1. Introduction
The coagulation process is a fundamental step in water treatment that involves the aggregation of small, suspended particles into larger ones, making them easier to remove through sedimentation or filtration [
1]. This process is initiated by adding chemical coagulants to the water, which neutralize the charges on the particles, allowing them to come together and form flocs. In addition to flocculation, coagulation also promotes the precipitation of dissolved contaminants, such as phosphorus, by forming insoluble compounds that can be easily removed from the water [
2,
3]. Commonly used coagulants in water treatment include aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and magnesium hydroxide [
1,
4,
5]. Each of these coagulants has its advantages and disadvantages. For instance, alum is widely available and effective over a wide pH range, but it can lower the pH and alkalinity of the water, potentially requiring further pH adjustment [
6,
7]. Ferric chloride is effective, and it promotes phosphorus removal through precipitation, but it can produce large amounts of sludge [
8,
9]. Magnesium hydroxide increases the alkalinity of the water, which can be beneficial, and it can precipitate phosphorus as magnesium phosphate, but it is generally less effective in phosphate removal compared to other coagulants [
10,
11,
12]. The choice of coagulant depends on the specific requirements of the water treatment process, including the type of contaminants present and the desired quality of the treated water.
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar elements, including lanthanides, scandium, and yttrium, that are widely distributed in the Earth's crust, although typically not found in concentrated forms. These elements are present in the Earth's crust at an average concentration of about 150 to 220 parts per million (ppm), with cerium being the most abundant, accounting for approximately 66 ppm [
13,
14]. The global production of rare earth elements is substantial, with around 240,000 metric tons produced annually, predominantly by China, which controls about 80% of the world's REE supply [
15,
16]. Cerium, in particular, is produced in large quantities, with an estimated production rate of around 40,000 to 45,000 metric tons per year. In water treatment, cerium materials have emerged as a promising adsorbent due to its ability to form stable, insoluble complexes with phosphorus and organic matter [
17,
18,
19]. Cerium's high affinity for phosphate ions enables it to precipitate phosphorus effectively, even at low concentrations. This makes cerium an excellent choice for removing nutrients from wastewater, especially in scenarios where stringent nutrient limits must be met. Additionally, cerium's ability to adsorb organic matter contributes to its effectiveness in reducing chemical oxygen demand (COD) and improving water clarity [
20,
21]. These characteristics, along with its strong performance across a wide pH range and relatively low dosage requirements, make cerium a potentially superior alternative to traditional coagulants like aluminum and iron salts, particularly in applications requiring high-efficiency nutrient removal.
Despite cerium's demonstrated ability to remove various contaminants from water, there remains a significant research gap in fully understanding its performance as a coagulant, particularly in real-world water treatment applications. Most existing studies have focused on laboratory-scale experiments with controlled conditions, leaving a lack of comprehensive data on cerium's effectiveness in treating highly contaminated wastewater, such as that found in dewatered wastewater. Dewatered wastewater, a byproduct of sludge dewatering processes, often contains elevated levels of phosphorus, nitrogen, organic matter, and suspended solids, posing a substantial challenge for conventional treatment methods. Additionally, much of the existing research on cerium has concentrated on its use in adsorption processes, where cerium is employed to modify adsorbents like granular activated carbon (GAC) for improved nutrient and contaminant removal [
22,
23,
24,
25]. While adsorption is effective, the process of synthesizing and modifying adsorbents can be costly and resource-intensive, making the overall treatment process expensive. In contrast, coagulation, which involves the direct application of cerium as a coagulant, offers a more cost-effective alternative by reducing the need for advanced material preparation and enhancing operational efficiency [
26].
This study aims to bridge the research gap by conducting a comparative assessment of cerium coagulant's performance against alum, a widely used traditional coagulant. By utilizing extremely contaminated wastewater, this study will, for the first time, present detailed insights into the efficiency and operational considerations of using cerium coagulants in the treatment of highly polluted wastewater. This research will contribute to the broader understanding of cerium's potential in addressing the complex challenges of wastewater treatment, particularly in scenarios with extreme pollutant loads.
