Submitted:
06 December 2024
Posted:
09 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
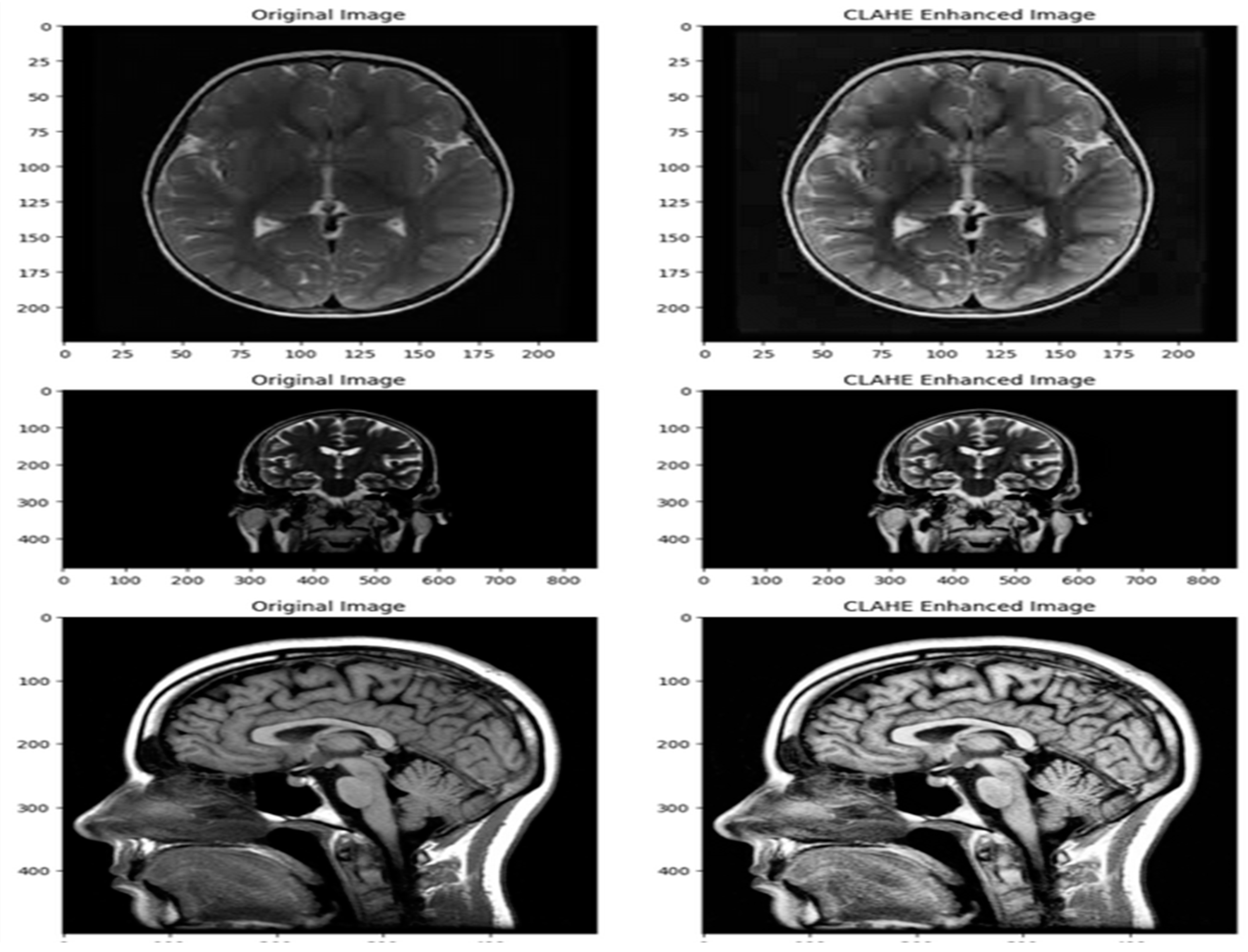
- Pre-processing the MRI Images using Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE).
- features are extracted using Histograms of Oriented Gradients (HOGs), Local Binary Patterns (LBPs) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA).
- To classify the brain tumor into tumor and non tumor, Five machine learning techniques (Random Forests, Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), XGBoost, AdaBoost, Neural Network) are implemented.
- The comparison of implemented machine learning techniques is performed using accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and precision.
- The impact of different feature extraction methods on different metrics was also studied.
