Submitted:
06 March 2025
Posted:
07 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Concern on P scarcity: Rock P reserves and resources are of non-renewable nature.
- Need for P application in P-deficient soils of many world regions: Under-application has been largely reported for cropping systems of Africa and South America as well as in many regions of other countries.
- Mitigation and reduction of environmental impacts of excessive P applications: Over- application of P has impacted water quality in many areas of the world. Work done in recent years has emphasized the need for suitable P management under these conditions.
- Improve P use efficiency, recovery and recycling, as it relates to the previous three points.
2. P in the Soil-Crop Ecosystem
2.1. P Cycle in Field Crop Systems
2.2. P Functions in Plants
2.3. P Requirements of Field Crops
3. P Use Efficiency in Cereal-Based Cropping Systems Around the World
- Improving P fertilizer recommendations
- Managing soil pH to optimize soil P availability
- Utilizing legacy P
- Developing plant traits for PUE
- Increasing plant accessibility to P sources
- Developing innovative P sources, management techniques and biotechnologies
- Minimizing soil P losses by erosion and runoff
- Developing P-efficient cropping systems through novel crop combinations
- improving management of low PUE crops
- Optimizing farm size and mechanization
- Promoting precision ag and P budgeting
- Increasing recycling from manure and waste
- North America
- South America
- Africa
- Europe
- Asia
- Oceania
4. Fertilizer Best Management Practices for P
4.1. What Are BMPs?
- “The goal of fertilizer best management practices is to match nutrient supply with crop requirements to optimize yield while minimizing nutrient losses to the environment” (IFA)
- “BMPs can be described as research proven and farm-tested practices that optimize production potential, input efficiency, and environmental protection” (Roberts and Johnston, 2015).
- “Practices that will ensure the production of safe and high-quality products, animals and plants, while preserving the environment and contributing to the social well-being of society” (Science Direct)
- “Site-specific, economically feasible practices that farmers use to maintain agricultural production while considering environmental and public health impacts. BMPs are industry-driven and are intended to provide guidance for farmers, not to be regulatory” ( Google AI)
- “An industry driven effort to maintain agricultural production in a profitable, environmentally sensitive and sustainable manner. BMPs are not meant to be regulatory as every farm operation and site is different and may require special practices. But BMPs are meant to provide guidance as to practices that farmers can strive towards implementing on their farms” (University of Massachussets)
- “Methods and practices designed to reduce or prevent soil and water pollution without affecting farm productivity” (Drizo et al., 2022).
- “Farming methods that are designed to minimize adverse environmental effects while maintaining agricultural production. Nutrient BMPs, referred to as the 4Rs—Right rate, Right timing, Right source, and Right placement—should be used on all cropping systems and is the first line of defense. Additional BMPs should be used to control nutrients as they move from application area to the water resource. Put together, these BMPs form a system to avoid, control, and trap nutrients” (North Carolina State University)
4.2. Approaches for BMPs in Field Crop Systems
4.3. BMPs for Fertilizer P
- o
- Field nutrient budgeting.
- o
- Crop rotation for efficient nutrient cycling (legumes).
- o
- Synchronize nutrient supply with plant demand.
- o
- Precise application of nutrients.
- o
- Select lower impact fertilizers.
4.4. Four Rs for Phosphorus: Right Source, Right Rate, Right Place, Right Time
4.4.1. Right Source
Rock Phosphates
Conventional Commercial P Fertilizers
Dry Bulk Blends
Organic Wastes
Mineral Wastes
Biofertilizers
Innovative Fertilizer P Technologies

- Fixation-inhibitor fertilizers: fertilizers with additives to reduce reactions of precipitation and adsorption of P. They could be classified as pH-modifiers, cation-sequestering agents or blockers
- Synergistic phosphate fertilizers: conventional P fertilizers with the addition of other nutrients, microorganisms, nanoparticles, or biostimulants.
- Chemically modified fertilizers: conventional P sources with changed solubility and/or chemical form at the production process by physical, chemical, or physical–chemical reactions that modify the interaction of P with other chemical compounds
- Controlled-release fertilizers: conventional fertilizers with coating which serve as a physical barrier and control the flow by diffusion
- Blends and multifunctional fertilizers: physical blend of conventional phosphate fertilizer granules and those that have some type of technology, as the indicated above.

4.4.2. Right Rate
Soil Testing
- Soil sampling,
- Analysis,
- Interpretation and recommendation.
- identify heterogenous areas within the field (cropping history, topography, others),
- collect an adequate number of sub-samples per sample (at least 10-20 cores),
- collect all sub-samples at the sampling depth recommended in the program,
- avoid sampling near fences or forests,
- homogenize the sample,
- properly preserve the samples until they reach the laboratory.
| Phosphorus recommendations for corn and soybean grain production (two-year rotation) with application before corn or soybean - PM 1688 Rev. February 2023 (Mallarino et al., 2023) | |||||
| Soil Test Category | Very Low | Low | Optimum* | High | Very High |
| Bray P1 and Mehlich-3 P | <9 | 10-17 | 18-25 | 26-34 | >351 |
| Olsen P | <6 | 7-10 | 11-15 | 16-20 | >21 |
| Mehlich-3 ICP | <16 | 17-27 | 28-40 | 41-51 | >52 |
| P to apply (kg/ha) | 93 | 66 | 57 | (0)** | 0 |
| Phosphorus recommendations for corn according to resin P analysis and expected yield (Raij et al., 1996) - Brazil | |||||||||
| Soil Test Category | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | |||||
| Resin P | < 6 | 7-15 | 16-40 | >41 | |||||
| Expected grain yield (t/ha) | P to apply (kg/ha) | ||||||||
| 2-4 | 60 | 40 | 30 | 20 | |||||
| 4-6 | 80 | 60 | 40 | 30 | |||||
| 6-8 | 90 | 70 | 50 | 30 | |||||
| 8-10 | - | 90 | 60 | 40 | |||||
| 10-12 | - | 100 | 70 | 50 | |||||
| Phosphorus recommendations for crops successive crops according to Mehlich-1 P analysis (Cubilla et al., 2012) - Paraguay | |||||||||
| Soil Test Category | Very Low | Low | Medium | High | Very high | ||||
| Grain yield (t/ha) | P to apply (kg/ha) | ||||||||
| 1st crop | 35 + M | 15 + M | 11 + M | M* | R** | ||||
| 2nd crop | 30 + M | 15 + M | M | M | R | ||||
| 3rd crop | 22 + M | 13 + M | M | M | R | ||||
| Total | 87 + 3M | 43 + 3M | 11 + 3M | 3M | 3R | ||||

Other Methodologies
Plant Analysis
Use of Remote Sensors
4.4.3. Right Placement
4.4.4. Right Time
4.5. Advances and Potential Developments on BMPs for P
4.5.1. Small Holders Cropping Systems
4.5.2. Organic Farming
4.5.3. Environmental Issues Related to P
- Reduce soil erosion and runoff.
- Avoid surface-broadcast applications in the hilly landscape and in the rainy season.
- Know soil and manure P levels.
- Match fertilizer and manure P to crop needs.
- Do not over-apply fertilizer or manure P on sites contiguous to rivers, streams, reservoirs or lakes.
- Establish buffer strips along river and stream banks, reservoirs and lakes.
4.5.4. P Fertilization and Soil Health
4.5.5. Modeling P Dynamics in Soil-Crop Systems
5. Looking for Sustainable P Use and Management in Cereal-Based Cropping Systems
- Large variability in soil P availability and PUE in cereal-based cropping systems across world regions and cereal-based cropping systems
- Knowledge of P cycling is key for successful P management
- BMPs are the foundation for improving PUE and decoupling production from externalities in P management
- Emphasis on Right source, Right rate, Right time, and Right placement
-
Essential BMPs:
- o
- Diagnosis of soil P status
- o
- Evaluation of P balance in the rotation: Budget P removal and application
- o
- Precise P fertilizer recommendations
- o
- Attend cropping system condition (rotation, crop, climate, farmer) and economics on deciding P source and placement/time
References
- Abdo, A.I.; El-Sobky, E.-S.E.A.; Zhang, J. Optimizing maize yields using growth stimulants under the strategy of replacing chemicals with biological fertilizers. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1069624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achat, D.L.; Sperandio, M.; Daumer, M.-L.; Santellani, A.-C.; Prud’Homme, L.; Akhtar, M.; Morel, C. Plant-Availability of Phosphorus Recycled from Pig Manures and Dairy Effluents as Assessed by Isotopic Labeling Techniques. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 24–33.
- AHDB (2023). Nutrient Management Guide (RB209). Section 4 Arable Crops. Available online: https://ahdb.org.uk/knowledge-library/rb209-section-4-arable-crops.
- Alewell, C.; Ringeval, B.; Ballabio, C.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P. Global phosphorus shortage will be aggravated by soil erosion. Nature communications 2020, 11, 4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harbi, S.F.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Modaihsh, A.S.; Mahjoub, M.O. . Effect of foliar and soil application of phosphorus on phosphorus uptake, use efficiency and wheat grain yield in calcareous soil. Journal of Applied Sciences 2013, 13, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan Jones, C.; Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. Modeling Phosphorus Dynamics in the Soil-Plant System. In Modeling Plant and Soil Systems; Hanks, J., Ritchie, J.T., Eds.; 1991. [CrossRef]
- Alvar-Beltrán, J.; Napoli, M.; Dao, A.; Ouattara, A.; Verdi, L.; Orlandini, S.; Dalla Marta, A. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium mass balances in an irrigated quinoa field. Italian Journal of Agronomy 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.; Steinbach, H.S. Modeling Soil Test Phosphorus Changes under Fertilized and Unfertilized Managements Using Artificial Neural Networks. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanullah., Ondrasek, G., Al –Tawaha, A. R. M. S., eds. Integrated nutrients management: An approach for sustainable crop production and food security in changing climates, 2nd ed.; Lausanne: Frontiers Media SA. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Amanullah, A.; Zakirullah, M.; Tariq, M.; Nawab, K.; Khan, A.Z.; Farhatullah, F.; Sha, Z.; Khalil, S.K.; Jan, M.T.; M.Sajid; Hussain, Z. Levels and time of phosphorus application influence growth, dry matter partitioning and harvest index in maize. Pakistan Journal of Botany 2010, 42, 4051-4061.
- Amorim, M.B.; Fontoura, S.M.V.; Tiecher, T.; Moraes, R.P.; Bayer, C. Use and recovery of P reserves in Southern Brazil Oxisols under no-till with low and high P availability. Rev Bras Cienc Solo. 2024, 48, e0230127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, S.C.; Barbagelata, P.A.; Melchiori, R.J.M. Is the Lack of Response of Maize to Fertilization in Soils with Low Bray1-P Related to Labile Organic Phosphorus? J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 2021, 21, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, S.C.; Carciochi, W.D.; Correndo, A.; Gutiérrez Boem, F.H.; Salvagiotti, F.; García, F.O.; Melchiori, R.J.M.; Barbagelata, P.A.; Ventimiglia, L.A.; Ferraris, G.N.; et al. Predicting soil test phosphorus decrease in non-P-fertilized conditions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, S.C.; Melchiori, R.J.; Barbagelata, P.A.; Novelli, L.E. Assessing organic phosphorus contributions for predicting soybean response to fertilization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 2016, 80, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelhans, S.C.; Novelli, L.E.; Melchiori, R.J.; Barbagelata, P.A. Does the fertilisation strategy affect the long-term legacy phosphorus dynamic? Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 153, 127035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argus-IFA. Phosphate Rock Resources & Reserves. 2023. Available online: https://www.fertilizer.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/2023_Argus_IFA_Phosphate_Rock_Resources_and_Reserves_Final.pdf.
- Aulakh, M.S.; Pasricha, N.S.; Bahl, G.S. Phosphorus fertilizer response in an irrigated soybean–wheat production system on a subtropical, semiarid soil. Field Crops Research 2003, 80, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, J.B.; Coulibaly, A.; Giller, K.E. Precision farming for increased land and labour productivity in semi-arid West Africa. A review. Agronomy for sustainable development 2017, 37, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Avsar, C. Novel Assessment Strategy for Nanotechnology in Agriculture: Evaluation of Nanohydroxyapatite as an Alternative Phosphorus Fertiliser. Kem. Ind. 2022, 71, 327–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, X. The critical soil P levels for crop yield, soil fertility and environmental safety in different soil types. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.B.; Johnson, L.T.; Confesor, R.B.; Crumrine, J.P. Vertical Stratification of Soil Phosphorus as a Concern for Dissolved Phosphorus Runoff in the Lake Erie Basin. Journal of Environmental Quality 2017, 46, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboa, G.R.; Ferguson, R.; Puntel, L. Irrigated corn yield and soil phosphorus response to long-term phosphorus fertilization. Agronomy Journal 2024, 116, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, P., Sainz Rozas, H., Covacevich, F., Echeverría, H. E. Phosphorus Placement Effects on Phosphorous Recovery Efficiency and Grain Yield of Wheat under No-Tillage in the Humid Pampas of Argentina, International Journal of Agronomy 2014, 2014, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Barth, G.; Francisco, E.; Suyama, J.T.; García, F.O. Nutrient Uptake Illustrated for Modern, High-Yielding Soybean. Better Crops 2018, 102, 11-14. [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J.; Barman, P.; Debnath, A. Three Residual Benefits of Applying Phosphate Fertilizer. Soil Science Society of America Journal 2018, 82, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegle, D. Assessing Soil Phosphorus for Crop Production by Soil Testing. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment; Sims, J.T., Sharpley, A.N., Westermann, D.T., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, G.; Ziadi, N.; Pageau, D.; Grant, C.; Högnäsbacka, M.; Virkajärvi, P.; Hu, Z.; Lu, J.; Lafond, J.; Nyiraneza, J. A Model of Critical Phosphorus Concentration in the Shoot Biomass of Wheat. Agronomy Journal 2015, 107, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.; Reuter, D.; Scott, B.; Sparrow, L.; Strong, W. Soil phosphorus–crop response calibration relationships and criteria for winter cereal crops grown in Australia. Crop and Pasture Science 2013, 64, 480–498. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, R.R.; Haegele, J.W.; Below, F.E. Nutrient Uptake, Partitioning, and Remobilization in Modern Soybean Varieties. Agronomy Journal 2015, 107, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, R.; Haegele, J.W.; Ruffo, M.L.; Below, F.E. Nutrient Uptake, Partitioning, and Remobilization in Modern, Transgenic Insect-Protected Maize Hybrids. Agronomy Journal 2013, 105, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindraban, P.S.; Dimkpa, C.; Nagarajan, L.; Roy, A.; Rabbinge, R. Revisiting fertilisers and fertilisation strategies for improved nutrient uptake by plants. Biology and Fertility of Soils 2015, 51, 897–911. [Google Scholar]
- Bindraban, P.S.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Pandey, R. Exploring phosphorus fertilizers and fertilization strategies for improved human and environmental health. Biology and Fertility of Soils 2020, 56, 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, B.; Darch, T.; Haslam, R. Phosphorus use efficiency and fertilizers: future opportunities for improvements. Front. Agr. Sci. Eng. 2019, 6, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvin, C.; Etter, B.; Udert, K.M. Plant uptake of phosphorus and nitrogen recycled from synthetic source-separated urine. AMBIO 2015, 44 (Suppl. S2), 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolster, C.H.; Correndo, A.A.; Pearce, A.W.; Spargo, J.T.; Slaton, N.A.; Osmond, D.L. A spreadsheet for determining critical soil test values using the modified arcsine-log calibration curve. Soil Science Society of America Journal 2023, 87, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boote, K.J.; Gallaher, R.N.; Robertson, W.K.; Hinson, K.; Hammond, L.C. Effect of Foliar Fertilization on Photosynthesis, Leaf Nutrition, and Yield of Soybeans1. Agronomy Journal 1978, 70, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soil. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J. Soil Testing: Sampling, correlation, calibration and interpretation. SSSA Spec. Pub. 21. SSSA. Madison, Wisconsin, EE.UU. 1987; 144 pag.
- Brownlie, W.J.; Sutton, M.A.; Heal, K.V.; Reay, D.S.; Spears, B.M. (Eds.) Our Phosphorus Future; UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology: Edinburgh, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruulsema, T.W. 4R Phosphorus Management Practices for Major Commodity Crops of North America. IPNI. Issue Review Ref #17023. 2017. Available online: http://phosphorus.ipni.net/article/PPP-3169.
- Bruulsema, T.W.; Peterson, H.M.; Prochnow, L.I. The Science of 4R Nutrient Stewardship for Phosphorus Management across Latitudes. J Environ Qual. 2019, 48, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundy, L.G.; Tunney, H.; Halvorson, A.D. Agronomic Aspects of Phosphorus Management. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment; Sims, J.T., Sharpley, A.N., Daniel, T.C., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresh, R.J.; Witt, C. Site-specific nutrient management. In Fertilizer Best Management Practices: Gneral principles, strategy for their adoption and voluntary initiatives vs regulations. In Proceedings of the IFA International Workshop on Fertilizer Best Management Practices, Brussels, Belgium, 7–9 March 2007; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFIA): Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt, L.L.; Moody, P.W.; Gourley, C.J.P.; Hannah, M.C. A simple phosphorus buffering index for Australian soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2002, 40, 497–513. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, E.; Salvi, L.; Paoli, F.; Fucile, M.; Masciandaro, G.; Manzi, D.; Masini, C.M.; Mattii, G.B. Application of Zeolites in Agriculture and Other Potential Uses: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Li, C.; Margenot, A.J. 33P-isotope labelling ammonium phosphate fertilizers reveals majority of early growth maize phosphorus is soil-derived. European Journal of Soil Science 2024, 75, e13578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Edmeades, D.; McBride, R.; Sahrawat, K.L. Review of maleic–itaconic acid copolymer purported as urease inhibitor and phosphorus enhancer in soils. Agronomy Journal 2014, 106, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Prochnow, L.I.; Cantarella, H. Recent developments of fertilizer production and use to improve nutrient efficiency and minimize environmental impacts. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 267–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Sikora, F.J.; Gilkes, R.; McLaughlin, M.J. Comparing of the difference and balance methods to calculate percent recovery of fertilizer phosphorus applied to soils: A critical discussion. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 2012, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivenge, P.; Zingore, S.; Ezui, K.S.; Njoroge, S.; Bunquin, M.A.; Dobermann, A.; Saito, K. Progress in research on site-specific nutrient management for smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa. Field Crops Res. 2022, 281, 108503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.B.; Zhang, X. Phosphorus use efficiency in agricultural systems: a comprehensive assessment through the review of national scale substance flow analyses, Ecol. Indicators, 2021, 121, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, L.; He, P.; Jin, J.; Li, S.; Grant, C.; Xu, X.; Zhou, W. Estimating nutrient uptake requirements for wheat in China. Field Crops Research 2013, 146, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampitti, I.; García, F.O. Requerimientos nutricionales. Absorción y extracción de macronutrientes y nutrientes secundarios: Cereales, Oleaginosos e Industriales. Informaciones Agronómicas No. 33. Archivo Agronómico No. 11. pp. 1-4. IPNI Cono Sur. Acassuso, Buenos Aires. 2007.
- Ciampitti, I.A.; García, F.O.; Picone, L.I.; Rubio, G. Phosphorus budget and soil extractable dynamics in field crop rotations in Mollisols. Soil Science Society of America Journal 2011, 75, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Murrell, S.T.; Camberato, J.J.; Vyn, T.J. Maize nutrient accumulations and partitioning in response to plant density and nitrogen rate: I. Macronutrients. Agronomy Journal 2013, 105, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.B. Sorghum. In Nutrient Deficiencies & Toxicities in Crop Plants, 1st ed.; Bennett, W.F., Ed.; APS Press: Minnesota, USA, 1993; pp. 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Cabello, M. J., Gutiérrez Boem, F. H., Quintero, C. E., & Rubio, G. (2016). Soil characteristics involved in phosphorus sorption in Mollisols. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 80, 1585-1590.
- Cox, F.R., & L. Unruh. (2000). Reference sufficiency ranges, field crops: Grain Sorghum. N.C. Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services. Available at http://www.ncagr.gov/agronomi. /: of Agriculture and Consumer Services. Available at http.
- Colwell JD (1963). The estimation of the phosphorus fertilizer requirements of wheat in southern New South Wales by soil analysis. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture and Animal Husbandry 3, 190–198. [CrossRef]
- Condron, L.M. , Turner, B.L. & Cade-Menun, B.J. (2005). Chemistry and Dynamics of Soil Organic Phosphorus. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment (eds J. Thomas Sims, A.N. Sharpley & D.T. Westermann). [CrossRef]
- Conyers M. K., Bell M. J., Wilhelm N. S., Bell R., Norton R. M., Walker C. (2013). Making Better Fertiliser Decisions for Cropping Systems in Australia (BFDC): knowledge gaps and lessons learnt. Crop and Pasture Science 64, 539-547.
- Cordell, D., Drangert, J. O. & White, S. (2009). The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Change 19, 292–305.
- Cordell, D.; Jackson, M.; White, S. (2013). Phosphorus flows through the Australian food system: Identifying intervention points as a roadmap to phosphorus security. Environ. Sci. Policy, 29, 87–102. [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; White, S. (2013). Sustainable Phosphorus Measures: Strategies and Technologies for Achieving Phosphorus Security. Agronomy, 3, 86-116. [CrossRef]
- Correndo, A. A., A. Pearce, C. Bolster, J. T. Spargo, D. Osmond, & I. A. Ciampitti. (2023). The soiltestcorr R package: An accessible framework for reproducible correlation analysis of crop yield and soil test data. SoftwareX, Volume 21, 101275. [CrossRef]
- Correndo A. A., Salvagiotti, F., García, F. O., & Gutiérrez-Boem, F. H. (2017). A modification of the arcsine-log calibration curve for analysing soil test value-relative yield relationships. Crop & Pasture Science, 68, 297–304. [CrossRef]
- Covacevich F, Echeverría HE, Aguirrezabal LA (2007). Soil available phosphorus status determines indigenous mycorrhizal colonization of field and glasshouse-grown spring wheat from Argentina. Appl Soil Ecol 35:1–9.
