Submitted:
29 November 2024
Posted:
02 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
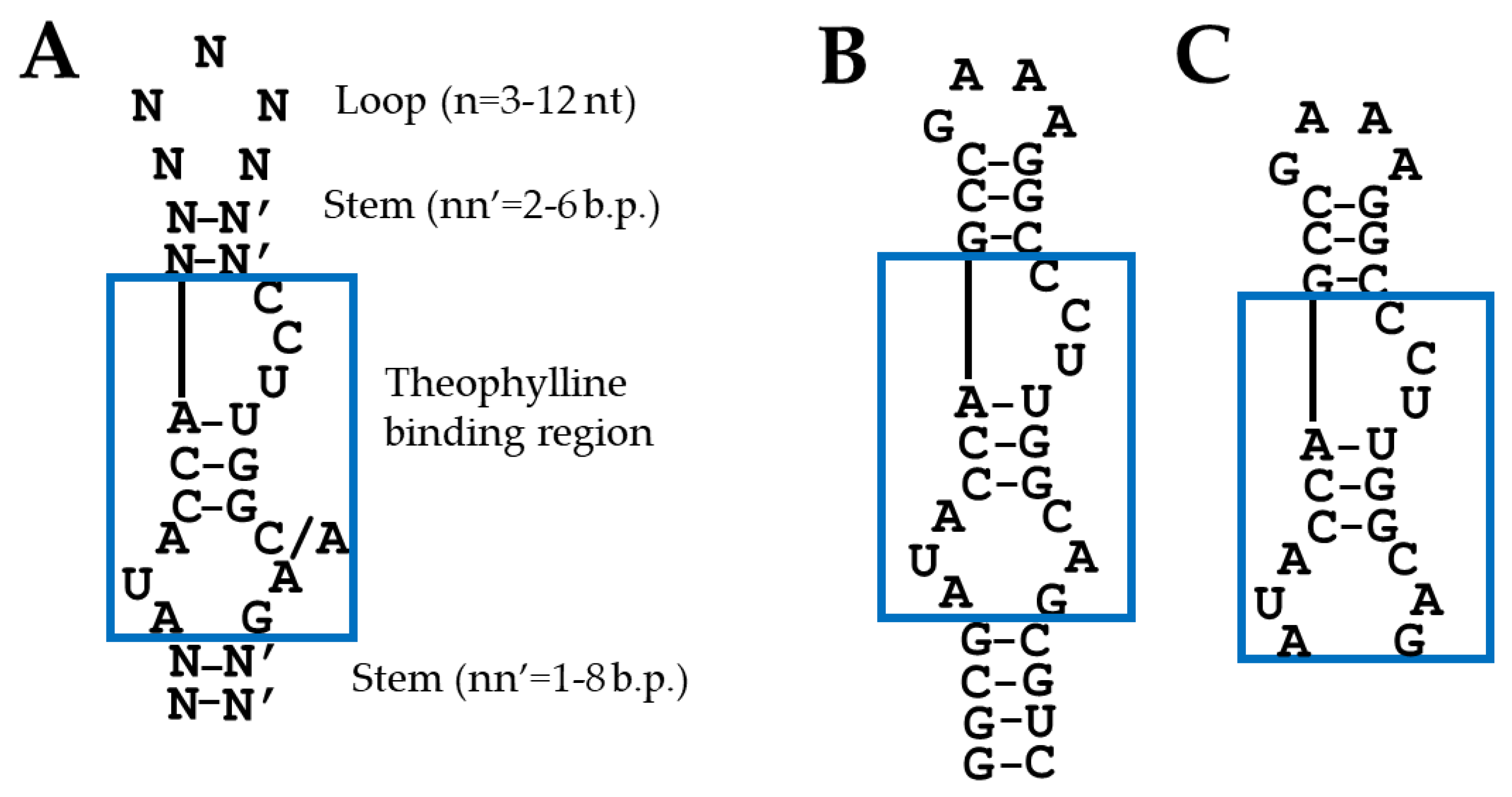
2.1. Aptamer Selection for Designing Chimeric Guide RNAs
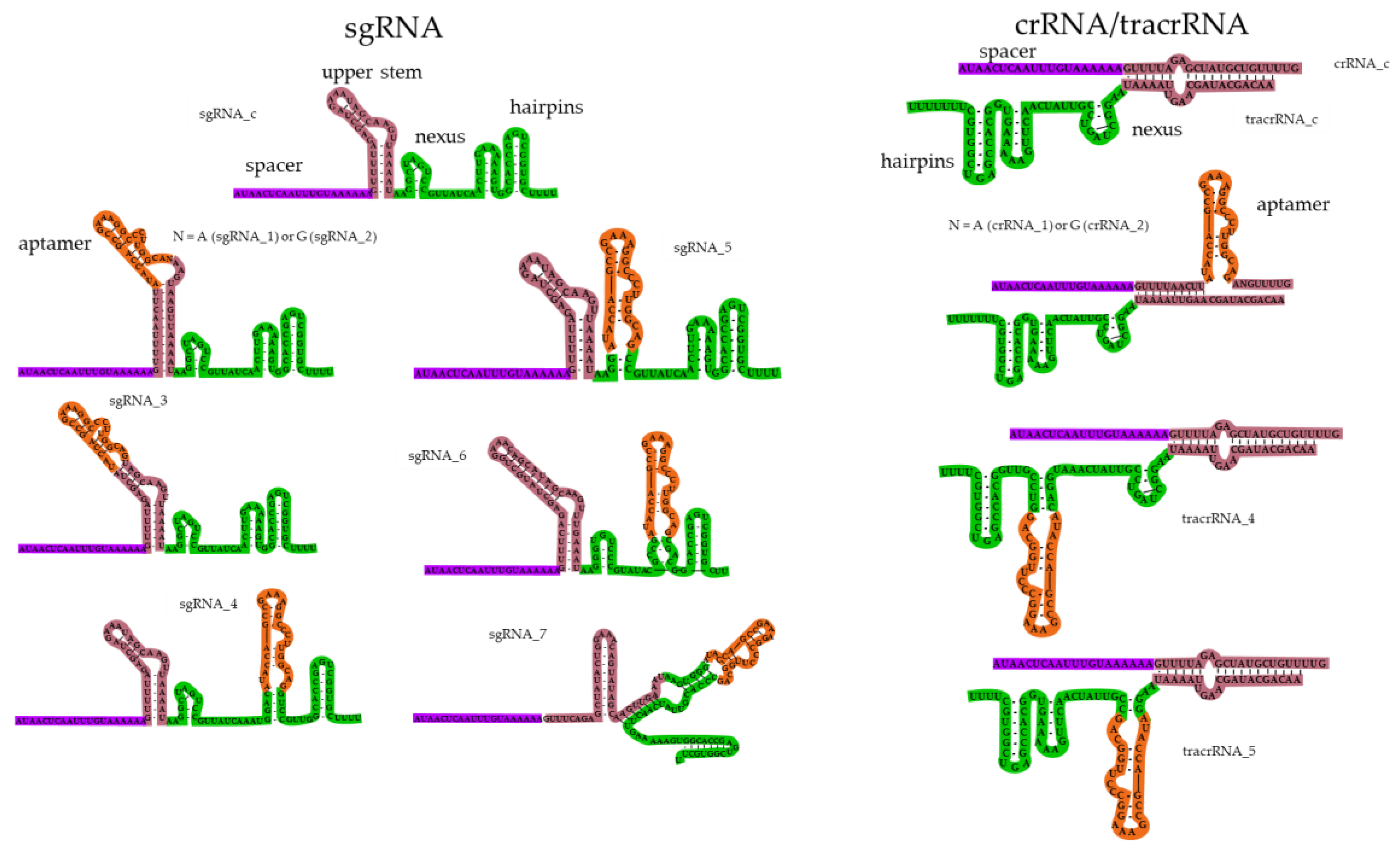
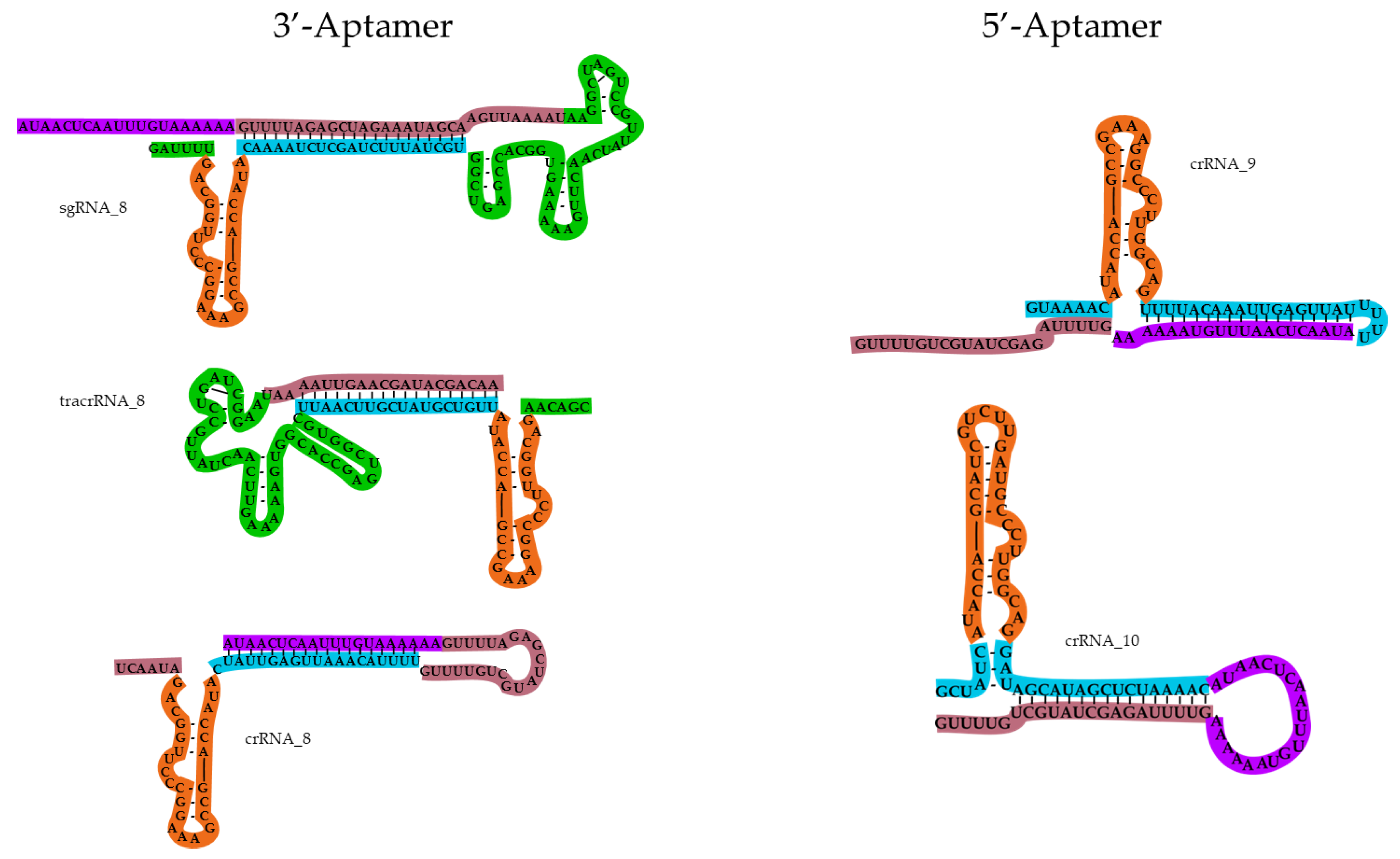
2.2. Design of Guide RNAs Containing the Theophylline Aptamer
2.3. Chemical Synthesis of Guide RNAs Containing the Theophylline Aptamer
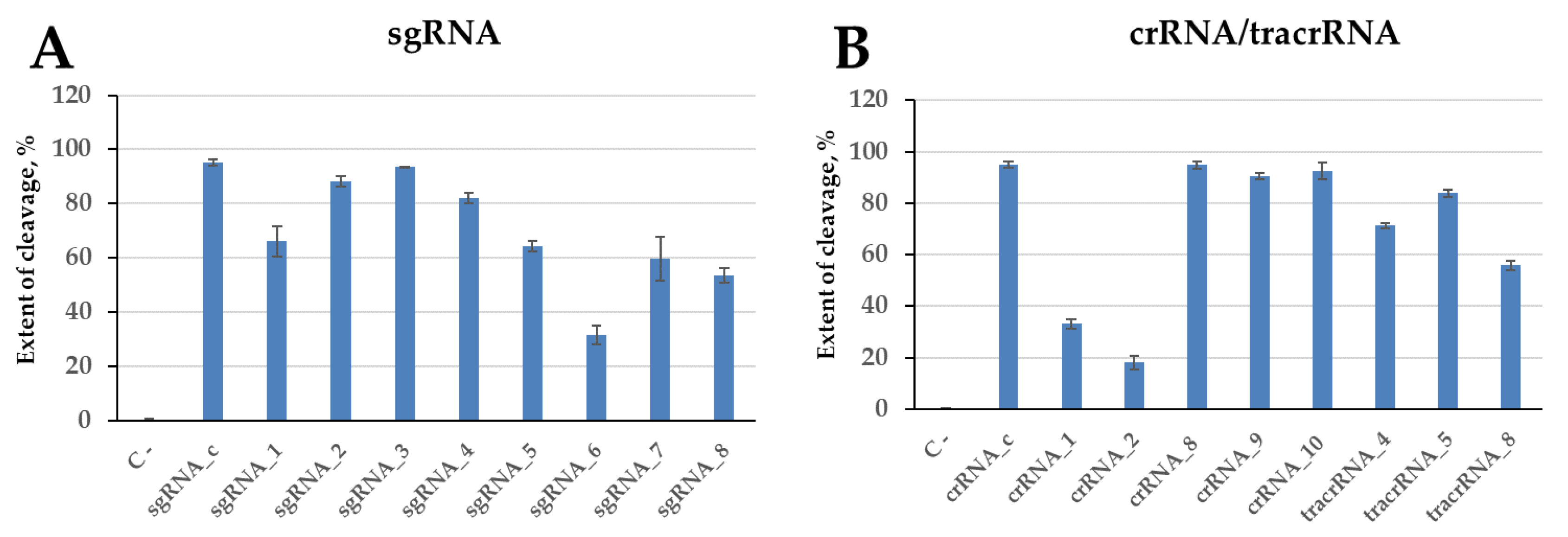
2.4. Cleavage of Model DNA by the Cas9 Nuclease in the Presence of Engineered Guide RNAs
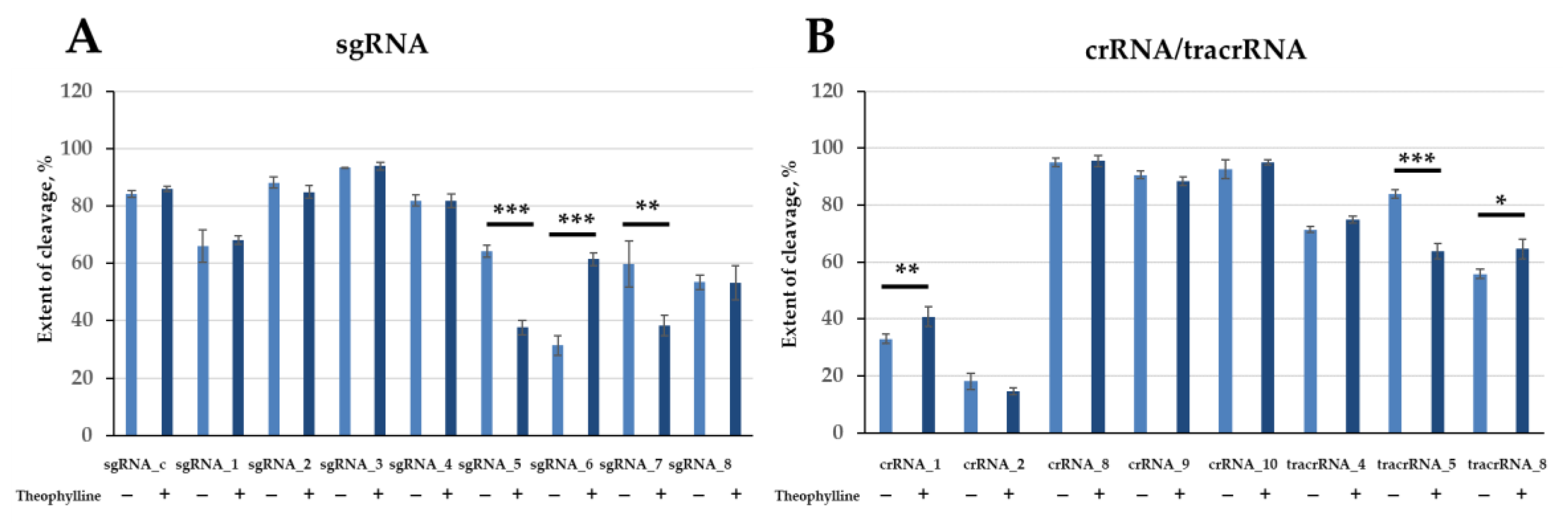
2.5. Effect of Theophylline on DNA Cleavage by Cas9 Nuclease in the Presence of Engineered Guide RNAs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals, Enzymes and Plasmids
3.2. Guide RNA Synthesis
3.3. Plasmid Digestion by CRISPR/Cas9
3.4. Investigation of Theophylline Influence to DNA Digestion
3.5. Cy5-Labelled Aptamer Preparation
3.6. Determination of Dissociation Constant of Aptamer to Theophylline by Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) Assay
3.7. Determination of Dissociation Constant of Aptamer to Theophylline by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) Technique
