Submitted:
13 January 2025
Posted:
14 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
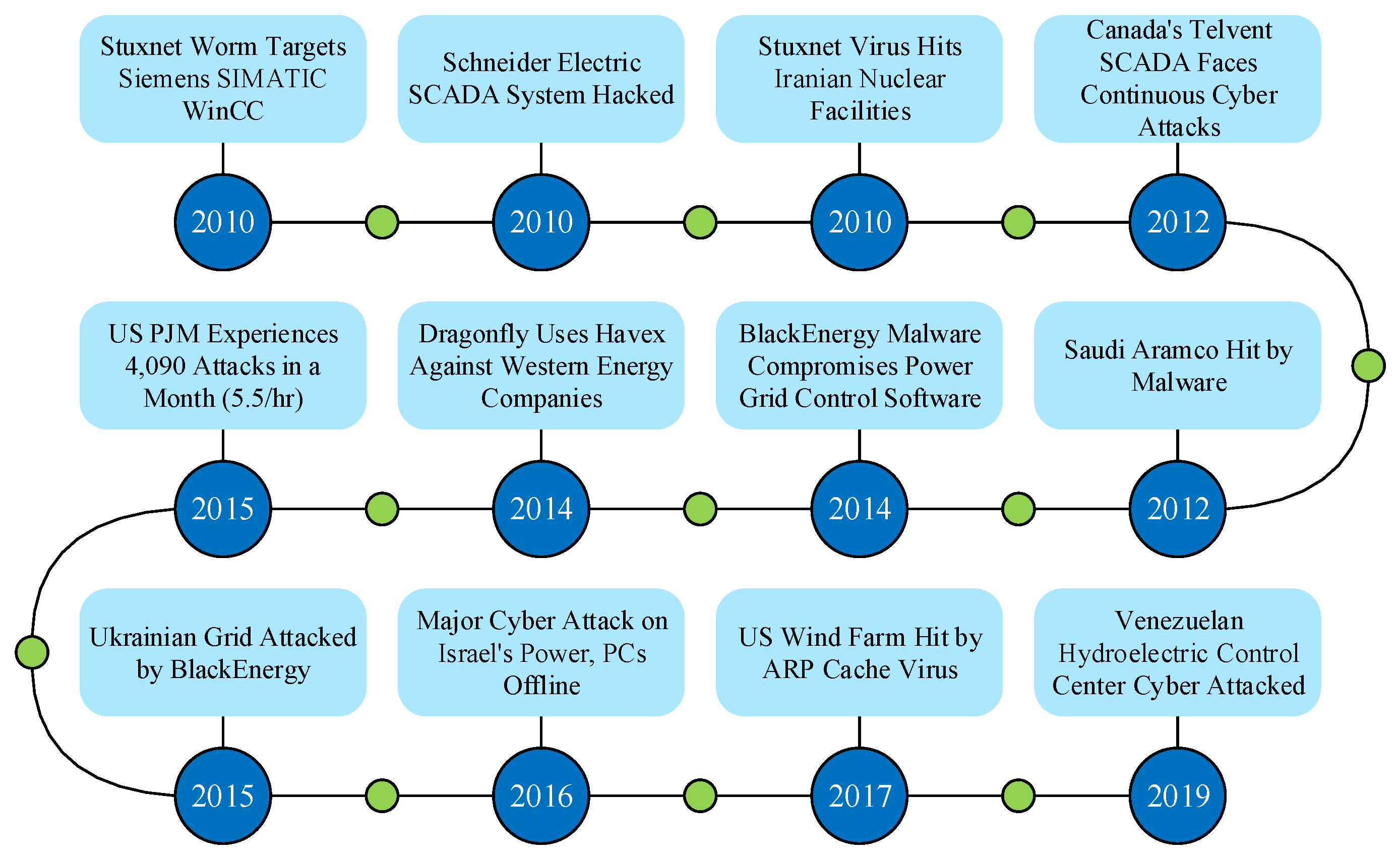
2. Domestic and International Research Status
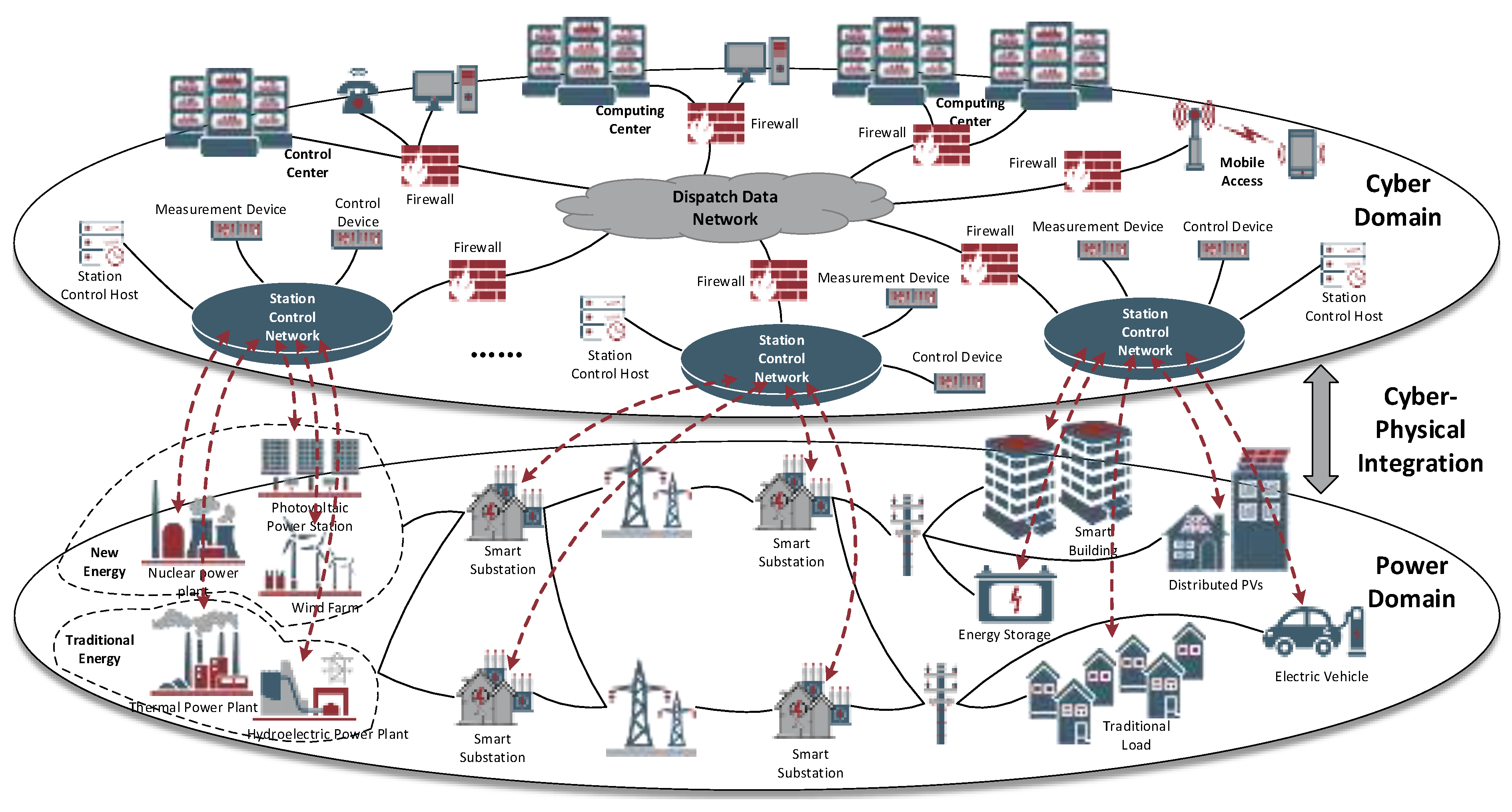
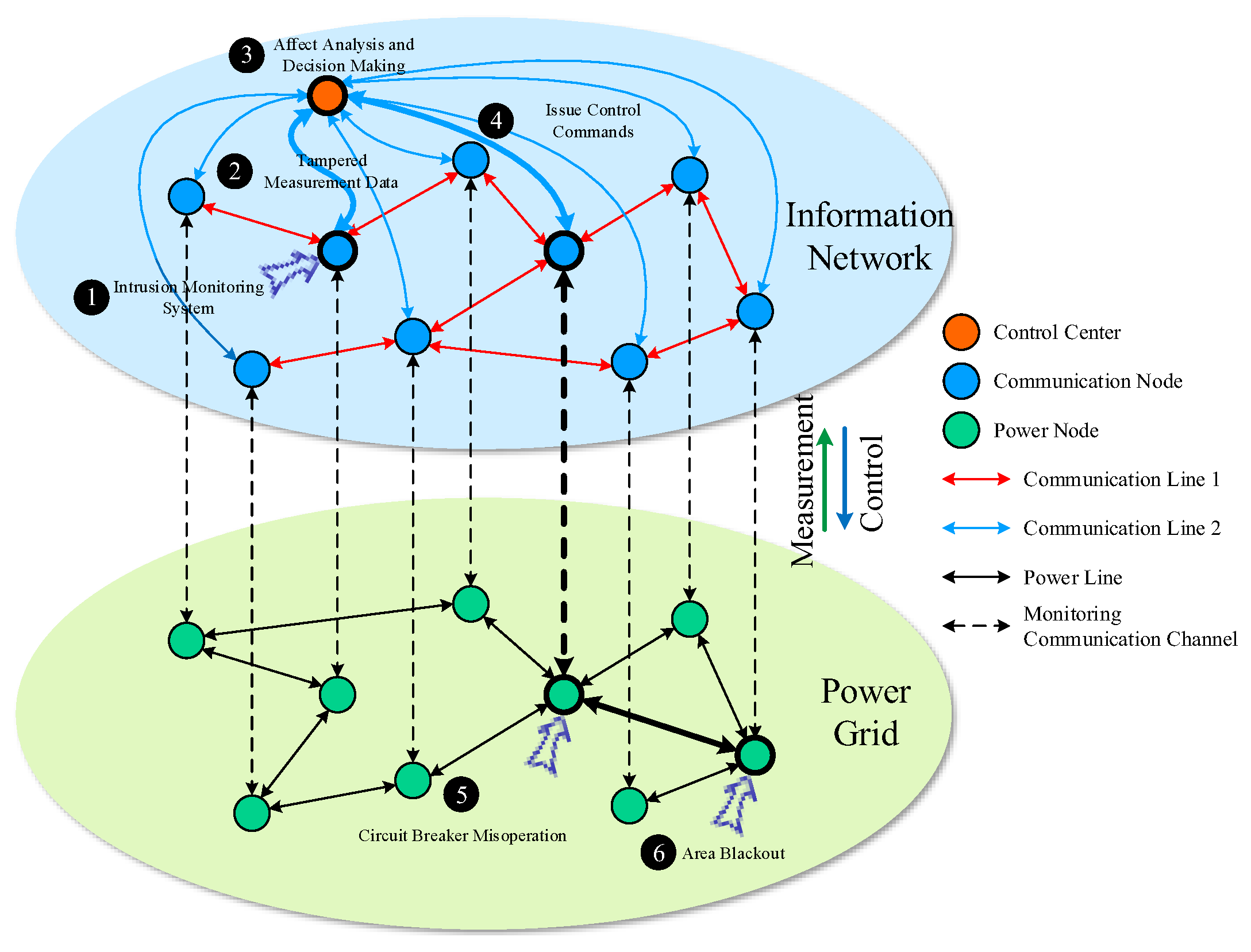
2.1. Power CPS Data Transmission Scenarios and False Data Injection Methods
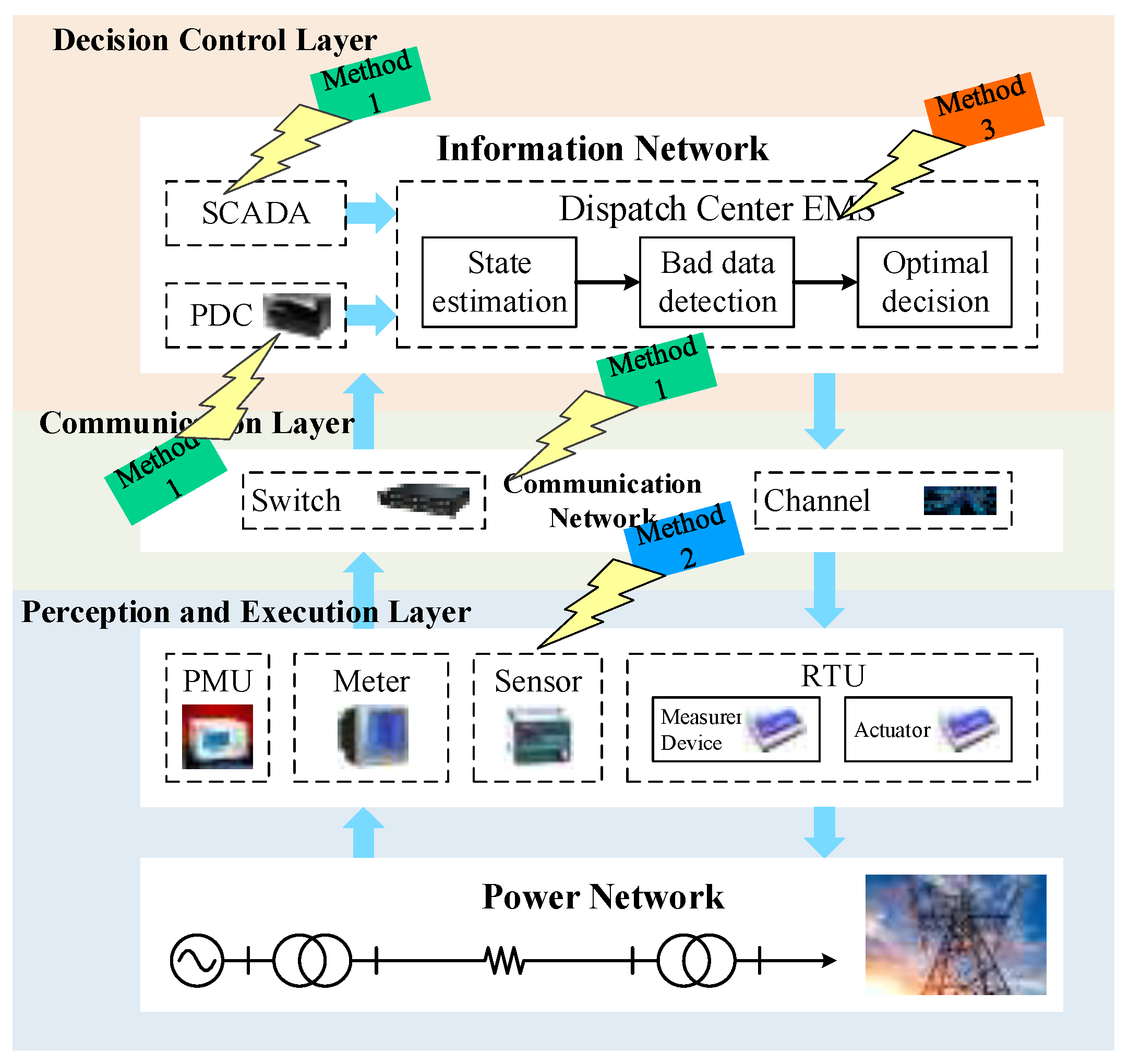
2.1.1. Information Communication Network Data Injection Attacks
2.1.2. Remote Terminal Device Data Injection Attacks
| Attack Phase | Attack Type | Attack Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Device Management Function | FDIAs targeting the device itself | Modification of device settings |
| Data Collection Process | FDIAs targeting measurement devices | Errors in collected switch and analog signals |
| Command Control Process | FDIAs targeting execution devices | Incorrect execution of control commands |
2.2. Current Research Status on False Data Injection Attacks in Power CPS
2.2.1. Characterization of the FDIA Evolutionary Process
2.2.2. FDIA Detection Training Data Enhancement
2.2.3. FDIA Detection Approaches
2.2.4. FDIAs Data Reconstruction in Power CPS
2.3. Challenges in Research on FDIAs in Power CPS
3. Future Research Directions
3.1. Comprehensive Characterization of FDIA Temporal-Spatial Evolution
3.2. Hybrid Detection Frameworks Integrating Model- and Data-Driven Approaches
3.3. Advanced Data Augmentation for FDIA Detection
3.4. Resilient Data Reconstruction Techniques
3.5. Information Security in Integrated Energy Systems
3.6. Integration of Emerging Technologies
3.7. Policy and Standardization
4. Conlcusions
References
- Zhou X, Chen S, Lu Z, et al. Technical Characteristics of China’s New Generation Power System during Energy Transition [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(7): 1893-1904.
- Guo Q, Xin S, Sun H, et al. Cyber-Physical Integration Modeling and Comprehensive Security Assessment of Power Systems: Drivers and Research Concepts [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(6): 1481-1489.
- Qu Z, Dong Y, Qu N, et al. Quantitative Assessment of Survivability of Power CPS Considering Load Optimization and Reconfiguration [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(6): 15-24.