- Crespo C., N. Wyngaard, H. R. Sainz Rozas, A. Pizzuto, P. Barbagelata, M. Barraco, V. Gudelj, & P. A. Barbieri. (2024). Cover crops affect phosphorus fractions in soybean-based sequences with different phosphorus availability in Mollisols. Soil Till. Res. 240, 106096. [CrossRef]
- Cubilla, M; Ademir, A; Wendling, F; Eltz, L; Amado, T & Mielniczuk, J. (2012). Recomendaciones de fertilización para soja, trigo, maíz y girasol bajo sistema de siembra directa en el Paraguay. Asunción, Paraguay, CAPECO. 88 p.
- Culman, S., Fulford, A., Camberato, J., & Steinke, K. (2020). Tri-State Fertilizer Recommendations. Bulletin 974. College of Food, Agricultural, and Environmental Sciences. Columbus, OH: The Ohio State University. extensionpubs.osu.edu.
- Culman, S., Fulford, A., LaBarge, G., Watters, H., Lindsey, L. E., Dorrance, A., & Deiss, L. (2023). Probability of crop response to phosphorus and potassium fertilizer: Lessons from 45 years of Ohio trials. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 87, 1207–1220. [CrossRef]
- Dahnke, W. C. , & Olson, R. A. (1990). Soil test correlation, calibration, and recommendation. In R. L.Westerman (Ed.), Soil testing and plant analysis (pp. 45–71). SSSA. [CrossRef]
- Das, B., Huth, N., Probert, M., Condron, L., & Schmidt, S. (2019). Soil phosphorus modeling for modern agriculture requires balance of science and practicality: A perspective. Journal of Environmental Quality, 48, 1281-1294.
- Degryse, F., B. Ajiboye, R.D. Armstrong, & M.K. McLaughlin. (2013). Sequestration of phosphorus-binding cations by complexing compounds is not a viable mechanism to increase P efficiency. Soil Science Society of America Journal 77:2050–2059. [CrossRef]
- Degryse, F. & McLaughlin, M.J. (2014). Phosphorus Diffusion from Fertilizer: Visualization, Chemical Measurements, and Modeling. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 78: 832-842. [CrossRef]
- Demay, J., Ringeval, B., Pellerin, S. et al. (2023). Half of global agricultural soil phosphorus fertility derived from anthropogenic sources. Nat. Geosci. 16, 69–74. [CrossRef]
- Deraoui, N.B., Mekliche, L.H. & Mekliche, A. (2021). Response of Wheat to Foliar and Soil P Fertilization on Grain Yield and Phosphorus use Efficiency in Southeastern Algeria. Indian Journal of Agricultural Research. 55, 99-104. [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, J. , Torres, G., Driver, E., Figueiredo, B. & Raun, W.R. (2017). World Phosphorus Use Efficiency in Cereal Crops. Agronomy Journal, 109: 1670-1677. [CrossRef]
- Dinca, L.C.; Grenni, P.; Onet, C.; Onet, A. (2022). Fertilization and Soil Microbial Community: A Review. Appl. Sci. 12, 1198.
- Divito G. A., A. A. Correndo & F. O. García. (2017). La nutrición del cultivo de trigo. In Manual del cultivo de trigo. G. A. Divito & F. O. García. International Plant Nutrition Institute, Acassuso, Buenos Aires, Argentina. 224 p. ISBN 978-987-46277-3-5.
- Djodjic, F., Bergström, L. & Grant, C. (2005). Phosphorus management in balanced agricultural systems. Soil Use and Management, 21: 94-101. [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A. (2007). Nutrient use efficiency – measurement and management. In: IFA International Workshop on Fertilizer Best Management Practices. Belgium, Brussels, pp. 1–28.
- Dobermann A, Bruulsema T, Cakmak I, Gerard B, Majumdar K, McLaughlin M, Reidsma P (2022). Responsible plant nutrition: a new paradigm to support food system transformation. Glob Food Sec 33:100636. [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, K.G. Cassman, C.P. Mamaril, J.E. Sheehy. (1998). Management of phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur in intensive, irrigated lowland rice, Field Crops Research, Volume 56, Issues 1–2, Pages 113-138. [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A. & Fairhurst, T. (2000). Rice: Nutrient disorders and nutrient management. Handbook Series, Potash and Phosphate Institute (PPI), Potash and Phosphate Institute of Canada (PPIC) and International Rice Research Institute, Philippine.
- Dobermann, A. & Witt, C. (2004). The evolution of site-specific nutrient management in irrigated rice systems of Asia. In Increasing productivity of intensive rice systems through site-specific nutrient management (eds. Dobermann, A., Witt, C. & Dawe, D.) 410 (Science Publisher Inc., and International Rice Research Institute (IRRI).
- Dodd, J.R. & Mallarino, A.P. (2005). Soil-Test Phosphorus and Crop Grain Yield Responses to Long-Term Phosphorus Fertilization for Corn-Soybean Rotations. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 69: 1118-1128. [CrossRef]
- Dodd R.J., Sharpley A.N. (2015). Recognizing the role of soil organic phosphorus in soil fertility and water quality. Res Conserv Recycl 105, Part B: 282-293. [CrossRef]
- Drizo, A.; Johnston, C.; Guðmundsson, J. (2022). An Inventory of Good Management Practices for Nutrient Reduction, Recycling and Recovery from Agricultural Runoff in Europe’s Northern Periphery and Arctic Region. Water, 14, 2132. [CrossRef]
- Drohan, P.J., Bechmann, M., Buda, A., Djodjic, F., Doody, D., Duncan, J.M., Iho, A., Jordan, P., Kleinman, P.J., McDowell, R., Mellander, P.-E., Thomas, I.A. & Withers, P.J.A. (2019). A Global Perspective on Phosphorus Management Decision Support in Agriculture: Lessons Learned and Future Directions. Journal of Environmental Quality, 48: 1218-1233. [CrossRef]
- Dudal, R. & R.N. Roy (eds.) (1995). Integrated Plant Production Systems. FAO Fertilizer and Plant Nutrition Bulletin. 12. Rome, Italy.: 139-154.
- Duncan, E.W., Osmond, D.L., Shober, A.L., Starr, L., Tomlinson, P., Kovar, J.L., Moorman, T.B., Peterson, H.M., Fiorellino, N.M. & Reid, K. (2019). Phosphorus and Soil Health Management Practices. Agricultural & Environmental Letters, 4: 190014. [CrossRef]
- Dunn, D. J., & Stevens, G. (2008). Response of rice yields to phosphorus fertilizer Rates and polymer coating. Crop Management. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.K., Majumdar, K. & Satyanarayana, T. (2014). India: Nutrient Expert: A precision nutrient management tool for smallholder production systems of India. Crops & Soils, 47: 23-25. [CrossRef]
- Dyson, C. B., & Conyers, M. K. (2013). Methodology for online biometric analysis of soil test-crop response datasets. Crop & Pasture Science, 64, 435–441. [CrossRef]
- Egner H, H. Riehm & W. R. Domingo. (1960). Untersuchungen uber die chemishe bodenanalyse als grundlage fur die beurteilung des nahrstoffzustandes.der boden. II. Chemische extraktions-methoden zur phosphor-und kalimbestimmung kungl. Lantbrukshoegsk. Ann. 26:204-209.
- European Commission (2018). Best Environmental Management Practice for the Agriculture Sector-Crop and Animal Production; Antonopoulos, I.S., Canfora, P., Dri, M., Gaudillat, P., Styles, D., Julie Williamson, J., Jewer, A., Haddaway, N., Price, M. (Eds.); Final Draft; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium. Available online: http://susproc.jrc.ec.europa.eu/activities/emas/documents/AgricultureBEMP.pdf.
- Fernández, M. C., Belinque, H., Gutierrez Boem, F. H. & Rubio, G. (2009). Compared Phosphorus Efficiency in Soybean, Sunflower and Maize. Journal of Plant Nutrition,32:12,2027- 2043. [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M. C., Gutiérrez Boem, F. H. & Rubio, G. (2011). Effect of indigenous mycorrhizal colonization on phosphorus-acquisition efficiency in soybean and sunflower J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2011, 174, 673–677. [CrossRef]
- Filippelli GM (2002). The global phosphorus cycle. In: Kohn M, Rakovan J, Hughes J (eds) Phosphates: Geochemical, Geobiological, and Materials Importance. Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry 48, pp 391-425.
- Filippelli G. (2008). The Global Phosphorus Cycle: Past, Present, and Future. Elements, V O L . 4, PP. 89–95. [CrossRef]
- Fixen, P.E. (1989). Agronomic Evaluations of MAP and DAP. Proc. (1989) North Central Extension-Industry Soil Fertility Conference, St. Louis, MO, US.
- Fixen, P.E., F. Brentrup, T. Bruulsema, F. Garcia, R. Norton, & S. Zingore. (2015). Nutrient/Fertilizer Use Efficiency: Measurement, Current Situation and Trends. In P. Drechsel, P. Heffer, H. Magen, R. Mikkelsen, D. Wichelns. (eds.). Managing Water and Fertilizer for Sustainable Agricultural Intensification. International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA), International, Water Management Institute (IWMI), International Plant Nutrition Institute (IPNI), and International Potash Institute (IPI). Paris, France. p 8-37.
- Fixen, P.E., & J. Grove. (1990). Testing soils for phosphorus. Pp. 141- 180. In: R.L. Westerman (ed.) Soil testing and plant analysis. 3a. edicion. SSSA Book Number 3. Madison, Wisconsin, EE.UU.
- Freiling M, von Tucher S, Schmidhalter U (2022). Factors influencing phosphorus placement and effects on yield and yield parameters: A meta-analysis. Soil Till Res 216:105257. [CrossRef]
- Fryer, M.S., Slaton, N.A., Roberts, T.L., Hardke, J.T. & Norman, R.J. (2019). Validation of Soil-Test-Based Phosphorus and Potassium Fertilizer Recommendations for Flood-Irrigated Rice. Agronomy Journal, 111: 2523-2535. [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, B., Ziadi, N., Bélanger, G., & Parent, G. (2020). Validation and use of critical phosphorus concentration in maize. European Journal of Agronomy, 120, 126147.
- Gangaiah B. (2019). Nutrient omission plot technique for yield response, indigenous nutrient supply and nutrient use efficiency estimation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop in Andaman & Nicobar Islands. Oryza Vol. 56 No. 4, 2019 (388-395). [CrossRef]
- García F. O. (2004). Avances en el manejo nutricional de los cultivos de trigo. Actas Congreso “A Todo Trigo”. FCEGAC. Mar del Plata, 13-14 Mayo. Pp. 55-62.
- García F. O., M. F. González Sanjuan, E. Ciarlo, & N. Reussi Calvo. (2024). Phosphorus use and balance in field crops of Argentina. 2024 Centennial Congress of IUSS. Florence, Italy, 19-21 May 2024.
- García F. O., L. Picone, & I. A. Ciampitti. (2014). Phosphorus. In Echeverría H. E. & F.O. García (ed.). Soil fertility and crop fertilization. Ed. INTA. 2a. Ed. Buenos Aires, Argentina. ISBN 9-789875-215658. p. 229-264. (In Spanish).
- Gatiboni, L., Brunetto, G., Pavinato, P. S., George, T., eds. (2021). Legacy Phosphorus in Agriculture: Role of Past Management and Perspectives for the Future. Lausanne: Frontiers Media SA. [CrossRef]
- George, T., Magbanua, R., Roder, W., Van Keer, K., Trébuil, G. & Reoma, V. (2001). Upland Rice Response to Phosphorus Fertilization in Asia. Agronomy Journal, 93: 1362-1370. [CrossRef]
- Girma, K., M., K. L., Freeman, K. W., Mosali, J., Teal, R. K., Raun, William. R., … Arnall, D. B. (2007). Determination of Optimum Rate and Growth Stage for Foliar-Applied Phosphorus in Corn. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 38(9–10), 1137–1154. [CrossRef]
- Gitau, M., Gburek, W., & Bishop, P. (2008). Use of the SWAT model to quantify water quality effects of agricultural BMPs at the farm-scale level. Transactions of the ASAE, 51, 1925-1936.
- Gomez de Sousa D., T. Rein, W. Goedert, E. Lobato, & R. de Souza Nunes. (2010). Fósforo. In L. I. Prochnow, V. Casarin, & S. R. Stipp (ed.). Proc. Symposium “Boas practicas para uso eficiente de efrtilizantes”. Piracicaba, SP, Brazil. Pag. Vol. 2. 67-132.
- Grant, C. & D. Flaten. (2019). 4R Management of Phosphorus Fertilizer in the Northern Great Plains. Journal of Environmental Quality 48:1356–1369. [CrossRef]
- Grieger, K., Merck, A., Deviney, A. et al. (2024). What are stakeholder views and needs for achieving phosphorus sustainability? Environ Syst Decis 44, 114–125. [CrossRef]
- Guejjoud, H., Curie, F., & Grosbois, C. (2024). Analyzing a century of agricultural phosphorus surplus and its long-term key drivers in France. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 1-19.
- Guelfi, D.; Nunes, A.P.P.; Sarkis, L.F.; Oliveira, D.P. (2022). Innovative Phosphate Fertilizer Technologies to Improve Phosphorus Use Efficiency in Agriculture. Sustainability, 14, 14266. [CrossRef]
- Hallama, M., Pekrun, C., Lambers, H. et al. (2019). Hidden miners – the roles of cover crops and soil microorganisms in phosphorus cycling through agroecosystems. Plant Soil 434, 7–45. [CrossRef]
- Hammond John P., Martin R. Broadley, Philip J. White. (2004). Genetic Responses to Phosphorus Deficiency, Annals of Botany, Volume 94, Issue 3, Pages 323–332. [CrossRef]
- Hansel, F. D., Ruiz Diaz, D. A., Amado, T. J., & Rosso, L. H. (2017). Deep banding increases phosphorus removal by soybean grown under no-tillage production systems. Agronomy Journal, 109, 1091-1098.
- Haq, M.U. & Mallarino, A.P. (2000). Soybean Yield and Nutrient Composition as Affected by Early Season Foliar Fertilization. Agronomy Journal, 92: 1624. [CrossRef]
- Havlin J., J. Beaton, S. Tisdale & W. Nelson. 2005. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers. Pearson Education Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, EE.UU. 7th. ed. 515 pag.
- Hedley, M. Mclaughlin, M. (2005). Reactions of phosphate fertilizers and by-products in soils. In: Sims, T. & Sharpley, A. N. (eds.) Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment. Madison, WI: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America.
- Hertzberger AJ, Cusick RD, Margenot AJ. (2020). A review and meta-analysis of the agricultural potential of struvite as a phosphorus fertilizer. Soil Science Society of America Journal ; 84: 653–671. [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S., Keesstra, S. D., Kadziuliene, Z., Jordan-Meille, L., Wall, D., Trinchera, A., Spiegel, H., Sandén, T., Baumgarten, A., Jensen, J. L., Hirte, J., Liebisch, F., Klages, S., Löw, P., Kuka, K., De Boever, M., D'Haene, K., Madenoglu, S., Ozcan, H., ... Vervuurt, W. (2022). Fertilisation Strategies across Europe: Current Situation, Potential and Limits for a Harmonised Approach. In Fertilisation Strategies across Europe: Current Situation, Potential and Limits for a Harmonised Approach (Vol. 875). International Fertiliser Society Proceedings. Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4258569.
- Hirzel, J. (2004). Fertilización del Cultivo. (in Spanish) In: Mellado, M. (Ed.), Boletín deTrigo 2004. Manejo Tecnológico. Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias, Chillán, Chile, pp. 49–75.
- Holloway, R E, Bertrand I, Frischke A J, Brace D M, McLaughlin M J & Shepperd W (2001). Improving fertilizer efficiency on calcareous and alkaline soils with fluid sources of P,N and Zn. Plant Soil. 236, 209–219.
- Hopkins, B.G. & Hansen, N.C. (2019). Phosphorus Management in High-Yield Systems. Journal of Environmental Quality, 48: 1265-1280. [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.G., Fernelius, K.J., Hansen, N.C. & Eggett, D.L. (2018). AVAIL Phosphorus Fertilizer Enhancer: Meta-Analysis of 503 Field Evaluations. Agronomy Journal, 110: 389-398. [CrossRef]
- Hornung, A., Khosla, R., Reich, R., Inman, D. & Westfall, D.G. (2006). Comparison of Site-Specific Management Zones: Soil-Color-Based and Yield-Based. Agronomy Journal, 98: 407-415. [CrossRef]
- Hue N. (2024). Phosphorus Nutrient in Organic Farming - A Review. Mod Concep Dev Agrono. 13. MCDA. 000820. [CrossRef]
- IFA (2022). Fertilizer use by crop and country for the 2017-2018 period. International Fertilizer Association (IFA), Paris, France; Available at https://www.ifastat.org/consumption/fertilizer-use-by-crop.
- IPNI (2012). 4R Plant Nutrition Manual: A Manual for Improving the Management of Plant Nutrition, (T.W. Bruulsema, P.E. Fixen, G.D. Sulewski eds.), International Plant Nutrition Institute, Norcross, GA, USA. 126 p.
- Jamal A, Saeed MF, Mihoub A, Hopkins BG, Ahmad I & Naeem A (2023). Integrated use of phosphorus fertilizer and farmyard manure improves wheat productivity by improving soil quality and P availability in calcareous soil under subhumid conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 14:1034421. [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.H., Guiking, F.C.T., van der Eijk, D., Smaling, E.M.A., Wolf, J. & van Reuler, H. (1990). A system for quantitative evaluation of the fertility of tropical soils (QUEFTS). Geoderma, 46:299-318.
- Jobbágy E. G. & O. E. Sala. (2014). The imprint of crop choice on global nutrient needs. Environ. Res. Lett. 9 084014. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.E. & Poulton, P.R. (2019). Phosphorus in Agriculture: A Review of Results from 175 Years of Research at Rothamsted, UK. Journal of Environmental Quality, 48: 1133-1144. [CrossRef]
- Johnston A. E., P. R. Poulton, P. E. Fixen, D. Curtin. (2014). Chapter Five - Phosphorus: Its Efficient Use in Agriculture, Editor(s): Donald L. Sparks, Advances in Agronomy, Academic Press, Volume 123, Pages 177-228. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.E., Poulton, P.R., White, R.P., MacDonald, A.J., (2016). Determining the longer term decline in plant-available soil phosphorus from short-term measured values. Soil Use Manage. 32, 151–161. [CrossRef]
- Jones, Jr. J.B. (1998). Plant Nutrition Manual. CRC Press. Boca Raton. Florida. USA. 149 pp.
- Jordan-Meille, L., Rubæk, G.H., Ehlert, P.A.I., Genot, V., Hofman, G., Goulding, K., Recknagel, J., Provolo, G. & Barraclough, P. (2012). An overview of fertilizer-P recommendations in Europe: soil testing, calibration and fertilizer recommendations. Soil Use Manage, 28: 419-435. [CrossRef]
- Kalinitchenko V. & V. Nosov. (2019). Phosphogypsum: P Fertilizer By-Product and Soil Amendment. Better Crops Vol. 103 (2019, No. 1) p.50-53.
- Kang, L.Y., Yue, S.C., Li, S.Q., (2014). Effects of phosphorus application in different soil layers on root growth, yield, and water-use efficiency of winter wheat grown under semi-arid conditions. J. Integr. Agr. 13, 2028–2039.
- Karbo, A., Woodard, H. J., & Bly, A. (2017). Crop production impacts on soil phosphorus removal and soil test levels. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 40, 1172–1179. [CrossRef]
- Khurana, H. S., Bijay-Singh, A. D., Phillips, S. B., & Sidhu, A. S. (2008). Site-specific nutrient management performance in a rice-wheat cropping system. Better Crops, 92, 26-28.
- Kitchen, N.R., D.G. Westfall, J.L. Havlin. (1990). Soil sampling under no-till banded phosphorus. Soil Science Society of America Journal 54:1661-1665. [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, P.J.A., Sharpley, A.N., McDowell, R.W. et al. (2011). Managing agricultural phosphorus for water quality protection: principles for progress. Plant Soil 349, 169–182. [CrossRef]
- Kokulan V., K. Schneider, M. L. Macrae, & H. Wilson. (2024). Struvite application to field corn decreases the risk of environmental phosphorus loss while maintaining crop yield. Ag. Eco. Env. 366. [CrossRef]
- Korcak R. (1998). Agricultural uses of phosphogypsum, gypsum, and other industrial byproducts. In: Wright RJ, Robert J, Kemper WD, Millner PD, Power JF, Korcak RF, editors. Agriculture uses of municipal animal, and industrial byproduct. Beltsville (MD): U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Conservation Research Report 44, p. 120–126.
- Krasilnikov, P.; Taboada, M.A.; Amanullah. (2022). Fertilizer Use, Soil Health and Agricultural Sustainability. Agriculture 12, 462. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S., Sindhu, S. S., & Kumar, R. (2022). Biofertilizers: an ecofriendly technology for nutrient recycling and environmental sustainability. Cur. Res. Microbial. Sci. 3, 100094. [CrossRef]
- Lamba J., A. M. Thompson, K.G. Karthikeyan, J. C. Panuska, L. W. Good. (2016). Effect of best management practice implementation on sediment and phosphorus load reductions at subwatershed and watershed scale using SWAT model. International Journal of Sediment Research 31 (4): 386-394. [CrossRef]
- Lambers H. (2022). Phosphorus Acquisition and Utilization in Plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology Vol. 73:17-42. [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.M., Lowenberg-DeBoer, J. & Malzer, G. (2007). Managing phosphorous soil dynamics over space and time. Agricultural Economics, 37: 43-53. [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L., Frazier, A.W., Stephenson, H.F. (1962). Identification of reaction products from phosphate fertilizers in soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 26, 446–452. [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E., M.J. McLaughlin, C. Johnston, R.D. Armstrong, & R.E. Holloway. (2004). Mobility and Lability of Phosphorus from Granular and Fluid Monoammonium Phosphate Differs in a Calcareous Soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal 68:682–689.
