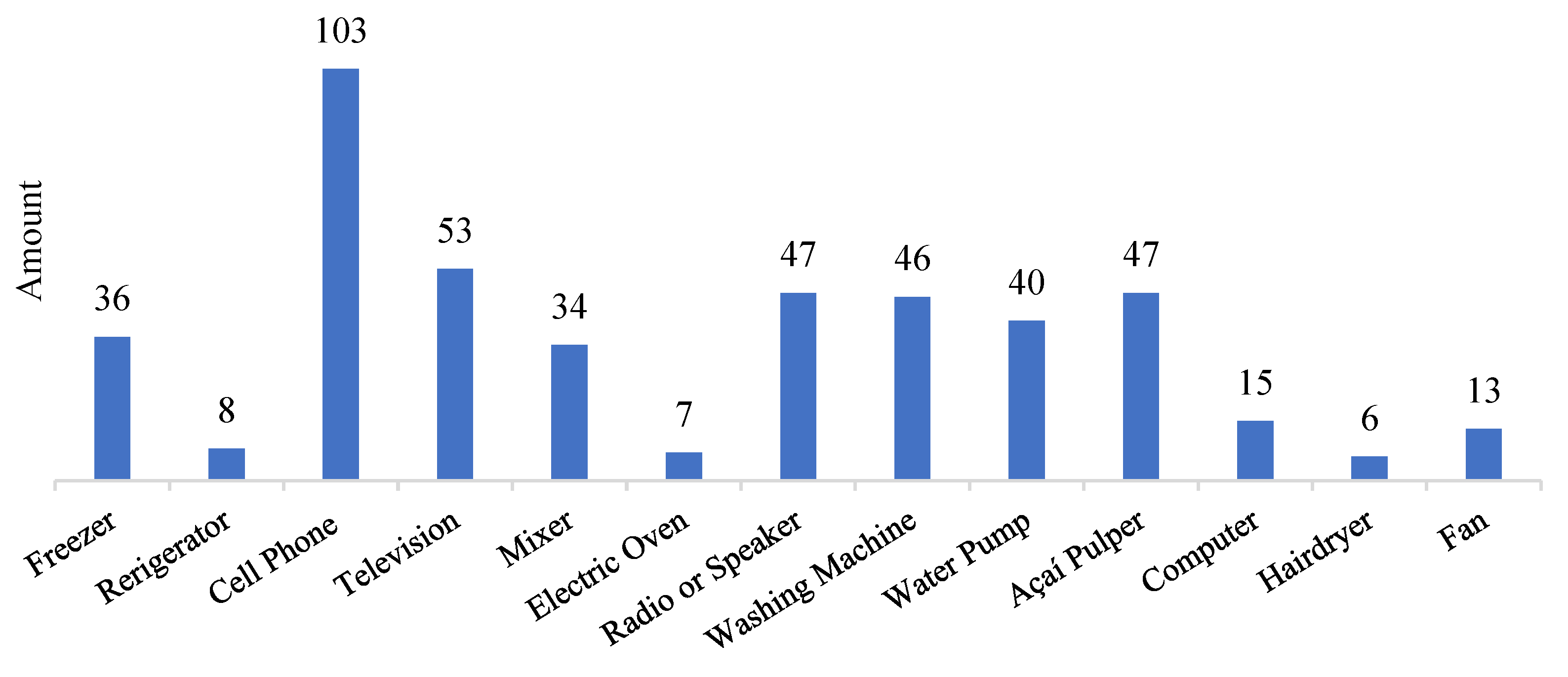1. Introduction
1.1. Electricity and Socio-Economic Development
Electricity is indispensable for the development of modern communities. The conduct of basic day-to-day activities such as education, health, entertainment, transportation, food, and leisure, are always related to this resource [
1]. In addition, more complex activities such as those developed in the industrial sector depend on the availability of electricity on a large scale.
“Clean and Affordable Energy” is one of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) established by the United Nations (UN) to be achieved by the year 2030 [
2]. This SDG is strongly linked to other objectives, which can be achieved more effectively with access to electricity, such as: “Zero Hunger and Sustainable Agriculture” (SDG 2); “Drinking Water and Sanitation” (SDG 6) and “Sustainable Cities and Communities” (SDG 11).
However, despite the development potential provided by electricity, almost 1 million people in the area covered by the Brazilian legal Amazon do not have access to electricity, even though there is a legal basis for the universalization of this resource [
3]. This situation is one of the barriers that hinders the development of several value chains in the region, such as açaí (
Euterpe oleracea Mart.) – consequently affecting Amazonian extractive communities [
4].
According to the Recommendations for Systemic Impacts on the Açaí Value Chain [
5], the world market for the fruit moves about BRL 720 million per year, where in Brazil alone it is estimated that the annual production value is BRL 6 billion. In the Amazon region, this industry plays a crucial role in generating income and promoting food security, involving more than 300,000 people, including 150,000 families.
The state of Pará, the world’s largest producer of fruit and pulp, produces approximately 53% of the quantity sold worldwide: in 2019 it handled about BRL 3.7 billion. In addition, açaí pulp is consumed daily by riverside families (those who live on the banks of rivers), and this food is one of the responsible for the low rates of food insecurity in certain communities, such as Ilha das Cinzas [
6].
Commonly, energy supply in riverside communities is done by isolated systems of fuel generators. However, it is a source of electricity that involves several problems, such as pollution and emission of Greenhouse Gases (GHG). In addition, recurring maintenance, dependence on the fluvial transport of fuel and water pollution by the spillage of oil and fuel, are recurring examples.
1.2. Photovoltaic Solar Energy Technologies on the Amazon
In this scenario, photovoltaic solar energy is highlighted. It is a renewable source of great potential in the Brazilian territory and has received several tax incentives over the years [
7,
8], which has enabled a heated market with well-developed technologies. According to the Brazilian Solar Atlas [
9], the average daily irradiation in the horizontal plane over a year can vary from 4.1 kWhm
-2 to 6.5 kWhm
-2 in the country (4 to 5 kWhm
-2 in the Amazon region) – average values that exceed those of Germany, one of the leaders in the generation of electricity from solar source.
One of the most relevant benefits for the generation of electricity from solar sources was the Light For All (LPT
1) program, which enabled the installation of photovoltaic (PV) systems in communities with favorable characteristics for this type of generation [
10]. In addition, from Normative Resolution (NR) No. 493/2012, of the National Electric Energy Agency (ANEEL
2), later replaced by NR No. 1000/2021 and No. 1059/2023, procedures and conditions of supply were established through Isolated Microsystems for Generation and Distribution of Electric Energy (MIGDI
3) or Individual Systems for Generation of Electric Energy with Intermittent Source (SIGFI
4).
For communities far from urban centers, Isolated Photovoltaic Systems (IPS) have characteristics consistent with reality, and may assume different configurations. The most common is the Domestic Photovoltaic System (DPS), used to meet everyday demands: televisions, lighting, refrigerators, appliances, pulpers (popularly called “mixers”) of açaí, motor pumps, etc.
An important component in DPS is the voltage inverter, responsible for converting direct current power to alternating current. It is an element sensitive to overloads, a frequent cause of damage. Some systems serve loads with single-phase motors driven with a direct start, causing a momentary peak power that results in a voltage drop much higher than the limits established in standards – which causes operational disturbances in command and protection equipment [
11].
Domestic systems have dimensions and economic feasibility studies known in the Amazon region: in the riverside housing of Manacapuru, a comparative study was carried out between a DPS and a diesel generator [
12]. Other studies showed similar results of economic viability for DPS sized in different Amazonian locations: Santarém and Ilha das Onças, both locations in the state of Pará [
13]. Recently, research has proposed the development of modular photovoltaic solar energy kits, with the capacity to be expanded according to demand [
14].
Another IPS configuration is the Direct Coupling Photovoltaic System (DCPS), specifically developed to operate with motors. In this scheme, the Variable Speed Driver (VSD) is an example of power conditioning equipment that can be used. By default, the VSDs requires high input voltage values, which requires the open circuit voltage of the Photovoltaic Array (PVA) modules to be within the limits of the VSD. This configuration does not include an energy accumulator, so the rotation speed of the machine varies with the availability of solar incidence. The machine is started gradually, avoiding current surges. In addition, VSDs are found in a wide range of power for different prices and with national manufacture and maintenance.
In recent decades, many works have been developed aimed at the application of VSDs in photovoltaic pumping systems, an application of DCPSs: one of the researches presents the appropriate procedures for connecting a PVA to VSDs to operate induction motors and submersible centrifugal motor pumps [
15]. Another performs tests with commercial VSDs to drive centrifugal motor pumps for water pumping purposes followed by technical and economic analysis [
16]. More recently, research makes the comparative simulation of two DCPSs with parallel VSDs, where in one system each VSD has an PVA and in the other system both VSD are energized by a single PVA [
17].
There are works that focus on the use of DCPSs in rural applications, evaluating the sharing of a DCPS used for pumping water and additionally a cassava grater [
18]; or the development of a technology aimed at the use of the açaí pulper from the energy provided by a DCPS (photovoltaic pulper) [
19].
Many of these technologies that use photovoltaic solar energy are classified as social technologies, as they are developed in interaction with the community in search of solutions closer to existing social problems [
20] – adapted to the reality of families, places, customs, culture, etc. Such technologies, unlike conventional ones, allow a more inclusive and sustainable solution, although not as efficient.
