Submitted:
10 December 2024
Posted:
10 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Framework
4. Purpose and Scope of the Study
5. Dataset and Method
6. STIRPAT Model in ARDL Form
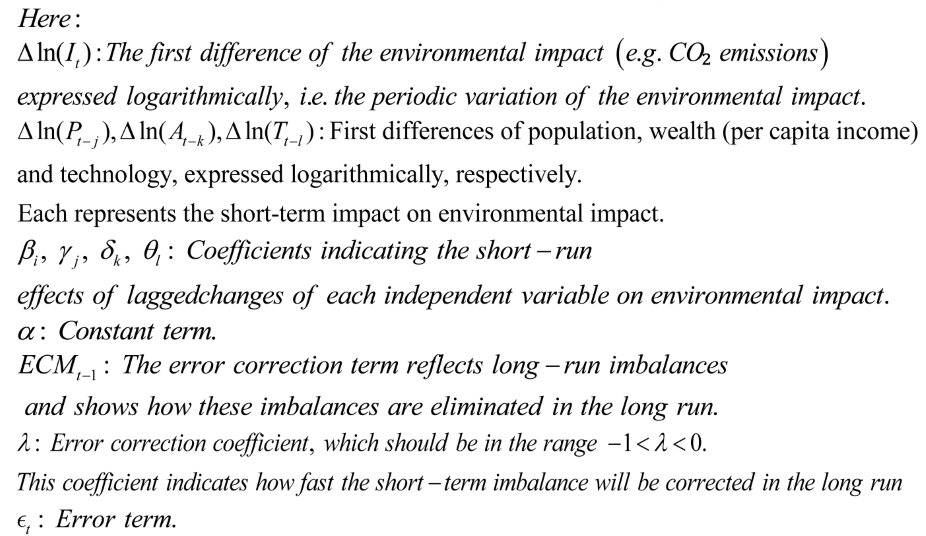
7. Results and Discussion
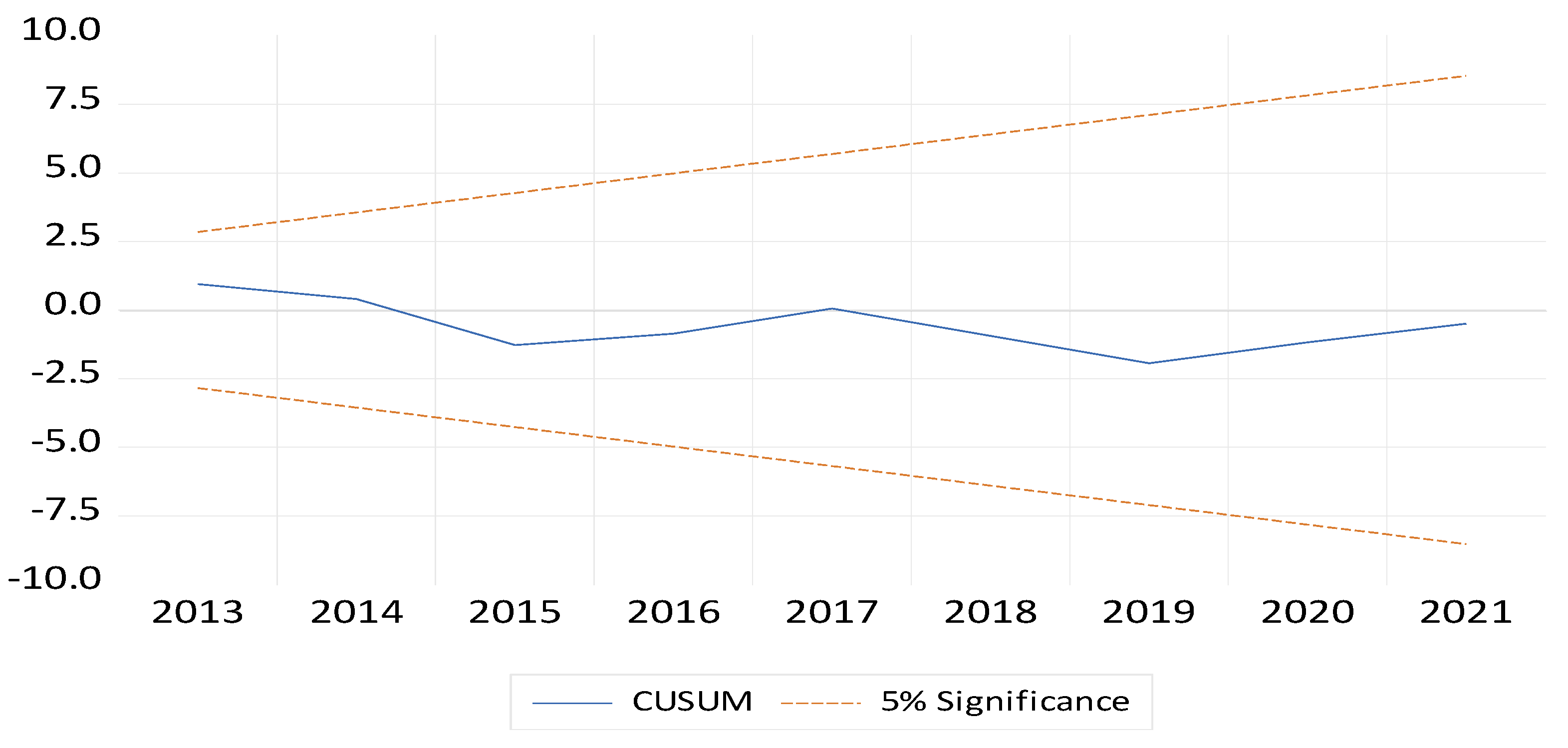
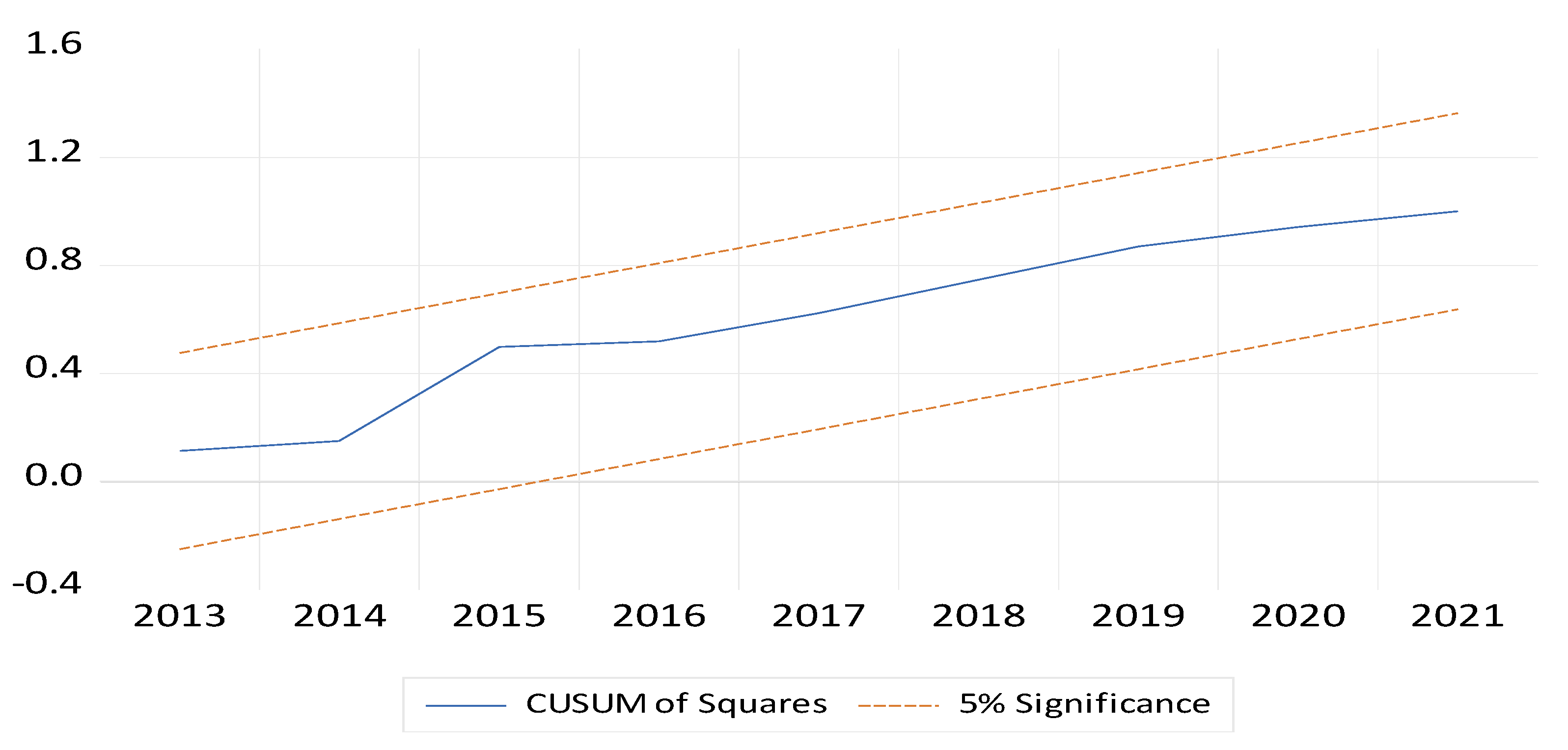
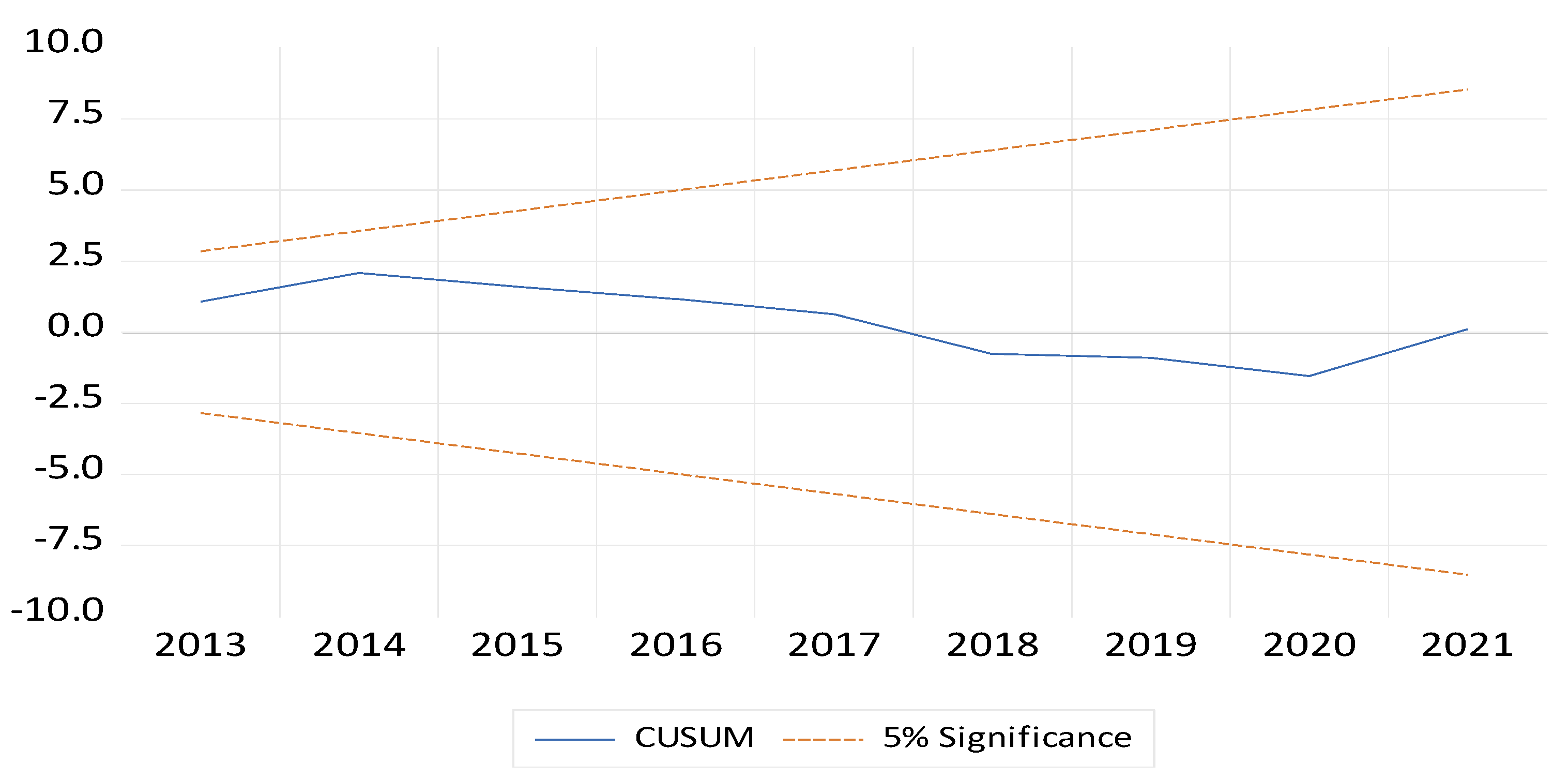
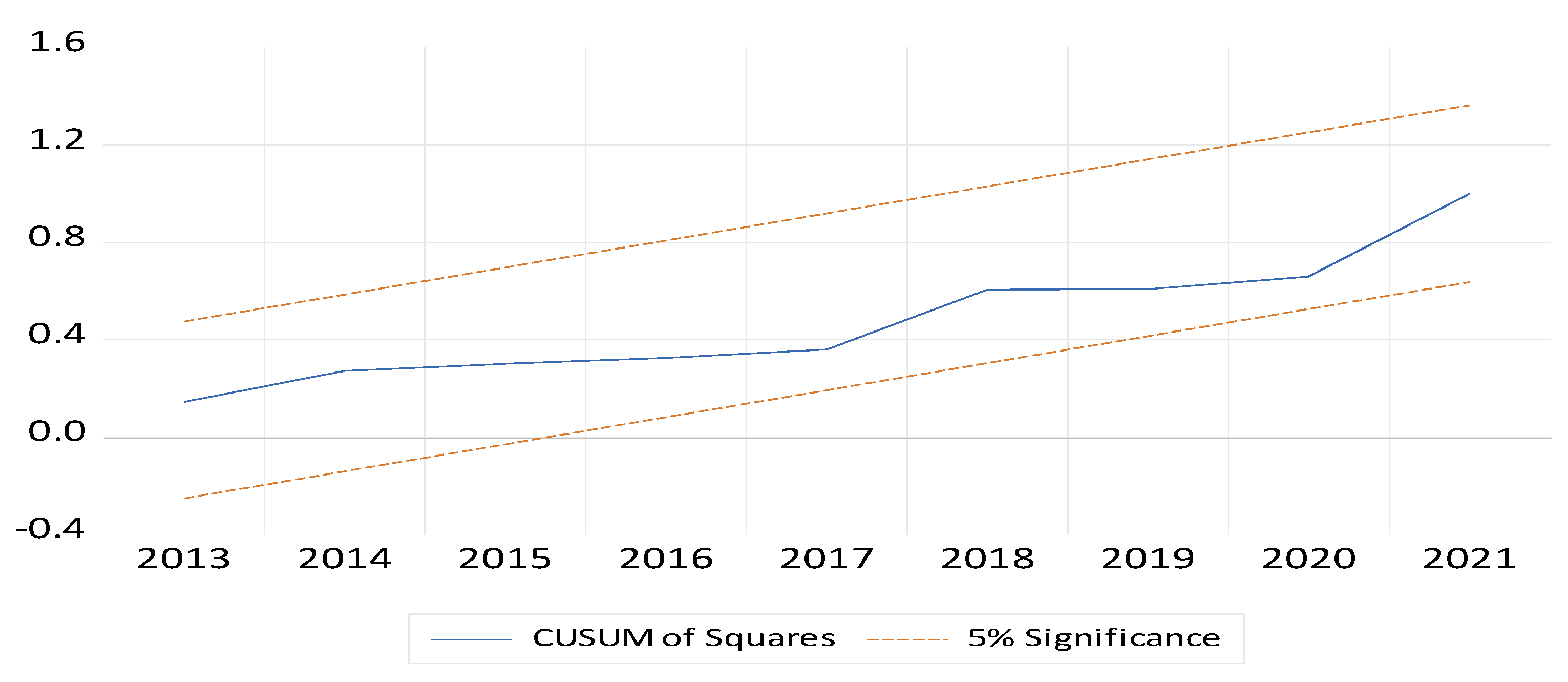
8. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinda, S. Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis: A survey. Ecological Economics 2004, 49, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D. I. The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Development 2004, 32, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. P.; Cheng, X. M. Energy consumption, carbon emissions, and economic growth in China. Ecological Economics 2009, 68, 2706–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anser, M. K.; Alharthi, M.; Aziz, B.; Wasim, S. Impact of urbanization, economic growth, and population size on residential carbon emissions in the SAARC countries. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy 2020, 22, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Álvarez, M.; Montañés, A. Energy consumption and CO2 emissions in economic growth models. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 328, 116979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E. A. Effects of population and affluence on CO2 emissions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1997, 94, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Mardani, A.; Cavallaro, F.; Loganathan, N.; Khoshnoudi, M. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and economic growth: A systematic review of two decades of research from 1995 to 2017. Science of the Total Environment 2019, 658, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Zarzoso, I.; Maruotti, A. The impact of population on CO2 emissions: Evidence from European countries. Environmental and Resource Economics 2011, 48, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Neill, B. C.; Dalton, M.; Fuchs, R.; Jiang, L.; Pachauri, S.; Zigova, K. Global demographic trends and future carbon emissions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2010, 107, 