Submitted:
01 December 2024
Posted:
02 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
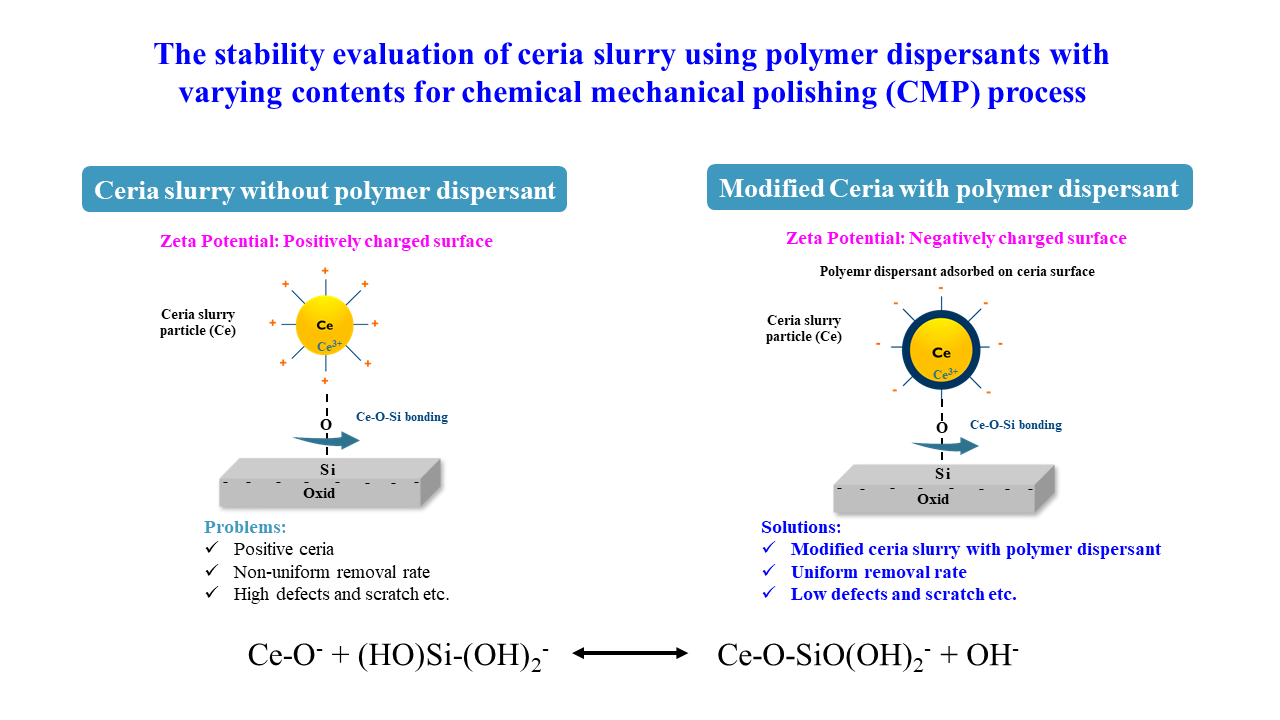
The CMP (chemical mechanical polishing/planarization) technique is a process used manufacturing to smooth and flatten the surface of a wafer by combining chemical reaction and mechanical force in semiconductor. This technique helps to achieve the desired surface quality and planarity required for subsequent layers and processing steps. However, the aggregation of slurry particles caused by abrasive materials can lead to scratches, defects, and increased surface roughness, degradation the quality and durability of the finished surface in milling processes during the CMP process. In this study, prepared ceria slurry using varying contents with 5, 6 and 7 wt.% (denoted by D5, D6 and D7), respectively, adapted with zinc salt of ethylene acrylic acid (EAA) copolymer to minimize the issue of particle aggregation commonly observed in CMP slurry. All samples characterized by pH, particle size, conductivity and viscosity to evaluate physico-chemical properties compared to commercial polymer dispersant. It was confirmed that the particle size of the CMP slurry decreased according to as the polymer dispersant content increased, such as 281.6 nm of 5%, 6% polymer dispersant at 251.8 nm, and 7% polymer dispersant at 227.2 nm, respectively. Among of them, prepared D7 sample showed smaller particle size than commercial ceria slurry. This was attributed to the influence of the carboxyl groups (-COOH) of the poly-acrylic acid polymer coated on the surface of the ceria particles. It is believed that the polymer dispersant more effectively adsorbs onto the particle surfaces, resulting in increased electrostatic repulsion between particles and a subsequent reduction in particle size. Furthermore, the stability tests of prepared slurry was evaluated by extreme conditions for three months at 25 °C (opened and closed condition), 4 °C, and 60 °C, respectively. It was observed that, the D7 slurry remained stable without significant changes. In addition to, the prepared D7 ceria slurry exhibited a slightly higher RR comparison with commercial slurry, which and be attributed to the fact that the ceria nanoparticles consists of smaller particle sizes than those in the commercial slurry. This suggests that the ceria colloidal stability of the prepared D7 sample is maintained better compared to commercial and D5 and D6 ceria slurry.