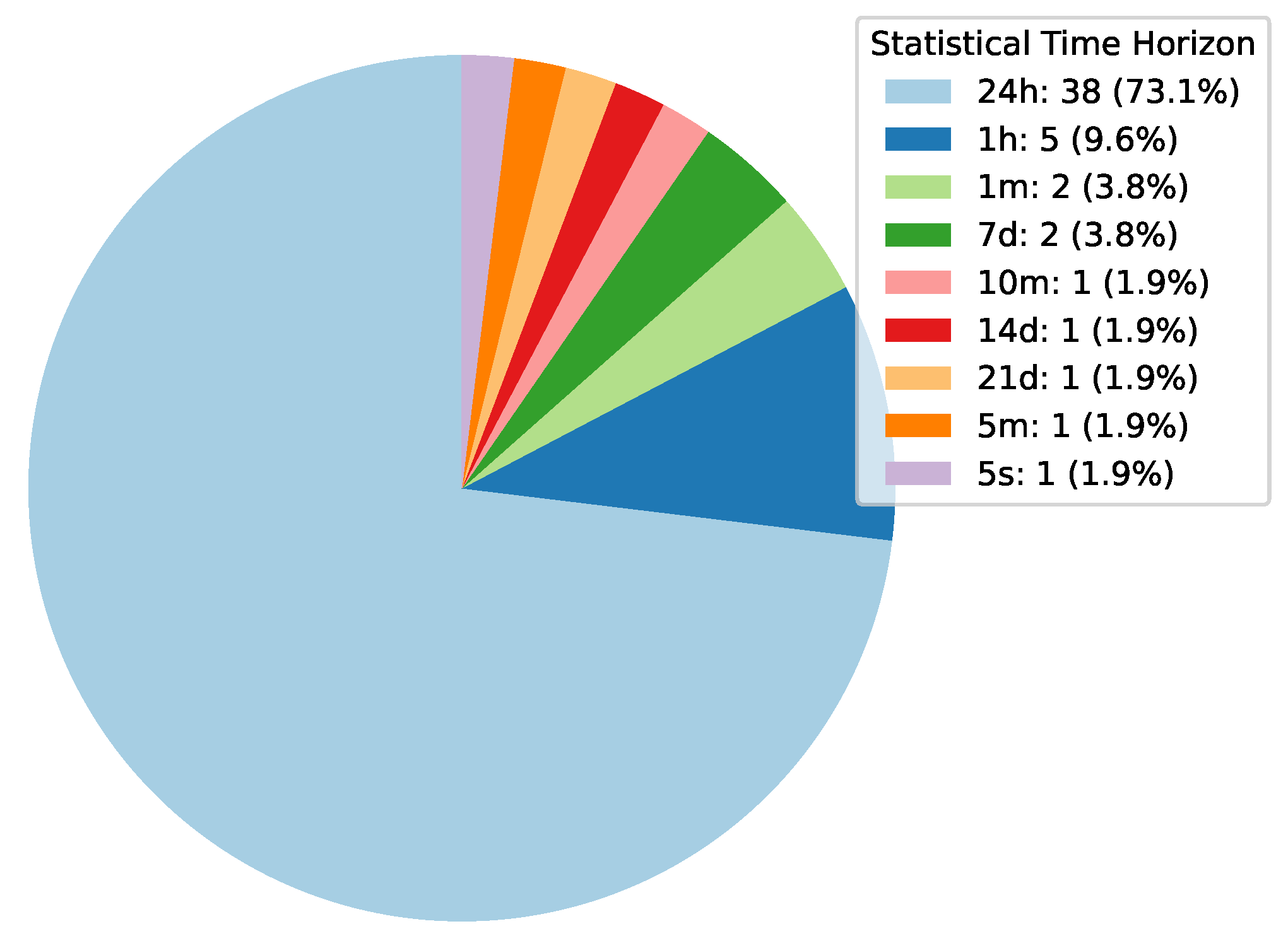
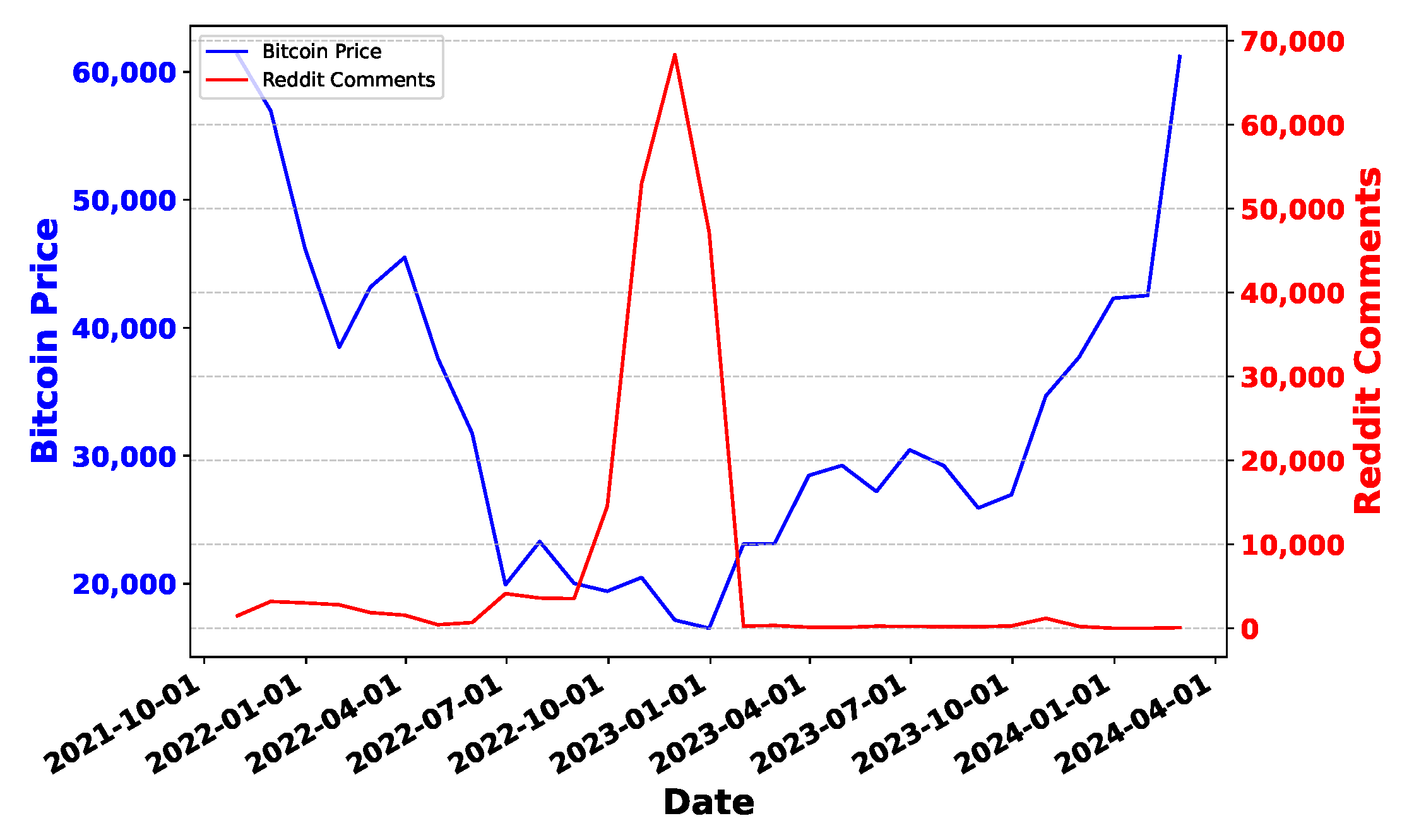
