Submitted:
27 January 2025
Posted:
29 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
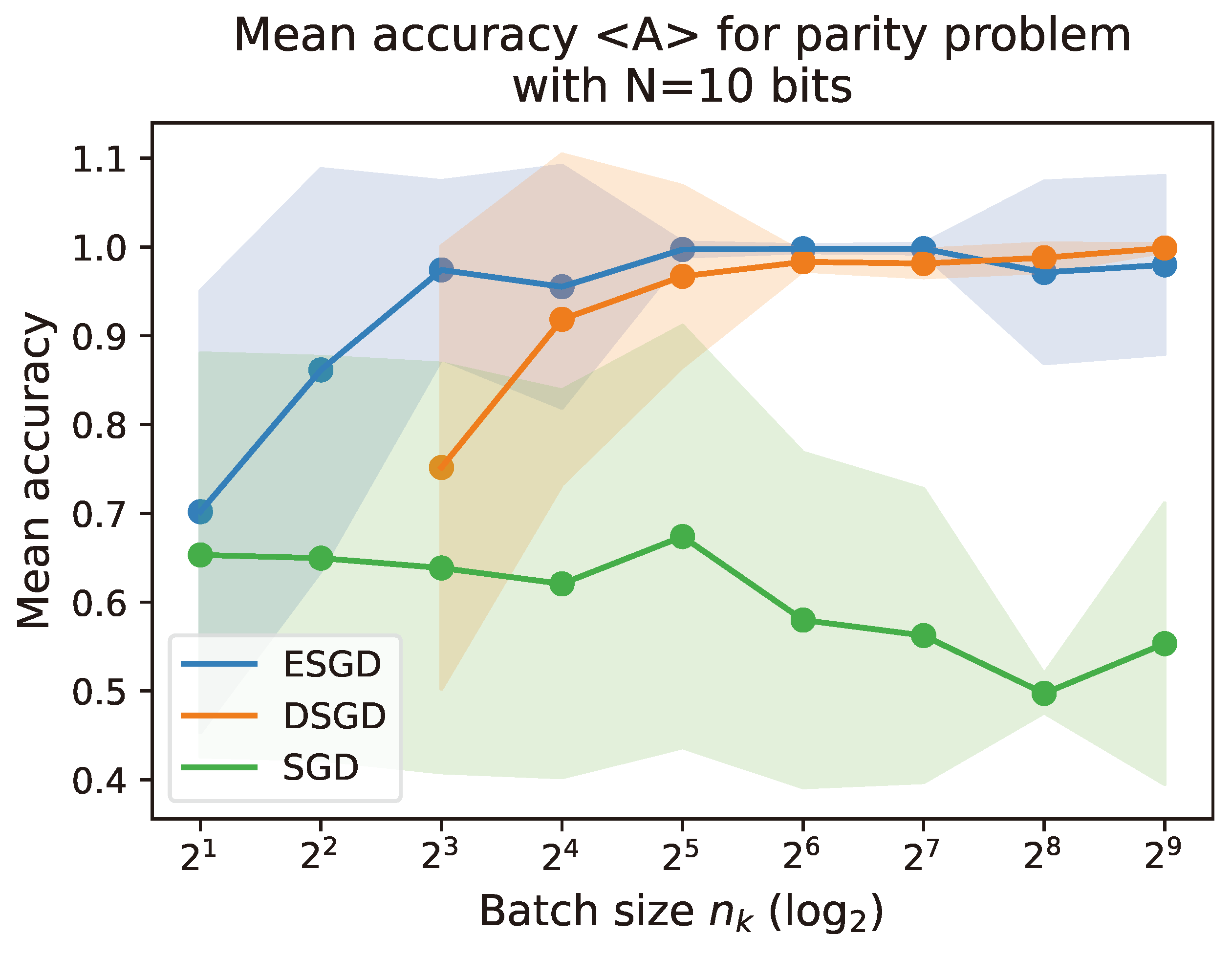
The parity problem, a generalization of the XOR problem to higher-dimensional inputs, is a challenging benchmark for evaluating learning algorithms, due to its increased complexity as the number of dimensions of the feature space grows. In this work, a single-qubit classifier is developed, which can efficiently learn the parity function from input data. Despite the qubit model’s simplicity, the solution landscape created in the context of the parity problem offers an attractive test bed for exploring optimization methods for quantum classifiers. We propose a new optimization method called Ensemble Stochastic Gradient Descent (ESGD), with which density matrices describing batches of quantum states are incorporated into the loss function. We demonstrate that ESGD outperforms both Gradient Descent and Stochastic Gradient Descent given the aforementioned problem. Additionally, we show that applying ESGD with only one measurement per data input does not lead to any performance degradation. Our findings not only highlight the potential of a single qubit model, but also offer valuable insights into the use of density matrices for optimization. Further to this, we complement the outcome with interesting results arising by the employment of a doubly stochastic gradient descent for training quantum variational circuits.
