Submitted:
29 March 2025
Posted:
31 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
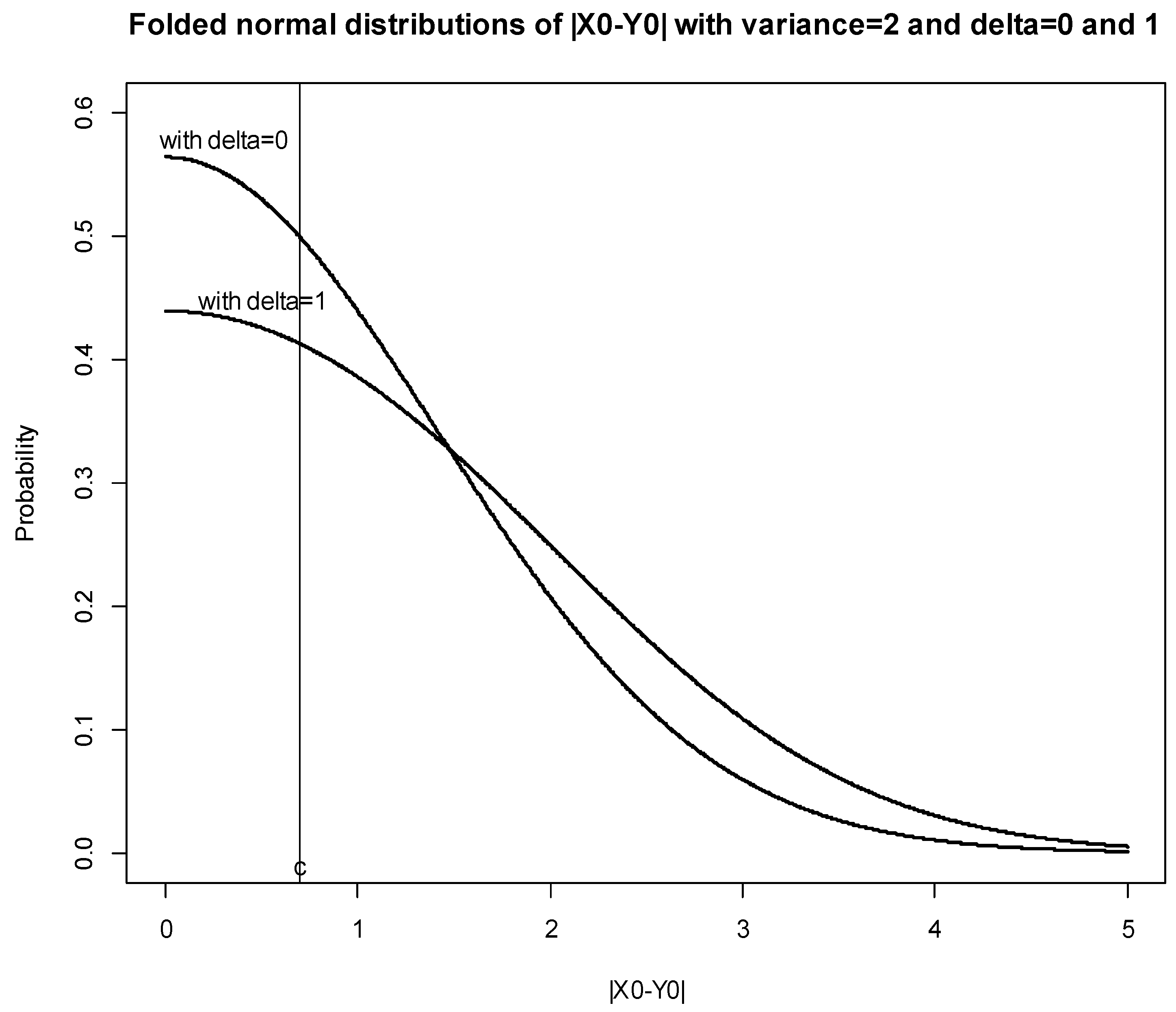
2.1. Folded Normal Distribution for Perception of Difference Between Two Samples in the DFC Test
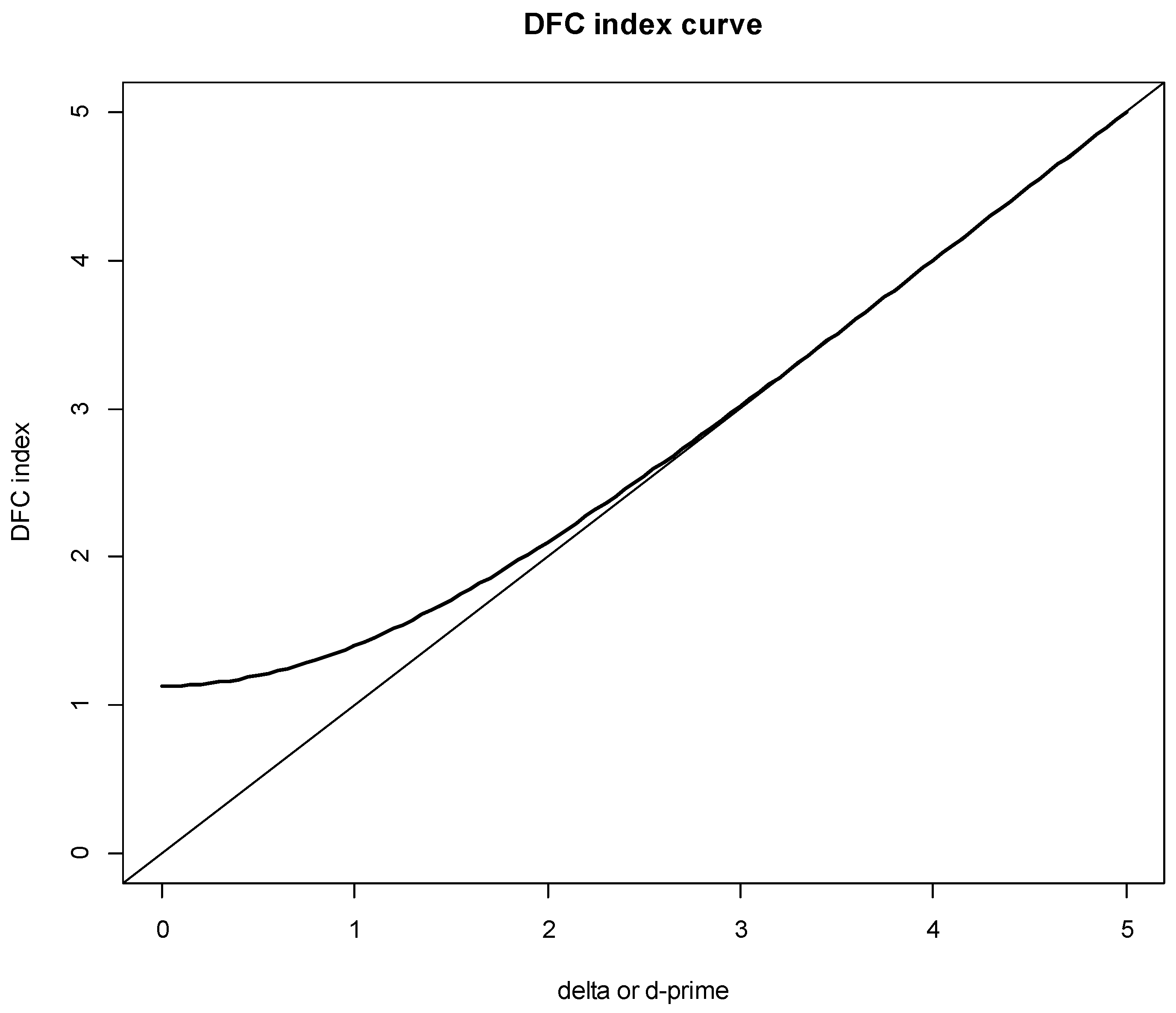
2.2. Two Indices and Related to DFC Method
2.3. The Maximum Likelihood Estimations (MLE) of
2.4. Ratings Data of the DFC Test
3. Results
3.1. Maximum Likelihood Estimations (MLE) of and
3.2. Statistical Tests for or
3.1.1. Difference Test Based on Individual d′ and Its Variance
3.1.2. One-Sided Equivalence/Similarity Test Based on Individual d′, Its Variance, and a Specified Similarity Limit
3.1.3. Difference Test Based on Multiple d′ Values and Their Variances
3.2.4. Multiple Comparisons for Multiple d′ Values and Their Variances
3.2.5. Equivalence/Similarity Test Based on Two d′ Values, Their Variances, and a Specified Similarity Limit
4. Discussion
4.1. Thurstonian Model for the DFC and the Ratings of the Same-Different
4.2. Scales Used in the DFC Test
4.3. Qualifier and Limitation of the DFC Test
5. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISO. ISO Standard 20613: Sensory analysis — General guidance for the application of sensory analysis in quality control. Switzerland. 2019.
- Muñoz, A.M.; Civille, G.V.; Carr, B.T. Sensory Evaluation in Quality Control. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1992.
- Costell, E. A comparison of sensory methods in quality control. Food Quality and Preference 2002, 13, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.; Civille, G.V.; Carr, B.T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques (4th ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press., 2007.