- Lombi, E., M.J. McLaughlin, C. Johnston, R.D. Armstrong, & R.E. Holloway. (2005). Mobility, solubility and lability of fluid and granular forms of P fertiliser in calcareous and noncalcareous soils under laboratory conditions. Plant Soil 269:25–34. [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, L.; P.E. Abbate & V.T. Manfreda, (2012). Incidence of the differences in the amount of P exported between wheat cultivars. Agriscientia XXIX: 1-13.
- Leikam D. F., Lamond R, Mengel D. (2003). Providing Flexibility in Phosphorus and Potassium Fertilizer Recommendations. Better Crops with Plant Food, 87, 6–10.
- Leikam D. F., W. N. Sutherland, & E.J. Penas. (1991). Phosphorus Sources for Corn Fertilization. National Corn Handbook NCH-13. Iowa State University Extension. https://store.extension.iastate.edu/product/2883.
- Ling, F., Silberbush, M. (2002). Response of maize to foliar vs. soil application of nitrogen-phosphorus- potassium fertilizers. Journal of Plant Nutrition. 25, 2333-2342.
- Liu, R., Lal, R. (2014) Synthetic apatite nanoparticles as a phosphorus fertilizer for soybean (Glycine max). Sci Rep 4, 5686. [CrossRef]
- Lizcano Toledo, R.; Lerda, C.; Moretti, B.; Miniotti, E.; Santoro, V.; Fernandez-Ondoño, E.; Martin, M.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Romani, M.; Celi, L. (2022). Cover Crops Increase N and P Cycling and Rice Productivity in Temperate Cropping Systems. Agronomy, 12, 2193. [CrossRef]
- López-Arredondo, D.L., & L. Herrera-Estrella. (2012). Engineering phosphorus me tabolism in plants to produce a dual fertilization and weed control system. Nat. Biotechnol. 30:889–893. [CrossRef]
- Lott, J.N.A., Bojarski, M., Kolasa, J., Batten, G.D. & Campbell, L.C. (2009). A review of the phosphorus content of dry cereal and legume crops of the world, Int. J. Agricultural Resources, Governance and Ecology, Vol. 8, Nos. 5/6, pp.351–370.
- Lu, Y., Gao, Y., Nie, J. et al. (2021). Substituting chemical P fertilizer with organic manure: effects on double-rice yield, phosphorus use efficiency and balance in subtropical China. Sci Rep 11, 8629. [CrossRef]
- Ludemann, Cameron I.; Hijbeek, Renske; van Loon, Marloes et al. (2023). Global data on crop nutrient concentration and harvest indices [Dataset]. Dryad. [CrossRef]
- Ludemann, C.I., Hijbeek, R., van Loon, M.P. T. S. Murrell, A. Dobermann, & M. K. van Ittersum. Tiered maize and wheat nutrient removal coefficients estimated from available data. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst (2024a). [CrossRef]
- Ludemann CI, Wanner N, Chivenge P, Dobermann A, Einarsson R, Grassini P, Gruere A, Jackson K, Lassaletta L, Maggi F, Obli-Laryea G, van Ittersum MK, Vishwakarma S, Zhang X, Tubiello FN (2024b). A global FAOSTAT reference database of cropland nutrient budgets and nutrient use efficiency (1961–2020): nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Earth Syst Sci Data 16:525–541.
- Łukowiak R., W. Grzebisz, & G. F. Sassenrath. (2016). New insights into phosphorus management in agriculture — A crop rotation approach. Science of The Total Environment, 542, Part B, 1062-1077. [CrossRef]
- Lun, F. , Liu, J., Ciais, P., Nesme, T., Chang, J., Wang, R., Goll, D., Sardans, J., Peñuelas, J., & Obersteiner, M. (2018). Global and regional phosphorus budgets in agricultural systems and their implications for phosphorus-use efficiency, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 10, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Lyons, S. E., Clark, J. D., Osmond, D. L., Parvej, M. R, Pearce, A. W., Slaton, N. A., & Spargo, J. T. (2023). Current status of US soil test phosphorus and potassium recommendations and analytical methods. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 87, 985–998. [CrossRef]
- Lyons SE, Osmond DL, Slaton NA, et al. (2020). FRST: A national soil testing database to improve fertility recommendations. Agric Environ Lett. 5:e20008. [CrossRef]
- Ma, W., L. Ma, J. Li, F. Wang, I. Sisák, F. Zhang. (2011). Phosphorus flows and use efficiencies in production and consumption of wheat, rice, and maize in China. Chemosphere 84: 814–821. [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, G. K., Bennett, E. M., Potter, P. A., & Ramankutty, N. (2011). Agronomic phosphorus imbalances across the world's croplands. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108, 3086-3091.
- MacDonald, G.K., Bennett, E.M. & Taranu, Z.E. (2012). The influence of time, soil characteristics, and land-use history on soil phosphorus legacies: a global meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol, 18: 1904-1917. [CrossRef]
- Macik, M., Gryta, A., Frac, M. (2020). Biofertilizers in agriculture: An overview on concepts, strategies, and effects on soil microorganisms. Adv. Agron. 160, 31.
- Maertens, M., Oyinbo, O., Abdoulaye, T., & Chamberlin, J. (2023). Sustainable maize intensification through site-specific nutrient management advice: Experimental evidence from Nigeria. Food Policy, 121, 102546. [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, E., G.C. Vitti, & S.A. de Oliveira. (1997). Avaliação do estado nutricional das plantas: principios e aplicações. 2da Ed. rev e atual. POTAFOS. Piracicaba-SP. 319 pp.
- Malhi, S. S., Johnston, A. M., Schoenau, J. J., Wang, Z. H. & Vera, C. L. (2006). Seasonal biomass accumulation and nutrient uptake of wheat, barley and oat on a Black Chernozem soil in Saskatchewan. Can. J. Plant Sci. 86: 1005–1014.
- Mallarino A. (2003). Field Calibration for Corn of the Mehlich-3 Soil Phosphorus Test with Colorimetric and Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectroscopy Determination Methods. Soil Science Society of America Journal 68:1928-1934.
- Mallarino, A. P., & Blackmer, A. M. (1992). Comparison of methods for determining critical concentrations of soil test phosphorus for corn. Agronomy Journal, 84, 850–856. [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P., Bordoli, J.M. & Borges, R. (1999). Phosphorus and Potassium Placement Effects on Early Growth and Nutrient Uptake of No-Till Corn and Relationships with Grain Yield. Agronomy Journal, 91: 37-45. [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P. , Haq, M.U., Wittry, D. & Bermudez, M. (2001). Variation in Soybean Response to Early Season Foliar Fertilization among and within Fields. Agronomy Journal, 93: 1220-1226. [CrossRef]
- Mallarino A. & J. Sawyer. (2018). Phosphorus and Potassium Tissue Testing in Corn and Soybean. Iowa State University Crop 3153. Ames, Iowa, US. Available at https://store.extension.iastate.edu/product/Phosphorus-and-Potassium-Tissue-Testing-in-Corn-and-Soybean.
- Mallarino A. P., J. E. Sawyer, S. K. Barnhart, & M. A. Licht. (2023). A General Guide for Crop Nutrient and Limestone Recommendations in Iowa. PM 1688 Revised February 2023. Iowa State University. Ames, Iowa, US.
- Mallarino, A.P. & Schepers, J.S. (2005). Role of Precision Agriculture in Phosphorus Management Practices. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment (eds J. Thomas Sims, A.N. Sharpley & T.C. Daniel). [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P., & D.J. Wittry. (2004). Efficacy of grid and zone soil sampling approaches for site-specific assessment of phosphorus, potassium, pH, and organic matter. Precision Agriculture 5:131-144. [CrossRef]
- Mardamootoo T., C. C. du Preez, & J. H. Barnard. (2021). Phosphorus management issues for crop production: A review. African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 17, 939-952. [CrossRef]
- Marschner H (1995). Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants (2nd edition). Academic, London.
- Martin T. M. P., F. Esculier, F. Levavasseur & S. Houot (2020): Human urine-based fertilizers: A review, Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. [CrossRef]
- Martinengo, S., Schiavon, M., Santoro, V. et al. (2023). Assessing phosphorus availability in paddy soils: the importance of integrating soil tests and plant responses. Biol Fertil Soils 59, 391–405. [CrossRef]
- Mason, S., McNeill, A., McLaughlin, M.J. et al. (2010). Prediction of wheat response to an application of phosphorus under field conditions using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) and extraction methods. Plant Soil 337, 243–258. [CrossRef]
- McArthur J. W. & G. C. McCord. (2017). Fertilizing growth: Agricultural inputs and their effects in economic development. Journal of Development Economics 127 133–152. [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W., Noble, A., Pletnyakov, P. et al. (2023). A Global Database of Soil Plant Available Phosphorus. Sci Data 10, 125. [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W., Pletnyakov, P. & Haygarth, P.M. (2024). Phosphorus applications adjusted to optimal crop yields can help sustain global phosphorus reserves. Nat Food 5, 332–339. [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.J., T.M. McBeath, R. Smernik, S.P. Stacey, B. Ajiboye, & C. Guppy. (2011). The chemical nature of P accumulation in agricultural soils: Implications for fertiliser management and design: An Australian perspective. Plant Soil 349:69–87. [CrossRef]
- Mehlich A. (1953). Determination of P, Ca, Mg, K, Na and NH4. North Carolina Soil Test Division. Mimeo 1958. North Carolina, EE.UU.
- Mehlich, A. (1984). Mehlich-3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 15:1409–1416.
- Mengel, K. (1997). Agronomic measures for better utilization of soil and fertilizer phosphates. European Journal of Agronomy, 7(1-3), 221-233.
- Mengel K, Kirkby EA (2001). Principles of Plant Nutrition (5th edition). Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
- Merrien, A., G. Arjaure, & C. Maisonneuve. (1986). Besoins en elements minéraux (majeurs, mineurs et oligo-éléments) chez le tornesol dans les conditions francaises. Informations Techniques CETIOM 95:8-19.
- Messiga, A.J., N. Ziadi, D. Plenet, L.-E. Parent, & C. Morel. (2010). Long-term changes in soil phosphorus status related to P budgets under maize monoculture and mineral fertilization. Soil Use and Manage 26: 354–364.
- Meus, L. D., Silva, M. R. Da Ribas, G. G. , Zanon, A. J. , Rossato, I. G. , Pereira, V. F. , Pilecco, I. B. , Ribeiro, B. San Martin Rolim , Souza, P. M. De, Nascimento, M. De F. Do., Poersch, A. H. , Duarte Junior, A. J. , Quintero, C. E. , Carracelas, G. , Carmona, L. De C., Streck, N. A. (2020). Ecofisiología del Arroz Buscando Altos Rendimientos. Santa Maria, RS (Brasil):FieldCrops, 312 p. ISBN 978-65-992356-4-1.
- Meyer, G., Bell, M. J., Kopittke, P. M., Lombi, E., Doolette, C. L., Brunetti, G., Klysubun, W., & Janke, C. K. (2023). Mobility and lability of phosphorus from highly concentrated fertiliser bands. Geoderma, 429, 116248. [CrossRef]
- Mihelcic, J.R., L.M. Fry, & R. Shaw. (2011). Global potential of phosphorus recovery from human urine and feces. Chemosphere 84: 832–839.
- Miransari M. (2011). Soil microbes and plant fertilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:875–885. [CrossRef]
- Mogollón J.M., A.H.W. Beusen, H.J.M van Grinsven, H. Westhoek, A.F. Bouwman. (2018). Future agricultural phosphorus demand according to the shared socioeconomic pathways. Global Environmental Change, Volume 50, Pages 149-163, ISSN 0959-3780. [CrossRef]
- Mollier A., S. Pellerin. (1999). Maize root system growth and development as influenced by phosphorus deficiency, Journal of Experimental Botany, Volume 50, Issue 333, Pages 487–497. [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, D., F. Degryse, & M.J. McLaughlin. (2014). Fluid fertilizers improve phosphorus diffusion but not lability in Andisols and Oxisols. Soil Science Society of America Journal 78:214–224. [CrossRef]
- Moody PW, Speirs SD, Scott BJ, Mason SD (2013). Soil phosphorus tests I: What soil phosphorus pools and processes do they measure? Crop & Pasture Science 64, 461–468.
- Morgan M.F. (1941). Chemical soil diagnosis by the Universal Soil Testing System. CT Agric. Exp. Sta. Bull. 450. Connecticut, EE.UU.
- Morse, G. K., Brett, S. W., Guy, J. A., & Lester, J. N. (1998). Review: phosphorus removal and recovery technologies. Science of the Total Environment, 212, 69–81. [CrossRef]
- Mosali, J., Desta, K., Teal, R. K., Freeman, K. W., Martin, K. L., Lawles, J. W., & Raun, W. R. (2006). Effect of Foliar Application of Phosphorus on Winter Wheat Grain Yield, Phosphorus Uptake, and Use Efficiency. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 29, 2147–2163. [CrossRef]
- Mubeena, P., A.S. Halepyati, & Chittapur, B.M. (2019). Effect of Date of Sowing and Nutrient Management on Nutrient Uptake and Yield of Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.). International Journal of Bio-resource and Stress Management, 10, 092-095. [CrossRef]
- Murrell, T.S. (2008). Measuring Nutrient Removal, Calculating Nutrient Budgets. In Soil Science Step-by-Step Field Analysis (eds S. Logsdon, D. Clay, D. Moore & T. Tsegaye). [CrossRef]
- Najdenko, E., Lorenz, F., Dittert, K., & Olfs, H. W. (2024). Rapid in-field soil analysis of plant-available nutrients and pH for precision agriculture—A review. Precision Agriculture, 25, 3189-3218.
- Nakayama, Y., Leon, P., Douglass, M., Becker, T., & Margenot, A. (2024). Optimum source, rate, timing, and placement of phosphorus fertilizer for Illinois soybean. Agronomy Journal, 116, 3300–3314. [CrossRef]
- Nash D., Hannah M., Clemow L., Halliwell D. , Webb B. Chapman D. (2003). A laboratory study of phosphorus mobilisation from commercial fertilisers. Soil Research 41, 1201-1212. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N. O., & Janke, R. R. (2007). Phosphorus Sources and Management in Organic Production Systems. HortTechnology 17, 442-454. Retrieved Oct 9, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D. N., Nguyen, T. T., Tran, Q. N., Macdonald, B., To, T. P., Tran, D. V., & Nguyen, Q. V. (2017). Soil and Rice Responses to Phosphate Fertilizer in Two Contrasting Seasons on Acid Sulfate Soil. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 48, 615–623. [CrossRef]
- Nishigaki, T., Tsujimoto, Y., Rinasoa, S. et al. (2019). Phosphorus uptake of rice plants is affected by phosphorus forms and physicochemical properties of tropical weathered soils. Plant Soil 435, 27–38. [CrossRef]
- Njoroge, S., Schut, A. G. T., Giller, K. E., & Zingore, S. (2019). Learning from the soil's memory: Tailoring of fertilizer application based on past manure applications increases fertilizer use efficiency and crop productivity on Kenyan smallholder farms. European Journal of Agronomy, 105, 52-61. [CrossRef]
- Nkebiwe, P.M., M. Weinmann, A. Bar-Tal, & T. Müller. (2016). Fertilizer placement to improve crop nutrient acquisition and yield: A review and meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 196:389–401. [CrossRef]
- Noack S. R., McBeath T. M., McLaughlin M. J. (2010). Potential for foliar phosphorus fertilisation of dryland cereal crops: a review. Crop and Pasture Science 61, 659-669.
- Noonari, S., Kalhoro, S. , Ali, A. , Mahar, A. , Raza, S. , Ahmed, M. , Shah, S. & Baloch, S. (2016). Effect of Different Levels of Phosphorus and Method of Application on the Growth and Yield of Wheat. Natural Science, 8, 305-314. [CrossRef]
- Norton, R.M. (2016). Nutrient Performance Indicators IPN00003 – A Scoping Study to Investigate the Development of Grains Industry Benchmarks Partial Factor Productivity, Partial Nutrient Balance, and Agronomic Efficiency of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, and Sulfur. International Plant Nutrition Institute (IPNI), Horsham, Victoria. 95pp.
- Nunes RS, de Sousa DMG, Goedert WJ, de Oliveira LEZ, Pavinato PS & Pinheiro TD (2020). Distribution of Soil Phosphorus Fractions as a Function of Long-Term Soil Tillage and Phosphate Fertilization Management. Front. Earth Sci. 8:350. [CrossRef]
- Olsen S.R., C.V. Cole, F.S. Watanabe & L.A. Dean (1954). Estimation of available P in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circ. 939.
- Olson, R. A. , Anderson, F. N., Frank, K. D., Grabouski, P. H., Rehm, G. W., & Shapiro, C. A. (2015). Soil testing interpretations: Sufficiency vs. build-up and maintenance. In J. R. Brown (Ed.), Soil testing: Sampling, correlation, calibration, and interpretation (Vol. 21, pp. 41–52). SSSA. [CrossRef]
- Osborne, S. L., Schepers, J. S., & Schlemmer, M. R. (2004). Detecting nitrogen and phosphorus stress in corn using multi-spectral imagery. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 35(3-4), 505-516.
- Osmond, D., Bolster, C., Sharpley, A., Cabrera, M., Feagley, S., Forsberg, A., Mitchell, C., Mylavarapu, R., Oldham, J.L., Radcliffe, D.E., Ramirez-Avila, J.J., Storm, D.E., Walker, F. & Zhang, H. (2017). Southern Phosphorus Indices, Water Quality Data, and Modeling (APEX, APLE, and TBET) Results: A Comparison. Journal of Environmental Quality, 46: 1296-1305. [CrossRef]
- Osmond, D.L., Shober, A.L., Sharpley, A.N., Duncan, E.W. & Hoag, D.L.K. (2019). Increasing the Effectiveness and Adoption of Agricultural Phosphorus Management Strategies to Minimize Water Quality Impairment. Journal of Environmental Quality, 48: 1204-1217. [CrossRef]
- Outbakat, M. , Choukr-Allah, R., Bouray, M., EL Gharous, M., EL Mejahed, K. (2023). Phosphogypsum: Properties and Potential Use in Agriculture. In: Choukr-Allah, R., Ragab, R. (eds) Biosaline Agriculture as a Climate Change Adaptation for Food Security. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Pampolino, M., Witt, C., Pasuquin, J.M., Johnston, A., Fisher, M.J. (2012). Development approach and evaluation of the Nutrient Expert software for nutrient management in cereal crops. Comput. Electron. Agric. 88, 103–110.
- Paramesh V, Mohan Kumar R, Rajanna GA, Gowda S, Nath AJ, Madival Y, Jinger D, Bhat S & Toraskar S (2023). Integrated nutrient management for improving crop yields, soil properties, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1173258. [CrossRef]
- Pavinato, P.S., Cherubin, M.R., Soltangheisi, A. et al. (2020). Revealing soil legacy phosphorus to promote sustainable agriculture in Brazil. Sci Rep 10, 15615. [CrossRef]
- Payne, W.A., Hossner, L.R., Onken, A.B. & Wendt, C.W. (1995). Nitrogen and Phosphorus Uptake in Pearl Millet and Its Relation to Nutrient and Transpiration Efficiency. Agronomy Journal, 87: 425-431. [CrossRef]
- Pearce, A. W., Slaton, N. A., Lyons, S. E., Bolster, C. H., Bruulsema, T. W., Grove, J. H., Jones, J. D., McGrath, J. M., Miguez, F. E., Nelson, N. O., Osmond, D. L., Parvej, M. R., Pena-Yewtukhiw, E. M., & Spargo, J. T. (2022). Defining relative yield for soil test correlation and calibration trials in the Fertilizer Recommendation Support Tool. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 86, 1338–1353. [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, S., Mollier, A. & Plénet, D. (2000). Phosphorus Deficiency Affects the Rate of Emergence and Number of Maize Adventitious Nodal Roots. Agronomy Journal, 92: 690-697. [CrossRef]
- Penn, C. J., & Camberato, J. J. (2019). A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture, 9, 120. [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas J. & J. Sardans. (2022). The global nitrogen-phosphorus imbalance. Science, 375 (6578). [CrossRef]
- Pierzynski, J. & Hettiarachchi, G.M. (2018). Reactions of Phosphorus Fertilizers with and without a Fertilizer Enhancer in Three Acidic Soils with High Phosphorus-Fixing Capacity. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 82: 1124-1139. [CrossRef]
- Pierzynski, G.M. , McDowell, R.W. & Thomas Sims, J. (2005). Chemistry, Cycling, and Potential Movement of Inorganic Phosphorus in Soils. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment (eds J. Thomas Sims, A.N. Sharpley & D.T. Westermann). [CrossRef]
- Plank, C.O., & S.J. Donohue. (2000). Reference sufficiency ranges, field crops: Small Grains. N.C. Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services. https://www.ncagr.gov/Divisions/Agronomic-Services.
- Pothuluri, J. V., Kissel, D. E., Whitney, D. A., & Thien, S. J. (1986). Phosphorus uptake from soil layers having different soil test phosphorus levels 1. Agronomy Journal, 78, 991-994.
