Submitted:
06 March 2024
Posted:
07 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
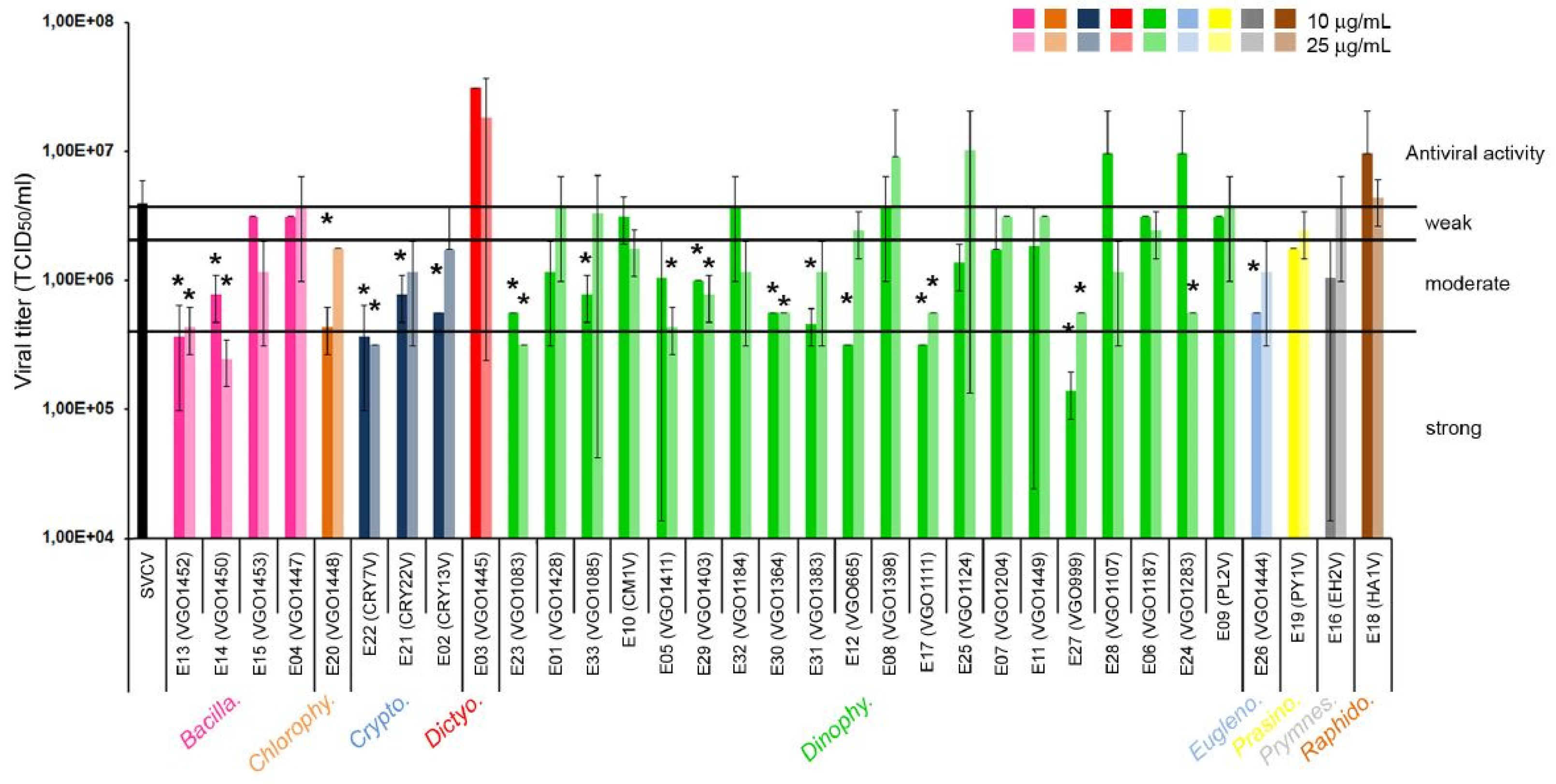
2.1. Antiviral Activity of the Extracts
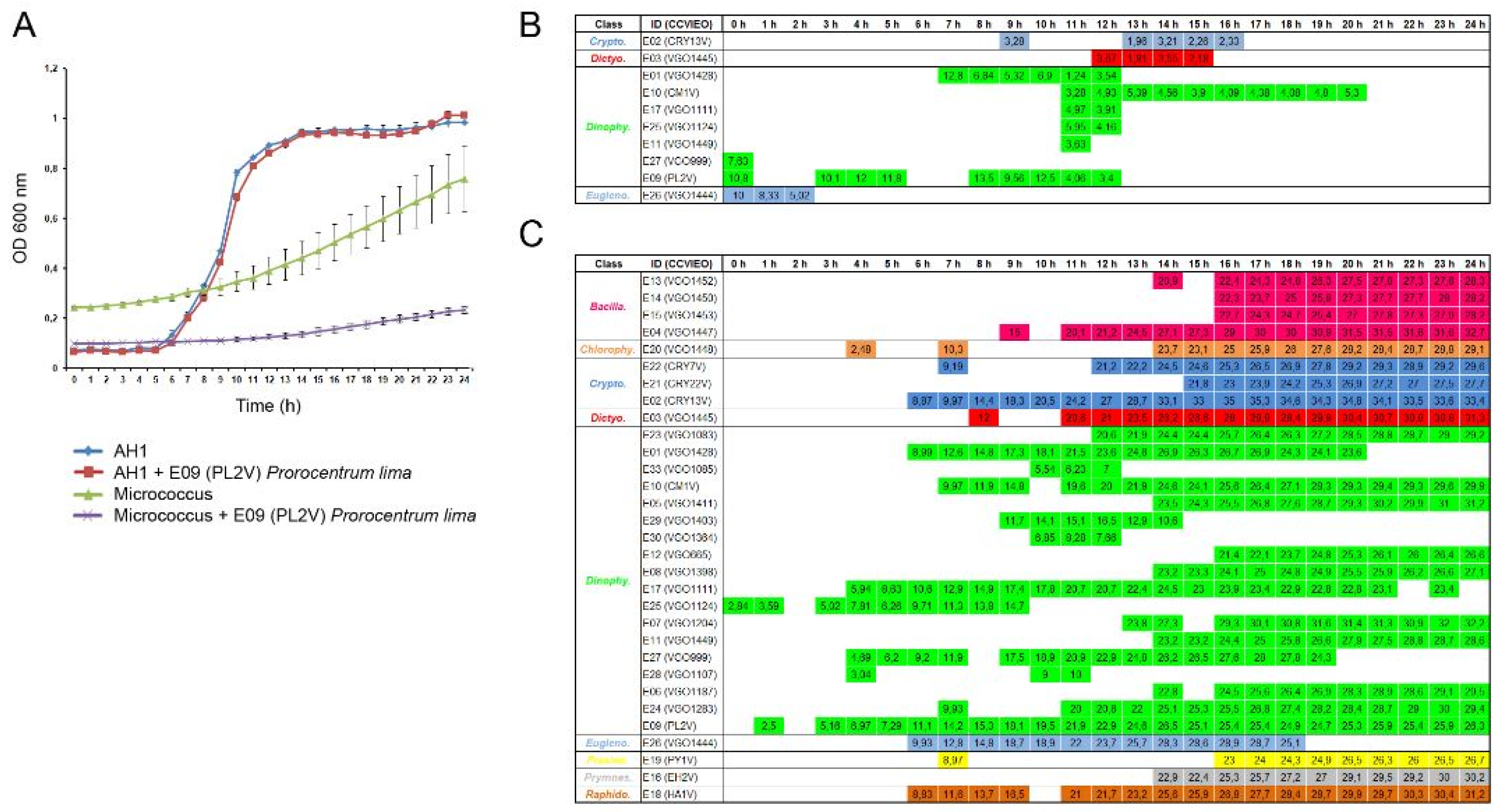
2.2. Antibacterial Activity of the Extracts
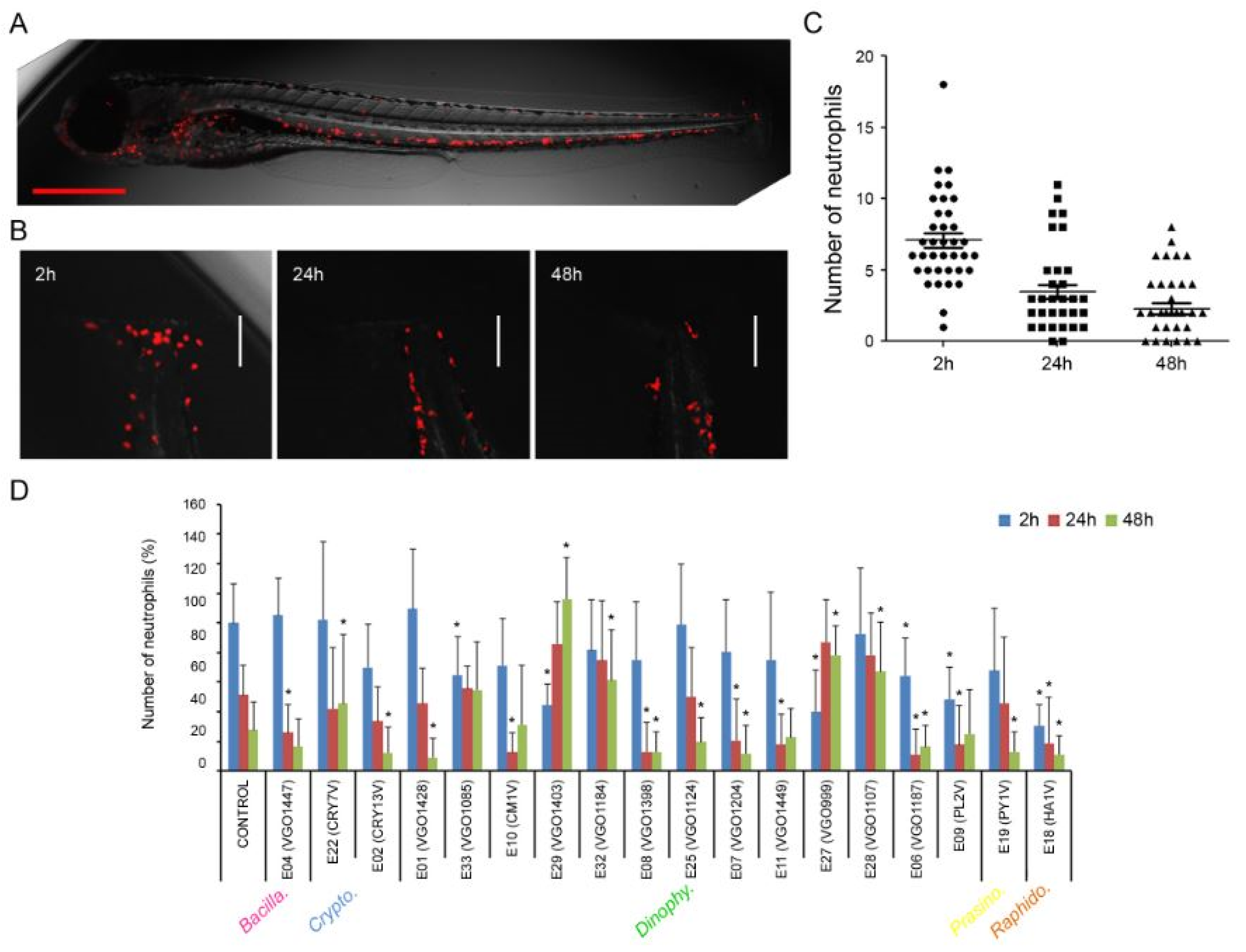
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Extracts
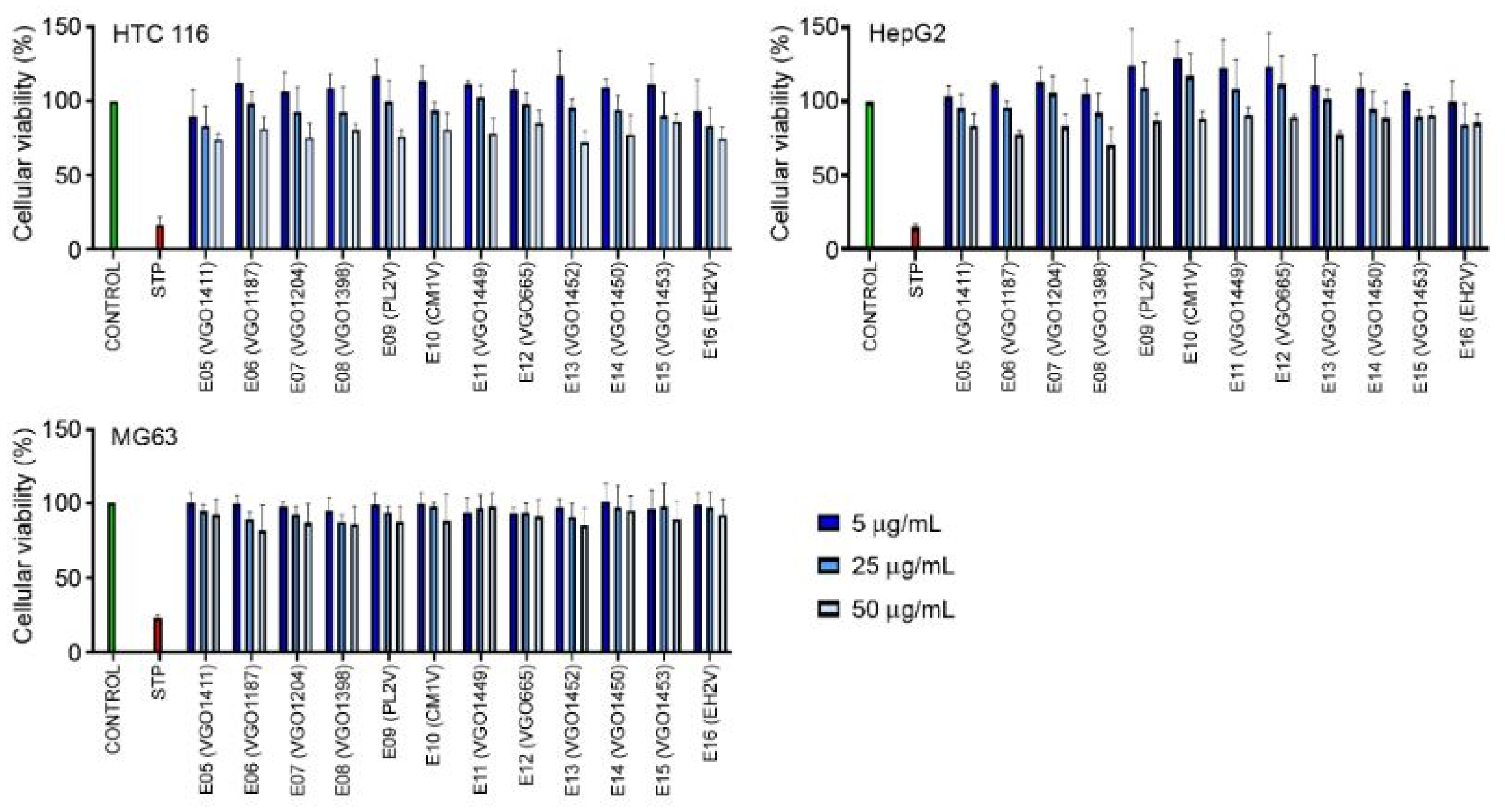
2.4. Cytotoxic Activity of the Extracts in the Cancer Lines
3. Discussion
3.1. Antiviral Activity of the Extracts
3.2. Antibacterial Activity
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.4. Anti-Cancer Activity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The CCVIEO Collection of Harmful Marine Microalgae
4.2. Culture and Preparation of Microalgae Extracts
4.3. Antiviral and Antibacterial Activity of the Extracts
4.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Extracts