Considering the context of energy exclusion in riverine communities in the Brazilian Amazon, the capacity for change that access to electricity allows, the solar potential for electricity generation in the region and the different configurations and technologies of photovoltaic solar energy, this research proposes the insertion of solar energy technologies in a riverine community as an integration mechanism between existing electrical demands, productive activities in the açaí value chain and present social technologies.
The hypothesis of this research is that a system with versatile and flexible topology, which considers the weaknesses and welfare needs of the community, can contribute to the development of the community by strengthening the açaí value chain and integrating the demands of families.
2. Materials and Methods
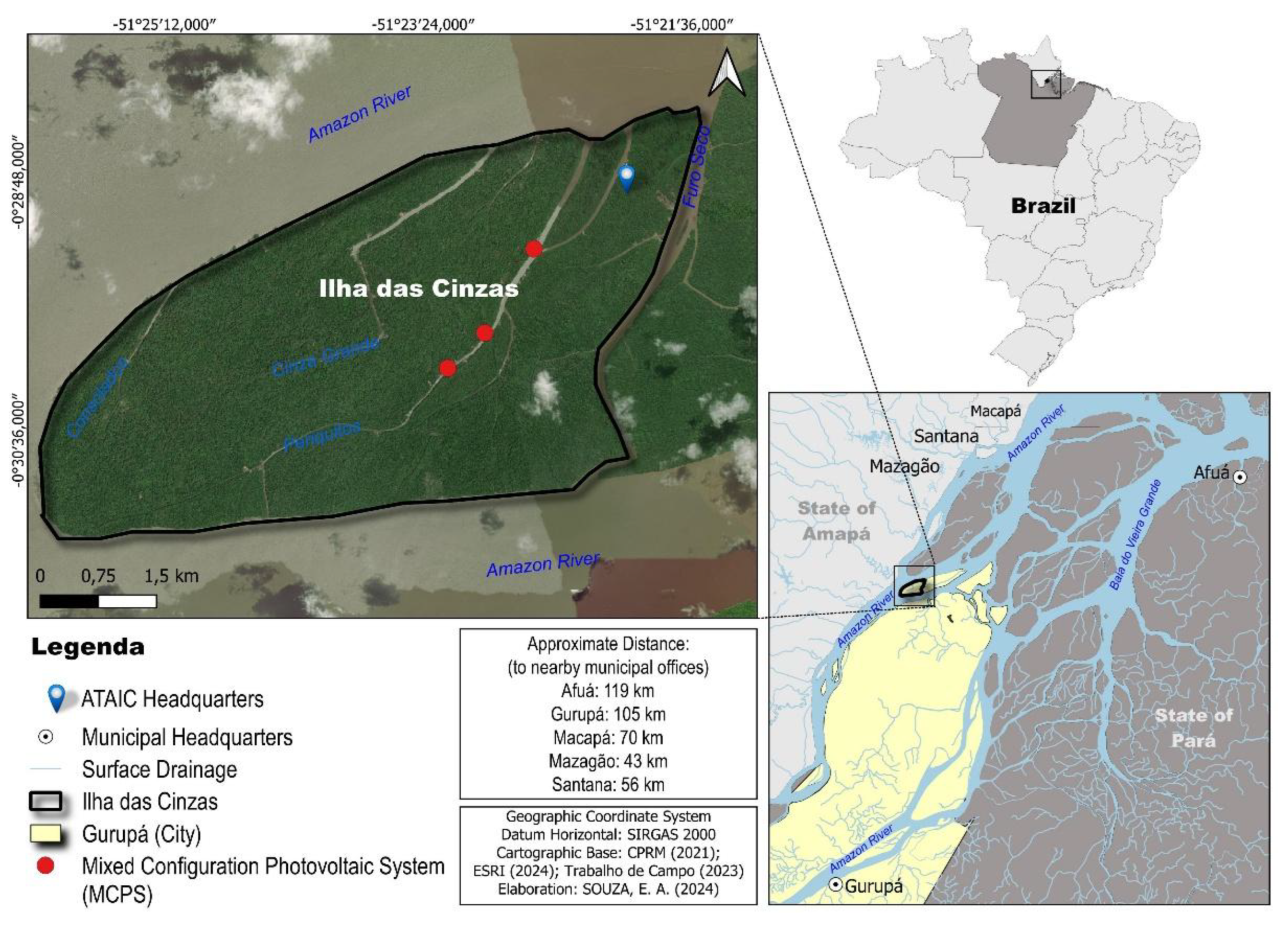
The study area selected was Ilha das Cinzas, a riverside community located in the estuary of the Amazon River, territory of Marajó). The community is characterized by its dependence on the açaí value chain and faces significant challenges related to energy exclusion and socioeconomic development.
To obtain information about the community, a Participatory Rapid Diagnosis (PRD) was performed [
21,
22] throughout 2021 and partially in 2023. It is a tool that allows the author to contact and participate in the problem situation and the agents involved. To perform the PRD, information from a form prepared and applied by the Association of Agroextractivist Workers of Ilha das Cinzas (ATAIC
5) was used. It addressed several aspects of the daily lives of families in the community:
General aspects of the family;
Availability of electricity;
Source of electricity used (if available);
Number of daily hours of electricity available;
Use of electricity for income generation;
Water treatment;
Sanitary sewage.
In addition to the form, data were collected from community research and field observations, vital for comparisons with the results obtained by the other two forms of data collection.
To analyze the information obtained from the PRD, a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) was carried out, a tool that at first is used only in business and industrial environments, nowadays it is often used as a strategic mechanism for the elaboration of action plans in different situations, such as in isolated communities [
23,
24,
25].
This research was carried out in two stages: in the first, internal and external factors were highlighted according to the information obtained in the PRD. These factors were scored from 1 to 5 according to their: “importance” (
), “intensity” (
) and “trend” (
). In the case of external factors, the “trend” factor is replaced by “urgency” (
). The final score (
) of the factor is given by multiplying these elements (1):
In the second stage, the five factors of each quantity of the SWOT matrix were separated and placed in an electronic questionnaire format via Google Forms. Members of ATAIC, members of partner institutions of the association and residents who actively participate in the organization of the community, but who are not part of the administration of ATAIC, were chosen. Each of these people scored the pre-established factors for calculating an average and obtaining the final SWOT matrix.
In possession of this matrix, the factors were crossed in order to define the best strategy to be adopted: offensive, defensive, reinforcement or confrontation. From the crossings, it was possible to carry out a grouping with the objective of using the same action plan aimed at different crossings of factors. The action plans focused on four main problem situations, highlighted in the later section.
3. Results
3.1. Participatory Rapid Diagnosis
Ilha das Cinzas is one of the first locations in the state to have an Agroextractivist Settlement Project – created as a “way to recognize the importance of riverside dwellers for the protection of local biodiversity”, as well as the maintenance of ways of life and socioeconomic and cultural reproduction [
6]. It is a community, as observed in
Figure 1, where the only possible means of transport is fluvial. Like several communities in the region, it has as one of the great challenges the logistics for the acquisition of daily resources and essential services such as health, education and electricity.
The PRD was carried out with the application of 68 forms per family during 2021. It was ratified that açaí is part of its source of income, with other complementary sources of income - except 20 families that did not fill in the field for this answer. Of the 48 responding families, 19 (39.58%) depend exclusively on açaí extraction, a similar result found in the research by [
26]. As for access to electricity,
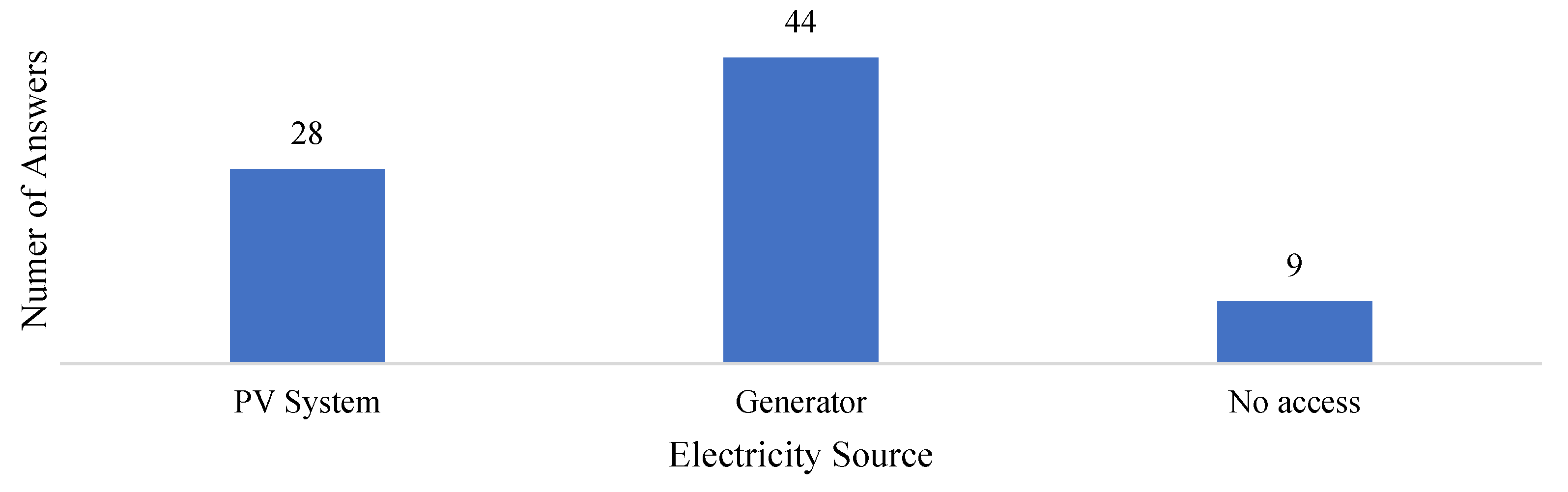
Figure 2 summarizes the information obtained.