- Qu Z, Zhao T, Zhang Y, et al. Determination Method of Network Risk Propagation Threshold in Power CPS Based on Percolation Theory [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(4): 16-23.
- Wang L, Qu Z, Li Y, et al. Method for Extracting Patterns of Coordinated Network Attacks on Electric Power CPS Based on Temporal-Topological Correlation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 57260-57272. [CrossRef]
- Qin B, Liu D. Research Progress and Prospects on Analysis and Control of Power Grid Cyber-Physical Systems [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(18): 5816-5826.
- Haes Alhelou H, Hamedani-Golshan M, Njenda T, et al. A Survey on Power System Blackout and Cascading Events: Research Motivations and Challenges[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(4): 682. [CrossRef]
- Yu T, Cheng L, Zhang X. Decentralized Microgrid Based on Integration of Information-Physical-Social Systems and Swarm Machine Learning: Theoretical Research and Analysis of Key Scientific Issues [J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2019, 49(12): 1541-1569.
- Ilić M, Xie L, Khan U, et al. Modeling of Future Cyber-Physical Energy Systems for Distributed Sensing and Control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part A: Systems and Humans, 2010, 40(4): 825-838. [CrossRef]
- Ilić M, Xie L, Khan U, et al. Modeling Future Cyber-Physical Energy Systems[C]// 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting - Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, 20-24 July 2008, Pittsburgh, PA, USA: 1-8.
- Zhao J, Wen F, Xue Y, et al. Research Framework for Modeling Analysis and Control of Cyber-Physical Systems in Power Engineering [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2011, 35(16): 1-8.
- Wang T, Sun C, Gu X, et al. Modeling of Power Communication Coupled Networks and Their Vulnerability Analysis [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(12): 3556-3567.
- Xu C, Abur A. A Massively Parallel Framework for Very Large Scale Linear State Estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2017, 33(4): 4407-4413. [CrossRef]