17521–17526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M. M.; Murad, M. W.; Noman, A. H. M.; Ozturk, I. Relationships among carbon emissions, economic growth, energy consumption and population growth: Testing Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis for Brazil, China, India and Indonesia. Ecological Indicators 2016, 70, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Hochman, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Li, H.; Liao, H. CO2 emissions, economic and population growth, and renewable energy: empirical evidence across regions. Energy Economics 2018, 75, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, G.; Galor, O. Is faster economic growth compatible with reductions in carbon emissions? The role of diminished population growth. Environmental Research Letters 2017, 12, 014003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, T.; Mookerjee, R. Population growth and global CO2 emissions: a secular perspective. Energy Policy 1996, 24, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Say, N. P.; Yücel, M. Energy consumption and CO2 emissions in Türkiye: Empirical analysis and future projection based on an economic growth. Energy policy 2006, 34, 3870–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Zarzoso, I.; Bengochea-Morancho, A.; Morales-Lage, R. The impact of population on CO 2 emissions: evidence from European countries. Environmental and Resource Economics 2007, 38, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Acaravci, A. CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Türkiye. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2010, 14, 3220–3225 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlan, R. The impact of population density, energy consumption, economic growth and trade openness on CO 2 emissions in India. Natural hazards 2015, 79, 1409–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R. A.; Sohag, K.; Abdullah, S. M. S.; Jaafar, M. CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic and population growth in Malaysia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 41, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Khan, A. Q.; Abdullah, H. B.; Qureshi, M. E. The impact of CO 2 emissions on economic growth: evidence from selected higher CO 2 emissions economies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2016, 23, 