4.5. Cytotoxic Activity of the Extracts in Cancer Cell Lines
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, T.; Pati, S.; Kari, Z.A.; Edinur, H.A.; Chakraborty, R. Novel Bioactive Compounds From Marine Sources as a Tool for Functional Food Development. Front Mar Sci 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverland, M.; Mydland, L.T.; Skrede, A. Marine Macroalgae as Sources of Protein and Bioactive Compounds in Feed for Monogastric Animals. J Sci Food Agric 2019, 99, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, S.; Divyashree, M.; Mani, M.K.; Mamatha, B.S. Algae and Cyanobacteria as a Source of Novel Bioactive Compounds for Biomedical Applications. In Advances in Cyanobacterial Biology; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 173–194. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Shukla, S.K.; Singh, H.R.; Singh, B.; Jha, S.K. Bioactive Compounds from Microalgae. In An Integration of Phycoremediation Processes in Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 337–358. [Google Scholar]
- Żak, A.; Kosakowska, A. Cyanobacterial and Microalgal Bioactive Compounds – the Role of Secondary Metabolites in Allelopathic Interactions. Oceanol Hydrobiol Stud 2016, 45, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saide, A.; Martínez, K.A.; Ianora, A.; Lauritano, C. Unlocking the Health Potential of Microalgae as Sustainable Sources of Bioactive Compounds. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Nelson, D.R.; Yi, Z.; Xu, M.; Khraiwesh, B.; Jijakli, K.; Chaiboonchoe, A.; Alzahmi, A.; Al-Khairy, D.; Brynjolfsson, S.; et al. Bioactive Compounds From Microalgae: Current Development and Prospects. In; 2017; pp. 199–225.
