Submitted:
27 December 2024
Posted:
30 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
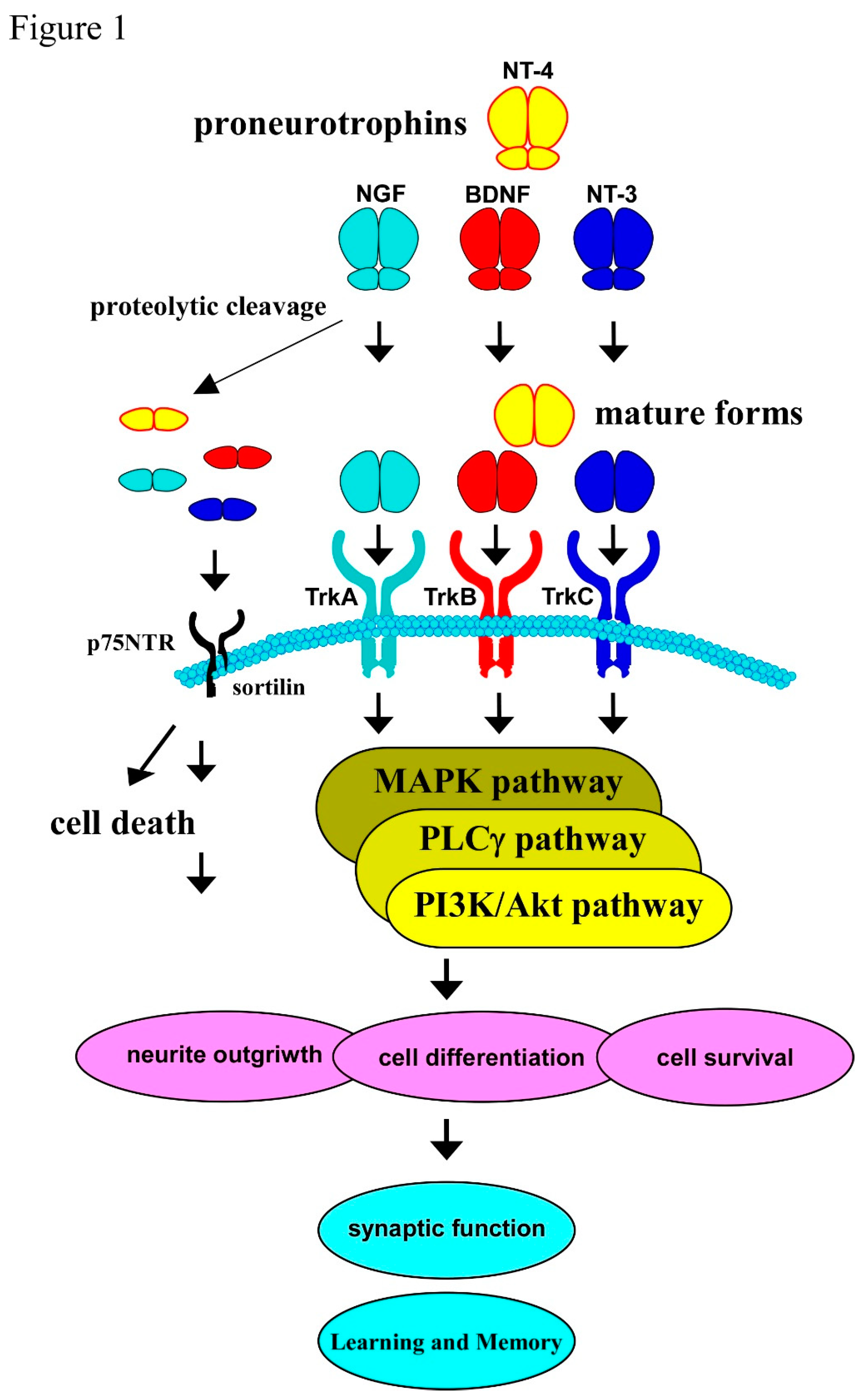
2. Biological Roles of BDNF/TrkB System and Its Downstream Intracellular Signaling
3. BDNF/TrkB System and Antidepressant Effects of Natural Compounds in Depression Models
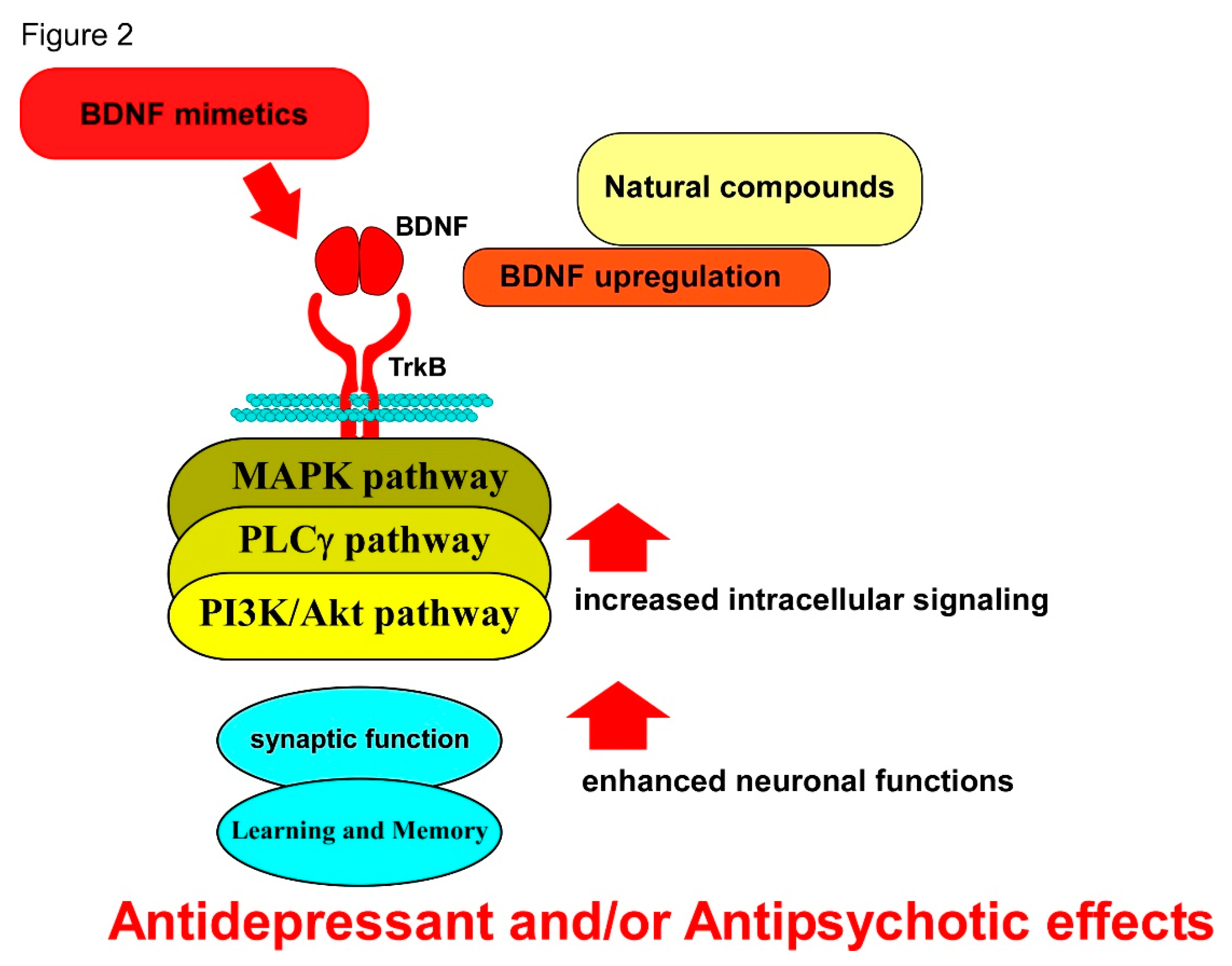
4. BDNF Mimetics and Their Antidepressant Effects in Depression Models
5. A Variety of Mechanisms Under the Influence of BDNF in Depression Models
6. Relationship Between BDNF/TrkB System and Schizophrenia
7. Contribution of BDNF/TrkB System in Antipsychotic Effects of Natural Compounds in Schizophrenia Models
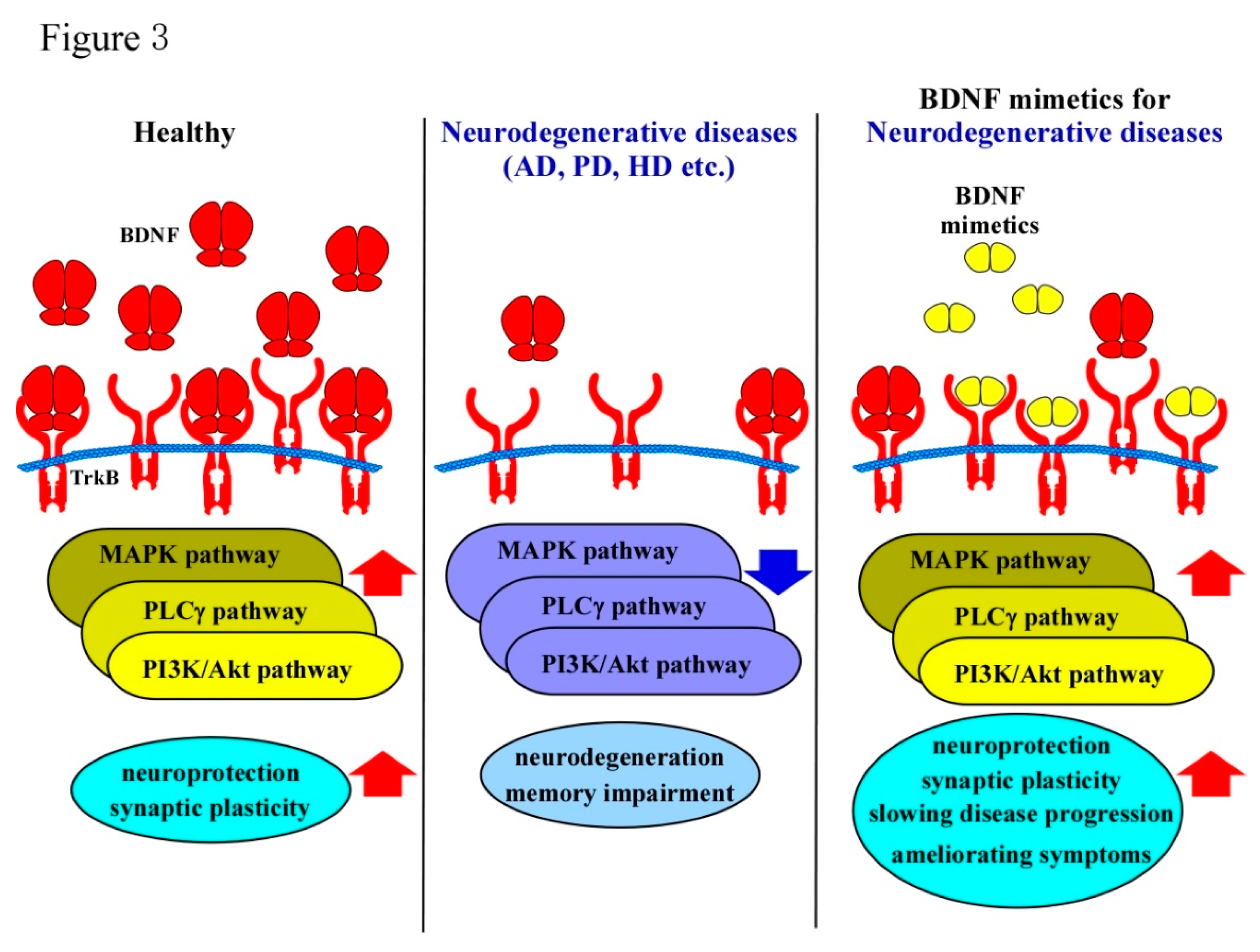
8. The Therapeutic Potential of BDNF Mimetics in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
8.1. The Role of BDNF in AD
8.2. Challenges in Direct BDNF Therapy
8.3. Small Molecule BDNF Mimetics: Early Efforts
8.4. Next-Generation BDNF Mimetics: Improved Selectivity and Potency
8.5. Preclinical and Clinical Development
9. The Therapeutic Potential of BDNF Mimetics in Parkinson's Disease (PD) and Huntington’s Disease (HD)
9.1. The Role of BDNF in PD
9.2. BDNF Mimetics in PD
9.3. The Role of BDNF in HD
9.4. BDNF Mimetics in HD
10. Conclusion and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alfonsetti, M.; d'Angelo, M.; Castelli, V. Neurotrophic factor-based pharmacological approaches in neurological disorders. Neural Regen Res 2023, 18, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D. Neurotrophic Factors: An Overview. Methods Mol Biol 2018, 1727, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Kajihara, R. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in the pathogenesis of stress-related brain diseases. Front Mol Neurosci 2023, 16, 1247422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.H.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Alnaaim, S.A.; Saad, H.M.; Batiha, G.E. The Molecular Pathway of p75 Neurotrophin Receptor (p75NTR) in Parkinson's Disease: The Way of New Inroads. Mol Neurobiol 2024, 61, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, H.K.; Teng, K.K.; Lee, R.; Wright, S.; Tevar, S.; Almeida, R.D.; Kermani, P.; Torkin, R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lee, F.S.; et al. ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Harte-Hargrove, L.C.; Siao, C.J.; Marinic, T.; Clarke, R.; Ma, Q.; Jing, D.; Lafrancois, J.J.; Bath, K.G.; Mark, W.; et al. proBDNF negatively regulates neuronal remodeling, synaptic transmission, and synaptic plasticity in hippocampus. Cell Rep 2014, 7, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, R.B.; Williams, K.S. The p75 neurotrophin receptor: at the crossroad of neural repair and death. Neural Regen Res 2015, 10, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxer, A.L.; Sperling, R. Accelerating Alzheimer's therapeutic development: The past and future of clinical trials. Cell 2023, 186, 4757–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Kajihara, R. An Interaction between Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Stress-Related Glucocorticoids in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palasz, E.; Wysocka, A.; Gasiorowska, A.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Niewiadomski, W.; Niewiadomska, G. BDNF as a Promising Therapeutic Agent in Parkinson's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Lalonde, K.; Truesdell, A.; Gomes Welter, P.; Brocardo, P.S.; Rosenstock, T.R.; Gil-Mohapel, J. New Avenues for the Treatment of Huntington's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F. Trk receptors: roles in neuronal signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 2003, 72, 609–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minichiello, L. TrkB signalling pathways in LTP and learning. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009, 10, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.; Moya-Alvarado, G.; Gonzalez-Billaut, C.; Bronfman, F.C. Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating neuronal growth by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 2016, 73, 612–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Yagasaki, Y.; Izumi, A.; Kunugi, H. Glucocorticoid receptor interaction with TrkB promotes BDNF-triggered PLC-gamma signaling for glutamate release via a glutamate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakawa, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ooshima, Y.; Chiba, S.; Furuta, M.; Izumi, A.; Ninomiya-Baba, M.; Odaka, H.; Hashido, K.; Adachi, N.; et al. Impairments in brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced glutamate release in cultured cortical neurons derived from rats with intrauterine growth retardation: possible involvement of suppression of TrkB/phospholipase C-γ activation. Neurochem Res 2014, 39, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, S.; Frisén, J.; del Río, J.A.; Soriano, E.; Barbacid, M.; Silos-Santiago, I. TrkB signaling is required for postnatal survival of CNS neurons and protects hippocampal and motor neurons from axotomy-induced cell death. J Neurosci 1997, 17, 3623–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: an update. Arch Toxicol 2015, 89, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Lahair, M.M.; Franklin, R.A. Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of the MAP kinase signaling pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal 2006, 8, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kumamaru, E.; Adachi, N.; Richards, M.; Kunugi, H. BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol Histopathol 2010, 25, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumamaru, E.; Numakawa, T.; Adachi, N.; Kunugi, H. Glucocorticoid suppresses BDNF-stimulated MAPK/ERK pathway via inhibiting interaction of Shp2 with TrkB. FEBS Lett 2011, 585, 3224–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puranik, N.; Jung, H.; Song, M. SPROUTY2, a Negative Feedback Regulator of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling, Associated with Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, V.; Singh, A.; Bhatt, M.; Tonk, R.K.; Azizov, S.; Raza, A.S.; Sengupta, S.; Kumar, D.; Garg, M. Multifaceted role of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, A.; Datta, S.R.; Greenberg, M.E. Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2001, 11, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Nito, C.; Kamada, H.; Nishi, T.; Chan, P.H. Activation of the Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathway mediates survival of vulnerable hippocampal neurons after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2006, 26, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 2007, 129, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarneshan, S.N.; Fakhri, S.; Khan, H. Targeting Akt/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway by ginsenosides in neurodegenerative diseases: A mechanistic approach. Pharmacol Res 2022, 177, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Dhapola, R.; Reddy, D.H. Apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease: insight into the signaling pathways and therapeutic avenues. Apoptosis 2023, 28, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autry, A.E. Function of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hypothalamus: Implications for depression pathology. Front Mol Neurosci 2022, 15, 1028223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Luan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Qiu, Z. Exploring the Association between BDNF related Signaling Pathways and Depression: A Literature Review. Brain Res Bull 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airaksinen, E.; Larsson, M.; Lundberg, I.; Forsell, Y. Cognitive functions in depressive disorders: evidence from a population-based study. Psychol Med 2004, 34, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Richards, M.; Nakajima, S.; Adachi, N.; Furuta, M.; Odaka, H.; Kunugi, H. The role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in comorbid depression: possible linkage with steroid hormones, cytokines, and nutrition. Front Psychiatry 2014, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Huang, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, X. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in the brain and its involvement in cognitive function. Neural Regen Res 2025, 20, 2520–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, S.; Peng, R.; Guo, Q.; Cui, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. Bupleurum in Treatment of Depression Disorder: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Mo, X.; He, L.; Ma, Q.; Cai, L.