2. Related Work
2.1. Problem Statement
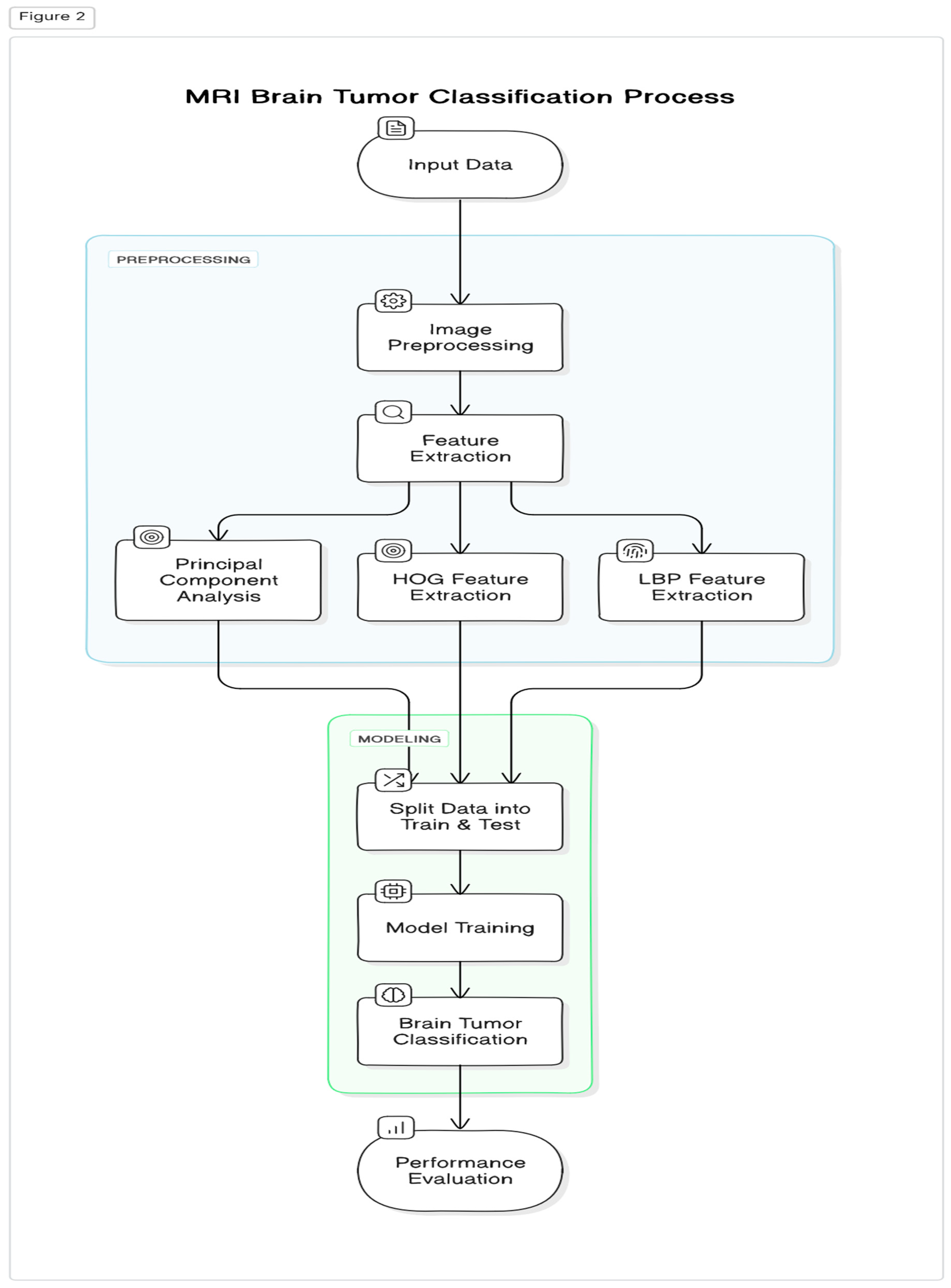
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Dataset Collection
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
3.3. Feature Extraction
3.3.1. Principal Component Analysis
3.3.2. HOG Feature Extraction
3.3.3. LBP Feature Extraction
4. Modelling
4.1. Data Splitting: Partitioning the Dataset for Model Training and Test
4.2. Training Models
4.3. Brain Tumor Classification
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
5.1. Confusion Matrix Table
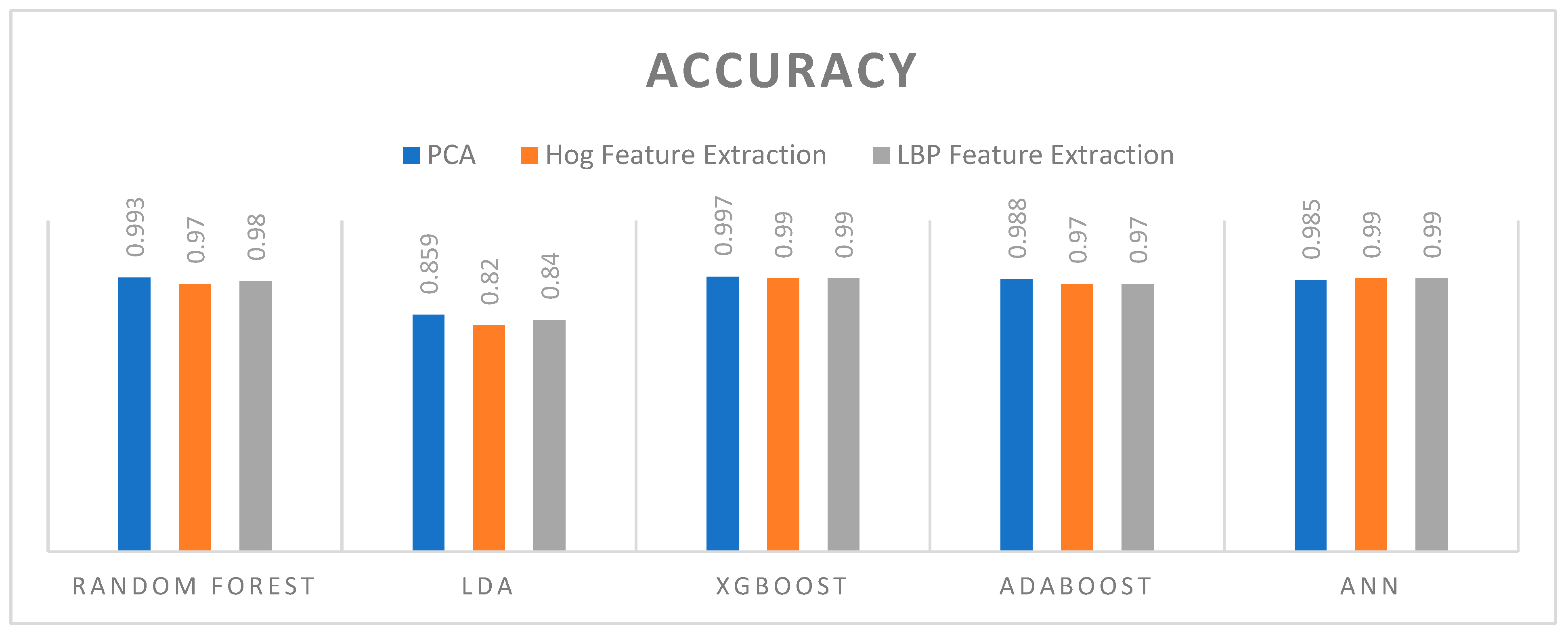
5.2. Accuracy
- Key Observation
- Random Forest: Achieved high accuracy across all feature extraction methods, with the best performance using PCA (0.993).
