Submitted:
05 December 2024
Posted:
06 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Supplements
2.4. VO2max
2.5. Muscle-Damaging Exercise Protocol
2.6. Muscle Soreness
2.7. Muscle Function Measures
2.7.1. Counter Movement Jump
2.7.2. Isometric Midthigh Pull
2.7.3. MVIC
2.8. Running Economy
2.9. Blood-Borne Biomarkers
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
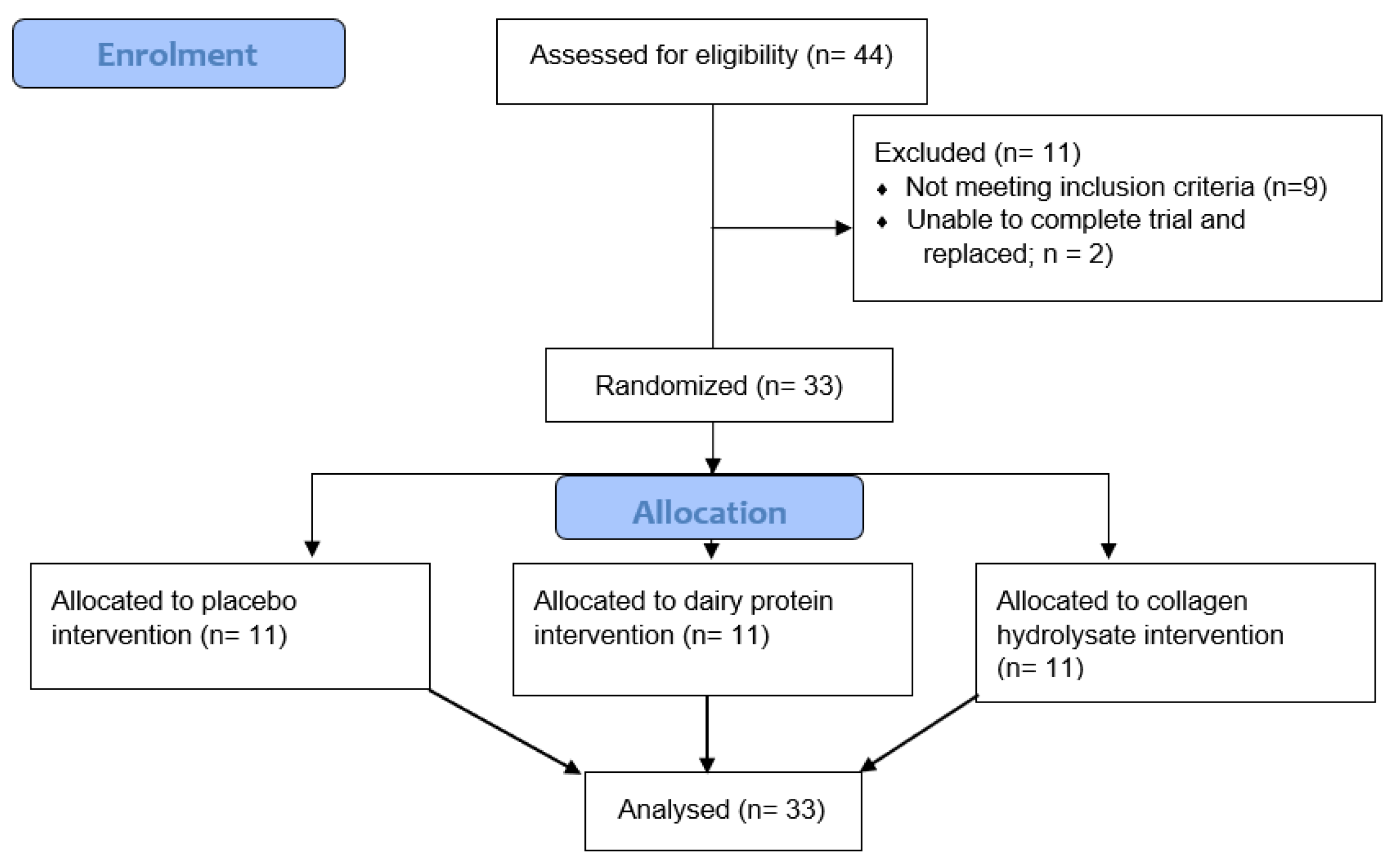
3.2. Muscle Soreness
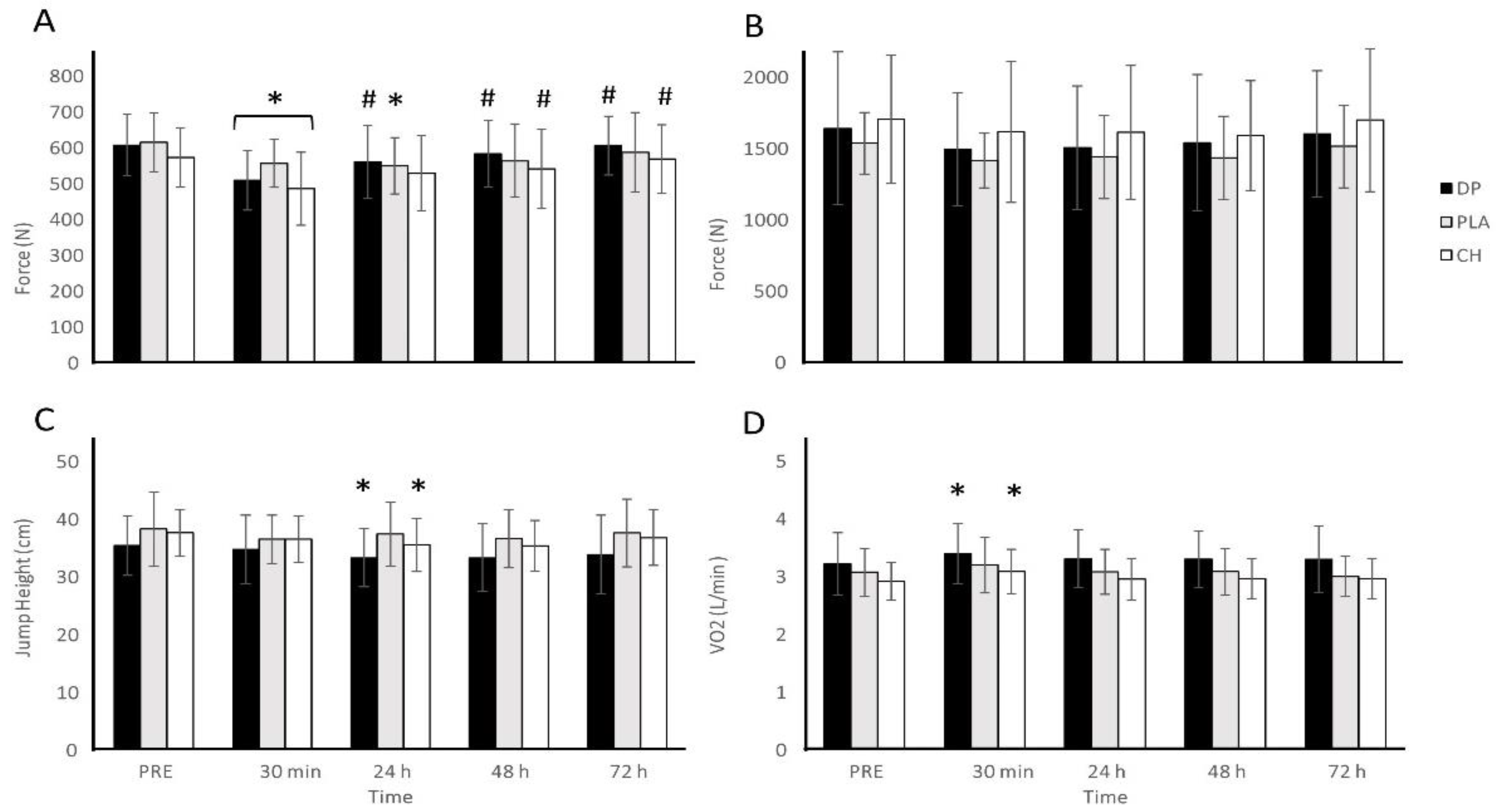
3.3. Muscle Function
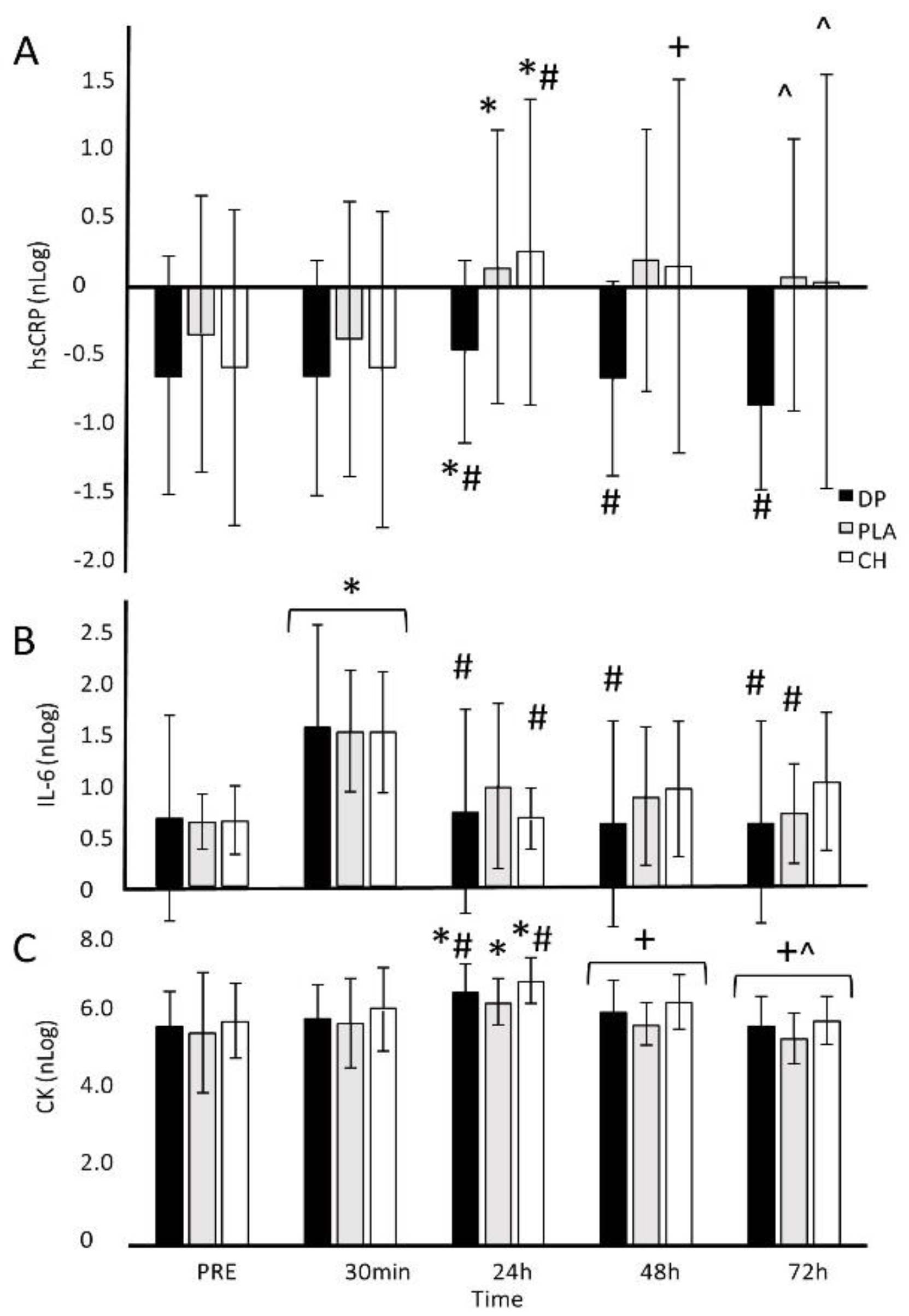
3.4. Blood-Borne Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Owens DJ, Twist C, Cobley JN, Howatson G, Close GL. Exercise-induced muscle damage: What is it, what causes it and what are the nutritional solutions? European Journal of Sport Science. 2019;19(1):71-85.