6376–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P. Y.; Chen, S. T.; Hsu, C. S.; Chen, C. C. Modeling the global relationships among economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 65, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aye, G. C.; Edoja, P. E. Effect of economic growth on CO2 emission in developing countries: Evidence from a dynamic panel threshold model. Cogent Economics & Finance 2017, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, C.; Abdul-Rahim, A. S. Population growth and CO2 emission in Nigeria: a recursive ARDL approach. Sage Open 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, G.; Fang, C. Urbanization, economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: Empirical evidence from countries with different income levels. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews 2018, 81, 2144–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdouli, M.; Kamoun, O.; Hamdi, B. The impact of economic growth, population density, and FDI inflows on CO 2 emissions in BRICTS countries: Does the Kuznets curve exist? . Empirical Economics 2018, 54, 1717–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikayilov, J. I.; Galeotti, M.; Hasanov, F. J. The impact of economic growth on CO2 emissions in Azerbaijan. Journal of cleaner production 2018, 197, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, A. O. Economic growth, CO2 emissions and energy consumption: what causes what and where? . Energy Economics 2018, 74, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.; Abbas, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ikram, M.; Iqbal, N. Integrated effect of energy consumption, economic development, and population growth on CO 2 based environmental degradation: a case of transport sector. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2019, 26, 32824–32835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, R.; Alam, K. Dynamic relationship among environmental regulation, innovation, CO2 emissions, population, and economic growth in OECD countries: A panel investigation. Journal of cleaner production 2019, 231, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Streimikiene, D.; Cavallaro, F.; Loganathan, N.; Khoshnoudi, M. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and economic growth: A systematic review of two decades of research from 1995 to 2017. Science of the total environment 2019, 649, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A. T.; Vo, D. H.; Le, Q. T. T. CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth: New evidence in the ASEAN countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management 2019, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohmmed, A.; Li, Z.; Arowolo, A. O.; Su, H.; Deng, X.; Najmuddin, O.; Zhang, Y. Driving factors of CO2 emissions and nexus with economic growth, development and human health in the Top Ten emitting countries. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 2019, 148, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. M.; Saidi, K.; Mbarek, M. B. Economic growth in South Asia: the role of CO2 emissions, population density and trade openness. Heliyon 2020, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odugbesan, J. A.; Rjoub, H. Relationship among economic growth, energy consumption, CO2 emission, and urbanization: evidence from MINT countries. Sage Open 2020, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Rehman, A. Exploring the dynamic interaction of CO2 emission on population growth, foreign investment, and renewable energy by employing ARDL bounds testing approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 39387–39397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namahoro, J. P.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, N. The impact of renewable energy, economic and population growth on CO2 emissions in the East African region: evidence from common correlated effect means group and asymmetric analysis. Energies 2021, 14, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachiyappan, D.; Ansari, Y.; Alam, M. S.; Thoudam, P.; Alagirisamy, K.; Manigandan, P. Short and long-run causal effects of CO2 emissions, energy use, GDP and population growth: evidence from India using the ARDL and VECM approaches. Energies 2021, 14, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, N.; Mu, H.; Pang, J.; Zhao, H.; Ahmad, M. Study on the long-term impact of economic globalization and population aging on CO2 emissions in OECD countries. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 787, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofrei, M.; Vatamanu, A. F.; Cigu, E. The relationship between economic growth and CO2 emissions in EU countries: A cointegration analysis. Frontiers in Environmental Science 2022, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, E.; Rehman, S. Modeling the nexus between carbon emissions, urbanization, population growth, energy consumption, and economic development in Asia: Evidence from grey relational analysis. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 5430–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzair Ali, M.; Gong, Z.; Ali, M. U.; Asmi, F.; Muhammad, R. CO2 emission, economic development, fossil fuel consumption and population density in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh: a panel investigation. International Journal of Finance & Economics 2022, 27, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Huan, W.; Ali, N.; Shafi, A.; Ehsan, M.; Abdelrahman, K. ; ... & Fnais, M. S. The effect of energy consumption, income, and population growth on CO2 emissions: evidence from NARDL and machine learning models. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Irfan, M.; Samad, S.; Ali, B.; Zhang, Y.; Badulescu, D.; Badulescu, A. The relationship between energy consumption, CO2 emissions, economic growth, and health indicators. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2023, 20, 1–20 https://wwwmdpicom/journal/ijerph. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Alam, M. M.; Ozturk, I.; Alvarado, R.; Murshed, M.; Işık, C.; Ma, H. Globalization and renewable energy use: how are they contributing to upsurge the CO2 emissions? A global perspective. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2023, 30, 9699–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Long, X.; Han, J. An aging giant at the center of global warming: Population dynamics and its effect on CO2 emissions in China. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 327, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitić, P.; Fedajev, A.; Radulescu, M.; Rehman, A. The relationship between CO2 emissions, economic growth, available energy, and employment in SEE countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2023, 30, 16140–16155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dritsaki, M.; Dritsaki, C. The relationship between health expenditure, CO2 emissions, and economic growth in G7: Evidence from heterogeneous panel