Submitted:
11 April 2025
Posted:
15 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Well Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Pre-Processing
2.4. Artificial Lift Classification
2.5. Machine Learning Modelling
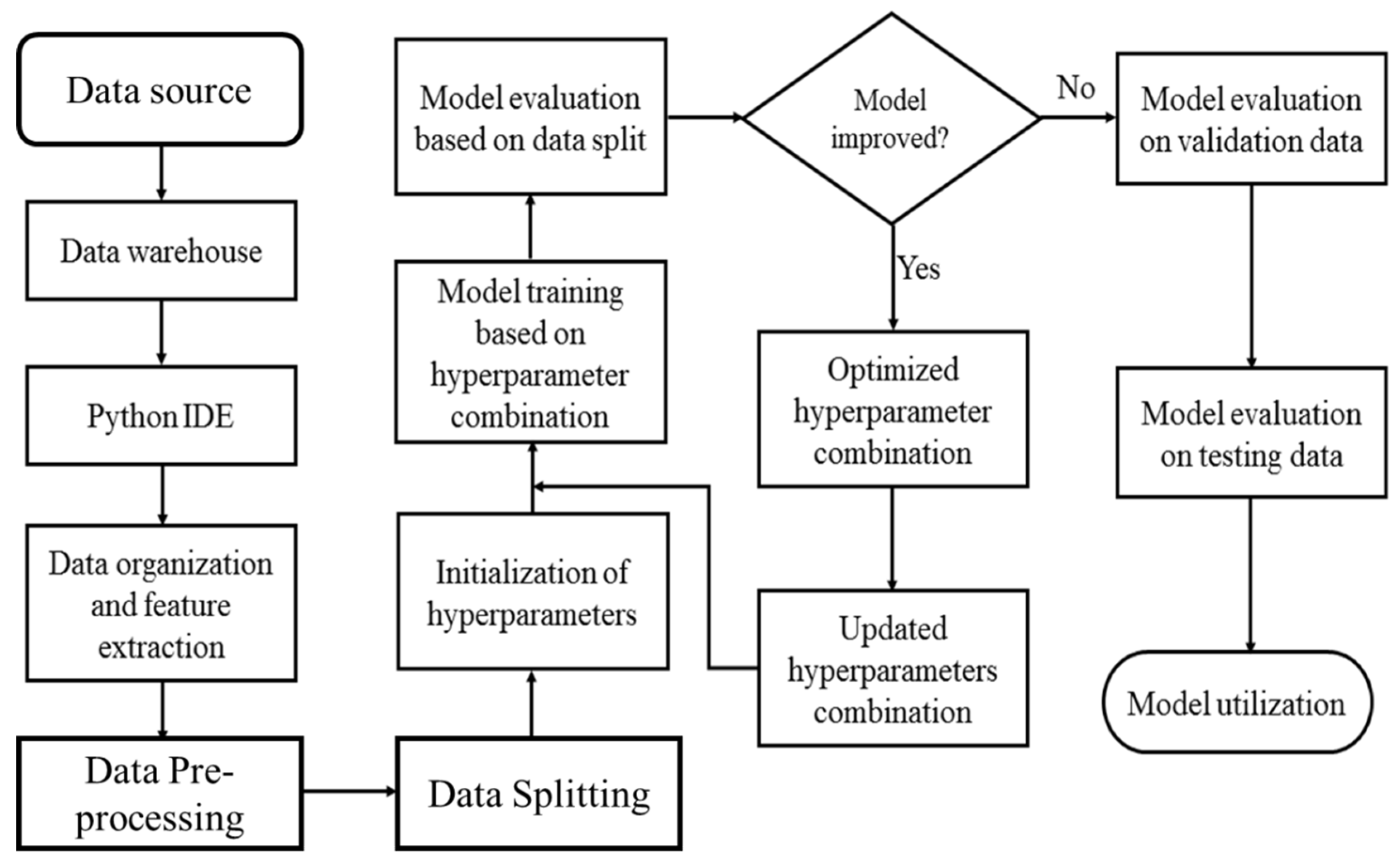
2.5.1. Machine Learning Models Utilised
- a.
- Random Forest
- b.
- Extreme Gradient Boosting
- c.
- Decision Tree
- d.
- Logistic Regression
- e.