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Lin, X.; Wu, M.; Ding, W.; et al. The role of BDNF transcription in the antidepressant-like effects of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid in a chronic social defeat stress model. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, C.; Potvin, S.; Khullar, A.; Tourjman, S.V. Down and High: Reflections Regarding Depression and Cannabis. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12, 625158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Anand, L.K.; Rashid, N.; Painuli, R.; Malik, F.; Singh, P.P. Synthesis and Evaluation of Natural and Unnatural Tetrahydrocannabiorcol for Its Potential Use in Neuropathologies. J Nat Prod 2024, 87, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.A.; Yadav, D.; Khan, F.; Song, M. Indole-3-Carbinol and Its Derivatives as Neuroprotective Modulators. Brain Sci 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, H.; Ye, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, H.; Huang, Y.; Tao, R.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. NMC-4 Ameliorates Depression-Like Behavior and Neuroinflammation Caused by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Chem Biol Drug Des 2024, 104, e14626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Ganesan, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Zheng, Y. Ononin ameliorates depression-like behaviors by regulating BDNF-TrkB-CREB signaling in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol 2024, 320, 117375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Xie, Z.; Chen, L.; Peng, X.; Luan, F.; Hu, J.; Xie, H.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Rosmarinic acid alleviate CORT-induced depressive-like behavior by promoting neurogenesis and regulating BDNF/TrkB/PI3K signaling axis. Biomed Pharmacother 2024, 170, 115994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakasugi, D.; Kondo, S.; Ferdousi, F.; Mizuno, S.; Yada, A.; Tominaga, K.; Takahashi, S.; Isoda, H. A rare olive compound oleacein functions as a TrkB agonist and mitigates neuroinflammation both in vitro and in vivo. Cell Commun Signal 2024, 22, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, Y.; Kubo, M.; Harada, K. The search for, and chemistry and mechanism of, neurotrophic natural products. J Nat Med 2020, 74, 648–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibova, T.L.; Kraineva, V.A.; Kotel'nikova, S.O.; Povarnina, P.Y.; Gudasheva, T.A.; Seredenin, S.B. Behavioral Effects of Dimeric Dipeptide BDNF Mimetic GSB-106 in a Rat Model of Depressive-Like State. Bull Exp Biol Med 2020, 169, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudasheva, T.A.; Tallerova, A.V.; Mezhlumyan, A.G.; Antipova, T.A.; Logvinov, I.O.; Firsova, Y.N.; Povarnina, P.Y.; Seredenin, S.B. Low-Molecular Weight BDNF Mimetic, Dimeric Dipeptide GSB-106, Reverses Depressive Symptoms in Mouse Chronic Social Defeat Stress. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povarnina, P.Y.; Antipova, T.A.; Logvinov, I.O.; Gudasheva, T.A.; Seredenin, S.B. Сhronically Administered BDNF Dipeptide Mimetic GSB-106 Prevents the Depressive-like Behavior and Memory Impairments after Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats. Curr Pharm Des 2023, 29, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiliwaerde, M.; Gao, N.; Yang, Y.; Jin, Z. A novel NMDA receptor modulator: the antidepressant effect and mechanism of GW043. CNS Neurosci Ther 2024, 30, e14598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Xiao, L.; Liu, R.; Du, J.; Liu, N.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, G. Antidepressant effect and mechanism of TMP269 on stress-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 2024, 225, 116320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Zeng, Z.H.; Wei, M.X.; Qiu, M.T.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Yi, L.T. Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Alleviate Depressive-like Symptoms in Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Mice via Microglial Regulation in Prefrontal Cortex. Polymers (Basel) 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, M.; Facchinetti, R.; Torazza, C.; Ciarla, C.; Bronzuoli, M.R.; Balbi, M.; Bonanno, G.; Popoli, M.; Steardo, L.; Milanese, M.; et al. Molecular signatures of astrocytes and microglia maladaptive responses to acute stress are rescued by a single administration of ketamine in a rodent model of PTSD. Transl Psychiatry 2024, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, K.; Xu, S.X.; Xie, X.H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z. Investigating Neuroplasticity Changes Reflected by BDNF Levels in Astrocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Patients with Depression. Int J Nanomedicine 2024, 19, 8971–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, M.; Ye, Y.; Li, M.; Ran, R.; Zou, Z. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels across psychiatric disorders: A systemic review and network meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2024, 131, 110954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcas, A.; Hindmarch, C.; Iftene, F. BDNF gene Val66Met polymorphisms as a predictor for clinical presentation in schizophrenia - recent findings. Front Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1234220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberona, A.; Jones, N.; Zúñiga, K.; Garrido, V.; Zelada, M.I.; Silva, H.; Nieto, R.R. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Predictor of Treatment Response in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Yang, F.; Lu, B. Corticosterone antagonist or TrkB agonist attenuates schizophrenia-like behavior in a mouse model combining Bdnf-e6 deficiency and developmental stress. iScience 2022, 25, 104609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkundin, A.; Halaris, A. Associations of BDNF/BDNF-AS SNPs with Depression, Schizophrenia, and Bipolar Disorder. J Pers Med 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gredicak, M.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Nedic Erjavec, G.; Uzun, S.; Kozumplik, O.; Svob Strac, D.; Pivac, N. Association between reduced plasma BDNF concentration and MMSE scores in both chronic schizophrenia and mild cognitive impairment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Yang, C.; Ishima, T.; Ren, Q.; Ma, M.; Dong, C.; Huang, X.F.; Hashimoto, K. Intake of 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone During Juvenile and Adolescent Stages Prevents Onset of Psychosis in Adult Offspring After Maternal Immune Activation. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 36087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, B.; Dunn, A.; Sundram, S.; Hill, R.A. Investigating 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone to combat maternal immune activation effects on offspring gene expression and behaviour. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, B.M.M.; Chaves Filho, A.J.M.; Costa, D.; de Menezes, A.T.; da Fonseca, A.C.C.; Gama, C.S.; Moura Neto, V.; de Lucena, D.F.; Vale, M.L.; Macêdo, D.S. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and clozapine abrogates poly I: C-induced immune alterations in primary hippocampal neurons. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2019, 90, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Li, Y.K.; Wang, W.; Wan, J.G.; Yu, B.; Wang, M.Z.; Hu, B. Small-molecule TrkB agonist 7,8-dihydroxyflavone reverses cognitive and synaptic plasticity deficits in a rat model of schizophrenia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2014, 122, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Azu, B.; Fokoua, A.R.; Annafi, O.S.; Adebayo, O.G.; Del Re, E.C.; Okuchukwu, N.; Aregbesola, G.J.; Ejenavi, A.C.; Isiwele, D.M.; Efezino, A.J.; et al. Effective action of silymarin against ketamine-induced schizophrenia in male mice: Insight into the biochemical and molecular mechanisms of action. J Psychiatr Res 2024, 179, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, I.; Saleem, U.; Ahmad, B.; Hawwal, M.F.; Mothana, R.A. NMDA receptor modulation by Esculetin: Investigating behavioral, biochemical and neurochemical effects in schizophrenic mice model. Saudi Pharm J 2024, 32, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, S.; Hajdu, R.; Bergstrom, J.; Quackenbush, E.; Xie, J.; Milligan, J.; Thornton, R.; Shei, G.J.; Card, D.; Keohane, C.; et al. Alteration of lymphocyte trafficking by sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonists. Science 2002, 296, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.A.; Chun, J. Mechanisms of fingolimod's efficacy and adverse effects in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2011, 69, 759–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirani, A.; Okuda, D.T.; Stüve, O. Therapeutic Advances and Future Prospects in Progressive Forms of Multiple Sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhuo, C.; Ma, X.