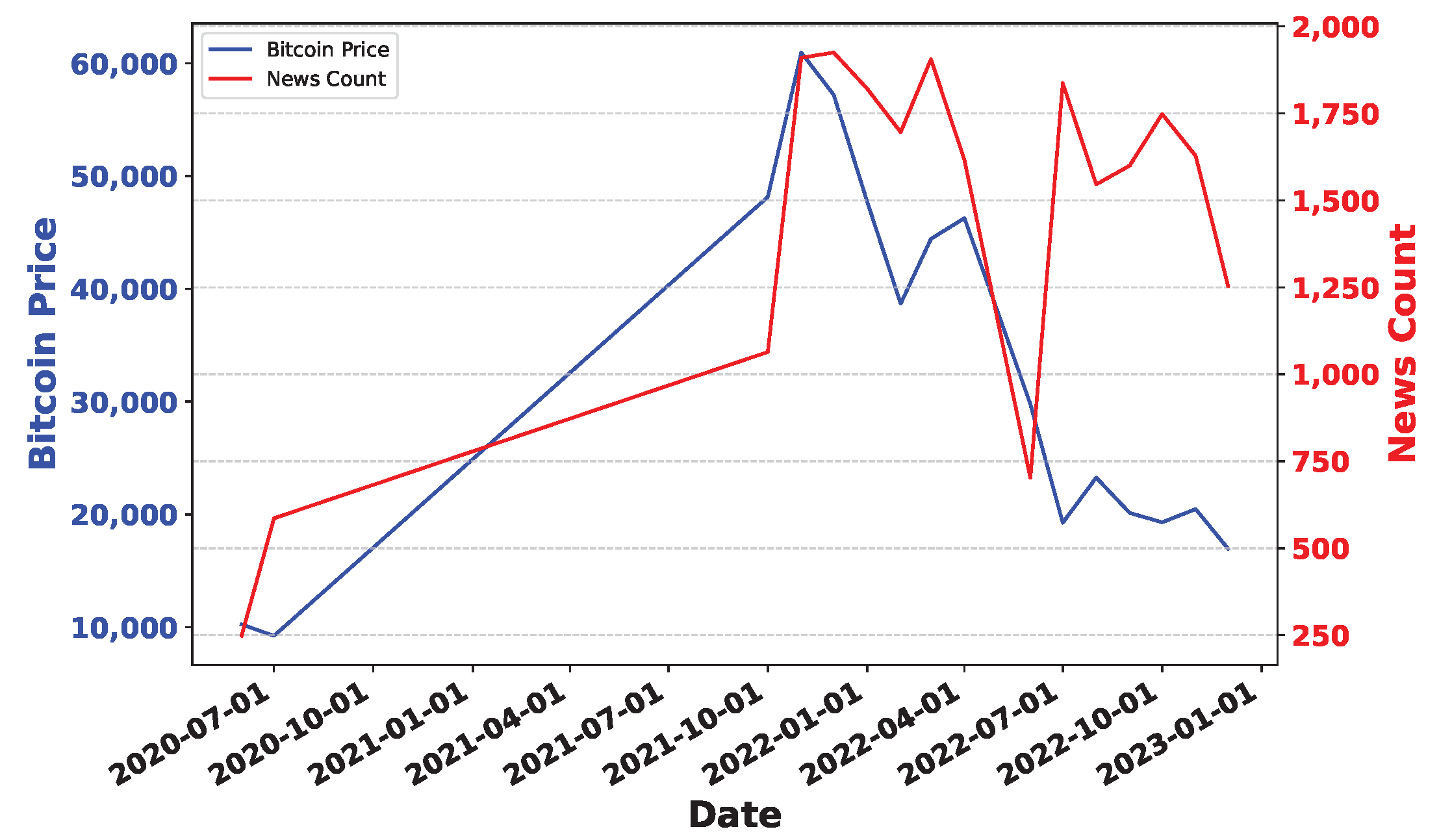
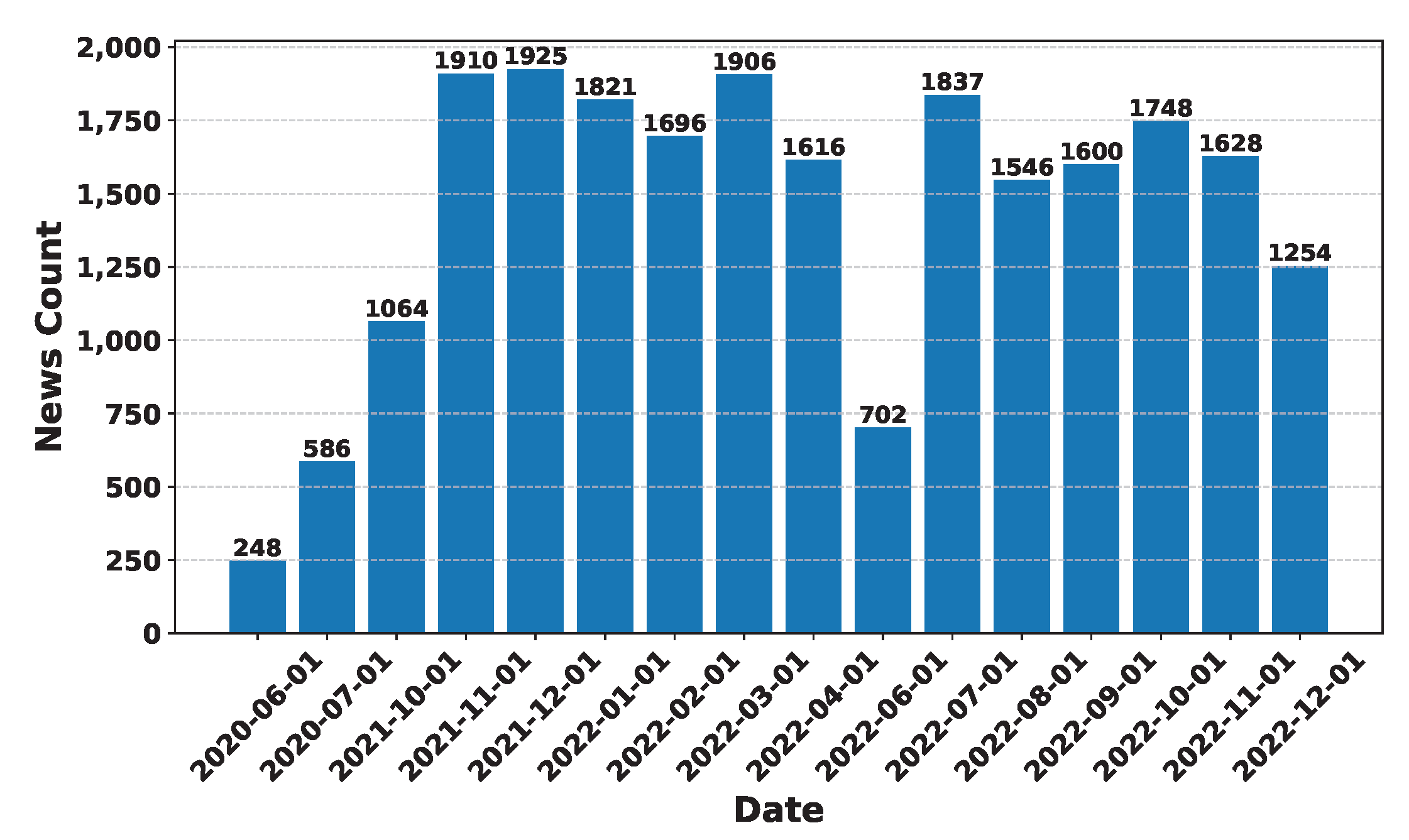