It was possible to identify scenarios in which the same photovoltaic system or the same generator was used to serve more than one family. Similarly, some families have both a photovoltaic system and a generator. Of the 44 families that had generators to have access to electricity, 31 depended exclusively on this energy source. Similarly, of the 28 families that used solar energy, 15 depended exclusively on this form of electricity generation. Consequently, 13 families had the two sources of electricity generation highlighted.
Commonly, children build houses near their parents’ homes in order to share energy. This situation is a potential problem, not only in Ilha das Cinzas, but in other communities as well, since this increase in demand is not foreseen and, in the case of photovoltaic systems, generates an overload in the inverter, which is one of the main causes of burns and failures of this equipment, as it is not common for protective devices to be present in the installation.
An important issue raised in the form was the use or not of electricity in some productive activity developed by the family. Of the 52 families who answered the question “Does the family use any form of solar energy or diesel generator engine in any production process that generates income for the family?”, 44 pointed out that they did not use it. This situation reflects how the energy exclusion of the community is a barrier to the economic development of families, who invest in their own electricity generation systems to first meet their daily demands and improve their quality of life.
The form also provided information on the main energy demands that were desired to be met with the purchase of an PV system (highlighted in
Figure 3). The main demand is for lighting, followed by food refrigeration, leisure activities and use of the açaí pulper and communication. These are loads common to all residents and should be considered when sizing any type of power generation.
Of the 68 families, 47 indicated that they had at least one açaí pulper in their home and 36 had a freezer, two essential loads for the açaí value chain. This demand for energy, directly linked to the self-consumption and food sovereignty of families, is directed to the well-being of people in the communities, as income generation occurs from the commercialization of açaí fruits and not from the pulp.
Another recurring demand in homes is for water pumps (40 families had them). Because they are stilt houses, the residences are relatively far from the river, so motor pumps are used to collect water from the river to a reservoir near the residence. However, water treatment is a problem in many families. It was identified that 33 of the 68 families apply the combination of chlorine and hypochlorite to treat water used in household tasks and some even for consumption. The problem in this matter is in the dosage of the product, since during field trips many families reported not having a measurement parameter for the use of chlorine and/or hypochlorite mixed with water.
Another characteristic of the community that must be carefully observed is the destination of the sewage of the residence. The responses to the forms showed that 47.04% (32) of the families dump the sanitary sewage directly into the floodplain near the toilets. This, added to the movements of the tide and the incorrect treatment of water can result in various health problems for families.
In some residences of Ilha das Cinzas (more precisely six) there were already biodigester septic tanks installed as an Alternative Sanitary Sewage System (ASSS). This structure is of interest to the work presented here because its final product is a liquid resulting from the anaerobic decomposition of human waste [
27] that can be used as a biofertilizer in plantations near the ASSS.
3.2. SWOT Analysis
The final SWOT matrix, after performing the steps presented in the methodology, can be seen in
Table 1. Here it is important to highlight how in addition to the “Strength”, all other factors have undergone changes in the general order, which ratifies how both the DRP and the SWOT analysis should be carried out in the most participatory way possible within a given methodology, as it is the active agents of the community that can highlight the problem situation with greater clarity.
One factor mentioned by the agents was the potential of the community in the development of new value chains, especially in the face of Weakness 1 of
Table 1, since a dependence on the açaí value chain can put families in a vulnerable situation in the face of an eventual crisis in this production.
The next stage of the SWOT analysis was the crossing between the factors to define the type of strategy that would be elaborated and later the action plans, as observed in
Table 2. It was observed that, after the crossings, the same action plan could be implemented for different crossings, even if for different types of strategies.
Action Plan 1 (AP1) sought to develop other links in the açaí value chain within the Ilha das Cinzas community. With the açaí market on the rise (O1) and the heated solar energy sector (O5), it is important to increase community forces (a well-organized workers’ association – S1, the familiarity of families with this value chain – S5) to take advantage of opportunities.
Most families in the community are part of the açaí production link. For the development of other links (processing and sale in mixers) it is necessary to confront weaknesses such as energy rationing (W5). The heated market for solar photovoltaic energy (O5) is one of the opportunities that can be taken advantage of; as is the presence of Ts in the region (O3).
The development of a technology capable of strengthening the açaí value chain using photovoltaic solar energy technologies through partnerships with these STIs is one way. However, the technology should not focus only on productive activity - it should be able to meet the daily demands of families and meet loads from the productive activity: açaí pulper, pulp refrigeration, açaí irrigation, pumping and water treatment, existing social technologies such as bio digesting tanks, among others that may be necessary.
Action Plan 2 (AP2) is complementary to AP1. As previously stated, most families in the community use the açaí value chain as their main source of income. Relying exclusively on a single source of income, in the scenario of climate crises as a threat (T1) and pests and diseases in acai trees (W1) can be dangerous.
Thus, the development of a technology that uses solar photovoltaic energy (O5), not only to strengthen the açaí value chain, but also to allow the development of other complementary productive activities is of great importance.
Objectively, photovoltaic solar energy technology must be versatile and capable of integrating different demands: the daily lives of families, the açaí value chain and other productive activities that can be developed by families.
Action Plan 3 (AP3) focused on family training activities – mainly young people seeking possible new professions since the local educational system is deficient (W2).
As much as an advanced technology is developed and implemented in the community, without the participation and communication with families, the implanted technology tends to become “distant” and, consequently, “strange” if it does not have technical monitoring. The transfer of technology to isolated communities without the training of its members is bound to fail, as it is a process that involves both the technical and social aspects.
To this end, during the stages of implementation of PV system in the community, the residents of the families always followed the process and often participated in an auxiliary way in the installation of the components. In addition, with the help of the partner STIs (O3), a theoretical and practical mini course was given, open to the public (without age, sex, or gender restrictions) on basic concepts of electricity and components of photovoltaic systems.
Finally, Action Plan 4 (AP4) focused mainly on sharing experiences and knowledge acquired not only by ATAIC, but by all partner agents. As there is a lack of well-organized communities (T5) such as Ilha das Cinzas in the region and the community itself finds it difficult to train new leaders (W4), it was essential to organize an event that could bring together key agents to share information on the successes and adversities of the project.
In view of the factors chosen and the intersections between them, the business spreadsheet used in the SWOT analysis reported that the favorability index, that is, how favorable is the situation of the riverside community of Ilha das Cinzas, is 51%, which corresponds to the concept “Favorable”: considering the correct SWOT analysis, it is necessary to maintain what is being done in the community and add actions to improve strengths and take advantage of opportunities, added to measures to contain possible weaknesses and threats. Thus, it is possible to infer that the community is in a favorable situation.