2. Methodology
2.1. Wastewater and Coagulants
The wastewater used in this study was collected from the Al Hayer Wastewater Treatment Plant (WTP) located in Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia. The wastewater sample was taken from the return dewatered sludge, which typically contains high concentrations of contaminants due to the recycling of dewatering byproducts. The chemical oxygen demand (COD) and phosphate (PO
43--P) levels in the collected wastewater were measured at 1381 ± 108 mg/L and 153 ± 8 mg/L, respectively, indicating significant pollution levels. The detailed characteristics of the wastewater are summarized in
Table 1. Upon collection, the wastewater was passed through paper towels to remove easily settleable materials. The treated wastewater was either used immediately for experiments or stored at 4°C until it was needed. Cerium chloride heptahydrate (CeCl₃.7H₂O; 99.9%; CAS: 18618-55-8) and aluminum sulfate (Al₂(SO₄)₃.14H₂O; 98%; CAS: 7784-31-8) were used as coagulants in the study. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) were utilized to adjust the pH of the water to the desired levels for the coagulation experiments.
2.2. Coagulation Studies
Coagulation studies were conducted with a focus on phosphate (PO₄³⁻-P) levels to establish the optimum operating conditions for the removal of phosphorus using cerium coagulant. PO₄³⁻-P was selected as the key performance indicator because nutrient loading is a critical factor in determining effluent water quality. The cerium-to-phosphorus (mass-based) doses tested ranged from 0.2 to 13.0 mg/mg. For the pH studies, a range of pH values between 3 and 11 was investigated at constant cerium or alum doses to determine the optimal pH conditions for coagulation. The experiments were conducted using a jar test, which involved three stages: coagulation, flocculation, and settling. The coagulation phase was carried out at a speed of 200 rpm for 1 minute, followed by the flocculation phase at 30 rpm for 15 minutes, and finally, the settling phase at 0 rpm for 30 minutes. This sequence was designed to simulate real-world water treatment processes and ensure thorough mixing, floc formation, and sedimentation.
2.3. Sample Analysis
Following treatment, the samples were promptly analyzed to assess various water quality parameters. COD, NH3-N, and PO₄³⁻-P concentrations were determined using Hach® analytical methods: 435 COD HR for COD, 343 N Ammonia HR TNT for nitrogen, and 540 P React HR for phosphate, all measured with a portable spectrophotometer, DR2800. Total dissolved solids (TDS) were determined using a Hanna® conductivity meter equipped with HI763093 probe. The removal efficiency of each coagulant was calculated as a percentage relative to the untreated wastewater. The structural analysis of the lanthanide-phosphate precipitate was conducted using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) with a Shimadzu IR Prestige-21 spectrophotometer and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis with a Bruker AXS D8 Advance Vario x-ray diffractometer.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH Effect
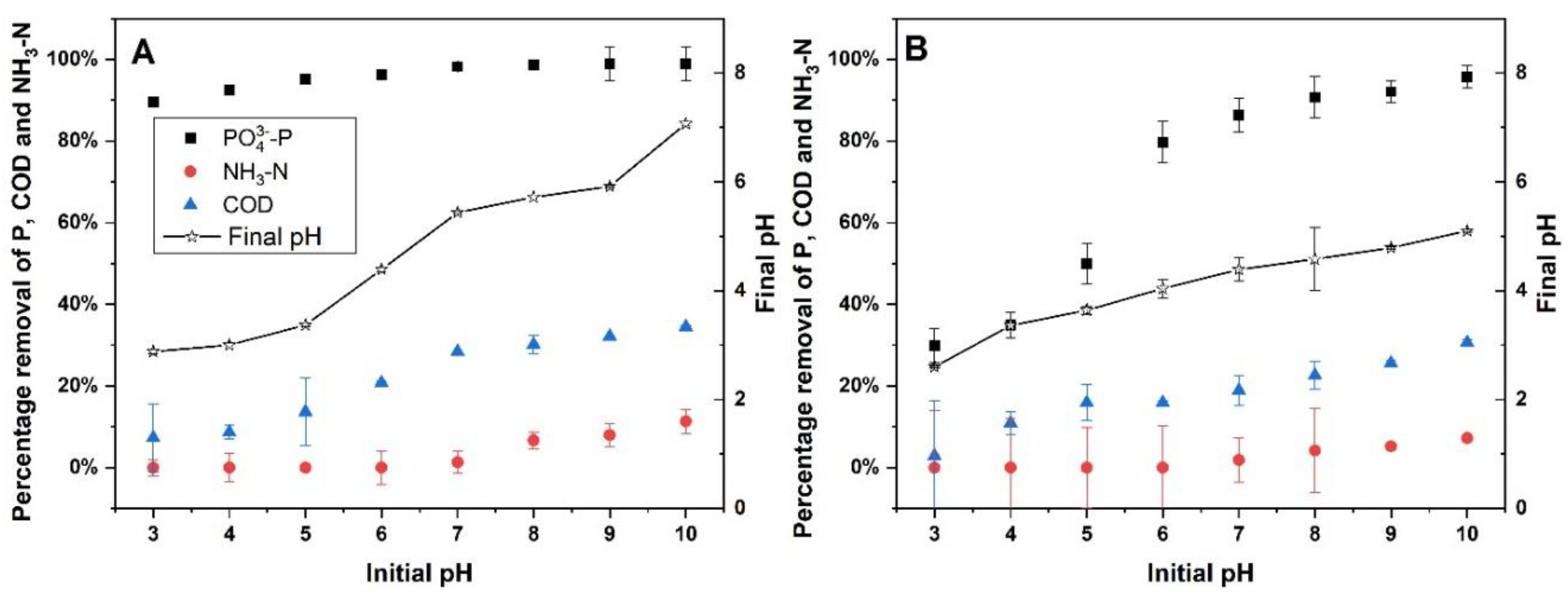
The results from the coagulation studies indicate that cerium is highly effective in removing PO₄³⁻-P across a wide range of pH levels, consistently achieving removal efficiencies between 89% and 98% (
