Submitted:
30 December 2024
Posted:
31 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Aquaculture
3. Chemical Total Synthesis and Semi-Synthesis
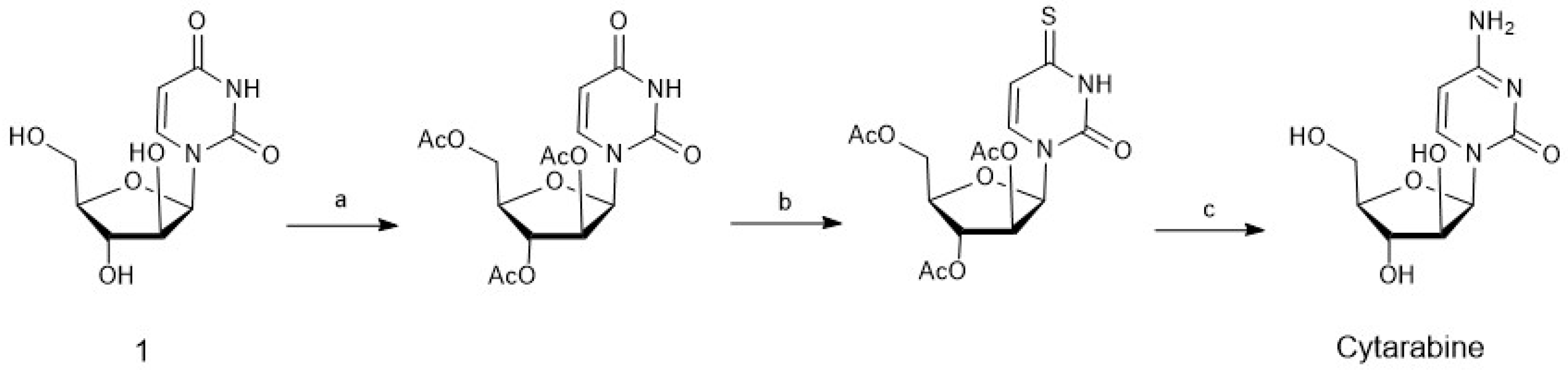
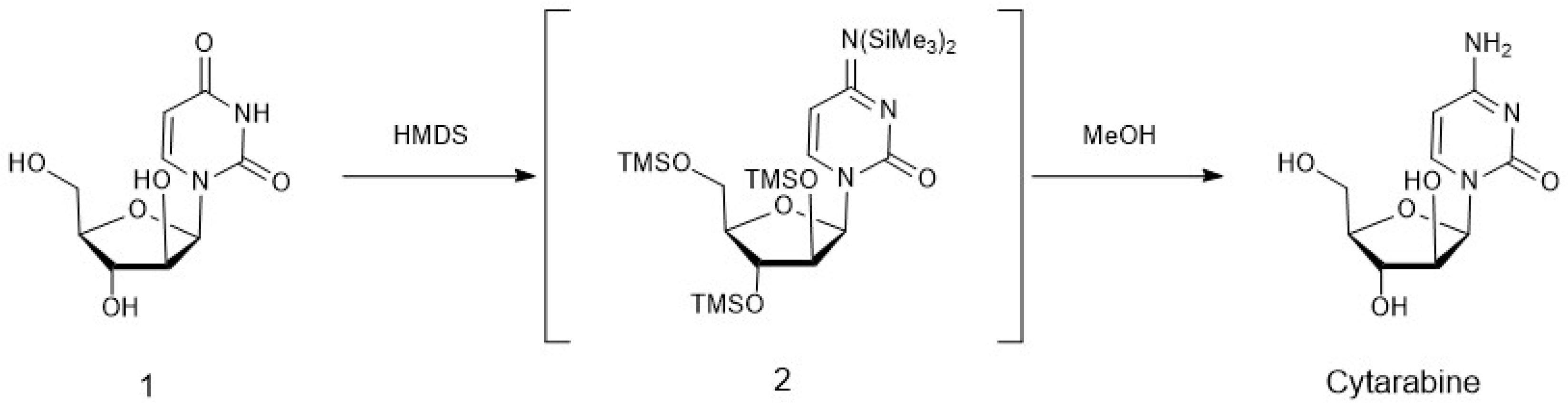
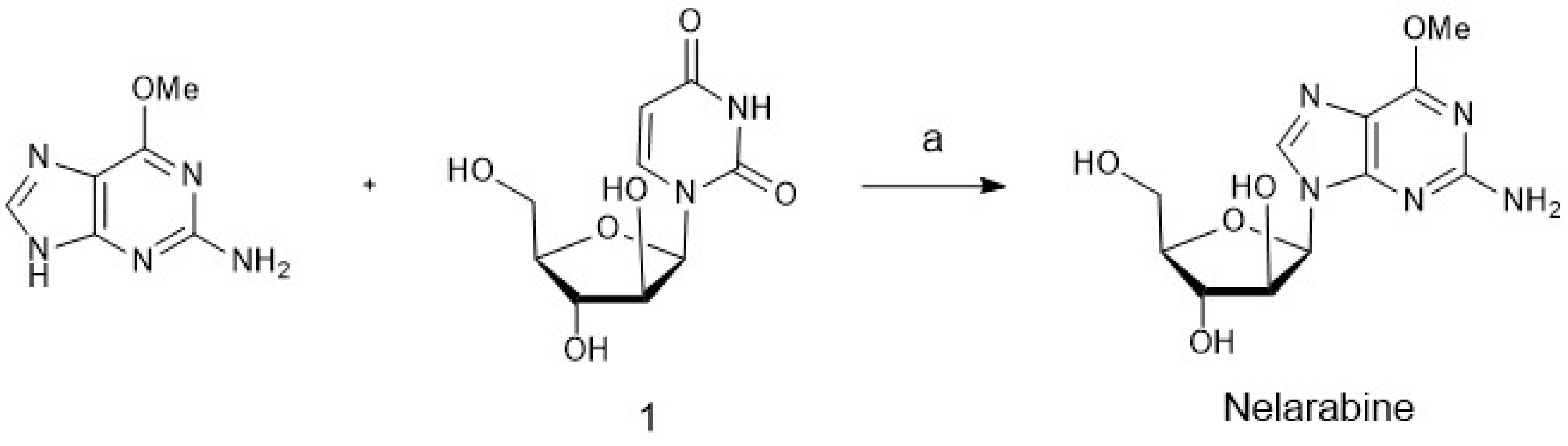
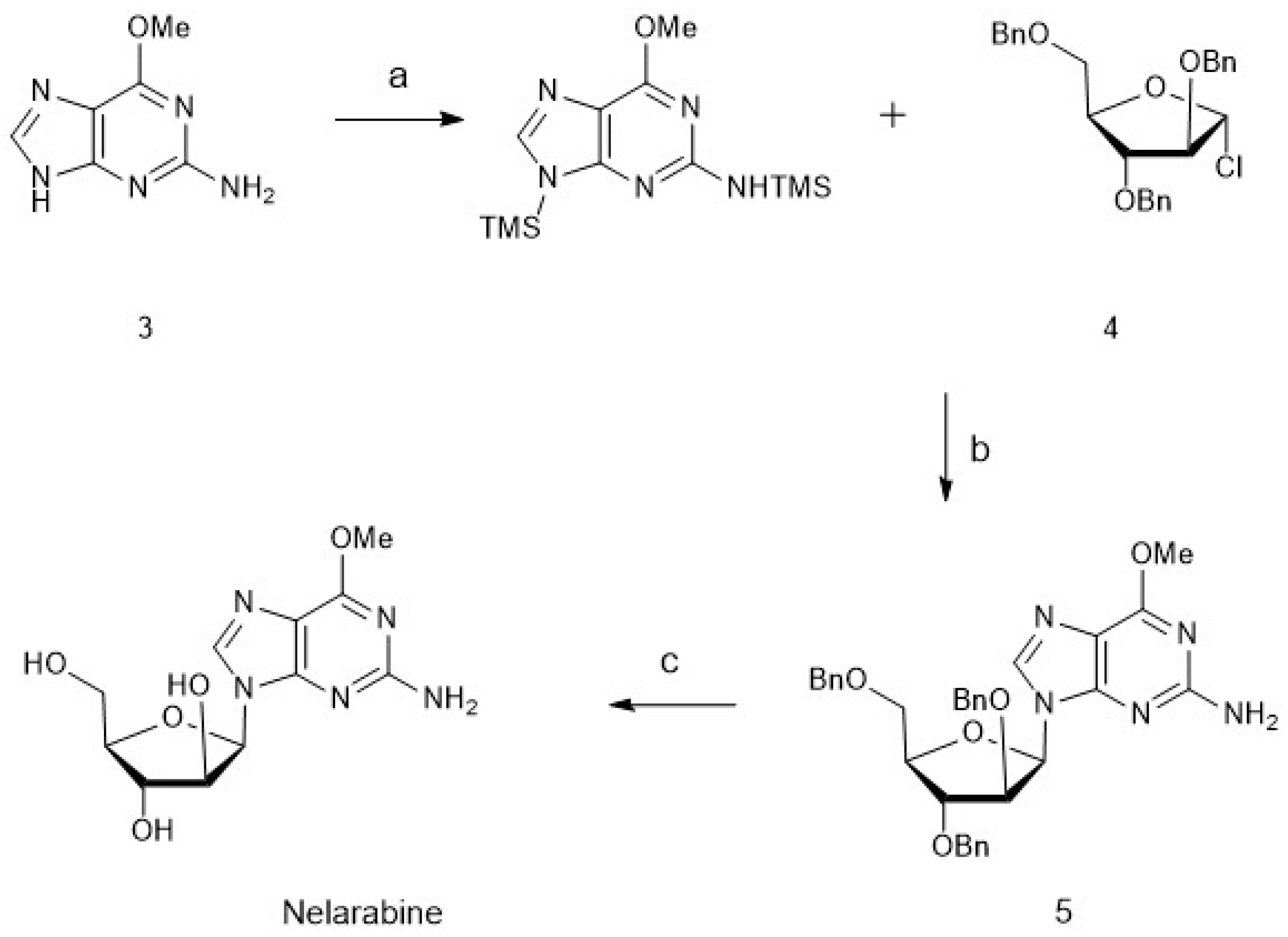
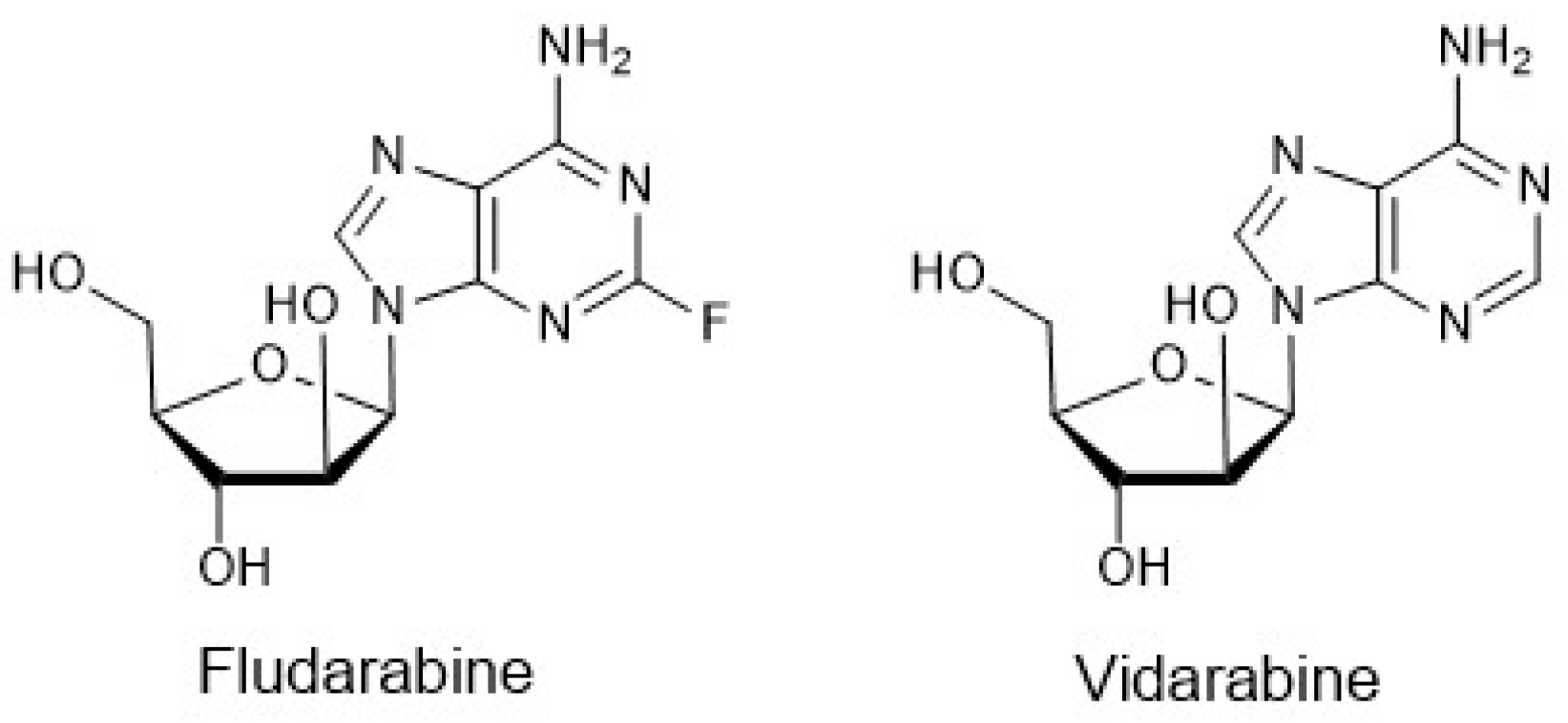
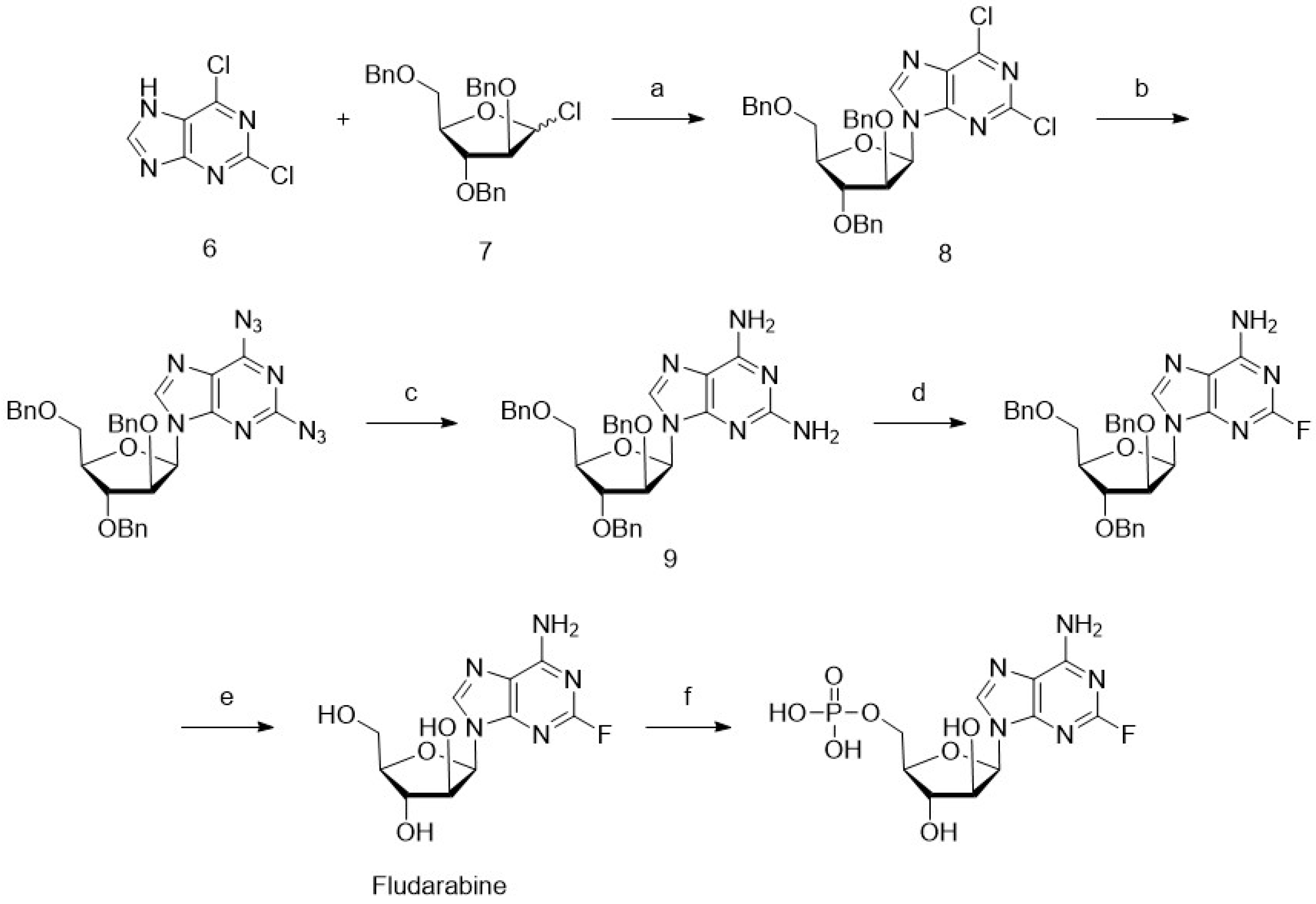
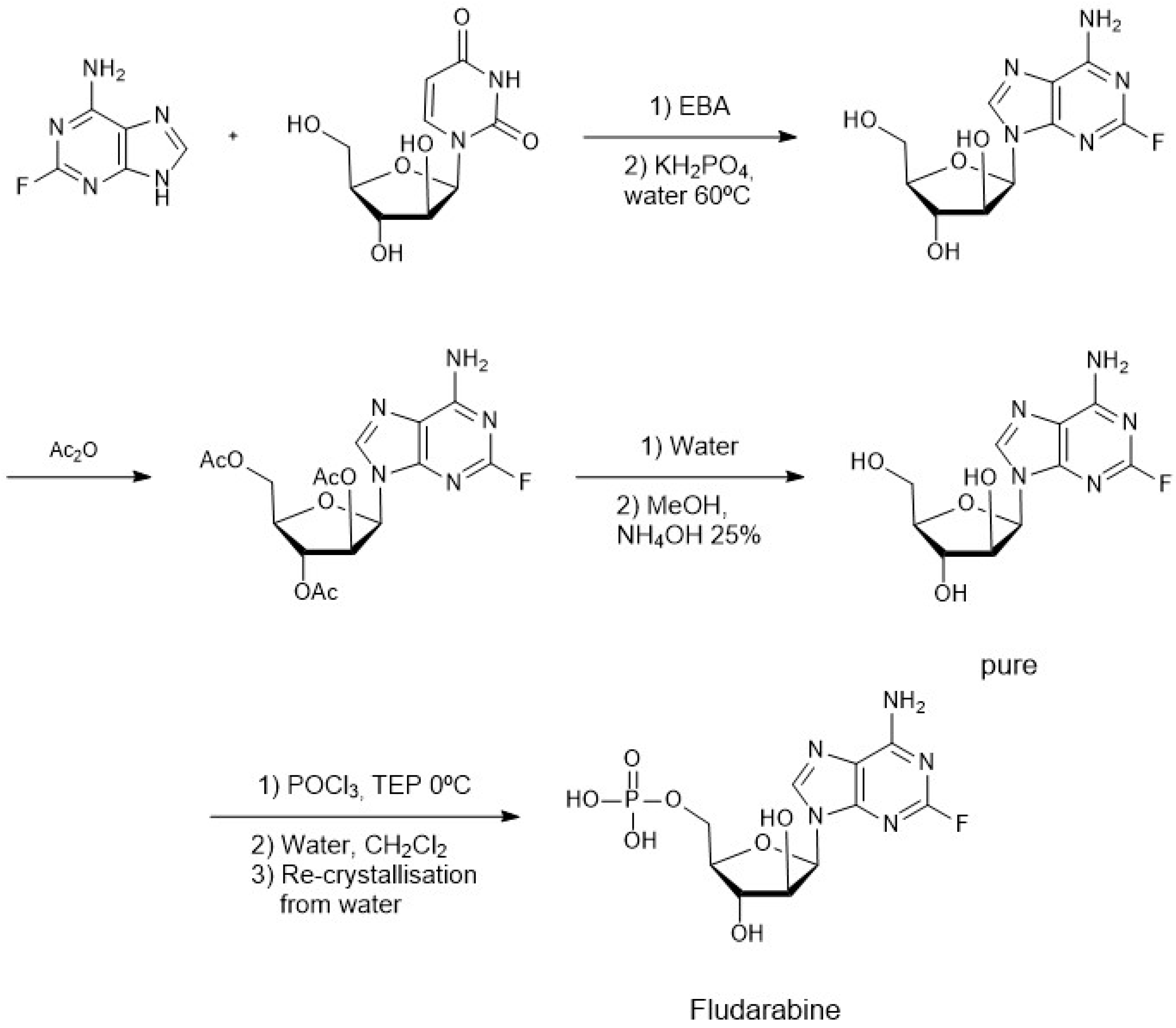
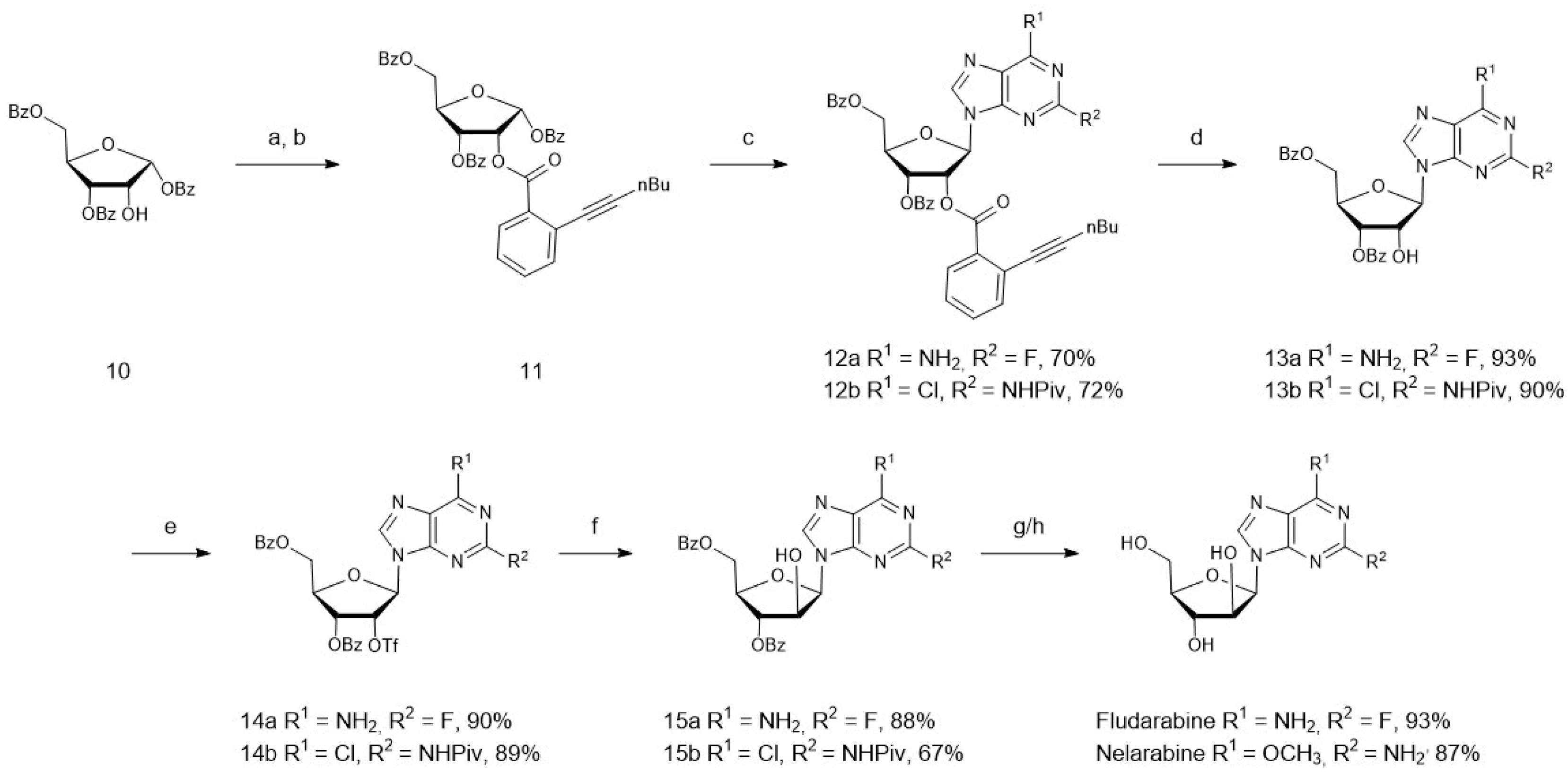
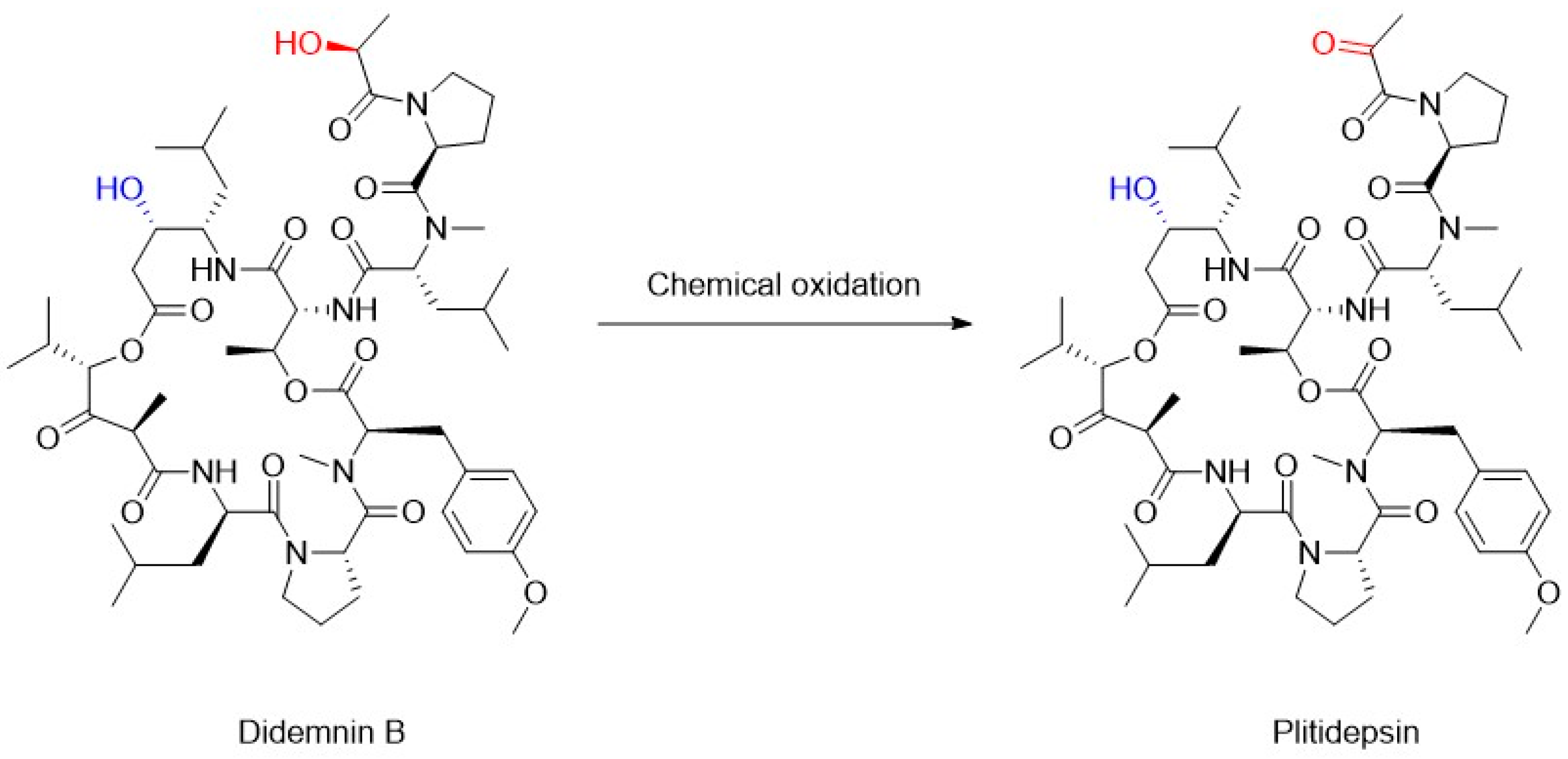
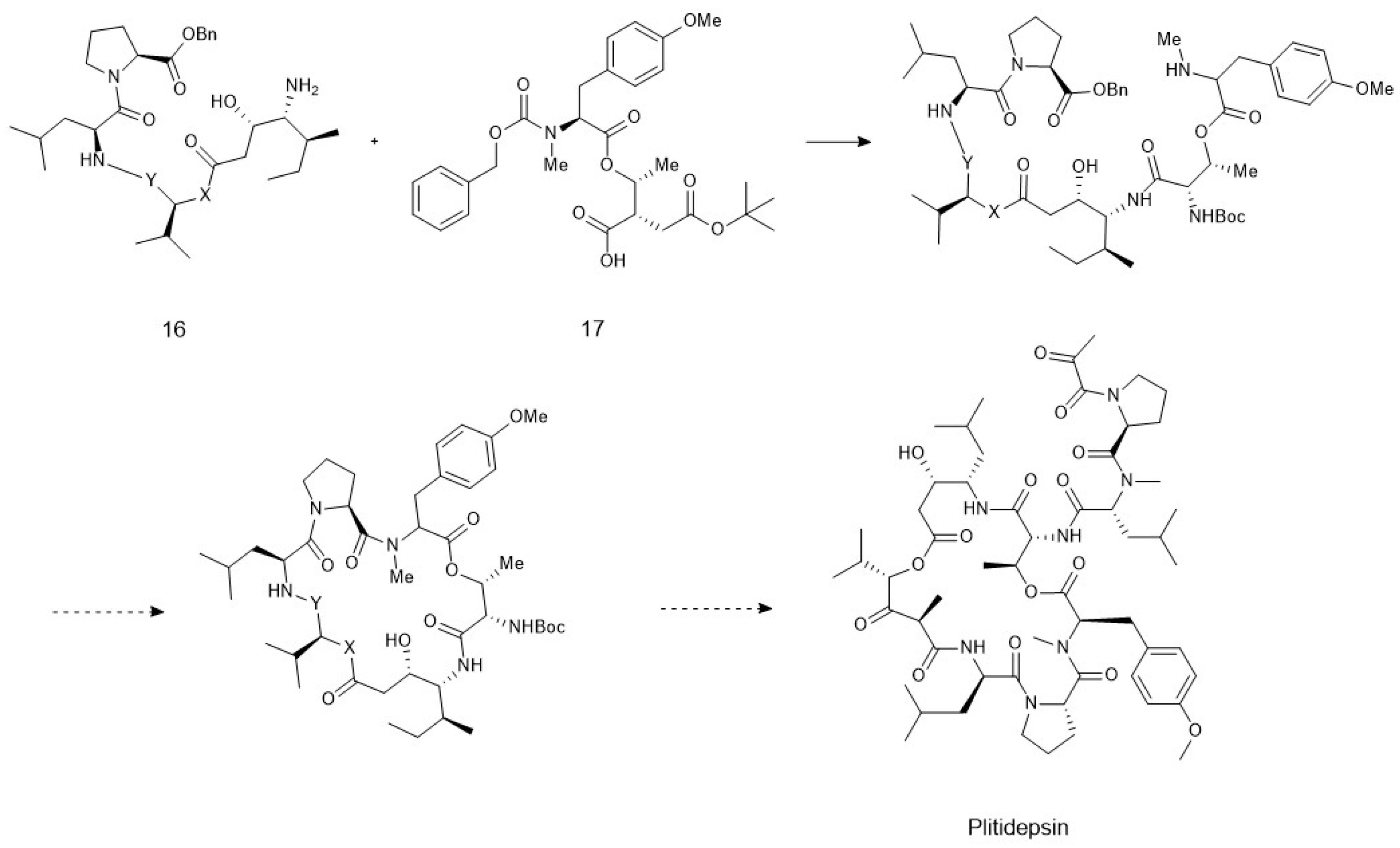
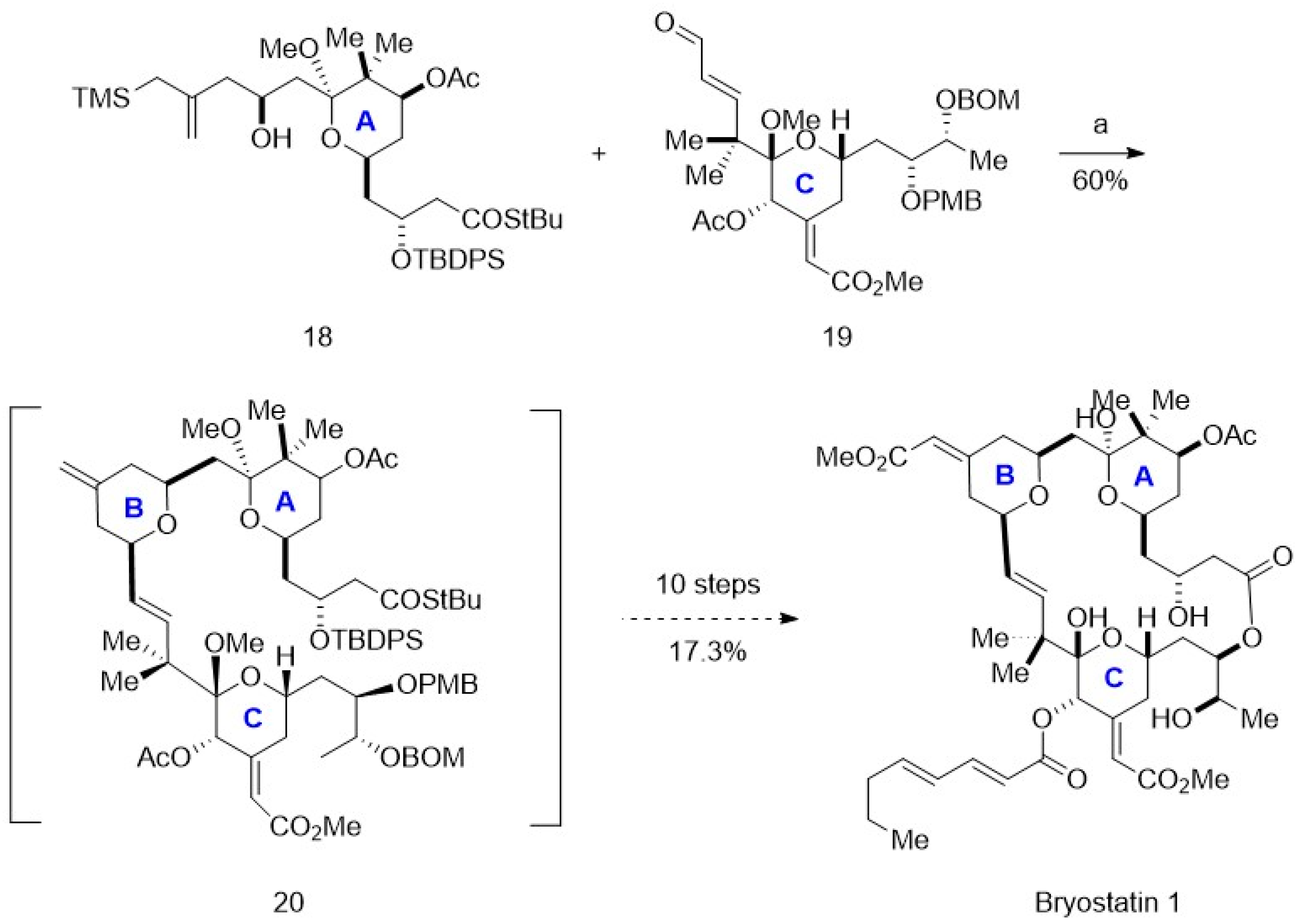
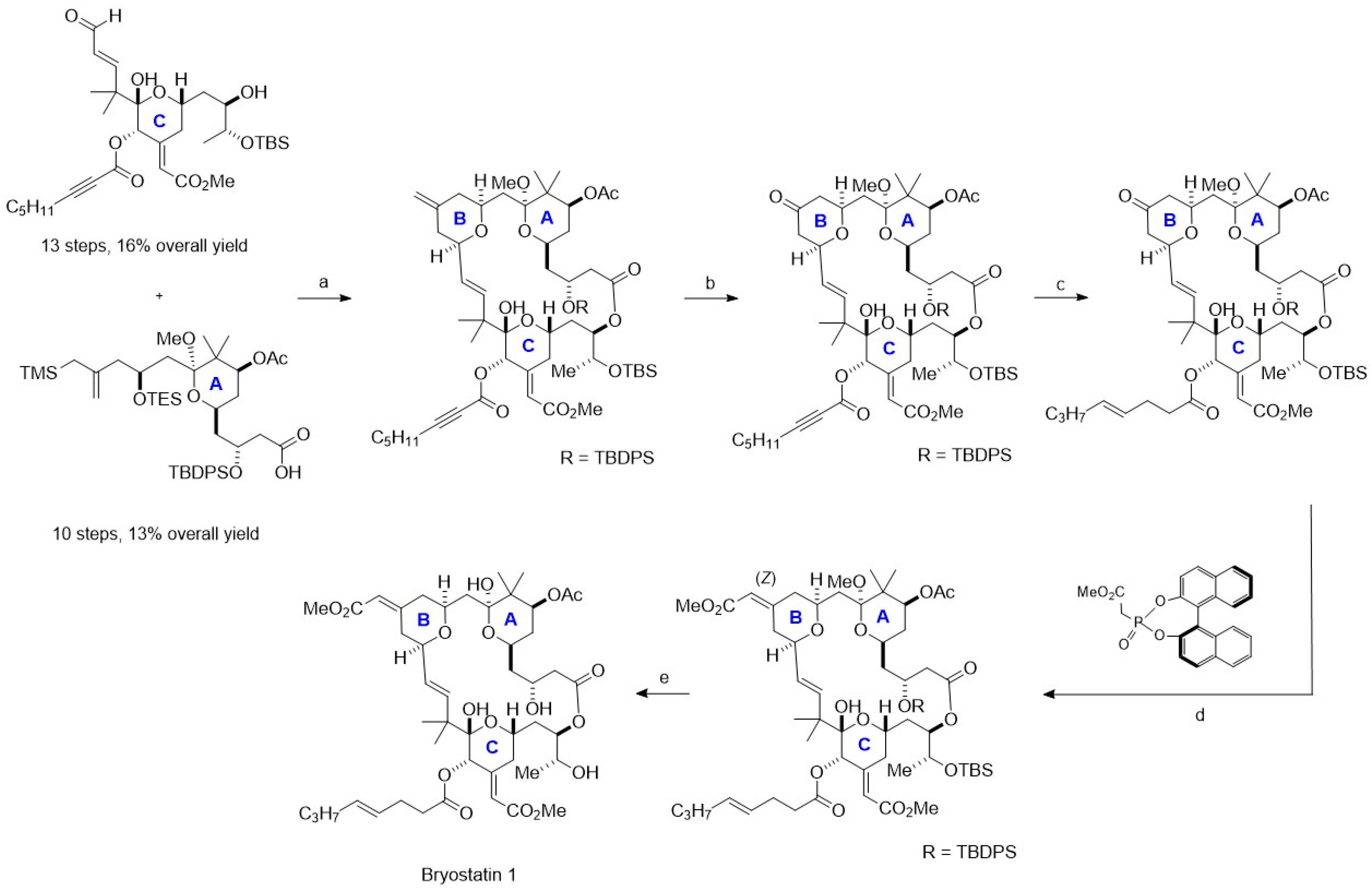
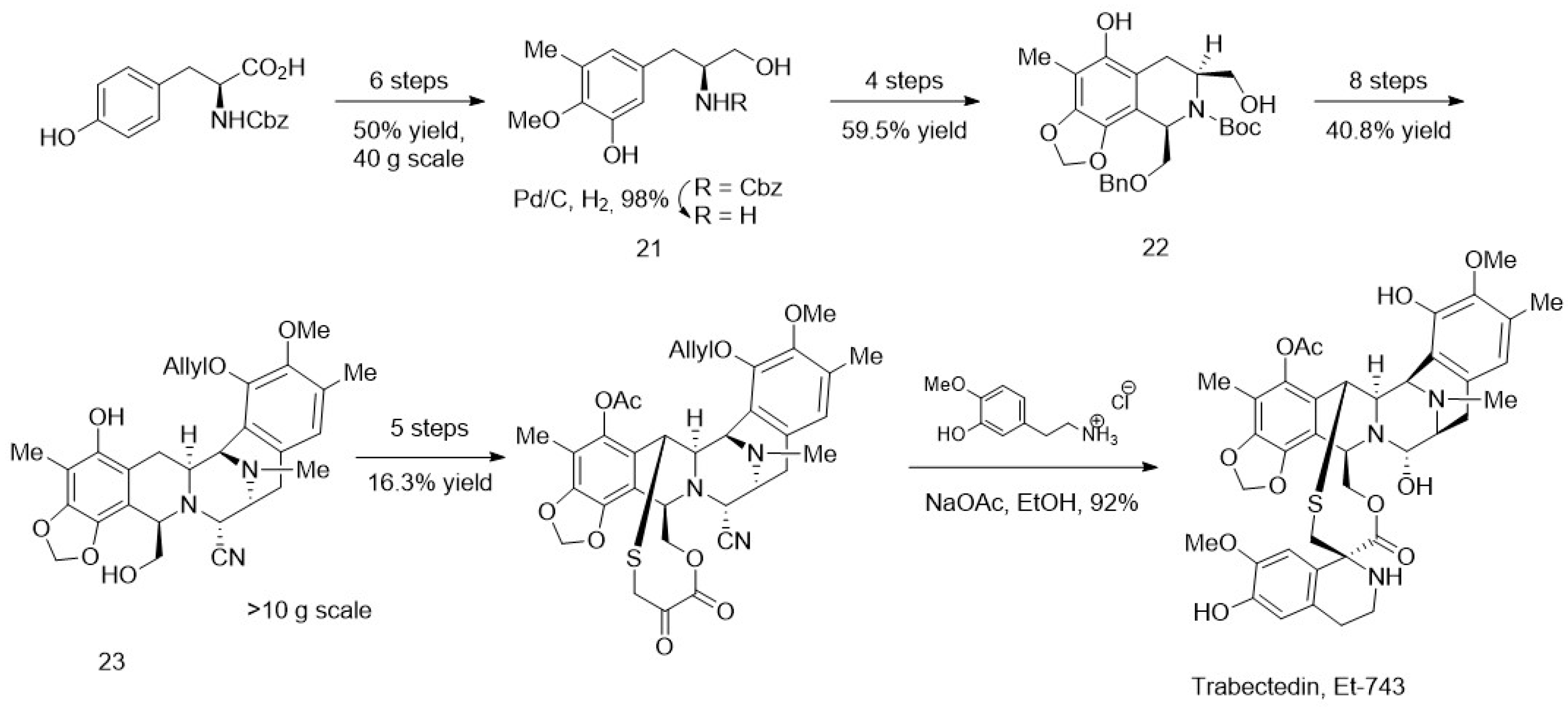
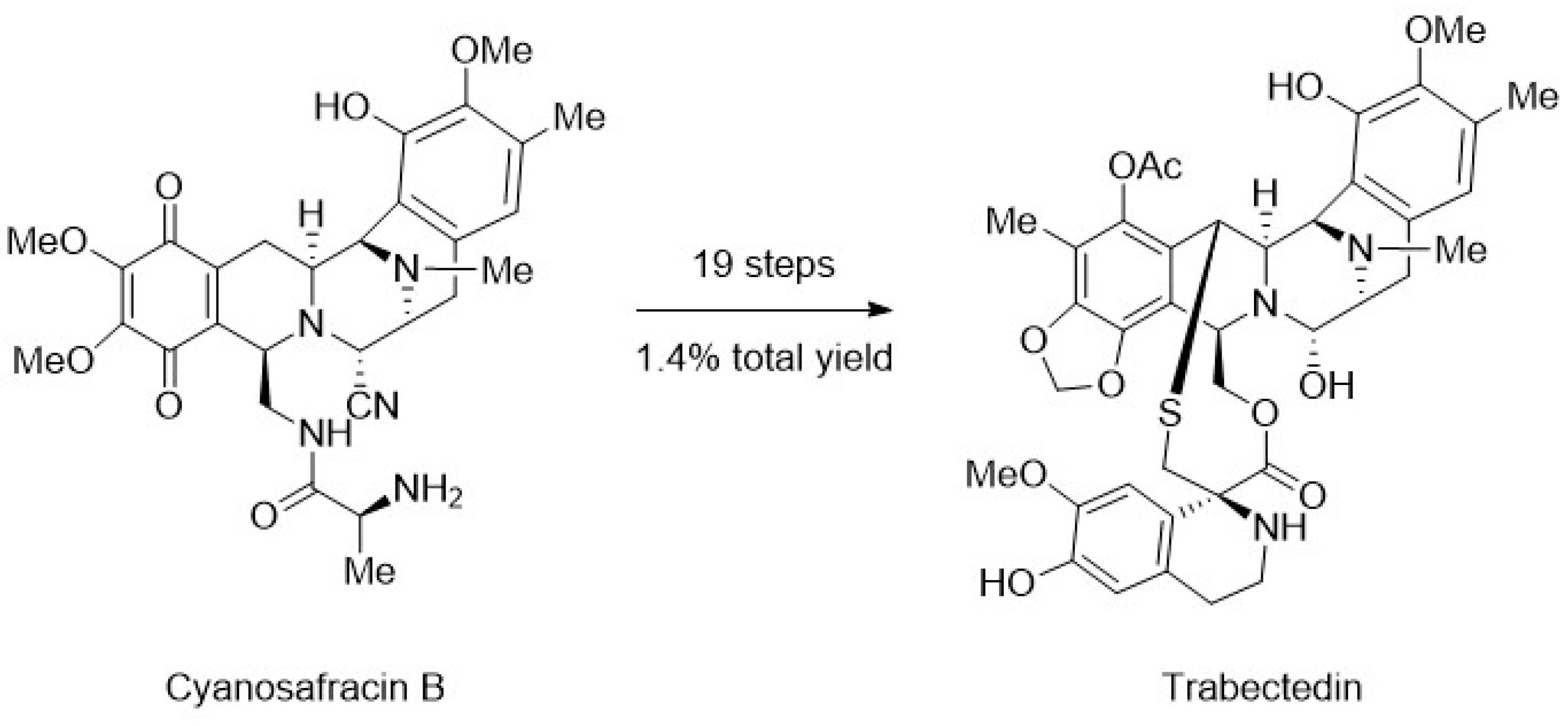
4. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Marine Natural Products
4.1. Enzymatic Desymmetrization of Meso- Compounds, Kinetic Resolution and Deracemization
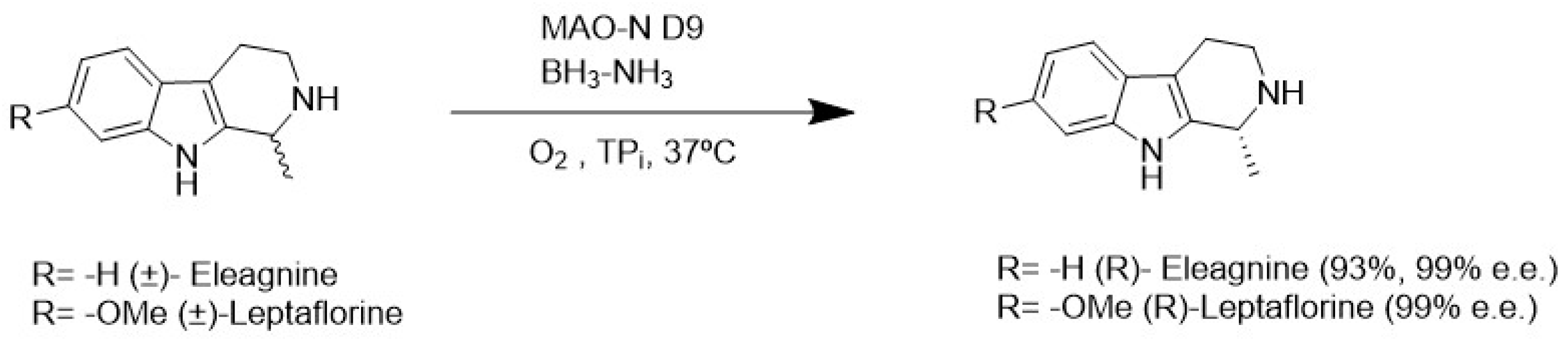
4.2. Enzymatic Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
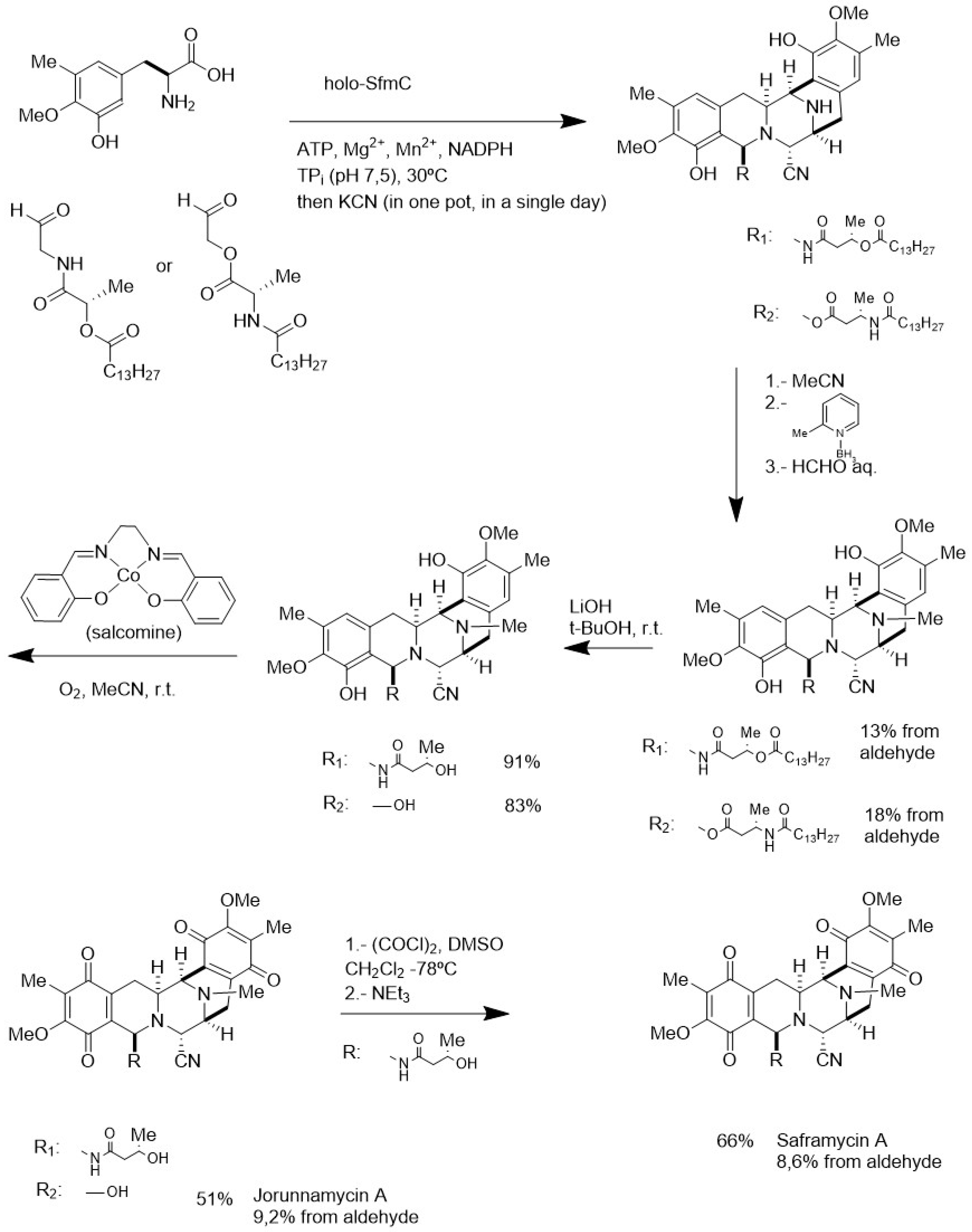
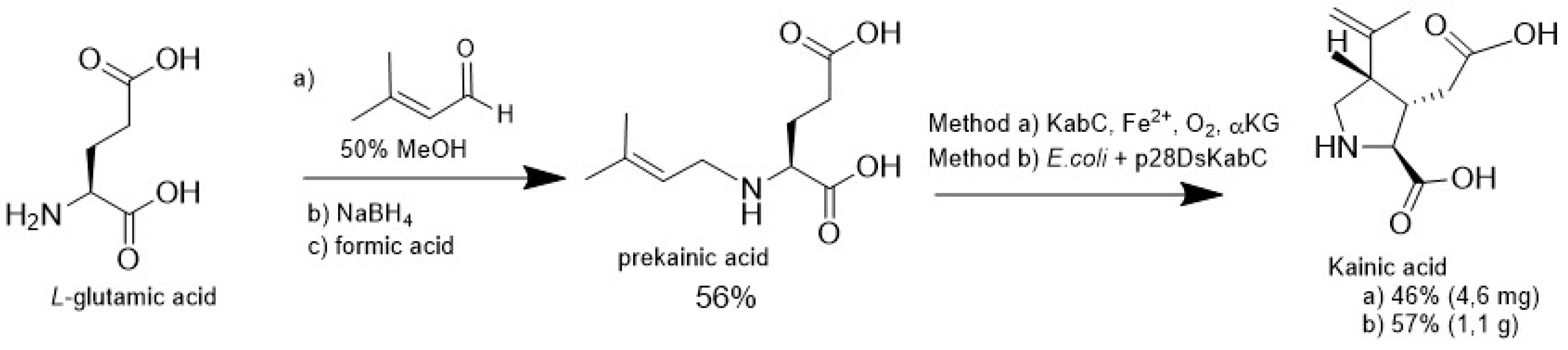
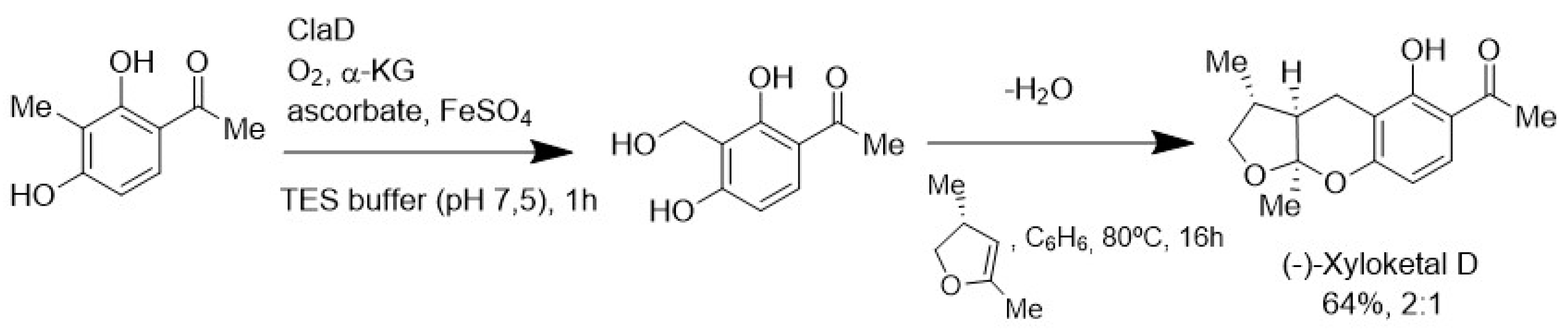
4.3. Biocatalytic Oxidation
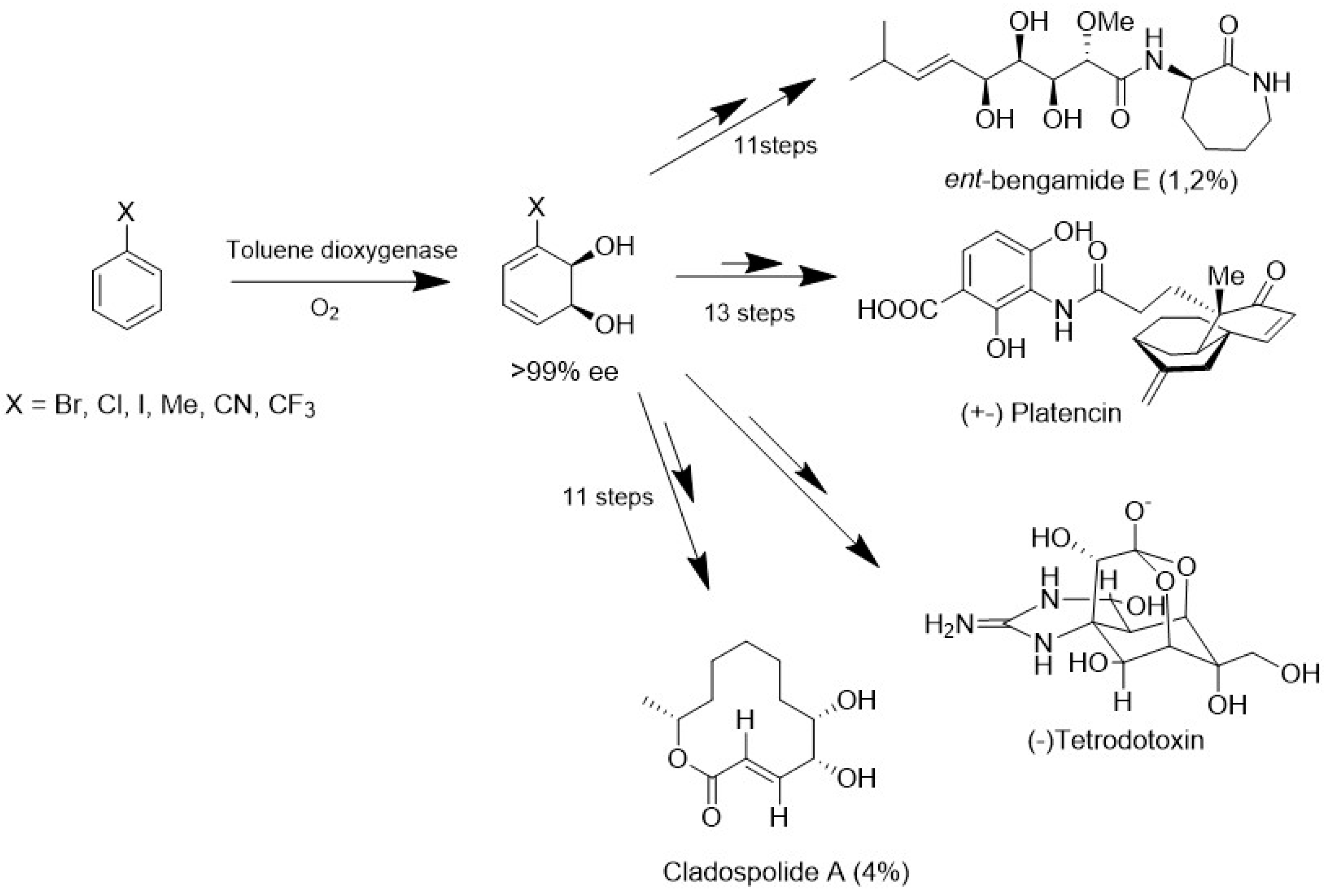
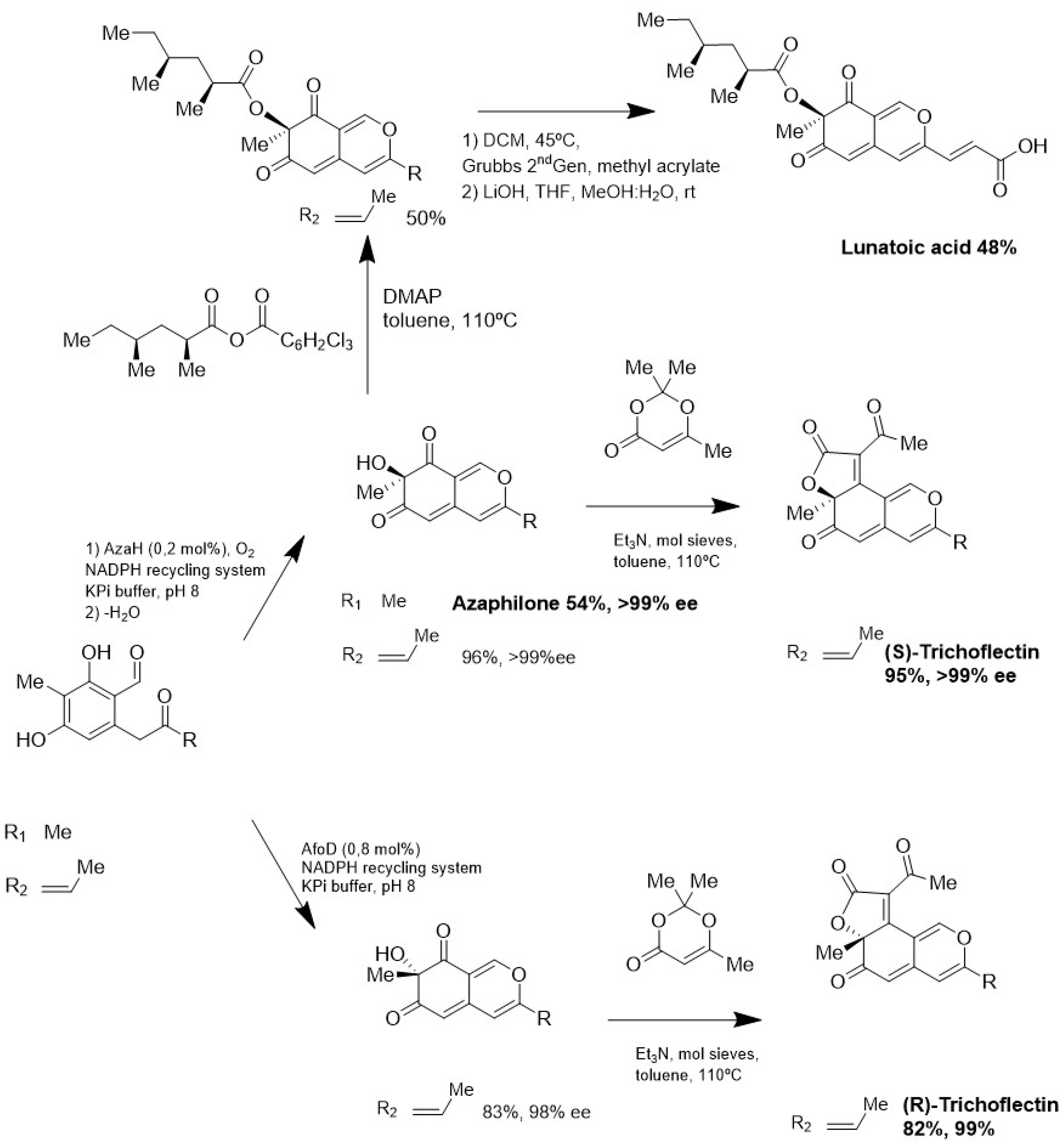
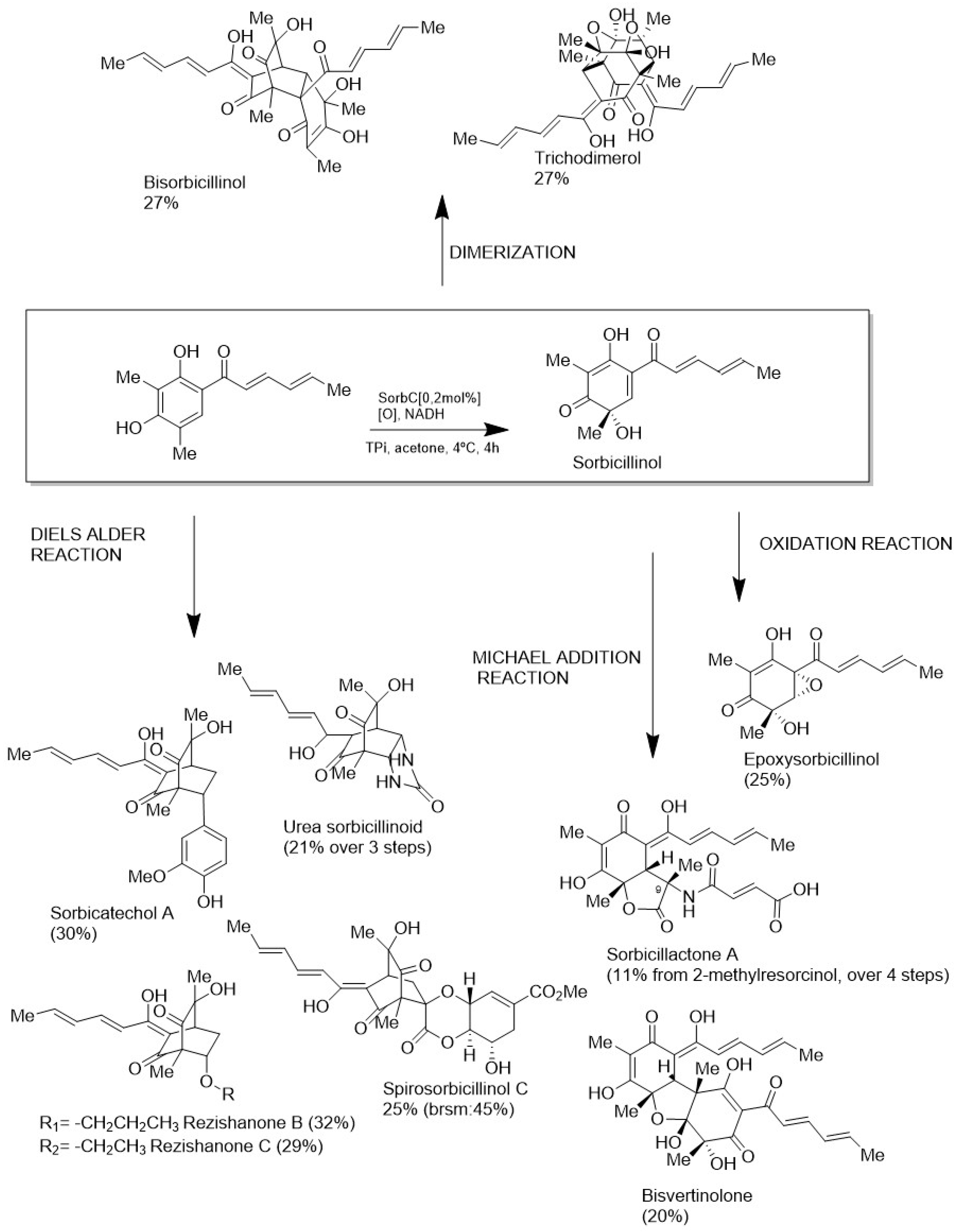
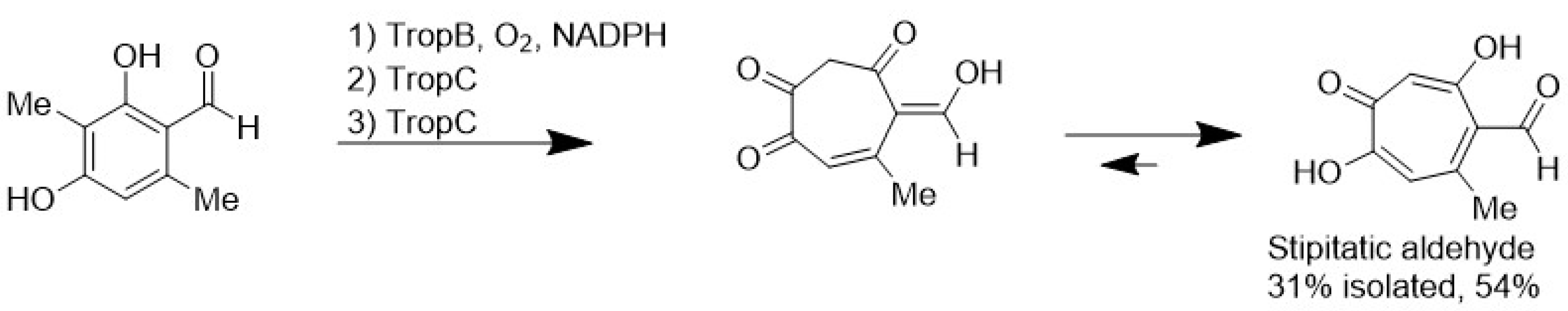
5. Production of MNPs by Biotechnological Approaches
5.1. Fermentation: Axenic Macroscale Culture and Mixed Fermentation
5.1.1. Axenic Macroscale Cultures
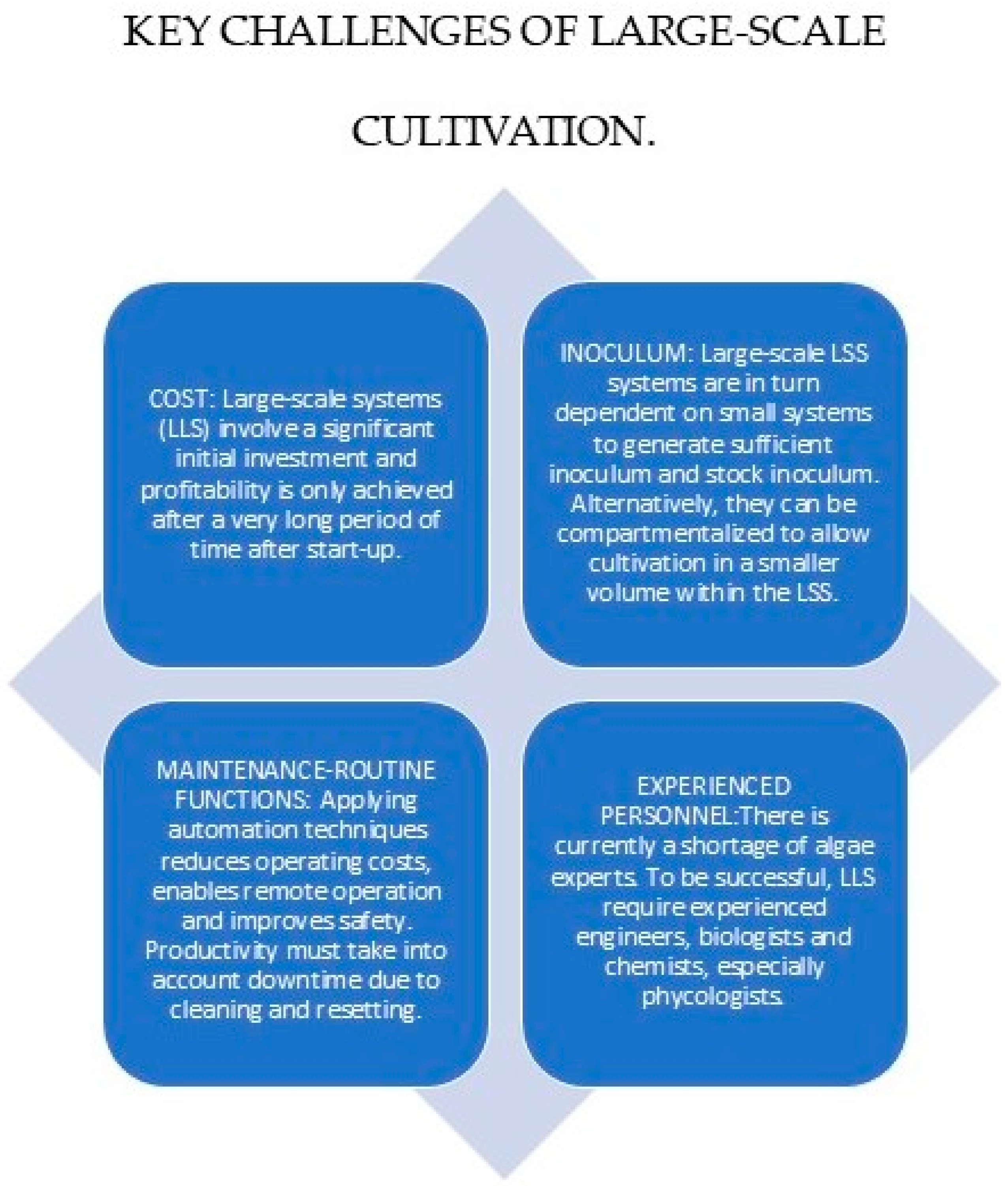
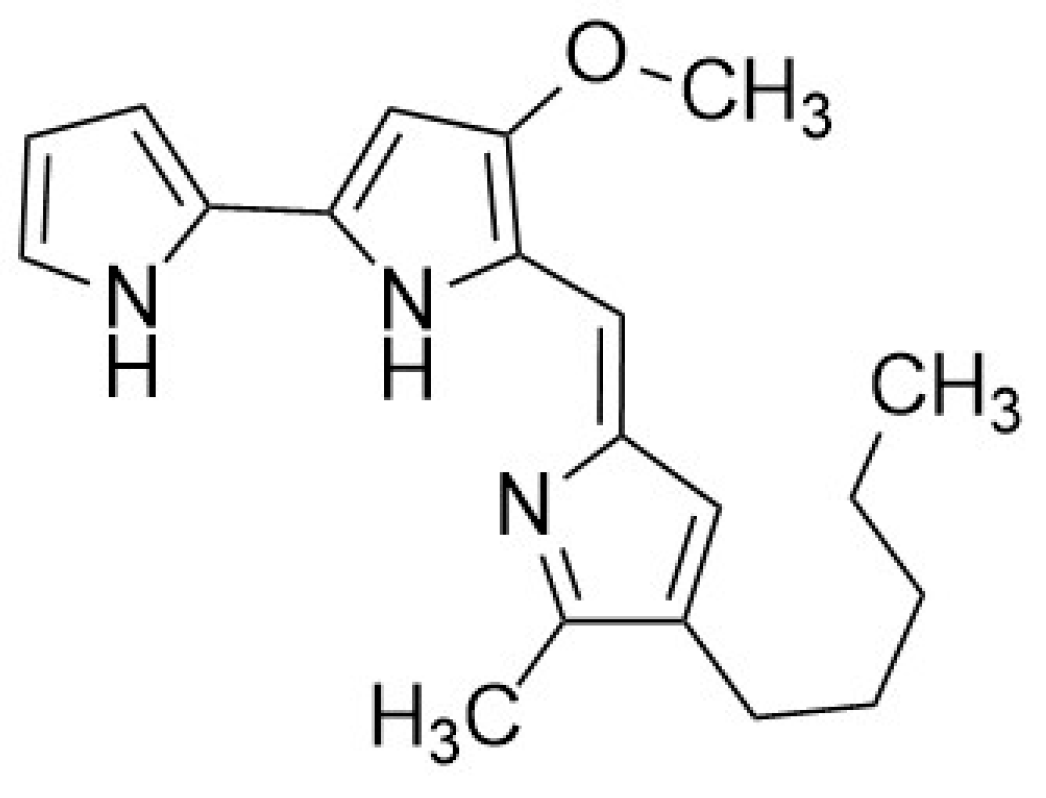
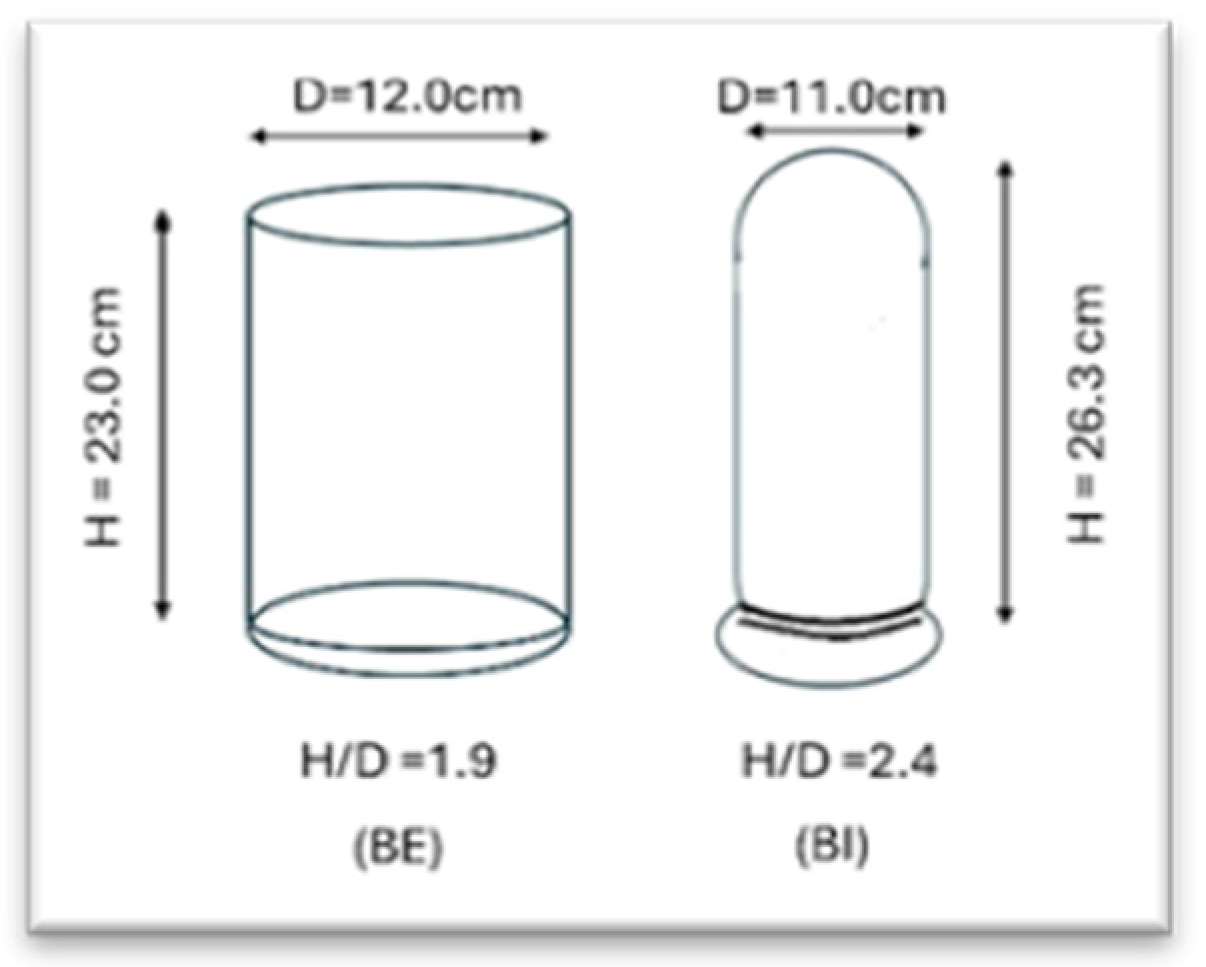
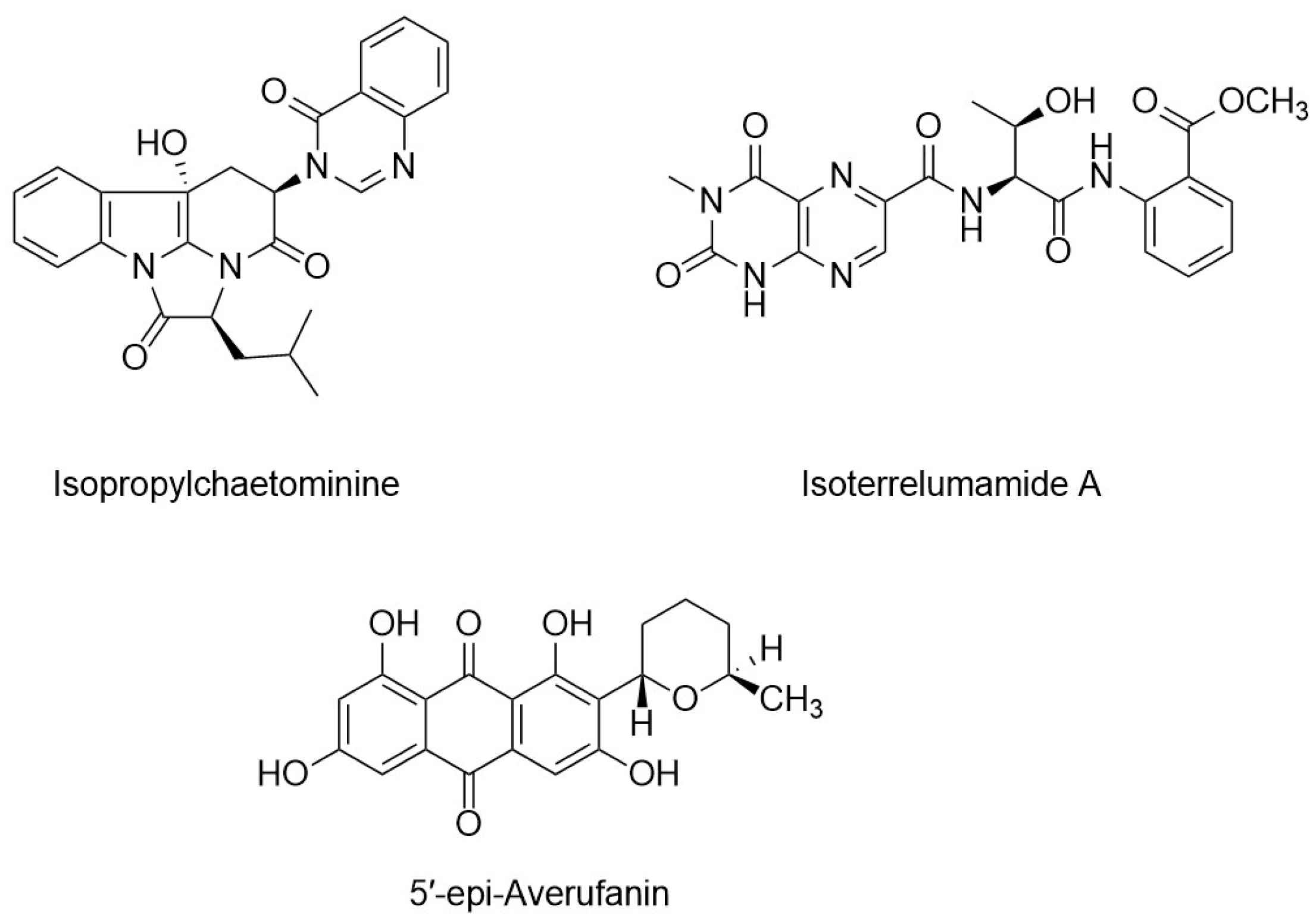
5.1.2. Mixed Fermentation or Co-Culture
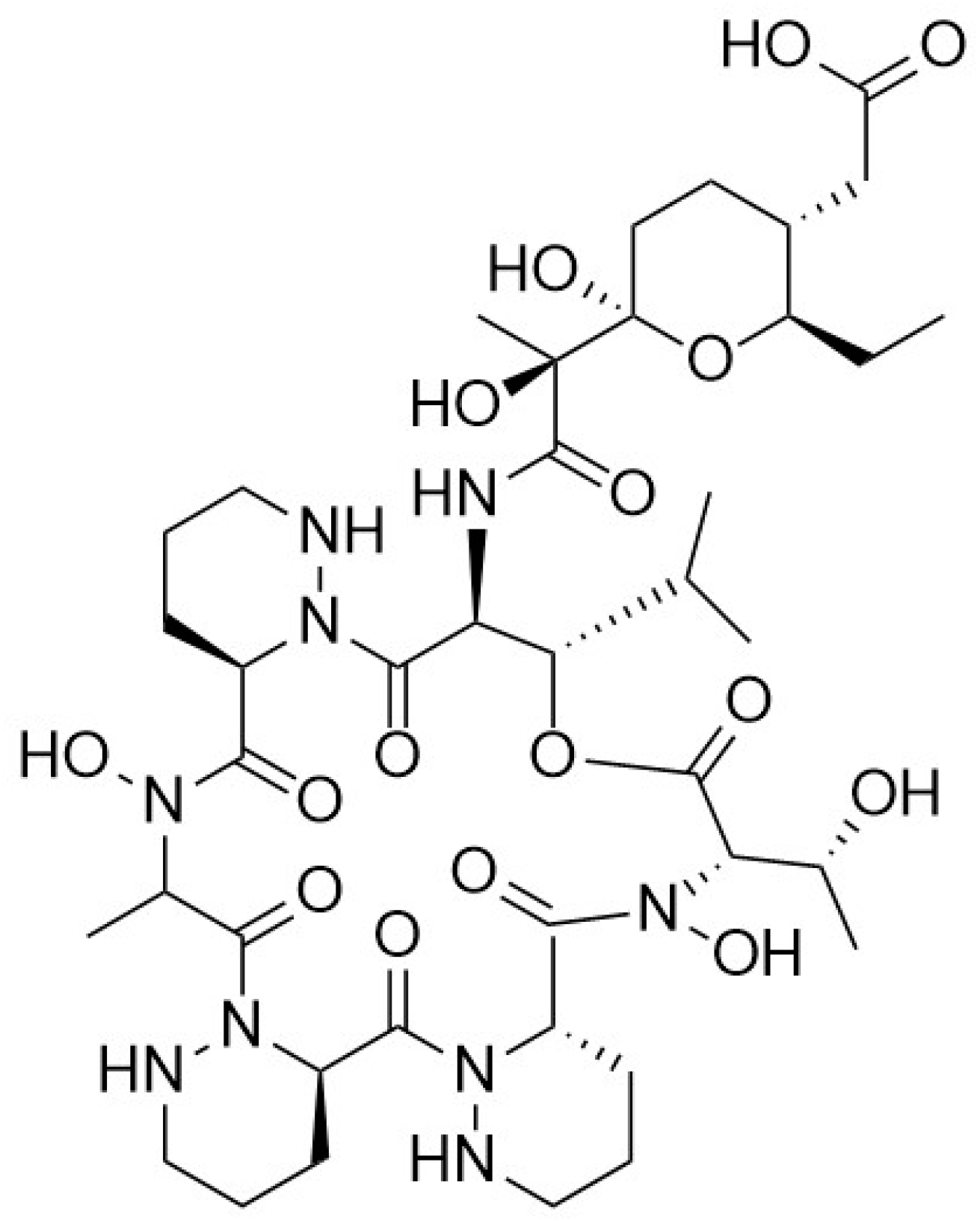
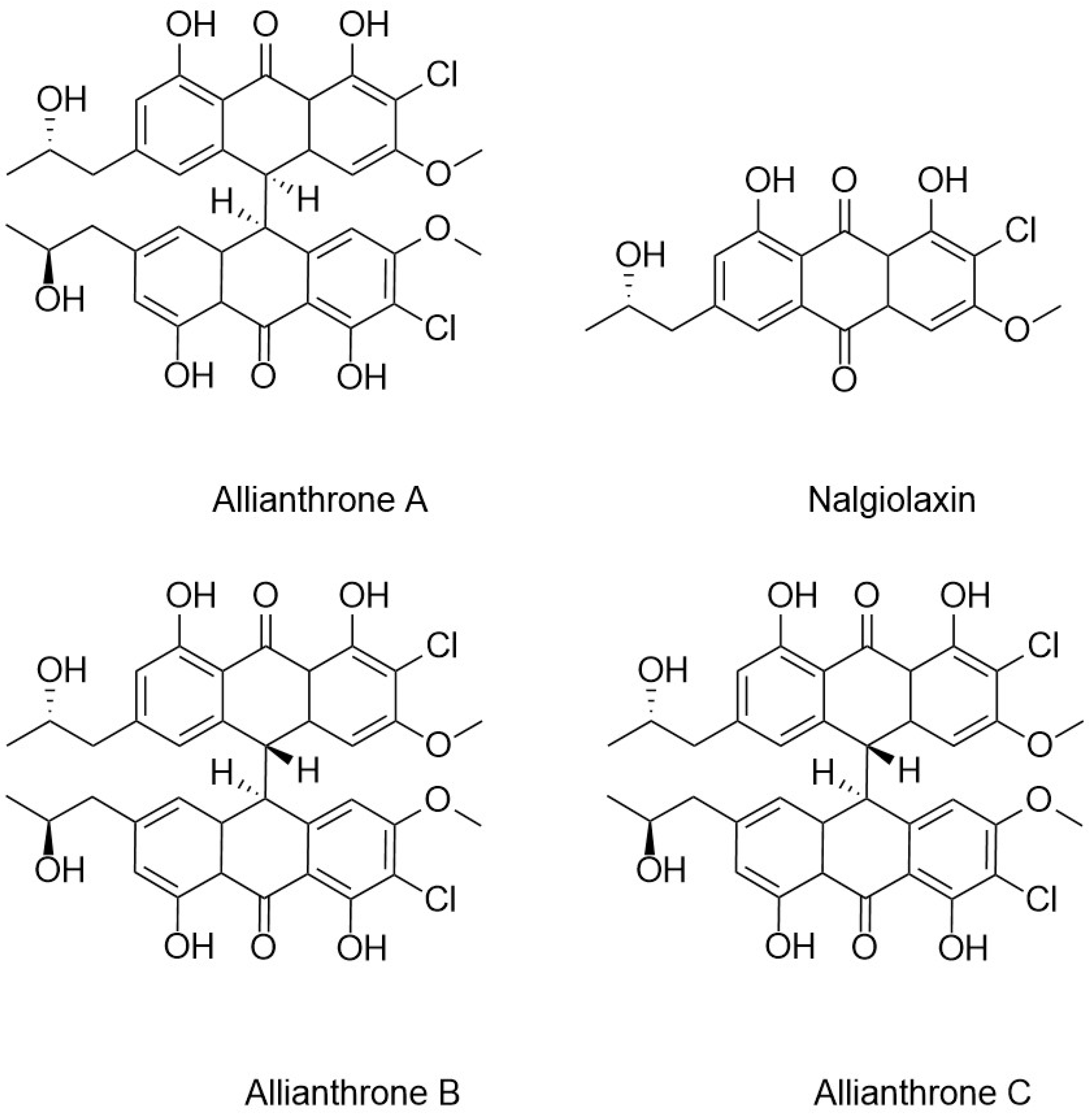
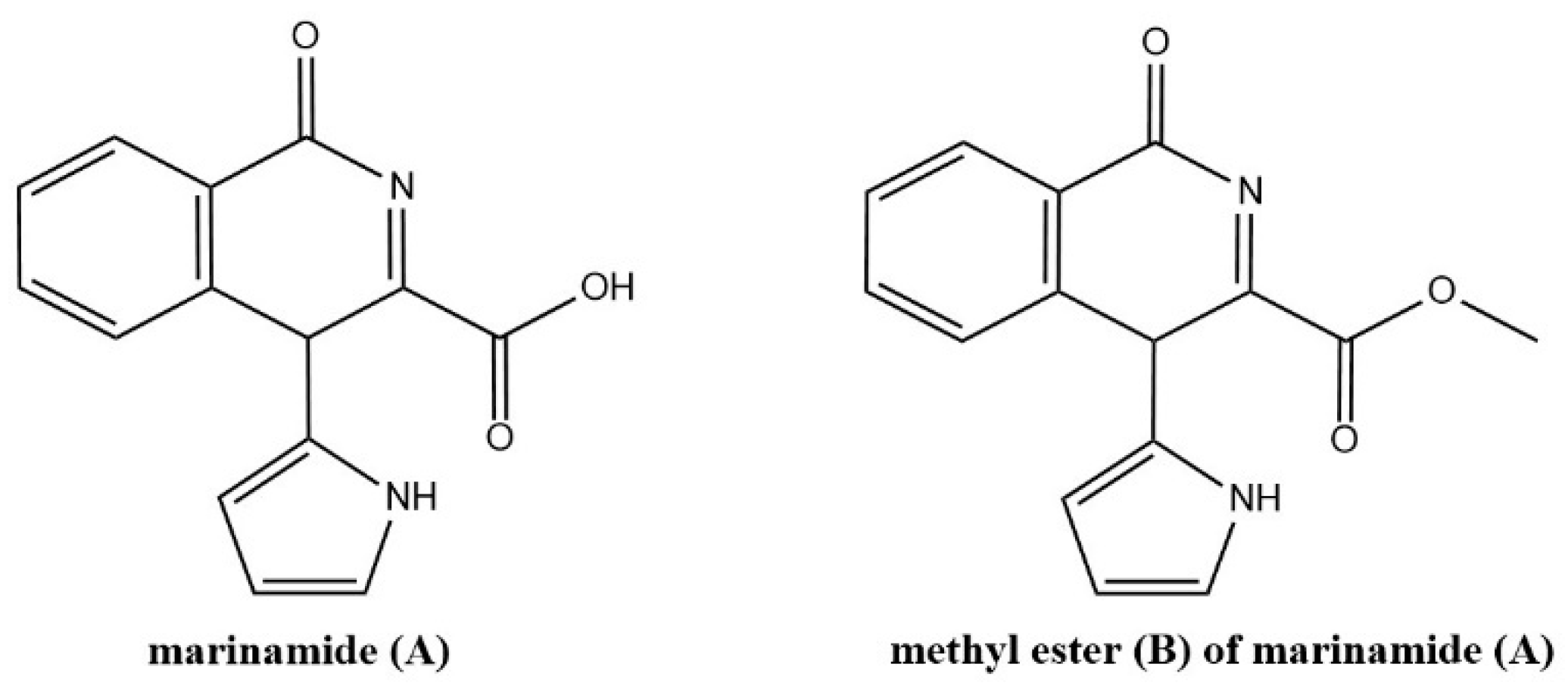
5.2. Ex Vivo Biosynthesis or In Vitro Multienzyme Synthesis
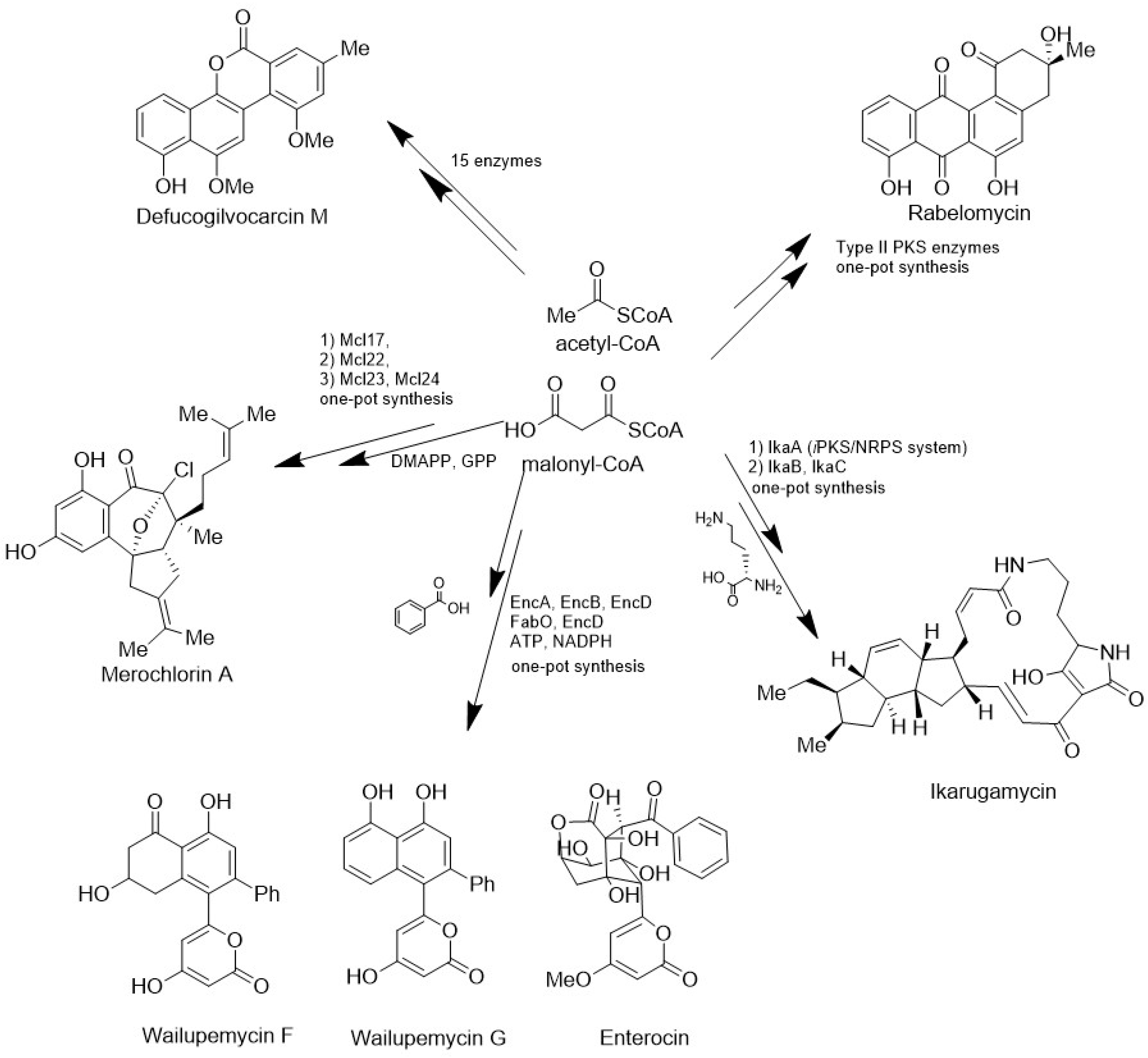
5.3. Heterologous Expression of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters (BGCs)
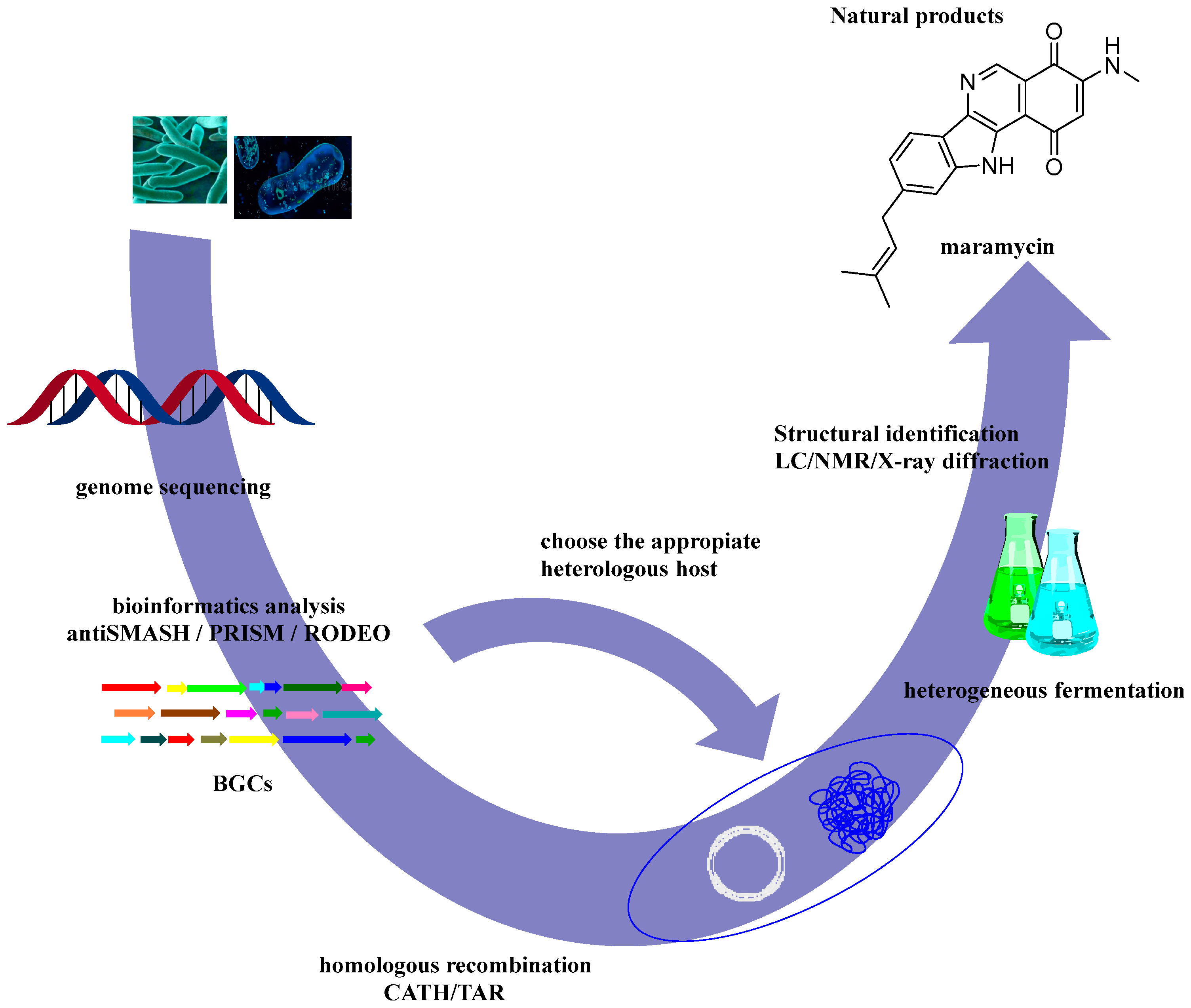
5.4. Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Metabolic Engineering
6. Computer-Aided Approaches to Development of Marine Natural Products
7. Artificial Intelligence in Marine Novel Drug Discovery
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia |
| ADC | Antibody drug conjugate |
| Ara-A | Arabinosyl adenine |
| Ara-C | Arabinosyl cytosine |
| Ara-G | Arabinosyl guanine |
| Ara-U | Arabinosyl uracil |
| BGC | Biosynthetic gene cluster |
| CAL B | Candida antarctica lipase B |
| Cbz | Carboxybenzyl |
| CDFT | Conceptual Density Functional Theory |