- Prashanth D V, R Krishnamurthy & D V Naveen. (2019). Long-term Effect of Integrated Nutrient Management on Soil Nutrient Status, Content and Uptake by Finger Millet Crop in a TypicKandiustalf of Eastern Dry Zone of Karnataka, Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis. [CrossRef]
- Preston, C.L., Ruiz Diaz, D.A. & Mengel, D.B. (2019). Corn Response to Long-Term Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rate and Placement with Strip-Tillage. Agronomy Journal, 111: 841-850. [CrossRef]
- Prochnow L. I., L. E. Caires, & C. Rodriguez. (2016). Phosphogypsum Use to Reduce Subsoil Acidity: The Brazilian Experience. Better Crops 100 (2): 13-15.
- Prochnow, L. I., Chien, S. H., Carmona, G., Dillard, E. F., Henao, J., & Austin, E. R. (2008). Plant availability of phosphorus in four superphosphate fertilizers varying in water-insoluble phosphate compounds. Soil Science Society of America Journal 72, 462–470.
- Prochnow, L. I.; Van Raij, B.; Kiehl, J. C. (2002). Effect of Water and Citrate Solubility on Agronomic Effectiveness of Acidulated Phosphates in Three Consecutive Corn Crops. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, vol. 26, núm. 3, pp. 729-736 Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do Solo Viçosa, Brasil.
- Qaswar, M. Qaswar, M., Dongchu, L., Jing, H. et al. (2020). Interaction of liming and long-term fertilization increased crop yield and phosphorus use efficiency (PUE) through mediating exchangeable cations in acidic soil under wheat–maize cropping system. Sci Rep 10, 19828. [CrossRef]
- Quintero, C. E., Boschetti, N. G., & Benavidez, R. A. (2003). Effect of Soil Buffer Capacity on Soil Test Phosphorus Interpretation and Fertilizer Requirement. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 34(9–10), 1435–1450. [CrossRef]
- Quintero, C.E., Gutiérrez-Boem, F., Befani Romina, M. & Boschetti, N.G. (2007). Effects of soil flooding on P transformations in soils of the Mesopotamia region, Argentina. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk., 170: 500-505. [CrossRef]
- Rabuffetti, A. (2017). La fertilidad del suelo y su manejo. Montevideo: Hemisferio Sur. Vo. 2 Cap. 9 pp. 397-513.
- Raij van, B., Cantarella H., Quaggio, J. A., & Furlani, A. M. (ed.) (1996). Recomendações de adubação e calagem para o Estado de Sao Paulo. Bol. Tec. 100. 2 ed. Campinas, SP, Brazil. Instituto Agronômica e Fundação IAC. 285p.
- Raij van, B., Quaggio, J. A., & da Silva, N. M. (1986). Extraction of phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium from soils by an ion-exchange resin procedure. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 17, 547–566. [CrossRef]
- Rakotoson, T., Tsujimoto, Y., & Nishigaki, T. (2022). Phosphorus management strategies to increase lowland rice yields in sub-Saharan Africa: A review. Field Crops Research, 275, 108370.
- Randall, G.W., Evans, S.D. & Iragavarapu, T.K. (1997). Long-Term P and K Applications: II. Effect on Corn and Soybean Yields and Plant P and K Concentrations. Journal of Production Agriculture, 10: 572-580. [CrossRef]
- Raniro, H.R., Papera, J., José, L.U. et al. (2023). New investments in phosphorus research and training are paramount for Brazilian long-term environmental and food security. Environ Syst Decis 43, 504–508. [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A., Z.I. Awan, & J. Ryan. (2005). Diagnosing phosphorus deficiency in spring wheat by plant analysis: Proposed critical concentration ranges. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 36:609–622.
- Rayne, N.; Aula, L. (2020). Livestock Manure and the Impacts on Soil Health: A Review. Soil Syst. , 4, 64. [CrossRef]
- Reussi Calvo, N. I., Cortez, D., Crespo, C., Wyngaard, N., Terrazas, J., Paz, C., Trujillo, R., Correndo, A., & Garcia, F. O. (2025). Soil test correlation of Olsen-P for corn and soybean in a subtropical humid region. Agronomy Journal, 117, e70009. [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E., Lynch, J.P., Ryan, P.R. et al. (2011). Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant Soil 349, 121–156. [CrossRef]
- Roberts Terry L., A. Edward Johnston. (2015). Phosphorus use efficiency and management in agriculture. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, Volume 105, Part B, Pages 275-281, ISSN 0921-3449. [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J., Edenhofer, O., Gaertner, J. et al. (2020). Planet-proofing the global food system. Nat Food 1, 3–5. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez D, Andrade FH, Goudriaan J (1999). Effects of phosphorus nutrition on tiller emergence in wheat. Plant Soil 209, 283–295. [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.B.H., Koopmans, G.F., van Groenigen, K.J. et al. (2020). Towards optimal use of phosphorus fertiliser. Sci Rep 10, 17804. [CrossRef]
- Roy, E., Richards, P., Martinelli, L. et al. The phosphorus cost of agricultural intensification in the tropics. Nature Plants 2, 16043 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Rubio, G., Cabello, M. J., Gutiérrez Boem, F. H., & Munaro, E. (2008). Estimating available soil phosphorus increases after phosphorus additions in Mollisols. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 72, 1721-1727.
- Sadzawka, A., Molina, R. (2005). Capacidad Tampón de Fósforo. Método de Determinación en el Laboratorio. (in Spanish) Informaciones Agronómicas 25,12–13. IPNI. Available at https://fertilizar.org.ar/wp-content/uploads/2005/03/Sadzawka-Pdeterminacio%CC%81n.pdf.
- Sainz Rozas H.R., Eyherabide M., Larrea G., Martínez Cuesta N., Angelini H., Reussi-Calvo N., Wyngaard N. (2019). Relevamiento y determinación de propiedades químicas en suelos de aptitud agrícola de la regi´on pampeana. Actas Simposio Fertilidad. Rosario, Argentina, 8-9 mayo 2019, pp141-158.
- Saito, K.; Vandamme, E.; Tanaka, A.; Senthilkumar, K.; Dieng, I.; Gbaguidi, F.; Segda, Z.; Bassoro, I.; Lamare, D.; Gbakatchetche, H.; Abera, B.B.; Jaiteh, F.; Bam, R.K.; Johnson, J.M.; Dogbe, W.; Sekou, K.; Rabeson, R.; Kamissoko, N.; Mossi, I.M.; Tarfa, B.D.; Bakare, S.O.; Kalisa, A.; Baggie, I.; Kajiru, G.J.; Ablede, K.; Ayeva, T.; Nanfumba, D.; Wopereis, M.C.S. (2019). Yield-limiting macronutrients for rice in sub-Saharan Africa. Geoderma. ISSN 0016-7061. 338. pp 546-554.
- Sandaña P. & D. Pinochet. (2011). Ecophysiological determinants of biomass and grain yield of wheat under P deficiency. Field Crops Research 120 (2011) 311–319.
- Sanusan, S., Polthanee, A., Seripong, S., Audebert, A., & Mouret, J. C. (2009). Rates and timing of phosphorus fertilizer on growth and yield of direct-seeded rice in rain-fed conditions. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B — Soil & Plant Science, 59, 491–499. [CrossRef]
- Salvagiotti F., L. Magnano, O. Ortez, J. Enrico, M. Barraco, P. Barbagelata, A. Condori, G. Di Mauro, A. Manlla, J. Rotundo, F. O. García, M. Ferrari, V. Gudelj, e I. Ciampitti (2021). Estimating nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur uptake and requirement in soybean. European Journal of Agronomy, Volume 127, 126289. [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, T.B., Jat, M.L., Rana, D.S. et al. (2021). Crop nutrient management using Nutrient Expert improves yield, increases farmers’ income and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. Sci Rep 11, 1564. [CrossRef]
- Sattari, S.Z., van Ittersum, M.K., Bouwman, A.F., Smit, A.L., Janssen, B.H. (2014). Crop yield response to soil fertility and N, P, K inputs in different environments: testing and improving the QUEFTS model. Field Crops Res. 157, 35–46.
- Savala C. E. N., Wiredu A. N., Okoth J. O., Kyei-Boahen S. (2021). Inoculant, nitrogen and phosphorus improves photosynthesis and water-use efficiency in soybean production. The Journal of Agricultural Science 159, 349–362. [CrossRef]
- Schepers, J.S., Schlemmer, M.R. & Ferguson, R.B. (2000). Site-Specific Considerations for Managing Phosphorus. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29: 125-130. [CrossRef]
- Schlindwein, J. , Bortolon, L. , Fioreli-Pereira, E. , Oliveira Bortolon, E. & Gianello, C. (2013). Phosphorus and potassium fertilization in no till southern Brazilian soils. Agricultural Sciences, 4, 39-49. [CrossRef]
- Scholz, R. W., Wellmer, F. W., Mew, M., & Steiner, G. (2025). The dynamics of increasing mineral resources and improving resource efficiency: Prospects for mid-and long-term security of phosphorus supply. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 213, 107993.
- Schoumans, O.F., Bouraoui, F., Kabbe, C., Oenema, O., van Dijk, K.C. (2015). Phosphorus management in Europe in a changing world. Ambio 44 (Suppl. 2), S180–S192. [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.J.; Smit, A.L.; Cordell, D.; Rosemarin, A. (2011). Improved phosphorus use efficiency in agriculture: A key requirement for its sustainable use. Chemosphere , 84, 822–831.
- Schut, A. G. T., & Giller, K. E. (2020). Soil-based, field-specific fertilizer recommendations are a pipe-dream. Geoderma, 380, Article 114680. [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Almutairi, K.F.; Alotaibi, M.; Shami, A.; Alhammad, B.A.; Battaglia, M.L. (2021). Nano- Fertilization as an Emerging Fertilization Technique: Why Can Modern Agriculture Benefit from Its Use? Plants, 10, 2. [CrossRef]
- Selim, M. M. (2020). Introduction to the integrated nutrient management strategies and their contribution to yield and soil properties. International Journal of Agronomy, (1), 2821678.
- Selles, F., Campbell, C. A., Zentner, R. P., Curtin, D., James, D. C. & Basnyat, P. (2011). Phosphorus use efficiency and long-term trends in soil available phosphorus in wheat production systems with and without nitrogen fertilizer. Can. J. Soil Sci. 91:39-52.
- Setiyono, T. D., Walters, D. T., Cassman, K. G., Witt, C., & Dobermann, A. (2010). Estimating maize nutrient uptake requirements. Field Crops Research, 118, 158-168.
- Shah A, Nazari M, Antar M, Msimbira LA, Naamala J, Lyu D, Rabileh M, Zajonc J & Smith DL. (2021). PGPR in Agriculture: A Sustainable Approach to Increasing Climate Change Resilience. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5:667546. [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Shi, S.; Obaid, H.; Dong, X.; He, X. (2024). Differential Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilization Rates and Fertilizer Placement Methods on P Accumulations in Maize. Plants, 13, 1778. [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N., Bergström, L., Aronsson, H. et al. (2015). Future agriculture with minimized phosphorus losses to waters: Research needs and direction. AMBIO 44 (Suppl 2), 163–179. [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N., Daniel, T., Gibson, G., Bundy, L., Cabrera, M., Sims, T., Stevens, R., Lemunyon, J., Kleinman, P.J., Parry, R. (2006). Best management practices to minimize agricultural phosphorus impacts on water quality. Agricultural Research Service Publication. 52 p.
- Sharpley A., P. Kleinman & J. Weld. (2004). Assessment of best management practices to minimise the runoff of manure-borne phosphorus in the United States, New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 47:4, 461-477. [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N., J. L. Weld, D.B. Beegle, P.J.A. Kleinman, W.J. Gburek, P.A. Moore, Jr., & G. Mullins. (2003). Development of Phosphorus Indices for nutrient management planning strategies in the United States. J. Soil Water Conserv, 58:137–151.
- Shen J., L. Yuan, J. Zhang, H. Li, Z. Bai, X. Chen, W. Zhang, F. Zhang. (2011). Phosphorus Dynamics: From Soil to Plant, Plant Physiology, Volume 156, Issue 3, Pages 997–1005. [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X., Ma, L. & Wendroth, O. (2018). Unified Weak and Strong Soil Tests to Estimate Intrinsic Plant Available Phosphorus Pools. Agronomy Journal, 110: 859 -867. [CrossRef]
- Sims J.T. (2000). Soil fertility evaluation. En M.E. Sumner (ed.). Handbook of Soil Science. CRC Press. Boca Raton, FL. pp. D113-D153.
- Singh, G.; Kaur, G.; Williard, K.; Schoonover, J.; Nelson, K.A. (2020). Managing Phosphorus Loss from Agroecosystems of the Midwestern United States: A Review. Agronomy, 10, 561. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K., Reddy, V.R. & Sicher, R.C. (2018). Seasonal critical concentration and relationships of leaf phosphorus and potassium status with biomass and yield traits of soybean. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci., 181: 575-585. [CrossRef]
- Slaton, N.A., Wilson, C.E., Norman, R.J., Ntamatungiro, S. & Frizzell, D.L. (2002), Rice Response to Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Rate and Timing on Alkaline Soils in Arkansas. Agronomy Journal, 94: 1393-1399. [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.L. M. Blom-Zandstra, A. van der Werf, & Bindraban, P.S. (2013). Plant strategies and cultural practices to improve the uptake of indigenous soil P and the efficiency of fertilization. VFRC Report 2013/14. Washington DC, USA. 34 p. https://hub.ifdc.org/items/28097750-567a-4035-9ae9-5f073eed9cd5.
- Smith, Douglas R., et al. (2015). Phosphorus Losses from Monitored Fields with Conservation Practices in the Lake Erie Basin, USA.” Ambio, vol. 44, pp. S319–31. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/24670883. Accessed 5 Nov. 2024.
- Soltanpour P.W.& A.P. Schwab. (1977). A new soil test for simultaneous extraction of macro-micronutrients in alkaline soils. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 8:195-207.
- Sousa, D.M.G.; Lobato, E. & Rein, T.A. (2002). Adubação com fósforo. In: Sousa, D.M.G. & Lobato, E., eds. Cerrado: correção do solo e adubação. Planaltina, Embrapa Cerrados,. p.147-168.
- Speirs, S. D., Scott, B. J., Moody, P. W., & Mason, S. D. (2013). Soil phosphorus tests II: A comparison of soil test–crop response relationships for different soil tests and wheat. Crop and Pasture Science, 64, 469-479.
- Stamm, C., Binder, C.R., Frossard, E. et al. (2022). Towards circular phosphorus: The need of inter- and transdisciplinary research to close the broken cycle. Ambio 51, 611–622. [CrossRef]
- Stammer, A.J. & Mallarino, A.P. (2018). Plant Tissue Analysis to Assess Phosphorus and Potassium Nutritional Status of Corn and Soybean. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 82: 260-270. [CrossRef]
- Steeneken, P.G., Kaiser, E., Verbiest, G.J. et al. (2023). Sensors in agriculture: towards an Internet of Plants. Nat Rev Methods Primers 3, 60. [CrossRef]
- Stewart W., D. Dibb, A. Johnston & T. Smyth. (2005a). The contribution of commercial fertilizer nutrients to food production. Agronomy Journal 97:1-6.
- Stewart, W.M., Hammond, L.L. & Van Kauwenbergh, S.J. (2005b). Phosphorus as a Natural Resource. In Phosphorus: Agriculture and the Environment (eds J. Thomas Sims, A.N. Sharpley & G.M. Pierzynski). [CrossRef]
- Steinfurth, K., Börjesson, G., Denoroy, P., Eichler-Löbermann, B., Gans, W., Heyn, J., Hirte, J., Jansen, F., Koch, D., Merbach, I., Mollier, A., Morel, C., Panten, K., Peiter, E., Poulton, P. R., Reitz, T., Rubæk, G. H., Spiegel, H., van Laak, M., … Buczko, U. (2024). Decrease in soil test phosphorus levels under omitted phosphorus fertilizer application. Soil Use and Management, 40, e13088. [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.I. (2015). The composition, leaching, and sorption behavior of some alternative sources of phosphorus for soils. AMBIO 44 (Suppl 2), 207–216. [CrossRef]
- Sucunza, F.A., Gutiérrez Boem, F.H., García, F.O., Boxler, M. & Rubio, G. (2018). Long-term phosphorus fertilization of wheat, soybean and maize on Mollisols: Soil test trends, critical levels and balances. European Journal of Agronomy, 96, 87-95.
- Suh, S., Yee, S. (2011). Phosphorus use-efficiency of agriculture and food system in the US. Chemosphere 84, 806e813. [CrossRef]
- Syers, J.K., Johnston, A.E., Curtin, D. (2008). Efficiency of Soil and Fertilizer Phosphorus. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, FAO Fertilizer and Plant Nutrition Bulletin 18, 107 pp.
- Talboys PJ, Healey JR, Withers PJA, Roose T, Edwards AC, Pavinato PS & Jones DL. (2020). Combining Seed Dressing and Foliar Applications of Phosphorus Fertilizer Can Give Similar Crop Growth and Yield Benefits to Soil Applications Together With Greater Recovery Rates. Front. Agron. 2:605655. [CrossRef]
- Talboys, P.J.; Heppell, J.; Roose, T.; Healey, J.R.; Jones, D.L.; Withers, P.J.A. (2016). Struvite: A Slow-Release Fertiliser for Sustainable Phosphorus Management? Plant Soil, 401, 109–123.
- Tang, X., Ma, Y., Hao, X. et al. (2009). Determining critical values of soil Olsen-P for maize and winter wheat from long-term experiments in China. Plant Soil 323, 143–151. [CrossRef]
- Thien, S.J. & Myers, R. (1992). Determination of Bioavailable Phosphorus in Soil. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 56: 814-818. [CrossRef]
- Tiecher, T., Fontoura, S. M., Ambrosini, V. G., Araújo, E. A., Alves, L. A., Bayer, C., & Gatiboni, L. C. (2023). Soil phosphorus forms and fertilizer use efficiency are affected by tillage and soil acidity management. Geoderma, 435, 116495.
- Tonini, D., Saveyn, H.G.M. & Huygens, D. (2019). Environmental and health co-benefits for advanced phosphorus recovery. Nat Sustain 2, 1051–1061. [CrossRef]
- Torri SI, Correa RS, Renella G. (2017). Biosolid application to agricultural land—a contribution to global phosphorus recycle: a review. Pedosphere;27,1–16.
- Valkama, E., Uusitalo, R., Ylivainio, K., Virkajärvi, P., & Turtola, E. (2009). Phosphorus fertilization: A meta-analysis of 80 years of research in Finland. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 130(3-4), 75-85.
- Vance, C.P., C. Uhde-Stone, & D.L. Allan. (2003). Phosphorus acquisition and use: Critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol. 157:423–448.
- Vanlauwe, B. , Amede, T., Bationo, A., Bindraban, P., Breman, H., Cardinae, R., Couede, A., Chivenge, P., Corbeels, M., Dobermann, A., Falconnier, G., Fatunbi, W., Giller, K., Harawa, R., Kamau, M., Merckx, R., Palm, C., Powlson, D. S., Rusinamhodzi, L., Six, J., Singh, U., Stewart, Z., Ittersum, M. V., Witt, C., Zingore, S. & Groot, R. (2023). Fertilizer and Soil Health in Africa The Role of Fertilizer in Building Soil Health to Sustain Farming and Address Climate Change. in: Fertilizer and Soil Health in Africa: The role of fertilizer in building soil health to sustain farming and address climate change International Fertilizer Development Center - IFDC.
- van de Wiel, C.C.M., van der Linden, C.G. & Scholten, O.E. (2016). Improving phosphorus use efficiency in agriculture: opportunities for breeding. Euphytica 207, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Veneklaas, E.J., Lambers, H., Bragg, J., Finnegan, P.M., Lovelock, C.E., Plaxton, W.C., Price, C.A., Scheible, W.-R., Shane, M.W., White, P.J. & Raven, J.A. (2012). Opportunities for improving phosphorus-use efficiency in crop plants. New Phytologist, 195: 306-320. [CrossRef]
- Vera-Morales, M.; López Medina, S.E.; Naranjo-Morán, J.; Quevedo, A.; Ratti, M.F. (2023). Nematophagous Fungi: A Review of Their Phosphorus Solubilization Potential. Microorganisms, 11, 137. [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R. C. B., Fontoura, S. M. V., Bayer, C., Moraes, R. P. de, & Carniel, E. (2015). Adubação Fosfatada para Alta Produtividade de Soja, Milho e Cereais de Inverno Cultivados em Rotação em Latossolos em Plantio Direto no Centro-Sul do Paraná. Revista Brasileira De Ciência Do Solo, 39, 794–808. [CrossRef]
- Vilela de Resende, A., Furtini Neto, A. E., Carvalho Alves, V. M., Muniz, J. A., Curi, N., Faquin, V., Ioshiteru Kimpara, D., Lopes Santos, J. Z. & Carneiro L. F. (2006). Fontes e modos de aplicação de fósforo para o milho em solo cultivado da região do Cerrado. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo.; 30,453-466. [CrossRef]
- Walker F. (2023). Best management practices for phosphorus in the environment. Agricultural Extension Service. University of Tennesse PB1645. https://utia.tennessee.edu/publications/wp-ontent/uploads/sites/269/2023/10/PB1645.pdf.
- Wall D. P. & N. T. McDonald. (2015). Phosphorus fertilisation: Achieving agronomic and environmental goals. Proceedings 779, International Fertiliser Society.
- Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Hou, P.; Hao, T.; Xue, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, T.; Lobanov, S.; Yang, L. (2023). Struvite as P Fertilizer on Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Soil Nutrient Status in the Rice–Wheat Rotation System: A Two-Year Field Observation. Agronomy, 13, 2948. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z.Z., Zhang T.Q., Tan C.S., Qi Z.M. (2020). Modeling of phosphorus loss from field to watershed: A review. Journal of Environmental Quality; 49: 1203–1224. [CrossRef]
- Waraich, E. A., Ahmad, R., Ashraf, M. Y., Saifullah, & Ahmad, M. (2011). Improving agricultural water use efficiency by nutrient management in crop plants. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B — Soil & Plant Science, 61, 291–304. [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D.M., Wong, M.T.F. (2011). Scope to improve phosphorus (P) management and balance efficiency of crop and pasture soils with contrasting P status and buffering indices. Plant Soil 349, 37–54. [CrossRef]
- Weeks Jr, J. J., & Hettiarachchi, G. M. (2019). A review of the latest in phosphorus fertilizer technology: possibilities and pragmatism. Journal of Environmental Quality, 48, 1300-1313.
- White P. J. & P. H. Brown. (2010). Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Annals of Botany 105: 1073–1080. available online at www.aob.oxfordjournals.org. [CrossRef]
- White P. J. & J. P. Hammond. (2008). Phosphorus nutrition of terrestrial plants. In P.J. White, J.P. Hammond (eds.) The Ecophysiology of Plant-Phosphorus Interactions, 51, Springer Science + Business Media B.V. pp. 51-81.
- Withers, P.J.A., Rodrigues, M., Soltangheisi, A. et al. (2018). Transitions to sustainable management of phosphorus in Brazilian agriculture. Sci Rep 8, 2537. [CrossRef]
- Withers P. J. A., R. Sylvester-Bradley, D. L. Jones, J. R. Healey, & P. J. Talboys. (2014). Feed the Crop Not the Soil: Rethinking Phosphorus Management in the Food Chain. Environmental Science & Technology 48 (12), 6523-6530. [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.A., Vadas, P.A., Uusitalo, R., Forber, K.J., Hart, M., Foy, R.H., Delgado, A., Dougherty, W., Lilja, H., Burkitt, L.L., Rubæk, G.H., Pote, D., Barlow, K., Rothwell, S. & Owens, P.R. (2019). A Global Perspective on Integrated Strategies to Manage Soil Phosphorus Status for Eutrophication Control without Limiting Land Productivity. Journal of Environmental Quality, 48: 1234-1246. [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.A., van Dijk, K.C., Neset, TS.S. et al. (2015). Stewardship to tackle global phosphorus inefficiency: The case of Europe. AMBIO 44 (Suppl 2), 193–206. [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, C., Shapiro, C., Shaver, T. & Mainz, M. (2018). High Soil Test Phosphorus Effect on Corn Yield. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 82: 1160-1167. [CrossRef]
- Xu, S., Nakayama, Y., Rothman, M. G., & Margenot, A. J. (2024). Depth-dependent soil phosphorus alteration is independent of 145-year phosphorus balances. European Journal of Soil Science, 75, e70006. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.P., He, P., Pampolino, M.F., Chuan, L.M., Johnston, A.M., Qiu, S.J., Zhao, S.C.,Zhou, W. (2013). Nutrient requirements for maize in China based on QUEFTS analysis. Field Crops Res. 150, 115–125.
- Xu, X., Xie, J., Hou, Y., He, P., Pampolino, M. F., Zhao, S., ... & Zhou, W. (2015). Estimating nutrient uptake requirements for rice in China. Field Crops Research, 180, 37-45.
- Zapata F. & R.N. Roy (ed.). (2004). Use of Phosphate Rocks for Sustainable Agriculture. Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Nuclear Techniques in Food and Agriculture, Vienna, Austria. Land and Water Development Division, FAO, Rome, Italy.
- Zhang H, Antonangelo J, Grove J, Osmond D, Slaton N A, Alford S, Florence R, Huluka G, Hardy D H, Lessl J, Maguire R, Mylavarapu R, Oldham J L, Pena-Yewtukhiw E M, Provin T, Sonon L, Sotomayor D, Wang J. (2021). Variation in soil-test-based phosphorus and potassium rate recommendations across the southern USA. Soil Science Society of America Journal.;85:975–988. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J., He, P., Xu, X.P., Ding, W.C., Ullah, S., Wang, Y.L., Jia, L.L., Cui, R.Z., Wang, H.T. & Zhou, W. (2018). Nutrient Expert Improves Nitrogen Efficiency and Environmental Benefits for Winter Wheat in China. Agronomy Journal, 110: 696-706. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Su, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, L. (2022). Effect of Different Types of Phosphate Fertilizer on Phosphorus Absorption and Desorption in Acidic Red Soil of Southwest China. Sustainability, 14, 9973. [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, N., Bélanger, G., Cambouris, A.N., Tremblay, N., Nolin, M.C. & Claessens, A. (2007). Relationship between P and N Concentrations in Corn. Agronomy Journal, 99: 833-841. [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, N., Bélanger, G., Cambouris, A.N., Tremblay, N., Nolin, M.C. & Claessens, A. (2008). Relationship between Phosphorus and Nitrogen Concentrations in Spring Wheat. Agronomy Journal, 100: 80-86. [CrossRef]