- Kurt M, Yılmaz Y, Wang X, et al. Distributed Quickest Detection of Cyber-Attacks in Smart Grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(8): 2015-2030. [CrossRef]
- BaSin D, Cremers C, Kim T, et al. Design, Analysis, and Implementation of ARPKI: an Attack-Resilient Public-Key Infrastructure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2016, 15(3): 393-408. [CrossRef]
- Lin H, Slagell A, Kalbarczyk Z, et al. Runtime Semantic Security Analysis to Detect and Mitigate Control-Related Attacks in Power Grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 9(1): 163-178. [CrossRef]
- Qu Z, Zhang Y, Qu N, et al. Method for Quantitative Estimation of the Risk Propagation Threshold in Electric Power CPS Based on Seepage Probability[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 68813-68823. [CrossRef]
- Qu Z, Bo X, Yu T, et al. Active and Passive Hybrid Detection Method for Power CPS False Data Injection Attacks with Improved AKF and GRU-CNN[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2022, 16: 1490-1508. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Xu P, Qu Z, et al. Coordinated Cyber-Attack Detection Model of Cyber-Physical Power System Based on the Operating State Data Link[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2021, 9: 666130. [CrossRef]
- Bo X, Chen X, Li H, et al. Modeling Method for the Coupling Relations of Microgrid Cyber-Physical Systems Driven by Hybrid Spatiotemporal Events[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 19619-19631. [CrossRef]
- Qu Z, Xie Q, Liu Y, et al. Power Cyber-Physical System Risk Area Prediction Using Dependent Markov Chain and Improved Grey Wolf Optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 82844-82854. [CrossRef]
- Wei J, Kundur D, Zourntos T, et al. A Flocking-Based Paradigm for Hierarchical Cyber-Physical Smart Grid Modeling and Control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2014, 5(6): 2687-2700. [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber R. Flocking for Multi-Agent Dynamic Systems: Algorithms and Theoty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006, 51(3): 401-420.