| CDFT-CP | Conceptual Density Functional Theory based Computational Peptidology |
| DCW | Dry cell weight |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| EBA | Enterobacter aerogenes |
| Et-743 | Trabectedin |
| F-ara-A | F- Arabinosyl adenosine |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FDMO | FAD dependent monooxygenase |
| GMPs | Good Manufacturing Practices |
| HDMS | Hexamethyldisilazane |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| I-SMEL | In situ Marine moleculE Logger |
| MNPs | Marine Natural Products |
| NAD+ | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NADP+ | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NCS | (S)-Norcoclaurine Synthase |
| PCR | Protein C Reactive |
| PCT | Patent Cooperation Treaty |
| PSTs | Paralytic shellfish toxins |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| RCM | Ring closing metathesis |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| STS | Soft tissue sarcoma |
| TEMPO | 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinyloxy |
References
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á.; Dias-da-Silva, D.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Biosynthetic Versatility of Marine-Derived Fungi on the Delivery of Novel Antibacterial Agents against Priority Pathogens. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2021, 140, 111756–111776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banday, A.H.; Azha, N. ul; Farooq, R.; Sheikh, S.A.; Ganie, M.A.; Parray, M.N.; Mushtaq, H.; Hameed, I.; Lone, M.A. Exploring the Potential of Marine Natural Products in Drug Development: A Comprehensive Review. Phytochem. Lett. 2024, 59, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharova, E.A.; Kopytina, N.I.; Slynko, E.E. Anti-Tumour Drugs of Marine Origin Currently at Various Stages of Clinical Trials (Review). Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2021, 12, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trincone, A. Enzymatic Processes in Marine Biotechnology. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 93–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, K.-H. Drugs from the Oceans: Marine Natural Products as Leads for Drug Discovery. Chimia (Aarau) 2017, 71, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Orhan, I.E.; Banach, M.; Rollinger, J.M.; Barreca, D.; Weckwerth, W.; Bauer, R.; Bayer, E.A.; et al. Natural Products in Drug Discovery: Advances and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, M.; Spanò, V.; Montalbano, A.; Cueto, M.; Díaz Marrero, A.R.; Deniz, I.; Erdoğan, A.; Bilela, L.L.; Moulin, C.; Taffin-De-Givenchy, E.; et al. Marine Anticancer Agents: An Overview with a Particular Focus on Their Chemical Classes. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 619–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.-X.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Y. Marine Natural Products as Sources of Novel Scaffolds: Achievement and Concern. Drug. Discov. Today 2010, 15, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D. Unlocking the Potential of Natural Products in Drug Discovery. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, P.C.; Wilke, D. V.; Branco, P.C.; Bauermeister, A.; Rezende-Teixeira, P.; Gaudêncio, S.P.; Costa-Lotufo, L. V. Enriching Cancer Pharmacology with Drugs of Marine Origin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, P.; Sufiyan, M.; Anwer, Z. Marine drugs. IJCRT 2022, 10, 18–40. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, N.; Parveen, S.; Tang, T.; Wei, J.; Huang, Z. Marine Natural Products in Clinical Use. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 520–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine Natural Products: A New Wave of Drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindequist, U. Marine-Derived Pharmaceuticals - Challenges and Opportunities. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2016, 24, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-Y.; Li, H.-J.; Li, Q.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C. Application of Marine Natural Products in Drug Research. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 35, 116058–116088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.B.; Evdokimov, N.M.; Lefranc, F.; Valentaõ, P.; Kornienko, A.; Pereira, D.M.; Andrade, P.B.; Gomes, N.G.M. Marine-Derived Anticancer Agents: Clinical Benefits, Innovative Mechanisms, and New Targets. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, A.; Naughton, L.M.; Montánchez, I.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Rai, D.K. Current Status and Future Prospects of Marine Natural Products (MNPs) as Antimicrobials. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 272–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.; Pinto, E.; Fernandes, C.; Sousa, E. Marine Cyclic Peptides: Antimicrobial Activity and Synthetic Strategies. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 397–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Jin, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Tai, J.; Chen, Q.; Shi, C.; Ye, J.; Wu, M.; et al. Application of Marine Natural Products against Alzheimer’s Disease: Past, Present and Future. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 25–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Honecker, F. Marine Compounds and Cancer: Updates 2020. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papon, N.; Copp, B.R.; Courdavault, V. Marine Drugs: Biology, Pipelines, Current and Future Prospects for Production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 54, 107871–107881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J. Developing Natural Product Drugs: Supply Problems and How They Have Been Overcome. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Dasari, R.; Chandra, S.; Kiss, R.; Kornienko, A. Marine Invertebrate Metabolites with Anticancer Activities: Solutions to the “Supply Problem”. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 98–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torjesen, I. Drug Development: The Journey of a Medicine from Lab to Shelf. Pharm. J. 2015, 926–932. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukimoto, M.; Nagaoka, M.; Shishido, Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Nishisaka, F.; Matsumoto, S.; Harunari, E.; Imada, C.; Matsuzaki, T. Bacterial Production of the Tunicate-Derived Antitumor Cyclic Depsipeptide Didemnin B. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2329–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, O. Why a Landmark Treaty to Stop Ocean Biopiracy Could Stymie Research. Nature 2020, 580, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug Development from Marine Natural Products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, A.; Barbier, M.; Bertoni, F.; Bones, A.M.; Cancela, M.L.; Carlsson, J.; Carvalho, M.F.; Cegłowska, M.; Chirivella-Martorell, J.; Conk Dalay, M.; et al. The Essentials of Marine Biotechnology. Front. Mar Sci. 2021, 8, 629629–629681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Vieira, H.; Gaspar, H.; Santos, S. Marketed Marine Natural Products in the Pharmaceutical and Cosmeceutical Industries: Tips for Success. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1066–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W. Cell-Free Synthetic Biology for in Vitro Biosynthesis of Pharmaceutical Natural Products. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanase, H.R.; Singh, K.N.M. Marine Pharmacology: Potential, Challenges, and Future in India. J. Med. Sci. (Taiwan) 2018, 38, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.S.; Collins, J.J. Synthetic Biology: Applications Come of Age. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Lee, S.Y. Metabolic Engineering for the Microbial Production of Marine Bioactive Compounds. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 1004–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, S.M.; McCarthy, C.; Eustace, S.; FitzPatrick, R.E.; Delahunt, E.; De Vito, G. Mineral Rich Algae with Pine Bark Improved Pain, Physical Function and Analgesic Use in Mild-Knee Joint Osteoarthritis, Compared to Glucosamine: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Complement Ther. Med. 2020, 50, 102349–102356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkendorff, K. Aquaculture and the Production of Pharmaceuticals and Nutraceuticals. In New Technologies in Aquaculture; Elsevier, 2009; pp. 866–891.
- Leal, M.C.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Calado, R.; Thompson, M.E.; Frischer, M.E.; Nejstgaard, J.C. Coral Feeding on Microalgae Assessed with Molecular Trophic Markers. In Proceedings of the Molecular Ecology; Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2014; Vol. 23, pp. 3870–3876.
- García-Poza, S.; Leandro, A.; Cotas, C.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. The Evolution Road of Seaweed Aquaculture: Cultivation Technologies and the Industry 4.0. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, P.; Le Goff, G.; Alonso, C.; Álvarez, P.A.; Gallard, J.-F.; Fokialakis, N.; Ouazzani, J. Innovative Approach to Sustainable Marine Invertebrate Chemistry and a Scale-Up Technology for Open Marine Ecosystems. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, M.B.; McMillan, E.A.; Rosales, T.I.; Kim, H.S.; Ou, Y.-H.; Toombs, J.E.; Brekken, R.A.; Minden, M.D.; MacMillan, J.B.; White, M.A. Mode of Action and Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers for Exceptional Responders to Didemnin B. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, H.G.; Davies, B.; Hoth, D.; Suffness, M.; Plowman, J.; Flora, K.; Grieshaber, C.; Leyland-Jones, B. Didemnin B. The First Marine Compound Entering Clinical Trials as an Antineoplastic Agent. Invest. New Drugs 1986, 4, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankisetty, S.; Khan, S.I.; Avula, B.; Gochfeld, D.; Khan, I.A.; Slattery, M. Chlorinated Didemnins from the Tunicate Trididemnum solidum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4478–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, C.; Francesch, A.; Galmarini, C.M.; Aviles, P.; Munt, S. Ecteinascidin-743 (Yondelis®). Aplidin® and Irvalec®. In Anticancer Agents from Natural Products.; 2012; Vol. 2, pp. 291–316.