- LDA: Showed the lowest accuracy among the algorithms, performing best with LBP feature extraction (0.84).
- XGBoost: Delivered the highest accuracy overall, consistently achieving 0.99 across both HOG and LBP feature extractions, and 0.997 with PCA.
- ADAboost: Exhibited strong performance, especially with PCA (0.988) and slightly lower with HOG and LBP (both 0.97).
- ANN: Showed high accuracy, matching XGBoost with 0.99 for both HOG and LBP, and 0.985 with PCA.
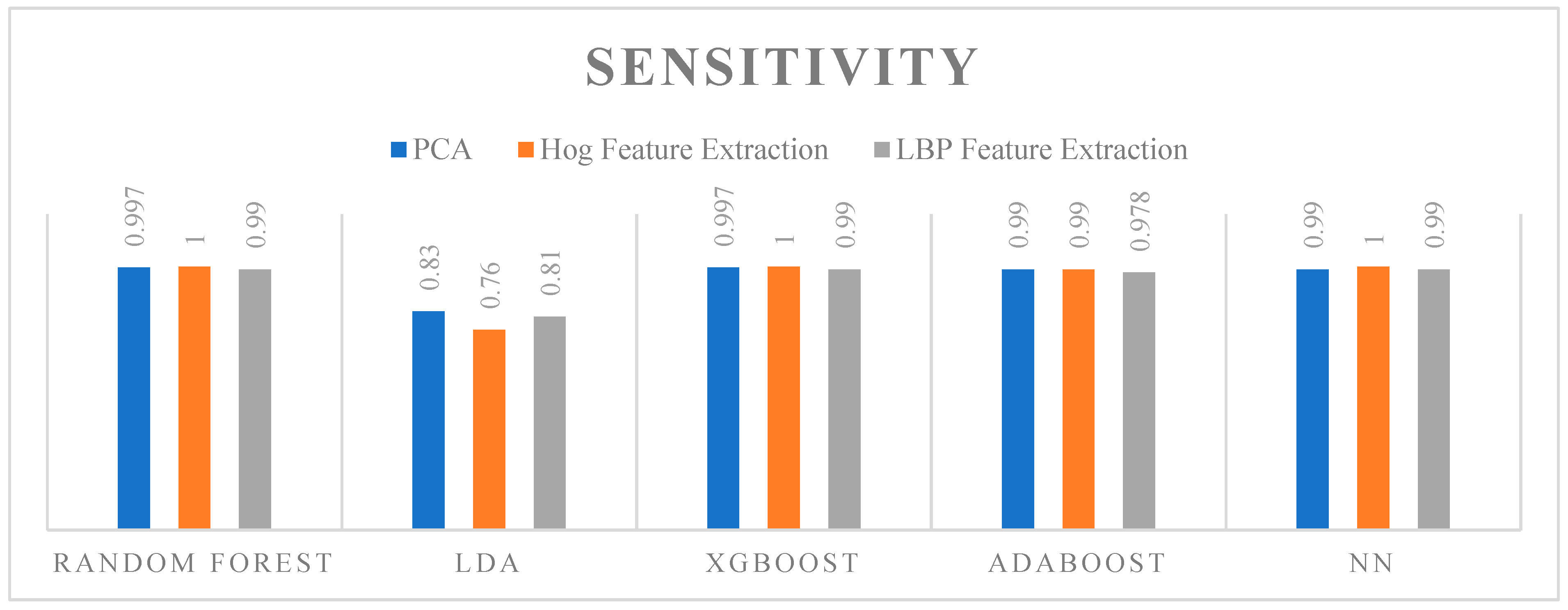
5.3. Sensitivity
- Key Observations
- Random Forest: Achieved perfect sensitivity with HOG (1), and very high sensitivity with PCA (0.997) and LBP (0.99).
- LDA: Showed the lowest sensitivity among the algorithms, performing best with PCA (0.83), followed by LBP (0.81), and the lowest with HOG (0.76).
- XGBoost: Delivered perfect sensitivity with both HOG (1) and very high sensitivity with PCA (0.997) and LBP (0.99).
- ADAboost: Exhibited very high sensitivity, especially with PCA (0.99) and HOG (0.99), and slightly lower with LBP (0.978).
- ANN: Showed perfect sensitivity with HOG (1), and very high sensitivity with PCA (0.99) and LBP (0.99).