- Wang Y, Liu D, Lu Y. Research on Hybrid System Modeling Methods for Power Grid Cyber-Physical Systems [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(6): 1464-1470.
- Lian X, Zhang W, Qian T, et al. Vulnerability Assessment Method for Power Cyber-Physical Systems Considering Information Node Failures [J]. Global Energy Interconnection, 2019, 2(6): 523-529.
- Lai K, Illindala M, Subramaniam K. A tri-level optimization model to mitigate coordinated attacks on electric power systems in a cyber-physical environment[J]. Applied energy, 2019, 235(FEB.1): 204-218. [CrossRef]
- Xin S, Guo Q, Sun H, et al. Cyber-Physical Modeling and Cyber-Contingency Assessment of Hierarchical Control Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6(5): 2375-2385. [CrossRef]
- Guo Q, Xin S, Wang J, et al. Comprehensive Security Assessment of Information-Energy Systems from the Ukraine Blackout Incident [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(5): 145-147.
- Liu X, Wu Z. Research on Online Defense against Stealthy Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(8): 2546-2558.
- Xue Y, Ni M, Yu W. Approach for Studying the Impact of Communication Failures on Power Grid[C]// 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), 17-21 July 2016, Boston, MA, USA: 1-5.
- Yu W, Xue Y, Luo J, et al. An UHV Grid Security and Stability Defense System: Considering the Risk of Power System Communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(1): 491-500. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Ning P, Reiter M. False Data Injection Attacks against State Estimation in Electric Power Grids[J]. ACM Transactions on Information and System Security (TISSEC), 2011, 14(1): 1-16.
- Li Y, Ma W, Li Y, et al. Enhancing Cyber-Resilience in Integrated Energy System Scheduling with Demand Response Using Deep Reinforcement Learning[J]. Applied Energy, 2025, 379:124831.
- Liang J, Sankar L, Kosut O. Vulnerability Analysis and Consequences of False Data Injection Attack on Power System State Estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 31(5): 3864-3872. [CrossRef]
- Xie L, Mo Y, Sinopoli B. False Data Injection Attacks in Electricity Markets[C]// 2010 First IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, 04-06 October 2010, Gaithersburg, MD, USA: 226-231.
- Liu S, Tan Y, Zhao F, et al. Coupled Modeling Method for Power Information Systems [J]. Journal of Power Systems and Automation, 2021, 33(3): 89-93.
- Ma S, Xu Z, Wang L. Construction Method of Power Grid Cyber-Physical System Model Based on Set Theory [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(6): 1-5.
- Qu Z, Dong Y, Li Y, et al. Localization of Dummy Data Injection Attacks in Power Systems Considering Incomplete Topological Information: A Spatio-Temporal Graph Wavelet Convolutional Neural Network Approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 360: 122736. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Wei X, Li Y, et al. Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grid: A Secure Federated Deep Learning Approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2022, 13(6): 4862-4872.
- Wang L, Qu Z, Li Y, et al. Method for Extracting Patterns of Coordinated Network Attacks on Electric Power CPS Based on Temporal–Topological Correlation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 57260-57272. [CrossRef]
- Qu Z, Dong Y, Qu N, et al. Survivability Evaluation Method for Cascading Failure of Electric Cyber Physical System Considering Load Optimal Allocation[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019, 2019: 2817586. [CrossRef]
- Qu Z, Qu N, Zhou Y, et al. Extraction of Typical Operating Scenarios of New Power System Based on Deep Time Series Aggregation[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2024, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Gu S, Wang Y, et al. Stacked Autoencoder Framework of False Data Injection Attack Detection in Smart Grid[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021(1): 2014345. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Li Z, Chen L, et al. A false data injection attack method for generator dynamic state estimation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34: 3651-3660.
- Zhao J, Srivastava A, Guo Y, et al. State Estimation for Integrated Energy Systems: Motivations, Advances, and Future Work[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2024: 1 -17. [CrossRef]
- Dai Q, Shi L, Ni Y. Risk Assessment for Cyberattack in Active Distribution Systems Considering the Role of Feeder Automation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34(4): 3230-3240. [CrossRef]
- Tian M, Dong Z, Wang X, et al. Analysis of Coordinated Cyber-Physical Attacks on Power Systems under Goal Conflicts [J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(7): 2336-2344.
- Wang X, Tian M, Cao M, et al. Countermeasures to False Data Injection Attacks On Power System State Estimation Based On Protecting Measurements[J]. Journal of Nanoelectronics and Optoelectronics, 2019, 14(5): 626-634. [CrossRef]
- Drayer E, Routtenberg T. Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids Based on Graph Signal Processing[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(2): 1886-1896. [CrossRef]
- Xue Y, Li M, Luo J, et al. Coupled Modeling Method of Power Grid Cyber-Physical Systems Based on Correlation Characteristic Matrix [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(2): 11-19.
- Shen Y, Zhang W, Ni H, et al. Guaranteed Cost Control of Networked Control Systems with DoS Attack and Time-varying Delay[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2019, 17(4): 811-821. [CrossRef]
- Nath S, Akingeneye I, Wu J, et al. Quickest Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grid with Dynamic Models[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2022, 10(1): 1292-1302. [CrossRef]
- Rawat D, Bajracharya C. Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grid Communication Systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(10): 1652-1656. [CrossRef]
- Jokar P, Leung V. Intrusion Detection and Prevention for ZigBee-Based Home Area Networks in Smart Grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018: 9(3): 1800-1811.
- Wang Z, Chen Y, Zeng J, et al. Modeling and Reliability Assessment of Microgrid Cyber-Physical Systems for Fully Distributed Control [J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(7): 2413-2421.
- Wang C, Dong X, Sun H, et al. Modeling Method of Power Cyber-Physical Systems Considering Multi-layer Coupling Characteristics [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(3): 83-91.