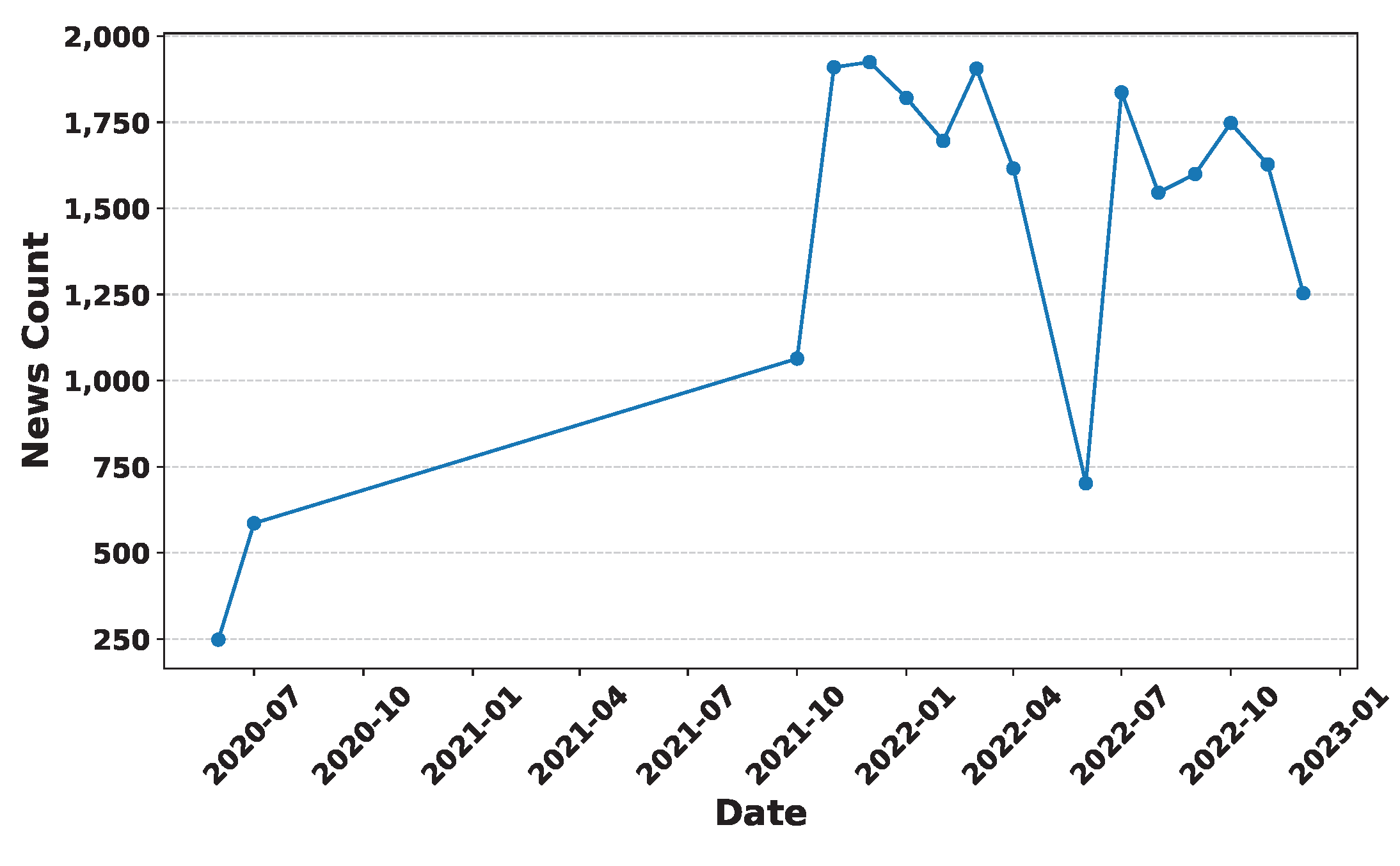
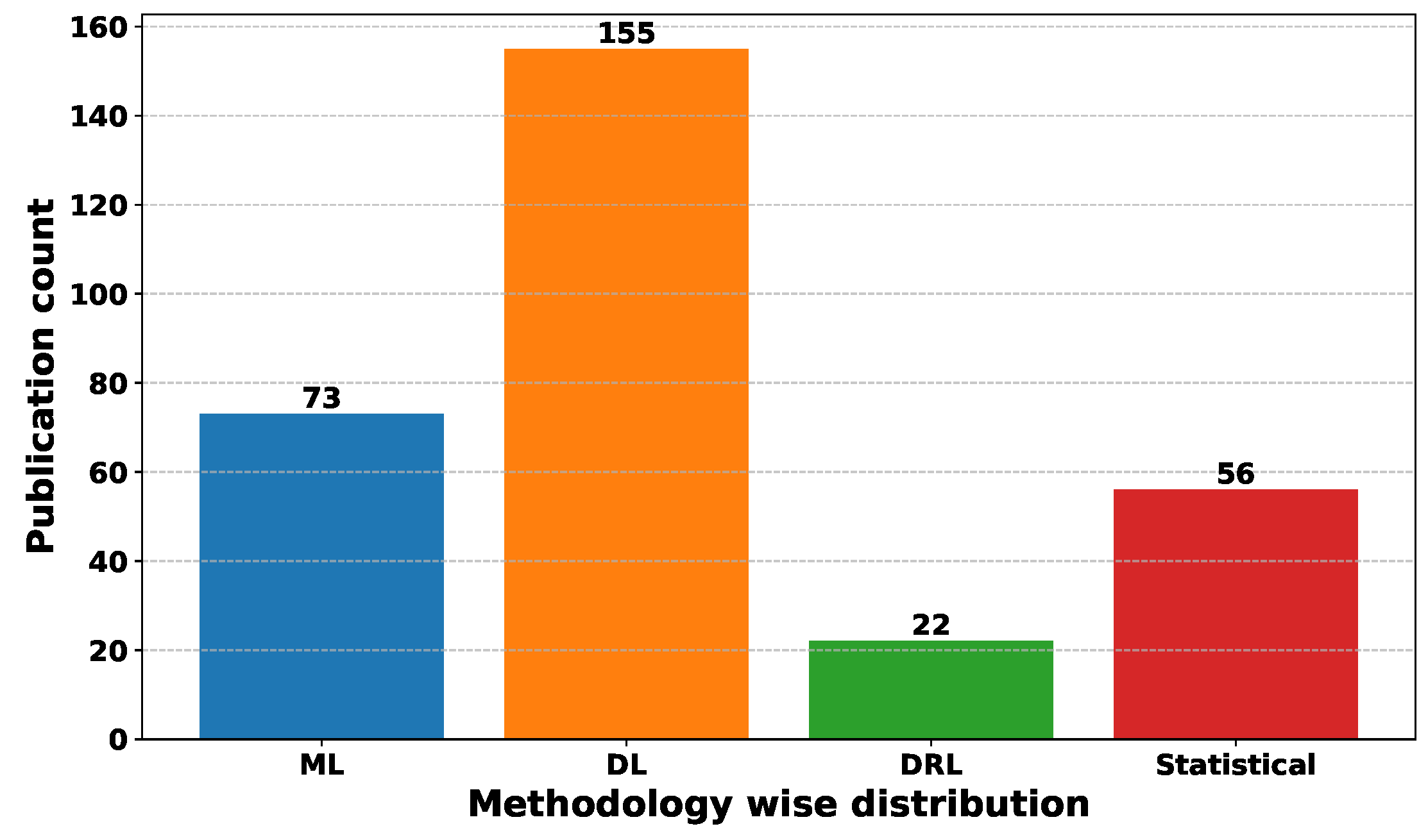
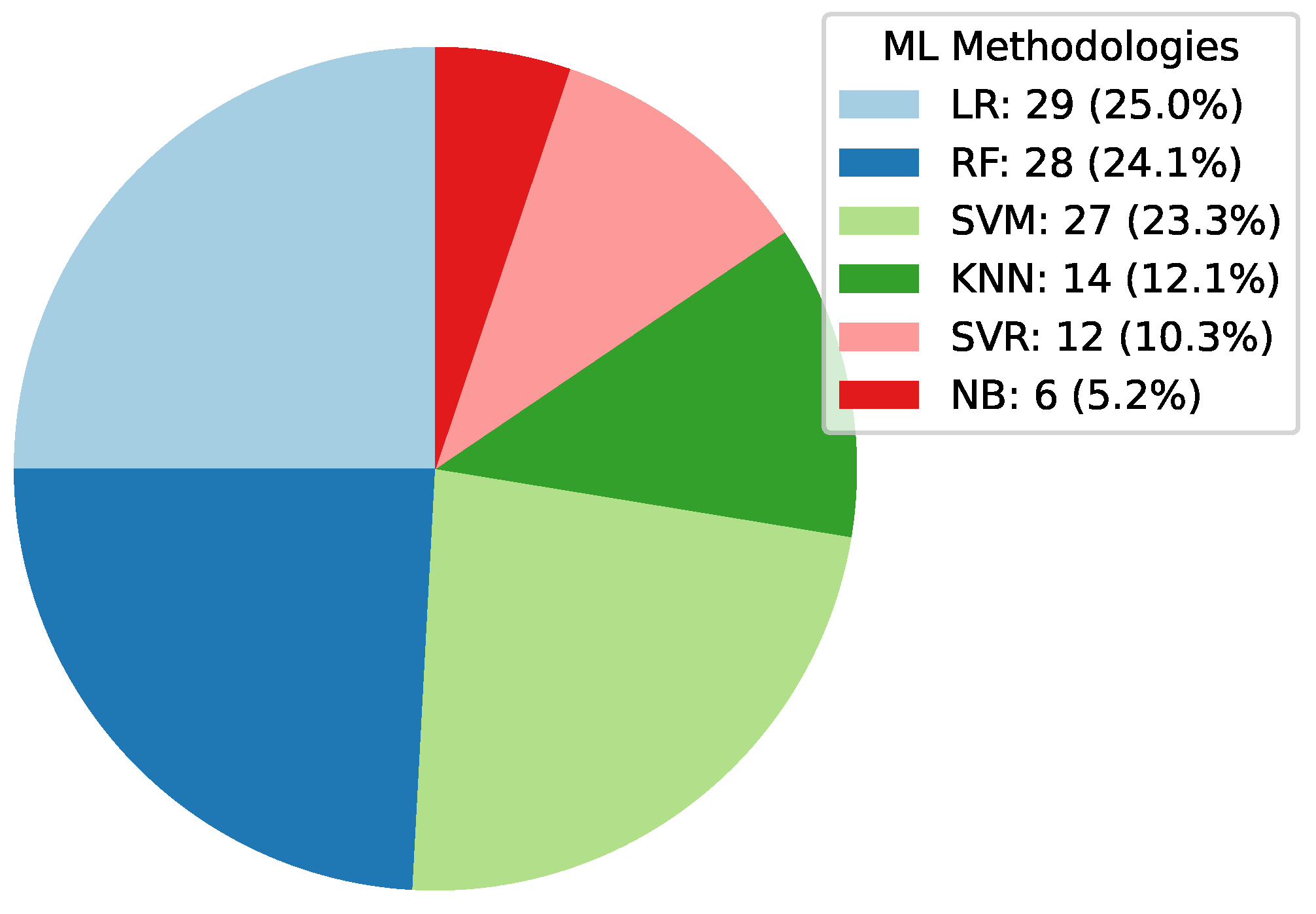
