Submitted:
04 December 2024
Posted:
04 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Ecosystem Health Assessment (EHA) is essential for comprehensively improving the ecological environment and socio-economic conditions, thereby promoting sustainable development of a specific area. Most previous EHA studies have focused on urbanized regions, paying insufficient attention to rural areas with urban enclaves and national natural parks. This study employed the Basic-Pressure-State-Response methodological approach. The composition of indicators (35) encompassed both spatiotemporal data and socio-economic information. The Random Forest algorithm was used on the Google Earth Engine platform to classify and evaluate changes in Land Use and Land Cover (LULC). In addition, weighting coefficients were calculated, and driving factors were subsequently identified. The analysis revealed that the rural administrative divisions in the central part of Zerendy district, where the city of Kokshetau is situated, exhibited a relatively low level of Ecosystem Health (EH). The southwestern rural administrative divisions of the studied district, where the national nature park and the reserve territories are located, exhibited a higher level of EH. Other rural administrative divisions located in the eastern parts of the district generally exhibited a moderate level of EH. Interested managers can use the results of our assessment to implement adequate measures aimed at improving the health of the Zerendy district ecosystem.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
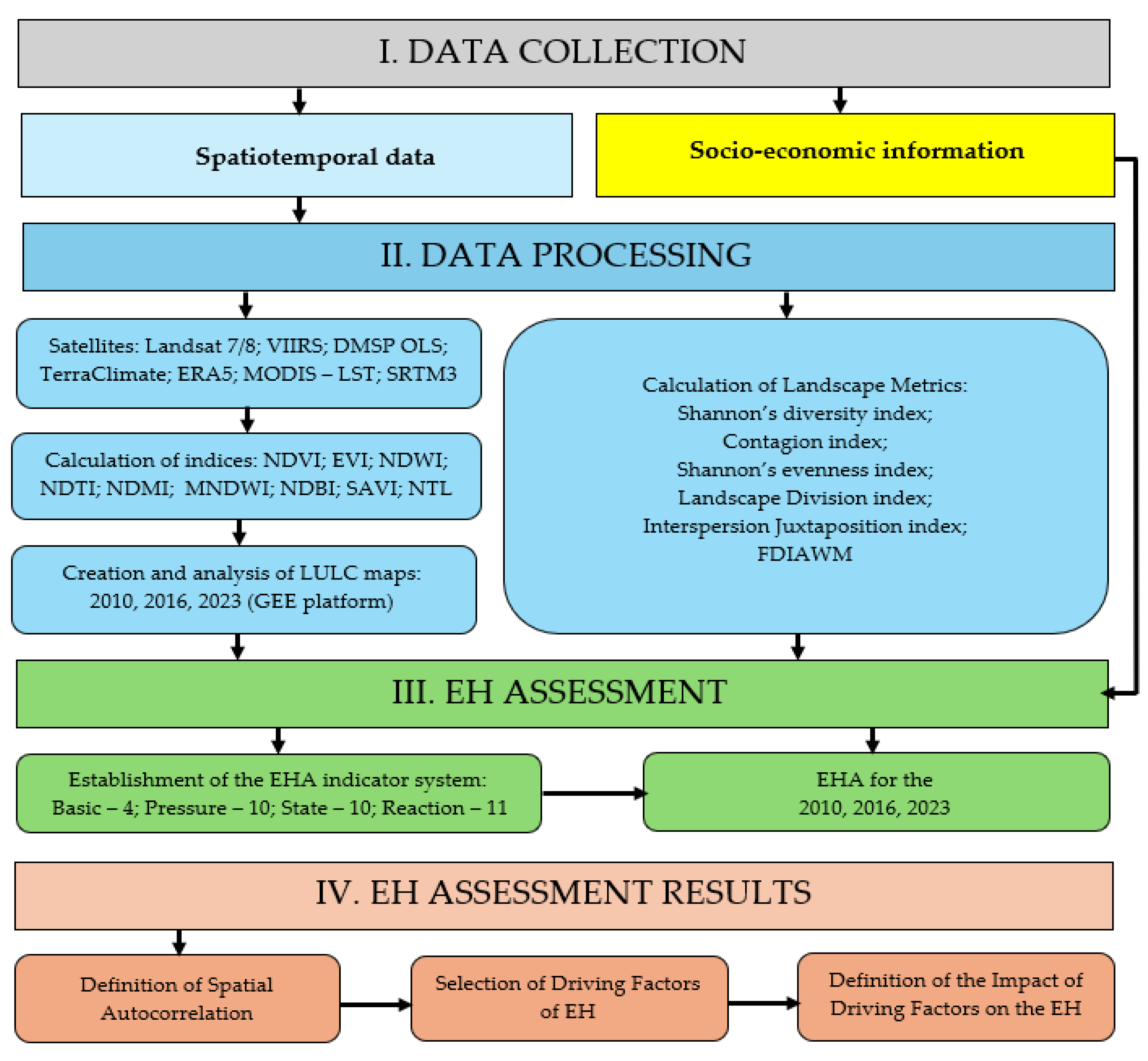
2. Materials and Methods
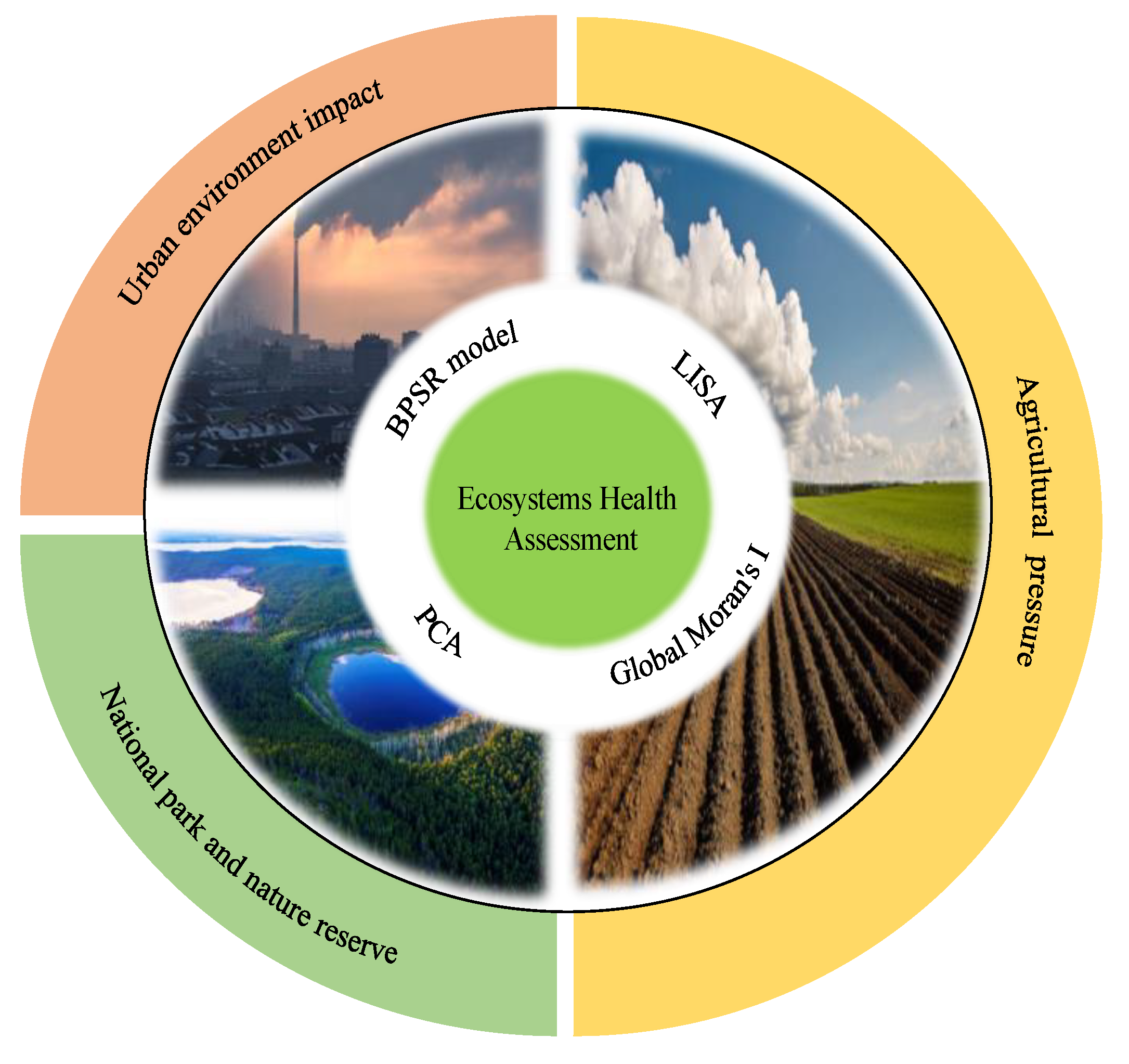
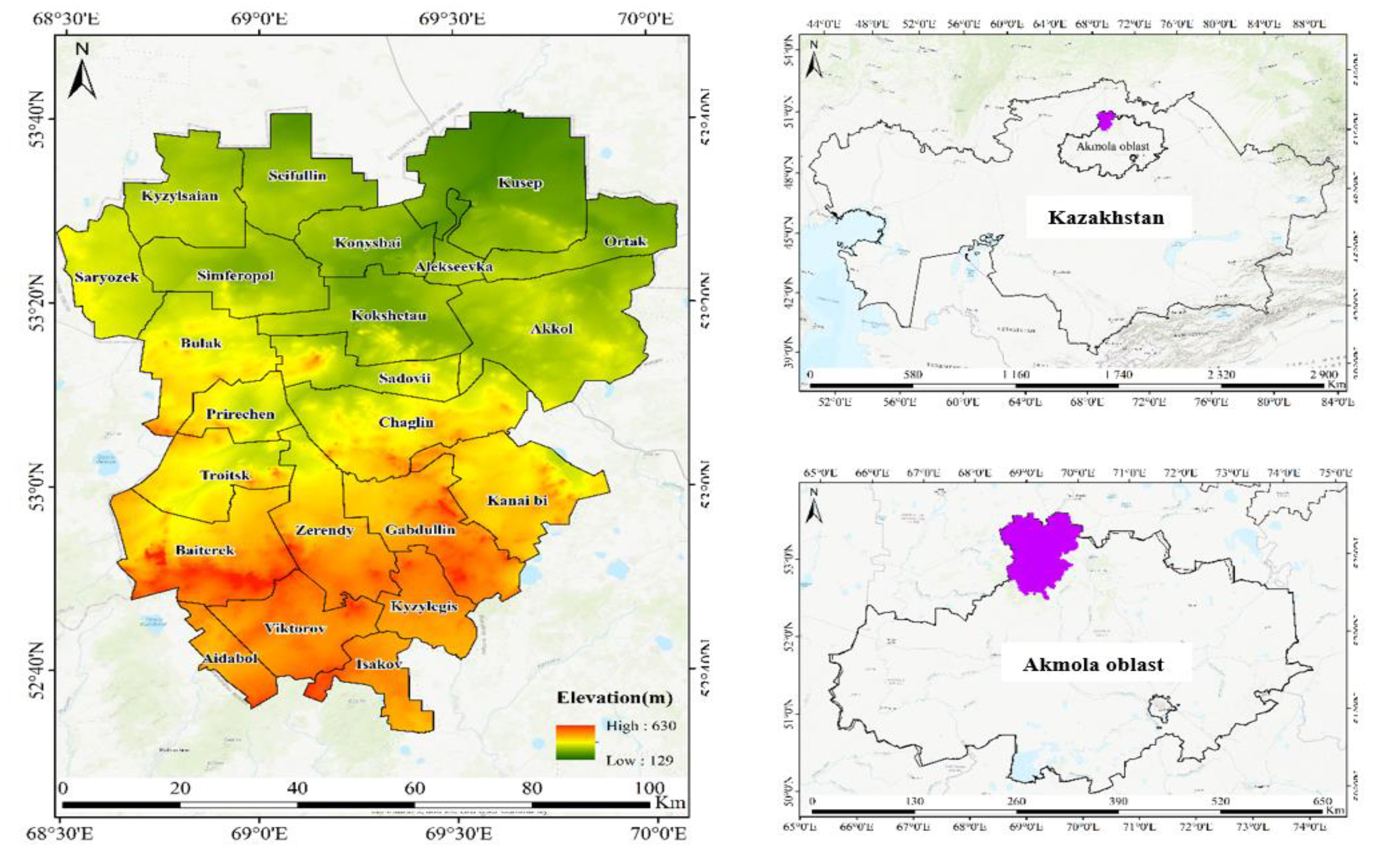
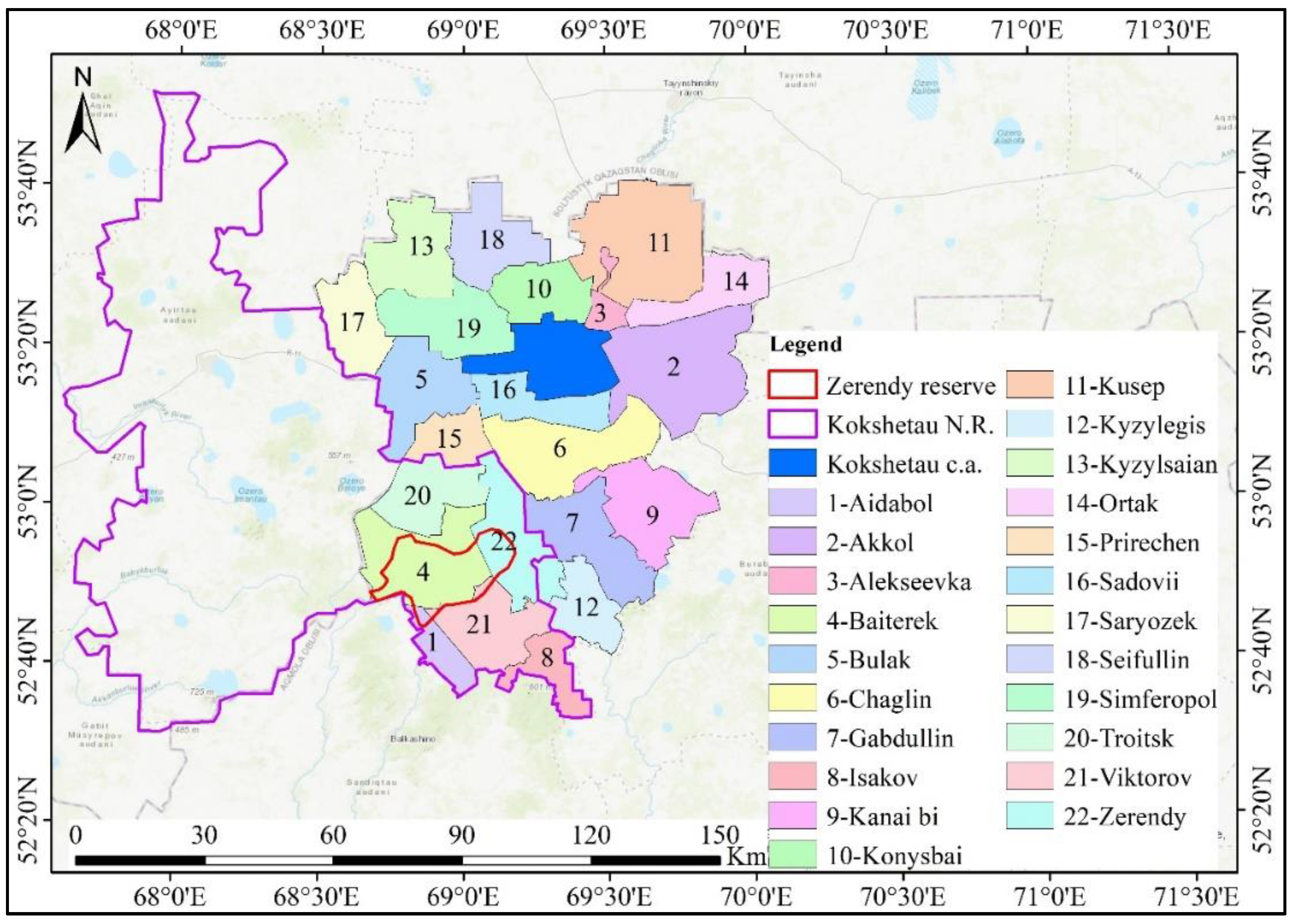
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Data Collection
2.2.2. Data Processing
- 1)
- >1) Cropland - CLD,
- 2)
- >2) Pasture - PTE,
- 3)
- >3) Forest - FET,
- 4)
- >4) Water Bodies -WBS,
- 5)
- >5) Urban Land – ULD
2.2.3. Ecosystem Health Assessment
2.2.4. Analysis Methods and Spatial Correlation Indicators for EH
Moran’s I Index
Application of Principal Component Analysis
3. Results
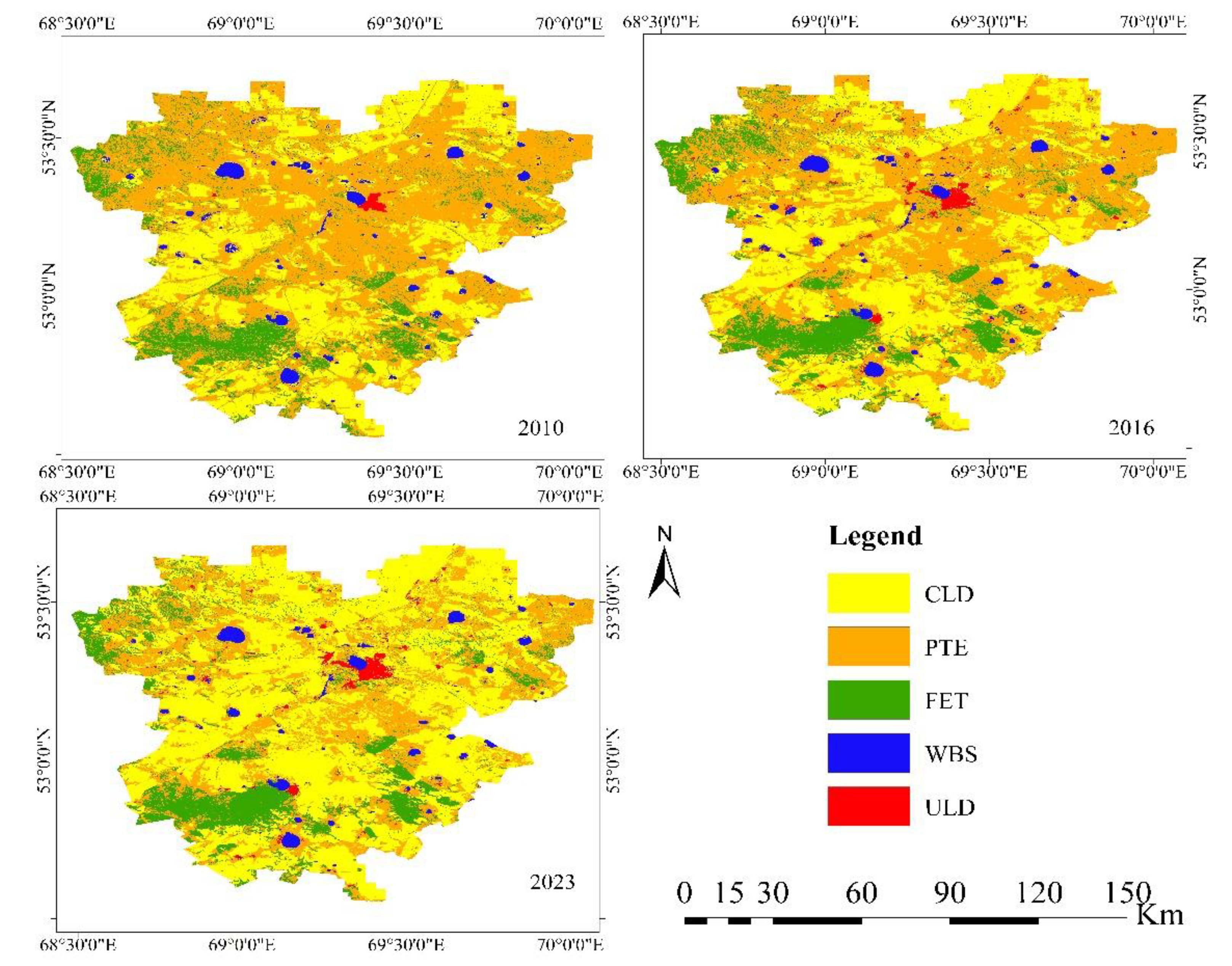
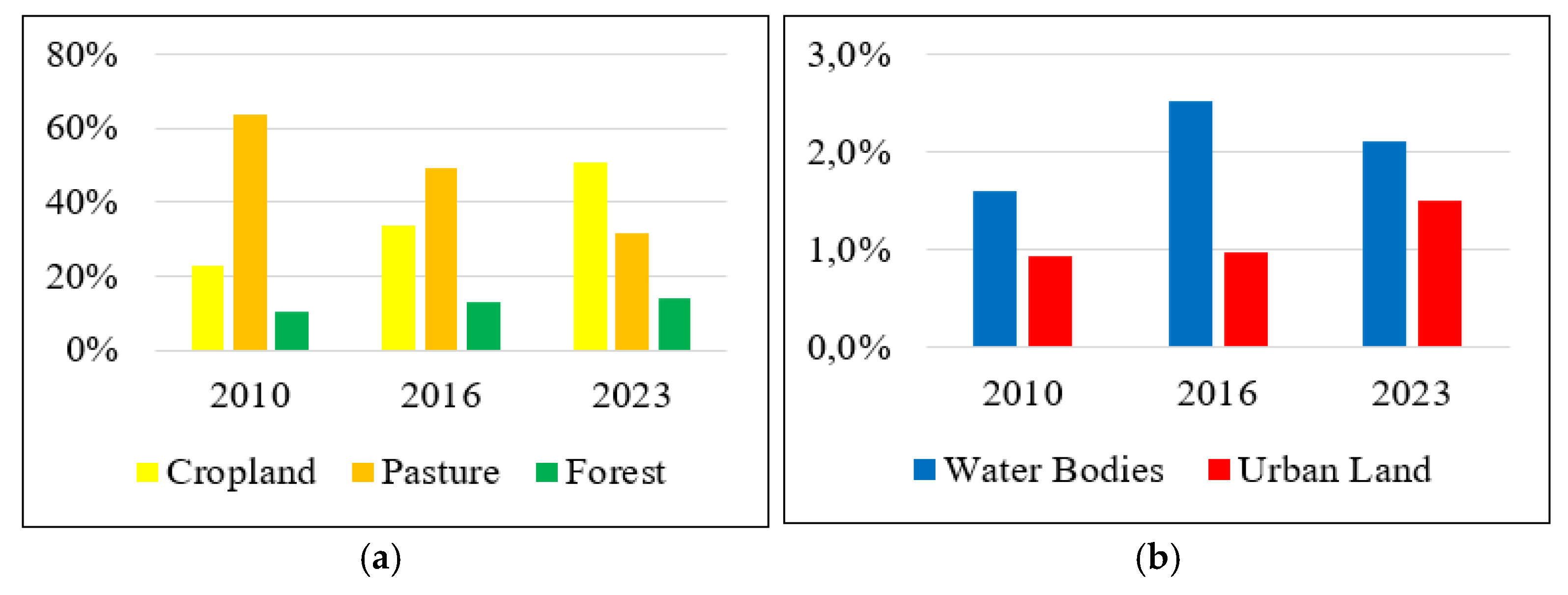
3.1. Analysis of Land Use and Land Cover Dynamics in the Zerendy District
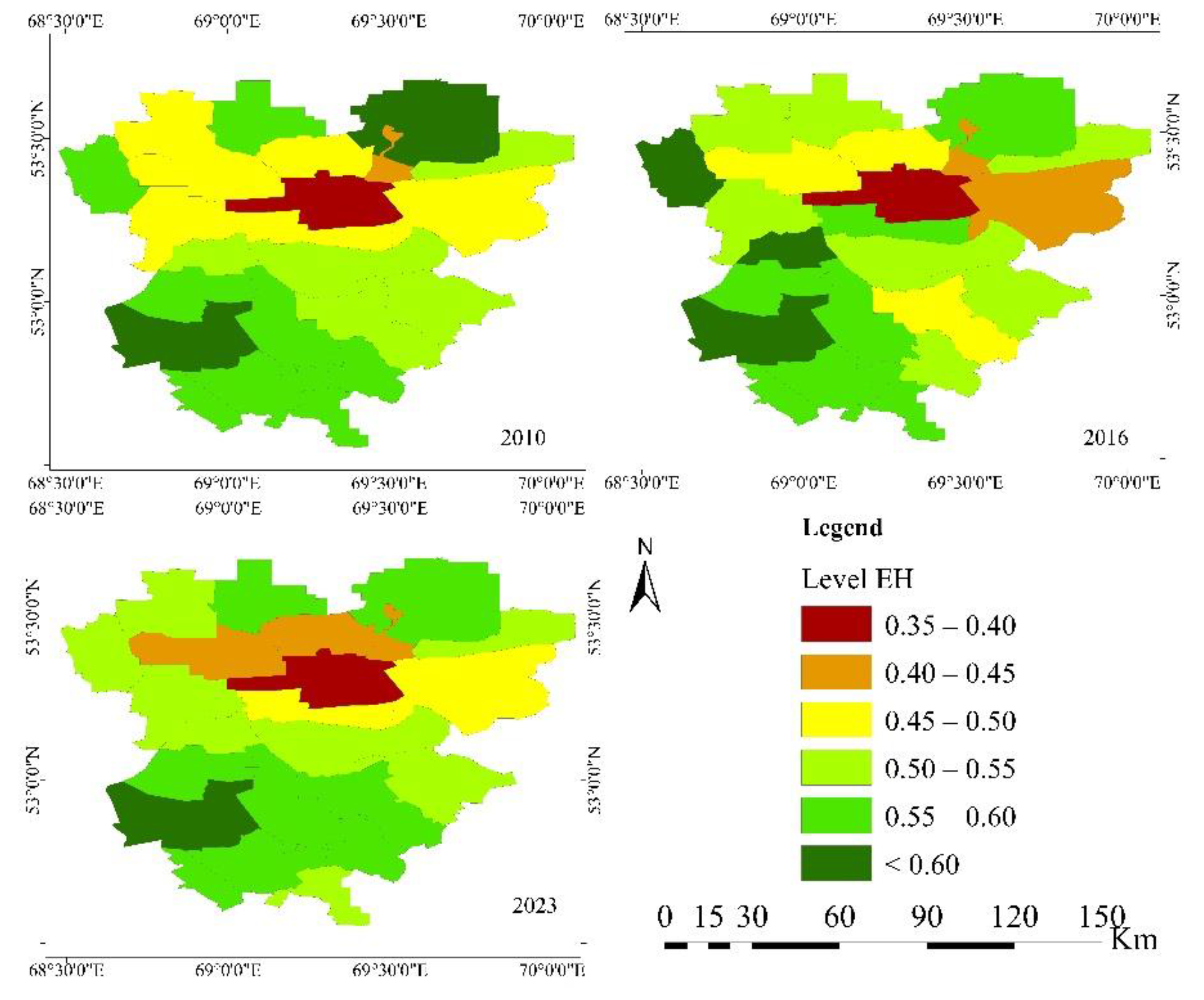
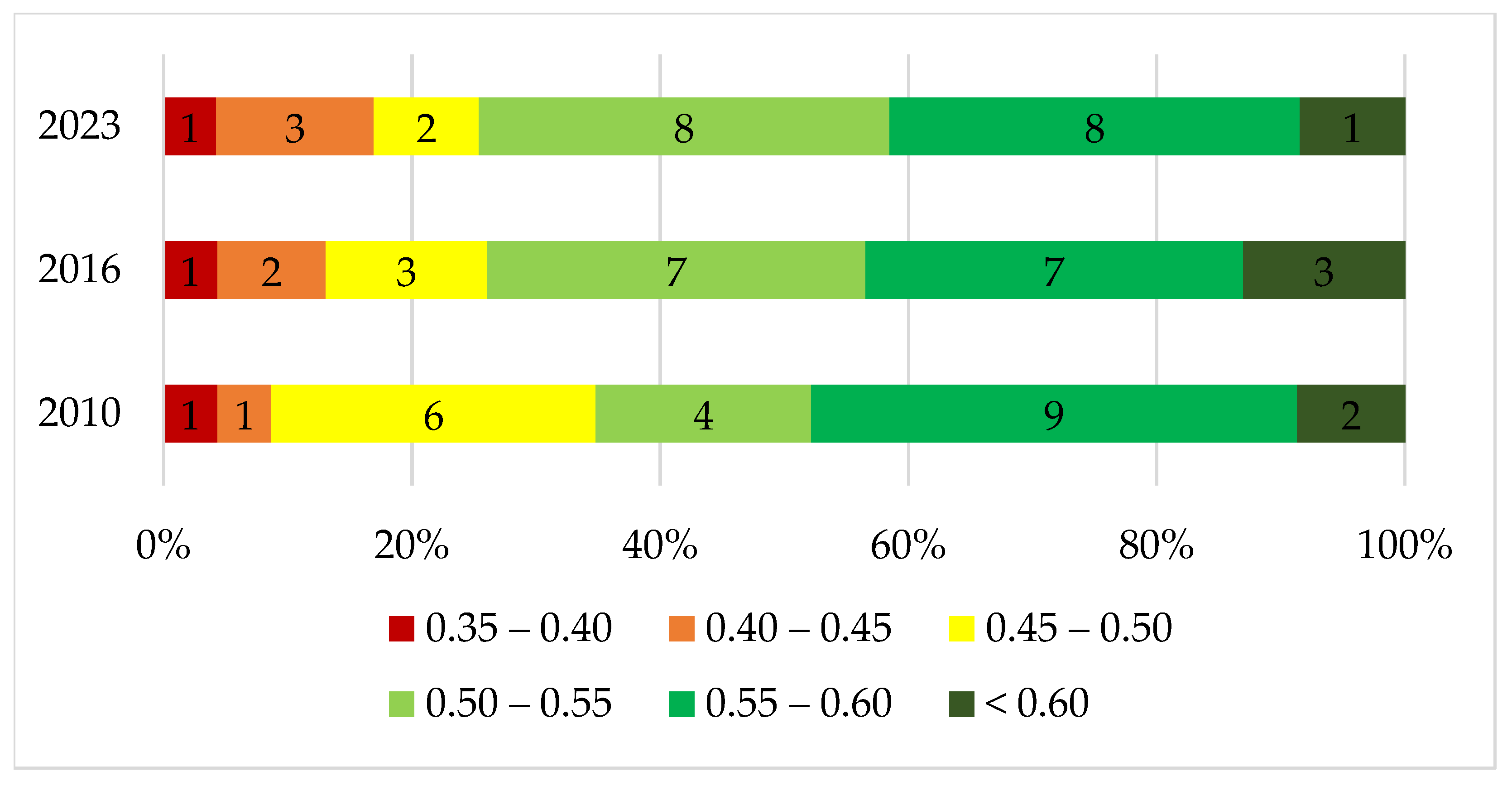
3.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in Ecosystem Health in the Zerendy District
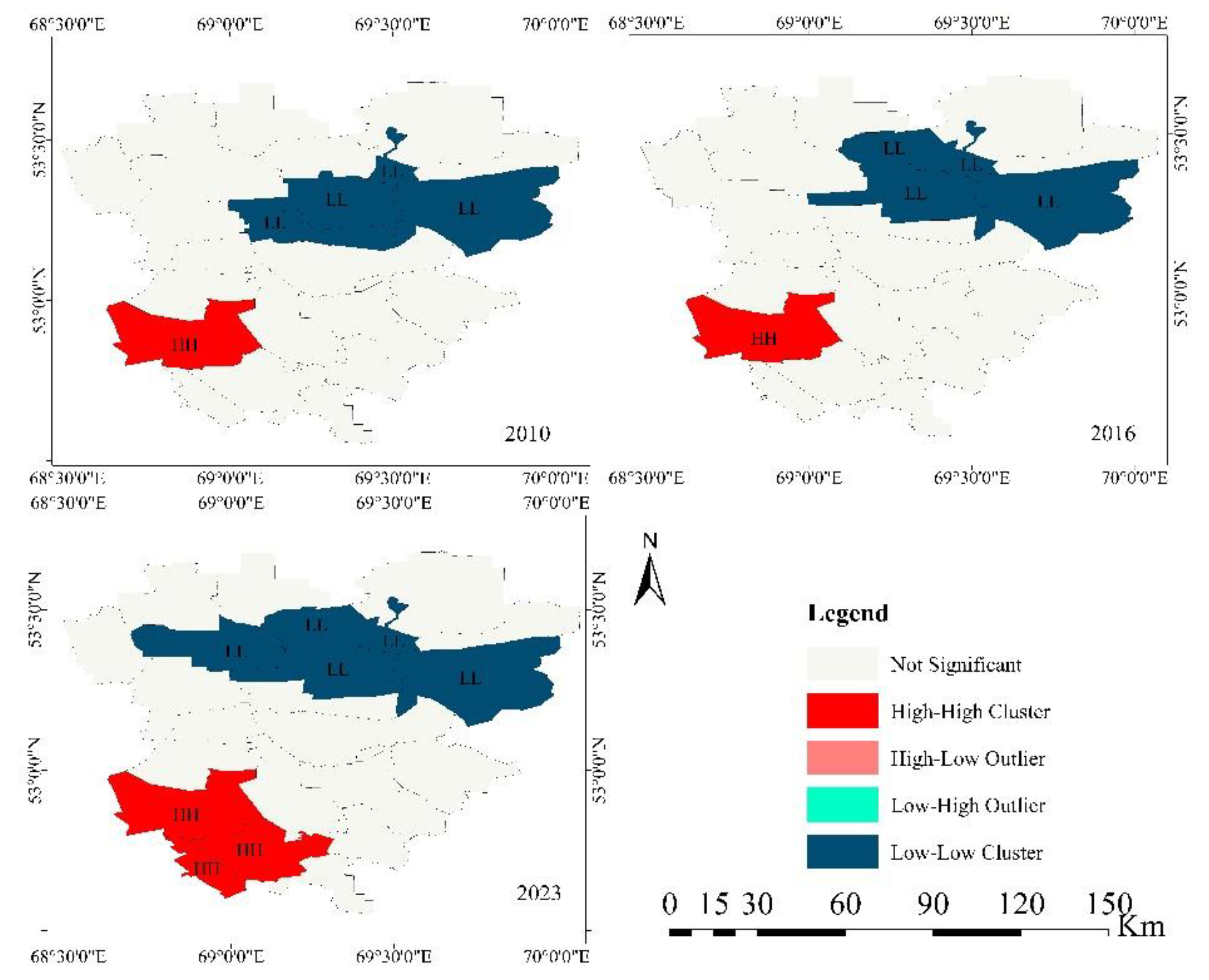
3.3. Spatial Dependence of Ecosystem Health of Zerendy District
3.4. Identifying the Role of Individual Factors in Ecosystem Health of Zerendy District Based on Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Ecosystem Health Assessment Model
4.2. Selection of Index System and Its Comparison with Previous Studies
4.3. Spatial and Temporal Changes in Ecosystem Health in the Zerendy District
4.4. Policy Implications
4.5. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sachs, J.D.; Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.; Drumm, E. Sustainable Development Report 2023: Implementing the SDG Stimulus, SDSN, United States of America. 2023. Available online: https://coilink.org/20.500.12592/0tpj28 (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Godden, L. The Principle of Sustainability: Transforming Law and Governance, Osgoode Hall Law Journal, 2009, 47, 807.
- Redclift, M. Sustainable development and global environmental change: Implications of a changing agenda. Global Environmental Change 1992, 2, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED). Our Common Future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development. Available online: http://www.worldinbalance.net/intagreements/1987-brundtland.php (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Zanotti, L.; Ma, Z.; Johnson, J.L.; Johnson, D.R.; Yu, D.J.; Burnham, M.; Carothers, C. Sustainability, resilience, adaptation, and transformation: tensions and plural approaches. Ecology and Society, 2020, 25(3):4. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Zanotti, L.; Ma, Z.; Yu, D.J.; Johnson, D.R.; Kirkham, A.; Carothers, C. Interplays of sustainability, resilience, adaptation and transformation. In Handbook of Sustainability and Social Science Research; Leal Filho, W., Marans, R.W., Callewaert, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roostaie, S.; Nawari, N.; Kibert, C.J. Sustainability and resilience: A review of definitions, relationships, and their integration into a combined building assessment framework. Building and Environment, 2019, 154, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmqvist, T.; Andersson, E.; Frantzeskaki, N.; et al. Sustainability and resilience for transformation in the urban century. Nature Sustainability 2019, 2, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupancic, N. Systematic Literature Review: Inter-Relatedness of Innovation, Resilience and Sustainability - Major, Emerging Themes and Future Research Directions. Circular Economy and Sustainability, 2023, 3, 1157–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Till, E.R.; Serger, S.S.; Axelsson, T.; Andersson, M. Transformation and resilience in times of change: A historical perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2024, 206, 123558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-López, C.; Martín-Blanco, C.; De la Torre Bayo, J.J.; Rubio-Rivera, B.; Zamorano, M. Analyzing the Scientific Evolution of the Sustainable Development Goals. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Ma, X.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L. Progress in Ecosystem Health Research and Future Prospects. Sustainability, 2022, 14, 15814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisitza, A.; Wolbring, G. Sustainability within the Academic EcoHealth Literature: Existing Engagement and Future Prospects. Sustainability, 2016, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Guo, X. Remote Sensing of Ecosystem Health: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Sensors, 2014, 14, 21117–21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shao, X.; Wu, M. A Review on Ecosystem Health Research: A Visualization Based on CiteSpace. Sustainability, 2019, 11, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hao, S. Ecosystem Health Assessment at County-Scale Using the Pressure-State-Response Framework on the Loess Plateau, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.H.; Zou, X.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, P.T.; Zhamangulova, N.; Xu, X.G.; Zhao, Y.F. Integrated ecosystem health assessment based on eco-exergy theory: A case study of the Jiangsu coastal area. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 48, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, Ch.; Su, W.; Ma, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, G. Spatiotemporal evaluation of alpine pastoral ecosystem health by using the Basic-Pressure-State-Response Framework: A case study of the Gannan region, northwest China. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 129, 108000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, Ch.; Jiang, Q.; Cheng, Z. Ecosystem health assessment based on AHP-DPSR model and impacts of climate change and human disturbances: A case study of Liaohe River Basin in Jilin Province, China. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 142, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; DeFries, R.; Dietz, T.; Mooney, H.A.; Polasky, S.; Reid, W.V.; Scholes, R.J. Millennium Ecosystem Assessment: Research Needs. Science, 2006, 314, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J.; Costanza, R.; McMichael, A.J. Assessing ecosystem health. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 1998, 13(10), 397-402. [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J.; Gaudet, C.; Karr, J.R.; Baron, J.S.; Bohlen, C.; Jackson, W.; Jones, B.; Naiman, R.J.; Norton, B.; Pollock, M.M. Evaluating landscape health: integrating societal goals and biophysical processes. Journal of Environmental Management, 1998, 53(1), 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J. Sustainability science: an ecohealth perspective. Sustainability Science, 2007, 2, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, B.; Ganguli, N.; Choi, E.; Tofighi, M.; van Loon, G.W.; Orbinski, J. Exploring the nexus: Comparing and aligning Planetary Health, One Health, and EcoHealth. Global Transitions, 2024, 6, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boevskiy, D.; Thomas, L. Ecosystem Health: A Systematic Review and Conceptual Framework. Academy of Management Proceedings, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, T.; Sun, M.; Hao, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y. Development