- Heydarizadeh, P.; Poirier, I.; Loizeau, D.; Ulmann, L.; Mimouni, V.; Schoefs, B.; Bertrand, M. Plastids of Marine Phytoplankton Produce Bioactive Pigments and Lipids. Mar Drugs 2013, 11, 3425–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandagopal, P.; Steven, A.N.; Chan, L.-W.; Rahmat, Z.; Jamaluddin, H.; Mohd Noh, N.I. Bioactive Metabolites Produced by Cyanobacteria for Growth Adaptation and Their Pharmacological Properties. Biology (Basel) 2021, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, C.; Andersen, J.H.; Hansen, E.; Albrigtsen, M.; Escalera, L.; Esposito, F.; Helland, K.; Hanssen, K.Ø.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. Bioactivity Screening of Microalgae for Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Anticancer, Anti-Diabetes, and Antibacterial Activities. Front Mar Sci 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, K.W.; Ko, J.-Y.; Shah, Md.M.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Kang, M.-C.; Kwon, O.-N.; Lee, J.-B.; Jeon, Y.-J. In Vitro Studies of Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Activities of Organic Solvent Extracts from Cultured Marine Microalgae. ALGAE 2013, 28, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Andrade, K.; Lauritano, C.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. Marine Microalgae with Anti-Cancer Properties. Mar Drugs 2018, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingebrigtsen, R.A.; Hansen, E.; Andersen, J.H.; Eilertsen, H.C. Light and Temperature Effects on Bioactivity in Diatoms. J Appl Phycol 2016, 28, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestegard, S.K.; Knutsen, G.; Herfindal, L. Adenosine Content and Growth in the Diatom Phaeodactylum Tricornutum (Bacillariophyceae): Effect of Salinity, Light, Temperature and Nitrate. Diatom Research 2014, 29, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeev, S.D.; Wasserman, L.A. Microalgae as Source of Biofuel, Food, Fodder, and Medicines. Appl Biochem Microbiol 2011, 47, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.A.; Pellone, P.; Lubritto, C.; Ciniglia, C. Evaluation of Microalgae Antiviral Activity and Their Bioactive Compounds. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, W.G.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, P.-S.; Lee, C.-K. In Vitro Inhibition of Influenza A Virus Infection by Marine Microalga-Derived Sulfated Polysaccharide p-KG03. Antiviral Res 2012, 93, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; Martín, J.; de la Cruz, M.; Reyes, F.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. First Identification of Marine Diatoms with Anti-Tuberculosis Activity. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.E.; Cheuk, C.; Yang, X.Q.G.; Patterson, G.M.L.; Bonjouklian, R.; Smitka, T.A.; Mynderse, J.S.; Foster, R.S.; Jones, N.D.; Swartzendruber, J.K.; et al. Hapalindoles, Antibacterial and Antimycotic Alkaloids from the Cyanophyte Hapalosiphon Fontinalis. J Org Chem 1987, 52, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.C.M.; Salles, T.S.; Moreira, M.F.; Barbarino, E.; do Valle, A.F.; Couto, M.A.P.G. Antiviral Activity of Microalgae Extracts against Mayaro Virus. Algal Res 2022, 61, 102577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, D.; Costantini, M.; Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Núñez Pons, L.; Ruocco, N.; di Prisco, G.; Ianora, A.; Verde, C. Biotechnological Applications of Bioactive Peptides From Marine Sources. In; 2018; pp. 171–220.
- Guedes, A.; Gião, M.; Seabra, R.; Ferreira, A.; Tamagnini, P.; Moradas-Ferreira, P.; Malcata, F. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Cell Extracts from Microalgae. Mar Drugs 2013, 11, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed Hatha, A.A.; Sumayya, N.S. Antioxidants from Marine Cyanobacteria. In Marine Antioxidants; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Lauritano, C.; Helland, K.; Riccio, G.; Andersen, J.H.; Ianora, A.; Hansen, E.H. Lysophosphatidylcholines and Chlorophyll-Derived Molecules from the Diatom Cylindrotheca Closterium with Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Mar Drugs 2020, 18, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccio, G.; Lauritano, C. Microalgae with Immunomodulatory Activities. Mar Drugs 2019, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patipong, T.; Hibino, T.; Waditee-Sirisattha, R.; Kageyama, H. Induction of Antioxidative Activity and Antioxidant Molecules in the Halotolerant Cyanobacterium Halothece Sp. PCC7418 by Temperature Shift. Nat Prod Commun 2019, 14, 1934578X1986568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Sitachitta, N.; Rossi, J. V.; Roberts, M.A.; Flatt, P.M.; Jia, J.; Sherman, D.H.; Gerwick, W.H. Biosynthetic Pathway and Gene Cluster Analysis of Curacin A, an Antitubulin Natural Product from the Tropical Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya m Ajuscula. J Nat Prod 2004, 67, 1356–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Garcia, M.; Costa-Rodrigues, J.; Costa, M.; Ribeiro, M.; Fernandes, M.; Barros, P.; Barreiro, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Martins, R. Exploring Bioactive Properties of Marine Cyanobacteria Isolated from the Portuguese Coast: High Potential as a Source of Anticancer Compounds. Mar Drugs 2013, 12, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, M.; Maruthanayagam, V.; Sundararaman, M. A Review of Pharmacological and Toxicological Potentials of Marine Cyanobacterial Metabolites. Journal of Applied Toxicology 2012, 32, 153–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller-Feuga, A.; Robert, R.; Cahu, C.; Robin, J.; Divanach, P. Uses of Microalgae in Aquaculture. In Live Feeds in Marine Aquaculture; Blackwell Science Ltd: Oxford, UK; pp. 253–299.