- The Stacked Model
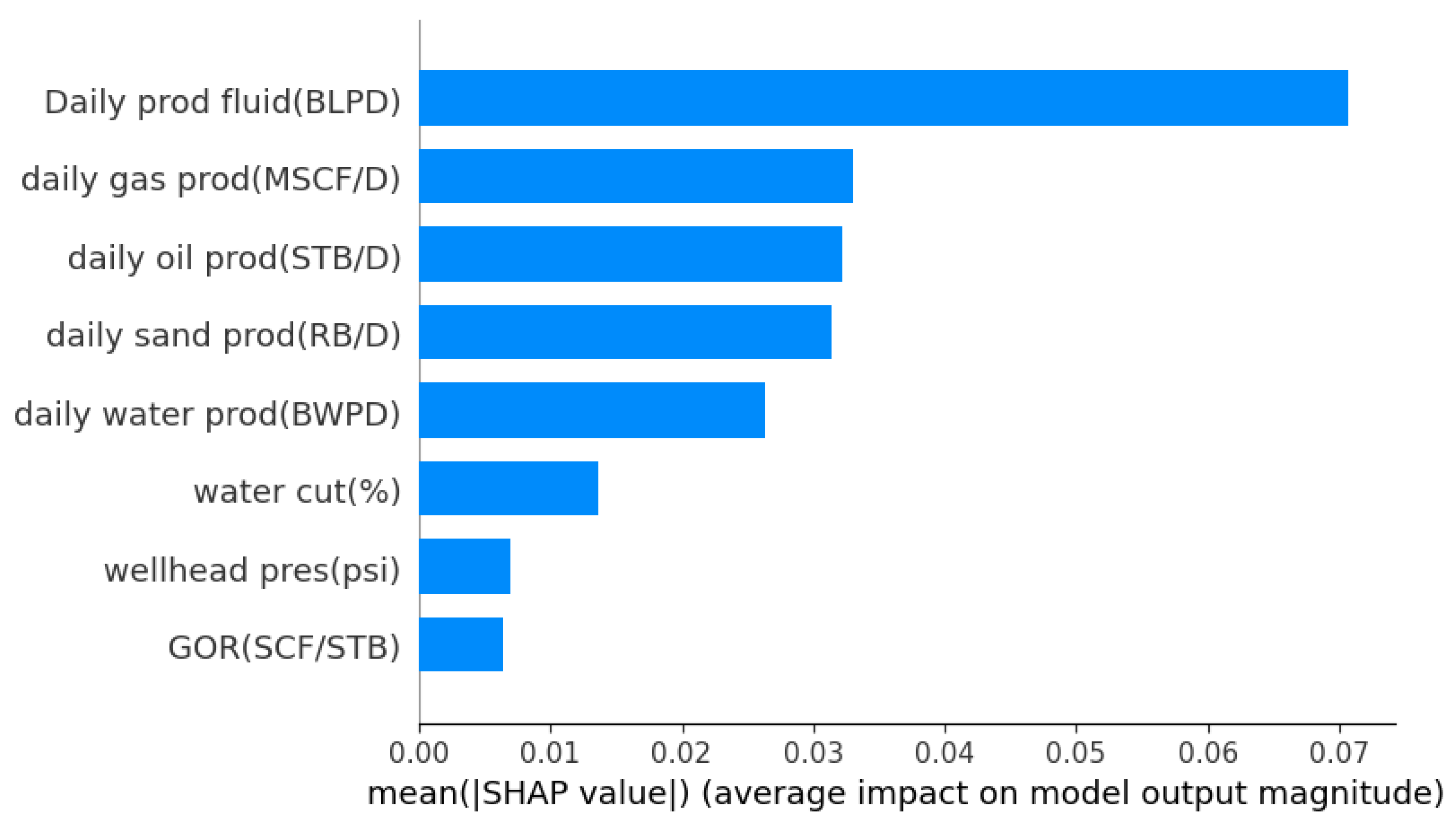
2.5.2. SHAP Analysis for Feature Importance
- represents a subset of all input features except .
- denotes the model’s prediction using only the features in subset .
- f measures the marginal contribution of
2.5.3. Model Performance Evaluation
- Accuracy measures the overall correctness of the model and is given by:
- Precision quantifies the proportion of correctly classified positive instances out of all predicted positive instances:
- Recall (Sensitivity) evaluates the model’s ability to identify all relevant positive instances:
- F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a balanced evaluation when dealing with imbalanced classes:
- Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC-ROC) measures the model’s ability to distinguish between classes at various threshold levels. A higher AUC value signifies better discrimination capability.
- Precision-Recall (PR) Curve is particularly useful when dealing with imbalanced datasets, illustrating the trade-off between precision and recall.
