1. Introduction
This research will provide information about the sustainable activities of green entrepreneurs who contribute to the green economy; the difficulties they face in sustainable green entrepreneurship activities will be examined. Green entrepreneurship is a topic that government institutions, policy makers, researchers and educators focus on due to climate change. When we type “Green Entrepreneurship” on Google Scholar on 24.12.2024, the fact that 14,100 articles were found shows that green entrepreneurship is a current research topic and thousands of academic articles have been written in the literature to solve the problems of global climate change. The universe of this research is Turkey. The Southeastern Anatolia Region was selected as a sample. Business owners who carry out green entrepreneurship activities in the Southeastern Anatolia Region, who adopt the principle of protecting the environment, were selected randomly.
The day of the interview was notified to the participants, the information given by the business owners was written down with permission and audio recorded. The research questions were taken at Istanbul Technical University It was prepared by Ece Turna, who prepared the master’s Thesis, and an application was made for ethical approval by obtaining the necessary permission from the researcher. In the research, after the evaluations related to green entrepreneurship and green economy in Şanlıurfa, Diyarbakır, Gaziantep, Şırnak were made, an empirical study was planned by conducting in-depth interviews with entrepreneurs. In the research, the purpose of the study, the method, the concepts of green entrepreneurship and green economy were introduced, and examples of green entrepreneurship were given. Between December 1, 2024, and January 2025, 12 people were randomly selected and interviewed. Green entrepreneurship is innovation, marketing, business development activities that aim to eliminate the damage that humans have caused to nature. The difference from traditional entrepreneurship is that the goal of making a profit in green entrepreneurship is combined with the mission of solving environmental problems. For example, conscious irrigation in agriculture, the installation of wind turbines and solar panels on agricultural lands, and the recycling of household waste, clothing, and food are green entrepreneurship activities. In Turkey, the incentives given by the Ministry of Trade, KOSGEB and the Ministry of Industry and Technology to small and large-scale investments aim to contribute to the country’s economy through environmental and economic returns. Social benefit-based entrepreneurship contributes to the increase in foreign investments in the production of goods and services by meeting the expectations of the society. Entrepreneurs seeking solutions to global climate change encounter trade barriers while trading in accordance with the policies of international organizations and cannot make a profit from the commercial work they do. International organizations have acted since climate change, which has emerged as a global problem, has reached dimensions that will cause the extinction of water and energy resources and all living species. International institutions and organizations such as the World Trade Organization, the European Union, the United Nations, and the World Bank, which seek solutions to international disputes, are seeking solutions to events that deeply affect the world. In the UN Climate Change Conference held in Rio in 1992, the issues of reducing greenhouse gas emissions in OECD member countries, combating climate change, financial technological assistance, and cooperation reporting in accordance with the “Common but Differentiated Responsibilities Principle” were discussed. The Global Green Growth Institute was established in 2012 by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, the United Nations Environment Program, and the World Bank (1) Trade in natural and agricultural goods is an important part of economic growth. In Turkey, the Twelfth Development Plan (2024-2028) includes the following topics: “to produce environmentally friendly, high value-added products with advanced technology, to achieve the sustainable development goal of green and digital technology in the industry, agriculture and service sectors, to increase efficiency in the medium and long term, to produce value-added products, to achieve “stable growth, strong economy”, “competitive production with green and digital transformation”, sustainable environment” and macroeconomic goals , etc. It is no coincidence that the UN focuses on Turkey’s environmental problems. Because most environmental problems arise due to economic reasons. According to UN data, 100-150 million tons of plastic were dumped into the seas and oceans in 2024 because it was costly to dispose of them. These plastics, which affect the lives of people who feed on marine creatures, cause the death of creatures living in the sea and ocean and damage the ecosystem [
2].
As technological developments increase, digital waste also increases and the problem of how to dispose of this waste arises. It is thought that “Green and digital transformation”, which is shown as a solution to global warming, will increase efficiency and welfare in international competition. As environmental problems increase, they affect political and economic systems, and the ecosystem is reshaped. Problems such as global climate change, increasing natural disasters, depletion of resources and technological and environmental pollution slow down economic development. Technological pollution, global warming threatens the continuation of all living species and states facing very serious health problems use a large portion of national income for health expenditures. In fact, according to a study conducted by Zerecan and Atakan in 2024 , countries with high Gross Domestic Product and population aged 65 and over are countries such as China, the USA, OECD member countries and Germany, have strong economies and can be included in the “old country” category and have a high population aged 65 and over [
3].