- Nagappan, S.; Das, P.; AbdulQuadir, M.; Thaher, M.; Khan, S.; Mahata, C.; Al-Jabri, H.; Vatland, A.K.; Kumar, G. Potential of Microalgae as a Sustainable Feed Ingredient for Aquaculture. J Biotechnol 2021, 341, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; El-Ashram, S.; Yilmaz, S.; Naiel, M.A.E.; Abdul Kari, Z.; Hamid, N.K.A.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Nowosad, J.; Kucharczyk, D. The Effectiveness of Arthrospira Platensis and Microalgae in Relieving Stressful Conditions Affecting Finfish and Shellfish Species: An Overview. Aquac Rep 2022, 24, 101135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahi, A.; Ramos-Vega, A.; Angulo, C.; Monreal-Escalante, E.; Guardiola, F.A. Microalgae with Immunomodulatory Effects on Fish. Rev Aquac 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Leong, J.-A. FISH VIRUSES. In Encyclopedia of Virology; Elsevier, 1999; pp. 558–568. [Google Scholar]
- Padhi, A.; Verghese, B. Detecting Positively Selected Codons in the Glycoprotein of Spring Viraemia of Carp Virus (SVCV) Isolates from the USA and China. J Fish Dis 2008, 31, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OIE Spring Viraemia of Carp. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals; 2021; pp. 1–18.
- Ashraf, U.; Lu, Y.; Lin, L.; Yuan, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, X. Spring Viraemia of Carp Virus: Recent Advances. Journal of General Virology 2016, 97, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.M.; Elkamel, A.A.; Ibrahim, S.; El-Matbouli, M.; Soliman, H.; Abdallah, E.S.H. Control of Spring Viremia of Carp in Common Carp Using RNA Interference. Aquaculture 2022, 559, 738417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Valente, C.; Wan, A.H.L. Vibrio and Major Commercially Important Vibriosis Diseases in Decapod Crustaceans. J Invertebr Pathol 2021, 181, 107527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshath, A.A.; Rajan, A.P.; Vimal, S.; Prabhakaran, V.-S.; Ganesan, R. Bacterial Pathogenesis in Various Fish Diseases: Recent Advances and Specific Challenges in Vaccine Development. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches-Fernandes, G.M.M.; Sá-Correia, I.; Costa, R. Vibriosis Outbreaks in Aquaculture: Addressing Environmental and Public Health Concerns and Preventive Therapies Using Gilthead Seabream Farming as a Model System. Front Microbiol 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semwal, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N. A Review on Pathogenicity of Aeromonas Hydrophila and Their Mitigation through Medicinal Herbs in Aquaculture. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Gai, C.; Ye, G.; An, J.; Liu, K.; Xu, L.; Cao, H. Aeromonas Hydrophila, an Emerging Causative Agent of Freshwater-Farmed Whiteleg Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pękala, A.; Paździor, E.; Antychowicz, J.; Bernad, A.; Głowacka, H.; Więcek, B.; Niemczuk, W. Kocuria Rhizophila and Micrococcus Luteus as Emerging Opportunist Pathogens in Brown Trout ( Salmo Trutta Linnaeus, 1758) and Rainbow Trout ( Oncorhynchus Mykiss Walbaum, 1792). Aquaculture 2018, 486, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, K.A. Natural Products as Antiviral Agents. In; 2000; pp. 473–572.