- Bongiovanni T, Genovesi F, Nemmer M, Carling C, Alberti G, Howatson G. Nutritional interventions for reducing the signs and symptoms of exercise-induced muscle damage and accelerate recovery in athletes: current knowledge, practical application and future perspectives. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2020;120:1965-96. [CrossRef]
- Hody S, Croisier J-L, Bury T, Rogister B, Leprince P. Eccentric muscle contractions: risks and benefits. Frontiers in Physiology. 2019;10:442082. [CrossRef]
- Tesarz J, Schuster AK, Hartmann M, Gerhardt A, Eich W. Pain perception in athletes compared to normally active controls: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Pain. 2012;153(6):1253-62. [CrossRef]
- O’Connor E, Mündel T, Barnes MJ. Nutritional compounds to improve post-exercise recovery. Nutrients. 2022;14(23):5069. [CrossRef]
- Robberechts R, Poffé C, Ampe N, Bogaerts S, Hespel P. Partly substituting whey for collagen peptide supplementation improves neither indices of muscle damage nor recovery of functional capacity during eccentric exercise training in fit males. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. 2023;1(aop):1-10. [CrossRef]
- West DW, Abou Sawan S, Mazzulla M, Williamson E, Moore DR. Whey protein supplementation enhances whole body protein metabolism and performance recovery after resistance exercise: a double-blind crossover study. Nutrients. 2017;9(7):735. [CrossRef]
- avis GF, Jameson TS, Dirks ML, Lee BP, Abdelrahman DR, Murton AJ, et al. Improved recovery from skeletal muscle damage is largely unexplained by myofibrillar protein synthesis or inflammatory and regenerative gene expression pathways. American Journal of Physiology. 2021;320(2):E291-E305. [CrossRef]
- Brown MA, Stevenson EJ, Howatson G. Whey protein hydrolysate supplementation accelerates recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage in females. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2018;43(4):324-30. [CrossRef]
- Buckley JD, Thomson RL, Coates AM, Howe PR, DeNichilo MO, Rowney MK. Supplementation with a whey protein hydrolysate enhances recovery of muscle force-generating capacity following eccentric exercise. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport. 2010;13(1):178-81. [CrossRef]
- Cooke MB, Rybalka E, Stathis CG, Cribb PJ, Hayes A. Whey protein isolate attenuates strength decline after eccentrically-induced muscle damage in healthy individuals. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2010;7:1-9. [CrossRef]
- Gee TI, Woolrich TJ, Smith MF. Effectiveness of whey protein hydrolysate and milk-based formulated drinks on recovery of strength and power following acute resistance exercise. Journal of Human Kinetics. 2019;68(1):193-202. [CrossRef]
- Nieman DC, Zwetsloot KA, Simonson AJ, Hoyle AT, Wang X, Nelson HK, et al. Effects of whey and pea protein supplementation on post-eccentric exercise muscle damage: a randomized trial. Nutrients. 2020;12(8):2382. [CrossRef]
- Ormsbee MJ, Saracino PG, Morrissey MC, Donaldson J, Rentería LI, McKune AJ. Pre-sleep protein supplementation after an acute bout of evening resistance exercise does not improve next day performance or recovery in resistance trained men. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2022;19(1):164-78. [CrossRef]
- Saracino PG, Saylor HE, Hanna BR, Hickner RC, Kim J-S, Ormsbee MJ. Effects of pre-sleep whey vs. plant-based protein consumption on muscle recovery following damaging morning exercise. Nutrients. 2020;12(7):2049. [CrossRef]
- Pearson AG, Hind K, Macnaughton LS. The impact of dietary protein supplementation on recovery from resistance exercise-induced muscle damage: A systematic review with meta-analysis. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2023;77(8):767-83. [CrossRef]
- Poore J, Nemecek T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science. 2018;360(6392):987-92. [CrossRef]
- Patel V, Aggarwal K, Dhawan A, Singh B, Shah P, Sawhney A, et al., editors. Protein supplementation: the double-edged sword. Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings; 2024: Taylor & Francis.
- Kurek MA, Onopiuk A, Pogorzelska-Nowicka E, Szpicer A, Zalewska M, Półtorak A. Novel protein sources for applications in meat-alternative products—Insight and challenges. Foods. 2022;11(7):957. [CrossRef]
- Holwerda AM, van Loon LJ. The impact of collagen protein ingestion on musculoskeletal connective tissue remodeling: a narrative review. Nutrition Reviews. 2022;80(6):1497-514.