- Tang Y, Li M, Wang Q, et al. A Review of Network Attacks and Defense Research in Power Cyber-Physical Systems (Part II: Detection and Protection) [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(10): 1-9+18.
- Zhao J, Wen F, Xue Y, et al. Architecture and Implementation Technologies and Challenges of Grid CPS [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2010, 34(16): 1-7.
- He R, Wang D, Zhang Y, et al. Research on Modeling and Static Computation Methods of Information Flow in Smart Grids [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(6): 1527-1535.
- Li Y, Yang Z. Application of EOS-ELM with Binary Jaya-Based Feature Selection to Real-Time Transient Stability Assessment Using PMU Data[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 23092-23101. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Li Z, Chen L. Dynamic State Estimation of Generators Under Cyber Attacks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 125252-125267. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Zhang Y, Cai Z, et al. Network Information Flow Tide Model and Computational Method for Smart Substation Process Layer [J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37(9): 2602-2607.
- Zhang Y, Cai Z, Li X, et al. Analytical Modeling of traffic Flow in the Substation Communication Network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2015, 30(5): 2119-2127. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Li J, Qi J, et al. Robust Cubature Kalman Filter for Dynamic State Estimation of Synchronous Machines Under Unknown Measurement Noise Statistics[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 29139-29148. [CrossRef]
- Buldyrev S, Parshani R, Paul G, et al. Catastrophic cascade of failures in interdependent networks[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7291): 1025-1028. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Gao K, Zhao T, et al. Cross-Space Cascading Failure Hazard Assessment of Power Cyber-Physical Systems Based on Improved Attack Graph [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(6): 1490-1499.
- Chen Y, Zhu Z, Lu X, et al. Intelligent Space Modeling Method Based on Information-Physical Space Mapping [J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2013, 25(2): 216-219+227.
- Ji X, Wang B, Dong C, et al. Vulnerability Assessment and Edge Protection Strategy for Power Information-Physical Interdependent Networks [J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(6): 1867-1873.
- Cai Ye, Cao Yijia, Li Yong, et al. Cascading failure analysis considering interaction between power grids and communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(1): 530-538.
- Wang Y, Lin Z, Liang X, et al. On modeling of electrical cyber-physical systems considering cyber security[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2016, 17(5): 465-478. [CrossRef]
- Wang L. Research on Cyber-Physical Coordinated Attack Detection and Sequence Pattern Mining Methods [D]. Jilin: Northeast Electric Power University, 2021.
- Li Y, Zhang S, Li Y, et al. PMU Measurements Based Short-Term Voltage Stability Assessment of Power Systems via Deep Transfer Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 2526111.
- Cao Y, Zhang Y, Bao Z, et al. Chain Failure Analysis under the Interactive Impact of Power System and Communication Network [J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2013, 33(1): 7-11.
- Sridhar S, Hahn A, Govindarasu M. Cyber-Physical System Security for the Electric Power Grid[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(1): 210-224. [CrossRef]
- Tang Y, Han X, Wu Y, et al. Comprehensive Vulnerability Assessment of Power Systems Considering the Impact of Communication Systems [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(23): 6066-6074.
- Xiong X, Hu S, Sun D, et al. Detection of false data injection attack in power information physical system based on SVM-GAB algorithm[J]. Energy Reports, 2022, 8(5): 1156-1164. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpourfard M, Sami A, Seifi A. A statistical unsupervised method against false data injection attacks: A visualization-based approach. Expert Systems With Applications[J]. 2017, 84: 242-261. [CrossRef]
- Wu T, Xue W, Wang H, et al. Extreme Learning Machine-Based State Reconstruction for Automatic Attack Filtering in Cyber Physical Power System[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(3): 1892-1904. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Chen Y, Liu F, et al. Power System Security Under False Data Injection Attacks With Exploitation and Exploration Based on Reinforcement Learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 48785-48796. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Huang S, Liu F, et al. Evaluation of Reinforcement Learning-Based False Data Injection Attack to Automatic Voltage Control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(2): 2158-2169. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Wang Y. Evolution Mechanism and Active Defense Exploration of Cross-Domain Cascading Failures in New Power Systems [J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55(2): 62-72+81.
- Wang Y. Research on Detection and Defense Against False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids [D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2020.
- Xue Y, Yu X. Beyond Smart Grid-Cyber-Physical-Social System in Energy Future[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(12): 2290-2292.
- Gao K, Wang Y, Zhao T, et al. Exploration of Information-Physical Interaction Mechanisms in the Operation of Power Cyber-Physical Systems [J]. Power System Technology, 2018, 42(10): 3101-3109.
- Liu T, Sun Y, Yang L, et al. Abnormal traffic-indexed state estimation: A cyber–physical fusion approach for Smart Grid attack detection[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2015, 49(8):94-103. [CrossRef]
- Susuki Y, Koo T, Ebina H, et al. A Hybrid System Approach to the Analysis and Design of Power Grid Dynamic Performance[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(1): 225-239. [CrossRef]
- Aluko A, Carpanen R, Dorrell D, et al. Vulnerability Analysis of False Data Injection Attacks on the Frequency Stability of Isolated Microgrids[C]// 2021 Southern African Universities Power Engineering Conference/Robotics and Mechatronics/Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa (SAUPEC/RobMech/PRASA), 27-29 January 2021, Potchefstroom, South Africa: 1-6.
- Liu X, Li Z, Shuai Z, et al. Cyber Attacks Against the Economic Operation of Power Systems: A Fast Solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(2): 1023-1025. [CrossRef]
- Pan K, Teixeira A, Cvetkovic M, et al. Cyber Risk Analysis of Combined Data Attacks Against Power System State Estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(3): 3044-3056. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Y, Goldsmith A, Poor H. Minimum Sparsity of Unobservable Power Network Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(7): 3354-3368. [CrossRef]
- Sanjab A, Saad W. Data Injection Attacks on Smart Grids With Multiple Adversaries: A Game-Theoretic Perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(4): 2038-2049. [CrossRef]
- Chin W, Lee C, Jiang T. Blind False Data Attacks Against AC State Estimation Based on Geometric Approach in Smart Grid Communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(6): 6298-6306. [CrossRef]
- Esmalifalak M, Nguyen H, Zheng R, et al. A Stealthy Attack Against Electricity Market Using Independent Component Analysis[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2018, 12(1): 297-307. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Bao Z, Lu D, et al. Modeling of Local False Data Injection Attacks With Reduced Network Information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6(4): 1686-1696. [CrossRef]
- Ding M, Li X, Zhang J. Impact of Cyber Attacks on Power System Reliability Targeting SCADA Systems [J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46(11): 37-45.