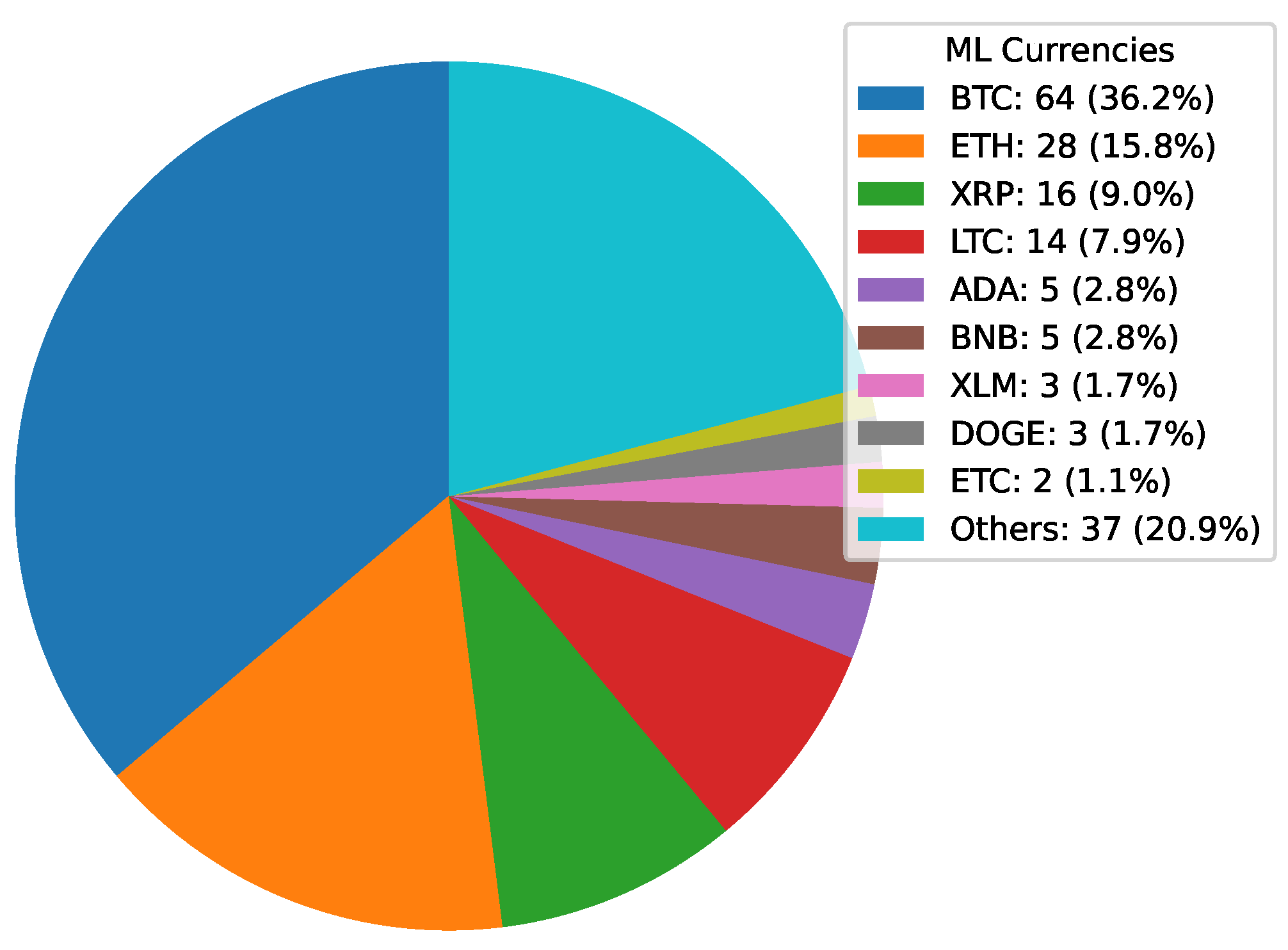
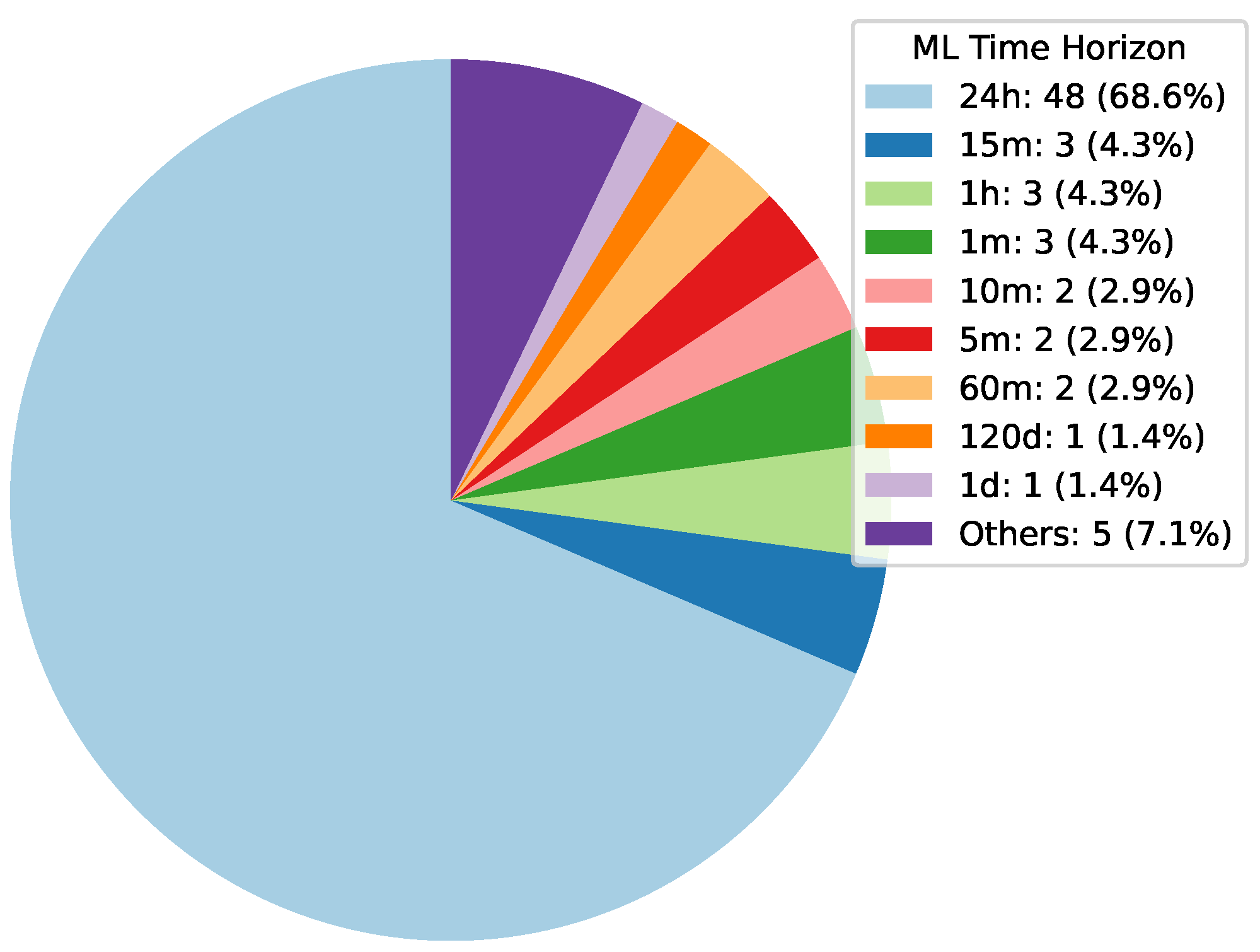