In
Table 1, Turkey is ranked 18th in terms of welfare level; 28th in terms of expenses related to diseases. It is ranked 23rd in terms of spending on environmental living conditions. Expenditures on health are higher than OECD countries. This situation affects Turkey’s per capita income (3). The damages that industrialization caused to human health after the industrial revolution, the spread of cancer and epidemic diseases; forced states to conduct research and investments in health. The increase in the world population also increases environmental problems. In fact, the world is aging, and it is reported by the World Health Organization (WHO) that 29.9 million cancer cases will be seen, and 15.3 million people will die due to cancer by 2040. According to the WHO, the development of cancer is 90% dependent on environmental factors and 10% dependent on genetic factors [
4]. The importance of entrepreneurs working to take precautions against diseases related to environmental effects such as cancer, epidemic diseases, factory waste, and air pollution and to find solutions to environmental problems is increasing day by day. According to the World Bank’s 2024 report, nine out of ten climate change events are water related. Drought pushed up to 132 million people into poverty in 2024, due to climate-related factors. For every
$1 spent on climate-resilient infrastructure failure,
$4 could be saved, but it has not been. The transition to low-carbon, resilient economies could create more than 65 million new jobs globally by 2030. The World Bank Group, in its Country Climate and Development Reports (warning systems and investing in vegetation restoration to reduce erosion and runoff. Approximately
$70 million of the financing contributes to the co-benefits of climate adaptation. It aims to increase access to water in water-scarce regions vulnerable to drought and floods, and to improve sanitation services in regions frequently affected by climate extremes [
5].. According to the information provided by Worldmeters, 5,198,463 hectares of forest will be lost in 2024 alone, and 6,998,537 hectares will be destroyed in 2024 alone. area has been lost to erosion. In the world in 2024 39,377,072,171 tons of CO2 emissions have been released into the environment [
6]. In short, global climate change, the damage that people cause to the environment is increasing day by day. Finding solutions to environmental problems has become a global issue. Research on green entrepreneurship and projects carried out by entrepreneurs in this field have gained value in the world.
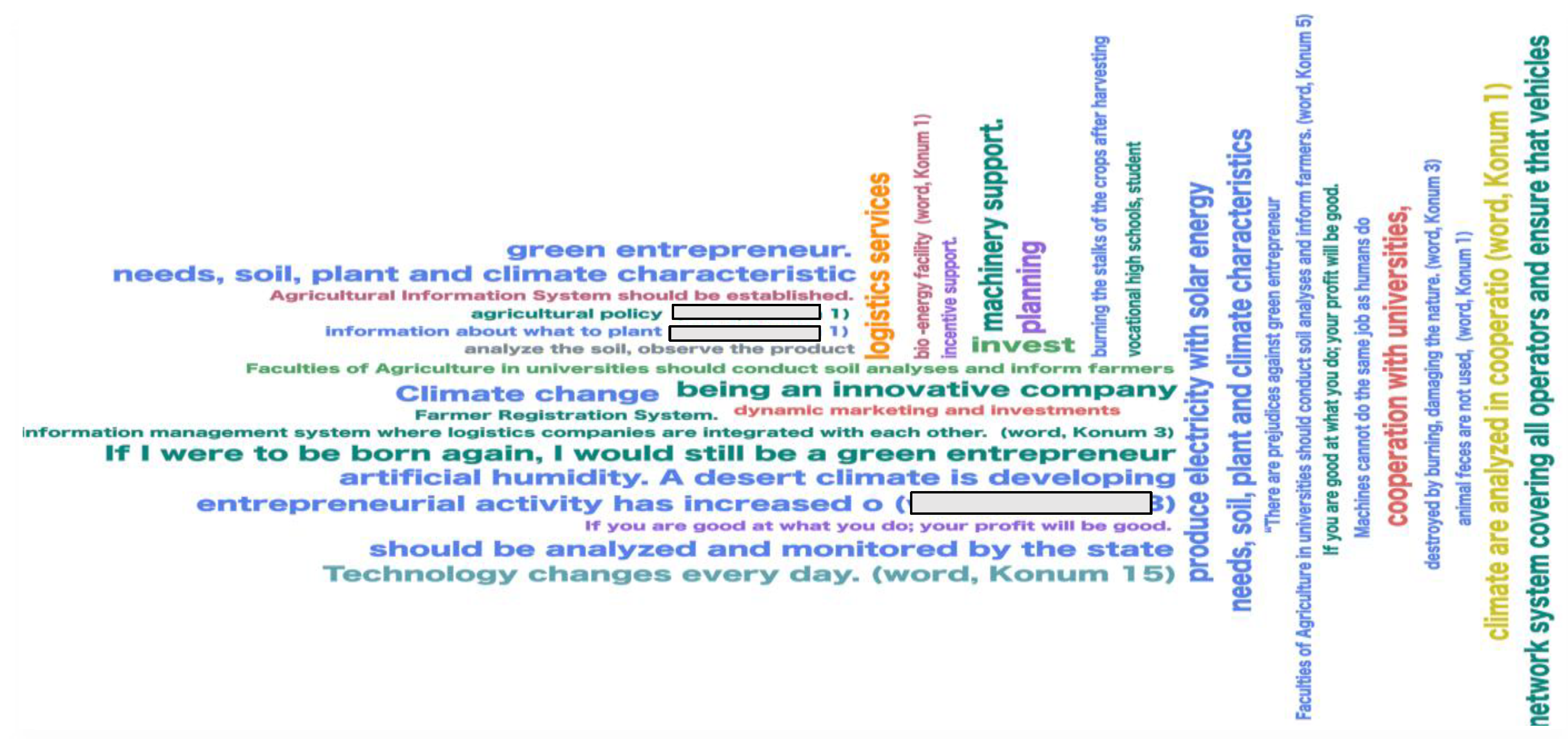
4. Findings
12 entrepreneurs were interviewed in the research. The problems the interviewees encounter in entrepreneurship are expressed as follows: 55-year-old entrepreneur from Şanlıurfa, who participated in the research, stated that he has been employing 800 workers on his land for 30 years. The entrepreneur stated the following about his green enterprise activities:
“ Wheat, corn, legumes make farmers happy in the world market. Producing vegetables, selling them domestically and abroad, can harm the seller and the producer, and vegetables can be delayed in logistics services and spoil quickly. “The state should determine what the producer will plant in the field, if the soil and climate are analyzed in cooperation with universities, everyone will know what to plant. If the planning is followed, the product will not be wasted. The state should decide what the farmer will produce. The farmer has no information about what to plant in which region. I plant the product that is supported in which region. For example, if there is no incentive for lentils in this region, I declare that I plant wheat. I plant the product that has the most incentive support. It is not clear whether large farmers or small-scale farmers are desired in agricultural policies in Turkey. Our agricultural policy is not clear on this issue. It is not clear where we will give the stalks of wheat during harvest time.”
The 40-year-old entrepreneur from Şanlıurfa, who participated in the research, stated that
The number of bio -energy facilities in our country should be increased. A bio -energy facility has just been established in the region we are in . Here, after the farmers receive their products, the valuable parts left at the bottom, the stems of the plant, could be used, but these stems are destroyed by burning, causing enormous damage to the environment. There is animal husbandry in the region, animal feces are not used, and while millions of money could be earned and contributed to the national income, fertilizers are thrown into garbage containers”.
Another participant who is engaged in entrepreneurship activities in the Southeastern Anatolia Region stated that he sends what he produces on his land in the Southeast to America and employs hundreds of people. The participant stated that burning the stalks of the crops after harvesting them is a national loss and that this process harms nature. The green entrepreneur stated the following regarding the research questions:
“There is a lot of rocky land in the Southeastern Anatolia Region and the grass and stems in this land are destroyed by burning, damaging the nature. With the state-university collaboration, the state can collect all the stems and fertilizers of farmers in these lands and generate national income. We also produce electricity with solar energy. However, we want to sell this electrical energy, which we need for 3 months to irrigate our agricultural land, to the state. The state may choose to buy it from us for 9 months. If the state buys the electricity produced by farmers in the Southeastern Anatolia Region; farmers would put electrical panels on their fields and produce electricity today. However, since the state does not buy the electricity produced by farmers, farmers produce what they need for three months and use it for irrigation.”