- Zhang Y, Wang L, Xiang Y. Power System Reliability Analysis With Intrusion Tolerance in SCADA Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(2): 669-683. [CrossRef]
- Liang G, Weller S, Zhao J, et al. A Framework for Cyber-Topology Attacks: Line-Switching and New Attack Scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(2): 1704-1712. [CrossRef]
- Liang G, Weller S, Luo F, et al. Generalized FDIA-Based Cyber Topology Attack With Application to the Australian Electricity Market Trading Mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(4): 3820-3829. [CrossRef]
- Deng R, Zhuang P, Liang H. CCPA: Coordinated Cyber-Physical Attacks and Countermeasures in Smart Grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(5): 2420-2430. [CrossRef]
- Jiang X, Zhang J, Harding B, et al. Spoofing GPS Receiver Clock Offset of Phasor Measurement Units[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28(3): 3253-3262. [CrossRef]
- Risbud P, Gatsis N, Taha A. Vulnerability Analysis of Smart Grids to GPS Spoofing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2019, 10(4): 3535-3548. [CrossRef]
- Barreto S, Pignati M, Dán G, et al. Undetectable Timing-Attack on Linear State-Estimation by Using Rank-1 Approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(4): 3530-3542. [CrossRef]
- Liu D, Qiao S, Zhang Y, et al. A Review of Data Sampling Methods for Imbalanced Classification[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2019, 33(7): 102-112.
- Zhou Y, Sun H, Fang Q, et al. A Review of Classification Methods for Imbalanced Datasets [J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(6): 1615-1621.
- Zhu T, Lin Y, Liu Y. Synthetic minority oversampling technique for multiclass imbalance problems[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 72: 327-340. [CrossRef]
- Dong M, Liu M, Jing C, et al. Multi-class Imbalanced Oversampling Algorithm Using Sampling Safety Coefficients[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Exploration, 2020, 14(10): 1776-1786.
- Dong M, Jiang Z, Jing C, et al. Multi-class Imbalanced Learning Algorithm Based on Hellinger Distance and SMOTE[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(1): 102-109.
- Cieslak D, Hoens T, Chawla N, et al. Hellinger distance decision trees are robust and skew-insensitive[J]. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2012, 24(1): 136-158. [CrossRef]
- Han M, Guo H, Wang W, et al. QSMOTE Method for Multi-class Imbalance Problems Based on Secondary Synthesis[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 55(1): 1-13.
- He H, Bai Y, Garcia E, et al. ADASYN: Adaptive Synthetic Sampling Approach for Imbalanced Learning[C]// 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), 01-08 June 2008, Hong Kong: 1322-1328.
- Deng M, Guo Y, Wang C, et al. An oversampling method for multi-class imbalanced data based on composite weights[J]. Plos one, 2021, 16(11): e0259227. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Shen L, et al. Under-sampling of Imbalanced Multi-class Support Vector Machine Based on Class Overlap Degree [J]. Journal of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 35(4): 536-543.
- Arafat M, Hoque S, Farid D. Cluster-based Under-sampling with Random Forest for Multi-Class Imbalanced Classification[C]// 2017 11th International Conference on Software, Knowledge, Information Management and Applications (SKIMA), 06-08 December 2017, Malabe, Sri Lanka: 1-6.
- Krawczyk B, Bellinger C, Corizzo B, et al. Undersampling with Support Vectors for Multi-Class Imbalanced Data Classification[C]// 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 18-22 July 2021, Shenzhen, China: 1-7.
- Agrawal A, Viktor H, Paquet E. SCUT: Multi-Class Imbalanced Data Classification using SMOTE and Cluster-based Undersampling[C]// 2015 7th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K), 12-14 November 2015, Lisbon, Portugal: 226-234.
- Pruengkarn R. Enhancing classification performance by handling noise and imbalanced data with fuzzy classification techniques[D]. Perth, Australia: Murdoch University, 2018.
- Hartono H, Ongko E. Combining Hybrid Approach Redefinition-Multiclass Imbalance (HAR-MI) and Hybrid Sampling in Handling Multi-Class Imbalance and Overlapping[J]. JOIV: International Journal on Informatics Visualization, 2021, 5(1): 22-26. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez J, Díez-Pastor J, Arnaiz-González Á, et al. Random Balance ensembles for multiclass imbalance learning[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 193(6): 105434. [CrossRef]
- Zhang R, Zhang J, Wu P, et al. An Improved AdaBoost.M2 Algorithm for Multi-class Imbalanced Protocol Traffic [J]. Application Research of Computers, 2019, 36(6): 1863-1867.
- Fernández A, Carmona C, Jose del Jesus M, et al. A Pareto-based Ensemble with Feature and Instance Selection for Learning from Multi-Class Imbalanced Datasets[J]. International Journal of neural systems, 2017, 27(6): 1750028. [CrossRef]
- Sreeja N. A weighted pattern matching approach for classification of imbalanced data with a fireworks-based algorithm for feature selection[J]. Connection Science, 2019, 31(2): 143-168. [CrossRef]
- Lango M, Stefanowski J. Multi-class and feature selection extensions of roughly balanced bagging for imbalanced data[J]. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 2018, 50(1): 97-127. [CrossRef]
- Chen H, Li T, Fan X, et al. Feature selection for imbalanced data based on neighborhood rough sets[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 483: 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Xue Y, Lai Y, et al. Integration of Big Energy Thinking and Big Data Thinking (Part I) Big Data and Power Big Data [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(1): 1-8.
- Li P, Liu Y, Xin H, et al. Vulnerability Assessment of Distribution Network Cyber-Physical Systems Under Distributed Collaborative Control Mode [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(10): 22-29+59.
- Hu Z, Wang Y, Tian X, et al. False Data Injection Attacks Identification for Smart Grids[C]// 2015 Third International Conference on Technological Advances in Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (TAEECE), 29 April 2015-01 May 2015, Beirut, Lebanon: 139-143.
- Bobba R, Davis K, WANG Q, et al. Detecting False Data Injection Attacks on DC State Estimation[C]// First Workshop on Secure Control Systems (SCS 2010), 12 April 2010, Stockholm, Switzerland: 1-9.
- Chakhchoukh Y, Ishii H. Enhancing Robustness to Cyber-Attacks in Power Systems Through Multiple Least Trimmed Squares State Estimations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 31(6): 4395-4405. [CrossRef]
- Gu Y, Liu T, Wang D, et al. Bad Data Detection Method for Smart Grids based on Distributed State Estimation[C]// 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), 09-13 June 2013, Budapest, Hungary: 4483-4487.