- Confusion Matrix provides a detailed breakdown of actual versus predicted classifications, helping identify patterns in misclassification.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hyperparameter Tuning
3.2. Model Performance Evaluation
3.2.1. Classification Report
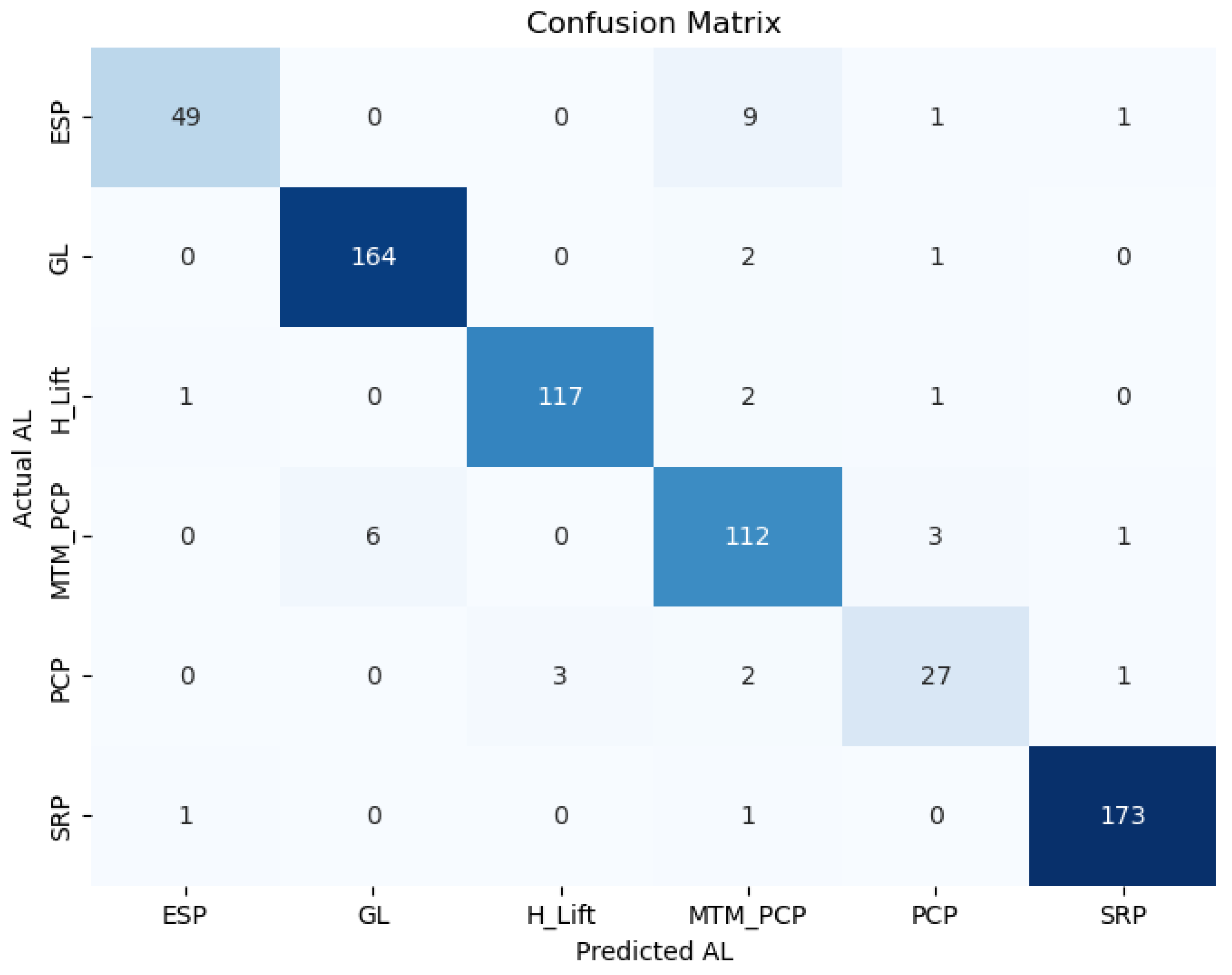
3.2.2. Confusion Matrix
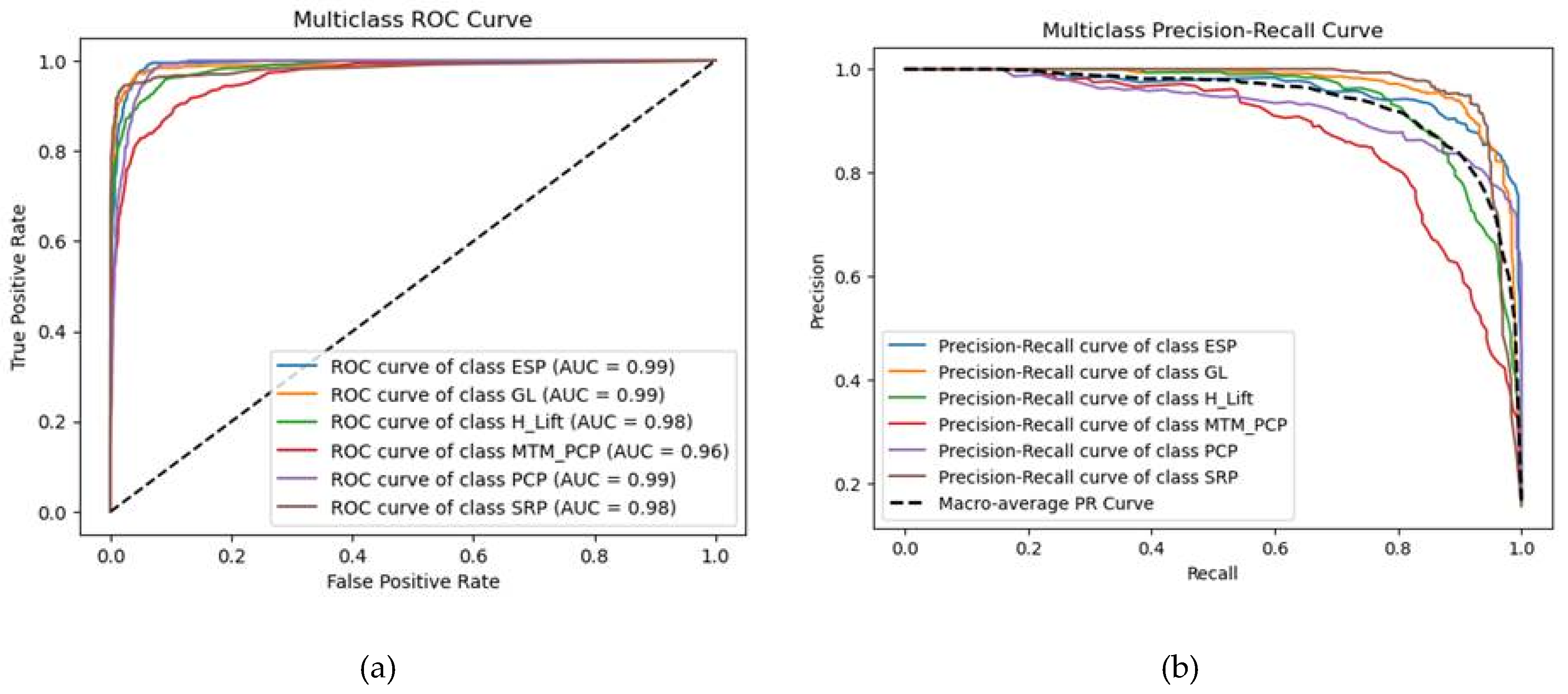
3.2.3. ROC AUC and PR AUC Analysis
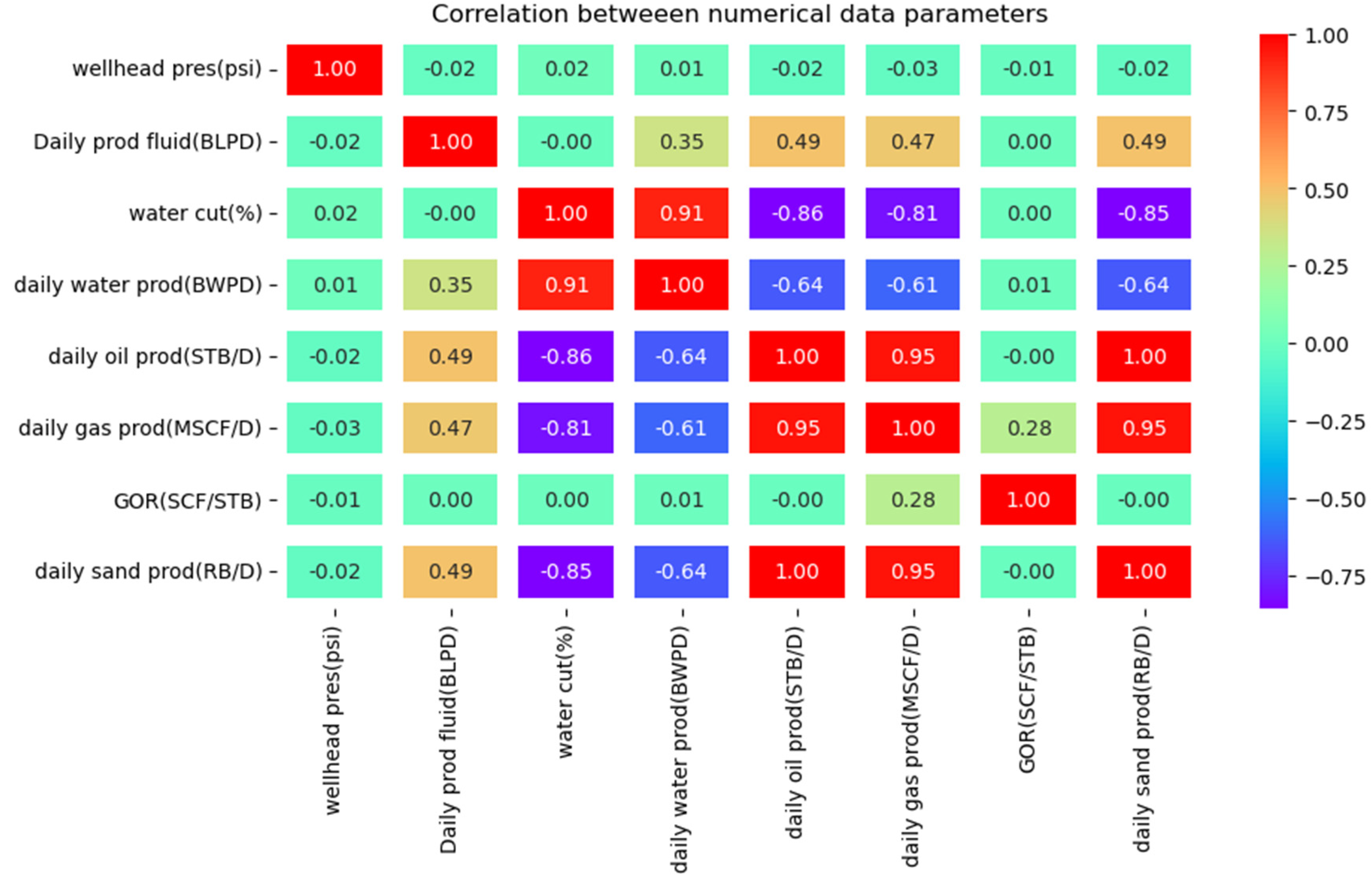
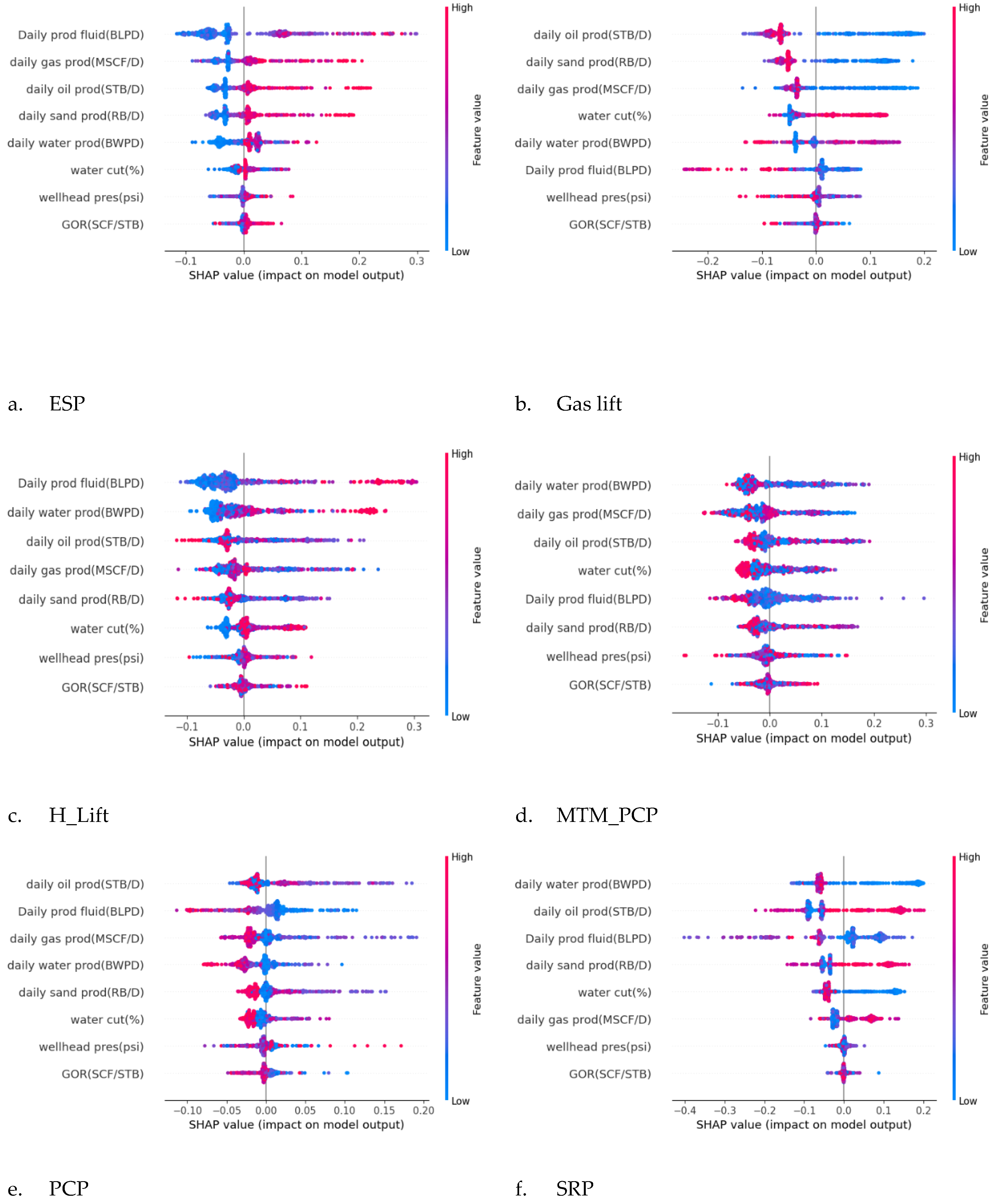
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
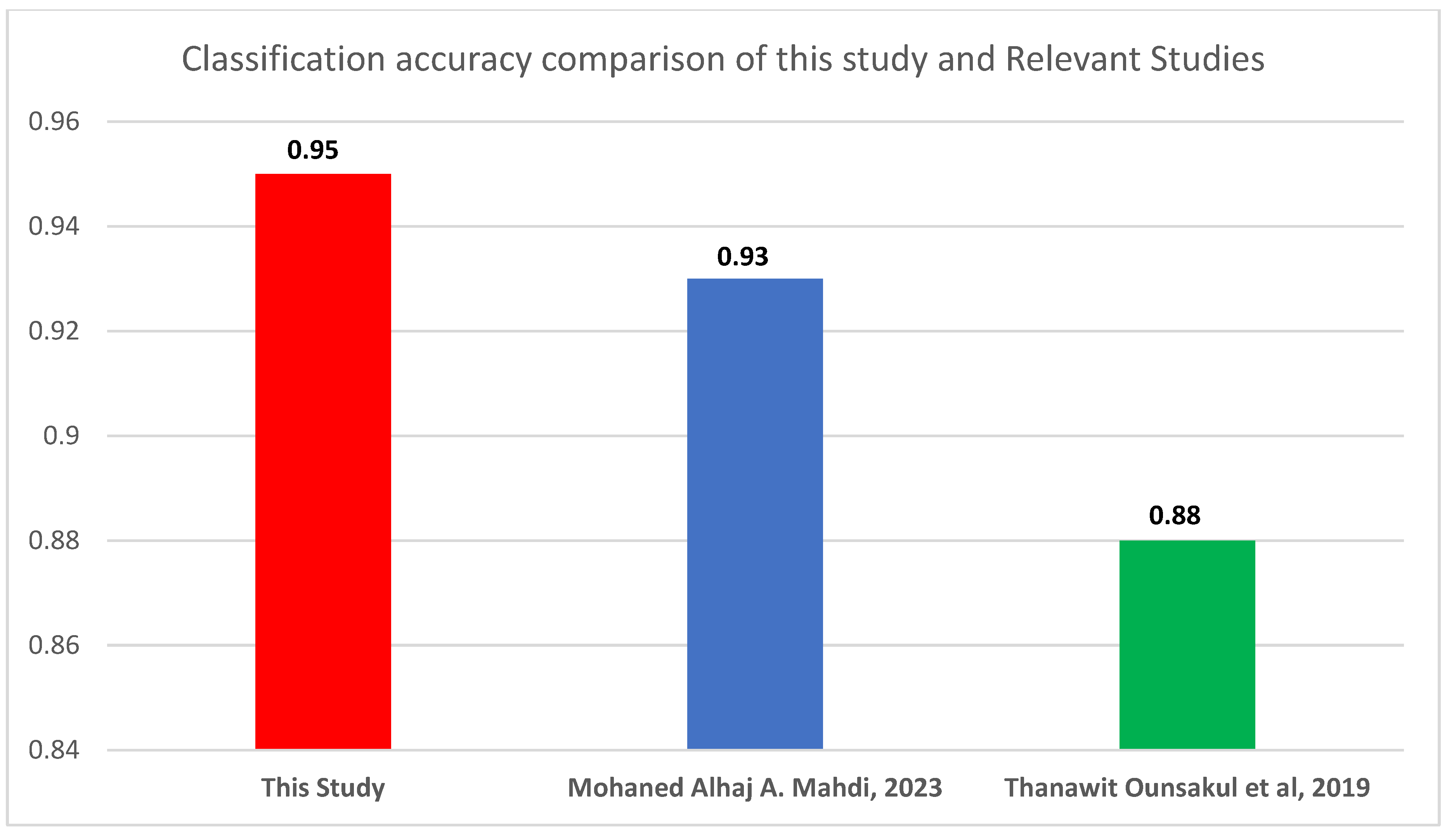
3.4. Comparison with Recent Literature
4. Conclusion
Funding
References
- Mohaned Alhaj A. Mahdi, M. A. and G. O. An Artificial Lift Selection Approach Using Machine Learning . Energies 2023, 16, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H. T., & Del Mundo, F. C. (2016). Improving artificial lift design through dynamic simulation. Society of Petroleum Engineers - SPE North America Artificial Lift Conference and Exhibition 2016, (October), 25–27. [CrossRef]
- Nosakhare, A., Igemhokhai, S., Aimhanesi, S., Ugbodu, F., & Iyore, N. (2024). Heliyon Data-driven intelligent modeling , optimization , and global sensitivity analysis of a xanthan gum biosynthesis process. Heliyon, 10(3), e25432. [CrossRef]