of Ecosystem Health Assessment (EHA) and Application Method: A Review. Sustainability, 2021, 13, 11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Online Source: IDRC. Available online: https://idrc-crdi.ca/en/about-idrc (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Online Source: International Association for Ecology and Health. Available online: https://www.omicsonline.org/societies/international-association-for-ecology-and-health/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Online Source: EcoHealth Alliance. Available online: https://www.ecohealthalliance.org/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Costanza, R.; Mageau, M.T. What is a healthy ecosystem? Aquatic Ecology, 1999, 33, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R. Toward an Operational Definition of Ecosystem Health. In Ecosystem Health: New Goals for Environmental Management; Karr, J.R., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 239–269. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Huang, X.; Ye, X.; Pan, Z.; Wang, H.; Luo, B.; Liu, D.; Hu, X. County Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on the VORS Model: A Case Study of 183 Counties in Sichuan Province, China. Sustainability, 2022, 14, 11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gan, X.; Feng, Y.; et al. A new framework for assessing ecosystem health with consideration of the sustainable supply of ecosystem services. Landscape Ecology, 2024, 39, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Shifaw, E.; Deng, Ch.; Sha, J.; Li, X.; Hanchiso, T.; Yang, W. Remote sensing-based assessment of ecosystem health by optimizing the vigor-organization-resilience model: A case study in Fuzhou City, China. Ecological Informatics, 2022, 72, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.D.; Tang, J.C.; Yu, D.H.; Song, Z.W.; Wang, P.G. Ecosystem health assessment: A PSR analysis combining AHP and FCE methods for Jiaozhou Bay, China. Ocean Coastal Management, 2019, 168, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Alves, I.; Subtil, R.; de Melo, J.J. Environmental Performance Policy Indicators for the Public Sector: The Case of the Defence Sector. https://core.ac.uk/reader/195352765?utm_source=linkout. Journal of Environmental Management, 2007, 82, 410–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, F.; Ledwich, G.; Xue, Y. Pressure-State-Response-Based Method for Evaluating Social Benefits from Smart Grid Development. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273405437_Pressure_State_Response-Based_Method_for_Evaluating_Social_Benefits_from_Smart_Grid_Development. Journal of Energy Engineering, 2015, 141, 04014020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qu, A.Y.; Wang, P.F.; Hou, J. Estuarine ecosystem health assessment based on the DPSIR framework: A case of the Yangtze Estuary, China. https://bioone.org/journals/journal-of-coastal-research/volume-65/issue-sp2/SI65-209.1/Estuarine-ecosystem-health-assessment-based-on-the-DPSIR-framework/10.2112/SI65-209.1.short. Journal of Coastal Research, 2013, 165, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, S. DPSIR = A Problem Structuring Method? An Exploration from the "Imagine" Approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 2012, 222, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.J.; Atkins, J.P.; Burdon, D.; Elliott, M. A Problem Structuring Method for Ecosystem-Based Management: The DPSIR Modelling Process. European Journal of Operational Research, 2013, 227, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wu, R.; Ma, Q.Y.; Yang, J. Ecosystem health assessment based on DPSIRM framework and health distance model in Nansi Lake, China. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279307774_Ecosystem_health_assessment_based_on_DPSIRM_framework_and_health_distance_model_in_Nansi_Lake_China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2016, 30, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwell, M.A.; Gentile, J.H.; McKinney, L.D.; Tunnell, J.W. Jr.; Dennison, W.C.; Kelsey, R.H.; Stanzel, K.M.; Stunz, G.W.; Withers, K. Conceptual Framework for Assessing Ecosystem Health. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 2019, 15, 544–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, B.; Faisal, K.; Veitch, B. Linkage-Based Frameworks for Sustainability Assessment: Making a Case for Driving Force-Pressure-State-Exposure-Effect-Action (DPSEEA) Frameworks. Sustainability, 2009, 1, 103–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Dong, Z.C.; Ren, L.; Ren, J.; Guan, X.K.; Zhong, D.Y. Using an improved interval technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution to assess river ecosystem health. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 2019, 21, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qu, A.Y.; Wang, P.F.; Hou, J.; Ao, Y.H. Development of a Multi-Index Ecosystem Health Assessment Model Using Back-Propagation Neural Network Approach: A Case Study of the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal, 2017, 16, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Wu, Y.X.; Liu, X.G. Regional ecosystem health assessment using the GA-BPANN model: A case study of Yunnan Province, China. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 2022, 8, 2084458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ding, X.; Shu, Y.; Abbas, Z. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem health in the Liuxi River Basin, Guangzhou, China. Ecological Informatics, 2022, 72, 101842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Huang, H.; Yao, P.; Zheng, P. Assessment Methods of Small Watershed Ecosystem Health. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2021, 30, 1749–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Zheng, Z.; Pan, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y. An Integrated Method for Assessing the Urban Ecosystem Health of Rapid Urbanized Areas in China based on SFPHD Framework. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 121, 107071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapport, D.J. What constitutes ecosystem health? https://www.sci-hub.ru/10.1353/pbm.1990.0004. Perspectives in Biology and Medicine, 1989, 33, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lin, A.; Zhao, Z.; Zou, L.; Sun, C. Assessment of Urban Ecosystem Health Based on Entropy Weight Extension Decision Model in Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability, 2016, 8, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.R.; Yang, Z.F.; Chen, B. Set pair analysis for urban ecosystem health assessment. https://www.academia.edu/9194457/Set_pair_analysis_for_urban_ecosystem_health_assessment. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2009, 14, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Xie, H.; Yue, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S. Urban ecosystem health evaluation for typical Chinese cities along the Belt and Road. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 101, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Fath, B.D.; Yang, Z. Urban ecosystem health assessment: A review. Science of The Total Environment, 2010, 408(12), 2425–2434. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Deng, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J. An integrated approach for assessing the urban ecosystem health of megacities in China. Cities, 2016, 53, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan Manshadi, Z.; Parivar, P.; Sotoudeh, A.; Ahad Sotoudeh, A.; Ali Morovati Sharifabadi. Exploring the spatio-temporal dynamics of life support system capacity of urban regions based on ecosystem health assessment (the case of Tehran, Iran). Environmental Development and Sustainability, 2024, 26, 10311–10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Das, A.; Mandal, A. Ecosystem Health (EH) assessment of a rapidly urbanizing metropolitan city region of eastern India – A study on Kolkata Metropolitan Area. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2020, 204, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieweger, A.; Döring, Th.F. Assessing health in agriculture – towards a common research framework for soils, plants, animals, humans and ecosystems. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, A.; Viswanathan, Ch. Scientific health assessments in agriculture ecosystems - Towards a common research framework for plants and human. In Scientific Health Assessments in Agriculture Ecosystems—Towards a Common Research Framework for Plants and Human, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Huang, J.; Dong, J. Assessment of rural ecosystem health and type classification in Jiangsu Province, China. The Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 615(5), 1218–1228. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, H. Rural Ecosystem Health Assessment and Spatial Divergence—A Case Study of Rural Areas around Qinling Mountain, Shaanxi Province, China. Sustainability, 2024, 16, 6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, A.; Wardiatno, Y.; Widyastuti, R.; Wulandari, D.; Natali, M. Development of ecosystem health index in rural areas of Java Island: Preliminary results. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 622, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Ch.; Tan, S.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, W. An approach to assess spatio-temporal heterogeneity of rural ecosystem health: A case study in Chongqing mountainous area, China. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 136, 108644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Xiao, C.; Ma, T.; Sang, W. Ecological Health Assessment of Chinese National Parks Based on Landscape Pattern: A Case Study in Shennongjia National Park. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18, 11487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Gu, Z. Study on the ecological health evaluation of a geopark based on DPSIR conceptual model – illustrated by the Qianjiang Xiaonanhai National Geopark of China. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 2018, 16(4), 3839–3859. [CrossRef]
- On Specially Protected Natural Areas. The Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 7 July 2006 № 175. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/eng/docs/Z060000175_ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Zerendy District: Geographical Description and Administrative Division. Available online: https://716.kz/raiony/16-zerendinskii-raion.html (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- On Administrative-Territorial Division of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated 8 December 1993, № 2572-XII. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/eng/docs/Z930004200_ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Administrative-territorial units of the Republic of Kazakhstan at the beginning of 2023. Available online: https://stat.gov.kz/ru/industries/economy/national-/publications/6381/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Ayagan, B.G. Kazakhstan. National Encyclopedia; Kazakh Encyclopedias Limited Liability Partnership: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Map of the Zherendy district with administrative divisions. Available online: https://yandex.kz/images/search?img_url=http%3A%2F%2Fturakmo.kz.akmol.kz%2Fstorage%2F18.03.2019%2F6.JPG&lr=163&pos=0&rpt=simage&source=serp&text=%D0%97%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B9%20%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%B9%D0%BE%D0%BD%20%D0%B3%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%86%D0%B0 (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Akmola Region. Available online: https://ru.ruwiki.ru/wiki/%D0%90%D0%BA%D0%BC%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B0%D1%8F_%D0%BE%D0%B1%D0%BB%D0%B0%D1%81%D1%82%D1%8C (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Zherendy district. Available online: https://map.akmol.kz/content/zerenda (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Earth Engine Data Catalog. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1979, 8(2), 127–150. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A. A feedback-based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(2), 457–465. [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Cheng, T.; Zhou, M.; Li, D.; Yao, X.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Improved estimation of rice aboveground biomass combining textural and spectral analysis of UAV imagery. Precision Agriculture, 2019, 20, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Sader, S.A. Comparison of Time Series Tasseled Cap Wetness and the Normalized Difference Moisture Index in Detecting Forest Disturbances. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 94, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalized difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DMSP OLS: Nighttime Lights Time Series Version 4, Defense Meteorological Program Operational Linescan System. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/NOAA_DMSP-OLS_NIGHTTIME_LIGHTS (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Alipbeki, O.; Mussaif, G.; Alipbekova, C.; Kapassova, A.; Grossul, P.; Aliyev, M.; Mineyev, N. Untangling the Integral Impact of Land Use Change, Economic, Ecological and Social Factors on the Development of Burabay District (Kazakhstan) during the Period 1999–2021. Sustainability, 2023, 15, 7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipbeki, O.; Alipbekova, C.; Mussaif, G.; Grossul, P.; Zhenshan, D.; Muzyka, O.; Turekeldiyeva, R.; Yelubayev, D.; Rakhimov, D.; Kupidura, P.; Aliken, E. Analysis and Prediction of Land Use/Land Cover Changes in Korgalzhyn District, Kazakhstan. Agronomy, 2024, 14, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, J. Regional ecosystem health response to rural land use change: A case study in Lijiang City, China. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 72, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps. Available online: https://www.fragstats.org/index.php/downloads (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Das, S.; Pradhan, B.; Shit, P.K.; Alamri, A.M. Assessment of Wetland Ecosystem Health Using the Pressure–State–Response (PSR) Model: A Case Study of Mursidabad District of West Bengal (India). Sustainability, 2020, 12, 5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushanjiang, A.; Zhang, F.; Tan, M.L. Spatial-temporal characteristics of ecosystem health in Central Asia. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2021, 105, 102635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, N.; Wang, X. Construction and Evaluation of the Integrated Perception Ecological Environment Indicator (IPEEI) Based on the DPSIR Framework for Smart Sustainable Cities. Sustainability, 2020, 12, 7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.H.; Yun, Y.; Sun, J.N. Entropy method for determination of weight of evaluating indicators in fuzzy synthetic evaluation for water quality assessment. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 18(5), 1020–1023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Shao, G. Assessment of Regional Ecosystem Health—A Case Study of the Golden Triangle of Southern Fujian Province, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A. The ESRI Guide to GIS Analysis, Volume 2. ESRI Press, 2005.
- How Spatial Autocorrelation (Global Moran’s I) works. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/tool-reference/spatial-statistics/h-how-spatial-autocorrelation-moran-s-i-spatial-st.htm (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- How Cluster and Outlier Analysis (Anselin Local Moran’s I) works. Available online: https://desktop.arcgis.com/ru/arcmap/latest/tools/spatial-statistics-toolbox/h-how-cluster-and-outlier-analysis-anselin-local-m.htm (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2016, 374. [CrossRef]
- IBM SPSS Statistics. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/products/spss-statistics/regression (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Rapport, D.J.; Regier, H.A.; Hutchinson, T.C. Ecosystem Behavior under Stress. Am. Nat. 1985, 125(5), 617–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissenschaftlicher Beirat der Bundesregierung Globale Umweltveränderungen, WBGU. Available online: https://www.wbgu.de/de/ (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Lu, Q.; Fan, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, W.; Xia, Y.; Yan, B. The Dominant Role of Human Activity Intensity in Spatial Pattern of Ecosystem Health in the Poyang Lake Ecological Economic Zone. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhang, S.; Fu, N.; Zhou, X.; He, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, H. Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on Analysis of a Land Use Database. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 44, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Qiao, Y.; Dong, X.; Ren, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Ye, Q.; Xiao, X. Ecosystem Health Assessment of the Manas River Basin: Application of the CC-PSR Model Improved by Coupling Coordination Degree. Land 2024, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gan, X.; Feng, Y. A New Framework for Assessing Ecosystem Health with Consideration of the Sustainable Supply of Ecosystem Services. Landsc. Ecol. 2024, 39, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Haroon, M.A.; Ahmad, S. Use of Remote Sensing-Based Pressure-State-Response Framework for the Spatial Ecosystem Health Assessment in Langfang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 89395–89414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, A.N.; Janalipour, M.; Hosseini, S.B. Monitoring the Urban Ecosystem Health by Introducing a Spatial Model Based on Pressure-State-Impact-Response Framework (Study Area: Sanandaj City). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Gup, Z. Study on the Ecological Health Evaluation of a Geopark Based on DPSIR Conceptual Model—Illustrated by the Qianjiang Xiaonanhai National Geopark of China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16(4), 3839–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, H. Rural Ecosystem Health Assessment and Spatial Divergence—A Case Study of Rural Areas around Qinling Mountain, Shaanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhou, G.; Yu, S. Study on Rural Ecological Resilience Measurement and Optimization Strategy Based on PSR—Taking Weiyuan in Gansu Province as an Example. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C. Evolution Process and Obstacle Factors of Ecological Security in Western China, a Case Study of Qinghai Province. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hao, J.Y.; He, W.; Lam, K.C.; Xu, F.L. Spatiotemporal Variations of Aquatic Ecosystem Health Status in Tolo Harbor, Hong Kong from 1986 to 2014. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 100, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R. Ecosystem Health Assessment Based on DPSIRM Framework and Health Distance Model in Nansi Lake, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y. Urbanization’s Impacts on Ecosystem Health Dynamics in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Qing, G.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, S.; Luo, N. Landscape Ecological Security of the Lijiang River Basin in China: Spatiotemporal Evolution and Pattern Optimization. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ren, Y.; Ai, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Ren, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y. Revealing the Spatial Interactions and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services: Enlightenments under Vegetation Restoration. Land 2024, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M. Spatiotemporal Variation in Ecosystem Health and Its Driving Factors in Guizhou Province. Land 2023, 12, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; Xiong, J.; Xu, Z. Spatiotemporal Changes and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Health in the Qinling-Daba Mountains. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data Sets | Date | Bands | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat 7 Collection 2 Tier 1 TOA Reflectance | 2010.05.10 2010.08.07 | B1-B7 | 30 m |
| Landsat 8 Collection 2 Tier 1 TOA Reflectance | 2016.04.25 2016.05.18 2016.06.03 2023.04.04 2023.05.06 2023.08.19 |
B2-B7 | 30 m |
| VIIRS Stray Light Corrected Nighttime | 2016.05.01 2023.06.01 |
avg_rad | 463.83 m |
| DMSP OLS: Nighttime Lights Time Series Version 4 | 2010.05.01 | avg_vis | 927.67 m |
| SRTM 3 | 2010, 2016, 2023 | elevation | 90 m |
| TerraClimate: Monthly Climate | 2010, 2016, 2023 for each month | Pr | 4638.3 m |
| MODIS - LST | 2010, 2016, 2023 for each month | LST_Day_1km | 1000 m |
| ERA5 Monthly Aggregates | 2010, 2016, 2023 for each month | total_precipitation | 27830 m |
| Target layer | Element layer (weight) | № | Indicator layer | Weight | Positive/ Negative | Calculation method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ecosystem Health |
Basic (0.108) | B1 | Average annual temperature | 0.026 | Positive | Processing satellite imagery data | |
| B2 | Average temperature during the growing season | 0.023 | Positive | ||||
| B3 | Average annual precipitation | 0.035 | Positive | ||||
| B4 | Average precipitation during the growing season | 0.025 | Positive | ||||
| Pressure (0.280) | P1 | Population density | 0.043 | Negative | Population/area | ||
| P2 | Share of cropland per capita | 0.026 | Positive | Cropland area/population | |||
| P3 | Share of pasture land per capita | 0.021 | Positive | Pasture land area/population | |||
| P4 | Share of water resources per capita | 0.021 | Positive | Water resource area/population | |||
| P5 | Number of cattle | 0.024 | Negative | Statistical data | |||