- Ziadi N., J. K. Whalen, A. J. Messiga, C. Morel. (2013). Assessment and Modeling of Soil Available Phosphorus in Sustainable Cropping Systems. In Donald L. Sparks (ed.), Advances in Agronomy, Academic Press, Volume 122, 2013, Pages 85-126, ISSN 0065-2113, ISBN 9780124171879. [CrossRef]
- Zou, T. Zou, T., Zhang, X. & Davidson, E.A. (2022). Global trends of cropland phosphorus use and sustainability challenges. Nature 611, 81–87. [CrossRef]
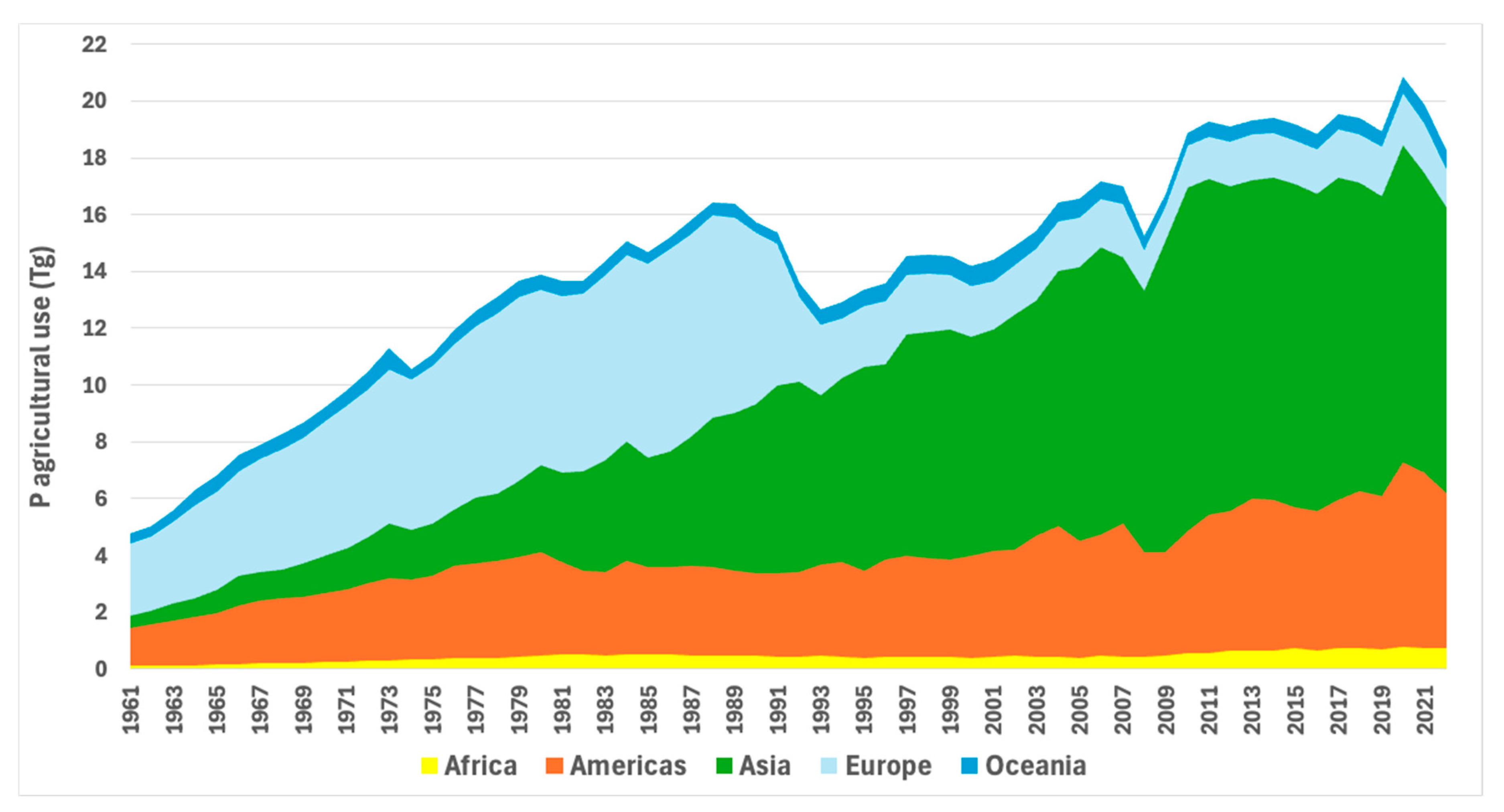
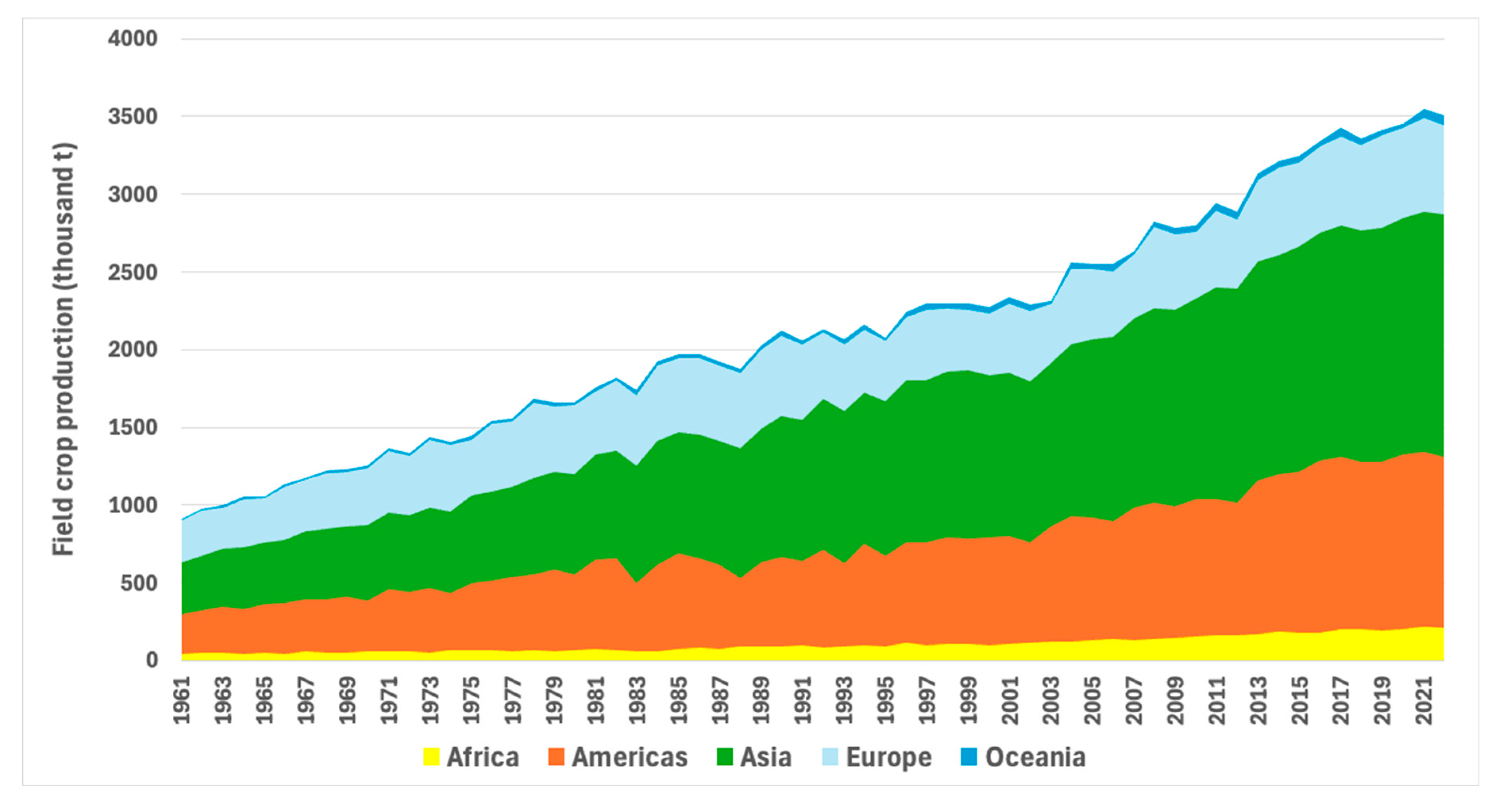
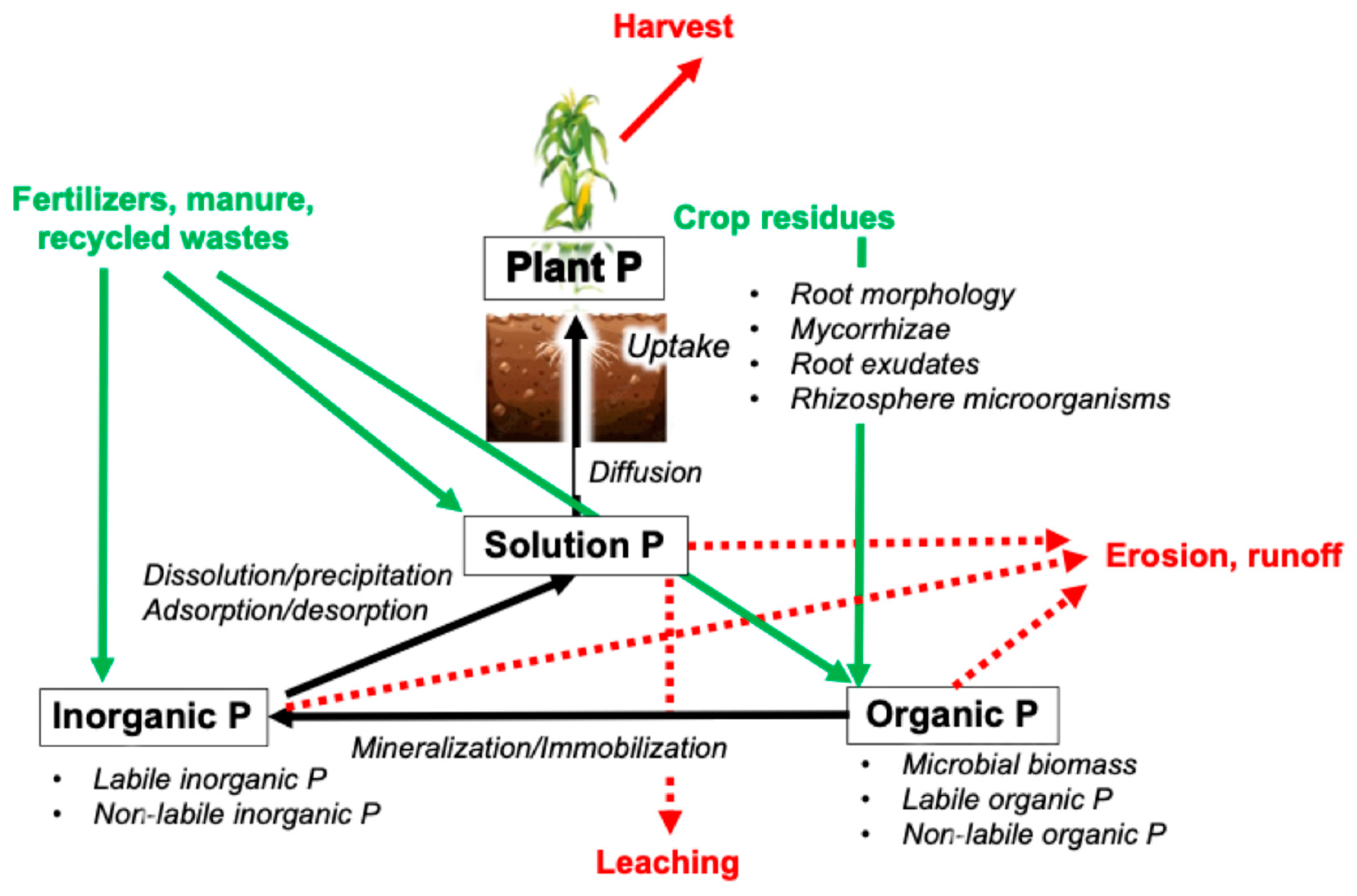
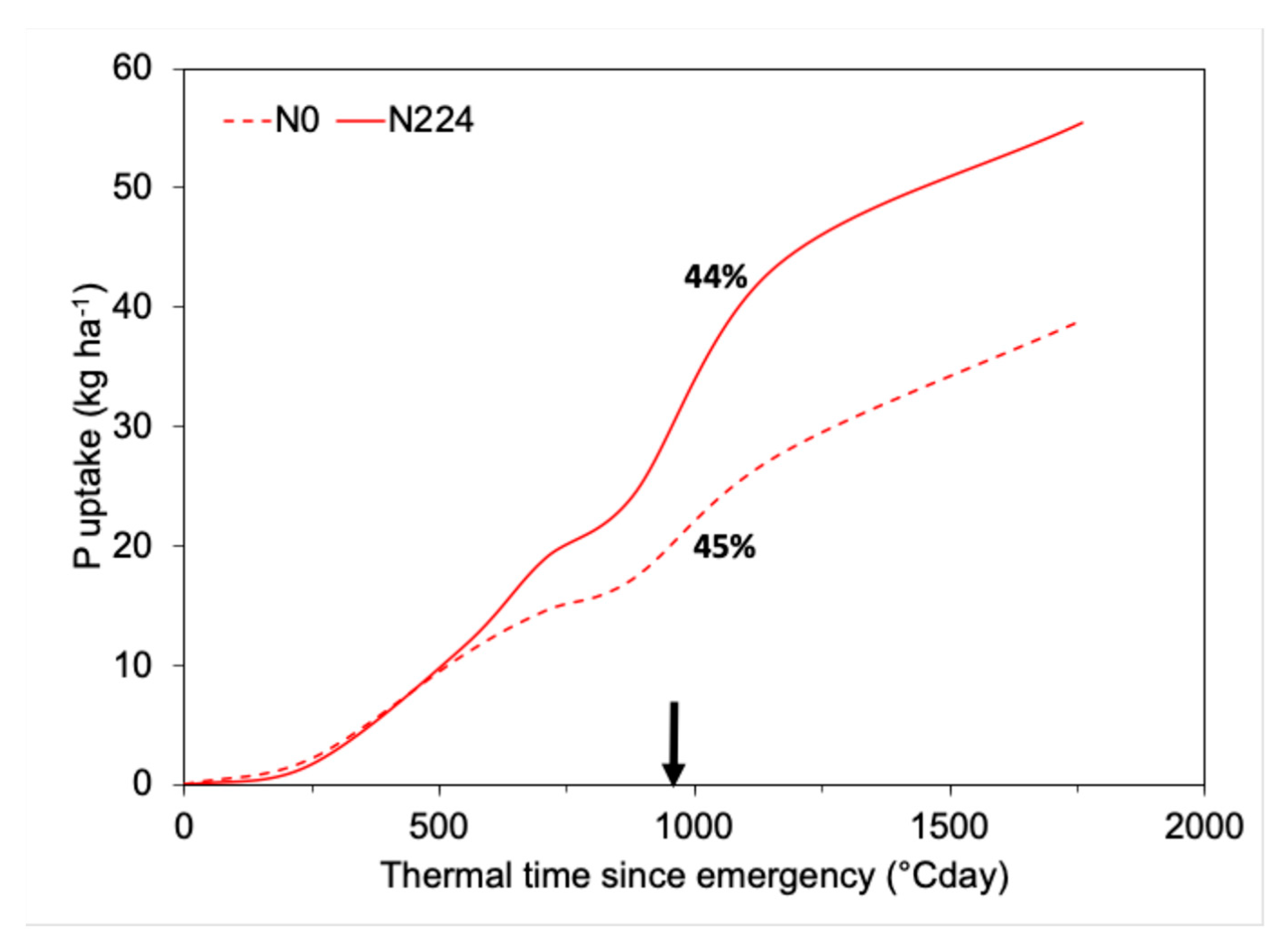
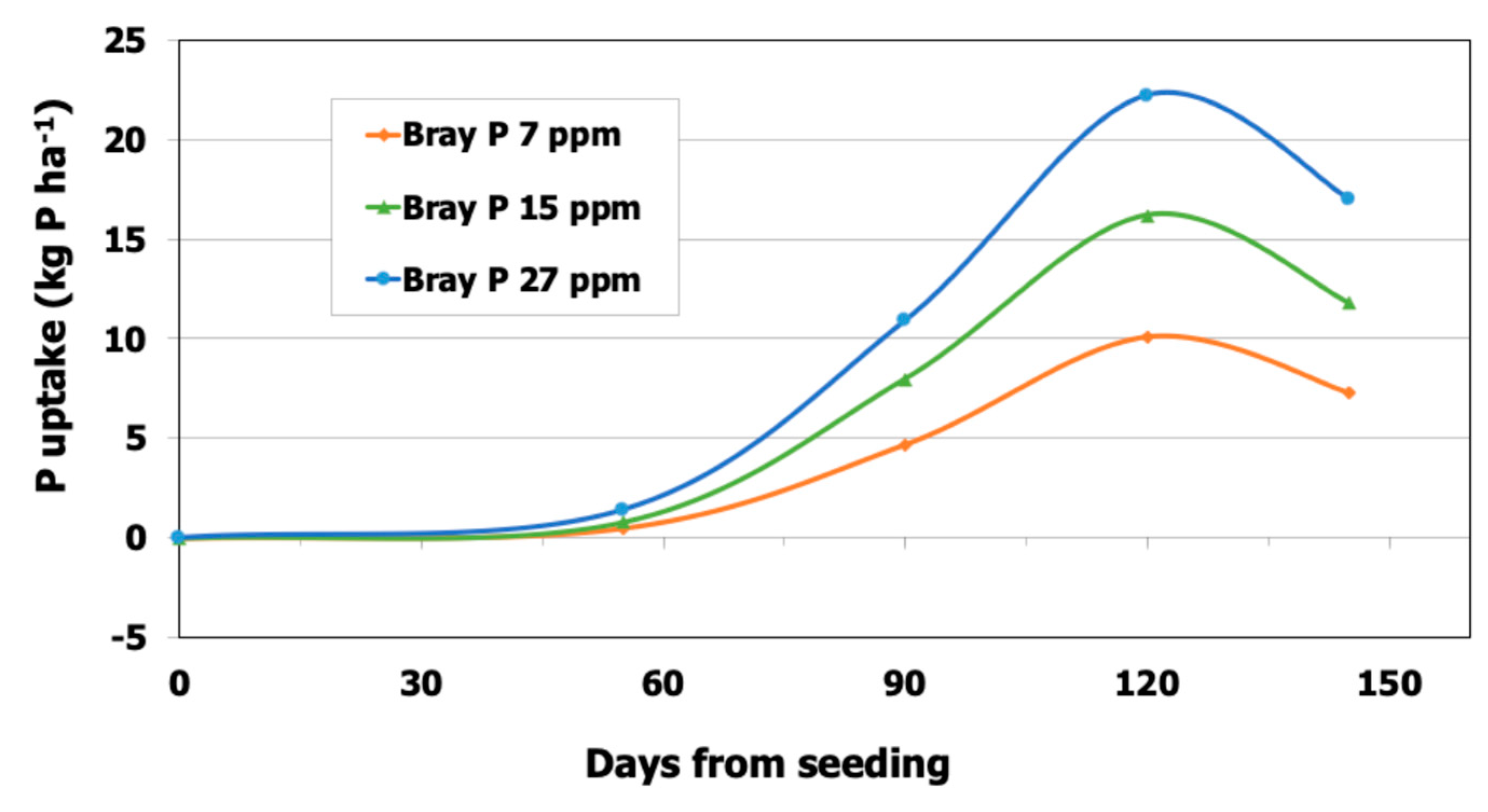
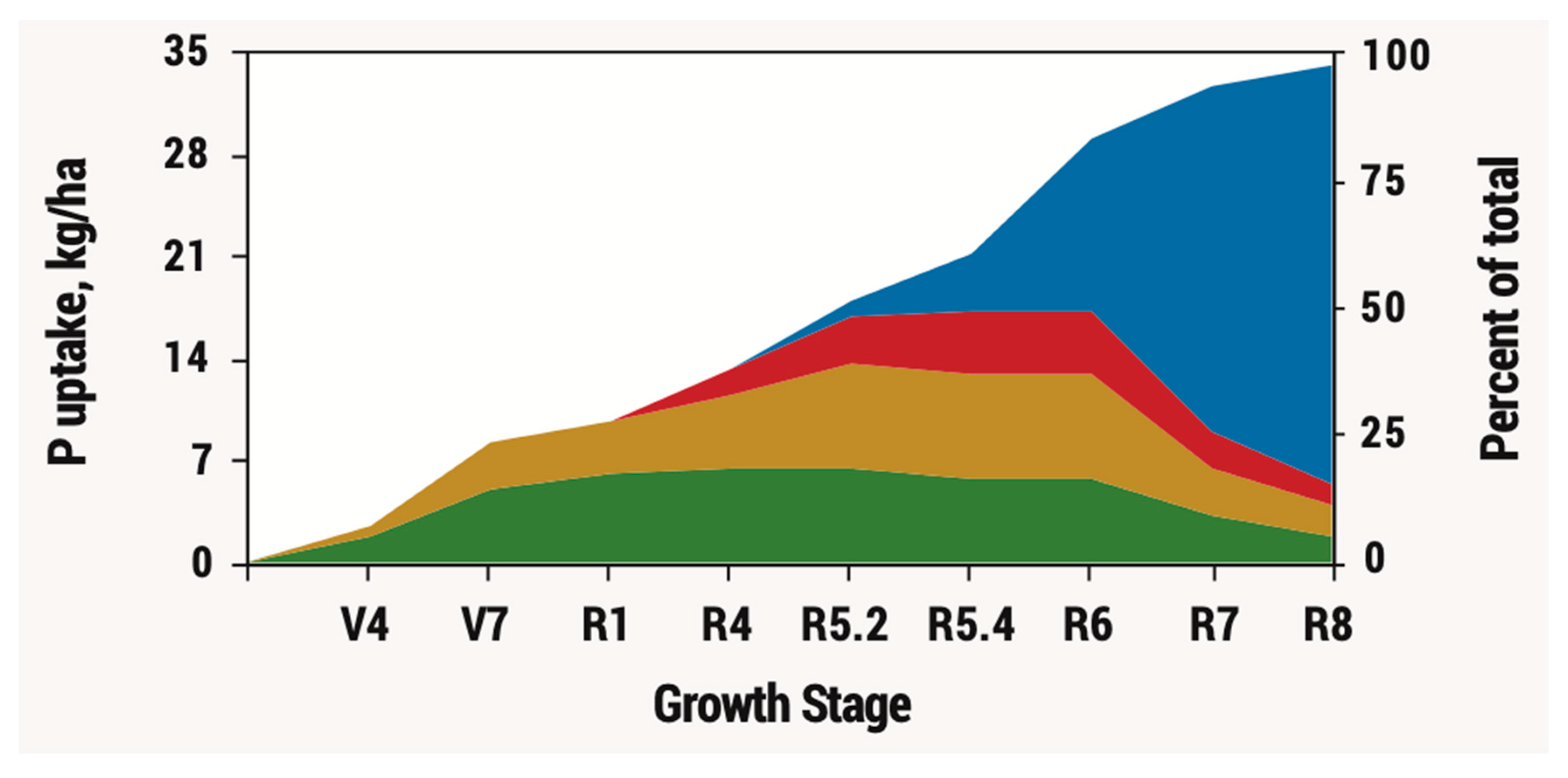
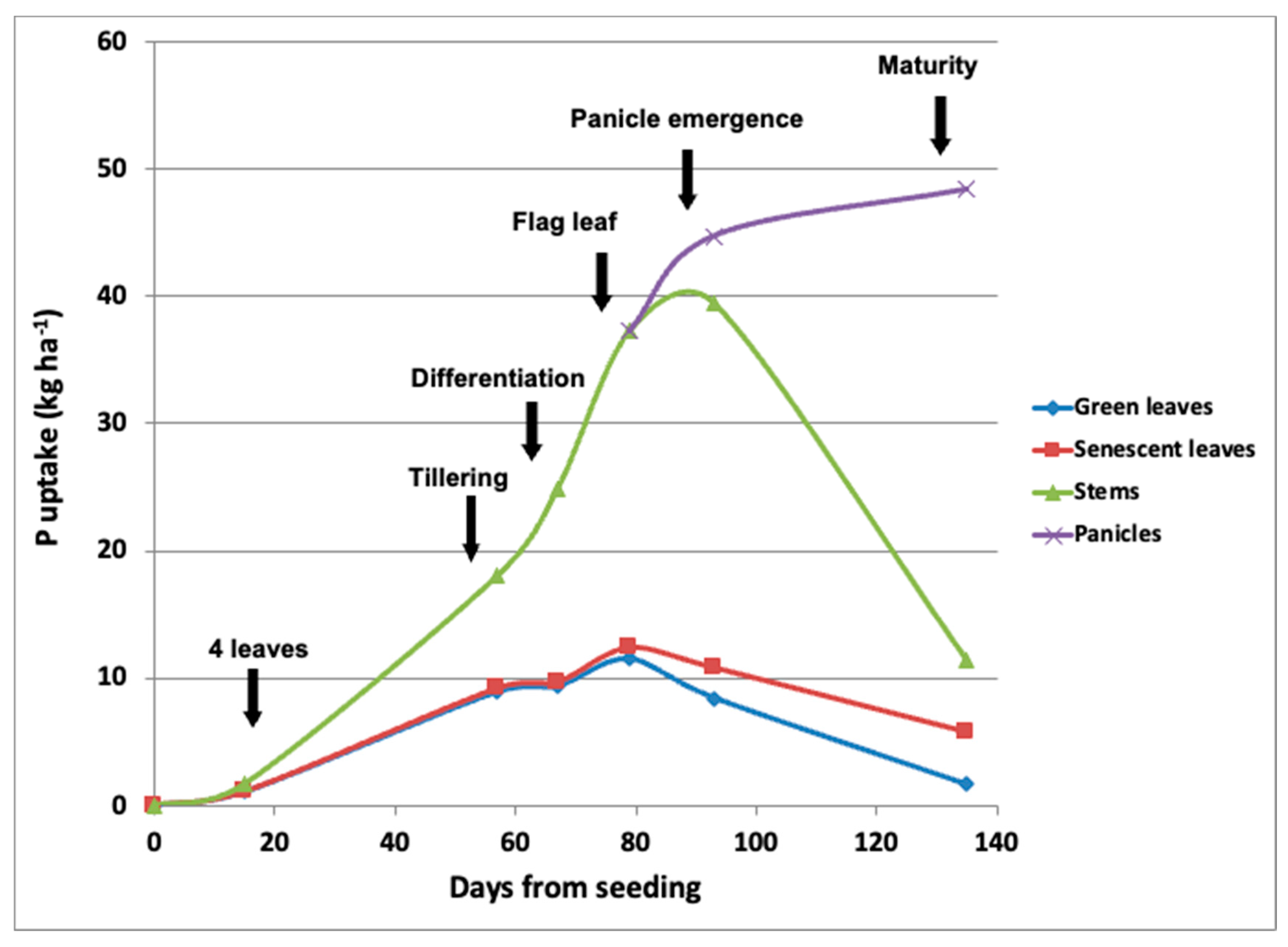
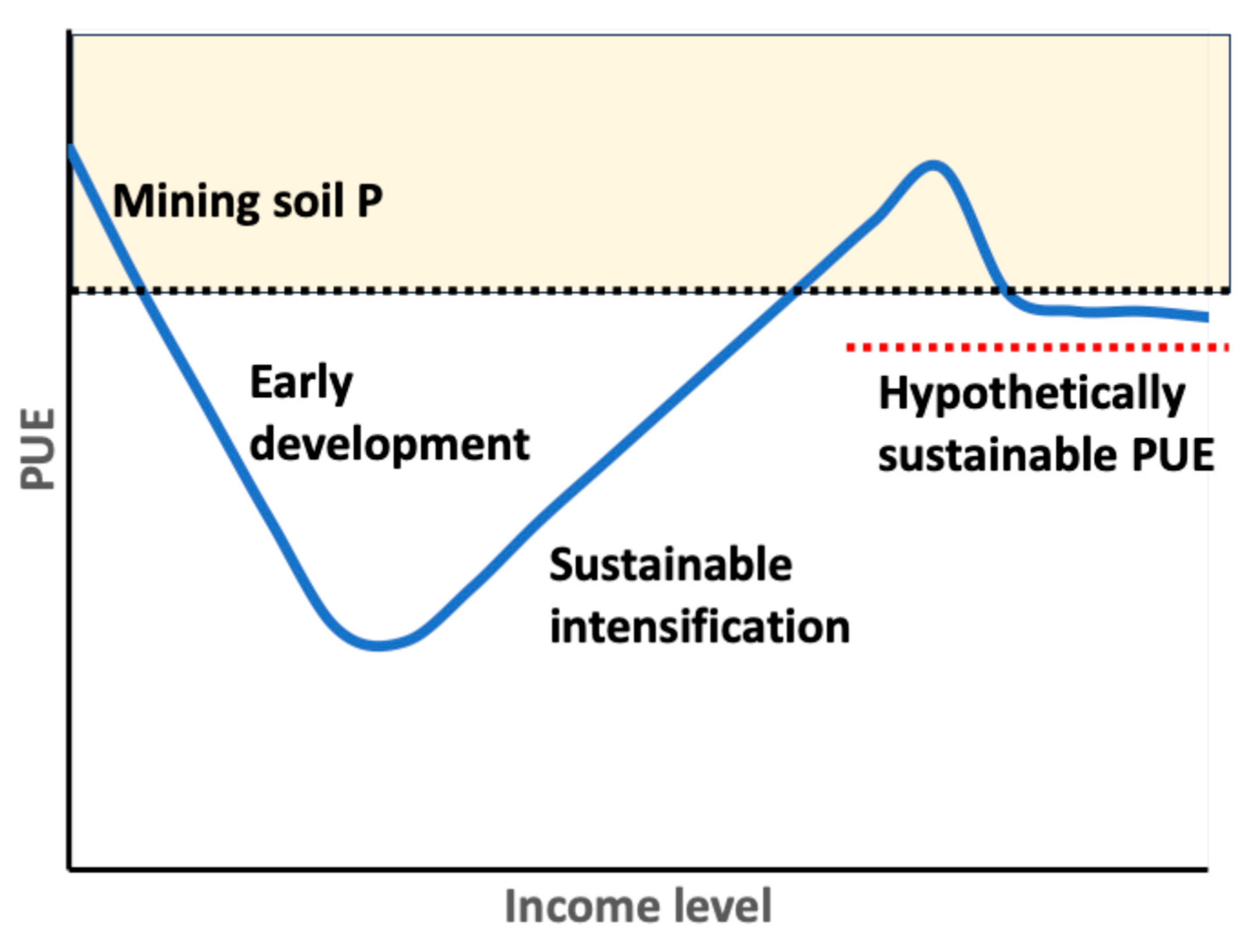
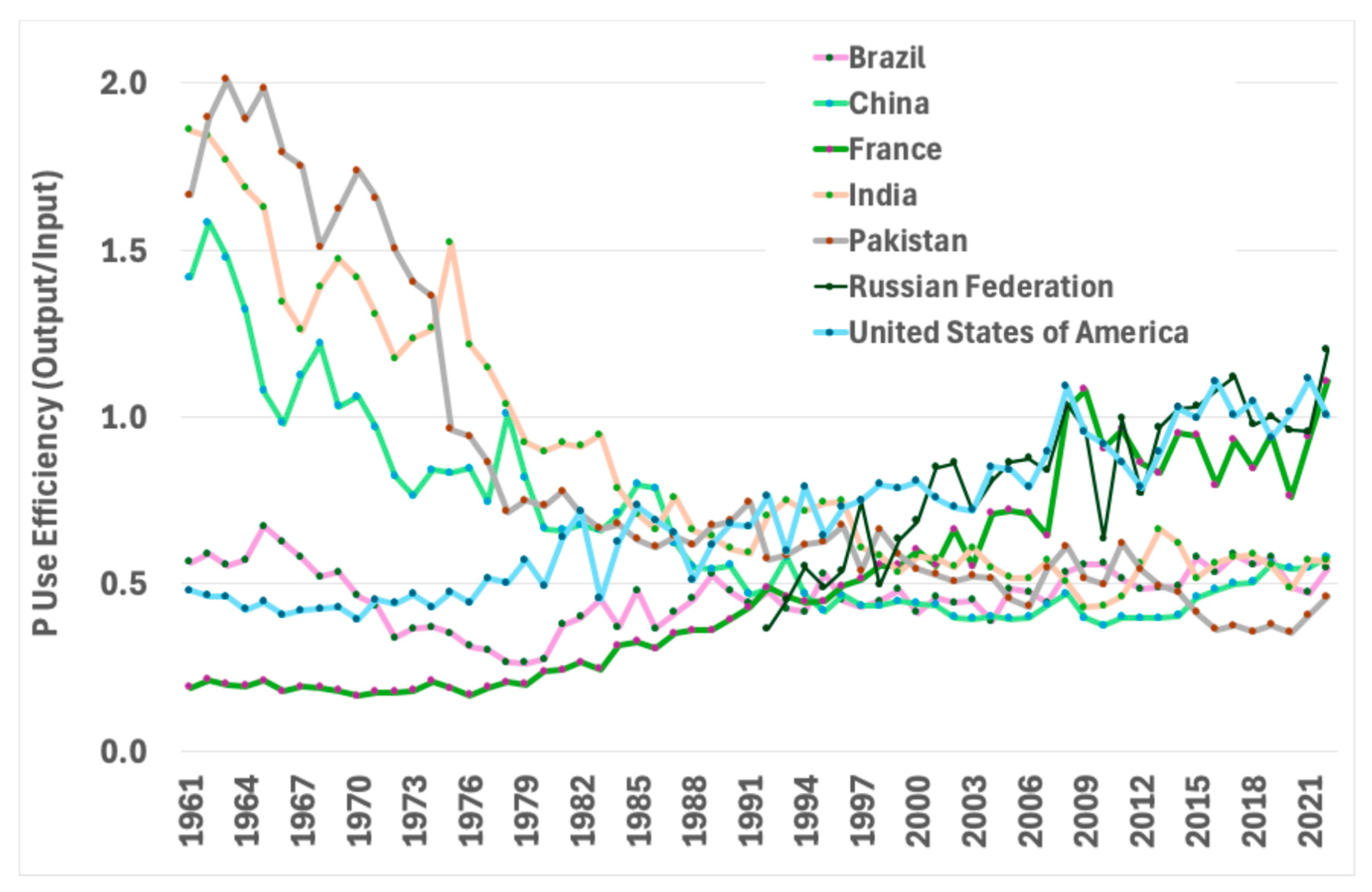
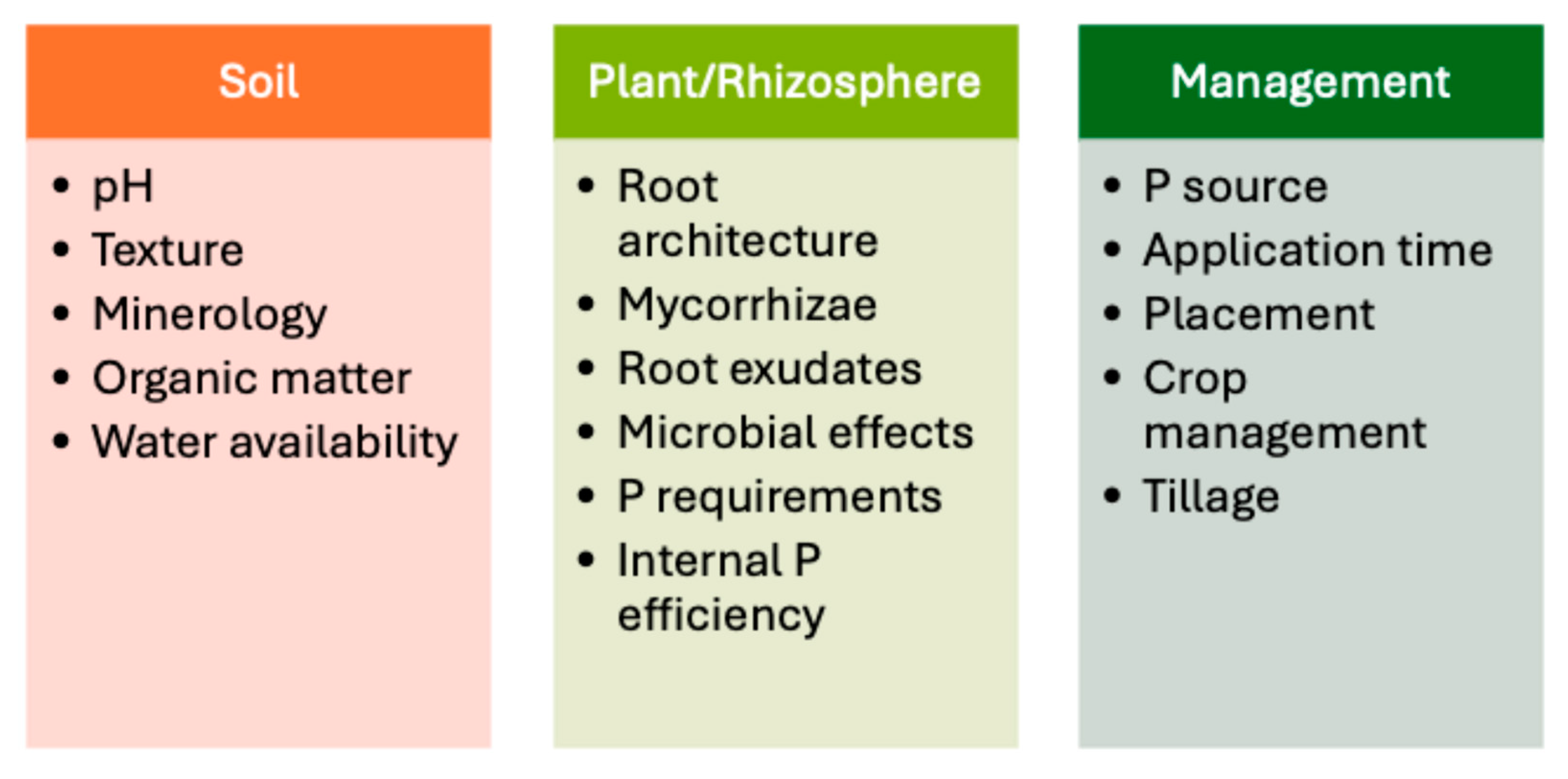
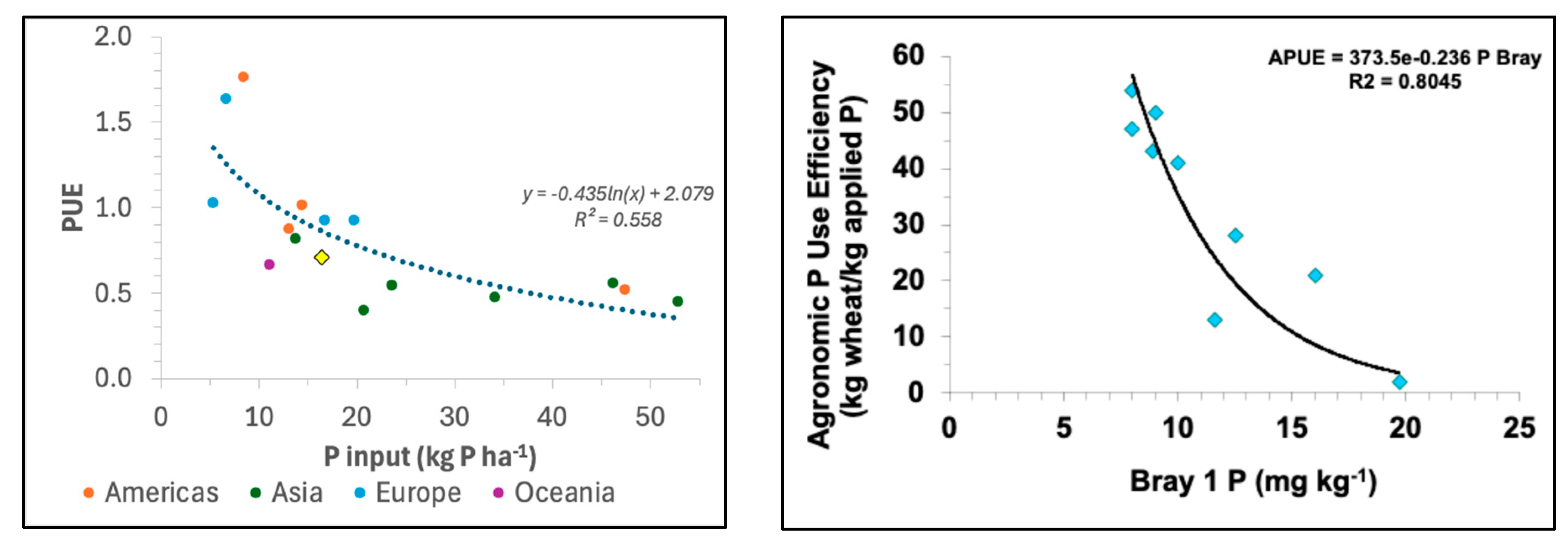
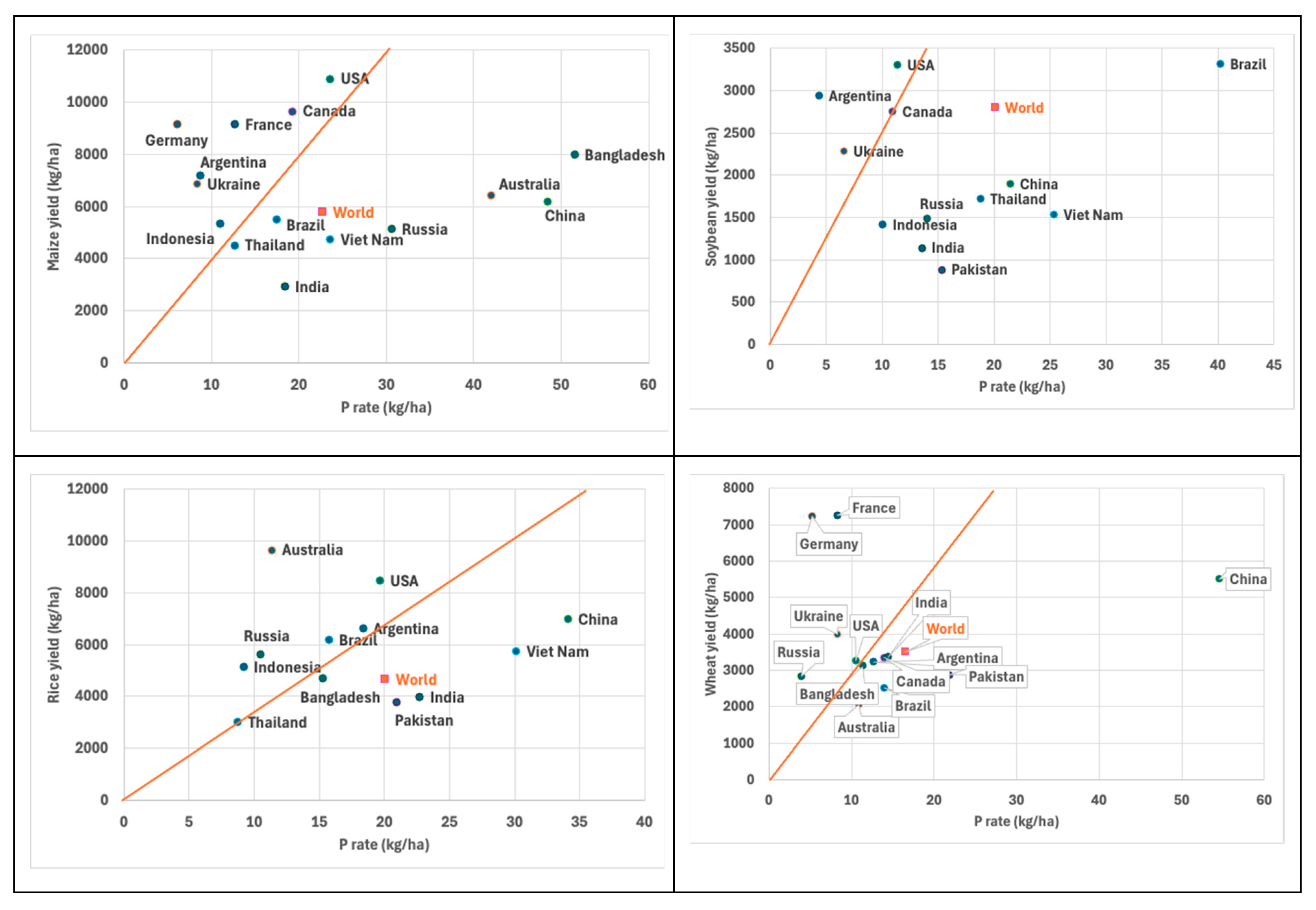
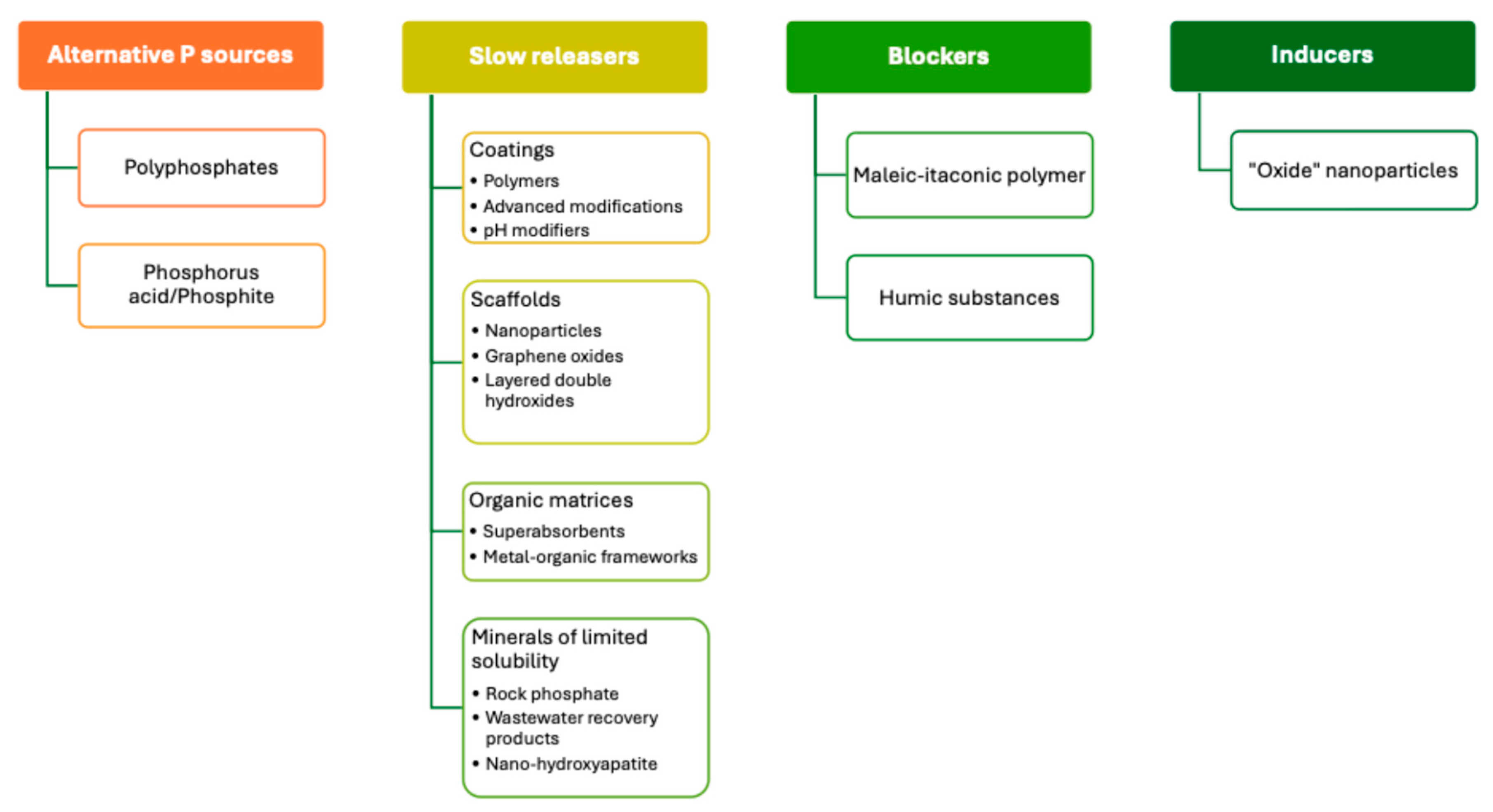
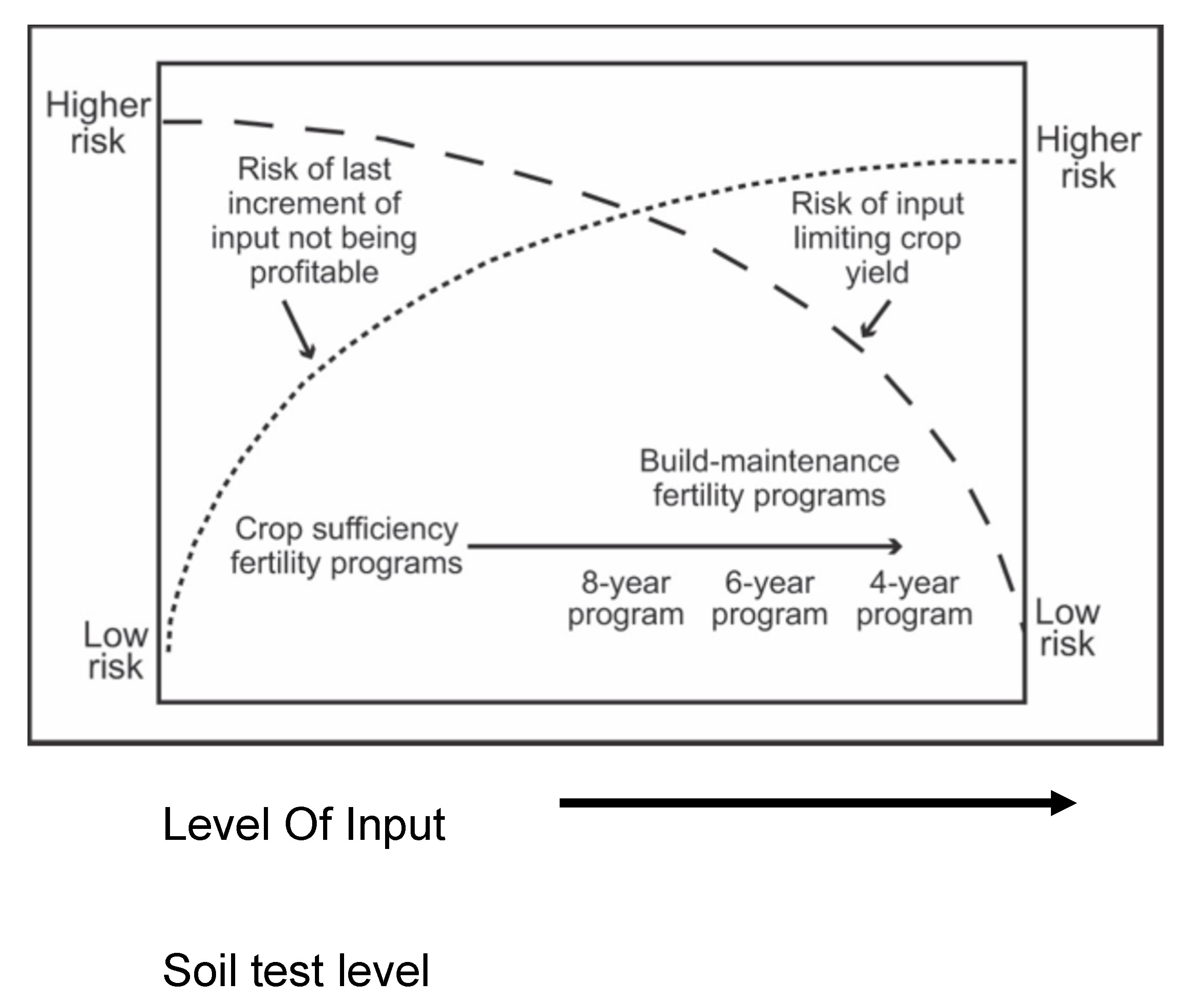
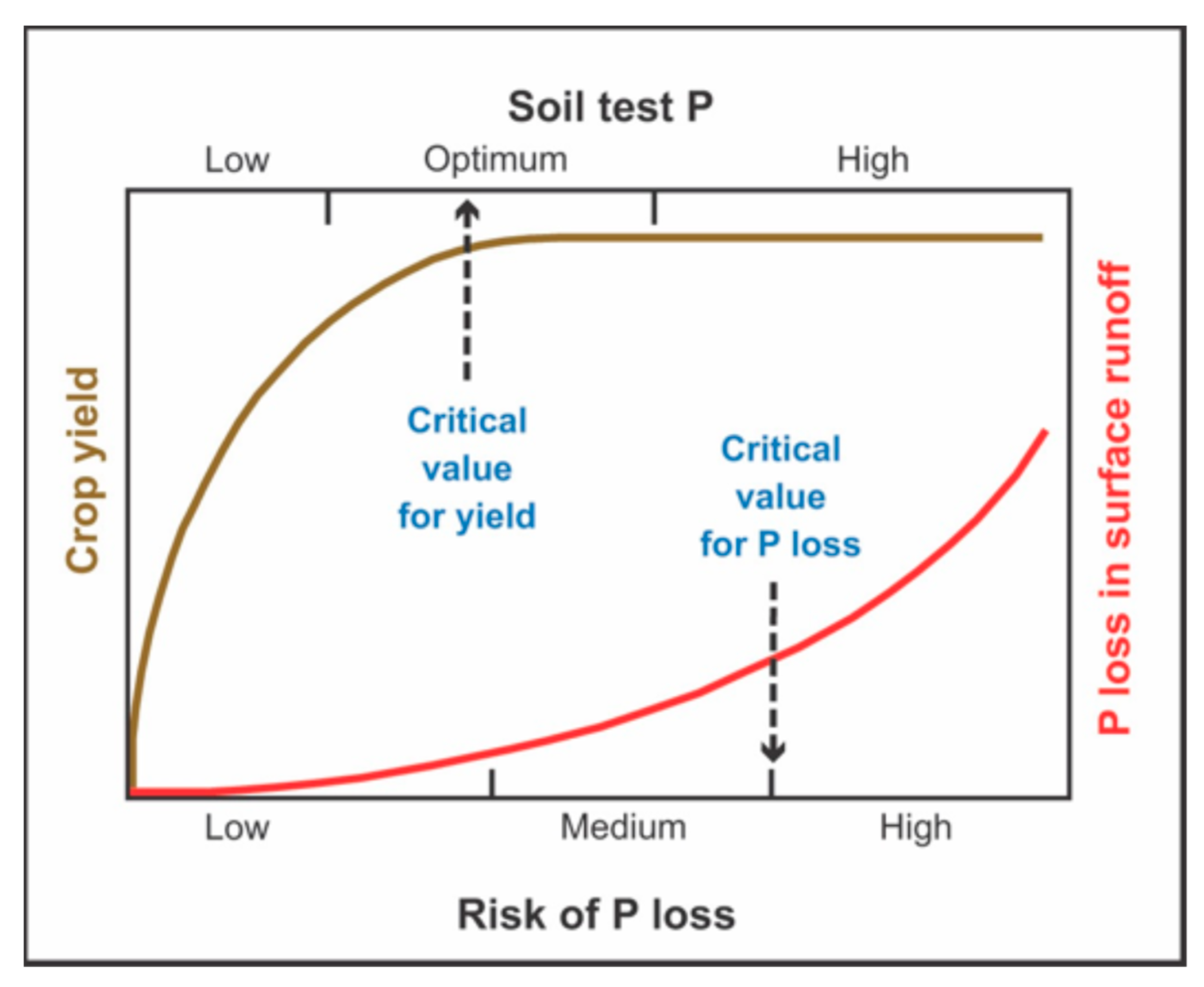
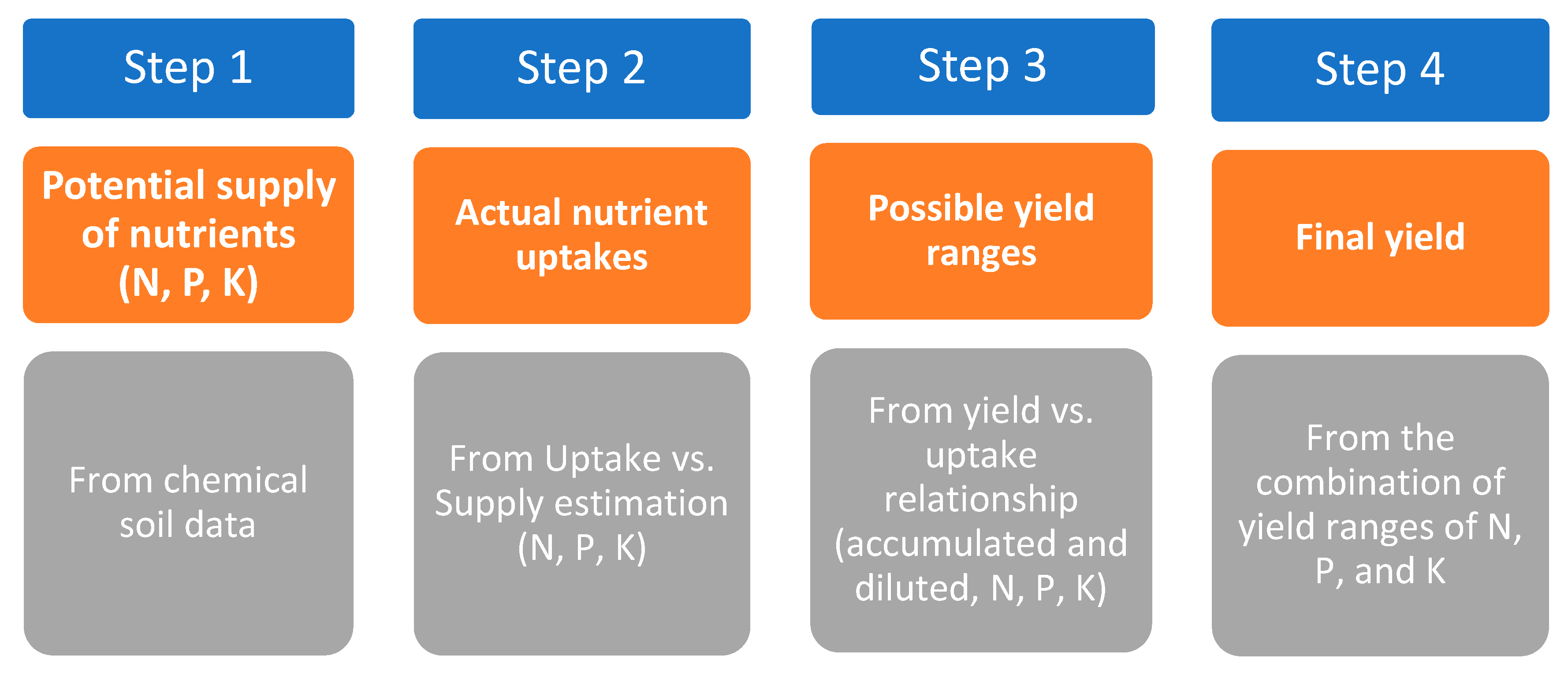
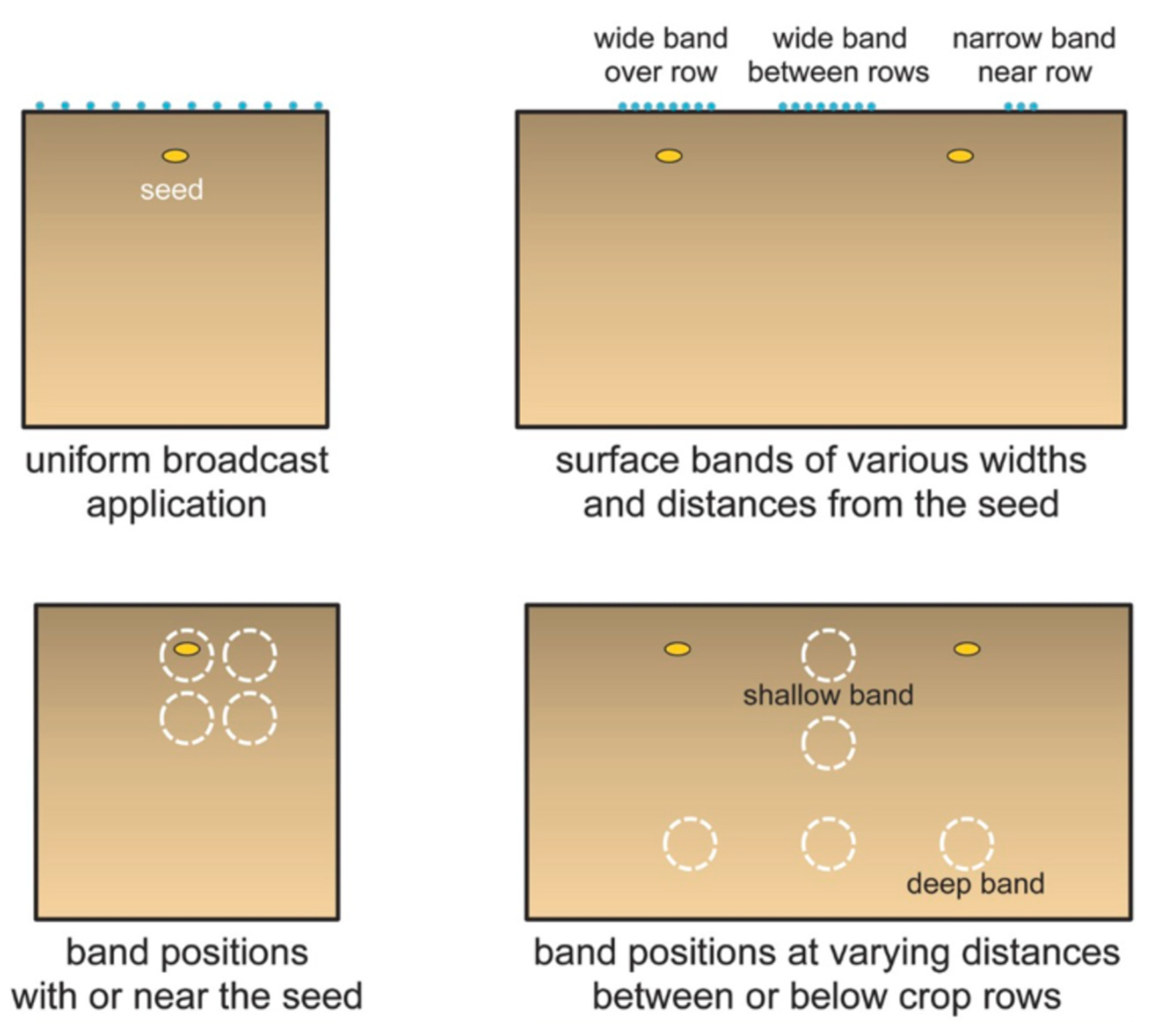
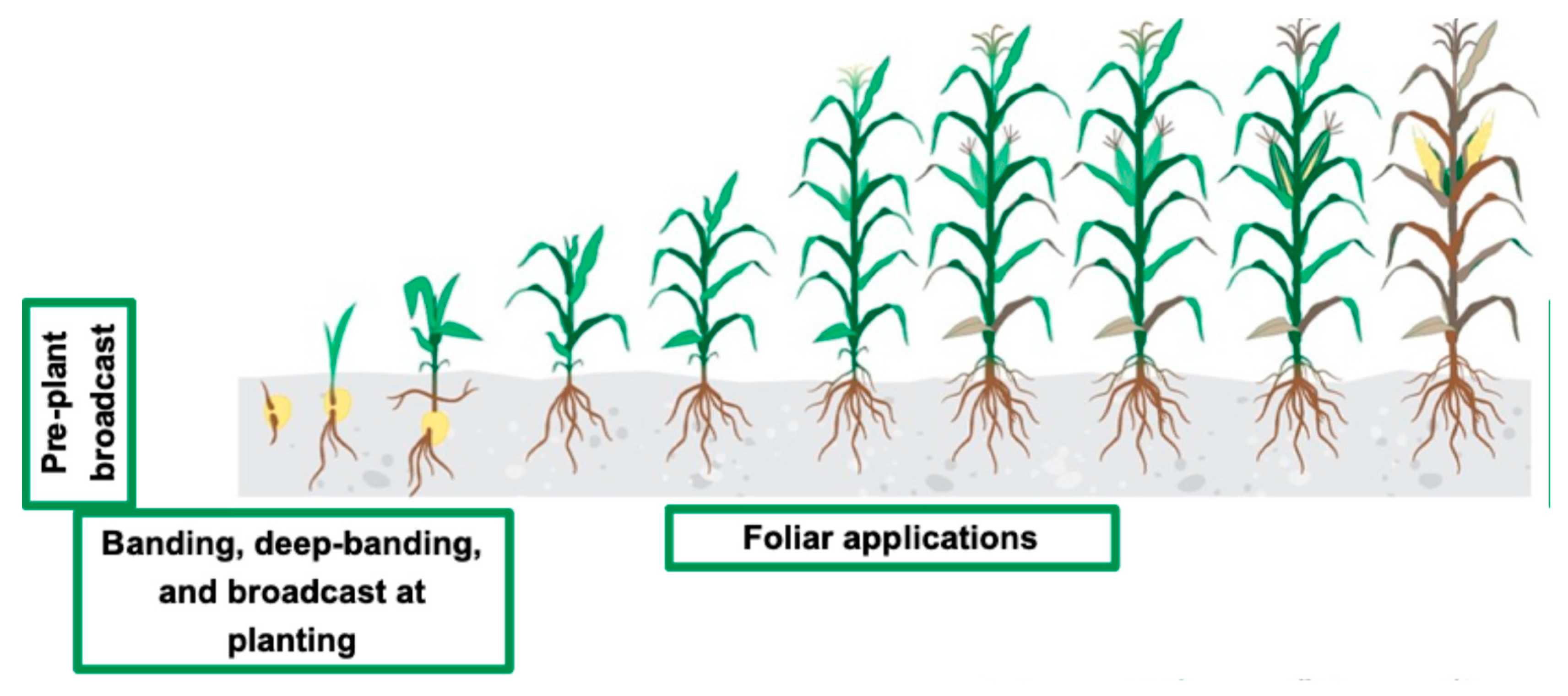
| Country | P balance |
| China | 21.2 |
| United States of America | 4.3 |
| India | 11.2 |
| Brazil | 23.3 |
| Russian Federation | 0.3 |
| Argentina | -6.2 |
| Canada | 2.5 |
| Ukraine | 4.1 |
| Indonesia | 4.1 |
| France | 2.4 |
| Bangladesh | 25.9 |
| Pakistan | 13.8 |
| Australia | 4.6 |
| Viet Nam | -0.5 |
| Germany | 3.4 |
| World | 13.9 |
| Crop (FAO nomenclature) |
P removal (kg P t-1 grain) |
| Barley | 3.46 |
| Beans, dry | 5.71 |
| Buckwheat | 2.20 |
| Canary seed | 2.90 |
| Chickpeas | 5.06 |
| Groundnuts, with shell | 3.61 |
| Lentils | 5.88 |
| Linseed | 7.04 |
| Lupins | 5.06 |
| Maize | 2.94 |
| Millet | 3.91 |
| Mustard seed | 9.24 |
| Oats | 3.73 |
| Peas, dry | 8.73 |
| Quinoa | 2.20 |
| Rapeseed | 7.04 |
| Rice, paddy | 2.87 |
| Rye | 3.42 |
| Safflower seed | 5.33 |
| Seed cotton | 11.62 |
| Sesame seed | 5.12 |
| Sorghum | 3.83 |
| Soybeans | 6.33 |
| Sunflower seed | 4.09 |
| Triticale | 2.86 |
| Wheat | 3.84 |
| Crop | Uptake | P harvest index | Removal in grain | References |
| kg t-1 | % | kg P t-1 grain | ||
| Maize | 2.7-4.5 | 69-85 | 2.3-3.7 | Bender et al., 2013 Setiyono et al., 2010 Ciampitti et al., 2013 Xu et al., 2013 Karbo et al., 2017 |
| Wheat | 2.7-5.2 | 68-90 | 2.2-4.5 | Malhi et al., 2006 Selles et al., 2011 Lazaro et al., 2012 Chuan et al., 2013 Wall and McDonald, 2015 Divito et al., 2017 Karbo et al., 2017 |
| 2.0-4.5 | 60-70 | 1.7-2.6 | Dobermann et al., 1998 Dobermann and Fairhurst, 2000 Xu et al., 2015 |
|
| Soybean | 8.23 6.54 |
83 67 |
6.83 4.36 3.8-6.2 |
Karbo et al., 2017 Salvagiotti et al., 2021 Nakayama et al., 2024 |
| Barley | 2.6-4.0 | 75-87 | 2.2-3.7 | Murrell, 2008 Malhi et al., 2006 |
| Sorghum | 4.4 | 82 | 3.6 | Ciampitti and García, 2007 Murrell, 2008 |
| Sunflower | 11.0 | 62 | 4.3-6.8 | Ciampitti and García, 2007 Murrell, 2008 |
| Canola | 15.0 | 73 | 11.0 | Ciampitti and García, 2007 |
| Oats | 3.3 | 87 | 2.6-3.9 | Murrell, 2008 Malhi et al., 2006 |
| Rye | 4.3 | 60 | 2.6-3.6 | Ciampitti and García, 2007 Murrell, 2008 |
| Foxtail Millet Setaria italica |
4.1-4.6 | - | - | Mubeena et al.2019 |
| Pearl millet Pennisetum glaucum |
- | - | 1.8-3.1 | Payne et al., 1995 |
| Finger millet Eleusine coracana |
2.9-5.0 | 48-56 | 1.2-2.8 | Prashanth et al. 2019 |
| Quinoa | 4.2-4.7 | 62-67 | 2.8 | Alvar-Beltran et al., 2021 |
| Country | P rate (kg P/ha) |
Grain yield (kg grain/ha) |
PNB-P |
| Maize | |||
| Burkina Faso | 8 | 1652 | 0.5 |
| Egypt | 12 | 6752 | 1.4 |
| Mali | 5 | 2821 | 1.4 |
| Morocco | 17 | 792 | 0.1 |
| Nigeria | 1 | 1729 | 5.2 |
| South Africa | 20 | 5130 | 0.7 |
| Tanzania | 1 | 1722 | 3.4 |
| Rice | |||
| Burkina Faso | 3 | 2091 | 1.8 |
| Egypt | 7 | 8811 | 3.6 |
| Mali | 9 | 3417 | 1.1 |
| Morocco | 17 | 7698 | 1.4 |