- Skov K, Oxfeldt M, Thøgersen R, Hansen M, Bertram HC. Enzymatic hydrolysis of a collagen hydrolysate enhances postprandial absorption rate—a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2019;11(5):1064. [CrossRef]
- Taga Y, Kusubata M, Ogawa-Goto K, Hattori S. Stable isotope-labeled collagen: a novel and versatile tool for quantitative collagen analyses using mass spectrometry. Journal of Proteome Research. 2014;13(8):3671-8. [CrossRef]
- Abe M, Hoshi T, Tajima A. Characteristics of transmural potential changes associated with the proton-peptide co-transport in toad small intestine. Journal of Physiology. 1987;394(1):481-99. [CrossRef]
- Sato K, Jimi S, Kusubata M. Generation of bioactive prolyl-hydroxyproline (Pro-Hyp) by oral administration of collagen hydrolysate and degradation of endogenous collagen. International Journal of Food Science & Technology. 2019;54(6):1976-80. [CrossRef]
- Sato K, Asai TT, Jimi S. Collagen-derived di-peptide, prolylhydroxyproline (Pro-Hyp): a new low molecular weight growth-initiating factor for specific fibroblasts associated with wound healing. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2020;8:548975. [CrossRef]
- Tenberg S, Nosaka K, Wilke J. The relationship between acute exercise-induced changes in extramuscular connective tissue thickness and delayed onset muscle soreness in healthy participants: a randomized controlled crossover trial. Sports Medicine-Open. 2022;8(1):57. [CrossRef]
- Prowting JL, Bemben D, Black CD, Day EA, Campbell JA. Effects of collagen peptides on recovery following eccentric exercise in resistance-trained males—A pilot study. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism. 2020;31(1):32-9. [CrossRef]
- Wilke J, Behringer M. Is “delayed onset muscle soreness” a false friend? The potential implication of the fascial connective tissue in post-exercise discomfort. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021;22(17):9482. [CrossRef]
- Clifford T, Ventress M, Allerton DM, Stansfield S, Tang JC, Fraser WD, et al. The effects of collagen peptides on muscle damage, inflammation and bone turnover following exercise: a randomized, controlled trial. Amino Acids. 2019;51:691-704. [CrossRef]
- Lopez HL, Ziegenfuss TN, Park J. Evaluation of the effects of biocell collagen, a novel cartilage extract, on connective tissue support and functional recovery from exercise. Integrative Medicine: A Clinician's Journal. 2015;14(3):30.
- Aussieker T, Hilkens L, Holwerda AM, Fuchs CJ, Houben LH, Senden JM, et al. Collagen protein ingestion during recovery from exercise does not increase muscle connective protein synthesis rates. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2023;55(10):1792. [CrossRef]
- Bayles MP. ACSM's exercise testing and prescription: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2023.
- Apweiler E, Wallace D, Stansfield S, Allerton DM, Brown MA, Stevenson EJ, et al. Pre-bed casein protein supplementation does not enhance acute functional recovery in physically active males and females when exercise is performed in the morning. Sports. 2018;7(1):5. [CrossRef]
- Betts JA, Toone RJ, Stokes KA, Thompson D. Systemic indices of skeletal muscle damage and recovery of muscle function after exercise: effect of combined carbohydrate–protein ingestion. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2009;34(4):773-84. [CrossRef]
- Cockburn E, Hayes PR, French DN, Stevenson E, St Clair Gibson A. Acute milk-based protein–CHO supplementation attenuates exercise-induced muscle damage. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2008;33(4):775-83. [CrossRef]
- Cockburn E, Stevenson E, Hayes PR, Robson-Ansley P, Howatson G. Effect of milk-based carbohydrate-protein supplement timing on the attenuation of exercise-induced muscle damage. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2010;35(3):270-7. [CrossRef]
- Davies RW, Bass JJ, Carson BP, Norton C, Kozior M, Wilkinson DJ, et al. The effect of whey protein supplementation on myofibrillar protein synthesis and performance recovery in resistance-trained men. Nutrients. 2020;12(3):845. [CrossRef]
- Hilkens L, Boerboom M, van Schijndel N, Bons J, van Loon LJ, van Dijk J-W. Bone turnover following high-impact exercise is not modulated by collagen supplementation in young men: A randomized cross-over trial. Bone. 2023;170:116705.