- Ounsakul, T., Sirirattanachatchawan, T., Pattarachupong, W., Yokrat, Y., & Ekkawong, P. (2019). Artificial lift selection using machine learning. International Petroleum Technology Conference 2019, IPTC 2019, (June). [CrossRef]
- Shi, J., Chen, S., Zhang, X., Zhao, R., Liu, Z., Liu, M., et al. (2019). Artificial lift methods optimising and selecting based on big data analysis technology. International Petroleum Technology Conference 2019, IPTC 2019. [CrossRef]
- Speiser, J. L., Miller, M. E., Tooze, J., & Ip, E. (2019). A comparison of random forest variable selection methods for classification prediction modeling. Expert Systems with Applications, 134, 93–101. [CrossRef]
- Akosa, J. Predictive accuracy: A misleading performance measure for highly imbalanced data. Proc. SAS Glob. Forum 2017, 12, 942. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, P.N.; Steinbach, M.; Kumar, V. Classification: Basic concepts, decision trees, and model evaluation. Introd. Data Min. 2006, 1, 145–205. [Google Scholar]
- Alshboul, O., Shehadeh, A., Almasabha, G., & Almuflih, A. S. (2022). Extreme Gradient Boosting-Based Machine Learning Approach for Green Building Cost Prediction. Sustainability, 14(11), 6651. [CrossRef]
- Shapley, L. (1997). 7. A Value for n-Person Games. Contributions to the Theory of Games II (1953) 307-317.. In H. Kuhn (Ed.), Classics in Game Theory (pp. 69-79). Princeton: Princeton University Press. [CrossRef]
- Štrumbelj, E., & Kononenko, I. (2014). Explaining prediction models and individual predictions with feature contributions. Knowledge and Information Systems, 41(3), 647–665. [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, S. D., Chandra, S., Aziz, P. A., et al. Integratedapplication of flow pattern map for long-term gas liftoptimization: A case study of Well T in Indonesia. Jour-nal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology,2020, 10(4): 1635-1641.
- Wood, D. A. Gamma-ray log derivative and volatility attributesassist facies characterization in clastic sedimentary se-quences for formulaic and machine learning analysis.Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2022, 6(1): 69-85.
- Yavari, H., Khosravanian, R., Wood, D. A., et al. Applicationof mathematical and machine learning models to predictdifferential pressure of autonomous downhole inflow con-trol devices. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2021,5(4): 386-406.
- Mahdiani, M. R., Khamehchi, E., Hajirezaie, S., et al. Mod-eling viscosity of crude oil using k-nearest neighbor al-gorithm. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2020, 4(4):435-447.
- Choubey, S., Karmakar, G. P. Artificial intelligence techniquesand their application in oil and gas industry. Artificial In-telligence Review, 2021, 54(5): 3665-3683.
- M. Ali, R. Prasad, Y. Xiang, Z.M. Yaseen, Complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition hybridized with random forest and kernel ridge regression model for monthly rainfall forecasts, J. Hydrol. 584 (2020) 124647. [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, J. Data Preparation for Machine Learning: Data Cleaning, Feature Selection, and Data Transforms in Python; Machine Learning Mastery: Vermont, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, C., Saputelli, L., Rivas, F., et al. State of the artof artificial intelligence and predictive analytics in theE&P industry: A technology survey. SPE Journal, 2014b,19(4): 547-563.