| Nigeria | 1 | 2388 | 8.2 |
| Soybeans | |||
| Egypt | 16 | 2890 | 0.7 |
| Nigeria | 1 | 935 | 2.7 |
| South Africa | 7 | 1950 | 1.0 |
| Wheat | |||
| Egypt | 10 | 6551 | 2.3 |
| Mali | 8 | 3901 | 1.6 |
| Morocco | 8 | 2092 | 0.9 |
| South Africa | 17 | 3225 | 0.7 |
| Scientific principles | BMPs | |
|---|---|---|
| Right source | Consider rate, time, and place of application Ensure balanced supply of nutrients Supply nutrients in plant-available form Suit soil physical and chemical properties Recognize synergisms among nutrient elements and sources Recognize blend compatibility Recognize benefits and sensitivities to associated elements |
Election of commercial fertilizer Use of enhance-efficient fertilizers Use of livestock manure Use of compost Use of wastes |
| Right rate | Consider source, time, and place of application Assess nutrient supply from all sources Assess plant nutrient demand Assess soil nutrient supply Assess all available nutrient sources Predict fertilizer use efficiency Consider soil resource impacts Consider economics |
Soil testing Estimate target yield Evaluate economics Balance crop removal |
| Right time | Consider source, rate, and place of application Assess the dynamics of crop uptake and soil supply Recognize dynamics of soil nutrient loss Evaluate logistics of field operations Determine timing of loss risk |
Select pre-plant, planting, in-season |
| Right place | Consider source, rate, and time of application Recognize crop rooting patterns Consider soil chemical reactions Suit the goals of the tillage system Manage spatial variability |
Select broadcast, banded/drilled/injected Variable-rate application Use conservation tillage practices to reduce erosion and runoff |
| Source | P concentration (%) | Water P solubility | Concentration of other nutrients (%) | Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rock phosphate | 10-18 Highly variable depending upon origin |
0-10% | Variable | Solid |
| Triple superphosphate (TSP) | 20-21 | 85-95% | 13-15 Ca | Solid |
| Single superphosphate (SSP) | 8-9 | 85-95% | 11-12 S 18-21 Ca |
Solid |
| Monoammonium phosphate (MAP) | 20-23 | 90-95% | 10-12 | Solid |
| Diammonium phosphate (DAP) | 20 | 90-95% | 18 | Solid |
| Ammonium polyphosphate (APP) | 15-16 | 100% | 10-11 N | Solution |
| Nitrophosphate | 6-8 | Up to 95% | 10-28 N 0-14 K |
Solid |
| Manure | 1-5 | Variable | Many, variable concentrations | Solid |
| Pig slurry | 0.1 | Variable | Many, variable concentrations | Slurry |
| Broiler litter | 0.8-2 | Variable | Many, variable concentrations | Solid |
| Dairy effluents | 0.8 | Variable | Many, variable concentrations | Liquid |
| Struvite | 8-12 | Low, variable | 10 Mg, 6 N | Solid |
| Extractant | Composition | Comments | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bray 1 | 0,03 M NH4F + 0,025 M HCl | For P in acidic and neutral soils | Bray and Kurtz, 1945 |
| Olsen | 0,5 M NaHCO3 - pH 8,5 0.5 h extraction in 1:20 soil:solution | For alkaline soils, also in neutral to acidic soils | Olsen et al., 1954 |
| Mehlich-1 | 0,05 M HCl + 0,0125 M H2SO4 | Multinutrient for acidic soils | Mehlich, 1953 |
| Mehlich-3 | 0,2 M CH3COOH + 0,25 M NH4NO3 + 0,015 N H4F + 0,013 M HNO3 + 0,001 M EDTA - pH 2,5 | Multinutrient for a wide range of soils. Correlates with Bray 1, Mehlich-1 and Olsen | Mehlich, 1984 |
| AB-DTPA | 1 M NH4HCO3 + 0,005 M DTPA - pH 7,5 | Multinutrient for alkaline soils |
Soltanpour and Schwab, 1977 |
| Colwell P | 0,5 M NaHCO3 - pH 8,5 16 h extraction in 1:100 soil:solution | Developed at Australia | Colwell, 1963 |
| Morgan and Morgan | Morgan: 0,7 M NaC2H3O2 + 0,54 M CH3COOH - pH 4,8 | Multinutrient used in the northeastern US for acidic soils. Not adapted to calcareous soils. | Morgan, 1941 |
| Ion Exchange resin | Adsorption of P by anion-exchange resin placed in a soil-water suspension | Useful for acid and alkaline soils, and soils treated with lime and rock phosphate | Raij et al., 1986 |
| Egner | 0,01 M lactato de Ca + 0,02 M HCl 0,10 M NH4 lactate+ HOAc –pH 3,75 |
Multinutrient used in Europe | Egner et al., 1960 |
| Method | Region | Critical threshold/range (mg kg-1) |
Reference | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bray-1 | Iowa (US) | 18-25 Other crops 24-30 Alfalfa and wheat |
Mallarino et al., 2023 | 0-15 cm |
| Nebraska (US) | 22.2 | Balboa et al., 2024 | 0-20 cm, continuous irrigated corn | |
| Pampas (Argentina) | 12-19 | Sucunza et al., 2018 | Wheat, maize, and soybean 0-20 cm |
|
| Uruguay | 16-18 | Rabuffetti, 2017 | Wheat | |