- Hirose N, Sato M, Yanagisawa O, Fukubayashi T. Milk peptide intake may decrease muscle damage after eccentric exercise. International Journal of Sport and Health Science. 2013;11:20-8. [CrossRef]
- White JP, Wilson JM, Austin KG, Greer BK, St John N, Panton LB. Effect of carbohydrate-protein supplement timing on acute exercise-induced muscle damage. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2008;5:1-7. [CrossRef]
- Markus I, Constantini K, Hoffman J, Bartolomei S, Gepner Y. Exercise-induced muscle damage: Mechanism, assessment and nutritional factors to accelerate recovery. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2021;121:969-92. [CrossRef]
- Rindom E, Nielsen M, Kececi K, Jensen M, Vissing K, Farup J. Effect of protein quality on recovery after intense resistance training. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2016;116:2225-36. [CrossRef]
- raganidis D, Chondrogianni N, Chatzinikolaou A, Terzis G, Karagounis LG, Sovatzidis A, et al. Protein ingestion preserves proteasome activity during intense aseptic inflammation and facilitates skeletal muscle recovery in humans. British Journal of Nutrition. 2017;118(3):189-200. [CrossRef]
- Bischof K, Stafilidis S, Bundschuh L, Oesser S, Baca A, König D. Reduction in systemic muscle stress markers after exercise-induced muscle damage following concurrent training and supplementation with specific collagen peptides–a randomized controlled trial. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2024;11:1384112. [CrossRef]
- Etheridge T, Philp A, Watt PW. A single protein meal increases recovery of muscle function following an acute eccentric exercise bout. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2008;33(3):483-8. [CrossRef]
- Hyldahl RD, Chen TC, Nosaka K. Mechanisms and mediators of the skeletal muscle repeated bout effect. Exercise and sport sciences reviews. 2017;45(1):24-33. [CrossRef]
- Bontemps B, Vercruyssen F, Gruet M, Louis J. Downhill running: what are the effects and how can we adapt? A narrative review. Sports Medicine. 2020;50(12):2083-110. [CrossRef]
- Chen TC, Nosaka K, Tu J-H. Changes in running economy following downhill running. Journal of Sports Sciences. 2007;25(1):55-63. [CrossRef]
- Chrismas BC, Taylor L, Siegler JC, Midgley AW. A reduction in maximal incremental exercise test duration 48 h post downhill run is associated with muscle damage derived exercise induced pain. Frontiers in Physiology. 2017;8:135. [CrossRef]
- Haff GG, Stone M, O'Bryant HS, Harman E, Dinan C, Johnson R, et al. Force-time dependent characteristics of dynamic and isometric muscle actions. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 1997;11(4):269-72.
- Beckham G, Mizuguchi S, Carter C, Sato K, Ramsey M, Lamont H, et al. Relationships of isometric mid-thigh pull variables to weightlifting performance. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness. 2013;53(5):573-81.
- Barnes MJ, Mündel T, Stannard SR. The effects of acute alcohol consumption and eccentric muscle damage on neuromuscular function. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2012;37(1):63-71. [CrossRef]
- Kuwaba K, Kusubata M, Taga Y, Igarashi H, Nakazato K, Mizuno K. Dietary collagen peptides alleviate exercise-induced muscle soreness in healthy middle-aged males: a randomized double-blinded crossover clinical trial. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2023;20(1):2206392. [CrossRef]
- Warren GL, Lowe DA, Armstrong RB. Measurement tools used in the study of eccentric contraction-induced injury. Sports medicine. 1999;27:43-59. [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio P, Maffulli N, Limongelli FM. Creatine kinase monitoring in sport medicine. British medical bulletin. 2007;81(1):209-30. [CrossRef]
- Paulsen G, Ramer Mikkelsen U, Raastad T, Peake JM. Leucocytes, cytokines and satellite cells: what role do they play in muscle damage and regeneration following eccentric exercise? Exercise immunology review. 2012;18.
- Nash D, Hughes MG, Butcher L, Aicheler R, Smith P, Cullen T, et al. IL-6 signaling in acute exercise and chronic training: Potential consequences for health and athletic performance. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports. 2023;33(1):4-19. [CrossRef]
- León-López A, Fuentes-Jiménez L, Hernández-Fuentes AD, Campos-Montiel RG, Aguirre-Álvarez G. Hydrolysed collagen from sheepskins as a source of functional peptides with antioxidant activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019;20(16):3931. [CrossRef]
- Burnley ECD, Olson AN, Sharp RL, Baier SM, Alekel DL. Impact of protein supplements on muscle recovery after exercise-induced muscle soreness. Journal of Exercise Science and Fitness. 2010;8(2):89-96. [CrossRef]
- Dahlstrom EC. Impact of protein supplementation on muscle recovery after exercise-induced muscle soreness: Iowa State University; 2007.