- Geetha Bai, R.; Tuvikene, R. Potential Antiviral Properties of Industrially Important Marine Algal Polysaccharides and Their Significance in Fighting a Future Viral Pandemic. Viruses 2021, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.G.; Cadamuro, R.D.; Cabral, A.C.; Thaís da Silva, I.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Fongaro, G. Broad Spectrum Algae Compounds Against Viruses. Front Microbiol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaise, C.; François, C.; Travers, M.-A.; Morga, B.; Haure, J.; Tremblay, R.; Turcotte, F.; Pasetto, P.; Gastineau, R.; Hardivillier, Y.; et al. Antimicrobial Compounds from Eukaryotic Microalgae against Human Pathogens and Diseases in Aquaculture. Mar Drugs 2016, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, J.; Das, B.K.; Sahu, S.; Marhual, N.P.; Swain, A.K.; Mishra, B.K.; Eknath, A.E. Traditional Antibacterial Activity of Freshwater Microalga Spirulina Platensis to Aquatic Pathogens. Aquac Res 2012, 43, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, V.; Rivas, L.; Cárdenas, C.; Guzmán, F. Cyanobacteria and Eukaryotic Microalgae as Emerging Sources of Antibacterial Peptides. Molecules 2020, 25, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Pradhan, J. Antibacterial Properties of Selected Freshwater Microalgae against Pathogenic Bacteria. Indian J Fisheries 2010, 57, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.; Bao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, S.; Wu, H.; Fan, J. Evaluation of Microalgae as Immunostimulants and Recombinant Vaccines for Diseases Prevention and Control in Aquaculture. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velichkova, K.; Sirakov, I.; Denev, S. In Vitro Antibacterial Effect of Lemna Minuta, Chlorella Vulgaris and Spirulina Sp. Extracts against Fish Pathogen Aeromonas Hydrophila. Aquac Aquar Conserv Legis 2019, 12, 936–940. [Google Scholar]
- Chénais, B. Algae and Microalgae and Their Bioactive Molecules for Human Health. Molecules 2021, 26, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.; Santos, R.A.; Iglesias, P.; Couto, A.; Serra, C.R.; Gouvinhas, I.; Barros, A.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P.; Díaz-Rosales, P. Effect of Extraction Method and Solvent System on the Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Selected Macro- and Microalgae Extracts. J Appl Phycol 2020, 32, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Lobato, Z.; Vázquez, M.; Navarro, F.; Fuentes, J.; Bermejo, E.; Garbayo, I.; Vílchez, C.; Cuaresma, M. Chemically-Induced Production of Anti-Inflammatory Molecules in Microalgae. Mar Drugs 2018, 16, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.M.; Reeves, G.; Billman, G.E.; Sturmberg, J.P. Inflammation–Nature’s Way to Efficiently Respond to All Types of Challenges: Implications for Understanding and Managing “the Epidemic” of Chronic Diseases. Front Med (Lausanne) 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.; Soos, B.-L.; Millard, P.J.; Kim, C.H.; King, B.L. Modeling Virus-Induced Inflammation in Zebrafish: A Balance Between Infection Control and Excessive Inflammation. Front Immunol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagoz, A.M.; Ambrosino, L.; Lauritano, C. De Novo Transcriptome of the Diatom Cylindrotheca Closterium Identifies Genes Involved in the Metabolism of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Kubota, T. Bioactive Metabolites from Marine Dinoflagellates. In Comprehensive Natural Products II; Elsevier, 2010; pp. 263–325. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.R.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Ko, J.Y.; Lakmal, H.H.C.; Lee, J.H.; An, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, J.B. Potentiality of Benthic Dinoflagellate Cultures and Screening of Their Bioactivities in Jeju Island, Korea. Afr J Biotechnol 2014, 13, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusidin, M.R.; Othman, R.; Shaleh, S.R.M.; Ching, F.F.; Senoo, S.; Oslan, S.N.H. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Marine Microalgae Extract against Vibrio Harveyi. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Yoon, H.-S. Effect of Different Cultivation Modes (Photoautotrophic, Mixotrophic, and Heterotrophic) on the Growth of Chlorella Sp. and Biocompositions. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanniyasi, E.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; Anbalagan, M.M.; Raj, P.P.; Gopal, R.K. In Vitro Anti-HIV-1 Activity of the Bioactive Compound Extracted and Purified from Two Different Marine Macroalgae (Seaweeds) (Dictyota Bartayesiana J.V.Lamouroux and Turbinaria Decurrens Bory). Sci Rep 2019, 9, 12185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuda, T.; Nishizawa, M.; Toshima, D.; Matsushima, K.; Yoshida, S.; Takahashi, H.; Kimura, B.; Yamagishi, T. Antioxidant and Anti-Norovirus Properties of Aqueous Acetic Acid Macromolecular Extracts of Edible Brown Macroalgae. LWT 2021, 141, 110942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjánsson, J.; Rolfsson, Ó. Virucidal Activity of a Proprietary Blend of Plant-Based Oils (Viruxal) against SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza Viruses—An in Vitro Study. bioRxiv 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zakaryan, H.; Arabyan, E.; Oo, A.; Zandi, K. Flavonoids: Promising Natural Compounds against Viral Infections. Arch Virol 2017, 162, 2539–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.; Lavrador, A.S.; Santos, R.; Rangel, F.; Iglesias, P.; Tárraga, M.; Couto, A.; Serra, C.R.; Tafalla, C.; Da Costa, E.; et al. Evaluation of the Potential of Marine Algae Extracts as a Source of Functional Ingredients Using Zebrafish as Animal Model for Aquaculture. Marine Biotechnology 2021, 23, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassudrie, M.; Soudant, P.; Nicolas, J.