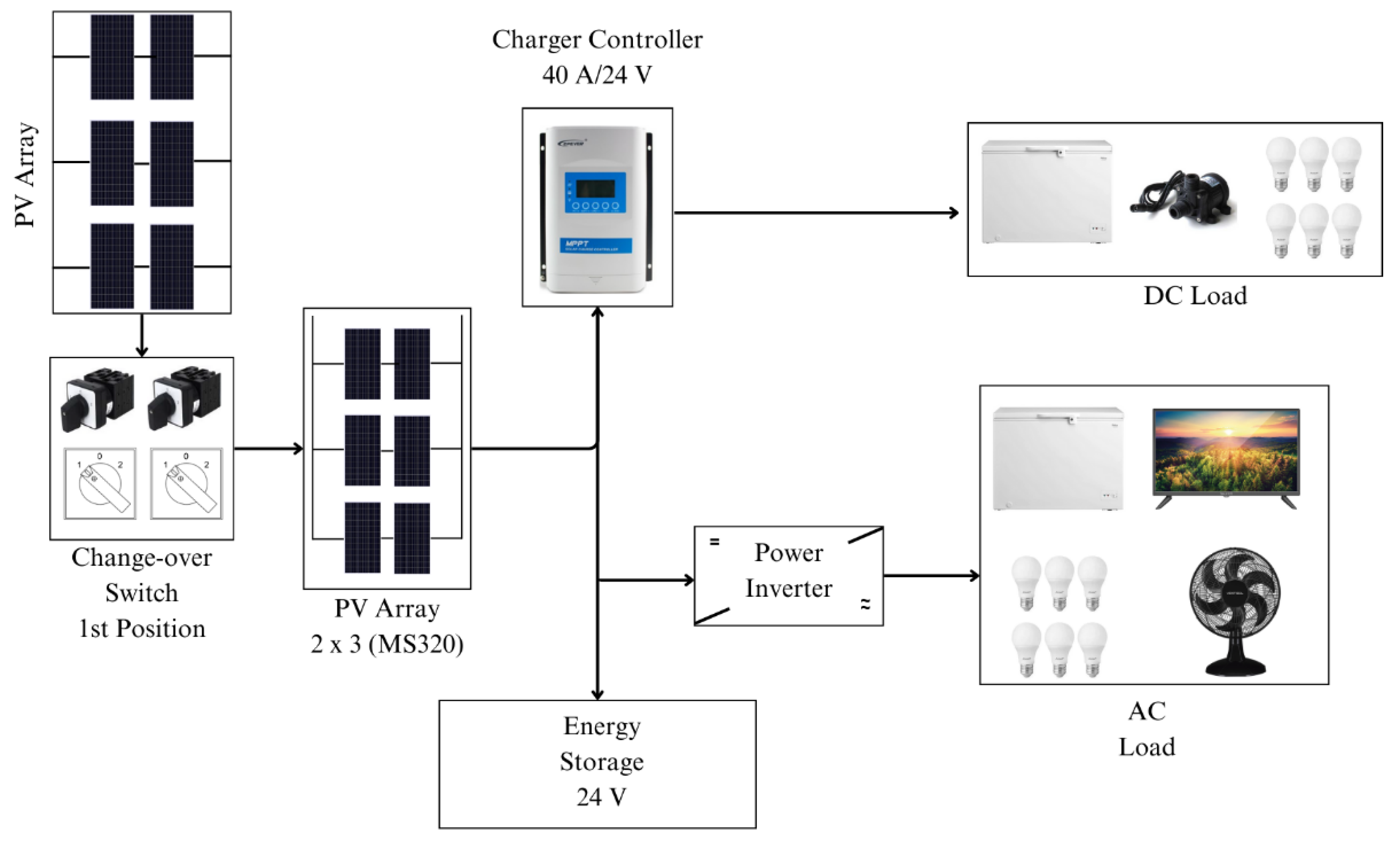
3.3. Mixed Configuration Photovoltaic System
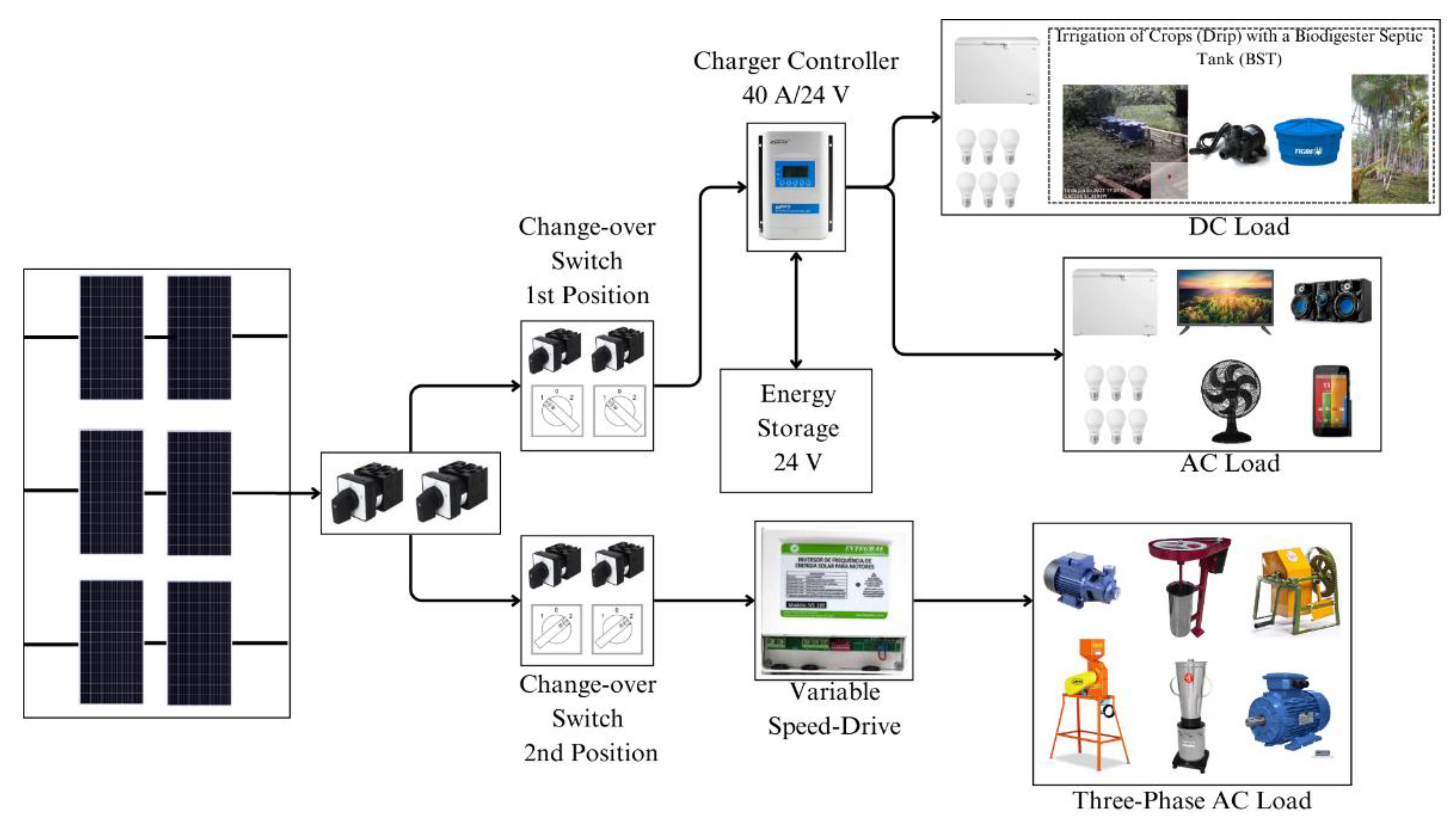
Based on AP1 and AP2 from, it was possible to define that photovoltaic solar energy technology should be developed to integrate diverse types of loads into different applications. The system needed to be flexible, allowing changes in its configuration and adapted to the reality of families.
To meet domestic loads, the most indicated PV system is the DPS. For productive activities that use driving loads, an appropriate topology is DCPS with VSD. However, acquiring photovoltaic modules for the two systems separately would make the project more expensive. Therefore, a new topology was developed, where the same PVA was used to energize either the DPS or the DCPS. For this new way of connecting two subsystems to the same array, the name of Mixed Configuration PV system (MCPS) was given.
According to the Brazilian Solar Energy Atlas, the region near Ilha das Cinzas has global daily irradiation in the horizontal plane in the range between 4,750 kWhm
-2 and 5 kWhm
-2 [
9].
For the sizing of the DPS PV array, an estimate of daily consumption per family was considered, considering the household appliances most mentioned in the form. The estimated total daily consumption was 3,59 kWh. Considering this demand (
L) and the Peak Sun Hours (PSH) parameter equal to 4,875 hours, the peak power (2) of the PVA can be obtained to meet a certain family.
Where and are power reduction factors related to losses due to external effects and electrical losses. Therefore, an installed peak power of at least 1,09 kWP is required to meet the daily energy demand of 3,59 kWh.
For the DCPS PV array, motor loads of up to 1.5 HP (approximately 1.104 kW) were considered. On average, three-phase induction motors have an efficiency (
) of approximately 85%. Therefore, the peak power of the PVA to meet this demand is (3):
For the design of the following systems, the technical data of the 72-cell polycrystalline module model MS320 from the manufacturer MinaSol were considered. Its data (
Table 3) under standard irradiance and temperature conditions (1000 W/m² and 25°C, respectively) were used in simulations for operating conditions closer to the Amazonian reality: module temperature equal to 60°C and irradiance equal to 1200 Wm
-2.
Thus, for the DPS it would be necessary (4):
For the DCPS it was necessary (5):
Therefore, to use the same set of panels to serve two subsystems that require different energy levels, the largest quantity required as a reference was used: 6 photovoltaic modules. As will be observed in the following text, the DPS and DCPS configurations operate with different arrays of modules, so a switching system that would allow the PVA to be used to energize the DPS and to energize the DCPS was necessary.
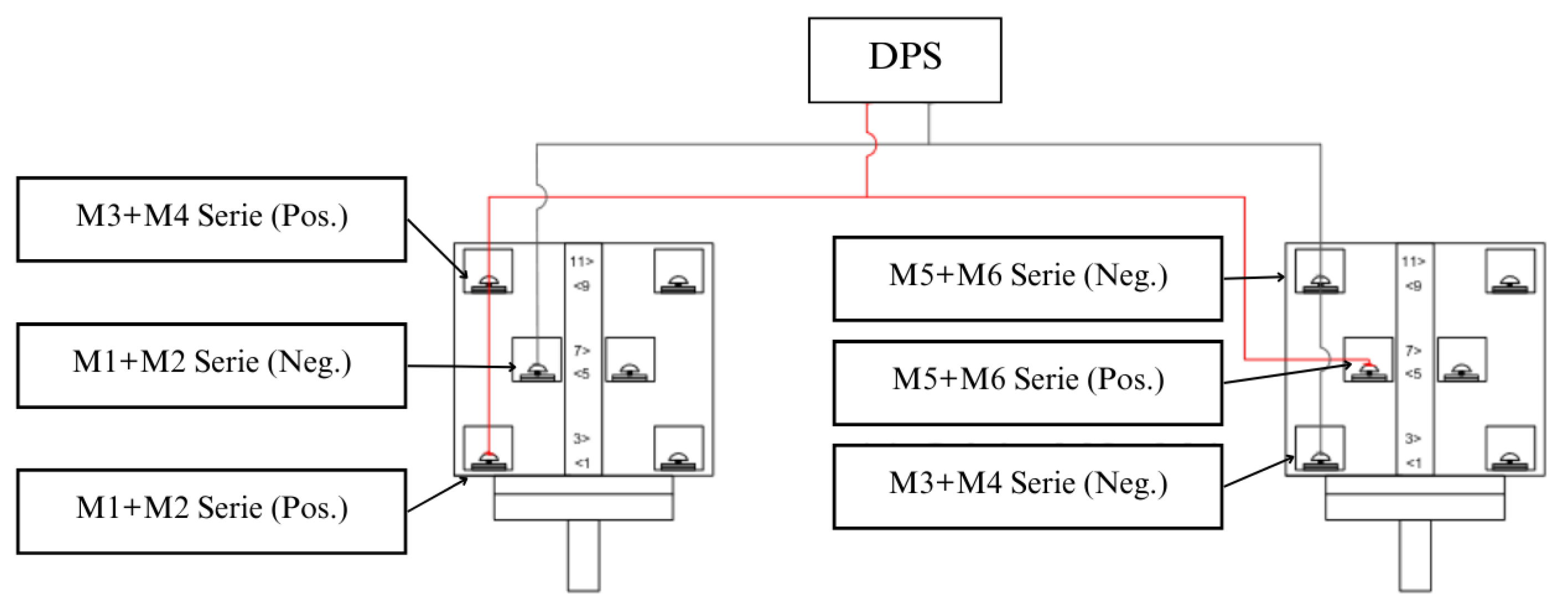
The switching system, detailed below, is based on the use of 3-position switches: position 0 being null, where there is no circulation of electric current; positions 1 and 2 correspond to DPS and DCPS, respectively.