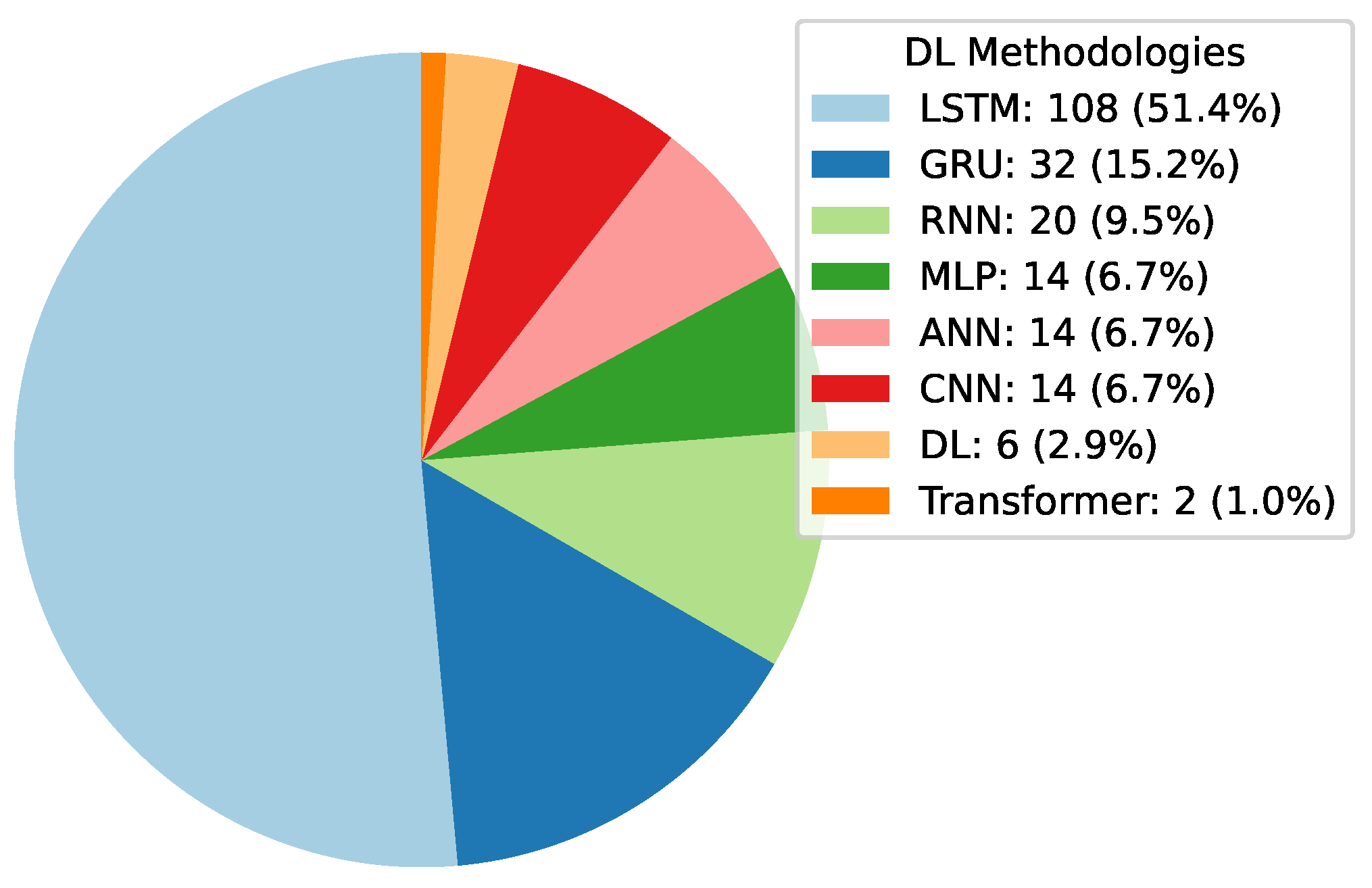
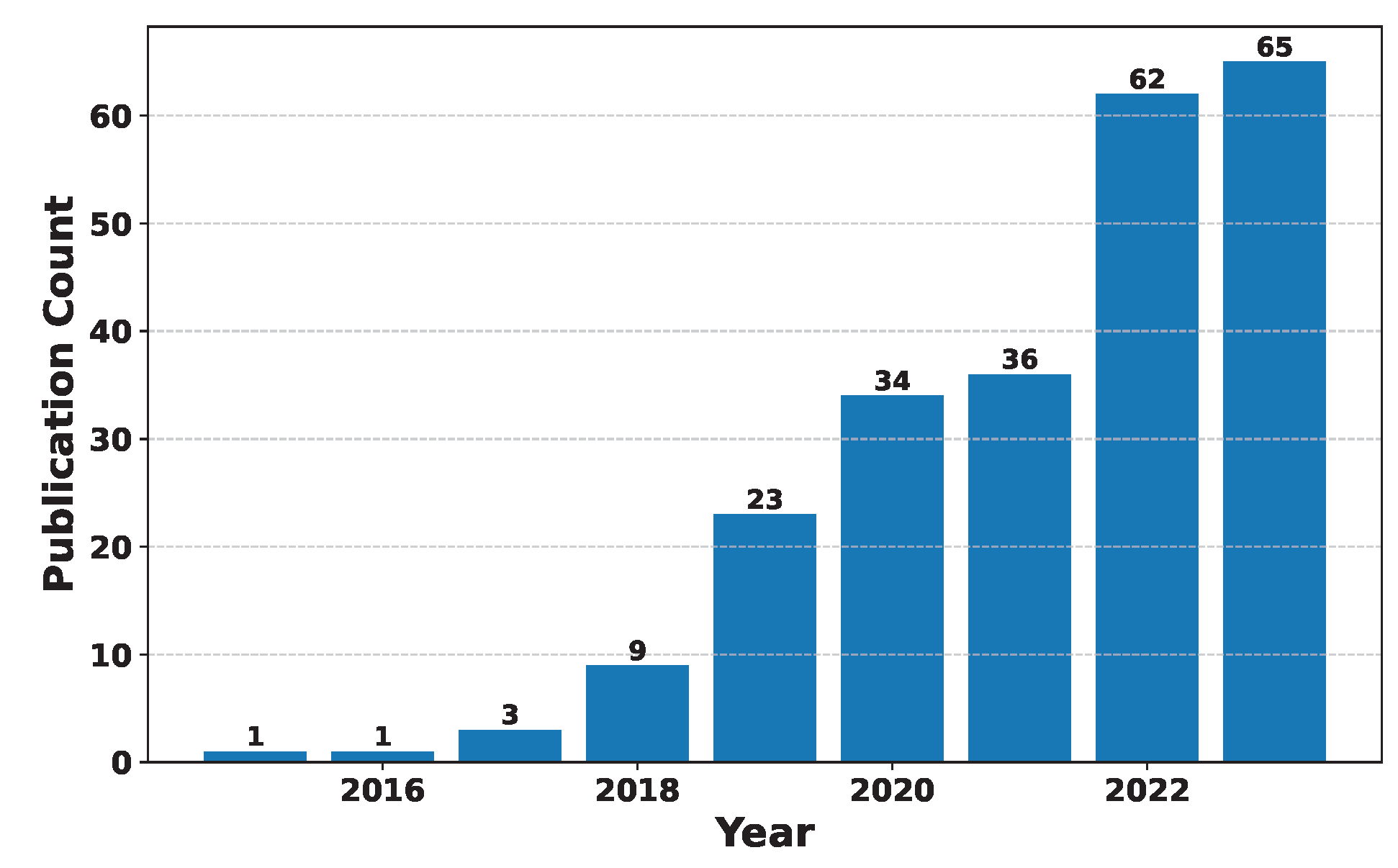