- Eddens L, Browne S, Stevenson EJ, Sanderson B, van Someren K, Howatson G. The efficacy of protein supplementation during recovery from muscle-damaging concurrent exercise. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism. 2017;42(7):716-24. [CrossRef]
- Ten Haaf DS, Flipsen MA, Horstman AM, Timmerman H, Steegers MA, De Groot LC, et al. The effect of protein supplementation versus carbohydrate supplementation on muscle damage markers and soreness following a 15-km road race: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2021;13(3):858. [CrossRef]
- Pasiakos SM, Lieberman HR, McLellan TM. Effects of protein supplements on muscle damage, soreness and recovery of muscle function and physical performance: a systematic review. Sports Medicine. 2014;44:655-70. [CrossRef]
- Oertzen-Hagemann V, Kirmse M, Eggers B, Pfeiffer K, Marcus K, de Marées M, et al. Effects of 12 weeks of hypertrophy resistance exercise training combined with collagen peptide supplementation on the skeletal muscle proteome in recreationally active men. Nutrients. 2019;11(5):1072. [CrossRef]
- Oikawa SY, Kamal MJ, Webb EK, McGlory C, Baker SK, Phillips SM. Whey protein but not collagen peptides stimulate acute and longer-term muscle protein synthesis with and without resistance exercise in healthy older women: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2020;111(3):708-18. [CrossRef]
- Shaw G, Lee-Barthel A, Ross ML, Wang B, Baar K. Vitamin C–enriched gelatin supplementation before intermittent activity augments collagen synthesis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2017;105(1):136-43. [CrossRef]
- Kviatkovsky SA, Hickner RC, Ormsbee MJ. Collagen peptide supplementation for pain and function: is it effective? Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care. 2022;25(6):401-6.
- Starkoff BE, Lenz EK, Mattern CO, Too D, Byrne HK. Protein Supplementation Does Not Enhance Recovery from Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. Journal of Exercise Physiology Online. 2020;23(1).
- Børsheim E, Cree MG, Tipton KD, Elliott TA, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR. Effect of carbohydrate intake on net muscle protein synthesis during recovery from resistance exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2004;96(2):674-8. [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld BJ, Aragon AA. How much protein can the body use in a single meal for muscle-building? Implications for daily protein distribution. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 2018;15:1-6. [CrossRef]
- Deane CS, Bass JJ, Crossland H, Phillips BE, Atherton PJ. Animal, plant, collagen and blended dietary proteins: effects on musculoskeletal outcomes. Nutrients. 2020;12(9):2670. [CrossRef]
| DP (n = 11) |
PLA (n = 11) |
CH (n = 11) |
P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 26.2 ± 7.2 | 23.5 ± 6.1 | 26.6 ± 6.4 | 0.468 |
| Height (cm) | 181.1 ± 11.4 | 182.0 ± 7.6 | 176.0 ± 5.3 | 0.220 |
| Weight (kg) | 87.0 ± 12.6 | 82.3 ± 13.1 | 82.6 ± 9.0 | 0.581 |
| VO2max (ml/kg/min) | 45.8 ± 5.2 | 46.3 ± 5.3 | 45.2 ± 5.7 | 0.896 |
| Protein (g/day)* | 117.9 ± 55.8 | 103.7 ± 38.3 | 102.8 ± 38.4 | 0.697 |
| Protein (g/day/kg BM)* | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 0.905 |
| Energy (MJ/day)* | 10.8 ± 5.6 | 8.3 ± 2.1 | 10.0 ± 2.7 | 0.353 |
| Variable | DP | PLA | CH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serving size (g)Energy (kJ) | 35.8 1000 |
53.2 1000 |
26.9 1000 |
| Protein (g) | 25.0 | 0.0 | 25.0 |
| CHO (g) | 32.9 | 58.8 | 33.8 |
| Fat (g) | 0.42 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