3.3.1. Domestic Photovoltaic System
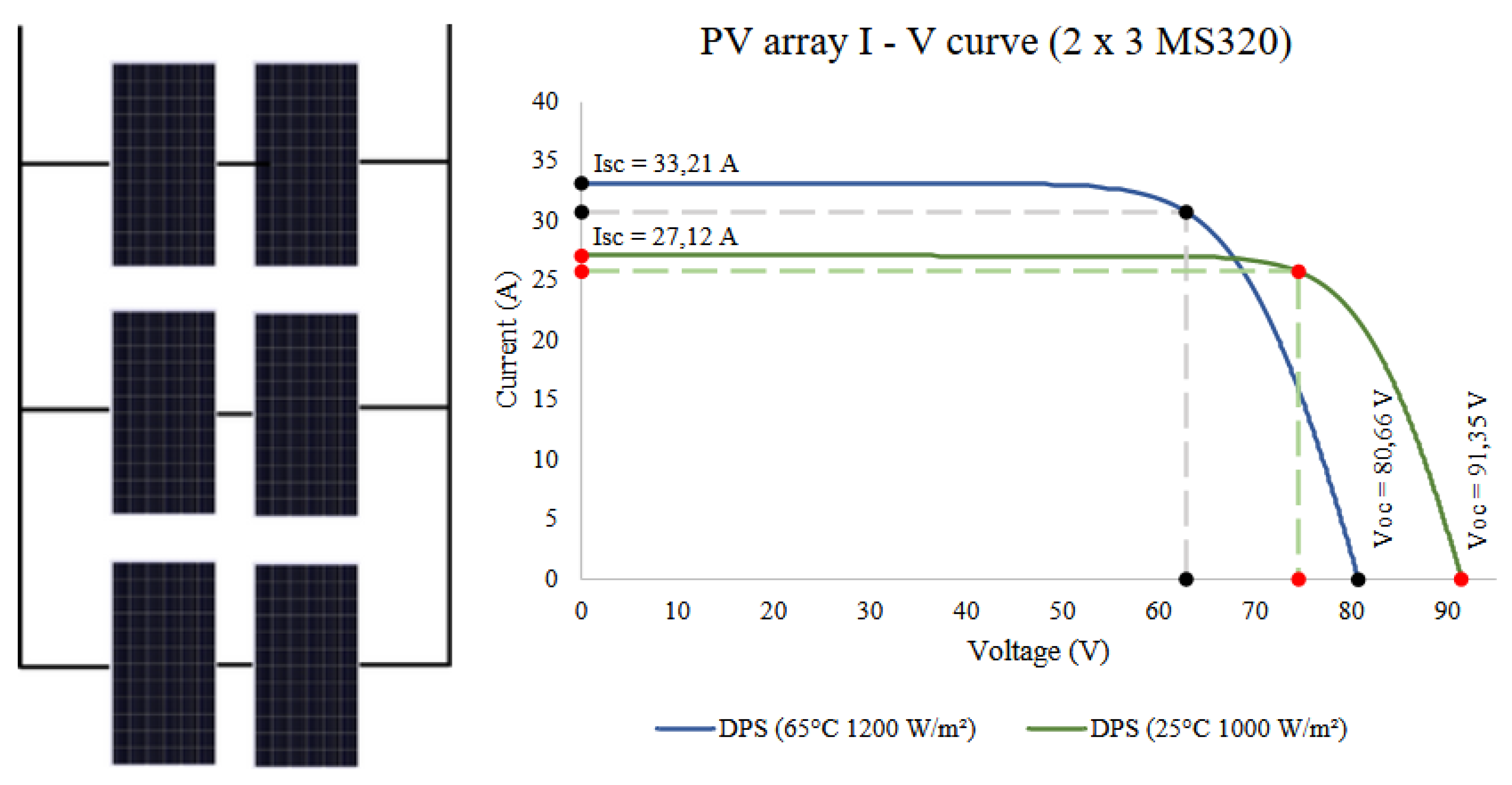
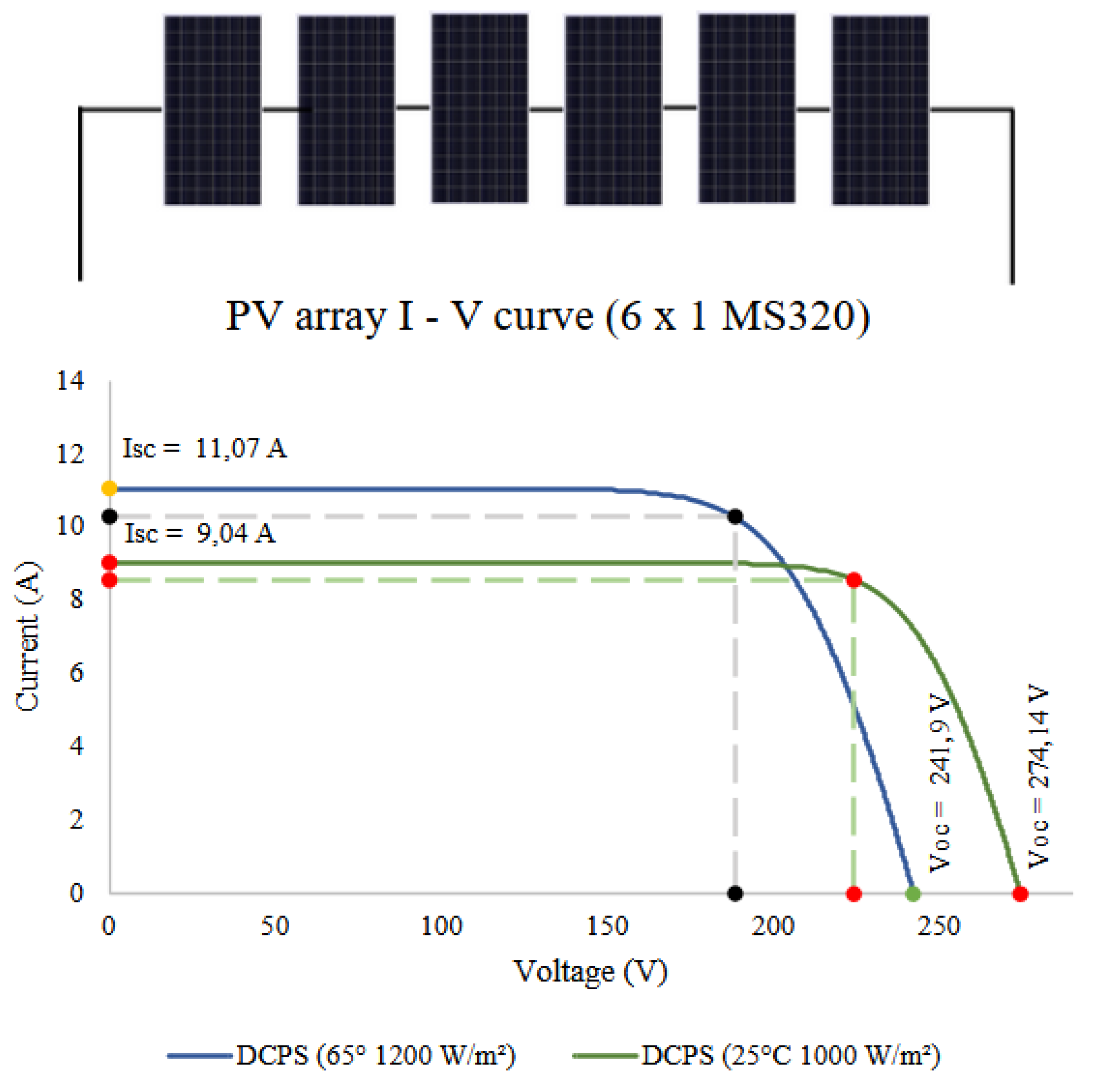
As the number of modules was defined in six, for the DPS they were associated in order to respect the voltage and current limits of the controller. The system uses the TRIRON4210N controller from the manufacturer EPEVER, which has an input voltage limit of 90 VDC to 100 VDC.
Thus, as the modules have an open circuit voltage equal to 45,7 V (
Table 3), the maximum number of modules in series is two. As there are six modules, the remaining four modules assume the association of two pairs in series and finally the three pairs in parallel (diagram on the left in
Figure 4.