- Kemp, S.E.; Hollowood, T.; Hort, J. Sensory Evaluation: A practical handbook. Wiley-Blackwell, UK, 2009.
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food: Principles and Practices, Second ed. Springer, New York, 2010.
- Whelan, V. J. Difference from control (DFC) test, in book: Discrimination Testing in Sensory Science: A Practical Handbook, edited by L. Rogers. 2017.
- ASTM-E2262-03; Standard Practice for Estimating Thurstonian Discriminal Distances. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Bradley, R.A. Comparison of Different-from-control, Triangle, and Duo-trio Tests in Tasting: Comparable Expected Performance. Memorandum prepared for the General Foods Corporation, November 12. 1957.
- Bradley, R.A. Some relationship among sensory difference tests. Biometrics 1963, 19, 385–397. [Google Scholar]
- Aust, L.B.; Gacula, M.C., Jr.; Beard, S.A.; Washam II, R.W. Degree of difference test method in sensory evaluation of heterogeneous product types. Journal of Food Science 1985, 50, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J. Statistical models for the Degree of Difference method. Journal of Food Quality and Preference 2002, 13, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Lee, H.S.; O'Mahony, M. Statistical analysis of ROC curves for the ratings of the A-Not A and the Same-Different methods. Journal of Sensory Studies 2013, 28, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, D.M.; Rousseau, B. A Thurstonian model for the degree of difference protocol. Journal of Food Quality and Preference 2015, 41, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ennis, J.M.; Christenson, R. A Thurstonian comparison of the Tetrad and Degree of Difference tests. Journal of Food Quality and Preference 2015, 40, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Ennis, D.M. Thurstonian Models: Categorical Decision Making in the Presence of Noise. The Institute for Perception. Richmond, VA, USA. ISBN:9780990644606, 099064460X, 2016.
- Christensen, R.H.B; Brockhoff, B.P.; Kuznetsova, A.; Birot, S.; Stachlewska, K.A.; Rafacz, D. Package ‘sensR’. Available from: http://www.r-project.org, 2023.
- Bi, J. Sensory Discrimination Tests and Measurements: Sensometrics in Sensory Evaluation. 2nd Edition, Oxford: Wiley/Blackwell Publishing, 2015.
- Read, C.B. Folded distributions. In Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences, Vol. 3. Edited by Kotz S. and Johnson, M.L., 1983.
- Leone, F.C.; Nelson, L.S.; Nottingham, R.B. The folded normal distribution. Technometrics 1961, 3, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Elandt, R.C. The Folded Normal Distribution: Two Methods of Estimating Parameters from Moments. Technometrics 1961, 3, 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, N.L. The folded normal distribution: Accuracy of estimation by maximum likelihood. Technometrics 1962, 4, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Tsagris, M.; Beneki, C.; Hassani, H. On the Folded Normal Distribution. Mathematics 2014, 2, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Chakraborty, A.K. A simple algorithm for calculating values for folded normal distribution. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation 2016, 86, 293–305. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. https://www.R-project.org/, 2023.
- Gilbert, P.; Varadhan, R. Accurate numerical derivatives R package “numDeriv.” Available from: http://www.r-project.org, 2019.
- Bi, J.; Kuesten, C. Thurstonian Scaling for Sensory Discrimination Methods. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insightful. S-PLUS 6. In Guide to Statistics Vol.1. for Windows; Insightful Corporation: Seattle, WA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, H.L.; Macmillan, N.A.; Creelman, C.D. Tables of d′ for variable-standard discrimination paradigms. Behavior Research Methods & Instrumentation 1978, 10, 796–813. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J. Variance of d′ from the same–different method. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers 2002, 34, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM-E2139-05; Standard Test Method for Same-Different Test. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
| Categories* | Blind Control vs Identified Control |
Test sample 1 vs Identified Control |
Test sample 2 vs Identified Control |
Test sample 3 vs Identified Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2 | 10 | 12 | 15 |
| 4 | 5 | 18 | 9 | 5 |
| 3 | 15 | 34 | 43 | 46 |
| 2 | 17 | 30 | 18 | 19 |
| 1 | 20 | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| 0 | 41 | 6 | 10 | 5 |
| Categories* | Blind Control vs Identified Control |
Test sample 1 vs Identified Control |
Test sample 2 vs Identified Control |
Test sample 3 vs Identified Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 28 | 8 | 20 |
| 2 | 32 | 64 | 45 | 65 |
| 1 | 61 | 8 | 47 | 15 |
| Categories* | Blind Control vs Identified Control |
Test sample 1 vs Identified Control |
Test sample 2 vs Identified Control |
Test sample 3 vs Identified Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 | 62 | 31 | 66 |
| 0 | 78 | 38 | 69 | 34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