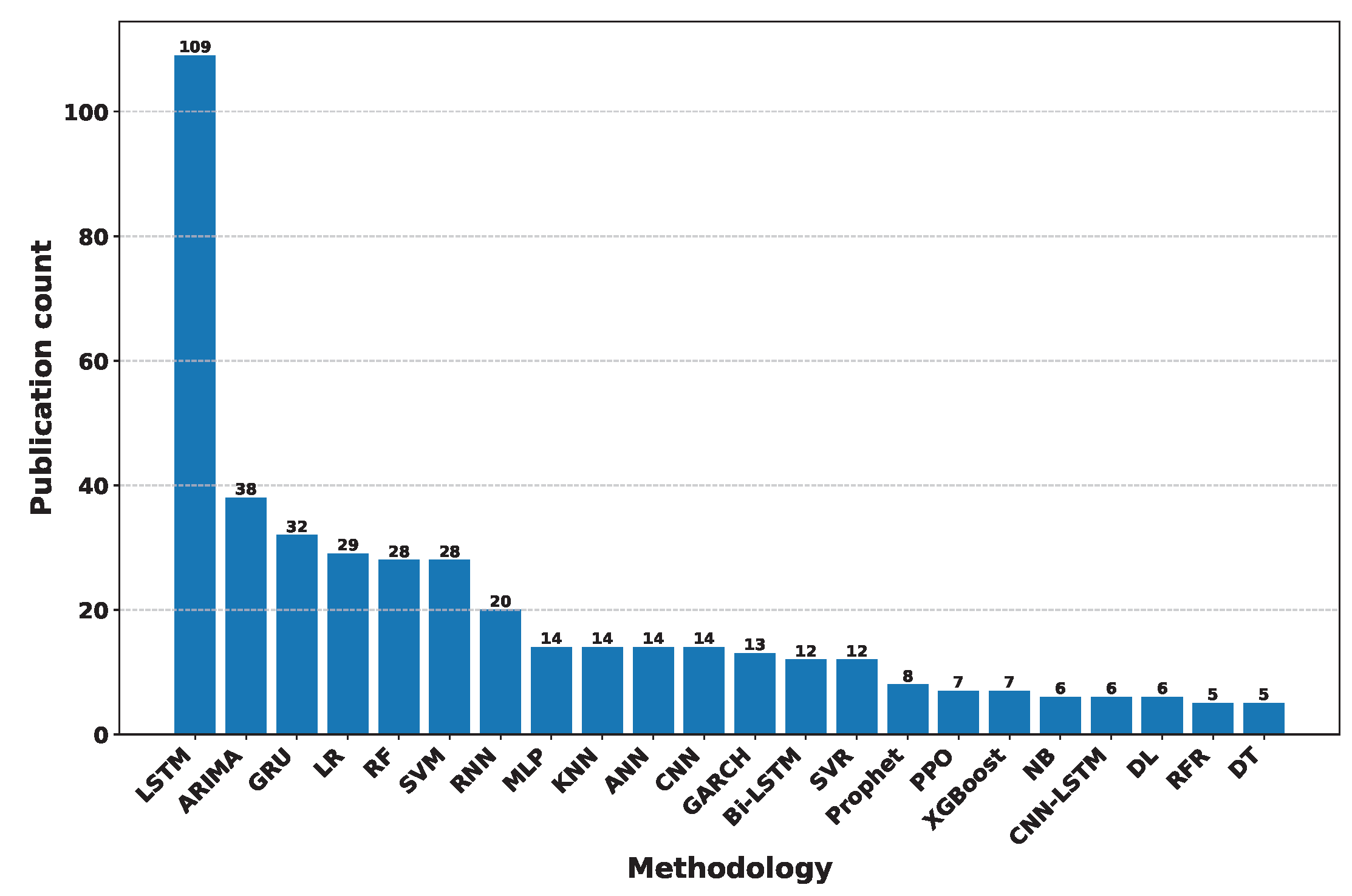
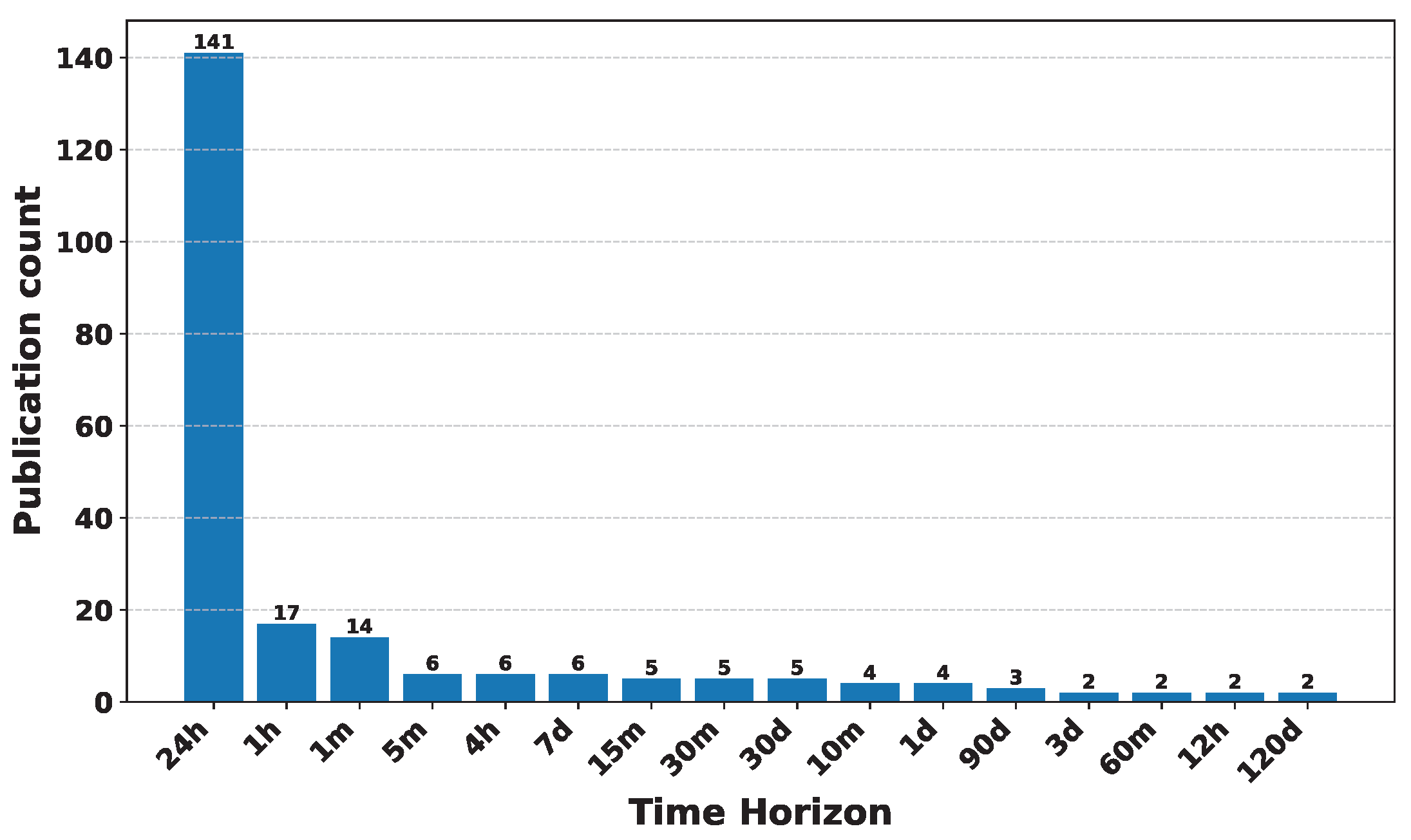
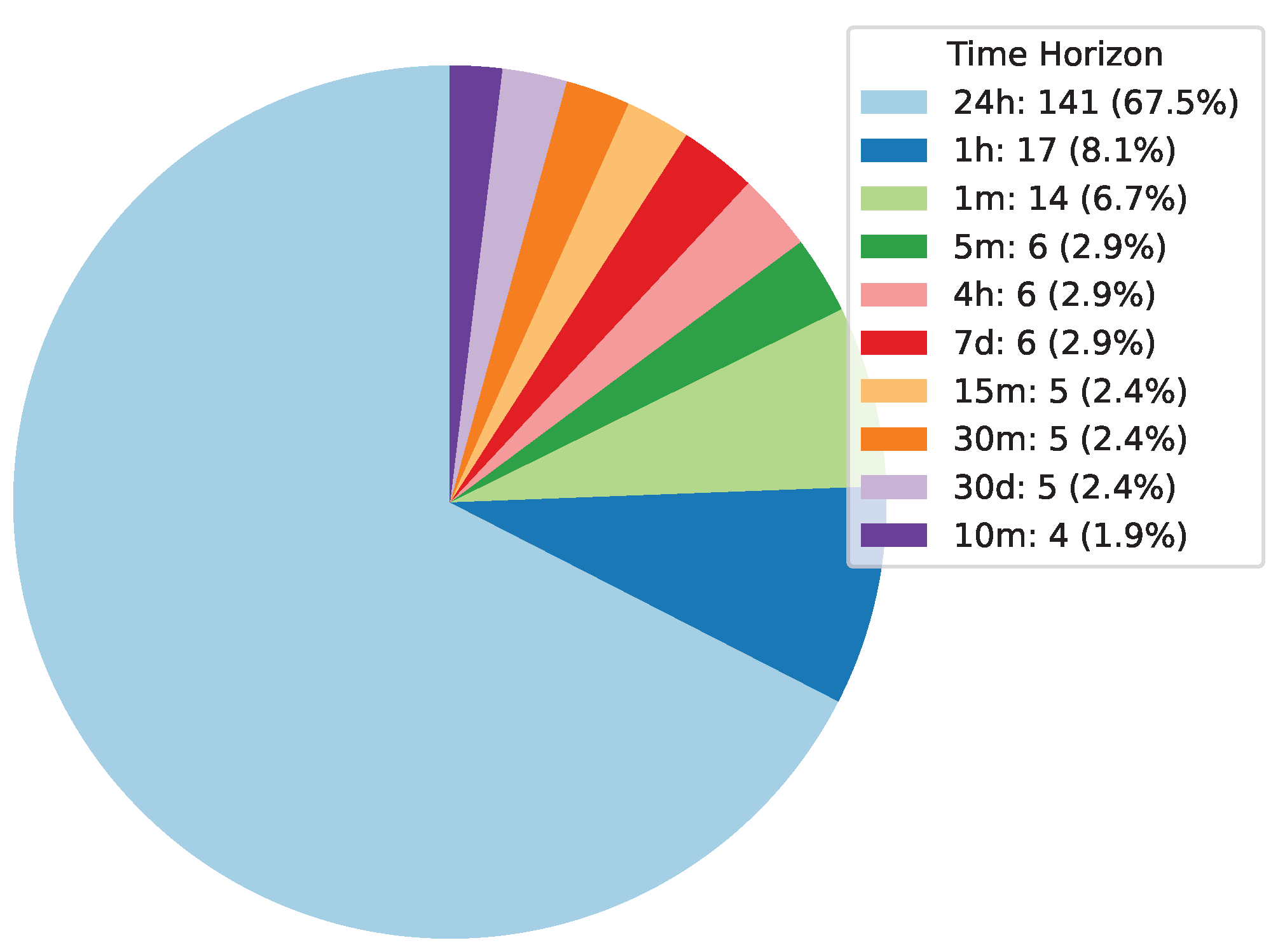
