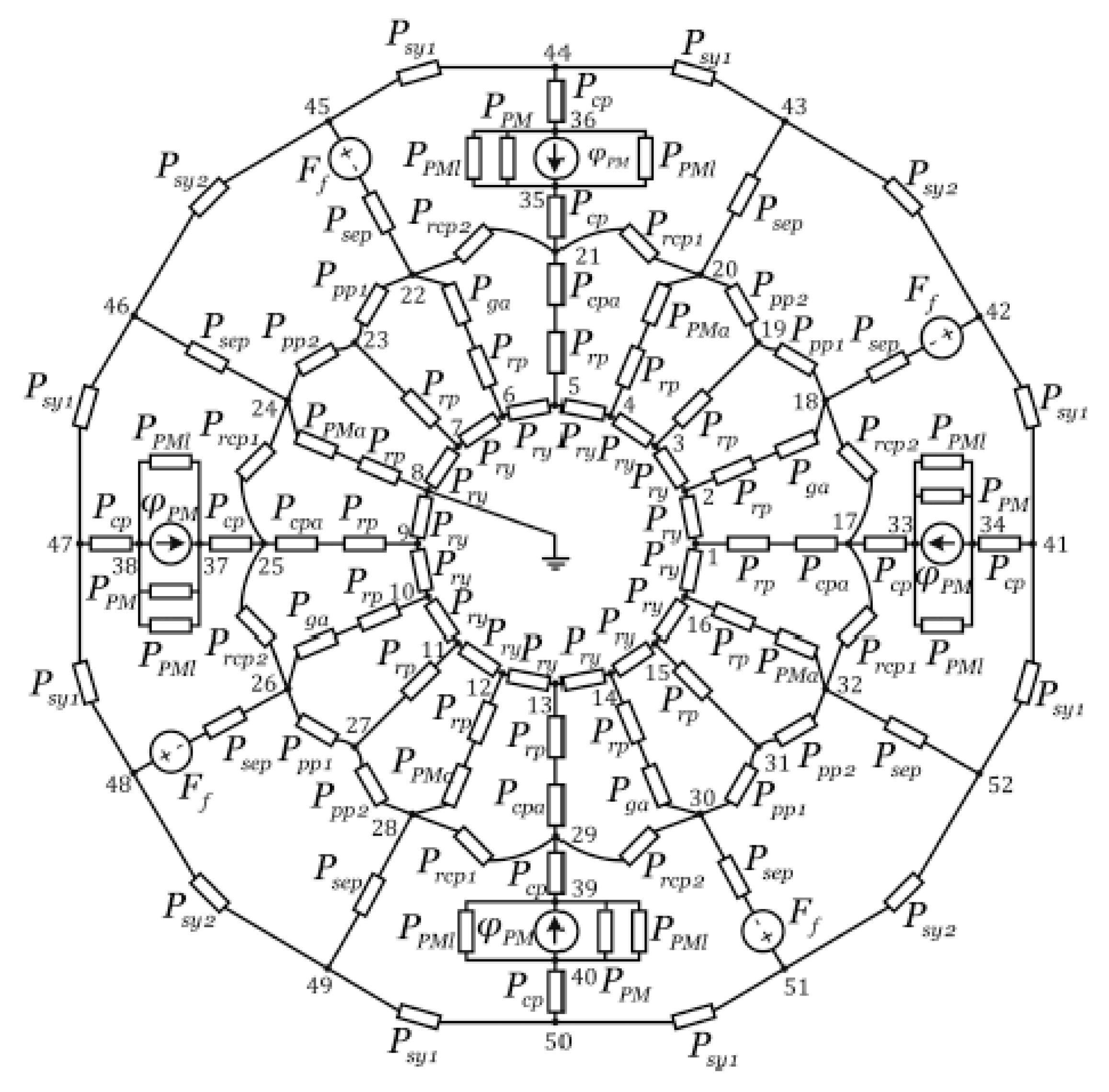
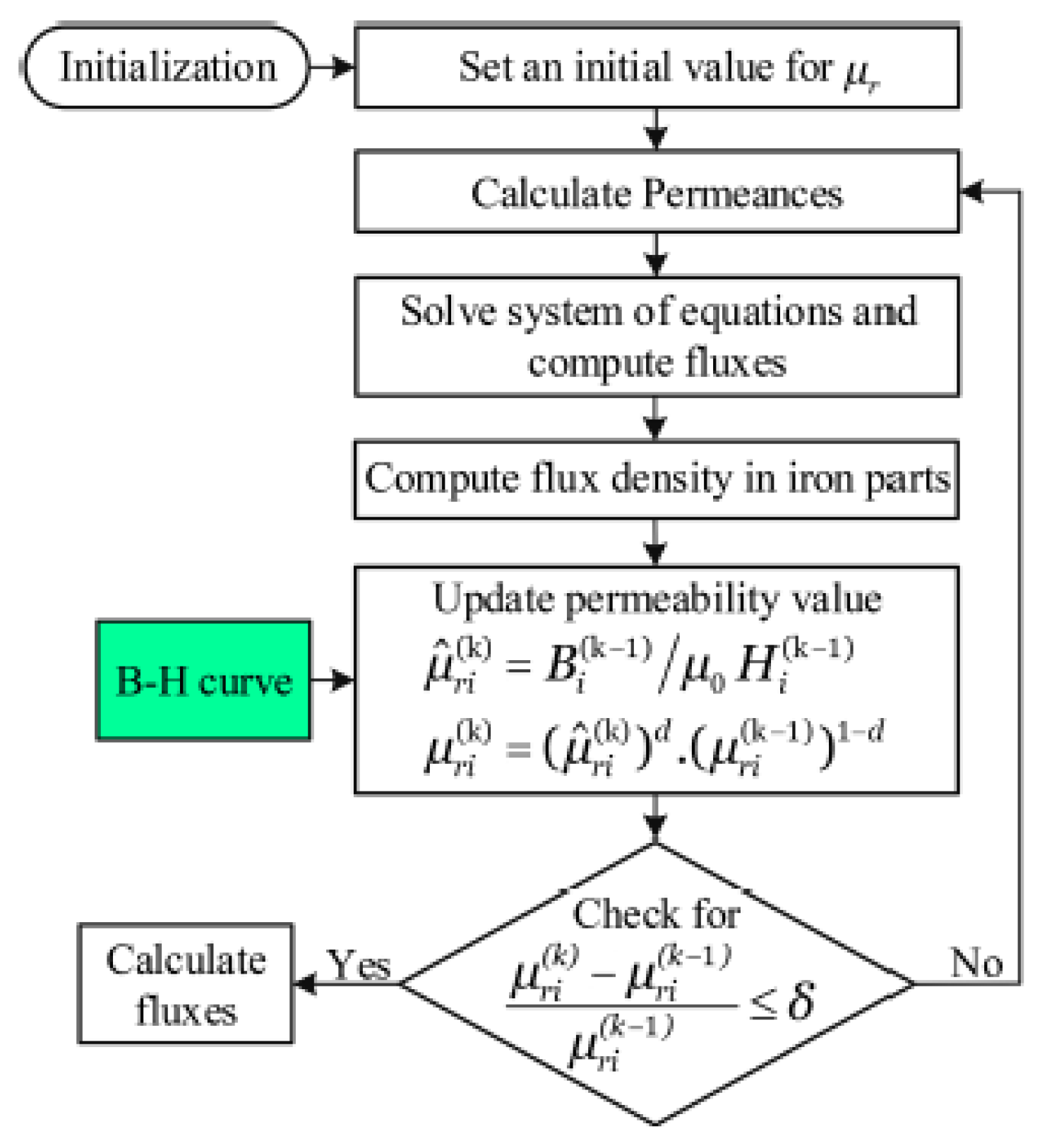
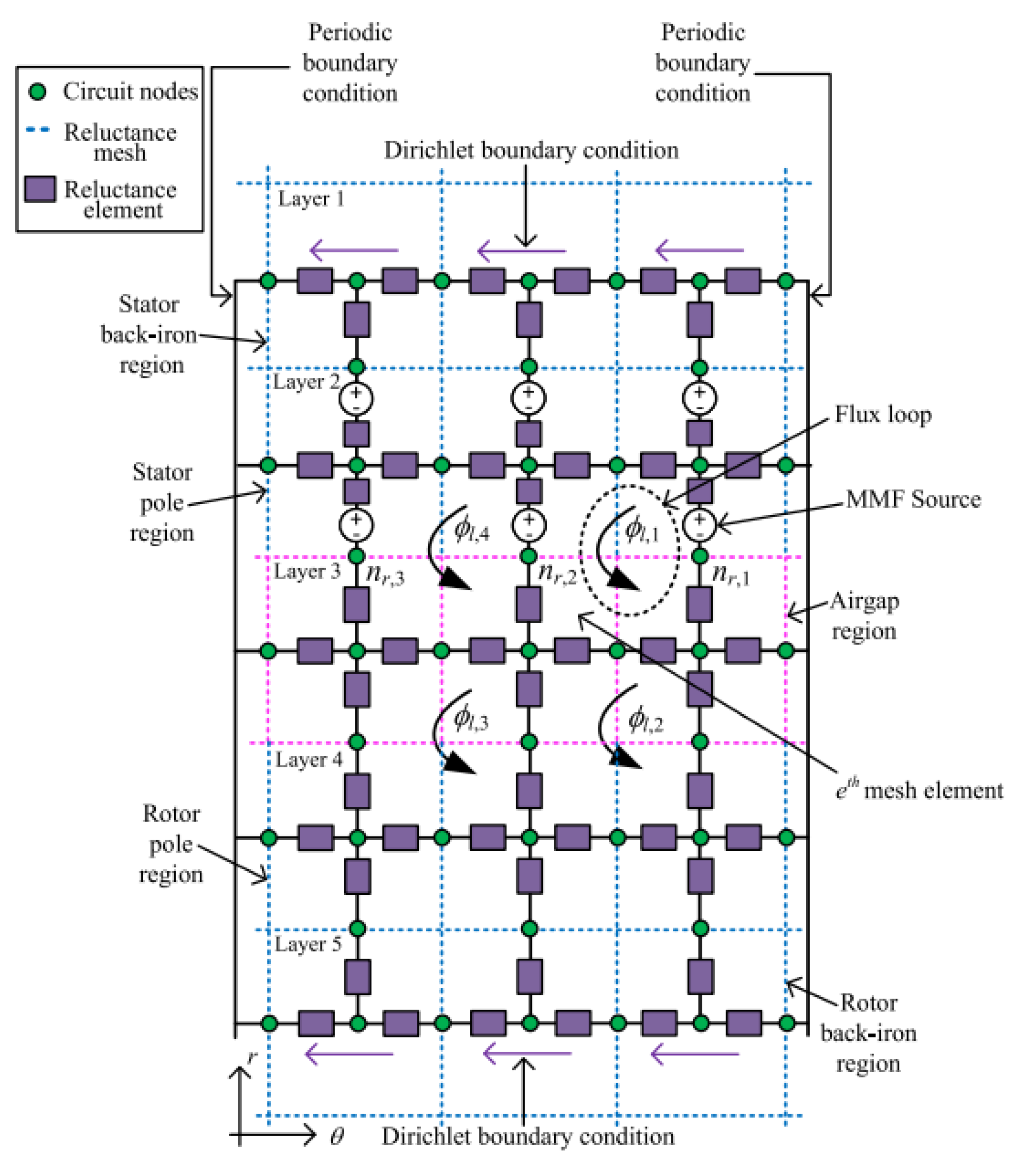
7.1. Magnetic Equivalent Circuits
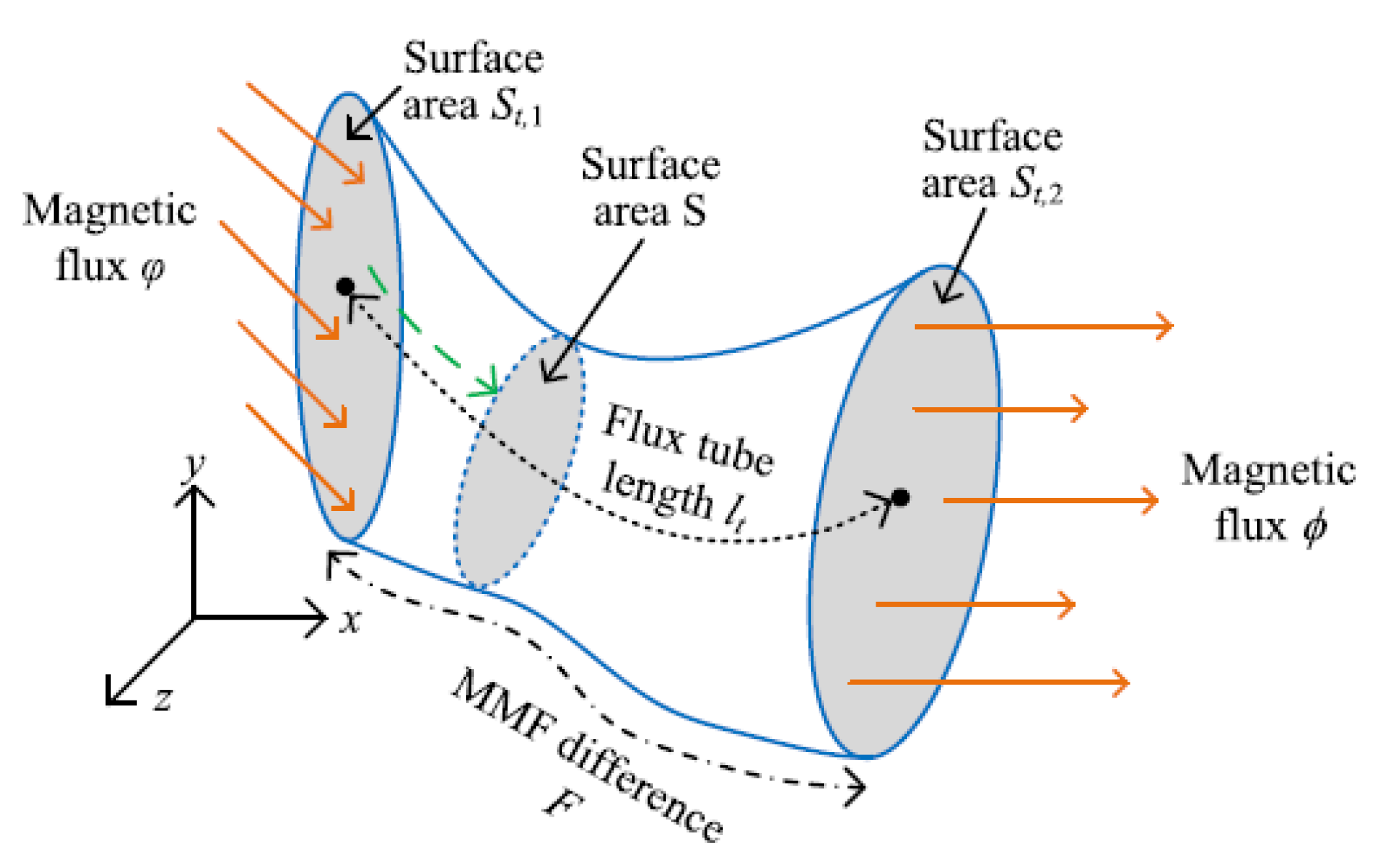
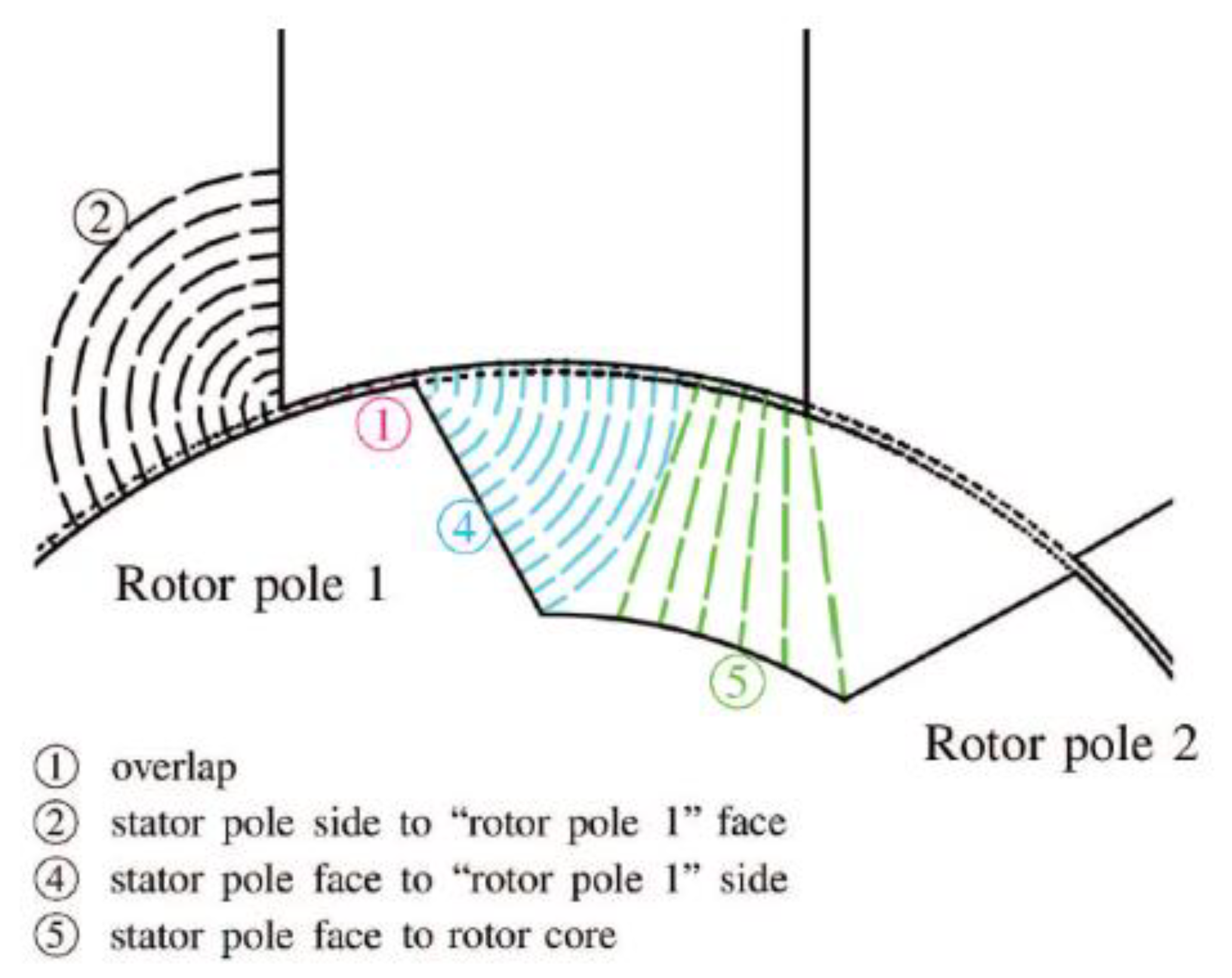
7.2. Reluctance Mesh and Flux Tubes
7.3. Maxwell Stress Tensor
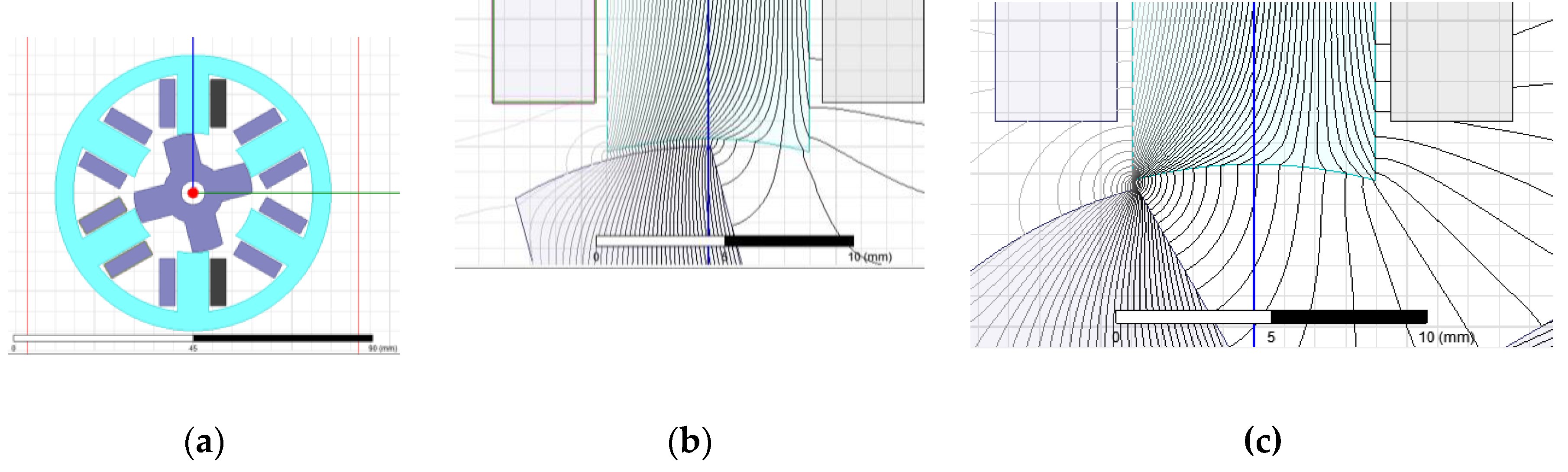
8. Potential Applications to Segmented Reluctance Motor Design
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BEA | Boundary element analysis |
| CSSR | Conventional stator, segmented rotor |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| MEC | Magnetic equivalent circuit |
| MMF | Magnetomotive force |
| MST | Maxwell stress tensor |
| SRM | Switched reluctance motor |
| SC | Schwarz-Christoffel (transform) |
| SSSR | Segmented stator, segmented rotor |
References
- K. Diao, X. Sun, G. Lei, G. Bramerdorfer, Y. Guo and J. Zhu. Robust Design Optimization of Switched Reluctance Motor Drive Systems Based on System-Level Sequential Taguchi Method. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2021, 36, 3199–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Li, S. Zhang, T. G. Habetler and R. G. Harley. Modeling, Design Optimization, and Applications of Switched Reluctance Machines—A Review. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2019, 55, 2660–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Diao, X. Sun, G. Bramerdorfer, Y. Cai, G. Lei, L. Chen. Design optimization of switched reluctance machines for performance and reliability enhancements: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2022, 168. [Google Scholar]