- Fern ́andez, A., Garc ́ıa, S., Galar, M., et al. Introduction toKDD and Data science, in Learning From Imbalanced Data Sets, edited by A. Fern ́andez, S. Garc ́ıa, M. Galar,et al., Springer, Berlin, pp. 1-16, 2018.
- Silla, C. N., Freitas, A. A. A survey of hierarchical classifi-cation across different application domains. Data Miningand Knowledge Discovery, 2011, 22, 31-72.
- De Carvalho, A. C. P., Freitas, A. A. A tutorial on multi-label classification techniques, in Foundations of Com-putational Intelligence, edited by A. Abraham., A. E.Hassanien, and V. Sn ́aˇsel, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany,pp. 177-195, 2009. 2009.
- Wolpert, D. H. (1992). Stacked generalization. Neural Networks, 5(2), 241-259. [CrossRef]
- Molnar, C. (2020). Interpretable machine learning. Lulu. com.
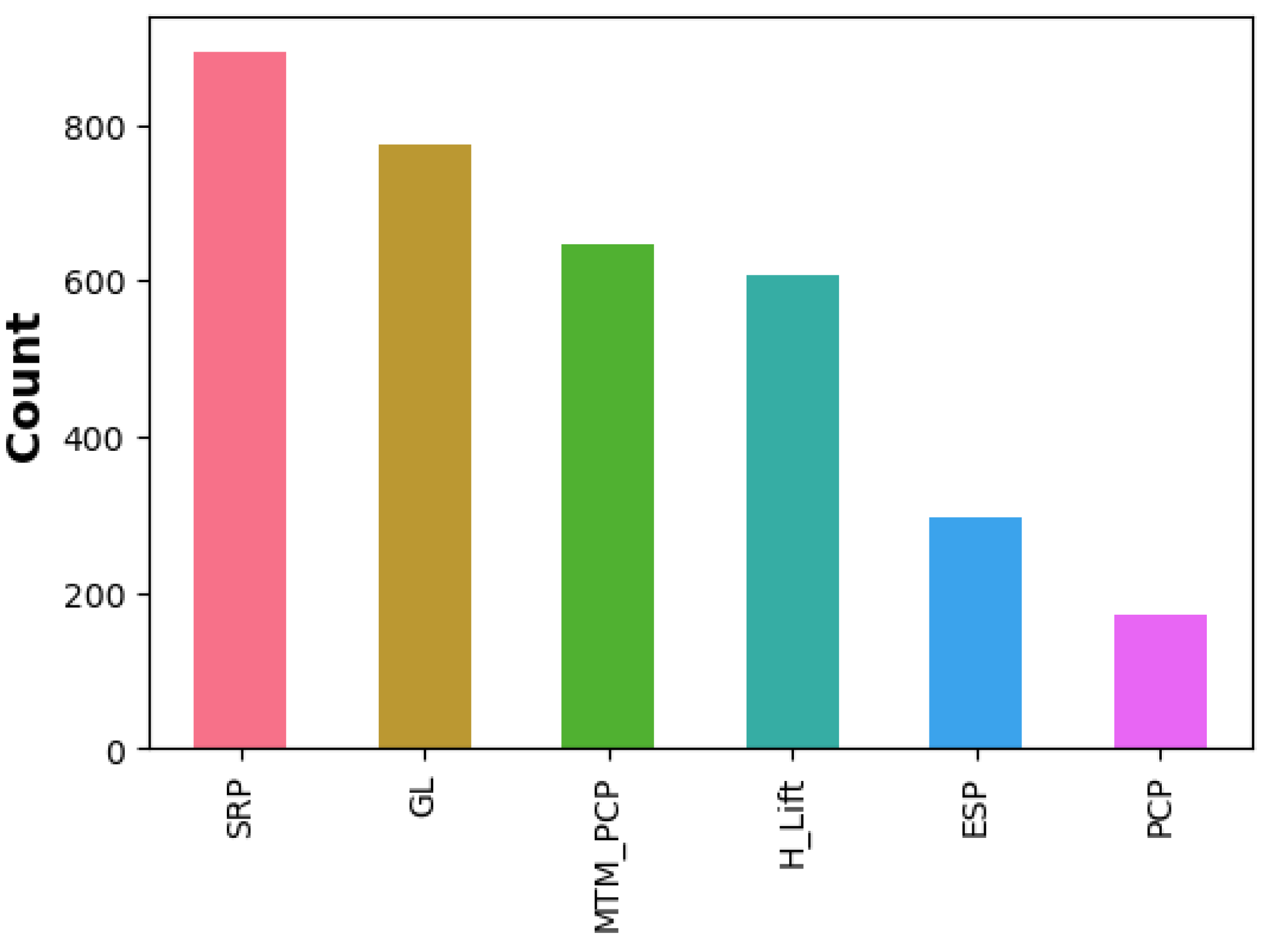
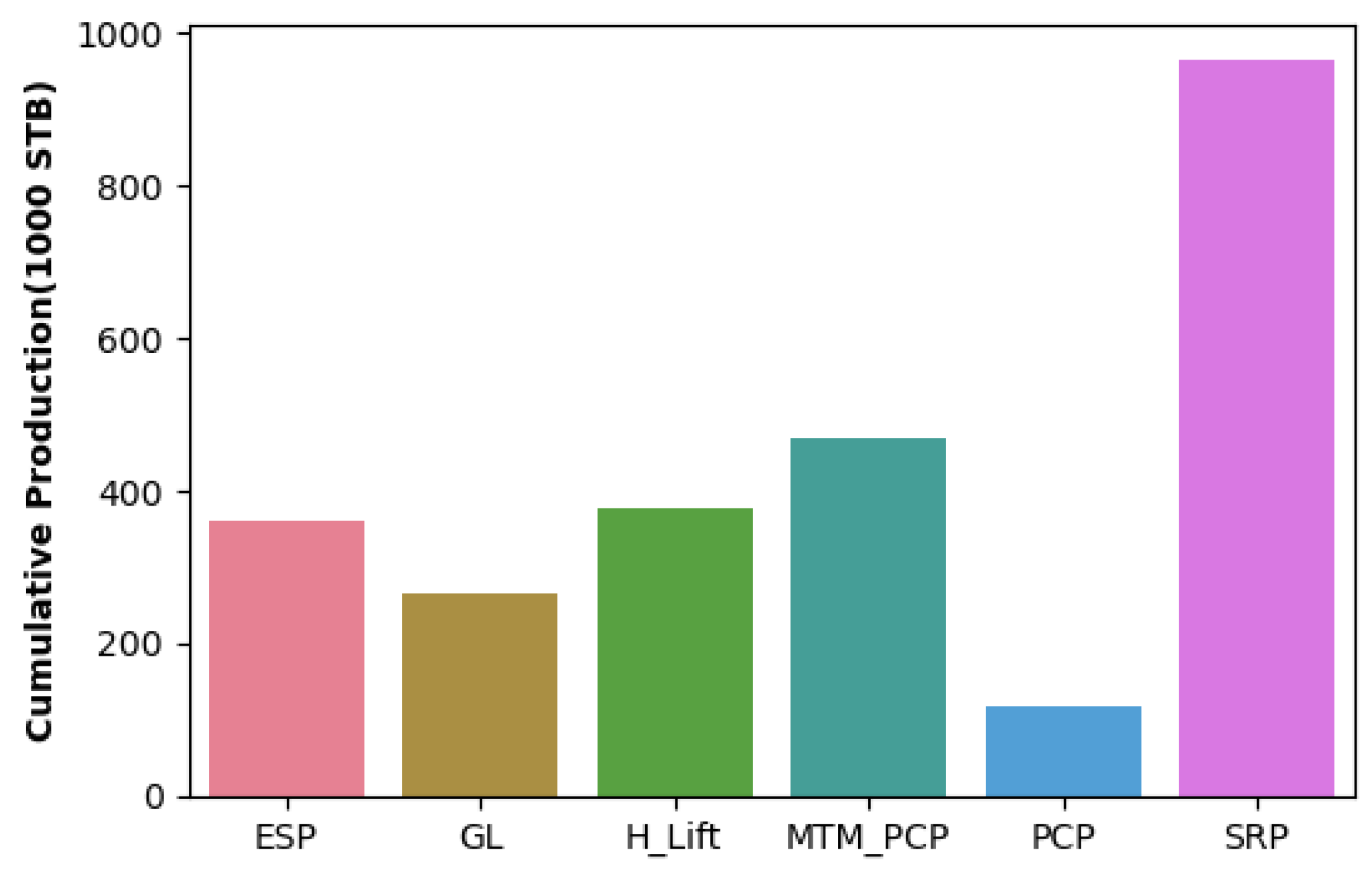

| Model | Hyperparameters | Final Optimized value |
|---|---|---|
| DT | max_depth | 5 |
| min_samples_split | 2 | |
| random_state | 9 | |