3.8. Statistical Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A Programmable Dual-RNA–Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science (1979) 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Pausch, P.; Doudna, J.A. Structural Biology of CRISPR–Cas Immunity and Genome Editing Enzymes. Nat Rev Microbiol 2022, 20, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Iranzo, J.; Shmakov, S.A.; Alkhnbashi, O.S.; Brouns, S.J.J.; Charpentier, E.; Cheng, D.; Haft, D.H.; Horvath, P.; et al. Evolutionary Classification of CRISPR–Cas Systems: A Burst of Class 2 and Derived Variants. Nat Rev Microbiol 2020, 18, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jia, R.; Ma, X.; Feng, Y.; Chen, H. G-Quadruplex-Based CRISPR Photoswitch for Spatiotemporal Control of Genomic Modulation. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, 4064–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, S.; Qi, Q.; Lei, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Fu, F.; Tian, T.; Zhou, X. G-Quadruplex-Guided RNA Engineering to Modulate CRISPR-Based Genomic Regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, 11387–11400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, I.A.P.; Zheng, L.; Eisenstein, M.; Soh, H.T. Rational Design of Aptamer Switches with Programmable PH Response. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Su, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, L.; Xing, X. Employing PH-Responsive RNA Triplex to Control CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Manipulation in Mammalian Cells. Chinese Chemical Letters 2024, 35, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-R.; Wu, L.-Y.; Huang, H.-Y.; Xiong, W.; Liu, J.; Wei, L.; Yin, P.; Tian, T.; Zhou, X. Conditional Control of RNA-Guided Nucleic Acid Cleavage and Gene Editing. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibian, M.; McKinlay, C.; Blake, T.R.; Kietrys, A.M.; Waymouth, R.M.; Wender, P.A.; Kool, E.T. Reversible RNA Acylation for Control of CRISPR–Cas9 Gene Editing. Chem Sci 2020, 11, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; An, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhang, H.; Song, J.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, W.; Song, Y.; Yang, C. Control of CRISPR-Cas9 with Small Molecule-Activated Allosteric Aptamer Regulating SgRNAs. Chemical Communications 2019, 55, 