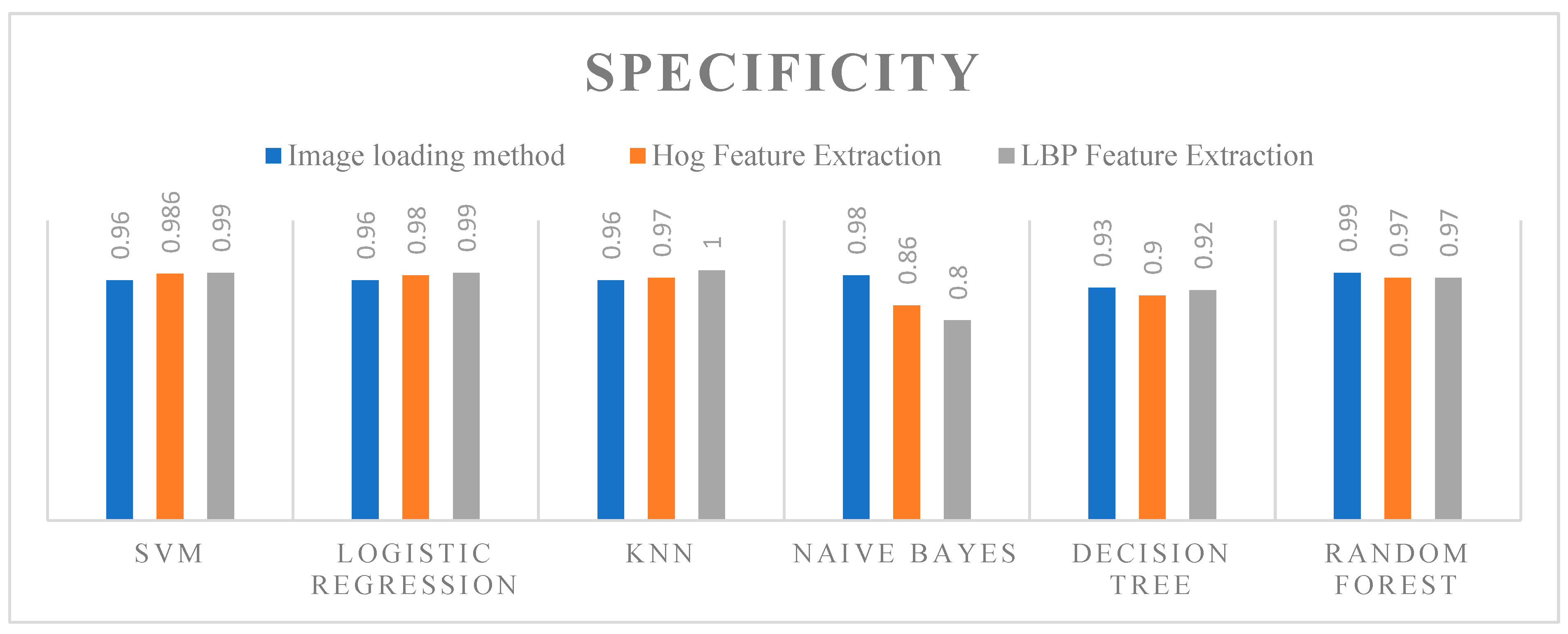
5.4. Specificity
- Key Observations
- Random Forest: Demonstrated high specificity across all feature extraction methods, with the best performance using PCA (0.991).
- LDA: Showed the lowest specificity among the algorithms, performing best with HOG (0.88), followed by PCA (0.88) and LBP (0.87).
- XGBoost: Delivered the highest specificity overall, achieving 0.997 with PCA and 0.98 with both HOG and LBP feature extraction methods.
- ADAboost: Exhibited very high specificity, especially with PCA (0.98) and slightly lower with HOG (0.96) and LBP (0.975).
- ANN: Showed high specificity, matching XGBoost with 0.98 for both PCA and HOG, and 0.988 with LBP.
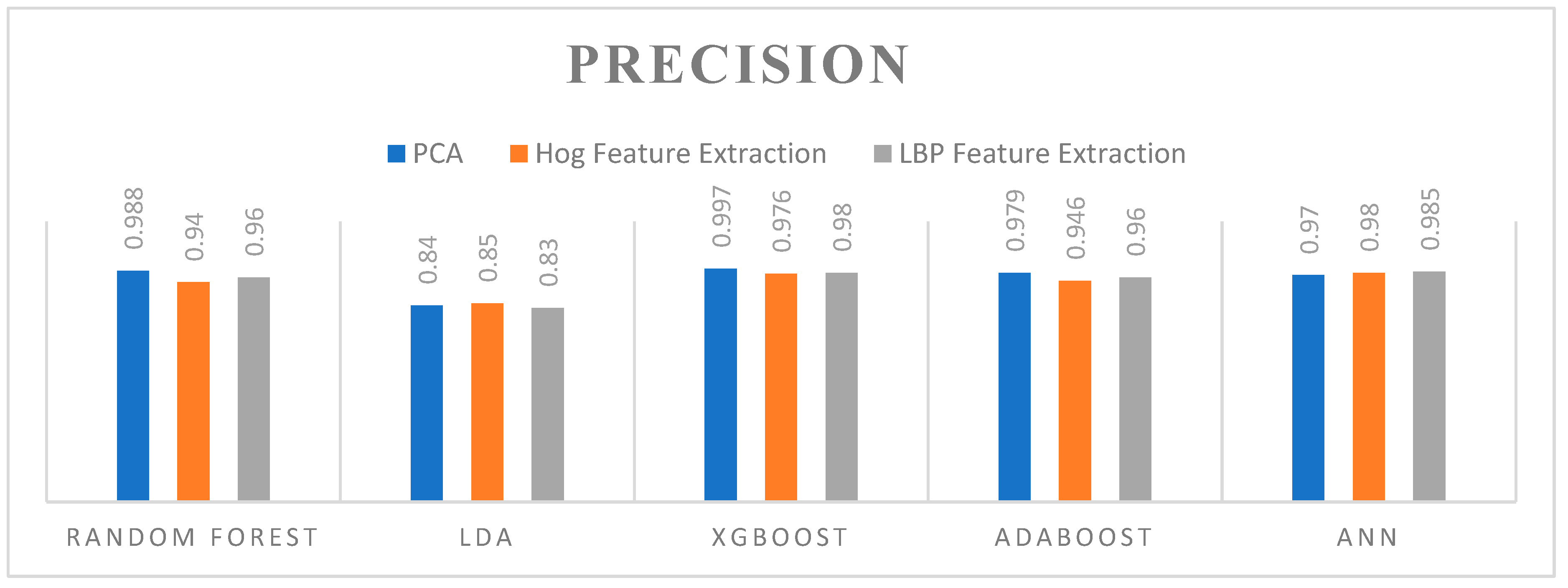
5.5. Precision
- Key Observations:
- Random Forest: Demonstrated high precision across all feature extraction methods, with the highest precision using PCA (0.988).
- LDA: Showed the lowest precision among the algorithms, performing best with HOG (0.85), followed by PCA (0.84) and LBP (0.83).
- XGBoost: Delivered the highest precision overall, achieving 0.997 with PCA, 0.976 with HOG, and 0.98 with LBP feature extraction methods.
- ADAboost: Exhibited very high precision, especially with PCA (0.979) and slightly lower with HOG (0.946) and LBP (0.96).
- ANN: Showed high precision, matching XGBoost with 0.98 for HOG, and 0.985 with LBP, and 0.97 with PCA.