Figure 1A). This high removal rate is maintained from pH 3 to pH 10, demonstrating cerium’s robustness as a coagulant in various pH conditions. At a low pH of 3, cerium removed approximately 89.5% of PO₄³⁻-P, and the efficiency increased to about 98.9% at a pH of 9 and 10, indicating that cerium is highly effective across both acidic and alkaline conditions. This efficiency can be attributed to cerium's strong affinity for phosphate ions, allowing for effective precipitation and removal regardless of the initial pH [
27]. In contrast, aluminum (alum) shows a more variable performance in phosphate removal, with efficiency improving as the pH increases (
Figure 1B). At a pH of 3, alum removes only around 30% of PO₄³⁻-P, but this increases significantly to approximately 85% to 95% at pH 7 and above. The lower performance of alum at acidic pH levels could be due to the reduced formation of effective flocs under these conditions, as alum’s coagulation efficiency is highly dependent on maintaining an optimal pH range [
28,
29].
For ammonia nitrogen (NH₃-N) removal, cerium exhibits minimal impact, with removal percentages close to zero or slightly positive at most pH levels, indicating that cerium is not particularly effective in precipitating or adsorbing NH₃-N. Similarly, alum does not show any significant NH₃-N removal. In water, NH₃-N primarily exists as either ammonia (NH₃) or ammonium ion (NH₄⁺), depending on the pH. At lower pH levels, more of the ammonia converts into ammonium (NH₄⁺). Ammonium is a small, positively charged ion, and coagulants like Ce³⁺ and Al³⁺ typically target negatively charged ions (such as phosphate, PO₄³⁻) and colloidal particles, which are neutralized and aggregated to form flocs. The observed 5-10% removal at pH levels greater than 8 can be attributed to the volatilization of NH₃, as it is the predominant species at this pH and is less soluble in water [
30].
When evaluating COD removal, cerium shows moderate effectiveness, with removal efficiencies ranging from 7% to 34%. The best COD removal performance with cerium is observed at neutral to slightly alkaline pH levels (pH 7-9). For example, cerium removes 30% to 34% of COD at a pH range of 7-9. Alum, on the other hand, displays a more variable COD removal efficiency, ranging from 0% at lower pH to up to 30% removal at higher pH. The improved COD removal with increasing pH for both cerium and alum could be associated with better floc formation and subsequent adsorption of organic matter. When Ce³⁺ or Al³⁺ is added to water, they dissociate into positively charged metal ions and hydroxides. These positively charged ions neutralize the negative charges on the organic matter, allowing the particles to aggregate into larger clumps (flocs), which are easier to remove via sedimentation. However, this process is weakened at low pH [
31].
During coagulation with cerium, the final pH values generally decreased slightly, with the pH dropping by about 1-2 units. For example, an initial pH of 4.0 resulted in a final pH of 3.0, while an initial pH of 9.0 resulted in a final pH of 5.9. In contrast, alum exhibited a more significant drop in pH after coagulation, particularly at higher initial pH levels. For instance, an initial pH of 9.0 decreased to a final pH of around 5.1, and an initial pH of 7.0 dropped to around 4.3 after treatment. This substantial reduction in pH is likely due to the release of acidic species during the hydrolysis of coagulants, which consume alkalinity, thus leading to a more pronounced decrease in pH [
32].