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, L. Exploring the molecular targets of fingolimod and siponimod for treating the impaired cognition of schizophrenia using network pharmacology and molecular docking. Schizophrenia (Heidelb) 2024, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, L.; Haddon, J.; Lancaster, T.M.; Sykes, A.; Azzouni, K.; Ihssen, N.; Moon, A.L.; Lin, T.E.; Linden, D.E.; Owen, M.J.; et al. Genetic Variation in the Psychiatric Risk Gene CACNA1C Modulates Reversal Learning Across Species. Schizophr Bull 2019, 45, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigaret, C.M.; Lin, T.E.; Morrell, E.R.; Sykes, L.; Moon, A.L.; O'Donovan, M.C.; Owen, M.J.; Wilkinson, L.S.; Jones, M.W.; Thomas, K.L.; et al. Neurotrophin receptor activation rescues cognitive and synaptic abnormalities caused by hemizygosity of the psychiatric risk gene Cacna1c. Mol Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1748–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Yu, X.; Wei, L.; Jiang, H.; Dong, J.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, L.; Deng, W.; Guo, W.; et al. Novel α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor (AMPAR) potentiator LT-102: A promising therapeutic agent for treating cognitive impairment associated with schizophrenia. CNS Neurosci Ther 2024, 30, e14713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidfar, M.; de Oliveira, J.; Kucharska, E.; Budni, J.; Kim, Y.K. The role of CREB and BDNF in neurobiology and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci 2020, 257, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wu, H.T.; Qin, X.Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Z.Z.; Cheng, Y. Postmortem Brain, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Blood Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Mol Neurosci 2018, 65, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wei, X.X.; Chang, L.S.; Dong, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, N.N. Ultrasound Combined With Microbubbles Loading BDNF Retrovirus to Open BloodBrain Barrier for Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 615104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Merrill, D.A.; Coppola, G.; Tsukada, S.; Schroeder, B.E.; Shaked, G.M.; Wang, L.; Blesch, A.; Kim, A.; Conner, J.M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rodent and primate models of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med 2009, 15, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Mateling, M.; Kovacs, I.; Wang, L.; Eggert, S.; Rockenstein, E.; Koo, E.H.; Masliah, E.; Tuszynski, M.H. Early BDNF treatment ameliorates cell loss in the entorhinal cortex of APP transgenic mice. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 15596–15602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braschi, C.; Capsoni, S.; Narducci, R.; Poli, A.; Sansevero, G.; Brandi, R.; Maffei, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Berardi, N. Intranasal delivery of BDNF rescues memory deficits in AD11 mice and reduces brain microgliosis. Aging Clin Exp Res 2021, 33, 1223–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, R.G.; Frey, W.H. , 2nd. Delivery of neurotrophic factors to the central nervous system: pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet 2001, 40, 907–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, G. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A Translational Perspective from the Mechanism to Drug Development. Curr Neuropharmacol 2022, 20, 1479–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.W.; Liu, X.; Yepes, M.; Shepherd, K.R.; Miller, G.W.; Liu, Y.; Wilson, W.D.; Xiao, G.; Blanchi, B.; Sun, Y.E.; et al. A selective TrkB agonist with potent neurotrophic activities by 7,8-dihydroxyflavone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 2687–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Dhaliwal, J.; Sah, S.P. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone improves cognitive functions in ICV-STZ rat model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease by reversing oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and insulin resistance. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2021, 238, 1991–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kang, E.J.; Kang, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, S.S.; Suh, S.W.; Ahn, E.H. GAP-43 closely interacts with BDNF in hippocampal neurons and is associated with Alzheimer's disease progression. Front Mol Neurosci 2023, 16, 1150399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Schroeder, J.P.; Chan, C.B.; Song, M.; Yu, S.P.; Weinshenker, D.; Ye, K. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone prevents synaptic loss and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.A.; Belichenko, N.P.; Yang, T.; Condon, C.; Monbureau, M.; Shamloo, M.; Jing, D.; Massa, S.M.; Longo, F.M. A small molecule TrkB ligand reduces motor impairment and neuropathology in R6/2 and BACHD mouse models of Huntington's disease. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 18712–18727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, O.T. Can Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Mimetics be a Way Out for Neurodegenerative Diseases? Curr Pharm Des 2023, 29, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, S.M.; Yang, T.; Xie, Y.; Shi, J.; Bilgen, M.; Joyce, J.N.; Nehama, D.; Rajadas, J.; Longo, F.M. Small molecule BDNF mimetics activate TrkB signaling and prevent neuronal degeneration in rodents. J Clin Invest 2010, 120, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Kang, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, K. The prodrug of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone development and therapeutic efficacy for treating Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ahn, E.H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.H.; Luo, S.; Liao, J.; Ye, K. Optimized TrkB Agonist Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease Pathologies and Improves Cognitive Functions via Inhibiting Delta-Secretase. ACS Chem Neurosci 2021, 12, 2448–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, I.; Yang, T.; Longo, F.M.; Katz, D.M. Restoration of motor learning in a mouse model of Rett syndrome following long-term treatment with a novel small-molecule activator of TrkB. Dis Model Mech 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascon, S.; Jann, J.; Langlois-Blais, C.; Plourde, M.; Lavoie, C.; Faucheux, N. Peptides Derived from Growth Factors to Treat Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povarnina, P.Y.; Volkova, A.A.; Vorontsova, O.N.; Kamensky, A.A.; Gudasheva, T.A.; Seredenin, S.B. A Low-Molecular-Weight BDNF Mimetic, Dipeptide GSB-214, Prevents Memory Impairment in Rat Models of Alzheimer's Disease. Acta Naturae 2022, 14, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Ahn, E.H.; Kang, S.S.; Liu, X.; Alam, A.; Ye, K. Gut dysbiosis contributes to amyloid pathology, associated with C/EBPβ/AEP signaling activation in Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Sci Adv 2020, 6, eaba0466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, C.; Hofer, M.; Barde, Y.A.; Juhasz, M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Squinto, S.P.; Lindsay, R.M. BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Nature 1991, 350, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W. Regulation of BDNF-TrkB Signaling and Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Parkinson's Disease. J Clin Med 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.H.; Leem, E.; Jeon, M.T.; Jeong, K.H.; Park, J.W.; Jung, U.J.; Kholodilov, N.; Burke, R.E.; Jin, B.K.; Kim, S.R. Induction of GDNF and BDNF by hRheb(S16H) transduction of SNpc neurons: neuroprotective mechanisms of hRheb(S16H) in a model of Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurobiol 2015, 51, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillin, O.; Diaz, J.; Carroll, P.; Griffon, N.; Schwartz, J.C.; Sokoloff, P. BDNF controls dopamine D3 receptor expression and triggers behavioural sensitization. Nature 2001, 411, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylska, I.; Marusiak, J.; Toczyłowska, B.; Stępień, A.; Brodacki, B.; Langfort, J.; Chalimoniuk, M. Association between the Val66Met (rs6265) polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene, BDNF protein level in the blood and the risk of developing early-onset Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2024, 84, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z. The Relationships Between Stress, Mental Disorders, and Epigenetic Regulation of BDNF. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Gamble, K.L.; Schultheiss, C.E.; Riddle, D.M.; West, A.B.; Lee, V.M. Formation of α-synuclein Lewy neurite-like aggregates in axons impedes the transport of distinct endosomes. Mol Biol Cell 2014, 25, 4010–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)-TrkB Signaling in Inflammation-related Depression and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Curr Neuropharmacol 2016, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Dai, C.; Yi, L.; Dong, Z. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone ameliorates motor deficits via regulating autophagy in MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Discov 2021, 7, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaquoi, M.S.; Liguore, W.A.; Churchill, M.J.; Moore, C.; Melrose, H.L.; Meshul, C.K. Gait Deficits and Loss of Striatal Tyrosine Hydroxlase/Trk-B are Restored Following 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone Treatment in a Progressive MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease. Neuroscience 2020, 433, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohankumar, T.; Chandramohan, V.; Lalithamba, H.S.; Jayaraj, R.L.; Kumaradhas, P.; Sivanandam, M.; Hunday, G.; Vijayakumar, R.; Balakrishnan, R.; Manimaran, D.; et al. Design and Molecular dynamic Investigations of 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone Derivatives as Potential Neuroprotective Agents Against Alpha-synuclein. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Dai, C.F.; Chen, L.; Zhou, W.T.; Han, H.L.; Dong, Z.F. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone Ameliorates Motor Deficits Via Suppressing α-synuclein Expression and Oxidative Stress in the MPTP-induced Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 2016, 22, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Park, C.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, N.D.; Choi, Y.H. 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone attenuates the release of pro-inflammatory mediators and cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells through the suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med 2014, 33, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.H.; Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; AlAseeri, A.A.; Alruwaili, M.; Saad, H.M.; Batiha, G.E. BDNF/TrkB activators in Parkinson's disease: A new therapeutic strategy. J Cell Mol Med 2024, 28, e18368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Edgington-Mitchell, L.; Ye, K. Treating Parkinson's Disease via Activation of BDNF/TrkB Signaling Pathways and Inhibition of Delta-Secretase. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzan, B.; Iravanpour, F.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Akparov, V.; Zaringhalam, J.; Ghasemi, R.; Maghsoudi, N. Dipeptide mimetic of BDNF ameliorates motor dysfunction and striatal apoptosis in 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson's rat model: Considering Akt and MAPKs signaling. Behav Brain Res 2023, 452, 114585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciammola, A.; Sassone, J.; Cannella, M.; Calza, S.; Poletti, B.; Frati, L.; Squitieri, F.; Silani, V. Low brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in serum of Huntington's disease patients. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2007, 144b, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzysztoń-Russjan, J.; Zielonka, D.; Jackiewicz, J.; Kuśmirek, S.; Bubko, I.; Klimberg, A.; Marcinkowski, J.T.; Anuszewska, E.L. A study of molecular changes relating to energy metabolism and cellular stress in people with Huntington's disease: looking for biomarkers. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2013, 45, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bithell, A.; Johnson, R.; Buckley, N.J. Transcriptional dysregulation of coding and non-coding genes in cellular models of Huntington's disease. Biochem Soc Trans 2009, 37, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Vaish, M.; Ratan, R.R. Transcriptional dysregulation in Huntington's disease: a failure of adaptive transcriptional homeostasis. Drug Discov Today 2014, 19, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, E.; Zuccato, C.; Tartari, M. Normal huntingtin function: an alternative approach to Huntington's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005, 6, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginés, S.; Bosch, M.; Marco, S.; Gavaldà, N.; Díaz-Hernández, M.; Lucas, J.J.; Canals, J.M.; Alberch, J. Reduced expression of the TrkB receptor in Huntington's disease mouse models and in human brain. Eur J Neurosci 2006, 23, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.R.; Benraiss, A.; Chmielnicki, E.; Samdani, A.; Economides, A.; Goldman, S.A. Induction of neostriatal neurogenesis slows disease progression in a transgenic murine model of Huntington disease. J Clin Invest 2007, 117, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, S.; Lahaye, R.A.; Vitet, H.; Scaramuzzino, C.; Virlogeux, A.; Capellano, L.; Genoux, A.; Gershoni-Emek, N.; Geva, M.; Hayden, M.R.; et al. Pridopidine rescues BDNF/TrkB trafficking dynamics and synapse homeostasis in a Huntington disease brain-on-a-chip model. Neurobiol Dis 2022, 173, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speidell, A.; Bin Abid, N.; Yano, H. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Dysregulation as an Essential Pathological Feature in Huntington's Disease: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kwatra, M.; Gawali, B.; Panda, S.R.; Naidu, V.G.M. Potential role of TrkB agonist in neuronal survival by promoting CREB/BDNF and PI3K/Akt signaling in vitro and in vivo model of 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP)-induced neuronal death. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz Barriga, G.; Giralt, A.; Anglada-Huguet, M.; Gaja-Capdevila, N.; Orlandi, J.G.; Soriano, J.; Canals, J.M.; Alberch, J. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone ameliorates cognitive and motor deficits in a Huntington's disease mouse model through specific activation of the PLCγ1 pathway. Hum Mol Genet 2017, 26, 3144–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Peng, Q.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mori, S.; Ross, C.A.; Ye, K.; Duan, W. Small-molecule TrkB receptor agonists improve motor function and extend survival in a mouse model of Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet 2013, 22, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, D.A. Modulating Neurotrophin Receptor Signaling as a Therapeutic Strategy for Huntington's Disease. J Huntingtons Dis 2017, 6, 303–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sada, N.; Fujita, Y.; Mizuta, N.; Ueno, M.; Furukawa, T.; Yamashita, T. Inhibition of HDAC increases BDNF expression and promotes neuronal rewiring and functional recovery after brain injury. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, G.C.; Malvezzi, A.M.; Kumar, A.; Andrade, N.S.; Wiedner, H.J.; Vilca, S.J.; Janczura, K.J.; Bagheri, A.; Al-Ali, H.; Powell, S.K.; et al. Enhancement of BDNF Expression and Memory by HDAC Inhibition Requires BET Bromodomain Reader Proteins. J Neurosci 2019, 39, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielcarek, M.; Benn, C.L.; Franklin, S.A.; Smith, D.L.; Woodman, B.; Marks, P.A.; Bates, G.P. SAHA decreases HDAC 2 and 4 levels in vivo and improves molecular phenotypes in the R6/2 mouse model of Huntington's disease. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.; Choi, J.; Sim, H.R.; Kim, J.; Jun, J.H.; Kyung, J.; Ha, N.; Kim, S.; Ryu, K.H.; Chung, S.S.; et al. A novel HDAC6 inhibitor, CKD-504, is effective in treating preclinical models of huntington's disease. BMB Rep 2023, 56, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elifani, F.; Amico, E.; Pepe, G.; Capocci, L.; Castaldo, S.; Rosa, P.; Montano, E.; Pollice, A.; Madonna, M.; Filosa, S.; et al. Curcumin dietary supplementation ameliorates disease phenotype in an animal model of Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet 2019, 28, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Al-Khazaleh, A.K.; Bhuyan, D.J.; Li, F.; Li, C.G. A Review of Recent Curcumin Analogues and Their Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anticancer Activities. Antioxidants (Basel) 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