- Wang D, Guan X, Liu T, et al. Extended Distributed State Estimation: A Detection Method against Tolerable False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids[J]. Energies, 2014, 7(3): 1517-1538. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Li Y, Huang M, et al. Robust Dynamic State Estimator of Integrated Energy Systems Based on Natural Gas Partial Differential Equations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58(3): 3303-3312. [CrossRef]
- Zhao J, Zhang G, Scala M, et al. Short-Term State Forecasting-Aided Method for Detection of Smart Grid General False Data Injection Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(4): 1580-1590. [CrossRef]
- Li S, Yılmaz Y, Wang X. Quickest Detection of False Data Injection Attack in Wide-Area Smart Grids[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6(6): 2725-2735. [CrossRef]
- Khalid H, Peng J. Immunity Toward Data-Injection Attacks Using Multisensor Track Fusion-Based Model Prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(2): 697-707. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Chang P, Sun Q. Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Power Grids Based on XGBoost and Unscented Kalman Filter Adaptive Hybrid Prediction [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(16): 5462-5476.
- He Y, Mendis G, Wei J. Real-Time Detection of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grid: A Deep Learning-Based Intelligent Mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2017, 8(5): 2505-2516. [CrossRef]
- Ozay M, Esnaola I, Vural F, et al. Machine Learning Methods for Attack Detection in the Smart Grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(8): 1773-1786. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Zeng J, et al. A Detection Method for False Data Injection Attacks in Power Grids Based on an Improved Convolutional Neural Network [J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(20): 97-104.
- Wang Q, Tai W, Tang Y, et al. A Review of False Data Injection Attack Research for Power Cyber-Physical Systems [J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 72-83.
- Li Y, Wang Y, Hu S. Online Generative Adversary Network Based Measurement Recovery in False Data Injection Attacks: A Cyber-Physical Approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(3): 2031-2043. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Wang Y. Developing graphical detection techniques for maintaining state estimation integrity against false data injection attack in integrated electric cyber-physical system[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2020, 105: 101705. [CrossRef]
- Fan X, Du L, Duan D. Synchrophasor Data Correction Under GPS Spoofing Attack: A State Estimation-Based Approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(5): 4538-4546. [CrossRef]
- Zeng J. Research on Defense Methods for Data Integrity Attacks in Smart Grids [D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2019.
- Khalid H, Peng J. A Bayesian Algorithm to Enhance the Resilience of WAMS Applications Against Cyber Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2016, 7(4): 2026-2037. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Hespanha J. Distributed Estimation of Power System Oscillation Modes Under Attacks on GPS Clocks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 67(7): 1626-1637. [CrossRef]
- Yang S. GPS Spoofing Attacks and Defense for PMUs [D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
- Li Y, Yang S. Defense Method for Smart Grid GPS Spoofing Attacks Based on Improved Self-Attention Mechanism Generative Adversarial Networks [J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41(11): 100-106.
- Huo W. Research on Malicious Data Attacks and Defense in Ubiquitous Power Internet of Things [D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
- Chen B, Li M. Research on a Data-Driven Framework for Defending Against False Data Injection Attacks in Power Systems [J]. Electric Measurement & Instrumentation, 2024, 61(12): 10-16.
- Ao W, Song Y, Wen C. Adaptive cyber-physical system attack detection and reconstruction with application to power systems[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 10(12): 1458-1468. [CrossRef]
- Farraj A, Hammad E, Kundur D. A Distributed Control Paradigm for Smart Grid to Address Attacks on Data Integrity and Availability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2018, 4(1): 70-81. [CrossRef]
- Chlela M, Mascarella D, Joós G. Fallback Control for Isochronous Energy Storage Systems in Autonomous Microgrids Under Denial-of-Service Cyber-Attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(5): 4702-4711. [CrossRef]
- Guo J, Han Y, Guo C, et al. Modeling and Vulnerability Analysis of Cyber-Physical Power Systems Considering Network Topology and Power Flow Properties[J]. Energies, 2017, 10(1): 87. [CrossRef]
- Sun C, Liu D, Li Q. Study on Dynamic Power Flow in Active Distribution Networks Integrated with Cyber-Physical Systems [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(6): 1509-1516.
- Cao K, Li R, Zhang X, et al. Research on Uncertainty for Complex Event Streams in Cyber-Physical Systems [J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2015, 37(3): 415-421.
- Yin Z, Zhang K, Du H, et al. Event-Driven Modeling of Cyber-Physical Systems [J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 2015, 32(12): 126-129.
- Makedon F, Le Z, Huang H, et al. An event driven framework for assistive CPS environments[J]. ACM Sigbed Review, 2009, 6(2): 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Xu G, Tao L, Zhang D, et al. Dual relations in physical and cyber space[J]. Chinese Science Bulltin, 2006, 51(1): 121-128. [CrossRef]
- Havlíková M, Jirgl M. Reliability Analysis in Man-Machine Systems[C]// 14th International Carpathian Control Conference (ICCC), 26-29 May 2013, Rytro, Poland: 111-116.
- Chen J, Wang Q, Tang Y, et al. Anomaly Detection Method for Power Cyber-Physical Systems Considering Bilateral Characteristics [J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46(6): 2339-2348.
- Fu Y, Chen L, Ma Z, et al. Preventive Control of Power Systems Including Data-Driven Stability Constraints [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(15): 5417-5430.
- Xue W, Wu T. Active Learning-Based XGBoost for Cyber Physical System Against Generic AC False Data Injection Attacks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 144575-144584. [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi M, Gheitasi K, Lucia W. A Blended Active Detection Strategy for False Data Injection Attacks in Cyber-Physical Systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2021, 8(1): 168-176. [CrossRef]
- Deng B, Ou Y. Optimal Defense Strategy Based on the Load Nodes’ Importance against Dummy Data Attacks in Smart Grids[J]. 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), 30 October 2020-01 November 2020, Wuhan, China: 3134-3138.
- Song J, Zhang Z, Mu Y, et al. Enhancing Environmental Sustainability Via Interval Optimization for Low-Carbon Economic Dispatch in Renewable Energy Power Systems: Leveraging the Flexible Cooperation of Wind Energy and Carbon Capture Power Plants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 442: 140937.
- Li Y, Han M, Yang Z, et al. Coordinating Flexible Demand Response and Renewable Uncertainties for Scheduling of Community Integrated Energy Systems with an Electric Vehicle Charging Station: A Bi-Level Approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2021, 12(4): 2321–2331. [CrossRef]
- Cui Y, et al. Deep reinforcement learning based optimal energy management of multi-energy microgrids with uncertainties[J]. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2024: 1-12.
- Li Y, Bu F, Li Y, et al. Optimal scheduling of island integrated energy systems considering multi-uncertainties and hydrothermal simultaneous transmission: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 333: 120540.