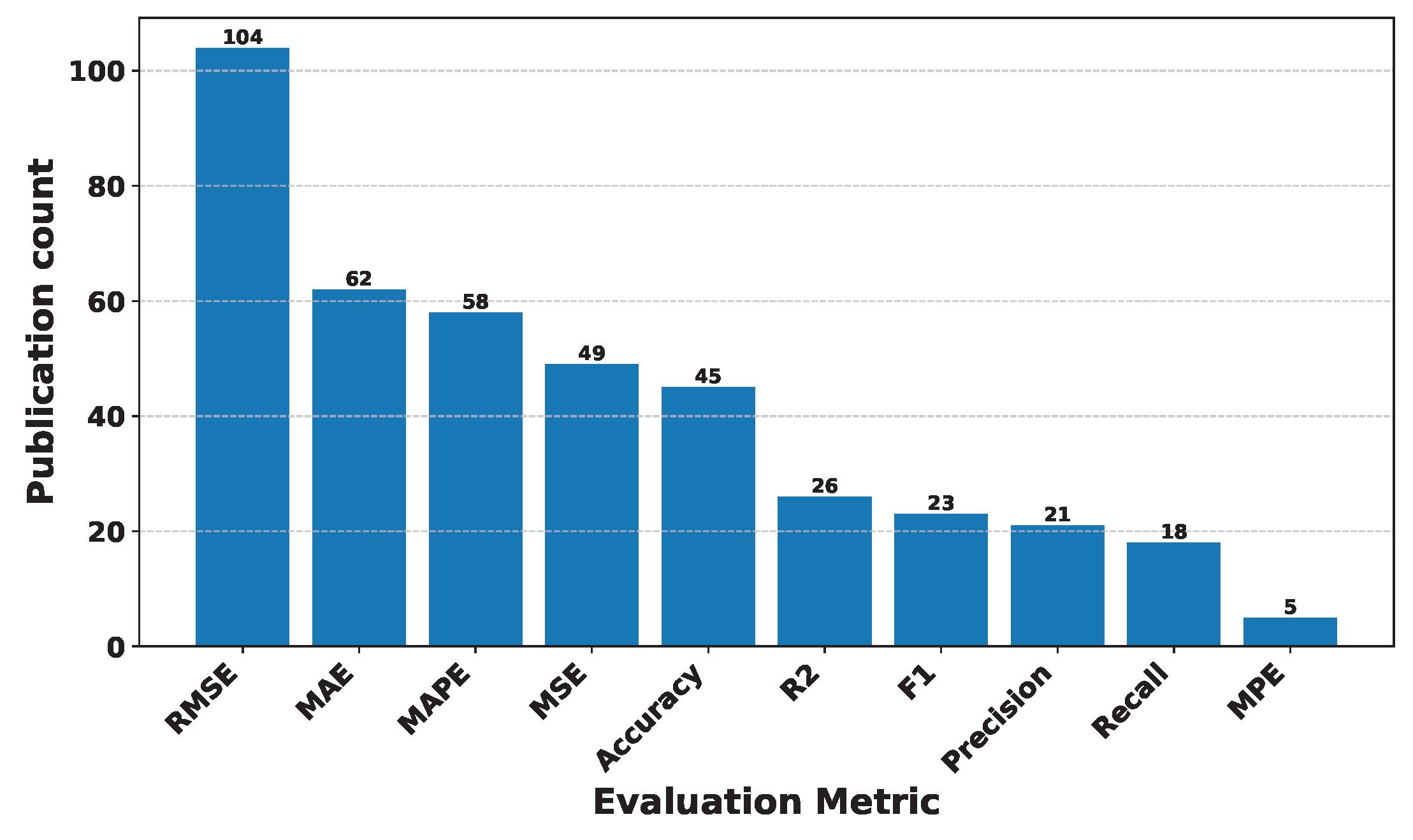
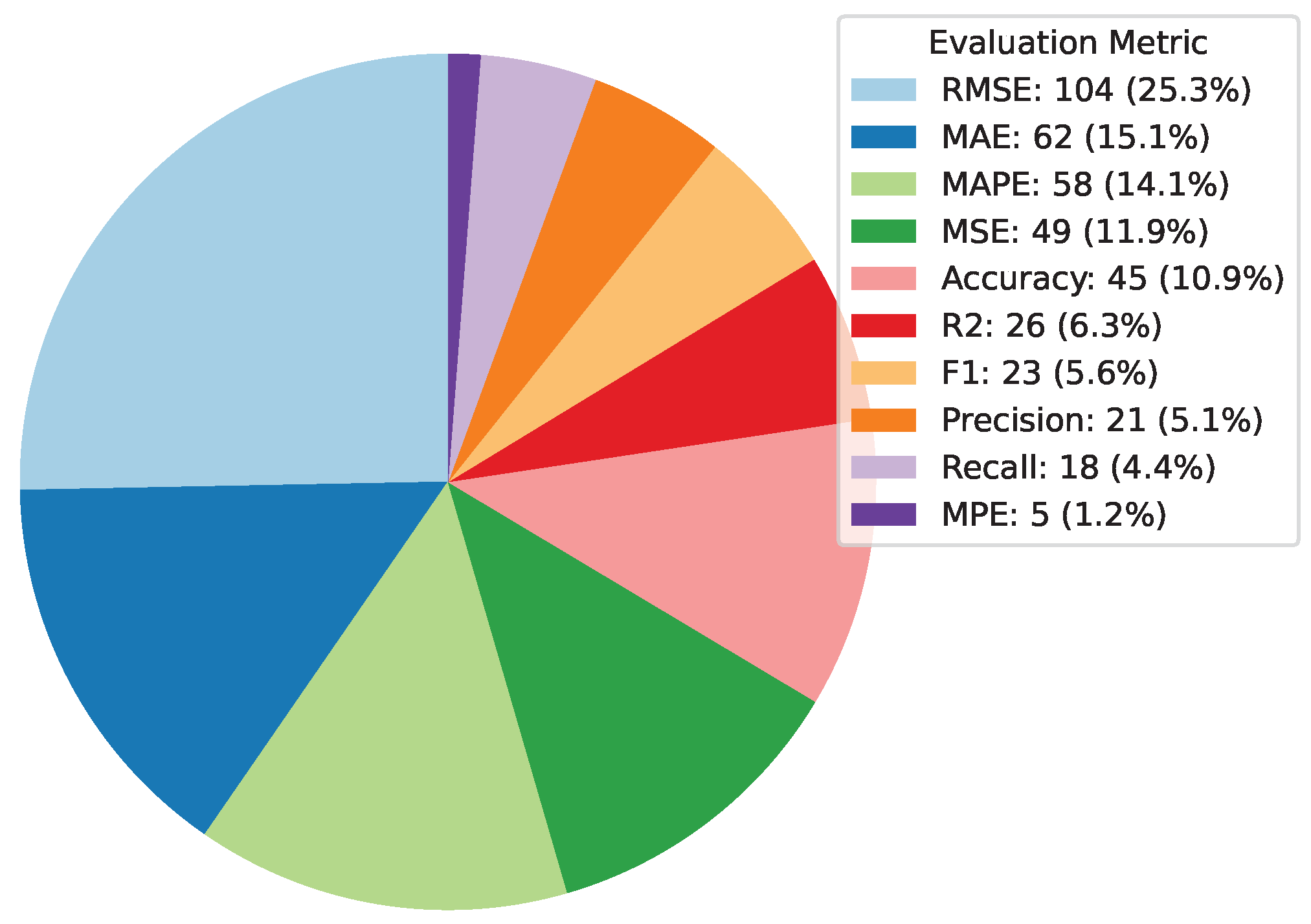