- Delgado-Calle, J.; Kurihara, N.; Atkinson, E.G.; Nelson, J.; Miyagawa, K.; Galmarini, C.M.; Roodman, G.D.; Bellido, T. Aplidin (Plitidepsin) Is a Novel Anti-Myeloma Agent with Potent Anti-Resorptive Activity Mediated by Direct Effects on Osteoclasts. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2709–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Pereira, R.B. Plitidepsin to Treat Multiple Myeloma. Drugs Today (Barc) 2020, 56, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufelberger, D.E.; Koleck, M.P.; Beutler, J.A.; Vatakis, A.M.; Alvarado, A.B.; Andrews, P.; Marzo, L. V.; Muschik, G.M.; Roach, J.; Ross, J.T.; et al. The Large-Scale Isolation of Bryostatin 1 from Bugula neritina Following Current Good Manufacturing Practices. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallifidas, D.; Dhakal, D.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Kokkaliari, S.; Colon Rosa, N.A.; Ratnayake, R.; Bruner, S.D.; Paul, V.J.; Ding, Y.; et al. Biosynthesis of Dolastatin 10 in Marine Cyanobacteria, a Prototype for Multiple Approved Cancer Drugs. Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauduit, M.; Derrien, M.; Grenier, M.; Greff, S.; Molinari, S.; Chevaldonné, P.; Simmler, C.; Pérez, T. In Situ Capture and Real-Time Enrichment of Marine Chemical Diversity. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 2084–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A. Story of Eribulin Mesylate: Development of the Longest Drug Synthesis. In Synthesis of Heterocycles in Contemporary Medicinal Chemistry. Topics in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Casar, Z., Ed.; Springer: Cham, 2016; Vol. 44, pp. 209–270.
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Pan, S.; Shelke, Y.; Rigol, S.; Bao, R.; Das, D.; Ye, Q. A Unified Strategy for the Total Syntheses of Eribulin and a Macrolactam Analogue of Halichondrin B. PNAS 2022, 119, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, J.; Lu, X.; Hollenbaugh, J.A.; Cho, J.H.; Amblard, F.; Schinazi, R.F. Metabolism, Biochemical Actions, and Chemical Synthesis of Anticancer Nucleosides, Nucleotides, and Base Analogs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14379–14455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.S. Sponges, Cancer Chemotherapy, and Cellular Aging. Perspect. Bio.l Med. 1963, 6, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Selawry, O.S.; Vietti, T.J.; Bodey, G.P. Prolonged Infusion of Arabinosyl Cytosine in Childhood Leukemia. Cancer 1970, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunhua, J.; Zhongwei, W.; Guorong, J.; Hongmei, L.; Xiaoli, W. ; Patent 03153692. 1 Preparing Method for Cytarabine 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Robak, T.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Korycka, A.; Robak, E. Purine Nucleoside Analogs as Immunosuppressive and Antineoplastic Agents: Mechanism of Action and Clinical Activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 3165–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudian, M.; Eaddy, J.; Dawson, M. Enzymic Acylation of 506U78 (2-Amino-9-Beta-D-Arabinofuranosyl-6- Methoxy-9H-Purine), a Powerful New Anti-Leukaemic Agent. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1999, 29, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, K.; Nimmanapalli, R.; Ravandi, F.; Keating, M.J.; Gandhi, V. Forodesine, an Inhibitor of Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase, Induces Apoptosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cells. Blood 2006, 108, 2392–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, W.R.A.; Chen, S.-H.; Giblett, E.R.; Biggar, W.D.; Ammann, A.A.; Scott, C.R. Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Deficiency. J. Clinical Investigation 1977, 60, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, C.O.; Gandhi, V. Arabinosylguanine-Induced Apoptosis of T-Lymphoblastic Cells: Incorporation into DNA Is a Necessary Step. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4937–4943. [Google Scholar]
- Gravatt, L.C.; Chaffee, S.; Hebert, M.E.; Halperin, E.C.; Friedman, H.S.; Kurtzberg, J. Efficacy and Toxicity of 9-Beta-D-Arabinofuranosylguanine (AraG) as an Agent to Purge Malignant T Cells from Murine Bone Marrow: Application to an in Vivo T-Leukemia Model. Leukemia 1993, 7, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.H.; Johnson, J.R.; Massie, T.; Sridhara, R.; McGuinn, W.D.; Abraham, S.; Booth, B.P.; Goheer, M.A.; Morse, D.; Chen, X.H.; et al. Approval Summary: Nelarabine for the Treatment of T-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5329–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford Hutman, R. Shorla Pharma Announces FDA Filing Acceptance and Priority Review for T-Cell Leukemia Treatment.
- Krenitsky, T.A.; Koszalka, G.W.; Jones, L.A.; Averett, D.R.; Moorman, A.R. EP Patent 0294114 Antiviral Compounds 1988.
- Yongli, Z.; Juan, W. Patent 201310460155.9 Synthetic Method for Preparing Nelarabine 2013.
- Buchanan, R.A.; Hess, F. Vidarabine (Vira-A®): Pharmacology and Clinical Experience. Pharmacol. Ther. 1980, 8, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Kaur, M.; Minneman, K.P. Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2619–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plunkett, W.; Gandhi, V. Evolution of the Arabinosides and the Pharmacology of Fludarabine. Drugs 1994, 47, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plunkett, W.; Chubb, S.; Alexander, L.; Montgomery, J.A. Comparison of the Toxicity and Metabolism of 9-Beta-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-Fluoroadenine and 9-Beta-D-Arabinofuranosyladenine in Human Lymphoblastoid Cells. Cancer Res. 1980, 40, 2349–2355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, V.; Chen, W.; Ayres, M.; Rhie, J.; Madden, T.; Newman, R. Plasma and Cellular Pharmacology of 8-Chloro-Adenosine in Mice and Rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2002, 50, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerrie, A.S.; Zypchen, L.N.; Connors, J.M. Fludarabine and Rituximab for Relapsed or Refractory Hairy Cell Leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 1988–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Chubb, S.; Plunkett, W. Termination of DNA Synthesis by 9-Beta-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-Fluoroadenine. A Mechanism for Cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 16617–16625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plunkett, W.; Saunders, P.P. Metabolism and Action of Purine Nucleoside Analogs. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 49, 239–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.; Hewson, K. Nucleosides of 2-Fluoroadenine. J. Med. Chem. 1969, 12, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.A. Patent 4188378 Anticancer and Antiviral Activity of 9-b-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-Fluoroadenine 1980.
- Montgomery, J.A.; Shortnacy, A.T. USPatent 4357324 Prodrug Derivatives of 9-b-D-Arabinofuranosyl-2-Fluoroadenine 1982.
- Kshirsagar, S.W.; Deshpande, M.S.; Sonawane, S.P.; Maikap, G.C.; Gurjar, M.K. Simple Modification To Obtain High Quality Fludarabine. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2012, 16, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, P.; Petrucciani, L.; Colombo, P.; Caprioli, G. EP1464708A1 A Process for the Preparation of Fludarabine Phosphate from 2-Fluoroadenine 2003.
- Shen, C.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, W.; Ding, H.; Bai, J.; Xiao, Q. Practical Synthesis of Fludarabine and Nelarabine. Synthesis (Stuttg) 2020, 52, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Álvarez, S.; Pardal, E.; Sánchez-Nieto, D.; Navarro, M.; Caballero, M.D.; Mateos, M.V.; Martin, A. Plitidepsin: Design, Development, and Potential Place in Therapy. Drug Des Devel Ther 2017, Volume11, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Venkatesan, J. Introduction to Marine Biomaterials. In Marine Biomaterials; CRC Press, 2013; pp. 3–16.
- Pelay-Gimeno, M.; Albericio, F.; Tulla-Puche, J. Synthesis of Complex Head-to-Side-Chain Cyclodepsipeptides. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1924–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hui, Z.; Cai, M.; Huang, S.; Shi, W.; Liang, M.; Lin, Y.; Shen, J.; Sui, M.; Li, X.; et al. Integration of Microbial and Chemical Synthesis for the Efficient Production of Plitidepsin, a Promising Anticancer and Antiviral Agent. BioRxiv 2023, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, I.; Polanco, C.; Cuevas, F.; Mandez, P.; Cuevas, C.; Gallego, P.; Munt, S.; Manzanares, I. WO2002002596A2, P. Synthetic Methods for Aplidin, and New Antitumoral Derivatives, Methods of Making and Using Them 2001.
- Kortmansky, J.; Schwartz, G.K. Bryostatin-1: A Novel PKC Inhibitor in Clinical Development. Cancer Invest. 2003, 21, 924–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etcheberrigaray, R.; Tan, M.; Dewachter, I.; Kuipéri, C.; Van der Auwera, I.; Wera, S.; Qiao, L.; Bank, B.; Nelson, T.J.; Kozikowski, A.P.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of PKC Activators in Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mice. PNAS 2004, 101, 11141–11146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornberg, M.D.; Smith, M.D.; Shirazi, H.A.; Calabresi, P.A.; Snyder, S.H.; Kim, P.M. Bryostatin-1 Alleviates Experimental Multiple Sclerosis. PNAS 2018, 115, 2186–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lu, X.-T.; Jiang, X.; Tian, J. Bryostatin-1: A Promising Compound for Neurological Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaufelberger, D.E.; Koleck, M.P.; Beutler, J.A.; Vatakis, A.M.; Alvarado, A.B.; Andrews, P.; Marzo, L. V; Muschik, G.M.; Roach, J.; Ross, J.T.; et al. The Large-Scale Isolation Fo Bryostatin 1 from Bugula neritina Following Current Good Manufacturing Practices. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R.; Kamano, Y.; Herald, C.L.; Tuinman, A.A.; Boettner, F.E.; Kizu, H.; Schmidt, J.M.; Baczynskyj, L.; Tomer, K.B.; Bontems, R.J. The Isolation and Structure of a Remarkable Marine Animal Antineoplastic Constituent: Dolastatin 10. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 6883–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaviazar, S.; Hale, K.J. Total Synthesis of Bryostatin 1: A Short Route. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8786–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaviazar, S.; Frigerio, M.; Bhatia, G.S.; Hummersone, M.G.; Aliev, A.E.; Hale, K.J. Enantioselective Formal Total Synthesis of the Antitumor Macrolide Bryostatin 7. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4477–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wender, P.A.; Hardman, C.T.; Ho, S.; Jeffreys, M.S.; Maclaren, J.K.; Quiroz, R. V.; Ryckbosch, S.M.; Shimizu, A.J.; Sloane, J.L.; Stevens, M.C. Scalable Synthesis of Bryostatin 1 and Analogs, Adjuvant Leads against Latent HIV. Science 2017, 358, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychnovsky, S.D.; Kim, J. Triphenylphosphine-Catalyzed Isomerizations of Enynes to (E,E,E)-Trienes: Phenol as a Cocatalyst. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 2659–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.M.; Seaman, F.C.; Hurley, L.H. NMR-Based Model of an Ecteinascidin 743−DNA Adduct. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 5475–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E.J.; Gin, D.Y.; Kania, R.S. Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Ecteinascidin 743. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 9202–9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, C.; Francesch, A. Development of Yondelis® (Trabectedin, ET-743). A Semisynthetic Process Solves the Supply Problem. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, E.J.; Corey, E.J. A New, More Efficient, and Effective Process for the Synthesis of a Key Pentacyclic Intermediate for Production of Ecteinascidin and Phthalascidin Antitumor Agents. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, A.; Yanagisawa, A.; Abe, M.; Tohma, S.; Kan, T.; Fukuyama, T. Total Synthesis of Ecteinascidin 743. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6552–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Bois-Choussy, M.; Zhu, J. Total Synthesis of Ecteinascidin 743. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Chan, C.; Furuuchi, T.; Wright, B.J.D.; Zhou, B.; Guo, J.; Danishefsky, S.J. Stereospecific Formal Total Synthesis of Ecteinascidin 743. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishlock, D.; Williams, R.M. Synthetic Studies on Et-743. Assembly of the Pentacyclic Core and a Formal Total Synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9594–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, D. A Scalable Total Synthesis of the Antitumor Agents Et-743 and Lurbinectedin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3972–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zhu, D.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, X. A New Approach to the Synthesis of L-3-Hydroxy-4-Methoxy-5-Methyl-Phenylalanine Derivatives from l-Tyrosine. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2010, 21, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, C.; Pérez, M.; Martín, M.J.; Chicharro, J.L.; Fernández-Rivas, C.; Flores, M.; Francesch, A.; Gallego, P.; Zarzuelo, M.; de la Calle, F.; et al. Synthesis of Ecteinascidin ET-743 and Phthalascidin Pt-650 from Cyanosafracin B. Org. Lett. 2000, 2, 2545–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirkkonen, H.; Brown, K. V.; Niemczura, M.; Faudemer, Z.; Brown, C.; Ponomareva, L. V.; Helmy, Y.A.; Thorson, J.S.; Nybo, S.E.; Metsä-Ketelä, M.; et al. Engineering BioBricks for Deoxysugar Biosynthesis and Generation of New Tetracenomycins. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 21237–21253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keasling, J.D.; Mendoza, A.; Baran, P.S. A Constructive Debate. Nature 2012, 492, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, R.; Kaysser, L.; Villaume, M.T.; Diethelm, S.; Carbullido, M.K.; Baran, P.S.; Moore, B.S. One-Pot Enzymatic Synthesis of Merochlorin A and B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11019–11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanifuji, R.; Minami, A.; Oguri, H.; Oikawa, H. Total Synthesis of Alkaloids Using Both Chemical and Biochemical Methods. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 1098–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Yun, E.J.; Kim, K.H. Multi-Step Enzymatic Production and Purification of 2-Keto-3-Deoxy-Galactonate from Red-Macroalgae-Derived Agarose. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, A.; Ramesh, R. Multifaceted Applications of Chitosan in Cancer Drug Delivery and Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 96–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Ramos, P.; Mirón, J.; Valcarcel, J.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I. Production of Chitin from Penaeus vannamei By-Products to Pilot Plant Scale Using a Combination of Enzymatic and Chemical Processes and Subsequent Optimization of the Chemical Production of Chitosan by Response Surface Methodology. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, E.L.; Finnigan, W.; France, S.P.; Green, A.P.; Hayes, M.A.; Hepworth, L.J.; Lovelock, S.L.; Niikura, H.; Osuna, S.; Romero, E.; et al. Biocatalysis. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, L.A.; Romine, J.L.; Lin, H.S.; Wright, J. Total Synthesis of (+)-Ikarugamycin. 1. Stereocontrolled Construction of the Decahydro-as-Indacene Subunit. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 9284–9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, P.N.; Howard, R.M.; Kumar, R.; Thompson, M.P.; Truppo, M.D.; Turner, N.J. Extending the Application of Biocatalysis to Meet the Challenges of Drug Development. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornscheuer, U.T.; Huisman, G.W.; Kazlauskas, R.J.; Lutz, S.; Moore, J.C.; Robins, K. Engineering the Third Wave of Biocatalysis. Nature 2012, 485, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanifuji, R.; Oguri, H. Chemo-Enzymatic Total Synthesis: Current Approaches toward the Integration of Chemical and Enzymatic Transformations. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1693–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrittwieser, J.H.; Resch, V. The Role of Biocatalysis in the Asymmetric Synthesis of Alkaloids. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17602–17632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigan, E.; Eggbauer, B.; Schrittwieser, J.H.; Kroutil, W. The Role of Biocatalysis in the Asymmetric Synthesis of Alkaloids - an Update. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 28223–28270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.S.; Zhang, D.; de Souza, F.Z.R.; Liu, L. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Marine-Derived Alkaloids via Enzymatic Reactions. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 368–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Amatuni, A.; Renata, H. Recent Advances in the Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Bioactive Natural Products. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 55, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Edmunds, G.; Gibbons, C.; Zhang, J.; Gadi, M.R.; Zhu, H.; Fang, J.; Liu, X.; Kong, Y.; Wang, P.G. Toward Automated Enzymatic Synthesis of Oligosaccharides. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 8151–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.T.; Adak, A.K.; Su, Y.Y.; Chang, T.W.; Lin, C.C. Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of the Neuritogenic Echinoderm Ganglioside LLG-5 and Related Analogues. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 3573–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Yamada, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Inagaki, M.; Higuchi, R. Neuritogenic Activity of Gangliosides from Echinoderms and Their Structure-Activity Relationship. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2007, 55, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, J.R.; Withers, S.G. A Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of the Neurogenic Starfish Ganglioside LLG-3 Using an Engineered and Evolved Synthase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8640–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lian, Z.; Peng, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H. Applications of Higenamine in Pharmacology and Medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 196, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisrivirat, D.; Sutthaphirom, C.; Pimviriyakul, P.; Chaiyen, P. Dual Activities of Oxidation and Oxidative Decarboxylation by Flavoenzymes. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibraheem, W.; Wils, Q.; Camiade, E.; Ahmed, E.; Thibonnet, J.; Thiery, E.; Petrignet, J. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Racemic Paecilocin A and Its Derivatives against Methicillin-Sensitive and -Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Tetrahedron Lett.. 2021, 67, 152888–152893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelakshmi, Ch.; Bhaskar Rao, A.; Lakshmi Narasu, M.; Janardhan Reddy, P.; Reddy, B.V.S. Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of Paecilocin A and 3-Butyl-7-Hydroxyphthalide. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 1303–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Ziarani, G.; Badiei, A.; Ziarani, M.; Reza, A. Chemoenzymatic Enantioselective Formal Synthesis of (-)-Gephyrotoxin-223. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2006, 25, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kanakkanthara, A.; Northcote, P.T.; Miller, J.H. Peloruside A: A Lead Non-Taxoid-Site Microtubule-Stabilizing Agent with Potential Activity against Cancer, Neurodegeneration, and Autoimmune Disease. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönherr, H.; Mollitor, J.; Schneider, C. A Chemoenzymatic Approach to the Stereocontrolled Synthesis of the C1-C11 Fragment of (+)-Peloruside A. European J. Org. Chem. 2010, 3908–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggen, M.; Georg, G.I. The Cryptophycins: Their Synthesis and Anticancer Activity. Med. Res. Rev. 2002, 22, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, Z.Q.; Aldrich, C.C.; Magarvey, N.A.; Georg, G.I.; Sherman, D.H. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Cryptophycin/Arenastatin Natural Products. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 13457–13466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.J.; Khatri, Y.; Brody, S.I.; Zhu, C.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Valeriote, F.A.; Sherman, D.H. A Versatile Chemoenzymatic Synthesis for the Discovery of Potent Cryptophycin Analogs. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, T.O.; Iwalewa, E.O.; Aderogba, M.A.; Akinpelu, B.A.; Ogundaini, A.O. Anticonceptive, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities of Eleagnine: An Alkaloid Isolated from Chrysophyllum albidum Seed Cotyledons. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 6, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, J.C. Various Alkaloid Profiles in Decoctions of Banisteriopsis Caapi. J. Psychoactive Drugs 2005, 37, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislieri, D.; Green, A.P.; Pontini, M.; Willies, S.C.; Rowles, I.; Frank, A.; Grogan, G.; Turner, N.J. Engineering an Enantioselective Amine Oxidase for the Synthesis of Pharmaceutical Building Blocks and Alkaloid Natural Products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10863–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, A.; Gupta, R. Role of Psilocybin in the Treatment of Depression. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 2017, 7, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, J.; Sherwood, A.; Kargbo, R.; Orry, A.; Blei, F.; Naschberger, A.; Rupp, B.; Hoffmeister, D. Enzymatic Route toward 6-Methylated Baeocystin and Psilocybin. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 2824–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, M.E.; Kevvai, K.; Grewal, P.S.; Narcross, L.; Choi, B.; Bourgeois, L.; Dueber, J.E.; Martin, V.J.J. A Yeast Platform for High-Level Synthesis of Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3337–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanifuji, R.; Oguri, H. A Chemo-Enzymatic Approach for the Rapid Assembly of Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids and Their Analogs. In Modern Natural Product Synthesis; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; pp. 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Faheem; Karan Kumar, B.; Venkata Gowri Chandra Sekhar, K.; Chander, S.; Kunjiappan, S.; Murugesan, S. 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline (THIQ) as Privileged Scaffold for Anticancer de Novo Drug Design. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov 2021, 16, 1119–1147. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanifuji, R.; Koketsu, K.; Takakura, M.; Asano, R.; Minami, A.; Oikawa, H.; Oguri, H. Chemo-Enzymatic Total Syntheses of Jorunnamycin A, Saframycin A, and N-Fmoc Saframycin Y3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10705–10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanifuji, R.; Haraguchi, N.; Oguri, H. Chemo-Enzymatic Total Syntheses of Bis-Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids and Systematic Exploration of the Substrate Scope of SfmC. Tetrahedron Chem. 2022, 1, 100010–100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, D.R.; Manalo, J.L. The Activation of Glutamate Receptors by Kainic Acid and Domoic Acid. Nat. Toxins 1998, 6, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathakis, C.I.; Yioti, E.G.; Gallos, J.K. Total Syntheses of (–)-α-Kainic Acid. European J. Org. Chem. 2012, 4661–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekan, J.R.; McKinnie, S.M.K.; Moore, M.L.; Poplawski, S.G.; Michael, T.P.; Moore, B.S. Scalable Biosynthesis of the Seaweed Neurochemical, Kainic Acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8454–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newmister, S.A.; Gober, C.M.; Romminger, S.; Yu, F.; Tripathi, A.; Parra, L.L.L.; Williams, R.M.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Joullié, M.M.; Sherman, D.H. OxaD: A Versatile Indolic Nitrone Synthase from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium oxalicum F30. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11176–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, R.; Andersson, M.A.; Hautaniemi, M.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.S. Toxic Indole Alkaloids Avrainvillamide and Stephacidin B Produced by a Biocide Tolerant Indoor Mold Aspergillus westerdijkiae. Toxicon 2015, 99, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loskot, S.A.; Romney, D.K.; Arnold, F.H.; Stoltz, B.M. Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Nigelladine A via Late-Stage C–H Oxidation Enabled by an Engineered P450 Enzyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10196–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Romero, E.O.; Pyser, J.B.; Yazarians, J.A.; Narayan, A.R.H. Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of Natural Products. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker Dockrey, S.A.; Doyon, T.J.; Perkins, J.C.; Narayan, A.R.H. Whole-cell Biocatalysis Platform for Gram-scale Oxidative Dearomatization of Phenols. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukowski, A.L.; Ellinwood, D.C.; Hinze, M.E.; DeLuca, R.J.; Du Bois, J.; Hall, S.; Narayan, A.R.H. C–H Hydroxylation in Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11863–11869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukowski, A.L.; Denomme, N.; Hinze, M.E.; Hall, S.; Isom, L.L.; Narayan, A.R.H. Biocatalytic Detoxification of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, M.A.; Brovetto, M.; Gamenara, D.; Bracco, P.; Zinola, G.; Seoane, G.; Rodríguez, S.; Carrera, I. Production of Cis-1,2-Dihydrocatechols of High Synthetic Value by Whole-Cell Fermentation Using Escherichia Coli JM109 (PDTG601): A Detailed Study. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 96, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, M.G.; Loong, D.T.J. A Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of the Phytotoxic Undecenolide (-)-Cladospolide A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2050–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thale, Z.; Kinder, F.R.; Bair, K.W.; Bontempo, J.; Czuchta, A.M.; Versace, R.W.; Phillips, P.E.; Sanders, M.L.; Wattanasin, S.; Crews, P. Bengamides Revisited: New Structures and Antitumor Studies. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banwell, M.G.; McRae, K.J. A Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of Ent -Bengamide E. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 6768–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.L.; Schwartz, B.D.; Draffan, A.G.; Banwell, M.G.; Willis, A.C. A Chemoenzymatic and Fully Stereocontrolled Total Synthesis of the Antibacterial Natural Product (-)-Platencin. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baidilov, D.; Rycek, L.; Trant, J.F.; Froese, J.; Murphy, B.; Hudlicky, T. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Advanced Intermediates for Formal Total Syntheses of Tetrodotoxin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10994–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova, M.; Rycek, L.; Hajicek, J.; Baidilov, D.; Hudlicky, T. Tetrodotoxin: History, Biology, and Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18338–18387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, N.A.; Fisher, K.M.; Lapointe, B.; du Souich, P.; Chary, S.; Moulin, D.; Sellers, E.; Ngoc, A.H. An Open-Label, Multi-Dose Efficacy and Safety Study of Intramuscular Tetrodotoxin in Patients with Severe Cancer-Related Pain. J. Pain Symptom. Manage. 2007, 34, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabala, A.O.; Xu, W.; Chooi, Y.H.; Tang, Y. Characterization of a Silent Azaphilone Gene Cluster from Aspergillus Niger ATCC 1015 Reveals a Hydroxylation-Mediated Pyran-Ring Formation. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker Dockrey, S.A.; Doyon, T.J.; Perkins, J.C.; Narayan, A.R.H. Whole-Cell Biocatalysis Platform for Gram-Scale Oxidative Dearomatization of Phenols. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Winter, J.M.; Kishimoto, S.; Noguchi, H.; Tang, Y.; Watanabe, K. Combinatorial Generation of Chemical Diversity by Redox Enzymes in Chaetoviridin Biosynthesis. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1446–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Wu, X.; Fields, J.K.; Johnson, D.K.; Lan, L.; Pratt, M.; Somoza, A.D.; Wang, C.C.C.; Karanicolas, J.; Oakley, B.R.; et al. The Fungal Natural Product Azaphilone-9 Binds to HuR and Inhibits HuR-RNA Interaction in Vitro. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0175471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Tahara, H.; Inokoshi, J.; Tanaka, H.; Masuma, R.; Omura, S. New Brominated and Halogen-Less Derivatives and Structure-Activity Relationship of Azaphilones Inhibiting Gp120-CD4 Binding. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1998, 51, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.-L.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Yang, T.; Yao, C.; Wu, L.-W.; Li, G.-Y. Azaphilone Alkaloids with Anti-Inflammatory Activity from Fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum Cib-411. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, L.M.; Pekari, K.; Sorensen, E.J. A Nucleophile-Catalyzed Cycloisomerization Permits a Concise Synthesis of (+)-Harziphilone. PNAS 2004, 101, 12064–12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Germain, A.R.; Porco, J.A. Synthesis of Azaphilones and Related Molecules by Employing Cycloisomerization of o -Alkynylbenzaldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyser, J.B.; Baker Dockrey, S.A.; Benítez, A.R.; Joyce, L.A.; Wiscons, R.A.; Smith, J.L.; Narayan, A.R.H. Stereodivergent, Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Azaphilone Natural Products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18551–18559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker Dockrey, S.A.; Lukowski, A.L.; Becker, M.R.; Narayan, A.R.H. Biocatalytic Site- and Enantioselective Oxidative Dearomatization of Phenols. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, D.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X.; Lai, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, G. Sorbicillinoids from Fungi and Their Bioactivities. Molecules 2016, 21, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Amatuni, A.; Renata, H. Recent Advances in the Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Bioactive Natural Products. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2020, 55, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sib, A.; Gulder, T.A.M. Stereoselective Total Synthesis of Bisorbicillinoid Natural Products by Enzymatic Oxidative Dearomatization/Dimerization. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 12888–12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sib, A.; Gulder, T.A.M. Chemo-enzymatic Total Synthesis of Oxosorbicillinol, Sorrentanone, Rezishanones B and C, Sorbicatechol A, Bisvertinolone, and (+)-Epoxysorbicillinol. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14650–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.I.; Gulder, T.A.M. Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of Sorbicillactone A. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milzarek, T.M.; Gulder, T.A.M. Chemo-Enzymatic Total Synthesis of the Spirosorbicillinols. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milzarek, T.M.; Schuler, S.; Matura, A.; Gulder, T.A.M. Evaluation of the Substrate Promiscuity of SorbC for the Chemo-Enzymatic Total Synthesis of Structurally Diverse Sorbicillinoids. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 1898–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sib, A.; Milzarek, T.M.; Herrmann, A.; Oubraham, L.; Müller, J.I.; Pichlmair, A.; Brack-Werner, R.; Gulder, T.A.M. Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of Sorbicatechol Structural Analogues and Evaluation of Their Antiviral Potential. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinkevich, B. Cell Cultures from Marine Invertebrates: Obstacles, New Approaches and Recent Improvements; 1999; Vol. 70., 133-153.