The 35-year-old entrepreneur from Şanlıurfa, who participated in the research, stated that
“I employ 1200 people in my business. I monitor the products I plant with drones. All products planted by farmers should be analyzed and monitored by the state, and an Agricultural Information System should be established. We should have a system that measures the moisture under the soil. All farmers should have data entries in the Farmer Registration System. The state should follow up on farmers and producers”.
The 43-year-old entrepreneur from Diyarbakir, who participated in the research, stated that
“The tax on agricultural earnings should be followed up by the state. We are moving towards whatever the state provides incentives. Farmers should be informed according to Turkey’s needs, soil, plant and climate characteristics, and the state should guide farmers in this regard. One of the deficiencies that entrepreneurs in Turkey encounter is the lack of an information management system where logistics companies are integrated with each other. For example, I sent products to Italy. There is no system yet where we can communicate with logistics companies so that trucks do not return empty. The Ministry of Transport and Infrastructure Services should establish a network system covering all operators and ensure that vehicles do not return empty when returning. This is a national loss. Although many companies try to find solutions to the problem among themselves, vehicles mostly return empty, and losses are incurred in logistics”.
The 42-year-old entrepreneur from Diyarbakir who participated in the research, stated that
“Our conscious entrepreneurial activity has increased our profits. Modern agriculture is very costly, Soil constantly wants us to invest and gives us back the product as we invest. I have 1 million dollars as capital. After becoming a green entrepreneur, my profit and the quality of my product increased. It became easier for me to expand abroad. The climate of the Southeastern Anatolia Region has changed due to global climate change. The products we used to plant do not grow immediately at harvest time as they did before. We have to leave the soil moister than before. We have to create artificial humidity. A desert climate is developing in the Southeast.”
45-year-old a green entrepreneur in Diyarbakir expressed his activities and experiences as follows:
“Climate change is changing the crop pattern. Due to climate change, analyses are needed to grow the right product in the right place. Faculties of Agriculture in universities should conduct soil analyses and inform farmers. District and district agricultural directorates should educate farmers”.
41-year-old entrepreneur from Şanlıurfa, who participated in the research, stated that
“The Soil Products Office said, “Plant the Safflower plant, I will buy it from you.” I planted it, but they did not buy it. I had to leave it to nature as bird food. I plant products that are beneficial to nature. Cereals take nitrogen from the soil and release phosphorus. Legumes do the opposite. I try to clean nature by planting both of them periodically. Machines cannot do the same job as humans do, for example, when cutting a tomato to dry, the machine cannot cut it as humans do. Machines also need to be developed. If you are going to establish a business, the business should be large and definitely branded. Products suitable for the region should be produced.”
Another entrepreneur in Şanlıurfa, aged 50, stated that he employs 1000 people in his business and that they export tomatoes to America and European countries. The participant said the following about his green entrepreneurship:
“There are prejudices against green entrepreneurs in Turkey. If you say you are a producer or a farmer outside, they look down on you. I have thousands of acres of land, thousands of employees, and when I enter a circle that does not know me at all, I feel underestimated without even hearing my last name because my family is a well-known family. I am a farmer, a green entrepreneur. I provide employment to thousands of people and I send tons of products to America and European countries. But when I say I am a farmer, people look down on me. I have more income than a district governor or a governor; but there are prejudices in our society about farmers. Farming and animal husbandry are looked down on in this country. Since young people want to work behind a desk, we employ Syrian immigrants as intermediate workers. Although we want to employ them with high salaries, young people do not want to be farmers. They become civil servants with a salary of one third of a farmer’s income, but they do not want to be associated with this profession. Even if agricultural and animal husbandry departments are opened in vocational high schools, students do not go to those high schools and study. Universities have been opened everywhere; however, graduates cannot do the job that intermediate workers can do. We need intermediate workers. Instead of university graduates working at desks, we need people who will go to the field and make analyses, follow animal diseases and developments, analyze the soil, observe the product during the process and know how to harvest, and work on renewable energy. That’s why I can’t give jobs to those who come in suits and want desk jobs. Our youth don’t want to work in agriculture. The importance of agriculture and green entrepreneurship should be explained to the youth through the press. Young people should be employed in agricultural fields. If I were to be born again, I would still be a green entrepreneur and do a job related to soil. Because agriculture will save the world. If it is planted consciously, if it is watered correctly and planted in the right soil, it is a very big source of income. Whatever we plant, no matter how much effort we put into it, the soil gives us more than enough. “
58-year-old a green entrepreneur in Şanlıurfa stated that he exports vegetables to America and constantly analyzes the products that Americans produce:“ Americans test whether we use chemicals in natural farming activities and perform quality control during the process, and as long as we work honestly, they are satisfied with us and want to sign a contract for the following year. They have standards. These standards allow us to be green entrepreneurs. When we put fertilizer on the soil, we put natural fertilizer. We produce our own electricity and use this electricity for irrigation. We went to visit an entrepreneurial business in America. A private institution in America was informing the entrepreneur we went to. The state decides which product grows in the soil. Planning should also be done in Turkey. Farmers, all entrepreneurs, should produce in accordance with this planning. In Turkey, incentives are given to large enterprises. There should be e-incentives for large enterprises. Small enterprises are supported in Turkey. Support should also be given to large enterprises. For example, machinery support. Purchasing machinery is very expensive. However, farmers are forced to buy it,” he said”.