| SE Asia | 7-20 | Dobermann and Fairhurst, 2000 | Rice | |
| Olsen | Australia | 9.8-14 | Speirs et al., 2013 | Wheat, 0-10 cm |
| Eastern plains of Bolivia | 6-14 | Reussi Calvo et al., 2025 | Miaze and soybean, 0-20 cm | |
| Southern Chile | 15-25 | Hirzel, 2004 | 0-20 cm | |
| China | 10-28 | Bai et al.., 2013 | Four LTE, maize, wheat and rice, 0-20 cm | |
| China | 12.1-17.3 (Maize) 12.5-19.0 (wheat) |
Tang et al., 2009 | Multisite LTE, 15 years, 0-20 cm | |
| SE Asia | 5 (non-calcareous soils) 25 (calcareous soils) |
Dobermann and Fairhurst (2000) | Rice | |
| UK | 16 | Johnston and Poulton, 2019 | ||
| Mehlich-1 | Paraguay | 12 15 |
Cubilla et al., 2012 | 0-10 cm 41-60% clay 21-40% clay |
| Paraná (Brazil) | 11.2 (wheat, barley, oats) 8.2 (maize, soybean) |
Vieira et al., 2015 | 0-20 cm | |
| Mehlich-3 | Iowa (US) | 18-25 (Other crops) 24-30 (Alfalfa and wheat) |
Mallarino et al., 2023 | 0-15 cm, Colorimetric method |
| Iowa (US) | 28-40 (Other crops) 33-44 (Alfalfa and wheat) |
Mallarino et al., 2023 | 0-15 cm, ICP method | |
| Australia | 23-35 | Speirs et al., 2013 | Wheat, 0-10 cm | |
| Ohio (US) | 20-40 (Maize and soybean) 30-50 (wheat and alfalfa) |
Culman et al., 2020 | 0-20 cm | |
| Resin | Cerrados Region (Brazil) | 15 | Sousa et al., 2002 | |
| Colwell | Australia | 22-30 | Speirs et al., 2013 | Wheat, 0-10 cm |
| Australia | 15-47 | Bell et al., 2013 | Wheat, 0-10 cm, analysis of 1777 experiments, variation according soil classification and pH | |
| DGT-P | Australia | 30-49 | Speirs et al., 2013 | Wheat, 0-10 cm |
| Australia | 66 | Mason et al., 2010 | Wheat, 0-10 cm | |
| Morgan | Ireland | 6.1-10 | Wall and McDonald, 2015 | Arable crops |
| Method | Categories | ||||
| Very low | Low | Medium | High | Very high | |
| -------------------- mg/kg -------------------- | |||||
| Bray-1 1 | <6 | 6-14 | 14-20 | 20-30 | >30 |
| Olsen 2 | <6 | 7-10 | 11-15 | 16-20 | >21 |
| Mehlich-1 3 | <5 | 4-8 | 8-12 | 12-24 | >24 |
| Mehlich-3 2 | <8 | 9-15 | 16-20 | 21-30 | >31 |
| Mehlich-34 | <11 | 11-27 | 28-54 | 54-107 | >107 |
| Resin5 | <6 | 7-15 | 16-40 | 41-80 | >80 |
| Sufficiency | Buildup and maintenance |
|---|---|
| Based on “crop response” to P | Based on “soil response” to P |
| For each value below the critical level, different rates determine the optimum economic yield. | Soil P test should be above the critical level/range |
| The effects of fertilization on nutrient levels in the soil are not considered. | If the P level is low, fertilization is not only used to achieve maximum yield, but also to ensure that the initial level is raised. |
| Requires good knowledge of the initial level and precision in the soil analysis, and of the optimal rates for each crop | The optimum P level would be reached in 4 to 6 years, and it should be maintained, generally based on the removal of nutrients by crops. |
| Great impact of calibration errors in soil analysis, recommendations and sampling | Less impact of calibration errors in soil analysis, recommendations and sampling |
| Requires frequent sampling and localized applications in many cases | Does not require frequent sampling, can be done every 2 to 4 years |
| Good option for “fixing” soils, and in fields under short-term lease | Reasonable in soils with little or no P fixation, and in own fields |
| It does not require high initial capital availability | It requires high initial capital availability |
| Crop | Sampling | Critical P concentration |
References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Plant at tillering stage | 0.2-0.5 | Jones, 1998; Malavolta et al., 1997; Plank and Donahue, 2000 |
| Top 4 leaves at heading-anthesis | 0.2-0.5 | ||
| Barley | Plant at heading | 0.2-0.5 | Jones, 1998; Malavolta et al., 1997 |
| Rice | Last full developed leaf at tillering-heading | 0.1-0.4 | Jones, 1998; Malavolta et al., 1997; Dobermann and Fairhurst, 2000 |
| Maize | Plant at 5-6 leaves stage | 0.48-0.58 | Stammer and Mallarino, 2018; Mallarino and Sawyer, 2018 |
| Ear leaves at R1 | 0.25-0.32 | ||
| Sorghum | Top third leaves at tillering | 0.4-0.8 | Jones, 1998; Malavolta et al., 1997; Clark, 1993; Cox and Unruh, 2000 |
| Last fully developed leaf at vegetative stages | 0.2-0.4 | ||
| Top second leaf at flowering | 0.2-0.35 | ||
| Soybean | Plant at 5-6 leaves stage | 0.33-0.41 | Stammer and Mallarino, 2018; Mallarino and Sawyer, 2018 |
| Trifoliate leaves at R2-3 | 0.35-0.42 | ||
| Sunflower | Top third leaves at flowering | 0.3-0.7 | Jones, 1998; Malavolta et al., 1997; Merrien et al., 1986 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