Keywords:
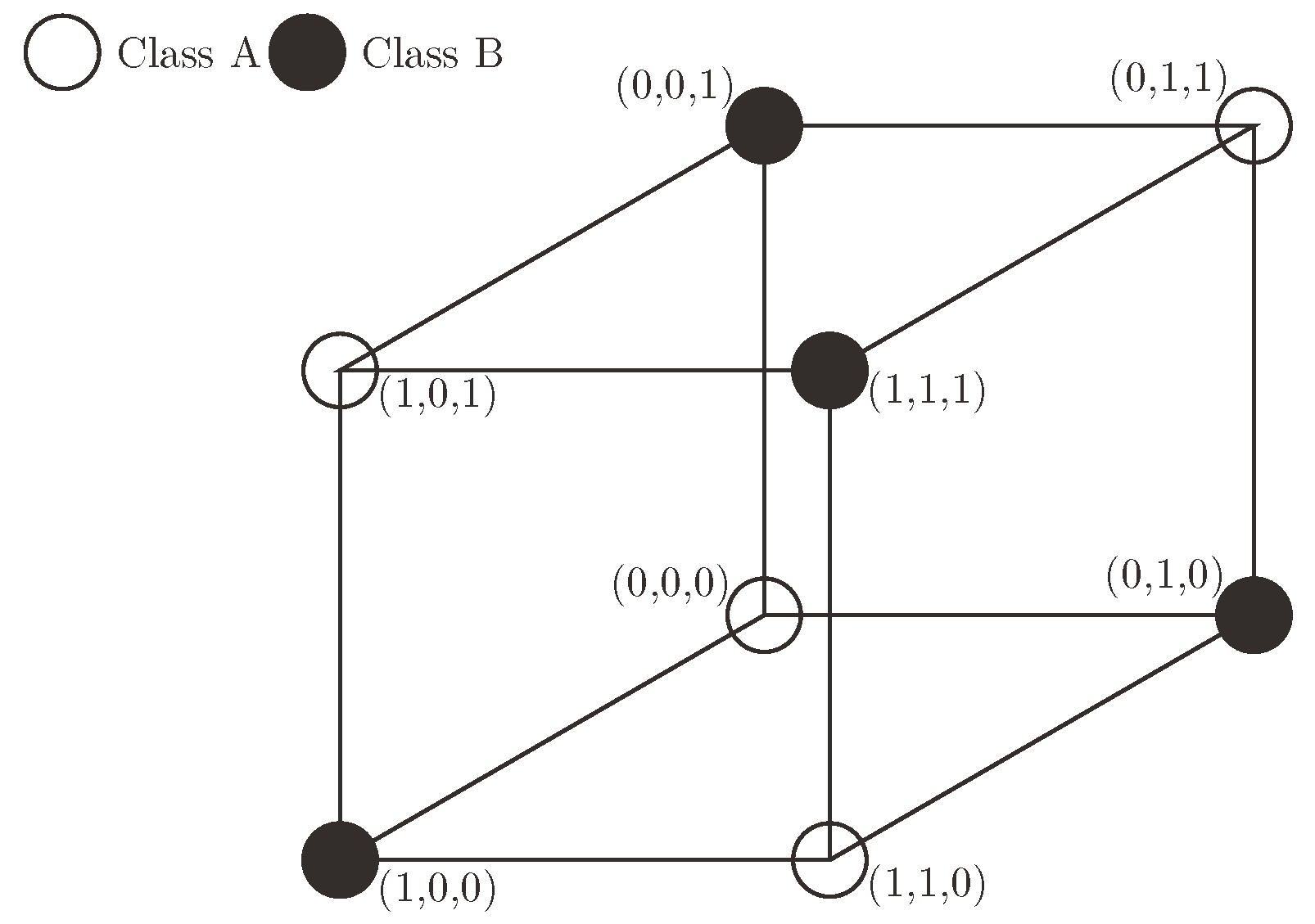
1. Introduction: The Parity Problem
2. A Single-Qubit Classifier For The Parity Problem
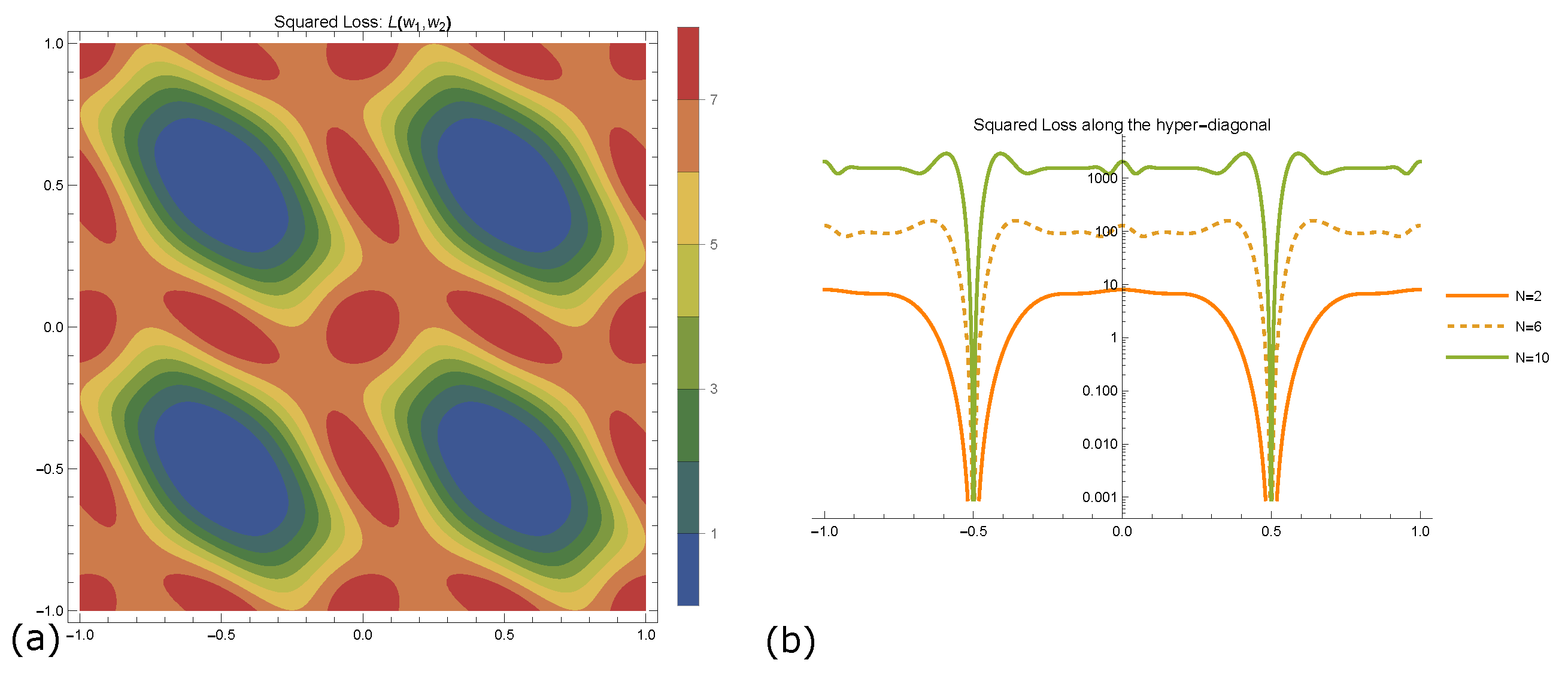
2.1. Landscape Of Solution
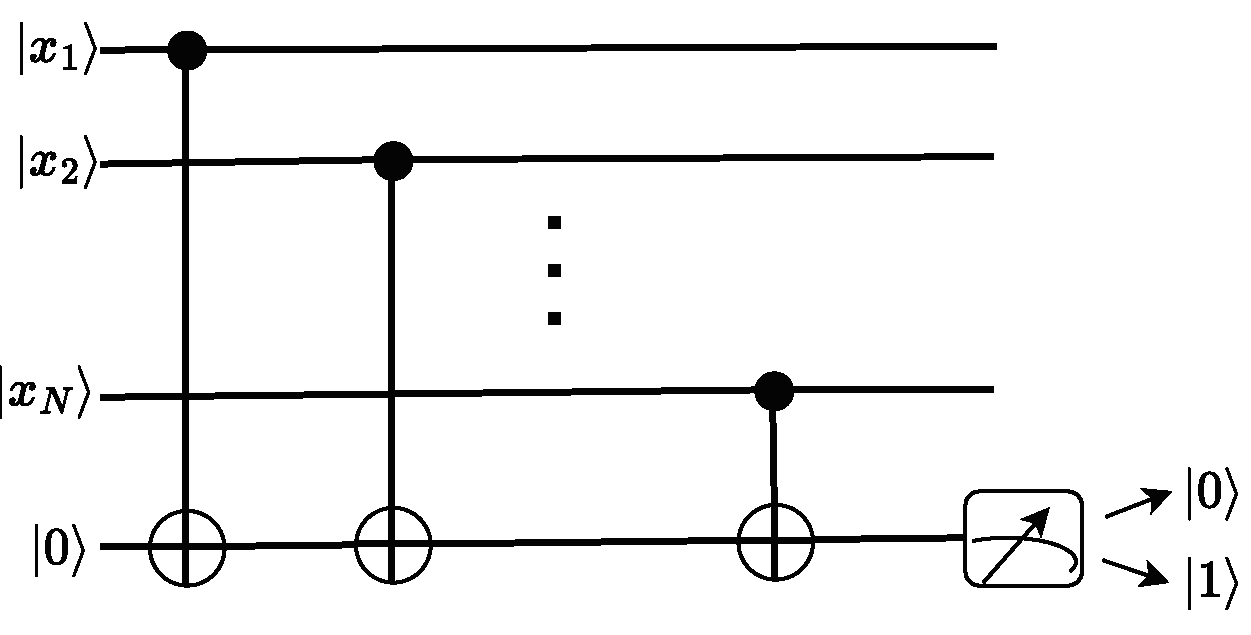
3. Learning Methods
3.1. The ESGD Method: Towards An Optimization With Single Measurement Sampling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESGD | Ensemble Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| NN | Neural Network |
| VQC | Variational Quantum Circuit |
| SQC | Single-Qubit Classifier |
| GD | Gradient Descent |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| DSGD | Doubly Stochastic Gradient Descent |
References
- Theodoridis, S.; Koutroumbas, K. Pattern Recognition, Fourth Edition; Academic Press, 2009.
- Fung, H.K.; Li, L.K. Minimal Feedforward Parity Networks Using Threshold Gates. Neural Computation 2001, 13, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.; Cannas, S. Generalization properties of modular networks: Implementing the parity function. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 2001, 12, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leerink, L.R.; Giles, C.L.; Horne, B.G.; Jabri, M.A. Learning with product units. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; NIPS’94, p. 537–544.
- Havlíček, V.; Córcoles, A.D.; Temme, K.; Harrow, A.W.; Kandala, A.; Chow, J.M.; Gambetta, J.M. Supervised learning with quantum-enhanced feature spaces. Nature 2019, 567, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuld, M.; Killoran, N. Quantum Machine Learning in Feature Hilbert Spaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 040504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuld, M.; Bocharov, A.; Svore, K.M.; Wiebe, N. Circuit-centric quantum classifiers. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 101, 032308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweke, R.; Wilde, F.; Meyer, J.; Schuld, M.; Faehrmann, P.K.; Meynard-Piganeau, B.; Eisert, J. Stochastic gradient descent for hybrid quantum-classical optimization. Quantum 2020, 4, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: 10th Anniversary Edition; Cambridge University Press, 2010.
- Farhi, E.; Goldstone, J.; Gutmann, S.; Sipser, M. Limit on the Speed of Quantum Computation in Determining Parity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 5442–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerbi, S.; Fiderer, L.J.; Poulsen Nautrup, H.; Kübler, J.M.; Briegel, H.J.; Dunjko, V. Quantum machine learning beyond kernel methods. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandilara, A.; Dellen, B.; Jaekel, U.; Valtinos, T.; Syvridis, D. Classification of data with a qudit, a geometric approach. Quantum Machine Intelligence 2024, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, G.E. Gradients of parameterized quantum gates using the parameter-shift rule and gate decomposition. arXiv: Quantum Physics 2019.
- Schuld, M.; Bergholm, V.; Gogolin, C.; Izaac, J.A.; Killoran, N. Evaluating analytic gradients on quantum hardware. Physical Review A 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrow, A.W.; Napp, J.C. Low-Depth Gradient Measurements Can Improve Convergence in Variational Hybrid Quantum-Classical Algorithms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 140502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kübler, J.M.; Arrasmith, A.; Cincio, L.; Coles, P.J. An Adaptive Optimizer for Measurement-Frugal Variational Algorithms. Quantum 2020, 4, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S.; Schuld, M.; Ijaz, A.; Izaac, J.; Killoran, N. Quantum embeddings for machine learning, 2020. arXiv:2001.03622.
| N | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | |
| 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.6 | 0.34 | 0.16 |
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # epocs | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 |
| 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.50 | 0.55 | |
| 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.15 | |
| 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.0 | 0.10 |
| 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # epocs | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 |
| 0.70 | 0.86 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.97 | 0.98 | |
| 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.10 | 0.10 | |
| 0.40 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.96 |
| 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # epocs | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 | 512 |
| 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.967 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.988 | 0.999 | |
| 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.004 | |
| 0.44 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 0.44 | 0.64 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