3.2. Phosphorus Precipitation
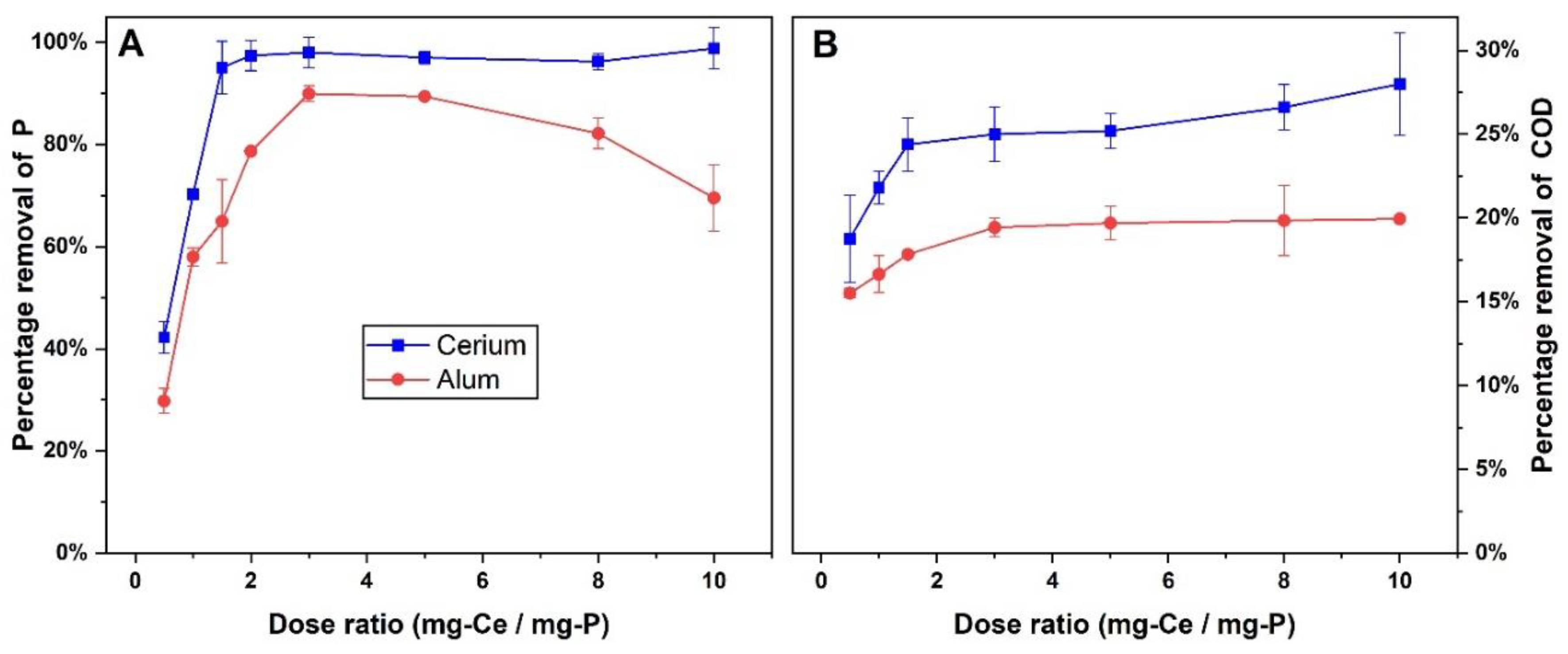
The results, as shown in
Figure 2A, demonstrate that cerium is highly effective in removing PO₄³⁻-P from wastewater, with removal efficiencies reaching as high as 98.9%. At a dose ratio of 1.5 mg-Ce/mg-P, cerium achieves approximately 95.1% phosphorus removal, and this efficiency continues to increase with higher doses, peaking at 98.9% at a dose ratio of 10 mg-Ce/mg-P. Beyond this point, the removal efficiency remains relatively stable, indicating that cerium is capable of maintaining high phosphorus removal across a wide range of dosages. The rapid increase in removal efficiency at low doses followed by stabilization at higher doses suggests that cerium has a strong affinity for phosphate ions, which allows for efficient precipitation even at lower concentrations. This robust performance can be attributed to cerium’s ability to form stable cerium phosphate (CePO₄) precipitates, which effectively capture and remove phosphate from solution [
27].
In contrast, alum exhibits a more gradual increase in phosphorus removal as the dose ratio increases. At a low dose ratio of 1.0 mg-Al/mg-P, alum removes approximately 64.8% of PO₄³⁻-P, and this gradually increases to around 89.5% at a dose ratio of 5 mg-Al/mg-P. However, further increases in the dose ratio do not significantly improve phosphorus removal, and at the highest tested dose of 10 mg-Al/mg-P, the removal efficiency decreases to 69.6%. This suggests that alum’s effectiveness may be limited by its ability to maintain stable floc formation at higher dosages. Additionally, the drop in pH associated with alum hydrolysis may hinder the coagulation process, as lower pH levels facilitate the formation of less negatively charged phosphorus species like H₂PO₄⁻ and H₃PO₄, which are not as easily precipitated by positively charged metal ions [
33].