| P6 | Built-up area | 0.036 | Negative | LULC maps | |||
| P7 | NDBI | 0.021 | Negative | Processing satellite imagery data | |||
| P8 | Amount of atmospheric emissions | 0.035 | Negative | Statistical data | |||
| P9 | Investments in fixed assets | 0.030 | Negative | Statistical data | |||
| P10 | Volume of industrial services produced | 0.022 | Negative | Statistical data | |||
| State (0.319) | S1 | Area of cropland | 0.023 | Negative | LULC maps | ||
| S2 | Area of pasture land | 0.026 | Positive | LULC maps | |||
| S3 | NDVI | 0.023 | Positive | Processing satellite imagery data | |||
| S4 | NDTI | 0.029 | Positive | ||||
| S5 | SAVI | 0.055 | Positive | ||||
| S6 | MNDWI | 0.022 | Positive | ||||
| S7 | NDMI | 0.044 | Positive | ||||
| S8 | EVI | 0.025 | Positive | ||||
| S9 | NDWI | 0.051 | Positive | ||||
| S10 | Ecosystem Resilience | 0.022 | Positive | ||||
| Reaction (0.293) | R1 | Shannon’s diversity index | 0.053 | Positive | Fragstats 4.2 calculation | ||
| R2 | Contagion index | 0.021 | Negative | ||||
| R3 | Shannon’s evenness index | 0.025 | Positive | ||||
| R4 | Landscape Division Index | 0.024 | Negative | ||||
| R5 | Interspersion Juxtaposition Index | 0.022 | Positive | ||||
| R6 | FDIAWM | 0.024 | Positive | ||||
| R7 | Forest Area | 0.021 | Positive | LULC maps | |||
| R8 | Number of economic entities | 0.026 | Negative | Statistical data | |||
| R9 | Water bodies area | 0.025 | Positive | LULC maps | |||
| R10 | Funding for environmental protection | 0.029 | Positive | Statistical data | |||
| R11 | Funding for waste disposal | 0.022 | Positive | Statistical data | |||
| LULC classes | Resilience | Resistance | EC |
| CLD | 0.30 | 0.60 | 0.51 |
| PTE | 0.50 | 0.70 | 0.64 |
| FET | 0.60 | 1.00 | 0.88 |
| WBS | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.77 |
| ULD | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.27 |
| Year | LULC classes | |||||
| CLD | PTE | FET | WBS | ULD | Total | |
| 2010 | 22.90% | 63.98% | 10.57% | 1.61% | 0.94% | 100.00% |
| 2016 | 33.78% | 49.51% | 13.22% | 2.52% | 0.97% | 100.00% |
| 2023 | 50.62% | 31.57% | 14.19% | 2.12% | 1.50% | 100.00% |
| Division | Level of EH | ||
| 2010 | 2016 | 2023 | |
| Aidabol | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.60 |
| Akkol | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.48 |
| Alekseevka | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.45 |
| Baiterek | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.63 |
| Bulak | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.54 |
| Chaglin | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.54 |
| Gabdullin | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.58 |
| Isakov | 0.58 | 0.56 | 0.54 |
| Kanai Bi | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.55 |
| Kokshetau | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.39 |
| Konysbay | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.42 |
| Kusep | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.57 |
| Kyzylegis | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.59 |
| Kyzylsaian | 0.49 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| Ortak | 0.55 | 0.55 | 0.51 |
| Prirechnoe | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.52 |
| Sadovyi | 0.47 | 0.59 | 0.46 |
| Sarozek | 0.60 | 0.61 | 0.53 |
| Seifullin | 0.58 | 0.54 | 0.56 |
| Simferopol | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.44 |
| Troitsk | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.57 |
| Viktorov | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.59 |
| Zerendy | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.57 |
| Year | Moran’s I Index | Z-score | P-value | Variance | Expected index |
| 2010 | 0.482278 | 4.191658 | 0.000028 | 0.015851 | -0.045455 |
| 2016 | 0.425480 | 3.758993 | 0.000171 | 0.015696 | -0.045455 |
| 2023 | 0.597864 | 5.069564 | 0.000000 | 0.016103 | -0.045455 |
| Variables* | Component F1 | Component F2 |
| Population density per sq. km | 0.995 | -0.037 |
| Cropland per capita | 0.991 | -0.050 |
| Share of built-up area in sq. km | 0.995 | -0.019 |
| Emissions | 0.995 | -0.019 |
| Pasture area | -0.453 | 0.332 |
| NDVI | 0.049 | 0.793 |
| SAVI | -0.043 | 0.855 |
| NDMI | 0.048 | 0.879 |
| EVI | -0.087 | 0.833 |
| NDWI | -0.198 | 0.851 |
| Waste disposal | 0.992 | 0.001 |
| Regression equation | R2 | p |
| 0.724 | p<0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