12223–12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundert, K.; Lucas, J.E.; Watters, K.E.; Fellmann, C.; Ng, A.H.; Heineike, B.M.; Fitzsimmons, C.M.; Oakes, B.L.; Qu, J.; Prasad, N.; et al. Controlling CRISPR-Cas9 with Ligand-Activated and Ligand-Deactivated SgRNAs. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Hu, J.H.; Liu, D.R. Aptazyme-Embedded Guide RNAs Enable Ligand-Responsive Genome Editing and Transcriptional Activation. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 15939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanidze, N.; Lenkeit, F.; Hartig, J.S.; Funck, D. A Theophylline-Responsive Riboswitch Regulates Expression of Nuclear-Encoded Genes. Plant Physiol 2020, 182, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, B.I.; Pollak, N.M.; Stefanovic, D.; Macdonald, J. Complexing Deoxyribozymes with RNA Aptamers for Detection of the Small Molecule Theophylline. Biosens Bioelectron 2022, 198, 113774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Jensen, M.C.; Smolke, C.D. Genetic Control of Mammalian T-Cell Proliferation with Synthetic RNA Regulatory Systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2010, 107, 8531–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Xu, L. Theophylline-Induced Synergic Activation of Guide RNA to Control CRISPR/Cas9 Function. Chemical Communications 2021, 57, 5418–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrist, A.; Sun, W.; Summers, R.M. The Theophylline Aptamer: 25 Years as an Important Tool in Cellular Engineering Research. ACS Synth Biol 2020, 9, 682–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZIMMERMANN, G.R.; WICK, C.L.; SHIELDS, T.P.; JENISON, R.D.; PARDI, A. Molecular Interactions and Metal Binding in the Theophylline-Binding Core of an RNA Aptamer. RNA 2000, 6, S1355838200000169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Lu, F. Identifying Conformational Changes of Aptamer Binding to Theophylline: A Combined Biolayer Interferometry, Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy, and Molecular Dynamics Study. Talanta 2020, 217, 121073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenison, R.D.; Gill, S.C.; Pardi, A.; Polisky, B. High-Resolution Molecular Discrimination by RNA. Science (1979) 1994, 263, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Cao, Y.; Lu, F. Identifying Conformational Changes of Aptamer Binding to Theophylline: A Combined Biolayer Interferometry, Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy, and Molecular Dynamics Study. Talanta 2020, 217, 121073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Threlfall, R.N.; Torres, A.G.; Krivenko, A.; Gait, M.J.; Caruthers, M.H. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Phosphonoacetate- and Thiophosphonoacetate-Modified 2′-O-Methyl Oligoribonucleotides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X. Coupling Activators for the Oligonucleotide Synthesis via Phosphoramidite Approach. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 3615–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakovina, L.; Vokhtantsev, I.; Vorobyeva, M.; Vorobyev, P.; Novopashina, D. Improving Stability and Specificity of CRISPR/Cas9 System by Selective Modification of Guide RNAs with 2′-Fluoro and Locked Nucleic Acid Nucleotides. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semikolenova, O.; Sakovina, L.; Akhmetova, E.; Kim, D.; Vokhtantsev, I.; Golyshev, V.; Vorobyeva, M.; Novopashin, S.; Novopashina, D. Photoactivatable Nanocrispr/Cas9 System Based on Crrna Reversibly Immobilized on Carbon Nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, C.; Jinek, M. In Vitro Enzymology of Cas9. In Methods Enzymol.; Doudna, J.A., Sontheimer, E.J., Eds.; 2014; Vol. 546, pp. 1–20.