45-year-old a green entrepreneur from Diyarbakir said the following about his activities:
“Removing too many wild animals or plants to take crops from the land and plant new ones can cause populations to decline and ultimately ecosystem collapse. Clearing land for crops removes essential habitat for wildlife and threatens water, air and soil resources,” he said.
40 years old a green entrepreneur from Diyarbakir stated the following:
“My business employs 5 people. With 3 partners who graduated from agricultural engineering, we carried out studies in the fertile lands of Şanlıurfa that would not harm the soil or nature. We entered this business to make the agricultural sector profitable, to bring more income, and to combat the climate crisis. Our aim was to protect the soil. Our profit margin did not increase too much with green entrepreneurship activities. Our number of customers did not decrease, we made very large investments. Since we are new in the field, our investment did not yield a very large profit margin at the moment. However, I see that the number of our customers is gradually increasing,” he said.
55-year-old a green entrepreneur from Şırnak said the following about his entrepreneurial activities:
Technology changes every day. Being resistant to these changes and being an innovative company, you should always follow technology, increase the range of your products, be very careful about what the customer wants and where the world is going. I obtained my capital with my previous savings. The company’s growth targets (opening a second branch, opening branches in different cities, increasing the number of employees, increasing product variety, etc.) can be increased according to needs.
The profits of companies are related to dynamic marketing and investments you make according to needs. If you are good at what you do; your profit will be good. The number of dealers increases in line with dynamic marketing and needs. Green entrepreneurship, which develops green economy, aims at sustainable environmental protection that contributes to the environment, ensuring that the environment is protected with the least damage in global climate change, and sustainability of environmentally friendly green activities. We had bakery products and many dealerships before. You can give direction to the future with feasibility reports and researches to be done in advance about what people need. We generally work with a dealership system in the production, marketing, and distribution of natural spring water. We have been doing this job for 17 years. We employ 25 people between the ages of 20 and 35. In feasibility studies, Şanlıurfa Siverek has a rich resource in terms of natural spring water and also has a very advantageous position in terms of logistics. “Green entrepreneurs should not create environmental pollution or harm ecosystem diversity by meeting their energy needs from renewable sources, ” he said .
Of the 21st Century when the new world order was established and to get success in economy Turkey should create new alternatives for himself (32). The promotion of environmentally focused, economic growth activities provides prestige in the international arena. In entrepreneurial activities, commercial activities in line with economic policy yield successful results because they are supported by the state. High value-added activities increase the producer’s profit margin. The UN Climate Change Conference held in Rio in 1992 gave all OECD member countries the responsibility of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change as a social responsibility. The mission of developing countries to provide financial and technological assistance to developing and underdeveloped countries in this regard was given. The questions were evaluated using the Maxqda 2024 program in the research. Analysis was performed with the code cloud code distribution model using the KIT Word Association Test Qualitative Research method. The descriptive research type, one of the qualitative research methods, was used in the study. The qualitative method is related to conceptual answers. According to Strauss and Corbin, coding constitutes the analysis process in the qualitative method. The coding process begins with conceptualization [
33]. The meaning of the topics that the participants focused on regarding Green Entrepreneurship, what they represent, the meaning of the data, the difficulties that the green entrepreneur participants encountered in their activities, and the deficiencies they saw in the application were coded with keywords. MAXQDA 2024 has a scope that allows the collection of data from text documents, pdf files, images, websites, audio and recorded videos, SPSS data files, focus group discussions, YouTube comments and social media platforms such as Twitter, and allows different analyses such as visualization on this data [
34]. The topics that the participants frequently focused on in the content analysis are given in
Figure 1.