data. Journal of the Knowledge Economy 2024, 15, 4886–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, P. R.; Holdren, J. P. Impact of population growth. Science 1971, 171, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D. I. The rise and fall of the environmental Kuznets curve. World Development 2004, 32, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Victor, D. G. The future mobility of the world population. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice 2000, 34, 171–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Martino, D.; Cai, Z.; Gwary, D.; Janzen, H.; Kumar, P.; ... & Smith, J. (2014). Agriculture. In O. Edenhofer et al. (Eds.), Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 811-922. Cambridge University Press. [CrossRef]
- Ravallion, M. Troubling tradeoffs in the Human Development Index. Journal of Development Economics 2012, 99, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perman, R.; Stern, D. I. Evidence from panel unit root and cointegration tests that the environmental Kuznets curve does not exist. Australian Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics 2003, 47, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M. H.; Shin, Y. An autoregressive distributed-lag modelling approach to cointegration analysis. Econometrics and Economic Theory in the 20th Century: The Ragnar Frisch Centennial Symposium 1998, 371-413.
- Pesaran, M. H.; Shin, Y.; Smith, R. J. Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. Journal of Applied Econometrics 2001, 16, 289–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, P. K. The saving and investment nexus for China: Evidence from cointegration tests. Applied Economics 2005, 37, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoro, E.; Uko, A. K. Autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) cointegration technique: Application and interpretation. Journal of Statistical and Econometric Methods 2016, 5, 63–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zivot, E.; Wang, J. (2006). Modeling financial time series with S-PLUS (2nd ed.). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Zhang, Z.; Sharifi, A. Analysis of decoupling between CO2 emissions and economic growth in China’s provincial capital cities: A Tapio model approach. Urban Climate 2024, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, K. C.; Mishra, B.; Mohapatra, S. M. Investigating the relationship between economic growth, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions: a comparative analysis of South Asian nations and G-7 countries. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. M. Do population density, economic growth, energy use and exports adversely affect environmental quality in Asian populous countries? . Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 77, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. C.; Zhao, Y. N. Heterogeneity analysis of factors influencing CO2 emissions: the role of human capital, urbanization, and FDI. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2023, 185, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LOGCO2 | LOGPOPULATION | LOGGROWTH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 19.53367 | 18.11838 | 9.553095 |
| Median | 19.54165 | 18.10466 | 9.616482 |
| Maximum | 19.96139 | 18.27781 | 11.36479 |
| Minimum | 19.13610 | 17.97023 | 7.049063 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.268532 | 0.098055 | 1.120131 |
| Skewness | -0.073138 | 0.229835 | -0.562768 |
| Kurtosis | 1.709517 | 1.789605 | 2.697803 |
| Jarque-Bera | 1.686744 | 1.676353 | 1.358156 |
| Probability | 0.430257 | 0.432499 | 0.507084 |
| Observations | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D(LOGCO2(-1)) | 0.466906 | 0.110200 | 4.236906 | 0.0022 |
| D(LOGCO2(-2)) | 0.260733 | 0.112703 | 2.313454 | 0.0460 |
| D(LOGCO2(-3)) | 0.263481 | 0.102463 | 2.571480 | 0.0301 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA) | 0.315177 | 0.070221 | 4.488349 | 0.0015 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA(-1)) | 0.021612 | 0.112672 | 0.191817 | 0.8521 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA(-2)) | -0.380254 | 0.109997 | -3.456937 | 0.0072 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA(-3)) | -0.412386 | 0.138473 | -2.978109 | 0.0155 |
| CointEq(-1)* | -1.406583 | 0.233770 | -6.016964 | 0.0002 |
| F-Bounds Test | ||||
| Test Statistic | Value | Signif. | I(0) | I(1) |
| F-statistic | 6.788223 | 10% | 2.63 | 3.35 |
| k | 2 | 5% | 3.1 | 3.87 |
| 2.5% | 3.55 | 4.38 | ||
| 1% | 4.13 | 5 | ||
| Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM Test: | ||||
| F-statistic | 4.398655 | Prob. F(2,7) | 0.0579 | |
