Submitted:
23 December 2024
Posted:
24 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The aim of this study was to compare the effect of increasing concentrations (0, 1, 2, 4%) of sea buckthorn oil (SBO) on the structural, physicochemical, release, and antioxidant properties of glycerol-plasticized sodi-um casein (NaCAS) and gelatin (GEL) films. Ultrasonic treatment ensured effective homogenization of SBO in both types of emulsions, resulting in yellow-tinted semi-opaque films with relatively low mi-cro-roughness. Generally, GEL films exhibited lower UV barrier properties and solubility, but better trans-parency, surface hydrophobicity, oxygen barrier performance, strength, and antiradical activity compared to NaCAS-based counterparts. Despite reducing the surface hydrophobicity of GEL films, the presence of SBO significantly limited their solubility and water absorption. SBO, in a concentration-independent man-ner, improved the water vapor barrier properties of both films and increased the oxygen permeability of the GEL film. At the highest SBO concentration, the tensile strength of NaCAS- and GEL-based films de-creased by 27% and 20%, respectively, while their antiradical activity increased by 9.3x and 4.3x (based on time required for the half-neutralization of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radicals). Migration studies showed that at the lowest concentration, SBO was released (into 95% ethanol) approximately 2x faster from the GEL-based film than from the NaCAS film, whereas at higher concentrations, the trend reversed.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Films
2.3. Thickness and Conditioning
2.4. Microtopography
2.5. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR/FTIR)
2.6. Optical Properties
2.7. Water Afinities
2.8. Oxygen Permeability (O2P)
2.9. Mechanical Properties
2.10. SBO Release and Mathemathical Modeling
2.11. Antioxidant Acticity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure
3.2. ATR/FTIR
3.1.1. ATR/FTIR of SBO
3.1.2. ATR/FTIR of the Films
3.3. Optical Properties
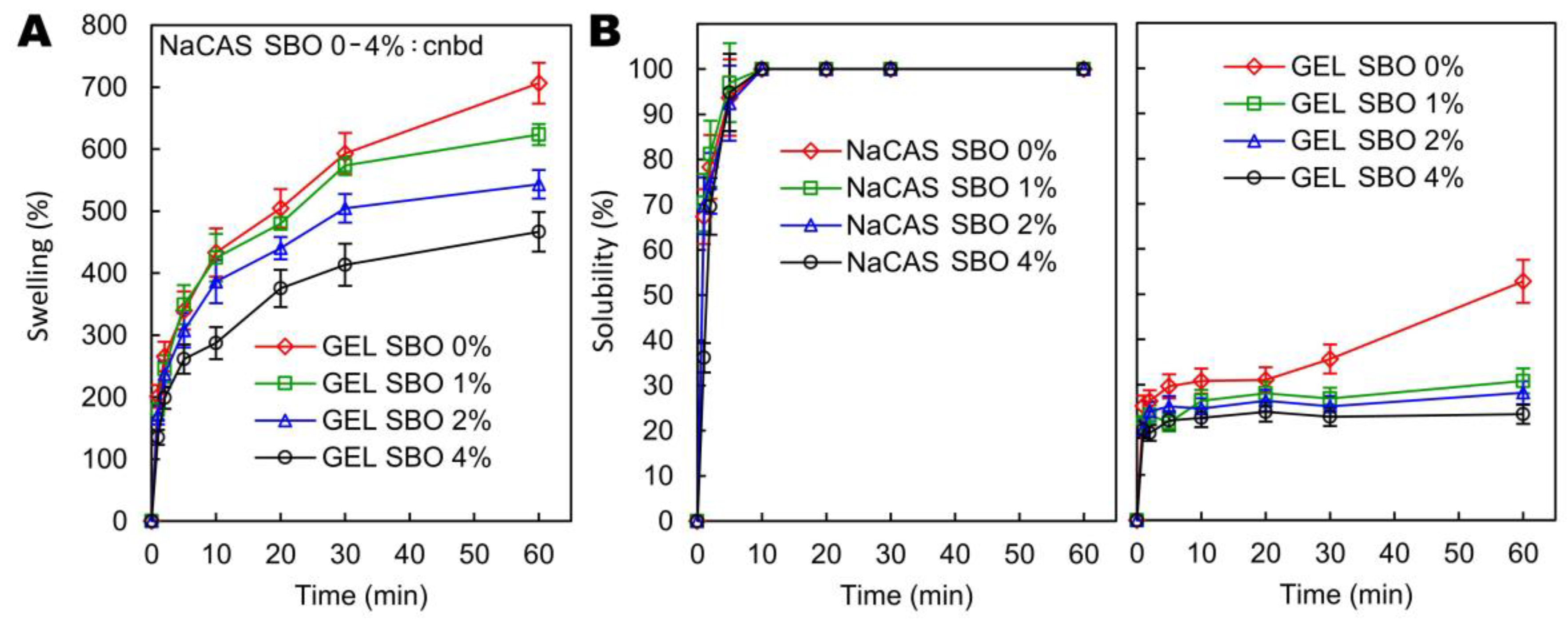
3.4. Water Affinities
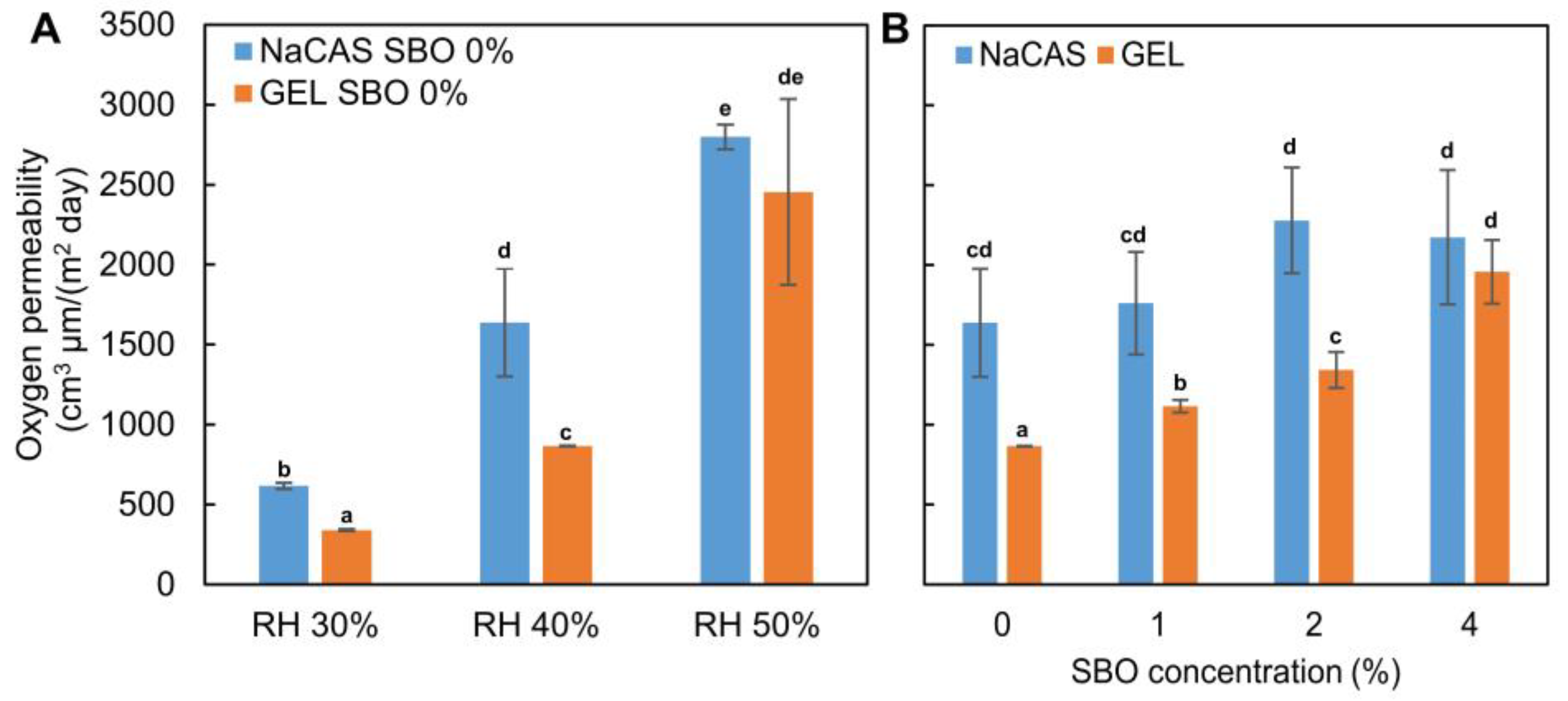
3.5. Oxygen Permeability
3.6. Mechanical Properties
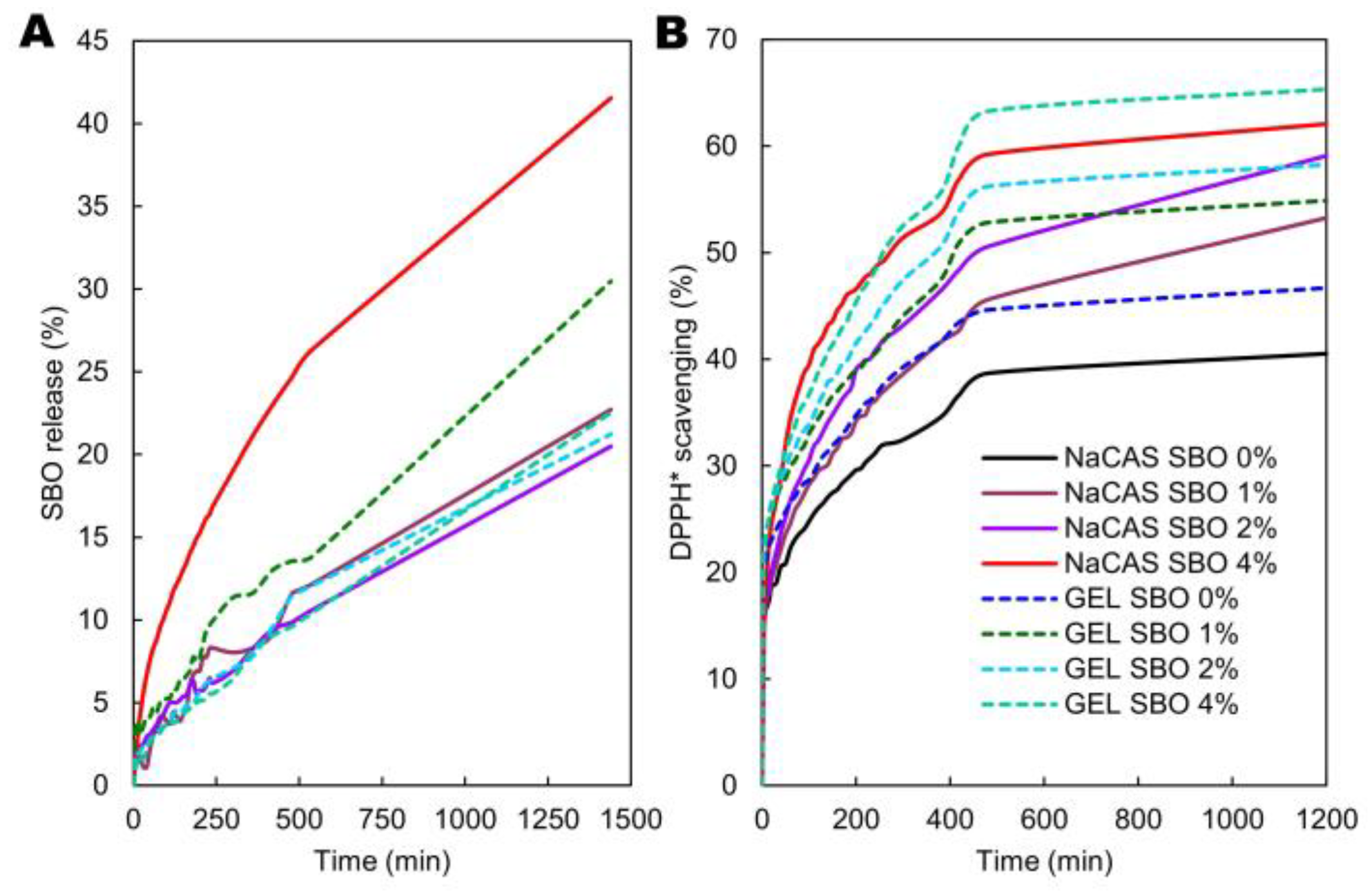
3.7. SBO Release