3.3. COD Removal
For COD removal, shown in
Figure 2B, both cerium and alum demonstrate moderate efficiencies, with cerium consistently outperforming alum across most dose ratios. Cerium achieves its highest COD removal of approximately 27.9% at a dose ratio of 10 mg-Ce/mg-P, which correlates with the upper end of the dose range used for phosphorus removal. Interestingly, at lower dose ratios (1.5 mg-Ce/mg-P), cerium achieves around 24% COD removal, and this efficiency remains relatively stable as the dose increases. This suggests that cerium’s ability to remove organic matter, as measured by COD, is moderately effective, though not as pronounced as its phosphorus removal capability. The relatively stable COD removal at higher doses could indicate that cerium’s ability to adsorb and precipitate organic matter is largely dependent on the available surface area of the flocs formed during coagulation.
In comparison, alum shows a peak COD removal of approximately 19.9% at its highest dose ratio of 10 mg-Al/mg-P. However, as with phosphorus removal, the COD removal efficiency tends to plateau at higher dose ratios. Alum achieves around 15.5% COD removal at a dose ratio of 0.5 mg-Al/mg-P, and while this improves slightly with increasing doses, the performance remains relatively limited. This could be due to alum’s reduced efficiency in removing certain types of dissolved organic matter, or its inability to maintain effective coagulation at very high dosages, possibly due to excessive pH reduction caused by alum hydrolysis [
31]. Overall, cerium demonstrates superior performance in both phosphorus and COD removal, requiring lower dosages to achieve higher removal efficiencies compared to alum. The ideal dose for cerium is 1.5 mg-Ce/mg-P, at which point approximately 24.4% COD removal is achieved, alongside high phosphorus removal of around 95.1%. In contrast, alum’s optimum dose for phosphorus removal is 3.0 mg-Al/mg-P, where approximately 17.3% COD removal is observed. Beyond these dose points, the effectiveness of both coagulants for COD removal remains relatively stable; however, cerium consistently maintains higher removal efficiencies compared to alum. Additionally, while cerium’s effectiveness is sustained at higher dosages, alum’s performance tends to decrease, particularly for phosphorus, at higher dose ratios. This suggests that cerium may offer a more reliable and efficient alternative to alum for treating wastewater with high levels of phosphorus and organic matter.
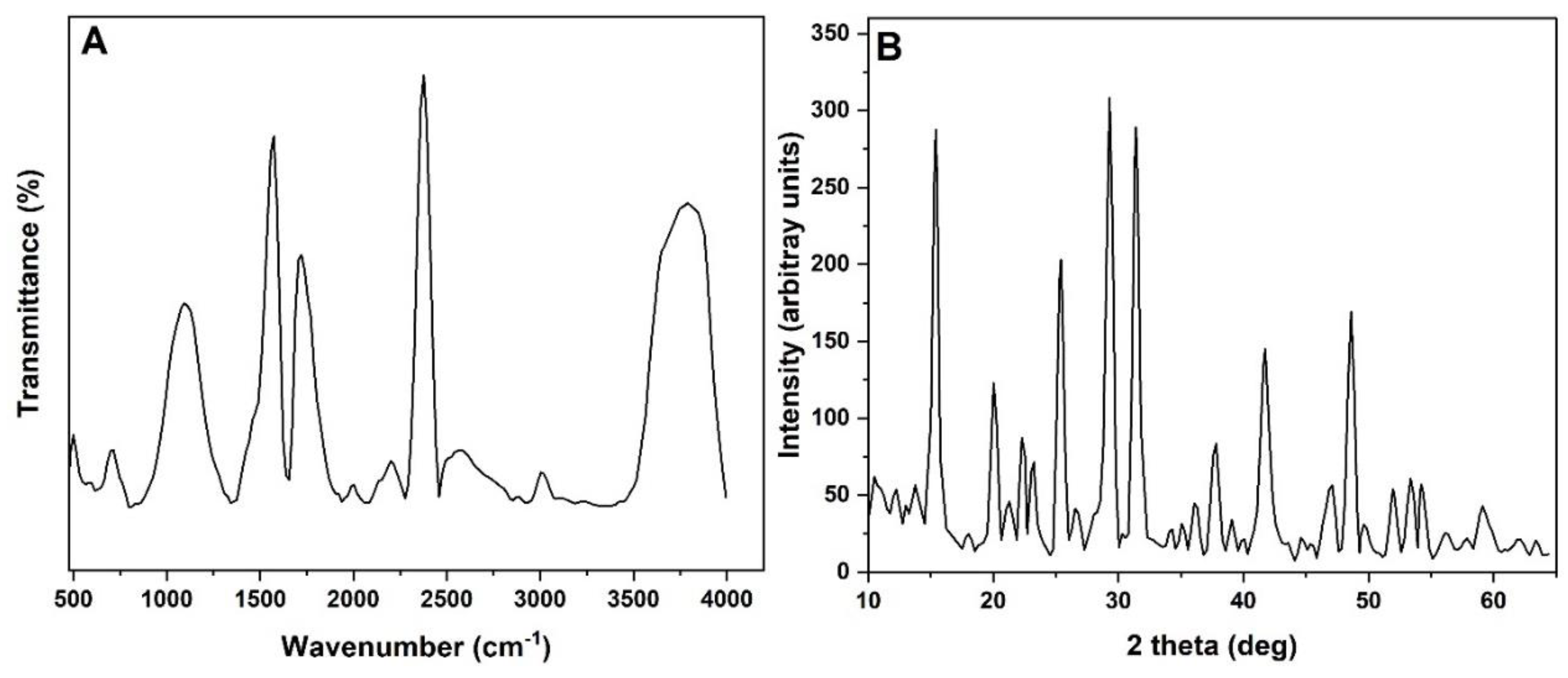
3.4. FTIR and XRD Analysis
The FTIR spectrum of the precipitates shows characteristic peaks that can be attributed to the formation of CePO₄, indicating the presence of cerium phosphate. The key peaks observed in the spectrum are as follows:
650 cm⁻¹: This peak is typically associated with metal-oxygen (M-O) vibrations, specifically related to Ce–O bonding. The presence of this peak suggests that cerium ions are interacting with oxygen atoms, which is a strong indicator of the formation of cerium oxide or cerium phosphate structures in the precipitates.