- M. Omar, E. Sayed, M., Abdalmagid, B. Bilgin, M. H. Bakr and A. Emadi. Review of Machine Learning Applications to the Modeling and Design Optimization of Switched Reluctance Motors. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 130444–130468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. Shao, C. Zhong, T. G. Habetler and S. Li, "Multi-Objective Design Optimization of Synchronous Reluctance Machines Based on the Analytical Model and the Evolutionary Algorithms," 2019 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Wichita, KS, USA, pp1-6, 17 February 2020. [CrossRef].
- B.C Mecrow, J.W. Finch, E.A. El-Kharashi, A.G. Jack. Switched reluctance motors with segmental rotors. IEE Proceedings-Electric Power Applications 2002, 149, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. Ding, S. Yang and Y. Hu. Development and Investigation on Segmented-Stator Hybrid-Excitation Switched Reluctance Machines With Different Rotor Pole Numbers. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2018, 65, 3784–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. D. Widmer and B. C. Mecrow, "Optimised Segmental Rotor Switched Reluctance Machines with a greater number of rotor segments than stator slots," 2011 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, pp. 1183-1188, 22 August 2011. [CrossRef].
- V. Rallabandi, J. Wu, P. Zhou, D. G. Dorrell and D. M. Ionel. Optimal Design of a Switched Reluctance Motor With Magnetically Disconnected Rotor Modules Using a Design of Experiments Differential Evolution FEA-Based Method. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 2018, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- C. Ma and L. Qu. Multiobjective Optimization of Switched Reluctance Motors Based on Design of Experiments and Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2015, 30, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Watthewaduge, E. Sayed, A. Emadi and B. Bilgin. Electromagnetic Modeling Techniques for Switched Reluctance Machines: State-of-the-Art Review. IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society 2020, 1, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Rocca, G. De Donato, P. Bolognesi, C. Boccaletti and F. G. Capponi. Improved Design-Oriented Analytical Modelling of Switched Reluctance Machines Based on Fröhlich-Kennelly Equations. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2023, 39, 734–746. [Google Scholar]
- M. Shi, Q. Wang, G. Li, J. Xu, Q. Han and Q. Ye. A New Adaptive Analytical Model for the Spherical Reluctance Motor Based on Hybrid Trigonometric Function–Power Function. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2023, 70, 6099–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. F. L. Santos and L. A. R. Tria, "A Response Surface Method Approach to Modular Stator, Segmented Rotor Switched Reluctance Motor Design," 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 2020, pp. 484-489, 9 March 2021. [CrossRef].
- M. H. Hesse. Air gap permeance in doubly-slotted asynchronous machines. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 1992, 7, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Krishnan, Switched Reluctance Motor Drives: Modeling, Simulation, Analysis, Design, and Applications, USA, CRC Press, 2001.