3.8. Antiradical Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Pires, A.F.; Díaz, O.; Cobos, A.; Pereira, C.D. A Review of Recent Developments in Edible Films and Coatings-Focus on Whey-Based Materials. Foods 2024, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.; Pintado, M.; Morais, R.; Morais, A. Recent Highlights in Sustainable Bio-Based Edible Films and Coatings for Fruit and Vegetable Applications. Foods 2024, 13, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi-Márquez, G.; Dávalos-Saucedo, C.A.; Di Pierro, P. Edible Films and Coatings Applied in the Food Industry. Coatings 2023, 13, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matloob, A.; Ayub, H.; Mohsin, M.; Ambreen, S.; Khan, F.A.; Oranab, S.; Rahim, M.A.; Khalid, W.; Nayik, G.A.; Ramniwas, S.; et al. A Review on Edible Coatings and Films: Advances, Composition, Production Methods, and Safety Concerns. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 28932–28944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Y.A.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Khan, T.S. Advancements in the Biopolymer Films for Food Packaging Applications: A Short Review. Biotechnology for Sustainable Materials 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Gogoi, J.; Dubey, S.; Chowdhury, D. Animal Derived Biopolymers for Food Packaging Applications: A Review. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 255, 128197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserez, A.; Yu, J.; Mohammadi, P. Protein-Based Biological Materials: Molecular Design and Artificial Production. Chem Rev 2023, 123, 2049–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, J.; Ioras, F.; Ratnasingam, J. Performance and Stability of Historic Casein Formaldehyde. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Https://Www.Lactips.Com/Solutions/Technology/?Lang=en.
- Schou, M.; Longares, A.; Montesinos-Herrero, C.; Monahan, F.J.; O’Riordan, D.; O’Sullivan, M. Properties of Edible Sodium Caseinate Films and Their Application as Food Wrapping. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2005, 38, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnaillie, L.; Zhang, H.; Akkurt, S.; Yam, K.; Tomasula, P. Casein Films: The Effects of Formulation, Environmental Conditions and the Addition of Citric Pectin on the Structure and Mechanical Properties. Polymers (Basel) 2014, 6, 2018–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchio, M.L.; Linck, Y.G.; Monti, G.A.; Gugliotta, L.M.; Minari, R.J.; Alvarez Igarzabal, C.I. Casein Films Crosslinked by Tannic Acid for Food Packaging Applications. Food Hydrocoll 2018, 84, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniciolli Rigueto, C.V.; Rosseto, M.; Alessandretti, I.; de Oliveira, R.; Wohlmuth, D.A.R.; Ferreira Menezes, J.; Loss, R.A.; Dettmer, A.; Pizzutti, I.R. Gelatin Films from Wastes: A Review of Production, Characterization, and Application Trends in Food Preservation and Agriculture. Food Research International 2022, 162, 112114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hossen, M.A.