1040 cm⁻¹: This peak is indicative of the P-O stretching vibrations from phosphate groups. The position of the peak at this wavenumber aligns well with the expected phosphate bonds (PO₄³⁻) in the cerium phosphate compound (CePO₄). Phosphorus bonding to oxygen in this structure is crucial for nutrient removal as it reflects the capture of phosphate ions from the water.
1664 cm⁻¹: This peak corresponds to bending vibrations of adsorbed water molecules (H-O-H bending). It indicates that some water is likely associated with the surface of the precipitates or within the structure. While water adsorption is common in precipitates, the presence of water molecules could also affect the overall crystal structure of the material.
2340 cm⁻¹: This peak may be attributed to carbonate species that could have been adsorbed onto the surface of the precipitates. Carbonate interactions might interfere slightly with the adsorption capacity of phosphate, although this is less significant compared to the formation of CePO₄.
3800 cm⁻¹: This peak is associated with O-H stretching vibrations, which could represent hydroxyl groups (OH⁻) bound to the surface of the precipitates. The presence of hydroxyl groups indicates surface reactivity and the possibility of further interactions with other ions, such as phosphate or organic matter in the water treatment process.
Figure 3.
(A) FTIR and (B) XRD results of precipitates. The precipitates indicate close responsibleness to CePO4 compound.
Figure 3.
(A) FTIR and (B) XRD results of precipitates. The precipitates indicate close responsibleness to CePO4 compound.
The XRD pattern of the precipitates reveals several sharp peaks, confirming the crystalline nature of the material. The diffraction peaks correspond to the characteristic reflections of the CePO₄ structure. The lattice parameters for the crystal structure are calculated as a=b=7.144A˚ and c=6.2814 A, which align with the hexagonal structure typical of cerium phosphate (monazite-type CePO₄). The peaks observed at 2θ values corresponding to approximately 26°, 28°, and 32° are significant and confirm the crystalline cerium phosphate phase. These peaks are indicative of the ordered arrangement of cerium and phosphate ions in the crystal lattice, confirming that the precipitate consists of CePO₄.
4. Implications for Water Treatment
The formation of crystalline CePO₄, as confirmed by the FTIR and XRD results, has significant implications for water treatment, particularly when compared with traditional coagulants such as alum (Al₂(SO₄)₃). The strong bonding between cerium and phosphate, as indicated by the 1040 cm⁻¹ peak in the FTIR spectrum, ensures effective capture and immobilization of phosphate ions, leading to efficient nutrient removal. Additionally, the stable crystalline structure of CePO₄, with its well-defined lattice parameters, enhances its ability to precipitate phosphate and maintain a high removal efficiency, even at relatively low dosages.