Maxqda 2024, it has been seen that entrepreneurs in the Southeastern Anatolia Region want a network to be established so that the vehicles do not return empty after the delivery of the product, as they need a logistics information system where carriers will communicate with each other in the logistics sector [
34]. In the logistics sector, GPS Tracking determines the location of the vehicles and delivery processes can be monitored. The Data Collection system provides information about the fuel, speed, and engine status data of the vehicles. With mobile networks and special radio frequencies, vehicles can send messages to each other and share current information. Cloud-Based Platform: collects all data. Thanks to artificial intelligence and machine learning of the Internet of Things, algorithms estimate traffic density. Thanks to Blockchain technology, vehicles are prevented from returning empty. Software that provides transparency and increased efficiency IoT (Internet of Things), sensors, communication modules, Cloud Computing: Cloud computing services are used to store and analyze data securely. Delivery Tracking, Arrival Estimation, Driver Performance, smart transportation, Logistics 4.0, GPS tracking, IoT logistics, Cloud-based logistics solutions, With the growth of the logistics sector in Turkey, various software has been developed for more efficient management of logistics processes. This software is used in many different areas such as tracking shipments, route planning, inventory management. There are software such as Lojisoft, Demsoft : Select Optimus : Capterra in Turkey . Smart and autonomous logistics systems are being developed in the field of artificial intelligence and logistics. However, this software needs to be widespread in the Southeastern Anatolia Region. One of the issues that green entrepreneurs focus on is that manure cannot be utilized and is thrown away. The number of bio energy facilities needs to be increased. The total installed capacity of Biogas in Turkey is 2,414 MW. In 2021, 7,371,770,000 kilowatt-hours of electricity were produced with Biogas, Biomass, Waste Heat and Pyrolytic Oil Power Plants.
Table 2.
Profile of Biogas Biomass Waste Heat and Pyrolytic Oil Power Plants in Turkey.
Table 2.
Profile of Biogas Biomass Waste Heat and Pyrolytic Oil Power Plants in Turkey.
| Number of Registered Switchboards |
187 |
| BES Installed Power |
2,414MWe Registered: 1,552 MWe |
| Installed Capacity Ratio: |
2.20% |
| Annual Electricity Production: |
~ 6,912 GWh |
| Production to Consumption Ratio: |
2.30% |
The Bio Energy Plants established in the Southeastern Anatolia Region and the amount of energy they produce. Entrepreneurs working in the region stated that these plants are not sufficient for the people engaged in animal husbandry.
Table 3.
Bio Power Plant Southeastern Anatolia Region.
Table 3.
Bio Power Plant Southeastern Anatolia Region.
| Gaziantep Solid Waste Biomass Power Plant |
Gaziantep |
Gazişehir Energy |
14 MW |
| Blue Flag East BES |
Mardin |
Blue Flag East Energy |
12 MW |
| Sanliurfa Biomass Power Plant |
Sanliurfa |
BBF Energy |
6.24 MW |
| Gaziantep Landfill Gas |
Gaziantep |
CEV Energy |
5.66 MW |
| Natural energy Biomass Power Plant |
Sanliurfa |
Natural Energy Services |
5.20 MW |
| Mardin Biogas Power Plant |
Mardin |
Sanvar Construction |
4.69 MW (9,384 MW) |
| GASKİ Wastewater Biogas Power Plant |
Gaziantep |
Gaziantep Metropolitan Municipality |
1.66 MW |
Green entrepreneur participants suggested that departments related to agriculture and animal husbandry should be opened in universities, that the public should not be prejudiced, that they should not underestimate the profession of farming, that the state should cooperate with universities to protect nature, and that it should provide incentives to small and large businesses.
Entrepreneurs stated that it should reduce agricultural income taxes, purchase electricity produced by farmers, educate farmers, conduct regional analyses and support people interested in agriculture in the face of climate change, educate entrepreneurs on the need to do agriculture appropriate to climate and soil, be in communication with farmers, inform entrepreneurs about the areas in which they will be engaged, bring investors and entrepreneurs together through the chamber of commerce, announce agricultural policy to producers and entrepreneurs in advance and be consistent in this regard.