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Gelatin-Based Composite Films and Their Application in Food Packaging: A Review. J Food Eng 2022, 313, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Baraniak, B. Effect of Candelilla Wax on Functional Properties of Biopolymer Emulsion Films - A Comparative Study. Food Hydrocoll 2014, 41, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łupina, K.; Kowalczyk, D.; Zięba, E.; Kazimierczak, W.; Mężyńska, M.; Basiura-Cembala, M.; Wiącek, A.E. Edible Films Made from Blends of Gelatin and Polysaccharide-Based Emulsifiers - A Comparative Study. Food Hydrocoll 2019, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamps, B.; Buntinx, M.; Peeters, R. Seal Materials in Flexible Plastic Food Packaging: A Review. Packaging Technology and Science 2023, 36, 507–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Chu, Y.; Tao, N.; Deng, S.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Application of Gelatin in Food Packaging: A Review. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Szymanowska, U.; Skrzypek, T.; Basiura-Cembala, M.; Łupina, K.; Biendl, M. Edible Films Based on Gelatin, Carboxymethyl Cellulose, and Their Blends as Carriers of Potassium Salts of Iso-α-Acids: Structural, Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties. Food Hydrocoll 2021, 115, 106574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Biendl, M. Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Biopolymer/Candelilla Wax Emulsion Films Containing Hop Extract - A Comparative Study. Food Hydrocoll 2016, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.-P.; Yen, T.-W.; Tseng, Y.-P.; Yuen, T.; Yuen, M.; Yuen, H.; Liang, C.-H. The Impact of Oral Sea-Buckthorn Oil on Skin, Blood Markers, Ocular, and Vaginal Health: A Randomized Control Trial. J Funct Foods 2024, 112, 105973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B. The Beneficial Health Aspects of Sea Buckthorn ( Elaeagnus Rhamnoides (L.) A.Nelson) Oil. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 213, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gâtlan, A.-M.; Gutt, G. Sea Buckthorn in Plant Based Diets. An Analytical Approach of Sea Buckthorn Fruits Composition: Nutritional Value, Applications, and Health Benefits. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.K.; Shukla, S.; Shukla, V.; Singh, S. Sea Buckthorn: A Potential Dietary Supplement with Multifaceted Therapeutic Activities. Intelligent Pharmacy 2024, 2, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Nowak, I. Abundance of Active Ingredients in Sea-Buckthorn Oil. Lipids Health Dis 2017, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gęgotek, A.; Jastrząb, A.