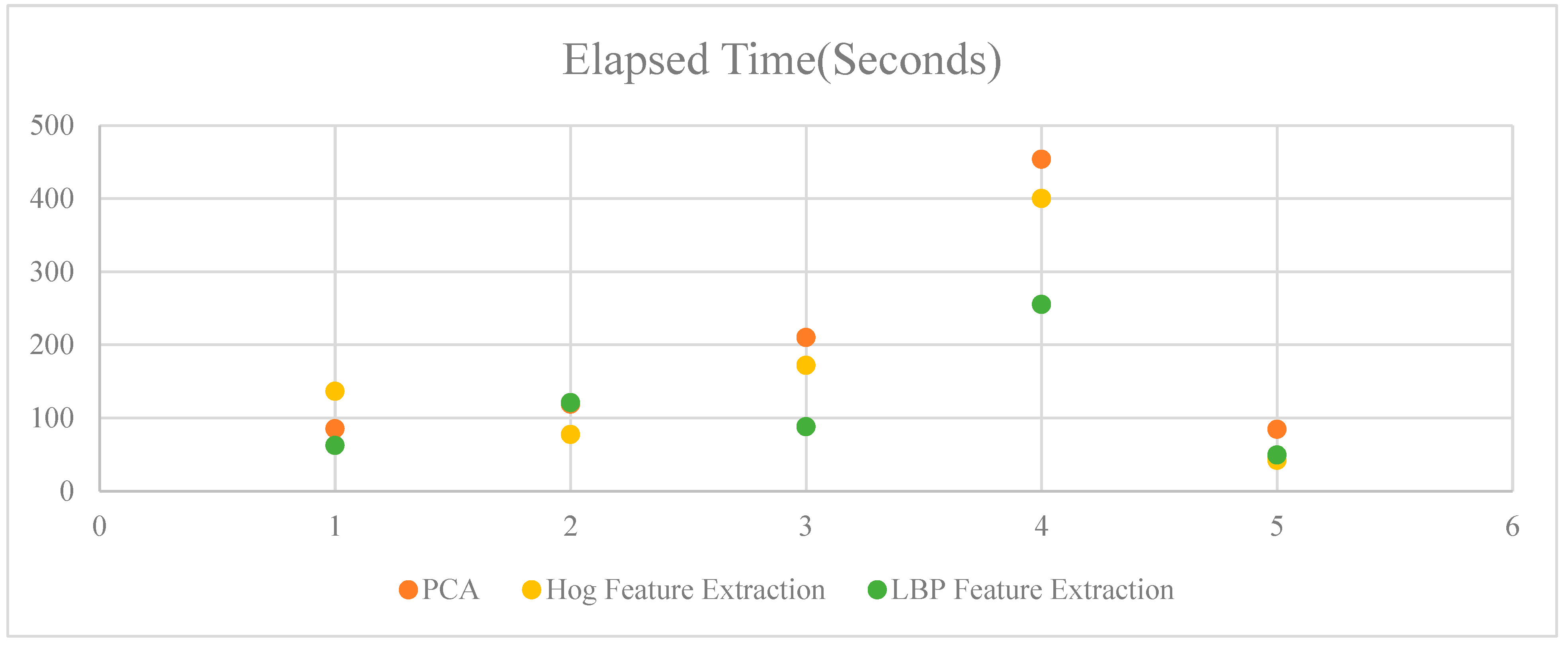
5.6. Elapsed Time
- Random Forest: Exhibited moderate elapsed times across all feature extraction methods, with the quickest performance using LBP (62.5 seconds) and the slowest with HOG (136.55 seconds).
- LDA: Showed varied elapsed times, with the quickest performance using HOG (77.3 seconds) and the slowest with LBP (121.07 seconds).
- XGBoost: Demonstrated relatively longer elapsed times compared to Random Forest and LDA, with the quickest performance using LBP (88.04 seconds) and the slowest with PCA (209.91 seconds).
- ADAboost: Had the longest elapsed times among all algorithms, with the quickest performance using LBP (255.32 seconds) and the slowest with PCA (453.7 seconds).
- ANN: Exhibited the shortest elapsed times across all feature extraction methods, with the quickest performance using HOG (41.97 seconds) and the slowest with PCA (84.33 seconds).