| Obs*R-squared | 11.13773 | Prob. Chi-Square(2) | 0.0538 | |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D(LOGPOPULATION(-1)) | 1.484185 | 0.194174 | 7.643563 | 0.0003 |
| D(LOGPOPULATION(-2)) | -0.309401 | 0.395535 | -0.782235 | 0.4638 |
| D(LOGPOPULATION(-3)) | 0.660272 | 0.280088 | 2.357371 | 0.0565 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA) | 0.016508 | 0.008568 | 1.926629 | 0.1023 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA(-1)) | 0.001240 | 0.008731 | 0.142013 | 0.8917 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA(-2)) | 0.025359 | 0.009858 | 2.572529 | 0.0422 |
| D(LOGGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT PER CAPITA(-3)) | 0.013437 | 0.007768 | 1.729849 | 0.1344 |
| D(LOGCO2) | 0.028484 | 0.014115 | 2.017893 | 0.0902 |
| D(LOGCO2(-1)) | -0.055184 | 0.016309 | -3.383619 | 0.0148 |
| D(LOGCO2(-2)) | -0.028793 | 0.010618 | -2.711800 | 0.0350 |
| CointEq(-1)* | -0.438621 | 0.099400 | -4.412675 | 0.0045 |
| F-Bounds Test | ||||
| Test Statistic | Value | Signif. | I(0) | I(1) |
| F-statistic | 3.245283 | 10% | 2.63 | 3.35 |
| k | 2 | 5% | 3.1 | 3.87 |
| 2.5% | 3.55 | 4.38 | ||
| 1% | 4.13 | 5 | ||
| Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM Test: | ||||
| F-statistic | 3.118461 | Prob. F(4,2) | 0.2573 | |
| Obs*R-squared | 17.23639 | Prob. Chi-Square(4) | 0.2017 | |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D(LOGCO2) | 0.539473 | 0.186394 | 2.894263 | 0.0178 |
| D(LOGCO2(-1)) | 0.299143 | 0.177801 | 1.682461 | 0.1268 |
| D(LOGCO2(-2)) | -0.164511 | 0.154507 | -1.064748 | 0.3147 |
| D(LOGCO2(-3)) | -0.452009 | 0.155062 | -2.915016 | 0.0172 |
| D(LOGPOPULATION) | 6.497350 | 3.649440 | 1.780369 | 0.0087 |
| D(LOGPOPULATION(-1)) | -11.49908 | 6.394548 | -1.798263 | 0.1057 |
| D(LOGPOPULATION(-2)) | -10.86854 | 5.287504 | -2.055514 | 0.0700 |
| CointEq(-1)* | -0.612472 | 0.058780 | -10.41975 | 0.0000 |
| F-Bounds Test | ||||
| Test Statistic | Value | Signif. | I(0) | I(1) |
| F-statistic | 20.35709 | 10% | 2.63 | 3.35 |
| k | 2 | 5% | 3.1 | 3.87 |
| 2.5% | 3.55 | 4.38 | ||
| 1% | 4.13 | 5 | ||
| Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM Test: | ||||
| F-statistic | 4.121644 | Prob. F(2,7) | 0.0656 | |
| Obs*R-squared | 10.81563 | Prob. Chi-Square(2) | 0.0545 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