Simulations of the characteristic curves of the AFVs were performed in different configurations according to the needs of each subsystem. The simulations were carried out in the Crearray software [
29], where it was possible to compare the curves I – V under standard test conditions and in conditions closer to the Amazonian reality (graph on the right
Figure 4).
In the DPS it is possible to use loads in Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). The AC bus works from a power inverter connected to the energy accumulator (lead-acid battery bank). The DC bus works from a charge controller output at 24 V.
The use of a DC circuit is advantageous because, even in the event of a failure or eventual burning of the voltage inverter, the system will not be idle. In the pilot system, presented in a work by [
30], the DC bus energizes a 72L freezer and a lighting circuit with LED lamps. To use this subsystem, switching must be performed by turning the switches (detailed below) to position 1, as noted in
Figure 5.
After installing the system, it was observed that the charge controller has a limitation on the power used. As it has a nominal charge and discharge current limit of 40 A, connected to a 24 V energy accumulator, the maximum power that the controller is capable of managing is 960 W - only half of the installed power of the PVA.
To make better use of the power generated by the PVA, it would be necessary: either to change the voltage of the energy accumulator to 48 V (four batteries in series); or to replace the charge controller with one with a greater capacity.
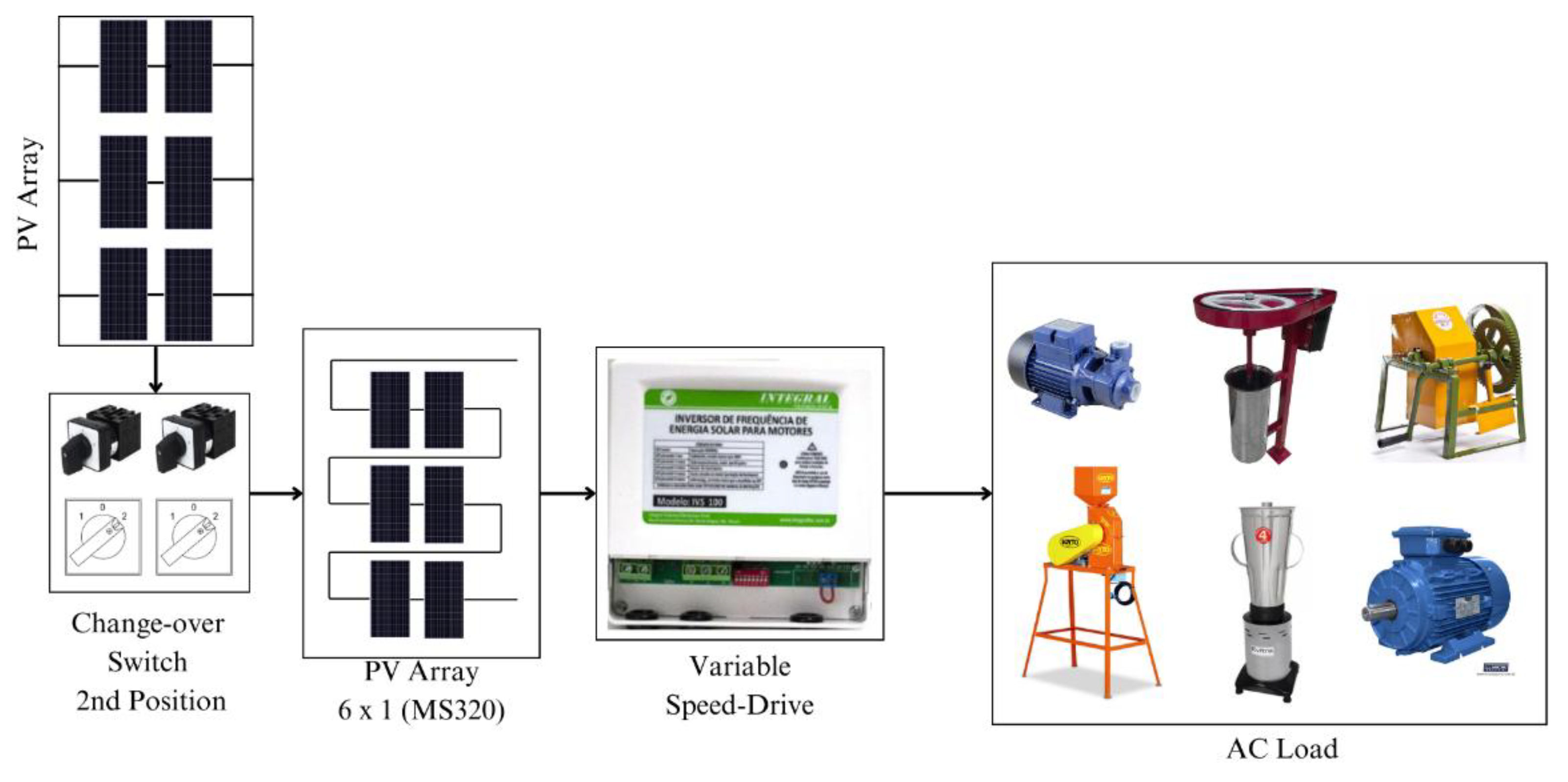
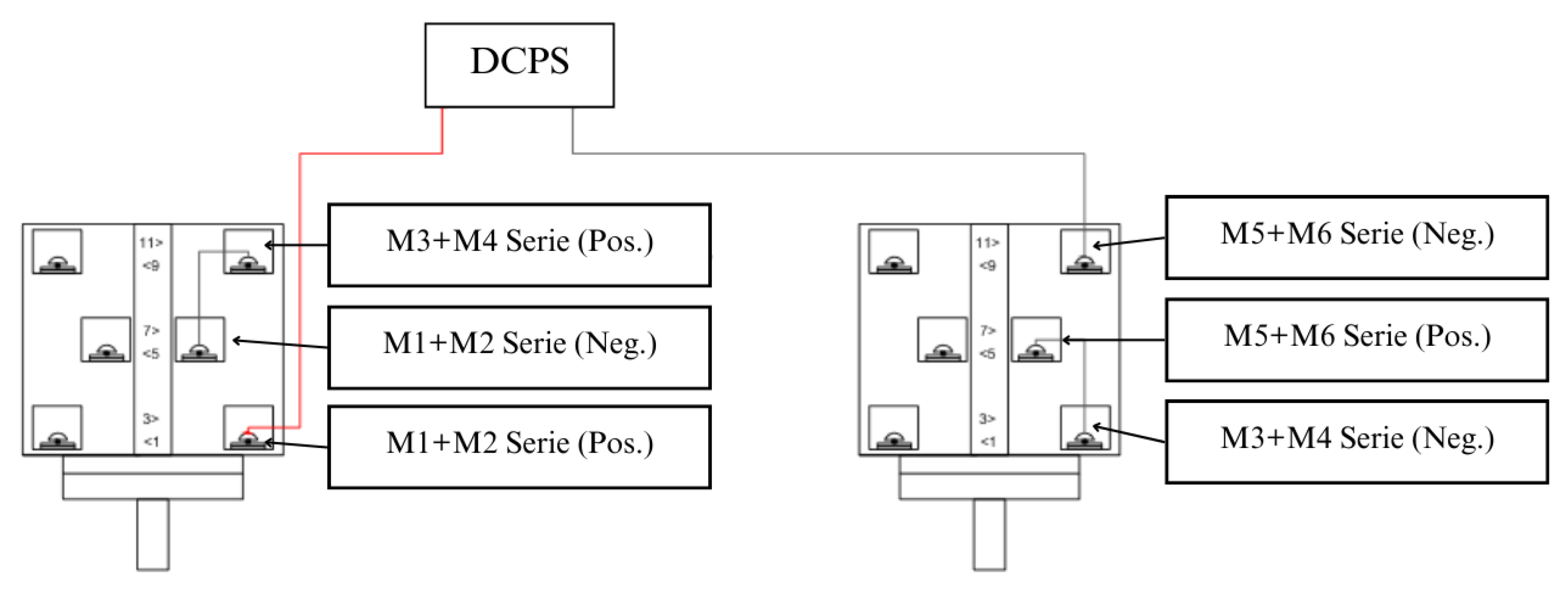
3.3.2. Direct Coupling Photovoltaic System
The DCPS consists of the direct connection of the PVA to the VSD that drives the desired driving load. The VSP model IVS100 of the manufacturer INTEGRALTEC was used. This model supports 220 V three-phase machines up to 1,5 HP.
As mentioned, VSD commonly operate with high voltage values. The model used in this work is one of them. Among the options available in the product instruction manual, there is the configuration of six 330 W
P photovoltaic modules in series [
31] (top diagram on
Figure 6). For the configuration of this subsystem, the simulation of the necessary PVA was also performed, as observed in the lower graph of
Figure 6.
From the values defined for the PVA, it is necessary to configure the VSD through the six
on-off switches (DIP switches). They are configured according to the power of the arrangement, the machine to be used, the reconnection time in cases of undervoltage, among other parameters. A work by [
30] presents the table with the settings used. To use the DCPS subsystem, it is necessary to switch the switches to position 2, as shown in
Figure 7.