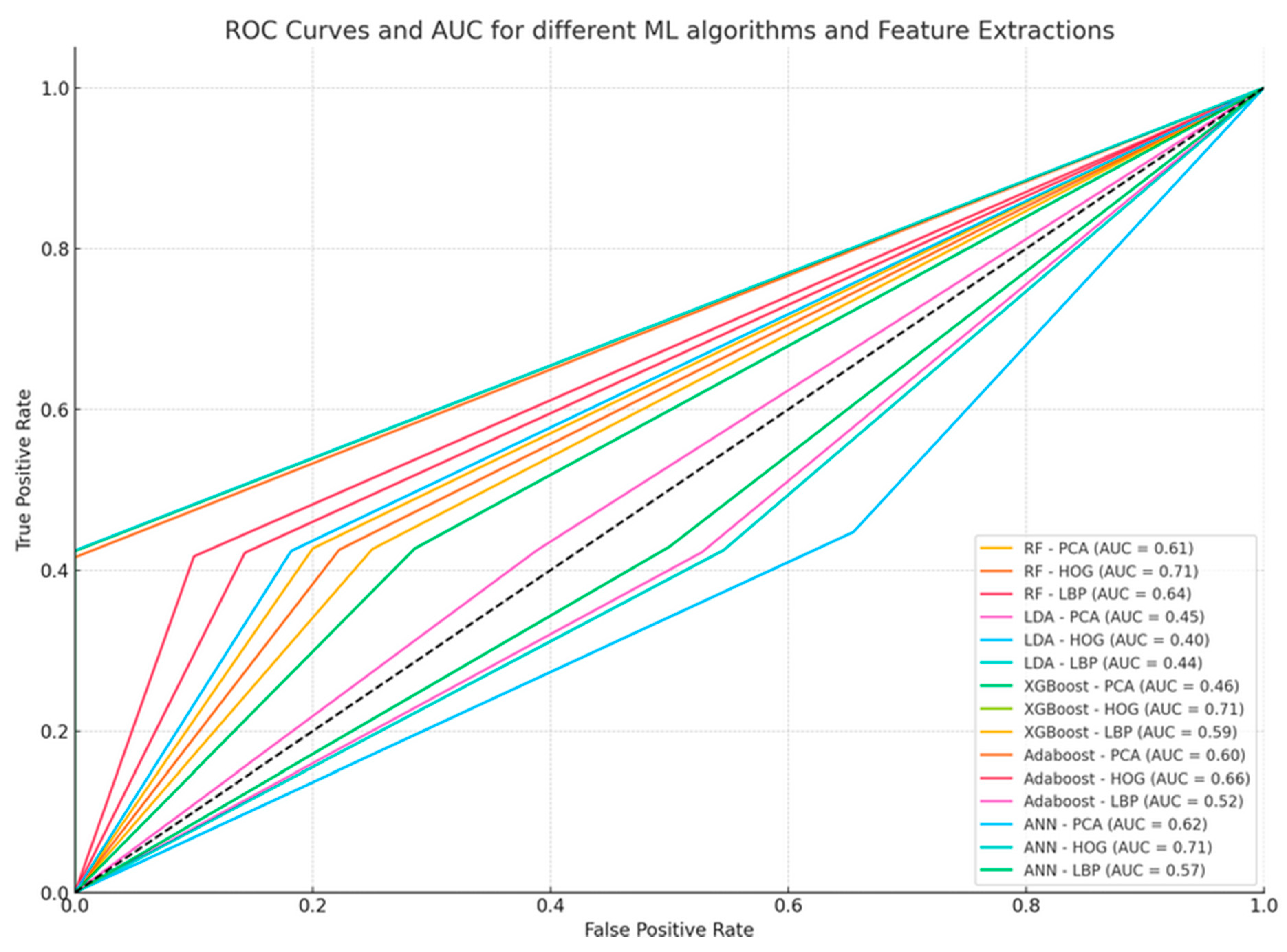
5.7. Area Under Curve
6. Discussion
7. Conclusion and Future Work
Funding
Ethical compliance
Declaration of competing interest
Data availability
References
- Al-Galal, S.A.Y.; Alshaikhli, I.F.T.; Abdulrazzaq, M.M. MRI brain tumor medical images analysis using deep learning techniques:A systematic review. Health Technol. 2021, 11, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/brain-tumor/statistics.
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodirov, J.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Whangbo, T.K. Attention 3D U-Net with Multiple Skip Connections for Segmentation of Brain Tumor Images. Sensors 2022, 22, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, A.S.M.; Rahman, M.B.; Anwar, T.; Halder, R.S.; Kays, H.E. Classification of brain tumors and auto-immune disease using ensemble learning. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 24, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Pinto, A.; Alves, V.; Silva, C.A. Brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks in MRI images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, S.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Gandhi, T.K. Enhanced performance of Dark-Nets for brain tumor classification and segmentation using colormap-based superpixel techniques. Mach. Learn Appl. 2022, 7, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Meier, R.; Alves, V.; Reyes, M.; Silva, C.A. Automatic Brain Tumor Grading from MRI Data Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Quality Assessment. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11038, pp. 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Tandel, G.S.; Tiwari, A.; Kakde, O.G. Performance optimisation of deep learning models using majority voting algorithm for brain tumour classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, K.; Sano, N.; Tangoku, A. Problems in histological grading of malignancy and its clinical significance in patients with operable breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2006, 13, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, F. Frangi, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris and Jerry L. Prince, Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, vol.37, issue.3, pp. 673 – 679, 2018.
- P.B. Kanade, and P. Gumaste, Brain tumor detection using MRI images. vol. Vol. 3. Brain, 2015.
- Amin, J.; Sharif, M.; Haldorai, A.; Yasmin, M.; Nayak, R.S. Brain tumor detection and classification using machine learning: A comprehensive survey. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 8, 3161–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; Alksas, A.; Shehata, M.; AbdelKhalek, A.; Abdel Baky, K.; El-Baz,A.;Helmy,E. Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics in Neuro-Oncology Imaging. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 152. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology. 2016 Feb;278(2):563-77. [CrossRef]
- Saad NM, Bakar SARSA, Muda AS, Mokji MM (2015) Review of brain lesion detection and classification using neuroimaging analysis techniques. J Teknol 74:1–13.
- Huang M, Yang W, Wu Y, Jiang J, Chen W, Feng Q (2014) Brain tumor segmentation based on local independent projection-based classification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61:2633–2645.
- Khan MA, Arshad H, Nisar W, Javed MY, Sharif M (2021) An integrated design of Fuzzy C-means and NCA-based multiproperties feature reduction for brain tumor recognition. Signal and image processing techniques for the development of intelligent healthcare systems.
- Tandel GS, Biswas M, Kakde OG, Tiwari A, Suri HS, Turk M et al. (2019) a review on a deep learning perspective in brain cancer classification. Cancers 11:1–32.
- El-Dahshan E-SA, Mohsen HM, Revett K, Salem A-BM (2014) Computer-aided diagnosis of human brain tumor through MRI: A survey and a new algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 41:5526–5545.
- Gordillo N, Montseny E, Sobrevilla P (2013) State of the art survey on MRI brain tumor segmentation. Magn Reson Imaging 31:1426–1438.
- Mohan G, Subashini MM (2018) MRI based medical image analysis: Survey on brain tumor grade classification. Biomed Signal Process Control 39:139–161.