- Shubsda, M.F.; Goodisman, J.; Dabrowiak, J.C. Quantitation of Ethidium-Stained Closed Circular DNA in Agarose Gels. J Biochem Biophys Methods 1997, 34, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Sequence, 5'-3' | Length, nt | Activation/ Deactivation |
|---|---|---|---|
| sgRNA | |||
| sgRNA_c | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAGAAAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCA-CCGAGUCGGUGCUUUU | 100 | none |
| sgRNA_1 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAACUUAUACCAGCC-GAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGAAGUAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGU-CCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUC-GGUGCUUUU | 119 | activation |
| sgRNA_2 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAACUUAUACCAGCCG-AAAGGCCCUUGGCAGAGGUAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUC-CGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGCUUUU | 119 | activation |
| sgРНК_3 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAAUACCAGCC-GAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCC-GUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGCUUUU | 121 | activation |
| sgRNA_4 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAGAAAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAAAUGGACAUACCAGCC-GAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGGUCCGUUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGCUUUU | 127 | activation |
| sgRNA_5 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAGAAAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGAUACCAGCCGAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGCCGUU-AUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGCUUUU | 120 | deactivation |
| sgRNA_6 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUCAGAGCUAUGCUGGAAACA-GCAUAGCAAGUUGAAATAAGGGUGUCCCGUAUACGCCGAUACC-AGCCGAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGCGACGGC-ACCGAGUCGGUGCUU | 128 | activation |
| sgRNA_7 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUCAGAGCUAUGCUGGAAAC-AGCAUAGCAAGUUGAAATAAGUGGGAUACCAGCCGAAAGGCC-CUUGGCAGCCUACGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGU-CGGUGCUU | 134 | deactivation |
| crRNA | |||
| crRNA_c | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAUGCUGUUUUG | 42 | none |
| crRNA_1 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAACUUAUACCAGCCGA-AAGGCCCUUGGCAGAAGUUUUG | 63 | activation |
| crRNA_2 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAACUUAUACCAGCCGA-AAGGCCCUUGGCAGAGGUUUUG | 63 | activation |
| tracrRNA | |||
| tracrRNA_c | AACAGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACC-GAGUCGGUGCUUUUUUU | 74 | none |
| tracrRNA_4 | AACAGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAAAUGGACAUACCAGCCGAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGGUCCGUUGGCACCGA-GUCGGUGCUUUU | 98 | activation |
| tracrRNA_5 | AACAGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGAUACCAGCCGAAAGGCC-CUUGGCAGCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUC-GGUGCUUUU | 91 | deactivation |
| Name | Sequence, 5'-3' | Length, nt | Activation/ Deactivation |
|---|---|---|---|
| sgRNA | |||
| sgRNA_8 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAGAAAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAA GGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCA-CCGAGUCGGUGCUAUUUCUAGCUCUAAAACAUACCAGCCGAAA-GGCCCUUGGCAGUUUUAG | 145 | activation |
| crRNA | |||
| crRNA_8 | AUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAUGCUGUUUUG-UUUUACAAAUUGAGUUAUCAUACCAGCCGAAAGGCCCUUG-GCAGAUAACU | 92 | activation |
| crRNA_9 | GUAAAACAUACAGCCGAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGUUUUACAAAUUGAGUUAUUUUUAUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGAGCUAUGCUGUUUUG | 96 | activation |
| crRNA_10 | GCUAUCAUACCAGCAUCGUCUUGAUGCCCUUGGCAGGAUAGCAUAGCUCUAAAACAUAACUCAAUUUGUAAAAAAGUUUUAGA-GCUAUGCUGUUUUG | 97 | activation |
| tracrRNA | |||
| tracrRNA_8 | AACAGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGG CACCGAGUCGGUGCUUAACUUGCUAUGCU-GUUAUACCAGCCGAAAGGCCCUUGGCAGAACAGC | 116 | activation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