When comparing cerium with alum, one of the key advantages of cerium coagulants is their ability to maintain stable performance across a wide pH range. The experimental results show that cerium achieves high phosphorus removal (up to 98.9%) at dose ratios as low as 1.5 mg-Ce/mg-P. This optimal removal is achieved while maintaining performance across varying pH levels, making cerium robust and efficient. In contrast, alum is highly sensitive to pH changes. Its optimal phosphorus removal performance occurs around a neutral pH, with maximum removal of around 89.5% at a dose ratio of 5 mg-Al/mg-P. However, as the pH decreases, particularly below 5, the removal efficiency declines significantly due to alum's tendency to lower the pH through hydrolysis. This causes the formation of less effective flocs and releases H₂PO₄⁻ and H₃PO₄ species, which are less efficiently captured by alum.
The significant reduction in pH with alum necessitates the addition of alkaline agents, such as lime or sodium hydroxide, to maintain a suitable pH for effective coagulation. This additional step increases both the complexity and cost of the treatment process. By contrast, cerium coagulants have minimal impact on pH, reducing the need for pH adjustment. Even at higher doses, cerium does not significantly acidify the water, thereby eliminating the need for extra chemicals to buffer the pH. This translates into a more cost-effective treatment process, as the overall chemical consumption is reduced.
Moreover, cerium’s ability to achieve high phosphorus removal while also providing significant COD removal at lower dosages compared to alum further enhances its cost-effectiveness. The ideal dose for cerium is 1.5 mg-Ce/mg-P, where approximately 24.4% COD removal is achieved. In comparison, alum requires a higher dose of 3 mg-Al/mg-P to reach its peak COD removal of around 19.9%. This lower required dose for cerium means that less chemical is needed to achieve the same or better nutrient removal performance, reducing the operational costs of water treatment.
An additional benefit of using cerium coagulants is that the captured CePO₄ precipitates can potentially serve as a source of phosphorus for agriculture owing to its low toxicity [
34]. The recovered CePO₄ could be repurposed as a nutrient-rich fertilizer, promoting sustainable agricultural practices and supporting a circular economy by turning waste into a valuable resource. This not only contributes to nutrient recycling but also reduces the environmental impact of wastewater treatment by providing an alternative to synthetic fertilizers.
Overall, cerium coagulants not only offer superior performance in phosphorus and organic matter removal but also provide significant operational, cost, and sustainability advantages. Cerium's minimal sensitivity to pH fluctuations reduces the need for additional chemicals, lowering treatment costs and simplifying the water treatment process. In contrast, alum’s high dependency on pH control and the necessity for additional chemicals make it a less efficient and more expensive option in water treatment, particularly in systems with varying pH levels. The potential of CePO₄ as a nutrient source for agriculture adds another dimension of sustainability, making cerium a more attractive and sustainable alternative for wastewater treatment.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interests.
References
- Bratby, J. Coagulation and flocculation in water and wastewater treatment; 3rd ed.; IWA Publishing: London, 2016; ISBN 9781780407494.
- Yang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qian, J.; Chen, G. Municipal wastewater phosphorus removal by coagulation. Environ. Technol. 2010, 31, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, Y. Enhanced phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater by coagulation with alum and iron salts. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, iCBBE 2010; 2010.
- Metcalf & Eddy Wastewater Engineering, Treatment and Resource Recovery; 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, NY, USA, 2014.
- Crittenden, J.C.; Trussell, R.R.; Hand, D.W.; Howe, K.J.; Tchobanoglous, G. MWH’s Water Treatment: Principles and Design; 3rd, Ed.; 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, 2012; ISBN 9780470405390.
- Muisa, N.; Nhapi, I.; Ruziwa, W.; Manyuchi, M.M. Utilization of alum sludge as adsorbent for phosphorus removal in municipal wastewater: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, K.B.; Jayasinghe, G.Y.; Surapaneni, A.; Hetherington, C. A review on alum sludge reuse with special reference to agricultural applications and future challenges. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.H.; Liu, Z.; Cui, L.; Yu, A.; Feng, Q.; Yang, H. Enhanced coagulation of ferric chloride aided by tannic acid for phosphorus removal from wastewater. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caravelli, A.H.; De Gregorio, C.; Zaritzky, N.E. Effect of operating conditions on the chemical phosphorus removal using ferric chloride by evaluating orthophosphate precipitation and sedimentation of formed precipitates in batch and continuous systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerjian, L.; Ayoub, G.M. High-pH-magnesium coagulation-flocculation in wastewater treatment. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Wu, F.; Liu, G.; Mu, Y.; Feng, C.; Wang, H.; Giesy, J.P. Removal of phosphate from eutrophic lakes through adsorption by in situ formation of magnesium hydroxide from diatomite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, X.; Duan, H.; Hu, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, M. Multifaceted benefits of magnesium hydroxide dosing in sewer systems: Impacts on downstream wastewater treatment processes. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haxel, G.B.; Hedrick, J.B.; Orris, G.J. Rare Earth Elements — Critical Resources for High Technology; 2002.