- Amreen Batool, Yung-Cheol Byun,Brain tumor detection with integrating traditional and computational intelligence approaches across diverse imaging modalities - Challenges and future directions,Computers in Biology and Medicine, Volume 175,2024,108412,ISSN 0010-4825. [CrossRef]
- Stijn Bonte, Ingeborg Goethals, Roel Van Holen, Machine learning based brain tumour segmentation on limited data using local texture and abnormality, Computers in Biology and Medicine,Volume 98,2018,Pages 39-47,ISSN 0010-4825. [CrossRef]
- Fusun Citak-Er, Zeynep Firat, Ilhami Kovanlikaya, Ugur Ture, Esin Ozturk-Isik, Machine-learning in grading of gliomas based on multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging at 3T, Computers in Biology and Medicine, Volume 99,2018,Pages 154-160,ISSN 0010-4825. [CrossRef]
- R. Ali, S. Al-jumaili, A. D. Duru, O. N. Uçan, A. Boyaci and D. G. Duru, "Classification of Brain Tumors using MRI images based on Convolutional Neural Network and Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms," 2022 International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 2022, pp. 822-827. [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C., & Tang, C. (2023). An optimized XGBoost technique for accurate brain tumor detection using feature selection and image segmentation. Healthcare Analytics, 4, 100217. [CrossRef]
- Zelli, V. , Manno, A., Compagnoni, C., Ibraheem, R. O., Zazzeroni, F., Alesse, E., Rossi, F., Arbib, C., & Tessitore, A. (2023). Classification of tumor types using XGBoost machine learning model: A vector space transformation of genomic alterations. Journal of Translational Medicine. [CrossRef]
- Elazab, N. , Gab-Allah, W. A., & Elmogy, M. (2024). A multi-class brain tumor grading system based on histopathological images using a hybrid YOLO and RESNET networks. Scientific Reports. [CrossRef]
- Rajkumaar, K., Boda, R., Choppakatla, N. et al. An optimized eagle adaboost model for brain tumor classification and severity analysis system. Multimed Tools Appl (2024). [CrossRef]
- Senan EM, Jadhav ME, Rassem TH, Aljaloud AS, Mohammed BA, Al-Mekhlafi ZG. Early diagnosis of brain tumour MRI images using hybrid techniques between deep and machine learning. Comput Math Methods Med 2022;2022. [CrossRef]
- Ravinder, M., Saluja, G., Allabun, S. et al. Enhanced brain tumor classification using graph convolutional neural network architecture. Sci Rep 13, 14938 (2023). [CrossRef]
- ZainEldin H, Gamel SA, El-Kenawy EM, Alharbi AH, Khafaga DS, Ibrahim A, Talaat FM. Brain Tumor Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning and Sine-Cosine Fitness Grey Wolf Optimization. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;10(1):18. [CrossRef]
- S. Shanthi, S. Saradha, J.A. Smitha, N. Prasath, H. Anandakumar, An efficient automatic brain tumor classification using optimized hybrid deep neural network, International Journal of Intelligent Networks, Volume 3,2022,Pages 188-196,ISSN 2666-6030. [CrossRef]
- Amaliah Faradibah, Dewi Widyawati, A Ulfah Tenripada Syahar, & Sitti Rahmah Jabir. (2023). Comparison analysis of random forest classifier, support vector machine, and artificial neural network performance in Multiclass brain tumor classification. Indonesian Journal of Data and Science, 4(2), 54-63. [CrossRef]
- Güler, M., & Namlı, E. (2024). Brain tumor detection with deep learning methods’ classifier optimization using medical images. Applied Sciences, 14(2), 642. [CrossRef]
- Waleed A. Mahmoud Al-Jawher, Sarah H. Awad,A proposed brain tumor detection algorithm using Multi wavelet Transform (MWT),Materials Today: Proceedings,Volume 65, Part 5,2022,Pages 2731-2737,ISSN 2214-7853. [CrossRef]
- A. Srinivasa Reddy, Effective CNN-MSO method for brain tumor detection and segmentation, Materials Today: Proceedings,Volume 57, Part 5,2022,Pages 1969-1974,ISSN 2214-7853. [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S., Liu, Y., Mirjalili, V., & Dzhulgakov, D. (2022). Machine learning with PyTorch and scikit-learn: Develop machine learning and deep learning models with Python. Packt Publishing.
- Abraham, A., Pedregosa, F., Eickenberg, M., Gervais, P., Mueller, A., Kossaifi, J., Gramfort, A., Thirion, B., & Varoquaux, G. (2014). Machine learning for neuroimaging with scikit-learn. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 8. [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S., Liu, Y., Mirjalili, V., & Dzhulgakov, D. (2022). Machine learning with PyTorch and scikit-learn: Develop machine learning and deep learning models with Python. Packt Publishing.
- Dalal, N., & Triggs, B. (n.d.). Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'05). [CrossRef]
- OpenCV: Cv::HOGDescriptor Struct reference. (n.d.). OpenCV documentation index. https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/d5/d33/structcv_1_1HOGDescriptor.
- Ahonen, T., Hadid, A., & Pietikainen, M. (2006). Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(12), 2037-2041. [CrossRef]
- OpenCV: Histograms - 1: Find, plot, analyze !!! (n.d.). OpenCV documentation index. https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/d1/db7/tutorial_py_histogram_begins.html Local binary pattern for texture classification — skimage 0.23.2 documentation. (n.d.). scikit-image: Image processing in Python — scikit-image. Retrieved May 6, 2024, from https://scikitimage.org/docs/stable/auto_examples/features_detection/plot_local_binary_pattern.html.
- Sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split. (n.d.). scikit-learn. Retrieved May 6, 2024, from https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split.html.
- Breiman, L. (2001). Random Forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5-32.
- Hastie, T. , Tibshirani, R., & Friedman, J. (2009). The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction (2nd Edition). Springer.
- Géron, A. (2019). Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow (2nd Edition).
- Schapire, R. E. , & Freund, Y. (2012). Boosting: Foundations and Algorithms. MIT Press.
- Goodfellow, I. , Bengio, Y., & Courville, A. (2016). Deep Learning. MIT Press.