| RF | n estimators | 500 |
| max depth | 5 | |
| max features | 3 | |
| random_state | 9 | |
| XGB | max depth | 5 |
| gamma | 0.01 | |
| n estimators | 500 | |
| subsample | 1 | |
| random state | 9 |
| precision | recall | f1-score | support | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESP | 0.960784 | 0.816667 | 0.882883 | 60 |
| GL | 0.964706 | 0.982036 | 0.973294 | 167 |
| H_Lift | 0.975 | 0.966942 | 0.970954 | 121 |
| MTM_PCP | 0.875 | 0.918033 | 0.896 | 122 |
| PCP | 0.818182 | 0.818182 | 0.818182 | 33 |
| SRP | 0.982955 | 0.988571 | 0.985755 | 175 |
| accuracy | 0.946903 | 0.946903 | 0.946903 | 0.946903 |
| macro avg | 0.929438 | 0.915072 | 0.921178 | 678 |
| weighted avg | 0.947633 | 0.946903 | 0.946634 | 678 |
| Class | ROC AUC | PR AUC |
|---|---|---|
| ESP | 0.99 | 0.9593 |
| GL | 0.99 | 0.9674 |
| H_Lift | 0.98 | 0.9397 |
| MTM_PCP | 0.96 | 0.8741 |
| PCP | 0.99 | 0.9272 |
| SRP | 0.98 | 0.9651 |
| Macro-Average | - | 0.9388 |
| Micro-Average | - | 0.9449 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