- Rinkevich, B. Marine Invertebrate Cell Cultures: New Millennium Trends. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnay-Verdier, S.; Dall’Osso, D.; Joli, N.; Olivré, J.; Priouzeau, F.; Zamoum, T.; Merle, P.L.; Furla, P. Establishment of Primary Cell Culture from the Temperate Symbiotic Cnidarian, Anemonia Viridis. Cytotechnology 2013, 65, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkevich, B. Cell Cultures from Marine Invertebrates: New Insights for Capturing Endless Stemness. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, P.; Toullec, G.; Fricano, C.; Chapron, L.; Meunier, V.; Röttinger, E.; Furla, P.; Barnay-Verdier, S. Cnidarian Primary Cell Culture as a Tool to Investigate the Effect of Thermal Stress at Cellular Level. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanase, H.R.; Singh, K.N.M. Marine Pharmacology: Potential, Challenges, and Future in India. J. Med. Sci. (Taiwan) 2018, 38, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, P.; Sufiyan, M.; Anwer, Z. Marine Drugs. Int. J. Creat. Res. Thoughts 2022, 10, 18–40. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, D.; Gupta, P.; Jaglan, S.; Roullier, C.; Grovel, O.; Bertrand, S. Expanding the Chemical Diversity through Microorganisms Co-Culture: Current Status and Outlook. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, S.; Bohni, N.; Schnee, S.; Schumpp, O.; Gindro, K.; Wolfender, J.L. Metabolite Induction via Microorganism Co-Culture: A Potential Way to Enhance Chemical Diversity for Drug Discovery. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1180–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, Z.; Choo, D.H.; Lee, H.; Parveen, A. Cyanobacteria: Review of Current Potentials and Applications. Environments 2020, 7, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web Annex, B. World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines for Children – 9th List, 2023. In: The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: Executive summary of the report of the 24th WHO Expert Committee on the Selection and Use of Essential Medicines, 24 – 28 April 2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2023 (WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.03). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.20232023.
- Panter, F.; Bader, C.D.; Müller, R. Synergizing the Potential of Bacterial Genomics and Metabolomics to Find Novel Antibiotics. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5994–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Hotta, K.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, R.; Quan, S.; Chen, X. Advances in Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2551–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Petersen, S.D.; Radivojevic, T.; Ramirez, A.; Pérez-Manríquez, A.; Abeliuk, E.; Sánchez, B.J.; Costello, Z.; Chen, Y.; Fero, M.J.; et al. Combining Mechanistic and Machine Learning Models for Predictive Engineering and Optimization of Tryptophan Metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4880–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Tang, X.; Moore, B.S. Genetic Platforms for Heterologous Expression of Microbial Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 1313–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, C.; Francesch, A. Development of Yondelis® (Trabectedin, ET-743). A Semisynthetic Process Solves the Supply Problem. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoveská, L.; Nielsen, S.L.; Eroldoğan, O.T.; Haznedaroglu, B.Z.; Rinkevich, B.; Fazi, S.; Robbens, J.; Vasquez, M.; Einarsson, H. Overview and Challenges of Large-Scale Cultivation of Photosynthetic Microalgae and Cyanobacteria. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 445–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug Development from Marine Natural Products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furmaniak, M.A.; Misztak, A.E.; Franczuk, M.D.; Wilmotte, A.; Waleron, M.; Waleron, K.F. Edible Cyanobacterial Genus Arthrospira: Actual State of the Art in Cultivation Methods, Genetics, and Application in Medicine. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Phorboxazoles A and B: Potent Cytostatic Macrolides from Marine Sponge Phorbas Sp. f; J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8126–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, J.B.; Guang, X.Z.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F. Phorbasides A-E, Cytotoxic Chlorocyclopropane Macrolide Glycosides from the Marine Sponge Phorbas Sp. CD Determination of C-Methyl Sugar Configurations. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, H.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Jia, Y.; Feng, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Yao, G. Screening and Genetic Engineering of Marine-Derived Aspergillus terreus for High-Efficient Production of Lovastatin. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2024, 23, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.F.S.; de Carvalho, C.C.C.R. Mimicking Marine Conditions to Improve Prodigiosin Yields in Bioreactor. Processes 2024, 12, 1794–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islan, G.A.; Rodenak-Kladniew, B.; Noacco, N.; Duran, N.; Castro, G.R. Prodigiosin: A Promising Biomolecule with Many Potential Biomedical Applications. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 14227–14258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srilekha, V.; Krishna, G.; Sreelatha, B.; Jagadeesh Kumar, E.; Rajeshwari, K.V.N. Prodigiosin: A Fascinating and the Most Versatile Bioactive Pigment with Diverse Applications. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanufacturing. 2024, 4, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.M.; Albanese, C.; Hamdy, N.M.; Sultan, A.S. Rise of the Natural Red Pigment ‘Prodigiosin’ as an Immunomodulator in Cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Deavours, B.E.; de Fáltima, Â.; Naoumkina, M.; Dixon, R.A.; Sumner, L.W. Integrated Metabolite and Transcript Profiling Identify a Biosynthetic Mechanism for Hispidol in Medicago truncatula Cell Cultures. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1096–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, L. Elicitor-like Effects of Low-Energy Ultrasound on Plant (Panax ginseng) Cells: Induction of Plant Defense Responses and Secondary Metabolite Production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Al-Mahdy, D.A.; Meyer, A.; Westphal, H.; Wessjohann, L.A. Metabolomics Reveals Biotic and Abiotic Elicitor Effects on the Soft Coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi Terpenoid Content. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Maamoun, A.A.; Meyer, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Salicylic Acid and Its Derivatives Elicit the Production of Diterpenes and Sterols in Corals and Their Algal Symbionts: A Metabolomics Approach to Elicitor SAR. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, A. Effect of Elicitors on the Production of Secondary Metabolites.; Elsevier Science.; New York: 1994; Vol. Volume 14.; 135-151.
- Romano, S.; Jackson, S.A.; Patry, S.; Dobson, A.D.W. Extending the “One Strain Many Compounds” (OSMAC) Principle to Marine Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 244–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkaya, F.C.; Ebrahim, W.; El-Neketi, M.; Tansel Tanrıkul, T.; Kalscheuer, R.; Müller, W.E.G.; Guo, Z.; Zou, K.; Liu, Z.; Proksch, P. Induction of New Metabolites from Sponge-Associated Fungus Aspergillus carneus by OSMAC Approach. Fitoterapia 2018, 131, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmann, A.; Aly, A.H.; Lin, W.; Wang, B.; Proksch, P. Co-Cultivation - A Powerful Emerging Tool for Enhancing the Chemical Diversity of Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strongman, D.B.; Miller, J.D.; Calhoun, L.; Findlay, J.A.; Whitney, N.J. The Biochemical Basis for Interference Competition among Some Lignicolous Marine Fungi 1; 1987; Vol. 30; 21-26.
- Grant Burgess, J.; Jordan, E.M.; Bregu, M.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Boyd, K.G. Microbial Antagonism: A Neglected Avenue of Natural Products Research; 1999; Vol. 70; 27-32.
- Sonnenbichler, J.; Dietrich, J.; Peipp, H. Secondary Fungal Metabolites and Their Biological Activities, V. Investigations Concerning the Induction of the Biosynthesis of Toxic Secondary Metabolites in Basidiomycetes; 1994; Vol. 375; 71-79.
- Gutierrez-Correa, M.; Tengerdy, R.P. Xylanase Production by Fungal Mixed Culture Solid Substrate Fermentation on Sugar Cane Bagasse; 1998; 45-47.
- Wiesel, I.; Rehm, · H J; Bisping, · B Improvement of Tempe Fermentations by Application of Mixed Cultures Consisting of Rhizopus Sp. and Bacterial Strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 47, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selegato, D.M.; Castro-Gamboa, I. Enhancing Chemical and Biological Diversity by Co-Cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117559–1117583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudal, F.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A. Impact of Co-Culture on the Metabolism of Marine Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L., D. W., & M.Z. Induced Production of Cytochalasans in Co-Culture of Marine Fungus Aspergillus flavipes and Actinomycete streptomyces Sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield, J.; Hassan, H.M.; Jaspars, M.; Ebel, R.; Rateb, M.E. Dual Induction of New Microbial Secondary Metabolites by Fungal Bacterial Co-Cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueto, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.; Fenical, W.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J. Pestalone, a New Antibiotic Produced by a Marine Fungus in Response to Bacterial Challenge. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1444–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.C.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.A.; Fenical, W. Libertellenones A-D: Induction of Cytotoxic Diterpenoid Biosynthesis by Marine Microbial Competition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5267–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abisado, R.G.; Benomar, S.; Klaus, J.R.; Dandekar, A.A.; Chandler, J.R. Bacterial Quorum Sensing and Microbial Community Interactions. mBio 2018, 9, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Byun, W.S.; Moon, K.; Kwon, Y.; Bae, M.; Um, S.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, D.C. Coculture of Marine Streptomyces Sp. with Bacillus Sp. Produces a New Piperazic Acid-Bearing Cyclic Peptide. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelare, P.E.; Adpressa, D.A.; Kaweesa, E.N.; Zakharov, L.N.; Loesgen, S. Coculture of Two Developmental Stages of a Marine-Derived Aspergillus alliaceus Results in the Production of the Cytotoxic Bianthrone Allianthrone A. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Lin, Y. Marinamide, a Novel Alkaloid and Its Methyl Ester Produced by the Application of Mixed Fermentation Technique to Two Mangrove Endophytic Fungi from the South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1426–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, A.F.; Zhang, Y.; Adil, M.; Deng, Y. Antibiotic Discovery: Combining Isolation Chip (IChip) Technology and Co-Culture Technique. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7333–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macintyre, L.W.; Charles, M.J.; Haltli, B.A.; Marchbank, D.H.; Kerr, R.G. An Ichip-Domesticated Sponge Bacterium Produces an N-Acyltyrosine Bearing an α-Methyl Substituent. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 7768–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Mateos, A.I.; Roura Padrosa, D.; Paradisi, F. Multistep Enzyme Cascades as a Route towards Green and Sustainable Pharmaceutical Syntheses. Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardao, I.; Hwang, E.T.; Zeng, A.-P. In Vitro Multienzymatic Reaction Systems for Biosynthesis. In Fundamentals and Application of New Bioproduction Systems. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Springer, 2013; Vol. 137, pp. 153–184.
- Roessner, C.A.; Scott, I. Achieving Natural Product Synthesis and Diversity via Catalytic Networking Ex Vivo. Chem. Biol. 1996, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecik, R.A. Natural Product Biosynthesis Moves in Vitro. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattely, E.S.; Fischbach, M.A.; Walsh, C.T. Total Biosynthesis: In Vitro Reconstitution of Polyketide and Nonribosomal Peptide Pathways. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 757–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfleger, B.F.; Prather, K.L.J. Biological Synthesis Unbounded? Nature Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1148–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, E.; Brucher, B.; Schrittwieser, J.H. Multi-Enzymatic Cascade Reactions: Overview and Perspectives. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2239–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancor, L.; Luckarift, H.R. Co-Immobilized Coupled Enzyme Systems in Biotechnology. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2010, 27, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
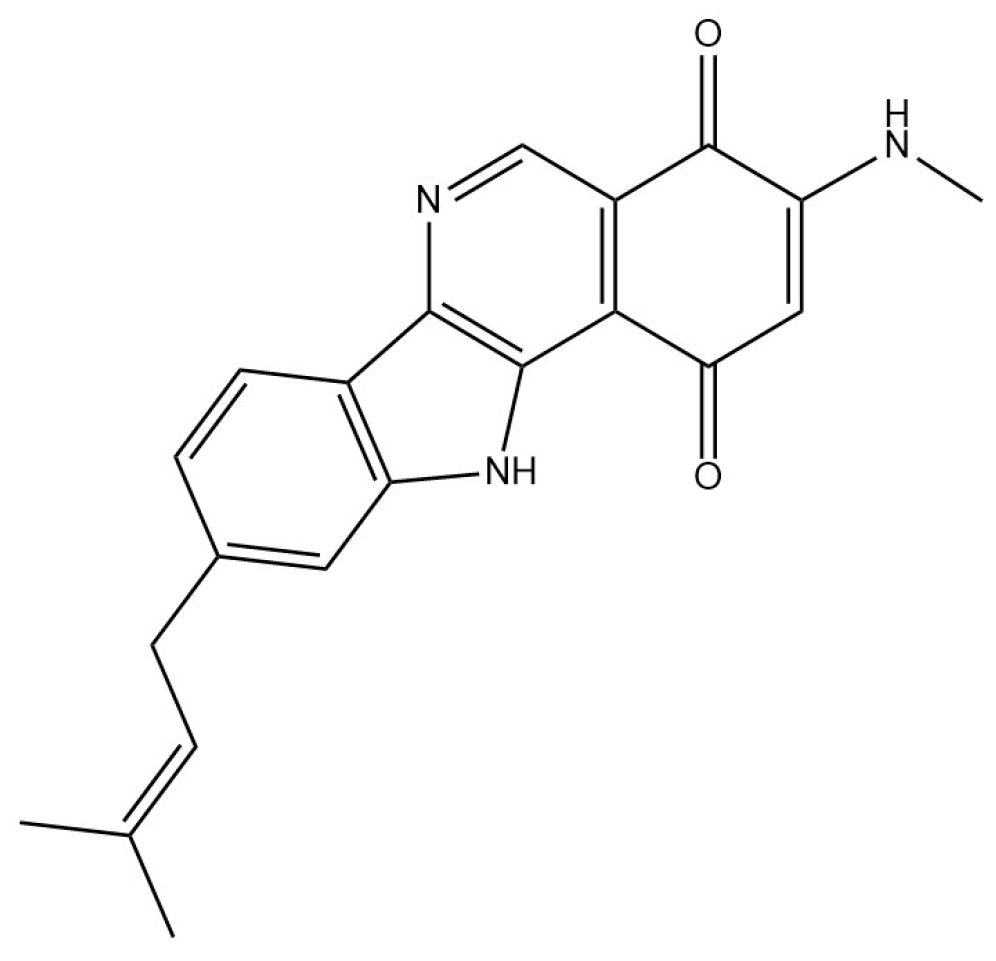
- Maleckis, M.; Wibowo, M.; Williams, S.E.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Sigrist, R.; Souza, L.D.O.; Cowled, M.S.; Charusanti, P.; Gren, T.; Saha, S.; et al. Maramycin, a Cytotoxic Isoquinolinequinone Terpenoid Produced through Heterologous Expression of a Bifunctional Indole Prenyltransferase/Tryptophan Indole-Lyase in S. Albidoflavus. ACS Chem. Biol. 2024, 19, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Marahiel, M.A. Where Chemistry Meets Biology: The Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Nonribosomal Peptides and Polyketides. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Xiang, L.; Izumikawa, M.; Meluzzi, D.; Moore, B.S. Enzymatic Total Synthesis of Enterocin Polyketides. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzis, J.A.; Cheng, Q.; Thomas, P.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Moore, B.S. In Vitro Biosynthesis of Unnatural Enterocin and Wailupemycin Polyketides. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharel, M.K.; Pahari, P.; Lian, H.; Rohr, J. Enzymatic Total Synthesis of Rabelomycin, an Angucycline Group Antibiotic. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 2814–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, M.K.; Pahari, P.; Shepherd, M.D.; Tibrewal, N.; Nybo, S.E.; Shaaban, K.A.; Rohr, J. Angucyclines: Biosynthesis, Mode-of-Action, New Natural Products, and Synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 264–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahari, P.; Kharel, M.K.; Shepherd, M.D.; Van Lanen, S.G.; Rohr, J. Enzymatic Total Synthesis of Defucogilvocarcin M and Its Implications for Gilvocarcin Biosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Rohr, J. One-Pot Enzymatic Total Synthesis of Presteffimycinone, an Early Intermediate of the Anthracycline Antibiotic Steffimycin Biosynthesis. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaysser, L.; Bernhardt, P.; Nam, S.-J.; Loesgen, S.; Ruby, J.G.; Skewes-Cox, P.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Moore, B.S. Merochlorins A–D, Cyclic Meroterpenoid Antibiotics Biosynthesized in Divergent Pathways with Vanadium-Dependent Chloroperoxidases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11988–11991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teufel, R.; Kaysser, L.; Villaume, M.T.; Diethelm, S.; Carbullido, M.K.; Baran, P.S.; Moore, B.S. One-Pot Enzymatic Synthesis of Merochlorin A and B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11019–11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, R.; Heiss, E.H.; Ferk, F.; Peschel, A.; Knasmueller, S.; Dirsch, V.M.; Krupitza, G.; Kopp, B. Ikarugamycin Induces DNA Damage, Intracellular Calcium Increase, P38 MAP Kinase Activation and Apoptosis in HL-60 Human Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells. Mutat. Res. - Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen 2011, 709–710, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Dong, F.; Da, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Weng, J.; Feng, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Ikarugamycin Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Cell Glycolysis by Targeting Hexokinase 2. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 3943–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greunke, C.; Glöckle, A.; Antosch, J.; Gulder, T.A.M. Biocatalytic Total Synthesis of Ikarugamycin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4351–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckman, R.K.; Weidner, C.H.; Perni, R.B.; Napier, J.J. An Enantioselective and Highly Convergent Synthesis of (+)-Ikarugamycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8036–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, L.A.; Macdonald, D.; Anderson, L.G. Total Synthesis of (+)-Ikarugamycin. 2. Elaboration of the Macrocyclic Lactam and Tetramic Acid Substructures and Complete Assembly of the Antibiotic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 9292–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roush, W.R.; Wada, C.K. Application of.Eta.4-Diene Iron Tricarbonyl Complexes in Acyclic Stereocontrol: Asymmetric Synthesis of the as-Indacene Unit of Ikarugamycin (A Formal Total Synthesis). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 2151–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Fetter, A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Metcalf, W.W.; Helfrich, E.J.N.; et al. AntiSMASH 7.0: New and Improved Predictions for Detection, Regulation, Chemical Structures and Visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W46–W50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinnider, M.A.; Johnston, C.W.; Gunabalasingam, M.; Merwin, N.J.; Kieliszek, A.M.; MacLellan, R.J.; Li, H.; Ranieri, M.R.M.; Webster, A.L.H.; Cao, M.P.T.; et al. Comprehensive Prediction of Secondary Metabolite Structure and Biological Activity from Microbial Genome Sequences. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 6058–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, J.I.; Schwalen, C.J.; Patel, P.S.; Maxson, T.; Blair, P.M.; Tai, H.C.; Zakai, U.I.; Mitchell, D.A. A New Genome-Mining Tool Redefines the Lasso Peptide Biosynthetic Landscape. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouprina, N.; Larionov, V. Selective Isolation of Genomic Loci from Complex Genomes by Transformation-Associated Recombination Cloning in the Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, X.; Gabrieli, T.; Lou, C.; Ebenstein, Y.; Zhu, T.F. Cas9-Assisted Targeting of CHromosome Segments CATCH Enables One-Step Targeted Cloning of Large Gene Clusters. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.G.; Young, L.; Chuang, R.Y.; Venter, J.C.; Hutchison, C.A.; Smith, H.O. Enzymatic Assembly of DNA Molecules up to Several Hundred Kilobases. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, B.; Akhgari, A.; Metsä-Ketelä, M. Activation of Microbial Secondary Metabolic Pathways: Avenues and Challenges. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Du, X.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Xu, J.; Wang, P. Recent Advances in the Heterologous Expression of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters for Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, H.; Pereira, A.R.; Ban, Y.H.; Yoo, Y.J.; Kim, E.; Park, J.W.; Sherman, D.H.; Gerwick, W.H.; et al. Heterologous Production of 4- O -Demethylbarbamide, a Marine Cyanobacterial Natural Product. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5824–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A. Heterologous Expression of Beauvericin in Aspergillus Nidulans. Anhui University: Hefei, China 2016.