- Kolker, A.; Lefticariu, L.; Anderson, S.T. Rare Earth Metals and Minerals Industries. In Rare Earth Metals and Minerals Industries; Murty, Y. V, Alvin, M.A., Lifton, J.., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2024 ISBN 978-3-031-31867-2.
- Chen, P.; Ilton, E.S.; Wang, Z.; Rosso, K.M.; Zhang, X. Global Rare Earth Element Resources: A Concise Review. Appl. Geochemistry 2024, 106158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Fan, H.R.; Liu, X.; Meng, J.; Butcher, A.R.; Yann, L.; Yang, K.F.; Li, X.C. Global rare earth elements projects: New developments and supply chains. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 157, 105428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz, A.; Chrzanowska, A.; Kierys, A. Highly Porous Ceria as an Adsorbent for Removing Artificial Dyes from Water. Environ. Process. 2024, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, M. Cerium oxide based materials for water treatment—A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, B.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, W.; Fu, M.L.; Yuan, B. Magnetic modification of cerium organic frame materials to improve the phosphorus adsorption performance: Modulating the valence state. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhooshani, K.R. Adsorption of chlorinated organic compounds from water with cerium oxide-activated carbon composite. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, J.K.; Gupta, S.K. Exceptional adsorption of different spectral indices of natural organic matter (NOM) by using cerium oxide nanoparticles (CONPs). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 45496–45505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gran, S.; Aziz, R.; Rafiq, M.T.; Abbasi, M.; Qayyum, A.; Elnaggar, A.Y.; Elganzory, H.H.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Hussein, E.E. Development of Cerium Oxide/Corncob Nanocomposite: A Cost-Effective and Eco-Friendly Adsorbent for the Removal of Heavy Metals. Polym. 2021, Vol. 13, Page 4464 2021, 13, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Xia, W.; Qu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Xiong, W.; Cheng, M.; Song, B.; et al. Structure–performance correlation guided cerium-based metal–organic frameworks: Superior adsorbents for fluoride removal in water. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Lai, B.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L. The enhanced removal of phosphate by structural defects and competitive fluoride adsorption on cerium-based adsorbent. Chemosphere 2020, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Qu, J.; Li, H.; Lim, T.C.; Liu, C. Effect of cerium valence on As(V) adsorption by cerium-doped titanium dioxide adsorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 175, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajjumba, G.W.; Marti, E.J. A review of the application of cerium and lanthanum in phosphorus removal during wastewater treatment: Characteristics, mechanism, and recovery. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajjumba, G.W.; Fischer, D.; Risso, L.; Koury, D.; Marti, E.J. Application of cerium and lanthanum coagulants in wastewater treatment—a comparative assessment to magnesium, aluminum, and iron coagulants. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 131268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q. Coagulation performance and residual aluminum speciation of Al2(SO4)3 and polyaluminum chloride (PAC) in Yellow River water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernitsky, D.J.; Edzwald, J.K. Selection of alum and polyaluminum coagulants: Principles and applications. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2006, 55, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, L.B.; Kissel, D.E. Ammonia Volatilization from Surface Applications of Ammonium Compounds on Calcareous Soils: I. General Theory. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1973, 37, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharuddin, S.M.; Othman, N.; Al-Maqtari, Q.A.; Al-towayti, W.A.H.; Arifin, S.N.H. The assessment of coagulation and flocculation performance and interpretation of mechanistic behavior of suspended particles aggregation by alum assisted by tapioca peel starch. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Wang, D.; Yu, J.; Ni, J.; Edwards, M.; Qu, J. Enhanced coagulation with polyaluminum chlorides: Role of pH/Alkalinity and speciation. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Wang, C.; Pei, Y. Comparison of different phosphate species adsorption by ferric and alum water treatment residuals. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2013, 25, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajjumba, G.W.; Attene-Ramos, M.; Marti, E.J. Toxicity of lanthanide coagulants assessed using four in vitro bioassays. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).