-L.; Fabioux, C.; Lambert, C.; Miner, P.; Le Grand, J.; Petton, B.; Hégaret, H. Interaction between Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium Catenella Exposure and Disease Associated with Herpesvirus OsHV-1 ΜVar in Pacific Oyster Spat Crassostrea Gigas. Harmful Algae 2015, 45, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Falcó, I.; Randazzo, W.; Sánchez, G.; López-Rubio, A. Antiviral and Antioxidant Properties of Active Alginate Edible Films Containing Phenolic Extracts. Food Hydrocoll 2018, 81, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, H.K. Characterization of a Novel Bioflocculant, p-KG03, from a Marine Dinoflagellate, Gyrodinium Impudicum KG03. Bioresour Technol 2007, 98, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizan, A.; Ahamad Bustamam, M.; Maulidiani, M.; Shaari, K.; Ismail, I.; Nagao, N.; Abas, F. Metabolite Profiling of the Microalgal Diatom Chaetoceros Calcitrans and Correlation with Antioxidant and Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Activities via 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics. Mar Drugs 2018, 16, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidizadegan, M.; Peltomaa, E.; Blomster, J. The Potential of Cryptophyte Algae in Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Front Pharmacol 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Riofrio, G.; Moreno, P.; García-Rosado, E.; Alonso, M.C.; Uribe-Tapia, E.; Abdala-Diaz, R.T.; Bejar, J. Tetraselmis Suecica and Porphyridium Cruentum Exopolysaccharides Show Anti-VHSV Activity on RTG-2 Cells. Aquaculture International 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.; De Morais, R.; Bernardo de Morais, A. Bioactivity and Applications of Sulphated Polysaccharides from Marine Microalgae. Mar Drugs 2013, 11, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial Free Fatty Acids: Activities, Mechanisms of Action and Biotechnological Potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2010, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoramoorthy, G.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Venkatesalu, V.; Hsu, M.J. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters of the Blind-Your-Eye Mangrove from India. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 2007, 38, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, D.F.; Bartolomeu Halicki, P.C.; da Silva Canielles Caprara, C.; Borges, P.; da R., M. D’Oca, C.; de Fátima C. Santos, M.; D’Oca, M.G.M.; Roselet, F.; Almeida da Silva, P.E.; Abreu, P.C. Chemical Profile and Antimicrobial Activity of the Marine Diatom Chaetoceros Muelleri. Chem Biodivers 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viso, A.C.; Pesando, D.; Baby, C. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Some Marine Diatoms in Culture. botm 1987, 30, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha shalini, A.; Syed Ali, M.; Anuradha, V.; Yogananth, N.; Bhuvana, P. GCMS Analysis and Invitro Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Study on Methanolic Extract of Thalassiosira Weissflogii. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2019, 19, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Fadillah, S.; Natsir, H.; Ahmad, A.; Karim, A.; Taba, P.; Nur fadillah, S. Extraction and Fractionation of Active Protein from Microalgae Nitzschia Sp. as Antimicrobial Agent. Egypt J Chem 2022, 0, 0–0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Krock, B.; Castrec, J.; Tillmann, U. Unknown Extracellular and Bioactive Metabolites of the Genus Alexandrium: A Review of Overlooked Toxins. Toxins (Basel) 2021, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Antimicrobial Activities of Polyether Compounds of Dinoflagellate Origins. J Appl Phycol 1990, 2, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussai, P.; Larsen, J.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Jeewon, R. Ribosomal DNA Sequence-Based Taxonomy and Antimicrobial Activity of Prorocentrum Spp. (Dinophyceae) from Mauritius Coastal Waters, South-West Indian Ocean. Mar Drugs 2023, 21, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wencheng, L.; Cho, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Takeshita, S.; Hwang, K.; Kim, D.; Oda, T. Photo-Induced Antibacterial Activity of a Porphyrin Derivative Isolated from the Harmful Dinoflagellate Heterocapsa Circularisquama. Aquatic Toxicology 2018, 201, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; You, Y.; Chu, J.; Jin, H.; Yan, X. [Screening and Characterization of Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Marine Bacteria Associated with Karlodinium Micrum]. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2010, 50, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Quijano-Scheggia, S. The Inhibitory Effect of a Non-Yessotoxin-Producing Dinoflagellate, Lingulodinium Polyedrum (Stein) Dodge, towards Vibrio Vulnificus and Staphylococcus Aureus. Rev Biol Trop 2016, 64, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveiro, S.S.; Melo, T.; Figueiredo, A.; Domingues, P.; Pereira, H.; Maia, I.B.; Silva, J.; Domingues, M.R.; Nunes, C.; Moreira, A.S.P. The Polar Lipidome of Cultured Emiliania Huxleyi: A Source of Bioactive Lipids with Relevance for Biotechnological Applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán; Wong; Román; Cárdenas; Alvárez; Schmitt; Albericio; Rojas Identification of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Microalgae Tetraselmis Suecica (Kylin) Butcher and Bactericidal Activity Improvement. Mar Drugs 2019, 17, 453. [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Maldonado, M.L.; Siverio-Mota, D.; Vicet-Muro, L.; Wilches-Arizábala, I.M.; Esguerra, C. V.; de Witte, P.A.M.; Crawford, A.D. Optimization and Pharmacological Validation of a Leukocyte Migration Assay in Zebrafish Larvae for the Rapid In Vivo Bioactivity Analysis of Anti-Inflammatory Secondary Metabolites. PLoS One 2013, 8, e75404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Choi, Y.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-S. “Anti-Inflammatory Activity on LPS-Stimulated in Vitro RAW 264.7 Cells and in Vivo Zebrafish of Heterosigma Akshiwo.”. Journal of Chitin and Chitosan 2017, 22, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, J.R.; Perrin, B.J.; Liu, T.-X.; Kanki, J.; Look, A.T.; Huttenlocher, A. Resolution of Inflammation by Retrograde Chemotaxis of Neutrophils in Transgenic Zebrafish. J Leukoc Biol 2006, 80, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renshaw, S.A.; Loynes, C.A.; Trushell, D.M.I.; Elworthy, S.; Ingham, P.W.; Whyte, M.K.B. A Transgenic Zebrafish Model of Neutrophilic Inflammation. Blood 2006, 108, 3976–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Meijer, A.H.; Schaaf, M.J.M. Modeling Inflammation in Zebrafish for the Development of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugulothu, P. “Bioactive Compound from Micro Algae and Their Anti-Cancer Properties.”. Biomed J Sci Tech Res 2022, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Abdullah, M.A. Anticancer Compounds Derived from Marine Diatoms. Mar Drugs 2020, 18, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Raj, A.; Tiwari, A. Exploring the Anti-Cancer Potential of Microalgae. In Progress in Microalgae Research - A Path for Shaping Sustainable Futures; IntechOpen, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Skjånes, K.; Aesoy, R.; Herfindal, L.; Skomedal, H. Bioactive Peptides from Microalgae: Focus on Anti-cancer and Immunomodulating Activity. Physiol Plant 2021, 173, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, M.R.; Paull, K.D. Some Practical Considerations and Applications of the National Cancer Institute in Vitro Anticancer Drug Discovery Screen. Drug Dev Res 1995, 34, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, J.; Zivanovic, A.; Skropeta, D. Bioassays for Anticancer Activities. In; 2013; pp. 191–205.