- Jin, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.; Qu, X.; Jia, X.; Lei, C. Analyzing and Engineering of the Biosynthetic Pathway of Mollemycin A for Enhancing Its Production. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2024, 9, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, I.; de Rond, T.; Chen, P.Y.T.; Moore, B.S. Ancient Plant-like Terpene Biosynthesis in Corals. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Du, X.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Xu, J.; Wang, P. Recent Advances in the Heterologous Expression of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters for Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox Ramos, A.E.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E.; Champy, P.; Beniddir, M.A. Natural Products Targeting Strategies Involving Molecular Networking: Different Manners, One Goal. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 960–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Tang, X.; Moore, B.S. Genetic Platforms for Heterologous Expression of Microbial Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 1313–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek Zerikly, G.L.C. Strategies for the Discovery of New Natural Products by Genome Mining. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra Mohana, N.; Yashavantha Rao, H.C.; Rakshith, D.; Mithun, P.R.; Nuthan, B.R.; Satish, S. Omics Based Approach for Biodiscovery of Microbial Natural Products in Antibiotic Resistance Era. J. Genet. Eng. & Biotechnol 2018, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tyc, O.; de Jager, V.C.L.; van den Berg, M.; Gerards, S.; Janssens, T.K.S.; Zaagman, N.; Kai, M.; Svatos, A.; Zweers, H.; Hordijk, C.; et al. Exploring Bacterial Interspecific Interactions for Discovery of Novel Antimicrobial Compounds. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M.; Snader, K.M. The Influence of Natural Products upon Drug Discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, J.R.; B.R.M. Mechanism of Action of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Am. J. Med 1998, 215–225.
- Krishnamurti, C.; Rao, S.S.C.C. The Isolation of Morphine by Serturner. Indian J Anaesth 2016, 60, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inturrisi, C.E. Clinical Pharmacology of Opioids for Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, 53–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, H.A.; Stueckle, T.A.; Tse, W.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Dinu, C.Z. Digitoxin and Its Analogs as Novel Cancer Therapeutics. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamirano, J.; Li, Y.; Desantiago, J.; Piacentino, V.; Houser, S.R.; Bers, D.M. The Inotropic Effect of Cardioactive Glycosides in Ventricular Myocytes Requires Na+-Ca2+ Exchanger Function. J. Physiol. 2006, 575, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.R.; Shaw, W.M.; Ellis, T. Biosynthesis of Therapeutic Natural Products Using Synthetic Biology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 105, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.M.; Silva, B.N.M. da; Barbosa, G.; Barreiro, E.J. β-Lactam Antibiotics: An Overview from a Medicinal Chemistry Perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112829–112854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleckis, M.; Wibowo, M.; Gren, T.; Jarmusch, S.A.; Sterndorff, E.B.; Booth, T.; Henriksen, N.N.S.E.; Whitford, C.M.; Jiang, X.; Jørgensen, T.S.; et al. Biosynthesis of the Azoxy Compound Azodyrecin from Streptomyces mirabilis P8-A2. ACS Chem. Biol. 2024, 19, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleckis, M.; Wibowo, M.; Williams, S.E.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Sigrist, R.; Souza, L.D.O.; Cowled, M.S.; Charusanti, P.; Gren, T.; Saha, S.; et al. Maramycin, a Cytotoxic Isoquinolinequinone Terpenoid Produced through Heterologous Expression of a Bifunctional Indole Prenyltransferase/Tryptophan Indole-Lyase in S. Albidoflavus. ACS Chem. Biol. 2024, 19, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ang, E.L. Recent Advances in Combinatorial Biosynthesis for Drug Discovery. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaitan Khosla; Jay D. Keasling Metabolic Engineering for Drug and Development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 1019–1025. [CrossRef]
- Culp, E.J.; Yim, G.; Waglechner, N.; Wang, W.; Pawlowski, A.C.; Wright, G.D. Hidden Antibiotics in Actinomycetes Can Be Identified by Inactivation of Gene Clusters for Common Antibiotics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, M.E.; Kevvai, K.; Grewal, P.S.; Narcross, L.; Choi, B.; Bourgeois, L.; Dueber, J.E.; Martin, V.J.J. A Yeast Platform for High-Level Synthesis of Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3337–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
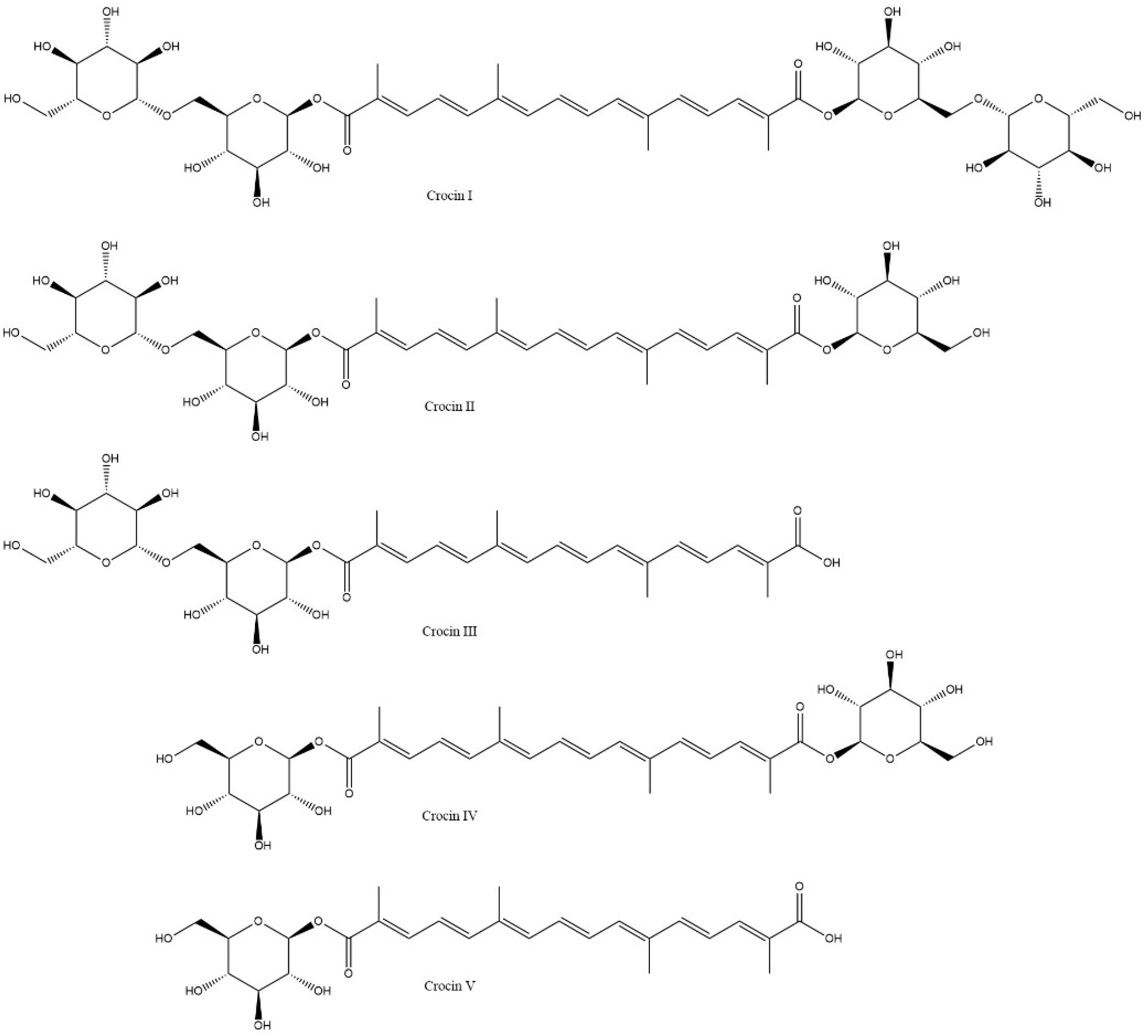
- Moraga, A.R.; Nohales, P.F.; Pérez, J.A.F.; Gómez-Gómez, L. Glucosylation of the Saffron Apocarotenoid Crocetin by a Glucosyltransferase Isolated from Crocus sativus Stigmas. Planta 2004, 219, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Lou, S. Research Progress in Heterologous Crocin Production. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, F.; Wang, Y.; Mei, X.; Yao, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiao, W.; Yuan, Y. Heterologous Biosynthesis and Manipulation of Crocetin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2017, 16, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, P.; Zhao, D.; Ye, L.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, J.; Bi, C. Construction of Escherichia coli Cell Factories for Crocin Biosynthesis. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2019, 18, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Luo, Z.; Jia, X.; Mo, C.; Huang, X.; Suo, Y.; Cui, S.; Zang, Y.; Liao, J.; Ma, X. Synthesis of Crocin I and Crocin II by Multigene Stacking in Nicotiana benthamiana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14139–14153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; L. D.; C.J. Lutein Production from Biomass: Marigold Flowers versus Microalgae. Technol. 2015, 184, 421–428. [Google Scholar]
- Pourkarimi, S.; Hallajisani, A.; Nouralishahi, A.; Alizadehdakhel, A.; Golzary, A. Factors Affecting Production of Beta-Carotene from Dunaliella salina Microalgae. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 101771–101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammuni, M.N.; Ariyadasa, T.U.; Nimarshana, P.H.V.; Attalage, R.A. Comparative Assessment on the Extraction of Carotenoids from Microalgal Sources: Astaxanthin from H. Pluvialis and β-Carotene from D. salina. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.D.; Clark, B.R.; Amadio, J. Metabolism of Fluoroorganic Compounds in Microorganisms: Impacts for the Environment and the Production of Fine Chemicals. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2009, 84, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Omari, M. El; König, G.M. Biohalogenation: Nature’s Way to Synthesize Halogenated Metabolites. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
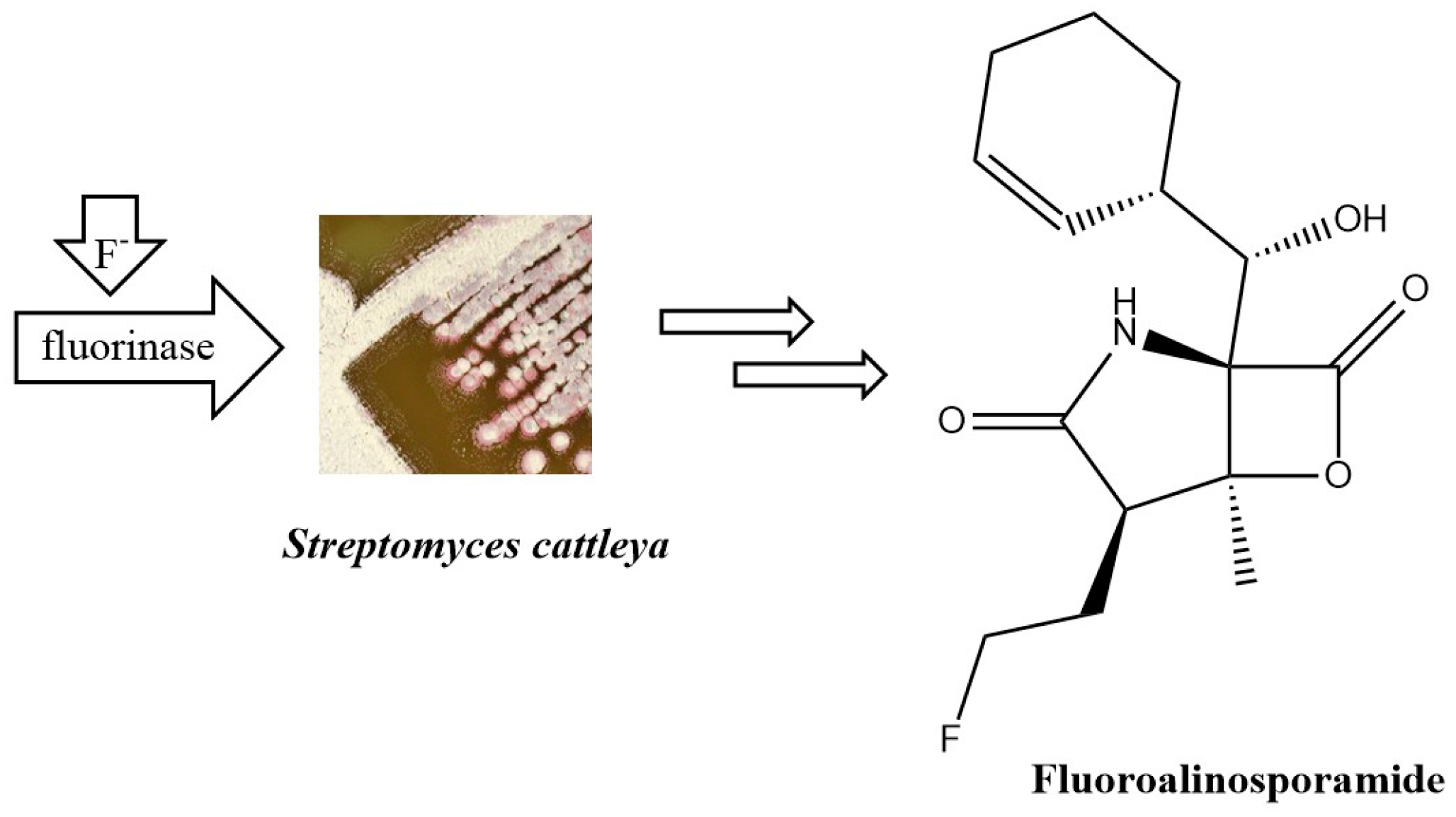
- Dong, C.; Huang, F.; Deng, H.; Schaffrath, C.; Spencer, J.B.; O’Hagan, D.; Naismith, J.H. Crystal Structure and Mechanism of a Bacterial Fluorinating Enzyme. Nature 2004, 427, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustáquio, A.S.; Pojer, F.; Noel, J.P.; Moore, B.S. Discovery and Characterization of a Marine Bacterial SAM-Dependent Chlorinase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 4, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustá Quio, A.S.; Mcglinchey, R.P.; Liu, Y.; Hazzard, C.; Beer, L.L.; Florova, G.; Alhamadsheh, M.M.; Lechner, A.; Kale, A.J.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Biosynthesis of the Salinosporamide A Polyketide Synthase Substrate Chloroethylmalonyl-Coenzyme A from S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine. PNAS 2009, 106, 12295–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustáquio, A.S.; O’Hagan, D.; Moore, B.S. Engineering Fluorometabolite Production: Fluorinase Expression in Salinispora Tropica Yields Fluorosalinosporamide. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudêncio, S.P.; Pereira, F. Marine Drug Discovery through Computer-Aided Approaches. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, F.; Aires-de-Sousa, J. Computational Methodologies in the Exploration of Marine Natural Product Leads. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 236–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Holguín, N.; Frau, J.; Glossman-Mitnik, D. Understanding the Chemical Reactivity and Biological Properties of Patellamides Using Theoretical and Computational Methods. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2023, 1229, 114329–114339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, P.; Kühl, M.; Comba, P.; Behrendt, L. Possible Functional Roles of Patellamides in the Ascidian-Prochloron Symbiosis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 272–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R. Parr, W.Y. Density-Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules.; Oxford University Press: New York, 1989; ISBN 0-19-504279-4. [Google Scholar]
- Geerlings, P.; Chamorro, E.; Chattaraj, P.K.; De Proft, F.; Gázquez, J.L.; Liu, S.; Morell, C.; Toro-Labbé, A.; Vela, A.; Ayers, P. Conceptual Density Functional Theory: Status, Prospects, Issues. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2020, 139, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Chattaraj, P.K. Conceptual Density Functional Theory Based Electronic Structure Principles. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 6264–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, L.R.; Ríos-Gutiérrez, M.; Pérez, P. Applications of the Conceptual Density Functional Theory Indices to Organic Chemistry Reactivity. Molecules 2016, 21, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, V.; Nurkolis, F.; Park, M.N.; Heriyanto, D.S.; Taslim, N.A.; Tallei, T.E.; Permatasari, H.K.; Tjandrawinata, R.R.; Moon, S.; Kim, B. Green Seaweed Caulerpa Racemosa as a Novel Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Inhibitor in Overcoming Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance: An Analysis Employing Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and In Vitro Research. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 272–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Srivastava, D.; Sahu, M.; Tiwari, S.; Ambasta, R.K.; Kumar, P. Artificial Intelligence to Deep Learning: Machine Intelligence Approach for Drug Discovery. Mol Divers 2021, 25, 1315–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, H.; Canová, N.K.; Arora, M. The Potential Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery and Development. Physiol. Res. 2021, 70, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Farias Silva, C.E.; Costa, G.Y.S.C.M.; Ferro, J.V.; de Oliveira Carvalho, F.; da Gama, B.M.V.; Meili, L.; dos Santos Silva, M.C.; Almeida, R.M.R.G.; Tonholo, J. Application of Machine Learning to Predict the Yield of Alginate Lyase Solid-State Fermentation by Cunninghamella Echinulata: Artificial Neural Networks and Support Vector Machine. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2022, 135, 3155–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchi, A.C.; Ito, S.; Escaramboni, B.; Neto, P. de O.; Herculano, R.D.; Romeiro Miranda, M.C.; Passalia, F.J.; Rocha, J.C.; Fernández Núñez, E.G. Artificial Intelligence Approach Based on Near-Infrared Spectral Data for Monitoring of Solid-State Fermentation. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañaga, P.; Calvo, B.; Santana, R.; Bielza, C.; Galdiano, J.; Inza, I.; Lozano, J.A.; Armañanzas, R.; Santafé, G.; Pérez, A.; et al. Machine Learning in Bioinformatics. Brief Bioinform. 2006, 7, 86–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuaje, F. Computational Models for Predicting Drug Responses in Cancer Research. Brief Bioinform. 2017, 18, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X.; Peng, W.; Zhou, H.M. Artificial Neural Network – Genetic Algorithm to Optimize Wheat Germ Fermentation Condition: Application to the Production of Two Anti-Tumor Benzoquinones. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.H.; Ren, D.F.; Lu, J. Mixed Fermentation of Spirulina Platensis with Lactobacillus Plantarum and Bacillus Subtilis by Random-Centroid Optimization. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