- Yang X, et al. Gaussian Mixture Model Uncertainty Modeling for Power Systems Considering Mutual Assistance of Latent Variables[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2024, 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, et al. Collaborative optimization of multi-microgrids system with shared energy storage based on multi-agent stochastic game and reinforcement learning[J]. Energy, 2023, 280: 128182. [CrossRef]
- Mansour R F. Artificial intelligence based optimization with deep learning model for blockchain enabled intrusion detection in CPS environment[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 12937. [CrossRef]
- Acharya S, Khan A A, Päivärinta T. Interoperability levels and challenges of digital twins in cyber-physical systems[J]. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2024: 100714. [CrossRef]
- Zhang F, Huang Z, Kou L, et al. Data Encryption Based on a 9D Complex Chaotic System with Quaternion for Smart Grid[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2023, 32(1): 010502. [CrossRef]
- Qu Z, Dong Y, Mugemanyi S, et al. Dynamic Exploitation Gaussian Bare-Bones Bat Algorithm for Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch to Improve the Safety and Stability of Power System[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2022, 16: 1401-1424. [CrossRef]
- Fang Z, Zhao D, Chen C, et al. Nonintrusive Appliance Identification with Appliance-Specific Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, 56(4): 3443-3452. [CrossRef]
- Iftemi A, Cernian A, Moisescu M A. Quantum Computing Applications and Impact for Cyber Physical Systems[C]//2023 24th International Conference on Control Systems and Computer Science (CSCS). IEEE, 2023: 377-382.
| Attack Phase | Attack Type | Attack Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Software Information System | FDIAs targeting software or systems | Modification of software and hardware information |
| FDIAs targeting control commands | Incorrect execution of control commands | |
| Network Access Process | FDIAs targeting protocol vulnerabilities | Manipulation of network access data |
| FDIAs targeting data packets | Data packet interception and tampering | |
| Physical Communication Process | FDIAs targeting positioning signals | GPS positioning information spoofing |
| FDIAs targeting time synchronization | PMU data desynchronization |
| FDIA Evolutionary Process Characterization Methods | Attack Target | Specific descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Quantity Manipulation Attack Characterization | Electrical quantity data collected by monitoring systems | Linear programming representation model [87] |
| Bilevel linear programming representation model [88] | ||
| Heuristic algorithm for solving the evolutionary representation model of an attack [89] | ||
| Sparse attack vector representation method [90] | ||
| Optimization representation method for attack-defense strategies based on a master-slave game model [91] | ||
| Feasible attack representation model constructed by minimizing angular deviation of data from both sides [92] | ||
| Representation method for inferring system topology and parameters from cyber-physical measurement data [93] | ||
| Feasible attack domain representation method using a mixed integer linear programming model [94] | ||
| Topological Manipulation Attack Characterization | The power system network topology | Using an attack tree representation model to implement FDIA topological manipulation attacks [95] |
| Using a markov representation model to calculate the probability of attack success [96] | ||
| Designing attack methods that involve adding and simultaneously increasing or decreasing lines [97] | ||
| Fdia representation model considering power flow constraints [98] | ||
| Constructing attack vectors based on topology and flow data after a line break [99] | ||
| GPS Synchronization Clock Forgery Attack Characterization | The timestamps of PMU data | Introducing an optimal attack representation method under the constraint of positional distance differences [100] |
| Constructing an attack vector that includes the attacked PMU position and optimal phase angle manipulation values [101] | ||
| Developing an undetectable GPS clock attack method [102] |
| Data enhancement methods | Specific descriptions | Principles |
|---|---|---|
| Over-sampling | K-nearest neighbor based SMOTE algorithm [105] | Introduce new minority samples for balance |
| Neighborhood safety coefficient based oversampling [106] | ||
| Heilinger distance guided sample synthesis direction [107,108] | ||
| Secondary synthetic sample strategy [109] | ||
| Adaptive synthetic oversampling algorithm [110] | ||
| Classification sorting and weight-based oversampling [111] | ||
| Under-sampling | Class overlap degree-based undersampling method [112] | Remove some majority samples for balance |
| Cluster-based undersampling method [113] | ||
| Undersampling + genetic algorithm [114] | ||
| Hybrid sampling | SMOTE oversampling + EM clustering undersampling [115] | Combine oversampling and undersampling for balance |
| SMOTE oversampling and fuzzy C-means clustering undersampling [116] | ||
| Minority oversampling + editing nearest neighbor undersampling [117] | ||
| Random undersampling + SMOTE oversampling [118] | ||
| SMOTE oversampling + clustering undersampling [119] | ||
| Feature selection | Feature selection + instance selection [120] | Select relevant features for dimension reduction |
| Firework algorithm based on feature weight selection [121] | ||
| Rough balance-based feature selection method [122] | ||
| Feature significance based feature selection method [123] |
| Detection Methods | Specific descriptions | Advantages and Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| State Estimation | Equivalent Measurement Transformation + Residual Detection Method [126] | Mature algorithms; fast but sensitive to threshold settings |
| Measurement Protection Strategy + State Variable Verification [127] | ||
| Parallel Estimators + Improved State Estimation Algorithm [128] | ||
| Graph Partitioning + Chi-Square Test Method [129,130,131] | ||
| Trajectory Prediction | Short-Term State Forecasting + Consistency Testing Method [132] | Detects false data well, but high complexity and slow; unsuitable for complex systems |
| Generalized Likelihood Ratio+ High-Performance Computing [133] | ||
| Multi-Sensor Track Fusion + Particle Filtering [134] | ||
| Artificial Intelligence | XGBoost Load Forecasting + UKF Dynamic Estimation [135] | Strong computational capabilities; clear framework; generally poor interpretability |
| Deep Learning Techniques + Feature Extraction [136] | ||
| Batch Processing + Online Learning Algorithms [137] | ||
| Convolutional Neural Network + Model Design [138] | ||
| Equivalent Measurement Transformation+ Residual Detection [110] |
| Reconstruction methods | Specific descriptions | Response Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| State Awareness Attack Data Reconstruction Method | Online GAN Measurement Data Reconstruction Method [140,141] | Response to Attacks Targeting State Awareness |
| Derivation of Reconstruction Matrix to Correct Attacked Angle Counters [142] | ||
| Using IGAN to Reconstruct Attacked Measurement Data [143] | ||
| Utilizing System Model to Calculate and Reconstruct Monitoring Errors [144] | ||
| Determining Mode Parameters and Reconstructing Mode Analysis Results [145] | ||
| Using SAGAN Generated Data to Restore Deceptive Data [146,147] | ||
| Using MisGAN to Reconstruct Malicious Attack Data [148] | ||
| Using WAE Model to Restore Anomalous Data [149] | ||
| Action Control Attack Data Reconstruction Method | Deriving FDIAS Signal and Its Reconstruction, Reference [150] | Response to Attacks Targeting Control Functions |
| Adjustment Method for Feedback Controller Gain Parameters [151] | ||
| DER Attack Scenario Data Reconstruction Control Scheme [152] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