3.3.3. Switching System
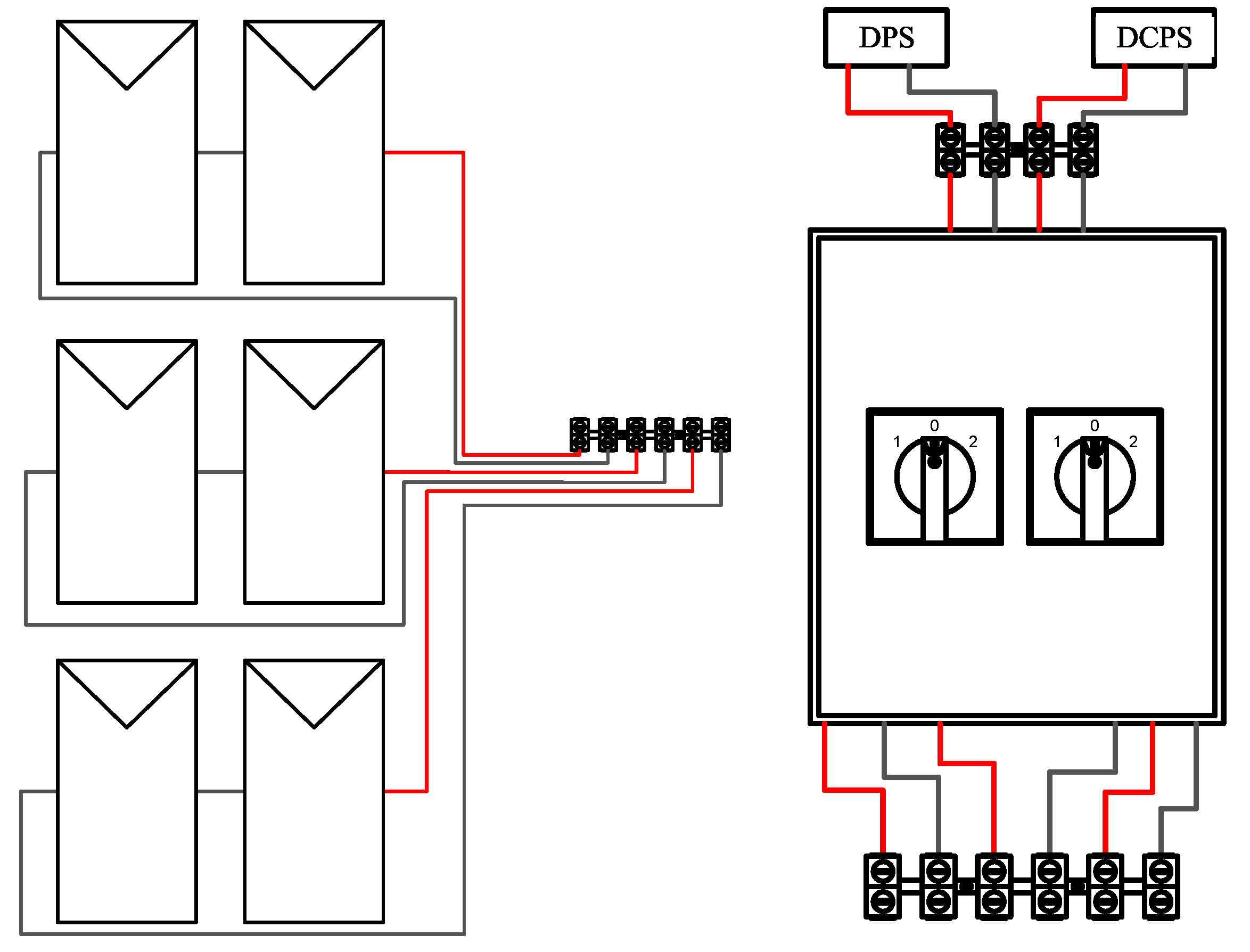
As for both DPS and DCPS, two modules are used in series, the PVA has three pairs of two modules in series, and it is necessary to extend the six terminals to the switchboard where the switches are fixed. In this framework there is: a positive and a negative, both resulting from the serial connection of every two modules and then fixed in a connection bar (
Figure 8).
To perform the switching between the DPS and DCPS subsystems, two three-pole switches of the model K356-40 from the manufacturer Metaltex were used. The six resulting terminals of the PVA fixed to the connection bar are connected to the switches – as they are tripolar, each switch connected to three terminals. The remaining serial and parallel associations are performed at their outputs, located at the top. The terminals resulting from these associations are then fixed in a connection bar from where the load controller and the VSD, related to the DPS and DCPS, respectively, will be connected.
For the DPS, the two transfer switches are switched to position 1. As the serial connections have already been made and the resulting terminals have been connected to the switches, the next step was to perform the connections in parallel - that is, interconnect all the positive and negative terminals resulting in two resulting conductors: one positive and one negative that is connected to the DPS (
Figure 9).
The series associations are made by connecting the poles 7 and 11 of the first switch and the poles 7 and 3 of the second (Figure 9). After the serial associations are made, the resulting positive (pole 3 of the first switch) and negative (pole 11 of the second switch) terminals are then fixed to the connection bar from where they are connected to the DCPS variable speed-drive.
Finally, the integrator system that has an PVA with a mixed configuration according to the need of the subsystem is summarized in
Figure 11.
The switches receive six terminals from three associations of two pairs of photovoltaic modules. Once the remaining associations have been carried out, as detailed above, it is possible to use the switches to switch between the systems as required. By placing them in positions 1, the PVA assumes the association of three connections of two modules in series and energizes the DPS, thus charging the battery bank. In position 2, the two switches connect the PVA terminals in the association of the six modules in series, thus energizing the DCPS that activates a three-phase induction motor for the development of some productive activity.
3.4. Training and Socialization of Knowledge and Experiences
As defined in AP3, the importance of training community families – especially young people – was highlighted. Throughout the process of implementing PV systems in the community, there were residents actively participating in the project. Even in situations where they would not be the ones benefiting from the installation of the system, they showed interest and participation in learning not only the principles of operation of the system components but also the practical execution of the installation.
In addition to monitoring the installation of systems, the community participated in a training held at the ATAIC headquarters with a focus on presenting basic concepts of electricity, the components that make up a photovoltaic system and practical installation activities so that everyone could follow the step by step.
The training, added to the residents who actively followed the installation of photovoltaic systems, made it possible for at least the basic concepts of photovoltaic systems to be fixed. Precautions such as: heating of the battery bank conductors, audible and/or luminous warnings of the charge controller and inverter, were some of the indicators passed on to the participants of the training.
AP4, which focused on sharing experiences and information from the project, with the objective of increasing the interest of young people and forming new leaders within the Ilha das Cinzas community and leaders from nearby communities, was executed by holding an event in early 2022 where it was possible to bring together all ATAIC partners and community leaders interested in the community organization. The event entitled “The social value of energy in building participatory, inclusive and sustainable communities”.
From the socialization of ATAIC’s experiences, other communities were able to reorganize themselves in similar ways. For example, through this event, the Association of Women Agroextractivist Producers of the Mouth of the Mazagão Velho River (AMPAFOZ
6) was able to participate in the selection process for financing projects of the Honnold Foundation and be one of the few communities contemplated for the implementation of photovoltaic systems.
4. Conclusions
Based on the PRD and SWOT analysis, four action plans were elaborated: (1) and (2) development of a photovoltaic system capable of assuming different configurations according to the daily demands of the açaí value chain and other complementary economic activities; (3) training of community residents; and (4) socialization of the experiences obtained during the execution of the project with leaders of other communities and ATAIC partner agents.
One of the main contributions of the project was the development of the photovoltaic system with versatile and flexible topology, which, being aligned with the weaknesses and needs of the community, could contribute to the improvement of the açaí value chain, in addition to enabling the integration of social technologies – which help in the development and autonomy of riverside communities.
The photovoltaic system of mixed configuration has the capacity to meet domestic loads in DC and AC in the daily life of the family through the DPS. Faced with the constant demand for motor loads (removal of açaí pulp, pumping water into the reservoir, irrigation of crops with biofertilizer, crushing of seeds and nuts), the resident has the possibility to use the other configuration, DCPS, switching the keys to the second position, thus energizing the electric motor. The final system enables several applications, not only in the açaí value chain, but in other productive activities and social technologies, whether with motor or domestic loads.
In addition to the application of switches to the photovoltaic systems developed here, this research highlights as another contribution the need for participation between the researcher and the community of the study area. The developed system went through three stages of improvements - all coming from responses from the community itself, either to make the system cheaper, practical and/or intuitive for those who would handle it: the riverside inhabitants.
In addition, community participation in the installation process was vital, as it enabled familiarization with this type of renewable technology, being aligned with AP3. This action plan sought to train families regarding the photovoltaic energy technology introduced in the community. Within the period of execution of this research, the action plan achieved its objective by making the installed systems more familiar to residents.
Finally, AP4 was executed with the holding of the workshop “The social value of energy in building participatory, inclusive and sustainable communities”. The event was attended by leaders from different riverine and land communities interested in organizing themselves in a similar way to ATAIC and Ilha das Cinzas to access national and international resources aimed at socioeconomic development with the help of renewable technologies.