- B. Gaussens, E. Hoang, O. de la Barriere, J. Saint-Michel, M. Lecrivain and M. Gabsi. Analytical Approach for Air-Gap Modeling of Field-Excited Flux-Switching Machine: No-Load Operation. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 2012, 48, 2505–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.E. Fitzgerald, S.D. Umans, Fitzgerald & Kingsley’s Electric Machinery, 7th ed. USA, McGraw-Hill 2014.
- S.J. Chapman, Electric Machinery Fundamentals, 5th ed. USA, McGraw-Hill 2012.
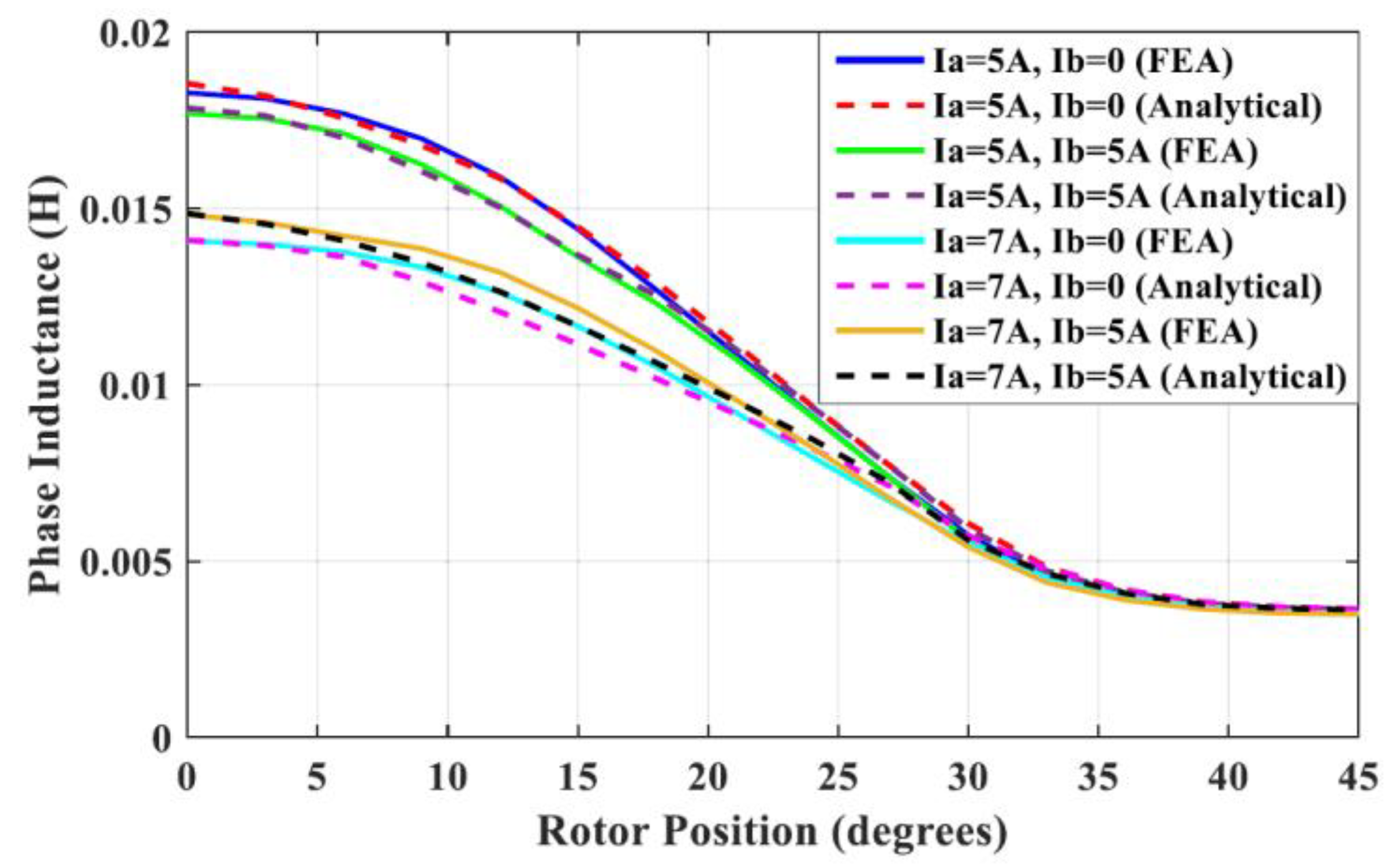
- S. Li, S. Zhang, C. Gong, T. G. Habetler and R. G. Harley, "An Enhanced Analytical Calculation of the Phase Inductance of Switched Reluctance Machines," in IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 1392-1407, March-April 2019. [CrossRef].
- H. Hua and W. Hua, "Analytical Prediction of Torque of Switched Reluctance Machines Considering Nonlinear Characteristics," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 69, no. 1, pp. 190-201, January 2022. [CrossRef].
- T.A. Lipo, Analysis of synchronous machines, 2nd ed, USA, CRC Press, 2012.
- Z. Q. Zhu and D. Howe, "Instantaneous magnetic field distribution in brushless permanent magnet DC motors. III. Effect of stator slotting," in IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 143-151, January 1993. [CrossRef].
- Z. Wu, Y. Fan, H. Chen, X. Wang and C. H. T. Lee, "Electromagnetic Force and Vibration Study of Dual-Stator Consequent-Pole Hybrid Excitation Motor for Electric Vehicles," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 70, no. 5, pp. 4377-4388, May 2021. [CrossRef].
- L. R. Huang, J. H. Feng, S. Y. Guo, J. X. Shi, W. Q. Chu and Z. Q. Zhu, "Analysis of Torque Production in Variable Flux Reluctance Machines," in IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 1297-1308, December 2017. [CrossRef].
- M. Takemoto, H. Suzuki, A. Chiba, T. Fukao and M. A. Rahman, "Improved analysis of a bearingless switched reluctance motor," in IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 26-34, January-February 2001. [CrossRef].
- F.W. Carter, “The magnetic field of the dynamo-electric machine”, The Journal of IEE, Vol. 64 No. 359, pp.1115-1138, 1 November 1926. [CrossRef].
- A. C. Viorel, I. -A. Viorel and L. Strete, "On the calculation of the Carter factor in the slotted electric machines," 2014 International Conference and Exposition on Electrical and Power Engineering (EPE), Iasi, Romania, pp. 332-336, 4 December 2014. [CrossRef].
- F. Parasiliti and M. Villani, "Magnetic analysis of flux barriers Synchronous Reluctance Motors," 2008 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Vilamoura, Portugal, pp. 1-6, 16 March 2009. [CrossRef].
- M. Cheng, P. Han and W. Hua, "General Airgap Field Modulation Theory for Electrical Machines," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 64, no. 8, pp. 6063-6074, August 2017. [CrossRef].
- B. Hannon, P. Sergeant, L. Dupré and P. -D. Pfister, "Two-Dimensional Fourier-Based Modeling of Electric Machines—An Overview," in IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 55, no. 10, pp. 1-17, October 2019. [CrossRef].
- J. Vanderlinde, Classical Electromagnetic Theory, 2nd Ed. USA. Springer Science+Business Media, Inc. 2005.
- G. Bacco and N. Bianchi. Design Criteria of Flux-Barriers in Synchronous Reluctance Machines. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2019, 55, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C.S Helrich, The Classical Theory of Fields: Electromagnetism, USA, Graduate Texts in Physics, Springer 2012.
- S. Li, S. Zhang, J. Dang, T. G. Habetler and R. G. Harley, "Calculating the unsaturated inductance of 4/2 switched reluctance motors at arbitrary rotor positions based on partial S. Li, S. Zhang, J. Dang, T. G. Habetler and R. G. Harley, "Calculating the unsaturated inductance of 4/2 switched reluctance motors at arbitrary rotor positions based on partial differential equations of magnetic potentials," 2015 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Charlotte, NC, USA, 23 November 2015. [CrossRef].
- W.J. Gibbs, Conformal Transformations in Electrical Engineering, United Kingdom, The British Thomson-Houston Co., Ltd. 1958.
- T.A. Driscoll, L. N. Trefethen, Schwarz-Christoffel Mapping, Australia, Cambridge University Press, 2002.
- E. Costamagna, P.D. Barba, and A. Savini, “An effective application of Schwarz–Christoffel transformations to the shape design of permanent magnet motors,” International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 21-37, February 2005. [CrossRef].