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Muszyńska, M.; Skrzydlewska, E. The Effect of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae Rhamnoides L.) Seed Oil on UV-Induced Changes in Lipid Metabolism of Human Skin Cells. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaplicki, S.; Tańska, M.; Konopka, I.; Czaplicki, S.; Tańska, M.; Konopka, I. Sea-Buckthorn Oil in Vegetable Oils Stabilisation; Vol. 28;
- Zhang, H.; Song, G.; Ma, W.; Guo, M.; Ling, X.; Yu, D.; Zhou, W.; Li, L. Microencapsulation Protects the Biological Activity of Sea Buckthorn Seed Oil. Front Nutr 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, D.; Ye, A.; Haisman, D.; Singh, H. Antioxidant Properties of Caseins and Whey Proteins in Model Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Int Dairy J 2010, 20, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Effects of Antioxidants, Proteins, and Their Combination on Emulsion Oxidation. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 8137–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.; Lin, L. Effect of a Sea Buckthorn Pomace Extract-Esterified Potato Starch Film on the Quality and Spoilage Bacteria of Beef Jerky Sold in Supermarket. Food Chem 2020, 326, 127001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łupina, K.; Kowalczyk, D.; Lis, M.; Basiura-Cembala, M. Antioxidant Polysaccharide/Gelatin Blend Films Loaded with Curcumin — A Comparative Study. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 236, 123945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-ISO 2528:2000 - Wersja Polska Available online:. Available online: https://sklep.pkn.pl/pn-iso-2528-2000p.html (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An Add-In Program for Modeling and Comparison of Drug Dissolution Profiles. AAPS J 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Lopez, G. Comparison of the Emulsifying Properties of Fish Gelatin and Commercial Milk Proteins. J Food Sci 2001, 66, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, E.; Forni, F.; Bernabei, M.T. Effect of Matrix Composition and Process Conditions on Casein–Gelatin Beads Floating Properties. Int J Pharm 2000, 198, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socaciu, C.; Fetea, F.; Ranga, F.; Bunea, A.; Dulf, F.; Socaci, S.; Pintea, A. Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) Coupled with Chemometrics, to Control the Botanical Authenticity and Quality of Cold-Pressed Functional Oils Commercialized in Romania. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topală, C.M.; Ducu, C. SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF SEA BUCKTHORN EXTRACTS. Current Trends in Natural Sciences 2014, 3, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Tang, C.-H.; Yin, S.-W.; Yang, X.-Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Wei, Z.-H. Characterization of Gelatin-Based Edible Films Incorporated with Olive Oil. Food Research International 2012, 49, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Kazimierczak, W.; Zięba, E.; Lis, M.; Wawrzkiewicz, M. Structural and Physicochemical Properties of Glycerol-Plasticized Edible Films Made from Pea Protein-Based Emulsions Containing Increasing Concentrations of Candelilla Wax or Oleic Acid. Molecules 2024, 29, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FTIRATR AND FLUORESCENCE STUDIES OF PROTEINLIPID SYSTEMS.
- Bonilla, J.; Sobral, P.J.A. Antioxidant and Physicochemical Properties of Blended Films Based on Gelatin-sodium Caseinate Activated with Natural Extracts. J Appl Polym Sci 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, F. Biological Macromolecules: UV-visible Spectrophotometry. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Wiley, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Łopusiewicz, Ł.; Jędra, F.; Bartkowiak, A. New Active Packaging Films Made from Gelatin Modified with Fungal Melanin; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Maharana, S.; Misra, P.K. Probing the Gelatin–Alkylammonium Salt Mixed Assemblies through Surface Tensiometry and Fluorimetry. J Phys Chem B 2018, 122, 5161–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, J.; Sobral, P.J.A. Antioxidant and Physicochemical Properties of Blended Films Based on Gelatin-sodium Caseinate Activated with Natural Extracts. J Appl Polym Sci 2017, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Ahmed, E.; Ismaiel, A.; Ashokkumar, M.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Ultrasonic Emulsification: An Overview on the Preparation of Different Emulsifiers-Stabilized Emulsions. Trends Food Sci Technol 2020, 105, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Juliano, P.; Williams, R.P.; Niere, J.; Augustin, M.A. Ultrasound Effects on the Assembly of Casein Micelles in Reconstituted Skim Milk. Journal of Dairy Research 2014, 81, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, G.-P.; Wang, H.; Lei, L.-W. Effect of Pores on Transmission Properties of Transparent Ceramics; 2011; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, O. V. Gelatin as It Is: History and Modernity. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.Y.; Dar, T.A.; Singh, L.R. Casein Proteins: Structural and Functional Aspects. In Milk Proteins - From Structure to Biological Properties and Health Aspects; InTech, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khin, M.N.; Ahammed, S.; Kamal, Md.M.; Saqib, M.N.; Liu, F.; Zhong, F. Investigating Next-Generation Edible Packaging: Protein-Based Films and Coatings for Delivering Active Compounds. Food Hydrocolloids for Health 2024, 6, 100182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Szymanowska, U.; Skrzypek, T.; Basiura-Cembala, M.; Bartkowiak, A.; Łupina, K. A Comprehensive Study on Gelatin- and Whey Protein Isolate-Based Edible Films as Carriers of Fireweed (Epilobium Angustifolium L.) Extract. Food Bioproc Tech 2022, 15, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Kordowska-Wiater, M.; Karaś, M.; Zięba, E.; Mężyńska, M.; Wiącek, A.E. Release Kinetics and Antimicrobial Properties of the Potassium Sorbate-Loaded Edible Films Made from Pullulan, Gelatin and Their Blends. Food Hydrocoll 2020, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulla-Huillca, P.V.; Gomes, A.; Quinta Barbosa Bittante, A.M.; Lourenço, R.V.; Sobral, P.J. do A. Wettability of Gelatin-Based Films: The Effects of Hydrophilic or Hydrophobic Plasticizers and Nanoparticle Loads. J Food Eng 2021, 297, 110480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyono, A.; Sato, H.; Matsubara, H.; Okubo, M.; Ohshima, H. Overshoot and Oscillation in Surface Tension of Gelatin Solutions. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2004, 39, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillery-Travis, A.; Mills, E.N.C.; Wilde, P. Protein-Lipid Interactions at Interfaces. Grasas y Aceites 2000, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Han, J.; Chang, Y. Development of Gelatin–Sodium Caseinate High-Oxygen-Barrier Film Containing Elderberry (Sambucus Nigra L.) Extract and Its Antioxidant Capacity on Pork. Food Biosci 2023, 53, 102617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, Md.S.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Effect of Heat Treatment of Film-Forming Solution on the Properties of Film from Cuttlefish (Sepia Pharaonis) Skin Gelatin. J Food Eng 2010, 96, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sha, X.-M.; Yang, H.-S.; Ren, Z.-Y.; Tu, Z.-C. Ultrasonic Treatment Regulates the Properties of Gelatin Emulsion to Obtain High-Quality Gelatin Film. Food Chem X 2023, 18, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Sit, N. Comparison of Properties of Films Prepared from Casein Modified by Ultrasound and Autoclave Treatment. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 2023, 17, 5426–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gago, M.B.; Nadaud, P.; Krochta, J.M. Water Vapor Permeability, Solubility, and Tensile Properties of Heat-denatured versus Native Whey Protein Films. J Food Sci 1999, 64, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckian, S.; Dwyer, C.; O’Sullivan, M.; O’Riordan, E.D.; Monahan, F.J. Properties of and Mechanisms of Protein Interactions in Films Formed from Different Proportions of Heated and Unheated Whey Protein Solutions. European Food Research and Technology 2006, 223, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Baraniak, B. Effects of Plasticizers, PH and Heating of Film-Forming Solution on the Properties of Pea Protein Isolate Films. J Food Eng 2011, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Thibault, R.; Cuq, B.; Guilbert, S. Influence of Relative Humidity and Film Composition on Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Permeabilities of Edible Films. J Agric Food Chem 1996, 44, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achet, D.; He, X.W. Determination of the Renaturation Level in Gelatin Films. Polymer (Guildf) 1995, 36, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihzadeh Khajavi, M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Yousefi, M.; Ahmadi, S.; Farhoodi, M.; Mirza Alizadeh, A.; Taslikh, M. Strategies for Producing Improved Oxygen Barrier Materials Appropriate for the Food Packaging Sector. Food Engineering Reviews 2020, 12, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Gustaw, W.; Zieba, E.; Lisiecki, S.; Stadnik, J.; Baraniak, B. Microstructure and Functional Properties of Sorbitol-Plasticized Pea Protein Isolate Emulsion Films: Effect of Lipid Type and Concentration. Food Hydrocoll 2016, 60, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadungath, C. Casein Micelle Structure: A Concise Review Internal Structure Model of Casein.
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on plastic materials and articles intended to come into contact with food (Text with EEA relevance) (OJ L 012 15.1.2011, p. 1).
- Crewther, W. The Precipitation of Gelatin by Ethanol, and Its Use in the Estimation of Proteolytic Activity. Aust J Biol Sci 1952, 5, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittle, C.A.; Custer, J.H. Purification and Some of the Properties of As-Casein and κ-Casein. J Dairy Sci 1963, 46, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, F.S.; Mohamed, S.S. Effect of Different Denaturating Methods on Lipid–Protein Complex Formation. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2004, 37, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B, I.K. Index Academic Sciences A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW OF MATHEMATICAL MODELS OF PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORMS; 2015; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Łupina, K.; Kowalczyk, D.; Drozłowska, E. Polysaccharide/Gelatin Blend Films as Carriers of Ascorbyl Palmitate – A Comparative Study. Food Chem 2020, 333, 127465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D. Biopolymer/Candelilla Wax Emulsion Films as Carriers of Ascorbic Acid - A Comparative Study. Food Hydrocoll 2016, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuine, R.; Rathnayake, A.U.; Byun, H.-G. Biological Activity of Peptides Purified from Fish Skin Hydrolysates. Fish Aquatic Sci 2019, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
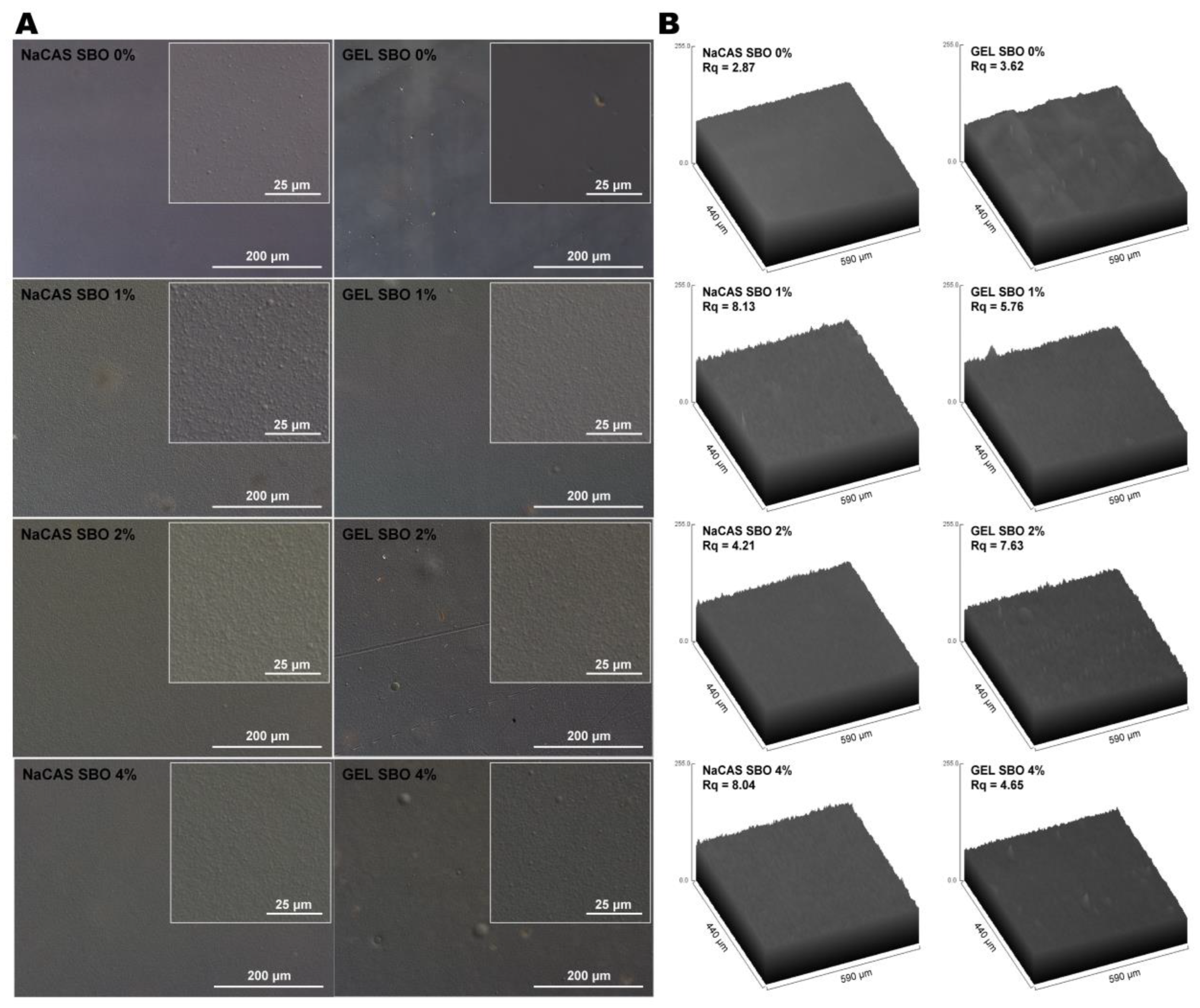
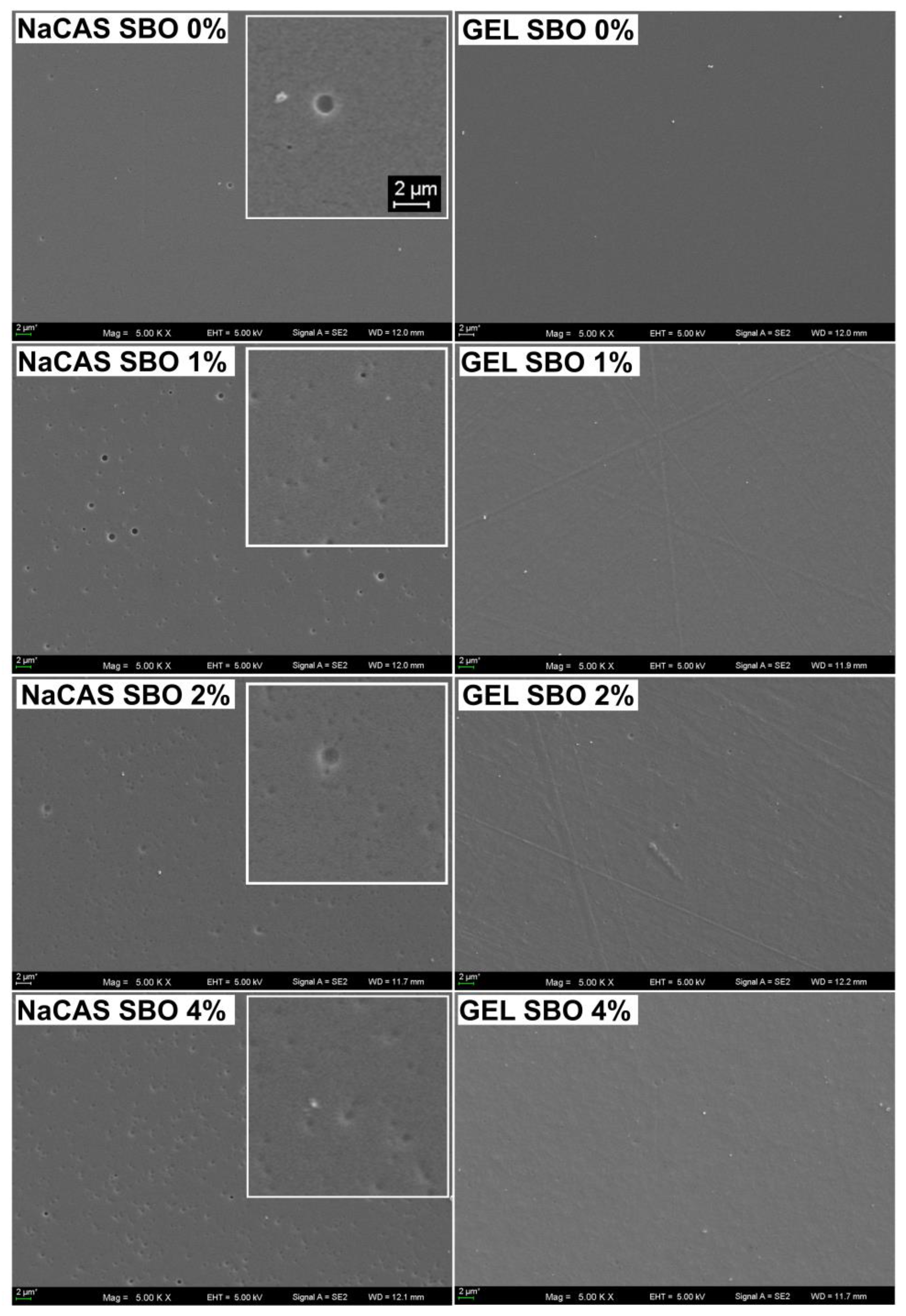
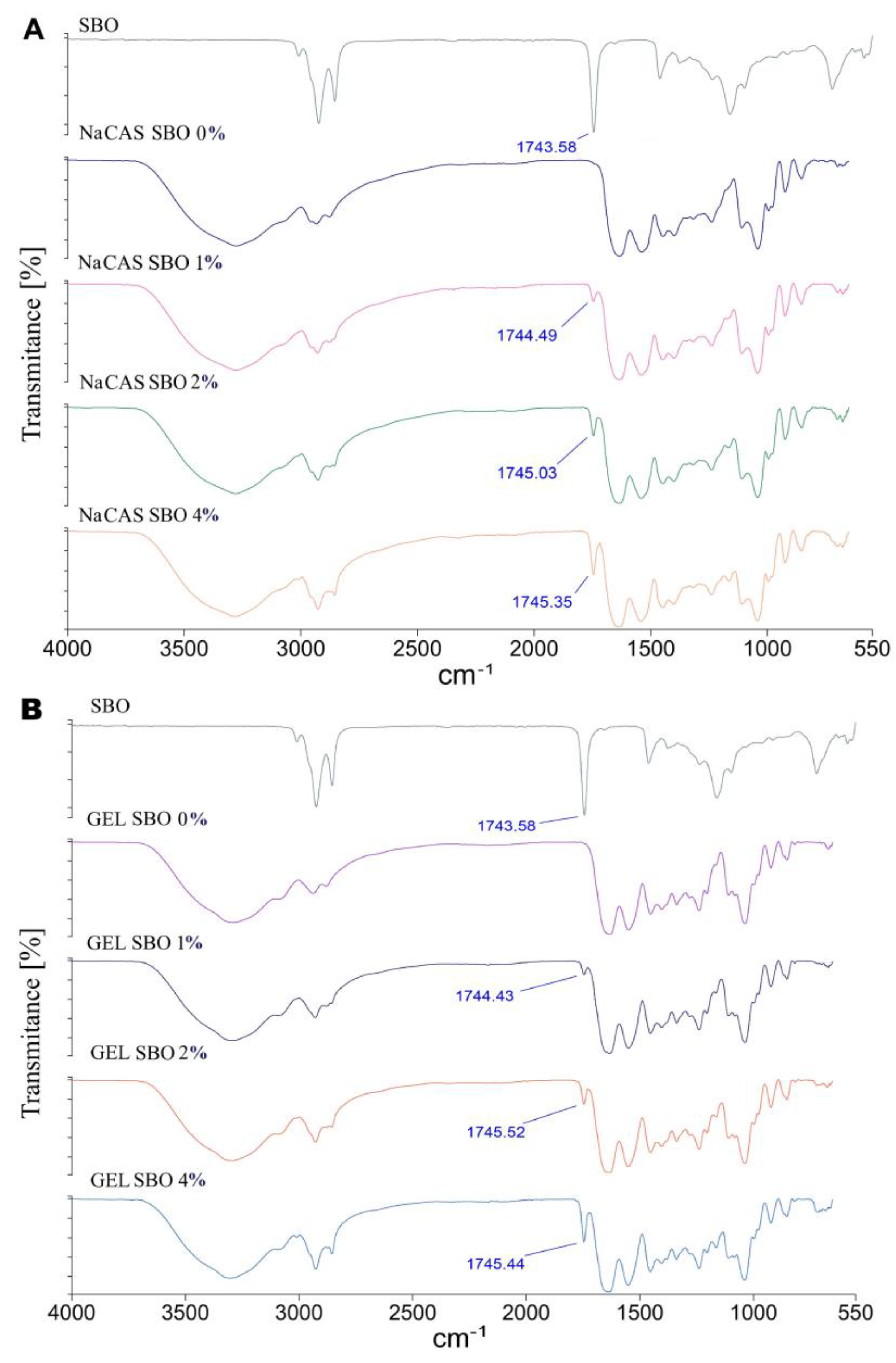
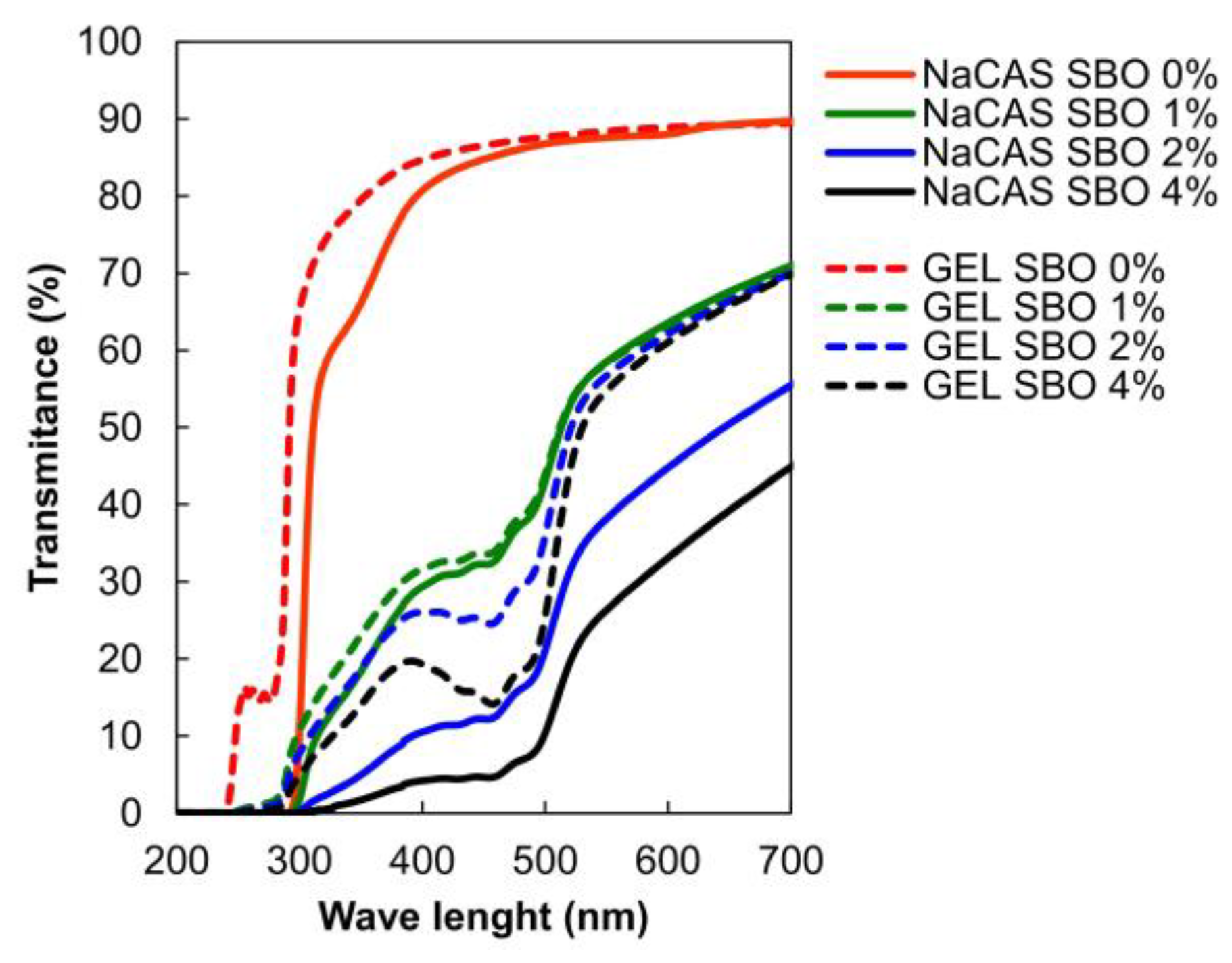
| Film type | SBO (%) | Opacity (A600/mm) | YI | MC (%) | WCA (o) | WVP (*) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCAS | 0 | 0.63±0.07a | -10.64±0.26a | 19.68±1.14d | 67.55±4.05a | 55.21±0.99bc |
| 1 | 2.33±0.14b | 58.20±3.80b | 18.34±1.49cd | 88.94±3.40b | 54.07±0.71abc | |
| 2 | 3.86±0.07c | 87.53±2.33c | 19.83±1.24d | 88.42±4.55b | 51.75±1.98ab | |
| 4 | 5.44±0.23d | 120.61±3.31d | 18.38±0.73cd | 90.02±5.63b | 50.68±1.89a | |
| GEL | 0 | 0.60±0.13a | -7.20±0.64a | 16.25±0.56ab | 118.08±3.37d | 63.24±0.26d |
| 1 | 2.43±0.16b | 52.12±3.55b | 17.32±1.11bc | 103.32±2.07c | 57.98±4.44c | |
| 2 | 2.40±0.09b | 92.02±1.09c | 16.89±1.70bc | 100.13±2.57c | 54.77±4.58abc | |
| 4 | 2.43±0.12b | 122.56±2.52d | 14.76±1.02a | 102.16±1.26c | 55.02±1.88abc |
| Film type | SBO (%) | TS (MPa) | EB (%) | EM (MPa) | t50%* (min) | n | tDPPH*50% (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCAS | 0 | 7.06±1.20b | 73.64±22.48ab | 184.40±39.37b | - | - | 2375.67P-S |
| 1 | 7.12±1.00b | 130.31±9.89de | 186.38±36.64b | 4631.90 M-B | 0.638 | 848.56 P-S | |
| 2 | 7.01±1.50b | 146.12±11.75e | 183.30±31.86b | 3208.98 M-B | 0.574 | 528.33 P-S | |
| 4 | 5.18±0.72a | 86.08±39.44bc | 144.11±22.05a | 2330.98 M-B | 0.518 | 258.39 P-S | |
| GEL | 0 | 16.18±0.94d | 56.10±9.02a | 339.72±24.76d | - | - | 1230.76 P-S |
| 1 | 16.97±2.24d | 89.79±8.42bc | 230.11±33.24c | 2182.53 M-B | 0.626 | 618.39 P-S | |
| 2 | 17.43±0.60d | 102.52±11.18c | 226.61±26.29c | 3797.28 M-B | 0.644 | 449.36 P-S | |
| 4 | 12.92±1.92c | 112.58±24.70cd | 165.33±9.92ab | 2850.30 M-B | 0.714 | 290.77 P-S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