The path taken indicates that the most promising means for the development of value chains in riverine communities is from the insertion of new technologies in the production process accompanied by the participation and training of the actors involved in this chain, because without this integration the transfer of technology tends to fail. Economic development is intricately linked to the social development of families, since after the installation of the system it is necessary that families are trained to handle the technology and understand its functioning and limitations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Allan Pena, Pedro Guedes, Marcelino Guedes and Alaan Brito; Data curation, Allan Pena, Marcelino Guedes, Davi François, Mary Parmentier and Alaan Brito; Formal analysis, Allan Pena, Marcelino Guedes and Alaan Brito; Funding acquisition, Francisco Malheiros, Davi François, Mary Parmentier and Alaan Brito; Investigation, Allan Pena, Pedro Guedes, Francisco Malheiros, Felipe Monteiro, Werbeston Oliveira, Marcelino Guedes, Márcio Oliveira, Gilmar Paixão, Moisés Sousa, Geraldo Maranhão, Alcides Júnior, André Ferreira, Davi François and Alaan Brito; Methodology, Allan Pena, Francisco Malheiros, Marcelino Guedes and Alaan Brito; Project administration, Alaan Brito; Resources, Marcelino Guedes and Alaan Brito; Software, Allan Pena, Francisco Malheiros and Felipe Monteiro; Supervision, Marcelino Guedes and Alaan Brito; Validation, Allan Pena, Francisco Malheiros, Marcelino Guedes, Alcides Júnior and Alaan Brito; Visualization, Alaan Brito; Writing – original draft, Allan Pena; Writing – review & editing, Allan Pena, Werbeston Oliveira, Marcelino Guedes, Moisés Sousa, Davi François, Mary Parmentier and Alaan Brito. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was developed within the scope of the projects “Solar Energy for Food Sovereignty of Riverside Families,” which received external funding from the Honnold Foundation, and “Generation and Integration of Biomass and Photovoltaic Energy with the Strengthening of Productive Chains in Isolated Communities in the Amazon River Estuary”. The Amazon+10 Initiative is a project of the National Council of State Research Support Foundations (Confap). The lead author received funding from a Master’s scholarship from the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Federal University of Pará under process 3.683.904 and registered in the National System for the Management of Genetic Heritage and Associated Traditional Knowledge under code number AA34484.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The table of intersections between all SWOT matrix factors can be found in the Annexes of the main author’s master’s research at the link: Access Link.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Araujo RO, Ribeiro FCP, Santos VO, Lima VMR, Santos JL, Vilaça JES, et al. Renewable Energy from Biomass: an Overview of the Amazon Region. Bioenergy Res. Springer; 2022. p. 834–49. [CrossRef]
- Organização das Nações Unidas. Accelerating SDG 7 Achievement - Summary for Policymakers. 2018.
- Leite CC, Sousa V de. Exclusão Elétrica na Amazônia Legal: quem ainda está sem Acesso à Energia Elétrica? Instituto de Energia e Meio Ambiente. 2020 Oct;35.
- Mazzone, A. Decentralised energy systems and sustainable livelihoods, what are the links? Evidence from two isolated villages of the Brazilian Amazon. Energy Build. 2019;186:138–46. [CrossRef]
- Diálogos Pró-Açaí. Recomendações para impactos sistêmicos na cadeia de valor do açaí [Internet]. 2023. Available from: https://www.dialogosproacai.org.br/acervos/dialogos-pro-acai.
- Santos ES, Ramos CA-, Guedes MC. Segurança alimentar de famílias extrativistas de açaí na Amazônia oriental brasileira: o caso da Ilha das Cinzas. Novos Cadernos NAEA. 2021;24:195–221. [CrossRef]
- Silva RM, da. ENERGIA SOLAR NO BRASIL: dos incentivos aos desafios [Internet]. Senado Federal. 2015 [cited 2022 Nov 14]. Available from: https://www12.senado.leg.
- Ponte GP, Calili RF, Souza RC. Energy generation in Brazilian isolated systems: Challenges and proposals for increasing the share of renewables based on a multicriteria analysis. Energy for Sustainable Development. 2021;61:74–88. [CrossRef]
- Pereira EB, Martins FR, Gonçalves AR, Costa RS, Lima FJL, Rüther R, et al. Atlas Brasileiro de Energia Solar. INPE [Internet]. 2017;1:80. Available from: http://urlib.net/rep/8JMKD3MGP3W34P/3PERDJE.
- Ministério de Minas e Energia (MME). PROGRAMA NACIONAL DE UNIVERSALIZAÇÃO DO ACESSO E USO DA ENERGIA ELÉTRICA. A. 2017.
- Mamede Filho, J. Instalações Elétricas Industriais. 9th ed. Rio de Janeiro: LTC; 2017.
- Junior J da SL, Pereira JIM, Lira R de L. Sistema individual de Energia Elétrica com fonte intermitente fotovoltaico off grid implantada em uma habitação ribeirinha no Município de Manacapuru - AM. Brazilian Journal of Development. 2021;7:118458–75. [CrossRef]
- Sousa MC de, Batista LM, Fiel LG, Monteiro Neto A, Freitas KM, Pereira R da S, et al. Sistema Fotovoltaico Off Grid para comunidade ribeirinha na Região Insular de Belém - Pará. Revista Ibero-Americana de Ciências Ambientais. 2021;12:312–24. [CrossRef]
- Torres NNS, Ledesma JJG, Cavallari MR, Ando Junior OH. Amazon Kit: Proposal for an Innovative Energy Generation and Storage Solution for Sustainable Development of Isolated Communities. Sustainability. 2024;16:6280. [CrossRef]
- Abella MA, Lorenzo E, Chenlo F. PV Water Pumping Systems Based on Standard Frequency C. Progress In Photovoltaics: Research and Applications. 2003;191:179–91. [CrossRef]
- Brito AU, Zilles R. Systematized procedure for parameter characterization of a variable-speed drive used in photovoltaic pumping applications. Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications. 2006;14:249–60. [CrossRef]
- Gasque M, González-Altozano P, Gutiérrez-Colomer RP, García-Marí E. Comparative evaluation of two photovoltaic multi-pump parallel system configurations for optimal distribution of the generated power. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments. 2021;48. [CrossRef]
- Queiroz AO, Brito AU. Direct Connection Photovoltaic System In Multi-motor Application For The Rural Sector. Engenharia Agrícola. 2020;4430:303–14. [CrossRef]
- Feijão AT, Almeida AMG, Brito AU. Photovoltaic acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) berry juice extractor machine. J Phys Conf Ser. IOP Publishing Ltd.; 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zucoloto GF, Pereira L de S. TECNOLOGIAS SOCIAIS E ECONOMIA SOLIDÁRIA: PROJETOS CERTIFICADOS PELA FUNDAÇÃO BANCO DO BRASIL. Dinâmicas da Economia Solidária no Brasil: organizações econômicas, representações sociais e políticas públicas. 2020. p. 187–205.
- Freitas AF de, Freitas AF de, Dias MM. O uso do diagnóstico rápido participativo (DRP) como metodologia de projetos de extensão universitária. Em Extensão [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2022 Nov 11];11:69–81. Available from: https://seer.ufu.br/index.php/revextensao/article/view/20780/11882.
- Cerqueira L. Guia do Diagnóstico Participativo [Internet]. 2 ed. FLACSO Brasil; 2021. Available from: http://flacso.org.br/files/2015/08/Guia-do-Diagnostico-Participativo.pdf.
- Ventura KS, Suquisaqui ABV. Aplicação de ferramentas SWOT e 5W2H para análise de consórcios intermunicipais de resíduos sólidos urbanos. Ambiente Construído. 2020;20:333–49. [CrossRef]
- Filho TAG, Júnior ASS, Ferreira ABS, Silva VL, Santos AM, Santos JLDM, et al. Matriz SWOT Como Ferramenta Estratégica Na Gestão De Instituições De Ensino: Implicações Para O Processo De Ensino E Aprendizagem. Business and Management. 2024;26:01–6.
- Martins, F. Promoção da saúde em comunidades isoladas através do abastecimento de energia. https://jornal.usp.br/?p=818139. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Silva BN, da. Ferramentas Adicionais ao Projeto de Sistemas Fotovoltaicos Isolados Para Unidades Familiares Ribeirinhas: Uma Experiência na Comunidade de Ilha das Cinzas - Gurupá, PA [Internet] [Dissertação]. Universidade Federal do Pará; 2018. Available from: www.tcpdf.
- Silva WTL, Marmo CR, Leonel LF. Memorial Descritivo: Montagem e Operação da Fossa Séptica Biodigestora [Internet]. São Paulo: Embrapa Instriumentação; 2017. Available from: www.embrapa.br/fale-conosco/sac.
- MINASOL. Módulo Fotovoltaico Policristalino MS320.
- Prieb CWM, Krenzinger A. DETERMINAÇÃO DE CURVA CARACTERÍSTICA DE ARRANJO FOTOVOLTAICO. 2007.
- Pena AGL, Brito AU, Guedes PML, Monteiro F, Malheiros JB, Malheiros FB, et al. SISTEMA FOTOVOLTAICO ISOLADO DE CONFIGURAÇÃO MISTA PARA FAMÍLIAS RIBEIRINHAS. Revista Brasileira de Energia Solar [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2023 Apr 3];13:203–12. https://rbens.emnuvens.com.br/rbens/article/view/399.
- Integral Tecnologia. Inversor de Frequência de Energia Solar para Motores - 1,5 CV; 3 CV; 5 CV - Modelos IVS100 - Manual de Instruções - V2.0 [Internet]. Integral Sistemas Eletrônicos Eireli. 2021 [cited 2022 Jun 23]. p. 3–6. Available from: https://www.integraltec.com.br/home/inversores-solares.
| 1 |
Luz Para Todos |
| 2 |
Agência Nacional de Energia Elétrica |
| 3 |
Microsistemas Isolados para Geração e Distirbuição de Energia Elétrica |
| 4 |
Sistemas Individual para Geração de Energia Elétrica com Fontes Intermitentes |
| 5 |
Associação dos Trabalhadores Agroextrativistas da Ilha das Cinzas |
| 6 |
Associação das Mulheres Produtoras Agroextrativistas da Foz do Rio Mazagão Velho |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).