- D. C. J. Krop, E. A. Lomonova and A. J. A. Vandenput. Application of Schwarz-Christoffel Mapping to Permanent-Magnet Linear Motor Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 2008, 44, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Zarko, D. Ban and T. A. Lipo. Analytical calculation of magnetic field distribution in the slotted air gap of a surface permanent-magnet motor using complex relative air-gap permeance. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 2006, 42, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E. Ilhan, E.T. Motoasca, J. Paulides, E. Lomonova, “Conformal mapping: Schwarz-Christoffel method for flux-switching PM machines,” in Mathematical Sciences vol. 6 no. 37, 18 September 2012. [CrossRef].
- D. -K. Lim et al., "Analysis and Design of a Multi-Layered and Multi-Segmented Interior Permanent Magnet Motor by Using an Analytic Method," in IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 1-8, June 2014. [CrossRef].
- A. Tessarolo, "Modeling and Analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Machines With Circular Flux Barriers Through Conformal Mapping," in IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 1-11, April 2015. [CrossRef].
- H. Shao, S. Li and T. G. Habetler, "Analytical Calculation of the Air-gap Flux Density and Magnetizing Inductance of Synchronous Reluctance Machines," 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Portland, OR, USA, pp. 5408-5413, 6 December 2018. [CrossRef].
- M. Masoumi, M.A.J. Kondelaji, M. Mirsalim, J.S. Moghani, ”Analytical modelling and experimental verification of E-type reluctance motors,” in IET Electric Power Applications, vol. 13 no. 1, 27 September 2018. [CrossRef].
- E. F. Farahani, M. A. J. Kondelaji and M. Mirsalim. An Innovative Hybrid-Excited Multi-Tooth Switched Reluctance Motor for Torque Enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2021, 68, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X. Sun, K. Diao, G. Lei, Y. Guo and J. Zhu, "Real-Time HIL Emulation for a Segmented-Rotor Switched Reluctance Motor Using a New Magnetic Equivalent Circuit," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 3841-3849, April 2020. [CrossRef].
- M. Hage Hassan, G. Krebs and C. Marchand, "A simplified time stepping nonlinear mesh based reluctance network for machine design," 2013 International Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 2013, pp. 879-884, 15 July 2013. [CrossRef].
- G. Watthewaduge and B. Bilgin. Reluctance Mesh-Based Magnetic Equivalent Circuit Modeling of Switched Reluctance Motors for Static and Dynamic Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2022, 8, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Watthewaduge and B. Bilgin, "Radial Force Density Calculation of Switched Reluctance Machines Using Reluctance Mesh-Based Magnetic Equivalent Circuit," in IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society, vol. 3, pp. 37-49, 28 December 2021. [CrossRef].
- S. Yavuz, N. Parspour and L. Ma, "Analytical modelling of a parametrized switched reluctance motor with adapting flux tube method," 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Lyon, France, 2018, pp. 335-340, 30 April 2018. [CrossRef].
- K. Hameyer, R. Belmans, Numerical Modelling and Design of Electric Machines and Devices, United Kingdom, WIT Press 1999.
- M. Popescu, “Prediction of the electromagnetic torque in synchronous machines through Maxwell stress harmonic filter (HFT) method,” in Electrical Engineering no. 89, pp 117-125, 19 December 2005. [CrossRef].
- N. Ida, J.P.A. Bastos, Electromagnetics and Calculation of Fields, 2nd Ed., USA, Springer-Verlag New York, Inc. 1997.
- Z. Xu, C. Huang, S. Yu, H. Wang, T. Yi and Z. Zhang, "Mathematical Model of 12/14 Hybrid Stator Pole Type Bearingless Switched Reluctance Motor Based on Maxwell Stress Tensor Method," 2022 IEEE 5th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Nangjing, China, 2022, pp. 2452-2457, 11 August 2022. [CrossRef].
- Y. Sun Kim, "Electromagnetic Force Calculation Method in Finite Element Analysis for Programmers," Universal Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2B, pp. 62 - 67, 2019. [CrossRef].
- N. Niguchi, K. Hirata and H. Suzuki, "Vibration Investigation of a 24/20 Switched Reluctance Motor Focusing on the Driving Methods," 2019 19th International Symposium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering (ISEF), Nancy, France, 2019, pp. 1-2, 20 May 2020. [CrossRef].
- X. D. Xue, K. W. E. Cheng, T. W. Ng and N. C. Cheung, "Multi-Objective Optimization Design of In-Wheel Switched Reluctance Motors in Electric Vehicles," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 57, no. 9, pp. 2980-2987, Sepember 2010. [CrossRef].
- B. C. Mecrow, E. A. El-Kharashi, J. W. Finch and A. G. Jack, "Performance evaluation of switched reluctance motors with segmental rotors," IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, 2003. IEMDC'03., Madison, WI, USA, pp. 568-574 vol.1, 15 July 2003. [CrossRef].
- H. Eskandari and M. Mirsalim, "An Improved 9/12 Two-Phase E-Core Switched Reluctance Machine," in IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 951-958, December 2013. [CrossRef].
- M. A. J. Kondelaji and M. Mirsalim. Segmented-Rotor Modular Switched Reluctance Motor With High Torque and Low Torque Ripple. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2020, 6, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Ruba, L. Szabo, “Segmental Switched Reluctance Machine for Safety-Critical Applications”, IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Vol. 48, No.6, 10 November 2012. [CrossRef].
- R. F. Santos, B. Sermeno and L. A. Tria, "Modular Stator, Segmented Rotor Switched Reluctance Motor Prototype: Assembly and Characterization," 2022 25th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiang Mai, Thailand, pp. 1-6, 21 December 2022. [CrossRef].
- J. Wu, X. Sun and J. Zhu, "Accurate torque modeling with PSO-based recursive robust LSSVR for a segmented-rotor switched reluctance motor," in CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 96-104, June 2020. [CrossRef].
- N. Abdulah, F.A.A. Shukor, R. Othman, S. Ahmad, N. Nasir, “Modelling methods and structure topology of the switched reluctance synchronous motor type machine: a review”, in International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems Vol. 14 No. 1, pp. 111-122, 23 March 2023. [CrossRef].
- Z. Xu, T. Li, F. Zhang, Y. Zhang, D. Lee, J. Ahn, “A Review on Segmented Switched Reluctance Motors” in Energies Vol. 15, No. 23. 5 December 2022. [CrossRef].