- Arakeri, M.P.; Reddy, G.R.M. Computeraided diagnosis system for tissue characterization of brain tumor on magnetic resonance images. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 9, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Du, S.; Ji, G.; Yan, J.; Phillips, P. Feed-forward neural network optimized by hybridization of PSOand ABC for abnormal brain detection. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2015, 25, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z., He, Q., Yang, J., & Luo, M. (2022). A supervised ML applied classification model for brain tumors MRI. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 13. [CrossRef]
- Rinesh, S. , Maheswari, K., Arthi, B., Sherubha, P., Vijay, A., Sridhar, S., Rajendran, T., Waji, Yosef Asrat, Investigations on Brain Tumor Classification Using Hybrid Machine Learning Algorithms, Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2022, 2761847, 9 pages, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Alaraimi, S. , Naimi, I. A., Manic, S., Hinai, N. A., & Shukaili, S. A. (2024). Enhancing brain tumor assessment: A comprehensive approach using computerized diagnostic tool and advanced MRI techniques. Procedia Computer Science. [CrossRef]
- Uvaneshwari M, Baskar M. Computer-Aided Diagnosis Model Using Machine Learning for Brain Tumor Detection and Classification n.d. [CrossRef]
- J.C.M. dos Santos, G.A. Carrijo, C. de Fátima dos Santos Cardoso, et al., Fundus image quality enhancement for blood vessel detection via a neural network using CLAHE and Wiener filter, Res. Biomed. Eng. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Shilaskar, T. Mahajan, S. Bhatlawande, S. Chaudhari, R. Mahajan and K. Junnare, "Machine Learning based Brain Tumor Detection and Classification using HOG Feature Descriptor," 2023 International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Smart Systems (ICSCSS), Coimbatore, India, 2023, pp. 67-75. [CrossRef]
- Guerroudji, M. A. , Hadjadj, Z., Lichouri, M., Amara, K., & Zenati, N. (2023). Efficient Machine Learning-based Approach for Brain Tumor Detection Using the CAD System. IETE Journal of Research. [CrossRef]
- Joo, B. , Ahn, S. S., Park, J., & Kim, H. S. (2022). Fully automated radiomics-based machine learning models for multiclass classification of single brain tumors: Glioblastoma, lymphoma, and metastasis. WFNOS 2022 Abstract Book. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. M. , Barua, P., Rahman, M., Ahammed, T., Akter, L., & Uddin, J. (2023). Transfer learning architectures with fine-tuning for brain tumor classification using magnetic resonance imaging. Healthcare Analytics. [CrossRef]
- Hamd, Z. Y. , Osman, E. G., Alorainy, A. I., Alqahtani, A. F., Alshammari, N. R., Bajamal, O., Alruwaili, S. H., Almohsen, S. S., Almusallam, R. I., & Khandaker, M. U. (2024). The role of machine learning in detecting primary brain tumors in Saudi pediatric patients through MRI images. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences. [CrossRef]
- Raghuwanshi, S., Sukhad, A., Rasool, A., Meena, V. K., Jadhav, A., & Shivakarthik, K. (2024). Early detection of brain tumor from MRI images using different machine learning techniques. Procedia Computer Science, 235, 3094-3104. [CrossRef]
| Methods | PCA Feature Extraction | Hog Feature Extraction | LBP Feature Extraction | |||||||||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | TP | TN | FP | FN | TP | TN | FP | FN | |
| RF | 333 | 4 | 1 | 447 | 319 | 18 | 0 | 448 | 325 | 12 | 2 | 446 |
| LDA | 285 | 52 | 58 | 390 | 289 | 48 | 91 | 357 | 282 | 55 | 66 | 382 |
| XGBoost | 336 | 1 | 1 | 447 | 329 | 8 | 0 | 448 | 331 | 6 | 2 | 446 |
| Adaboost | 330 | 7 | 2 | 446 | 319 | 18 | 2 | 446 | 326 | 11 | 7 | 441 |
| ANN | 328 | 9 | 2 | 446 | 330 | 7 | 0 | 448 | 332 | 5 | 2 | 446 |
| Ref | Dataset | Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tseng et al.[27] | 250 MRI Images | XGBoost, Naive Bayes, ID3 | 97% (XGBoost) |
| Zhengyu et al.[54] | REMBRANDT | Decision Tree (DT),SVM, KNN and NN | 95.9% (NN) |
| Rinesh et al.[55] | Kaggle | k-NN, DNN,PSO, LSVM, and DCNN | 95.30 %(DNN) |
| Saleh et al.[56] | BRATS 2016 | SVM, ANFIS, k-NN, Random Forest, Adaboost, CDT | 95 % (CDT) |
| Uvaneshwari et al.[57] | Not Mentioned | TDC-MOML (XG-Boost) | 97.83% (XGBoost) |
| Santos et al.[58] | Kaggle | RF, KNN, SVM, XGBoost, CatBoost, Extra Trees, Naive Bayes | 98.00 % (Extra Trees) |
| Shilaskar et al.[59] | Not Mentioned | SVM, Gradient Boost, KNN, XG Boost, and LR | 92.02%(XGBoost) |
| Guerroudji et al.[60] | Not Mentioned | Bayesian network SVM, MLP, KNN, RF, DT, XGBoost, LGBM, Gaussian Process, and RBF SVM. | 98%( Bayesian network) |
| Joo et al.[61] | 538 cases (300 glioblastomas, 73 lymphomas, and 165 metastases) | LASSO, Adaboost, and SVM with linear kernal | 76.3%( ensemble classifier) |
| Islam et al.[62] | figshare, SARTAJ,Br35H | InceptionV3, VGG19, DenseNet121, and MobileNet. | 99.60%(MobileNet) |
| Hamd et al.[63] | 6435 MR images | Gradient boosting, LR, Random Forest and ANN | 98.7%(ANN) |
| Raghuwanshi et al.[64] | BRATS | KNN,LR, VGG19, Inception V3 | 95.43%( Inception V3) |
| This Work | Kaggle | RF, XGBoost, AdaBoost, LDA, ANN | 99.3 %(RF) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