- Emtyazjoo, Mo.; Moghadasi, Z.; Rabbani, M.; Emtyazjoo, Ma.; Samadi, S.; Mossaffa, N. Anticancer Effect of Dunaliella Salina under Stress and Normal Conditions against Skin Carcinoma Cell Line A431 in Vitro. Iran J Fish Sci 2012, 11, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolides and Its Related Macrolides from Marine Dinoflagellates. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2008, 61, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi Nigjeh, S.; Yusoff, F.M.; Mohamed Alitheen, N.B.; Rasoli, M.; Keong, Y.S.; Omar, A.R. bin Cytotoxic Effect of Ethanol Extract of Microalga, Chaetoceros Calcitrans, and Its Mechanisms in Inducing Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cell Line. Biomed Res Int 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, K.; Yanase, K.; Suzuki, M.; Okutani, K.; Yamori, T.; Andoh, T. Inhibition of DNA Topoisomerases I and II, and Growth Inhibition of Human Cancer Cell Lines by a Marine Microalgal Polysaccharide. Biochem Pharmacol 2003, 66, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanniyasi, E.; Patrick, A.P.R.; Rajagopalan, K.; Gopal, R.K.; Damodharan, R. Characterization and in Vitro Anticancer Potential of Exopolysaccharide Extracted from a Freshwater Diatom Nitzschia Palea (Kütz.) W.Sm. 1856. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 22114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutignano, A.; Conte, M.; Tirino, V.; Del Vecchio, V.; De Angelis, R.; Nebbioso, A.; Altucci, L.; Romano, G. Cytotoxic Potential of the Marine Diatom Thalassiosira Rotula: Insights into Bioactivity of 24-Methylene Cholesterol. Mar Drugs 2022, 20, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.J.; Marquez, B.L.; Nogle, L.M.; McPhail, K.; Goeger, D.E.; Roberts, M.A.; Gerwick, W.H. Structure and Biosynthesis of the Jamaicamides, New Mixed Polyketide-Peptide Neurotoxins from the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya Majuscula. Chem Biol 2004, 11, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of Estimating Fifty Percent Endpoints. Am J Hyg 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, C.; Flores, M.V.; Storm, T.; Crosier, K.; Crosier, P. The Zebrafish Lysozyme C Promoter Drives Myeloid-Specific Expression in Transgenic Fish. BMC Dev Biol 2007, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Class | Species | ID (CCVIEO) | Temp (ºC) | Irradiance( E m2s-1) | Culture medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillariophyceae | Chaetoceros dichatoensis | E13 (VGO1452) | 16 | 150 | L1(+Si) |
| Nitzschia sp. | E14 (VGO1450) | 16 | 150 | L1(+Si) | |
| Pseudonitzschia australis | E15 (VGO1453) | 16 | 150 | L1(+Si) | |
| Thalassiosira delicatula | E04 (VGO1447) | 16 | 150 | L1(+Si) | |
| Chlorophyceae | Tetraselmis convolutae | E20 (VGO1448) | 16 | 150 | L1 |
| Cryptophyceae | Falcomonas sp. | E22 (CRY7V) | 16 | 150 | L1 |
| Guillardia theta | E21 (CRY22V) | 16 | 150 | L1 | |
| Teleaulax amphioxeia | E02 (CRY13V) | 16 | 150 | L1 | |
| Dictyochophyceae | Pseudopedinella elastica | E03 (VGO1445) | 19 | 150 | L1 |
| Dinophyceae | Alexandrium mediterraneum | E23 (VGO1083) | 19 | 150 | L1 |
| Alexandrium minutum | E01 (VGO1428) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Alexandrium tamarense | E33 (VGO1085) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Coolia monotis | E10 (CM1V) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Dinophysis acuminata | E05 (VGO1411) | 19 | 150 | L1 (/20) | |
| Dinophysis caudata | E29 (VGO1403) | 19 | 150 | L1 (/20) | |
| Gambierdiscus australes | E32 (VGO1184) | 25 | 80 | K/2 | |
| Gambierdiscus caribaeus | E30 (VGO1364) | 25 | 80 | K/2 | |
| Gambierdiscus excentricus | E31 (VGO1383) | 25 | 80 | K/2 | |
| Gymnodinium impudicum | E12 (VGO665) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Heterocapsa minima | E08 (VGO1398) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Karlodinium veneficum | E17 (VGO1111) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Kryptoperidinium foliaceum | E25 (VGO1124) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Lingulodinium polyedrum | E07 (VGO1204) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Matsuokaea loeblichii | E11 (VGO1449) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Ostreopsis fattorussoi | E27 (VGO999) | 25 | 80 | L1 | |
| Ostreopsis cf. ovata | E28 (VGO1107) | 25 | 80 | L1 | |
| Ostreopsis siamensis | E06 (VGO1187) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Prorocentrum hoffmannianum | E24 (VGO1283) | 25 | 80 | L1 | |
| Prorocentrum lima | E09 (PL2V) | 19 | 150 | L1 | |
| Euglenophyceae | Eutreptiella gymnastica | E26 (VGO1444) | 19 | 150 | L1 |
| Prasinophyceae | Pyramimonas sp. | E19 (PY1V) | 19 | 150 | L1 |
| Prymnesiophyceae | Emiliania huxleyi | E16 (EH2V) | 19 | 150 | L1 |
| Raphidophyceae | Heterosigma akashiwo | E18 (HA1V) | 19 | 150 | L1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