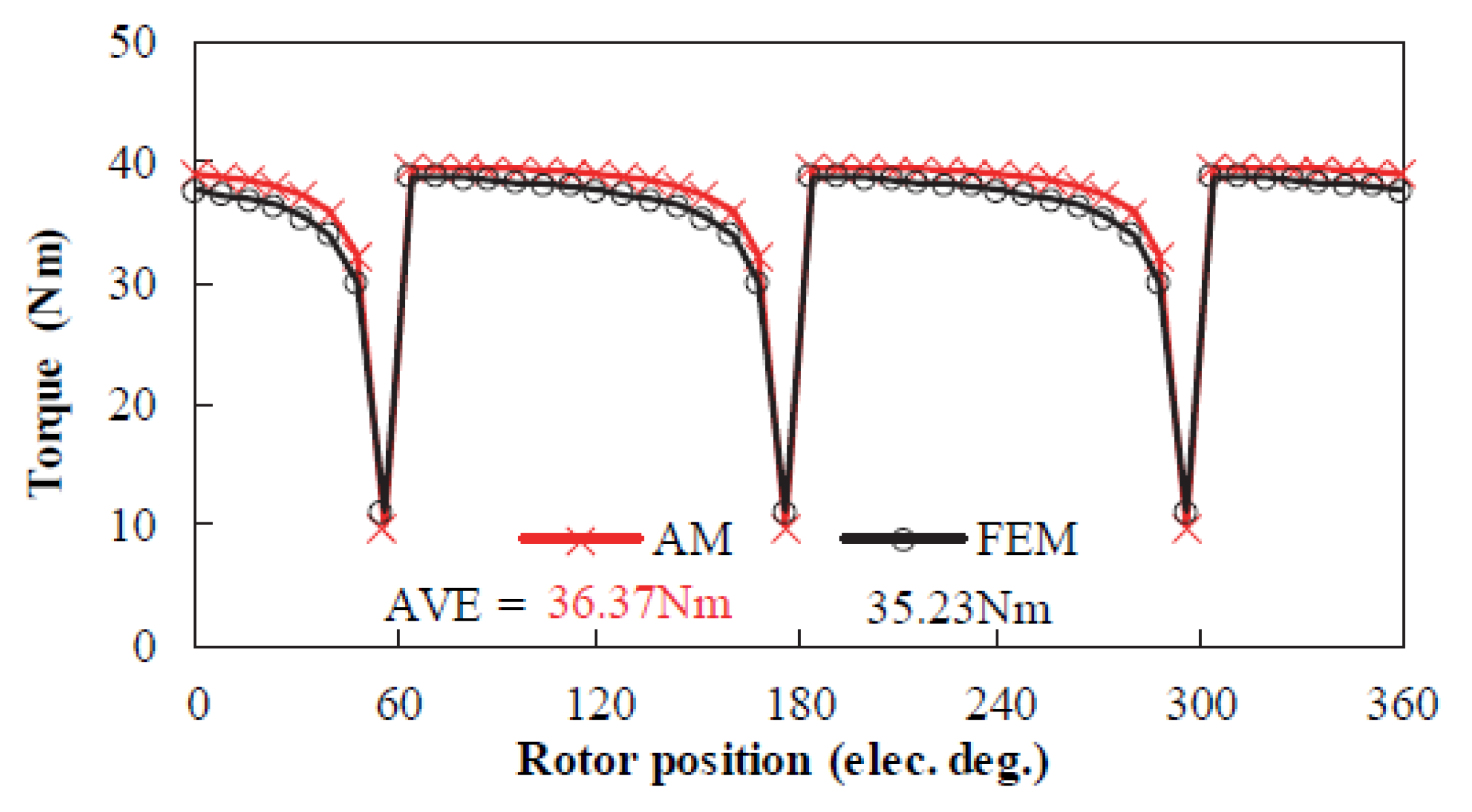
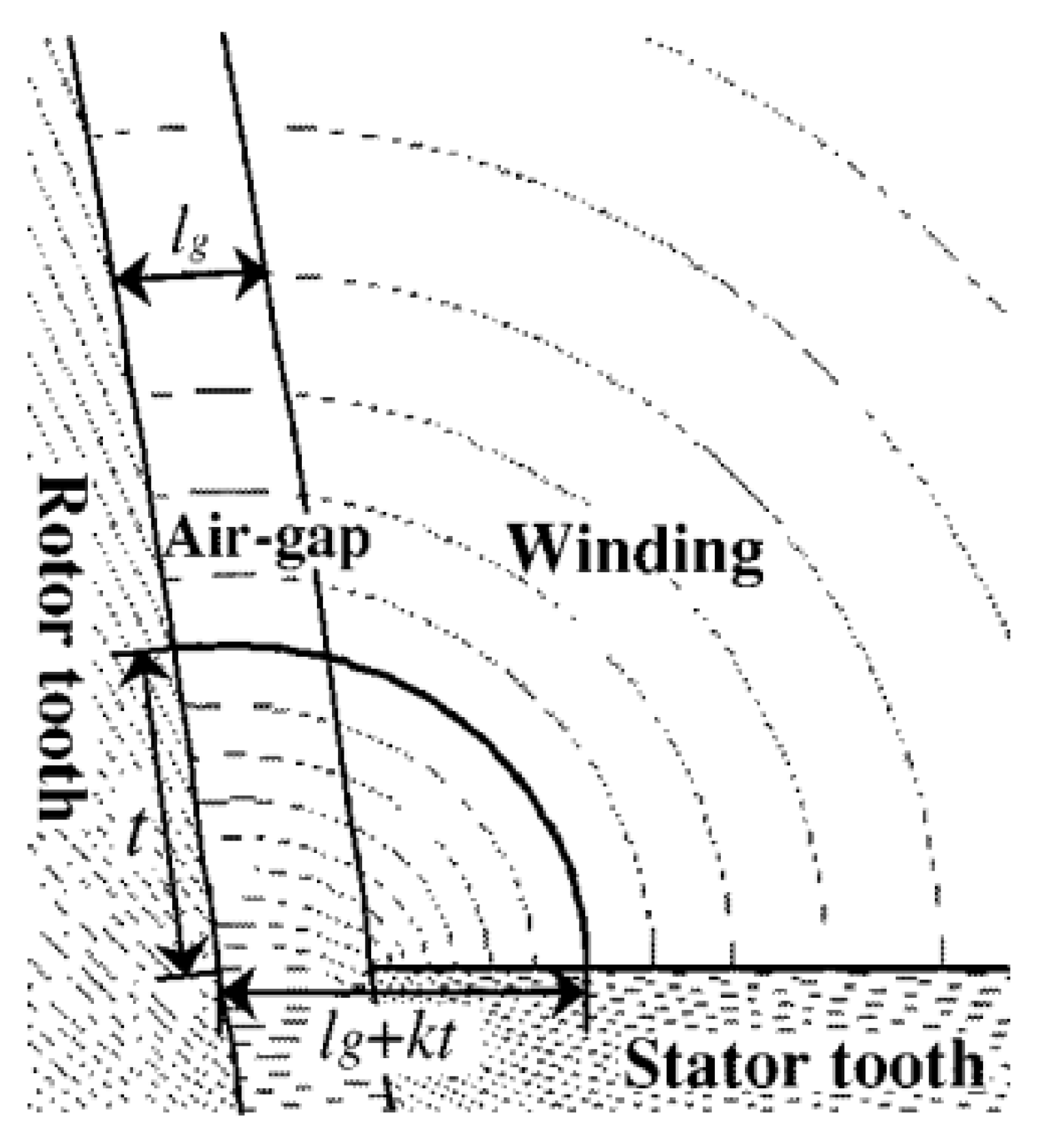
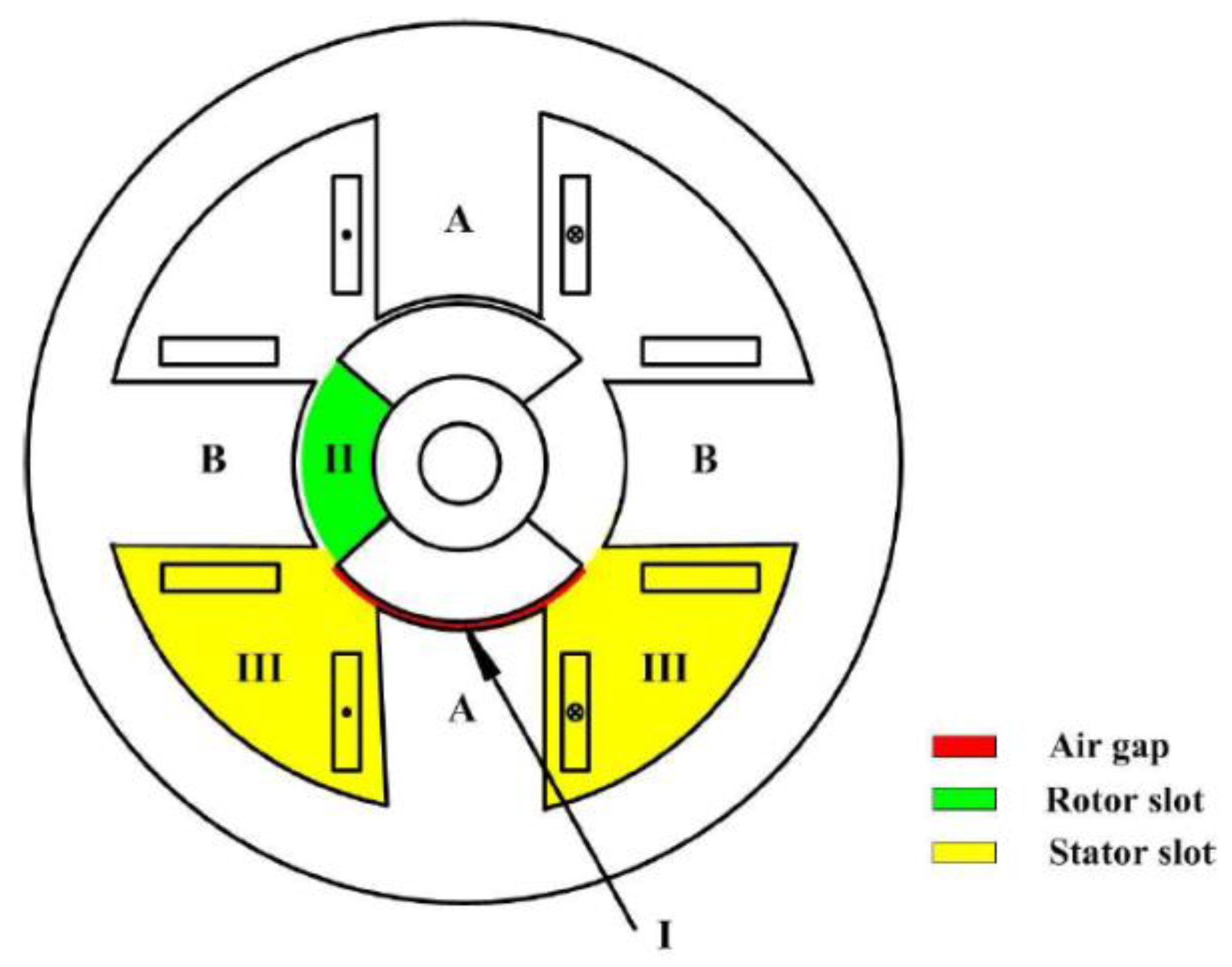
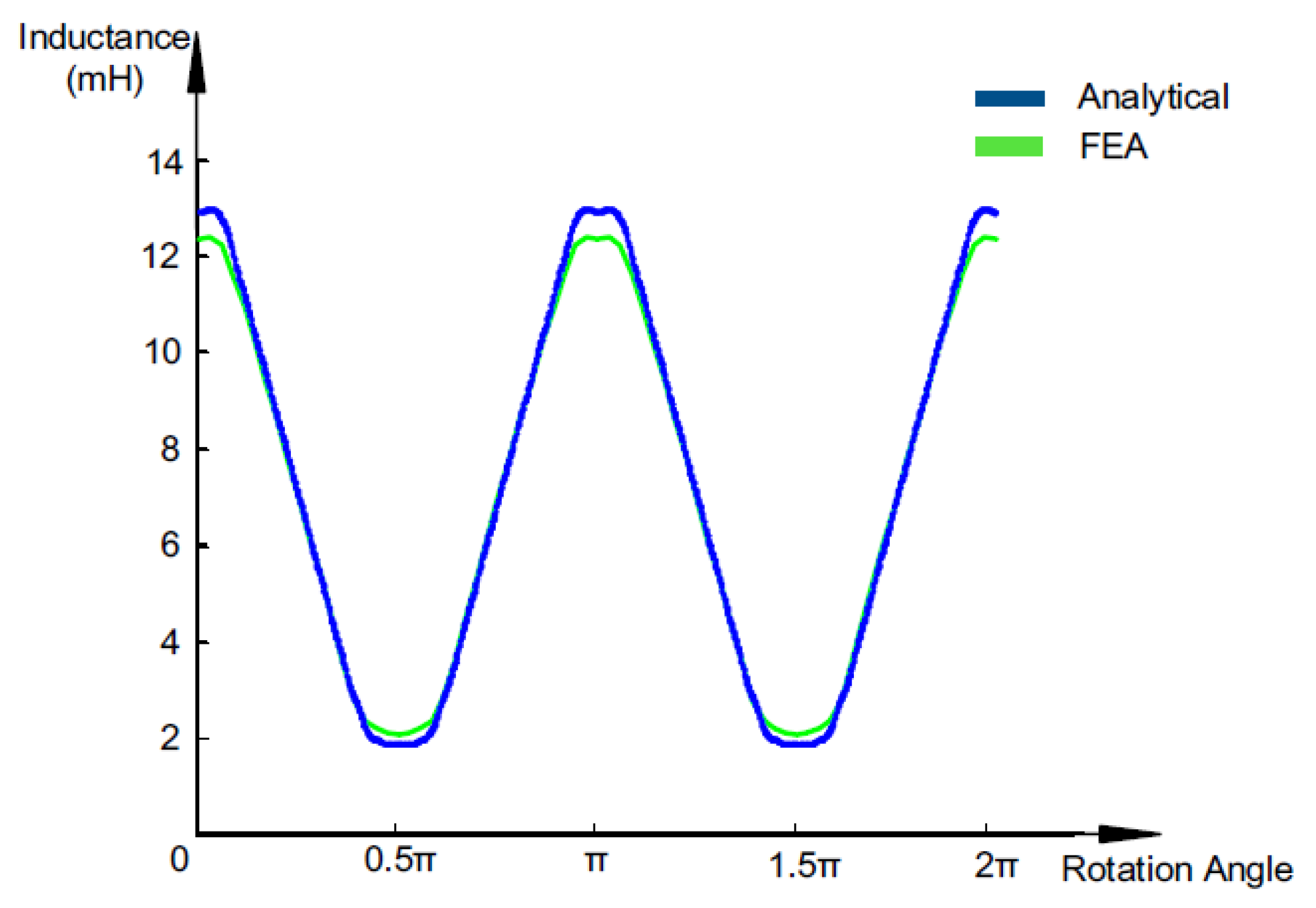
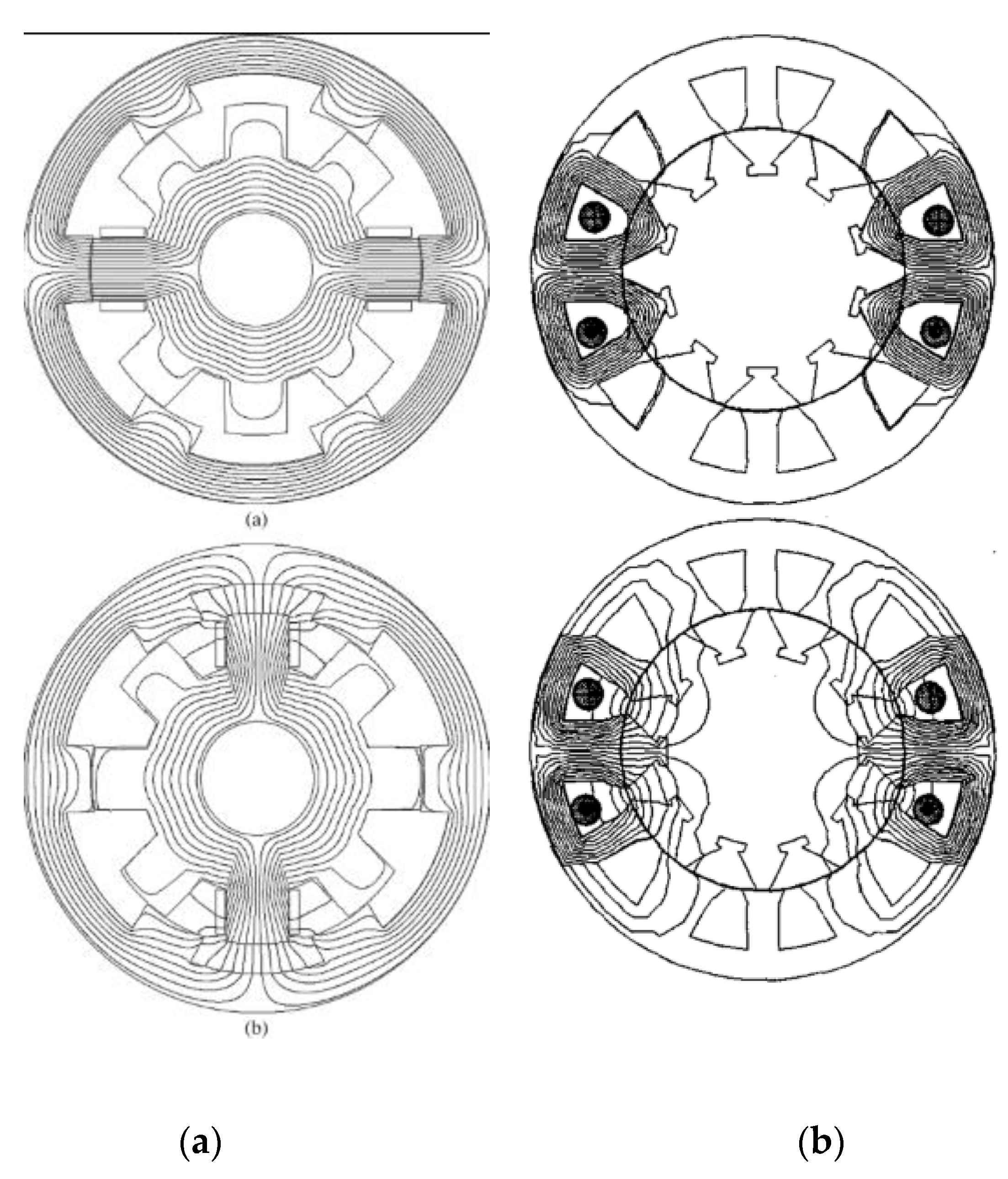
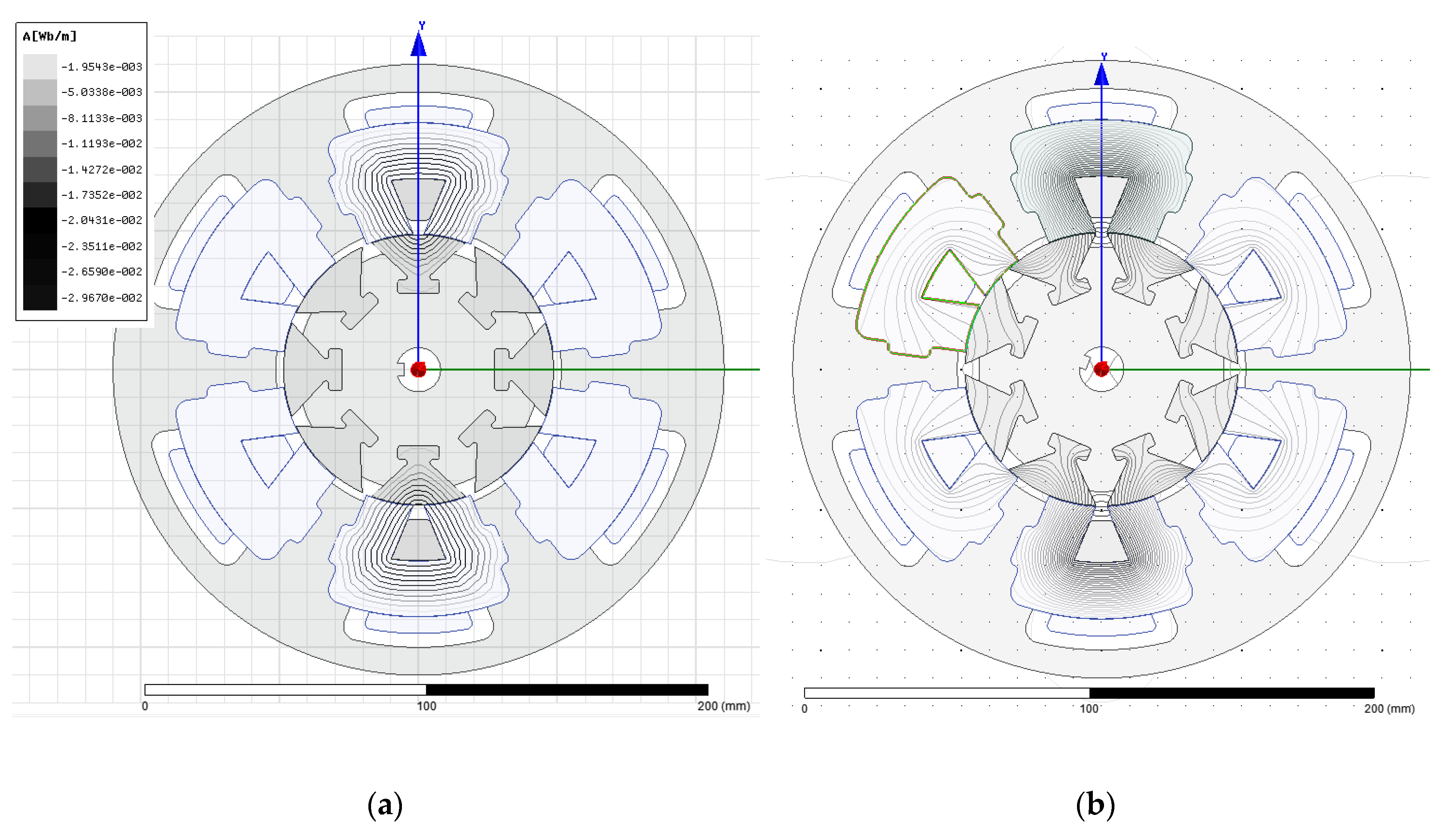
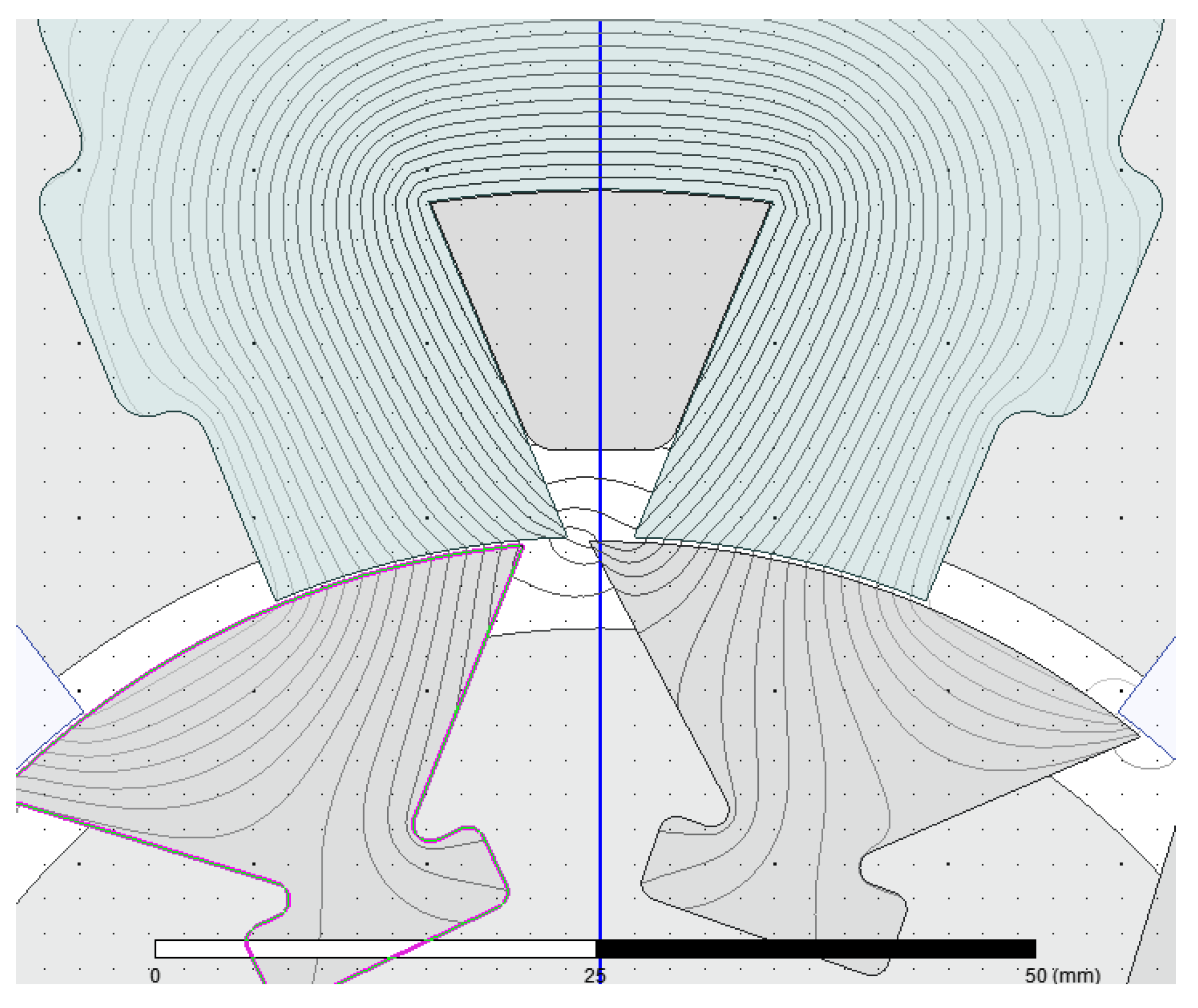
| Technique | Strengths | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Air gap permeance | Originates from a simplified expression for B around an air gap (see (1)) Assumed flux path shapes still predict simulated outputs well. |
Relies on assumptions regarding flux paths. Different authors use different mathematical definitions of permeance. Assumed air gap paths and lengths sensitive to the geometry of the motor |
| Magnetic potentials | Directly derives from Maxwell’s equations. Resulting magnetic field distribution dependent on imposed boundary conditions only. |
Boundary conditions for the scalar and vector potentials must be strongly defined. Solutions are sensitive to the geometry of the motor and may require distortions to ease derivation. |
| Conformal transformation | Can be used to extend to other techniques since obtained potential values are invariant. With the correct transformations, the solutions can take the motor geometry as is without distortions. |
Complex plane transformations used must correctly account for the actual geometry. Resulting integrals may require numerical solutions if not chosen appropriately. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