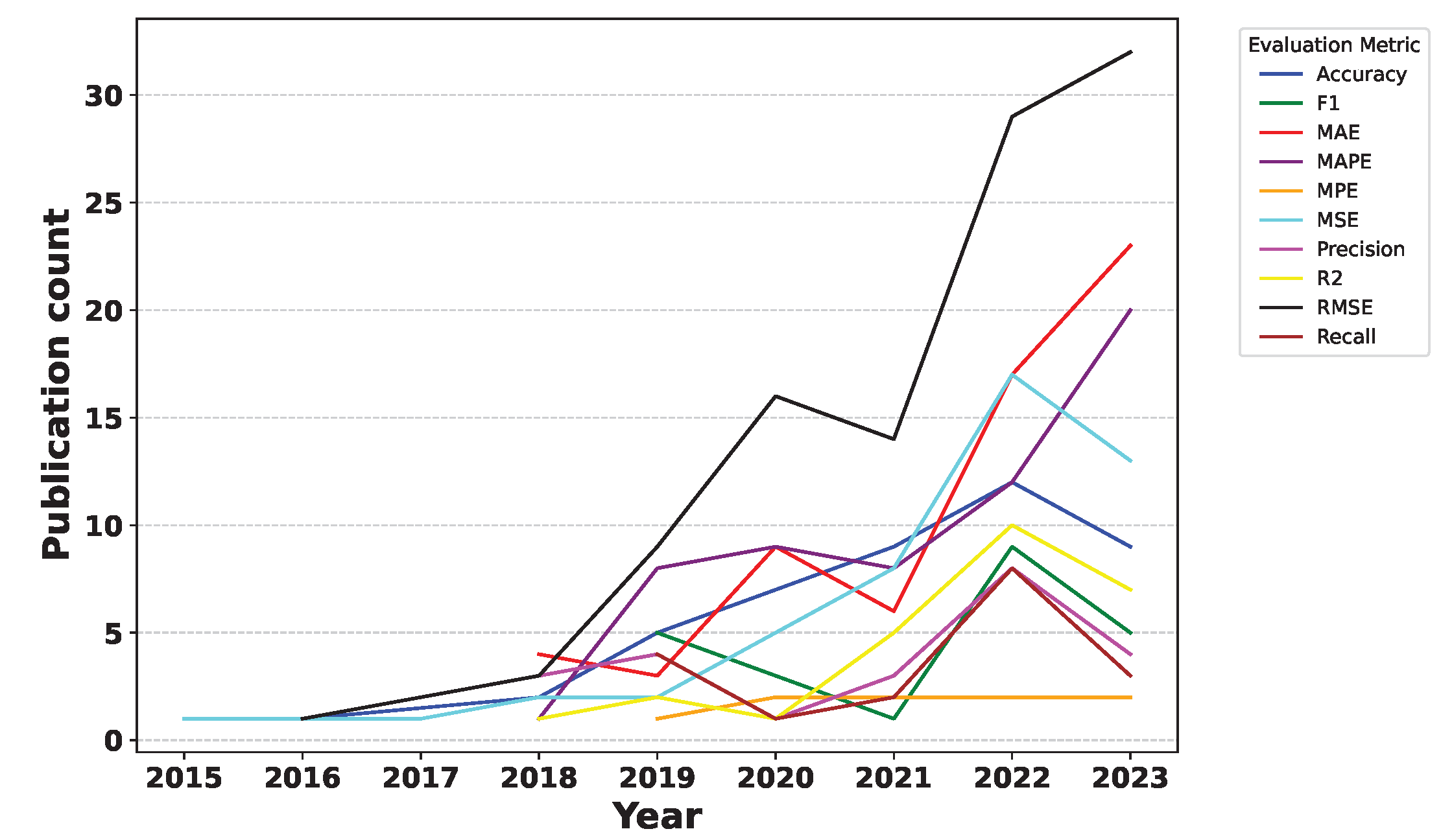
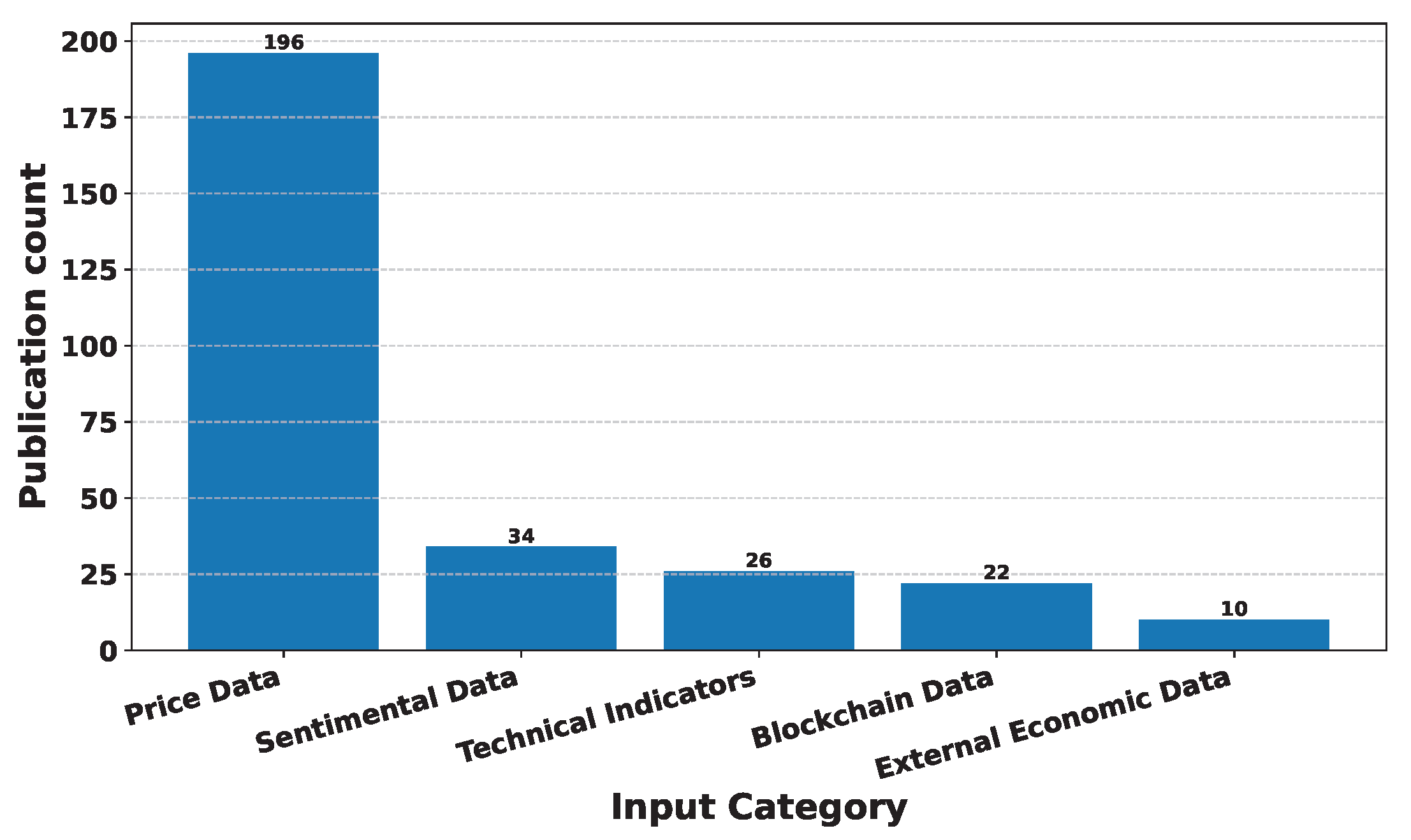
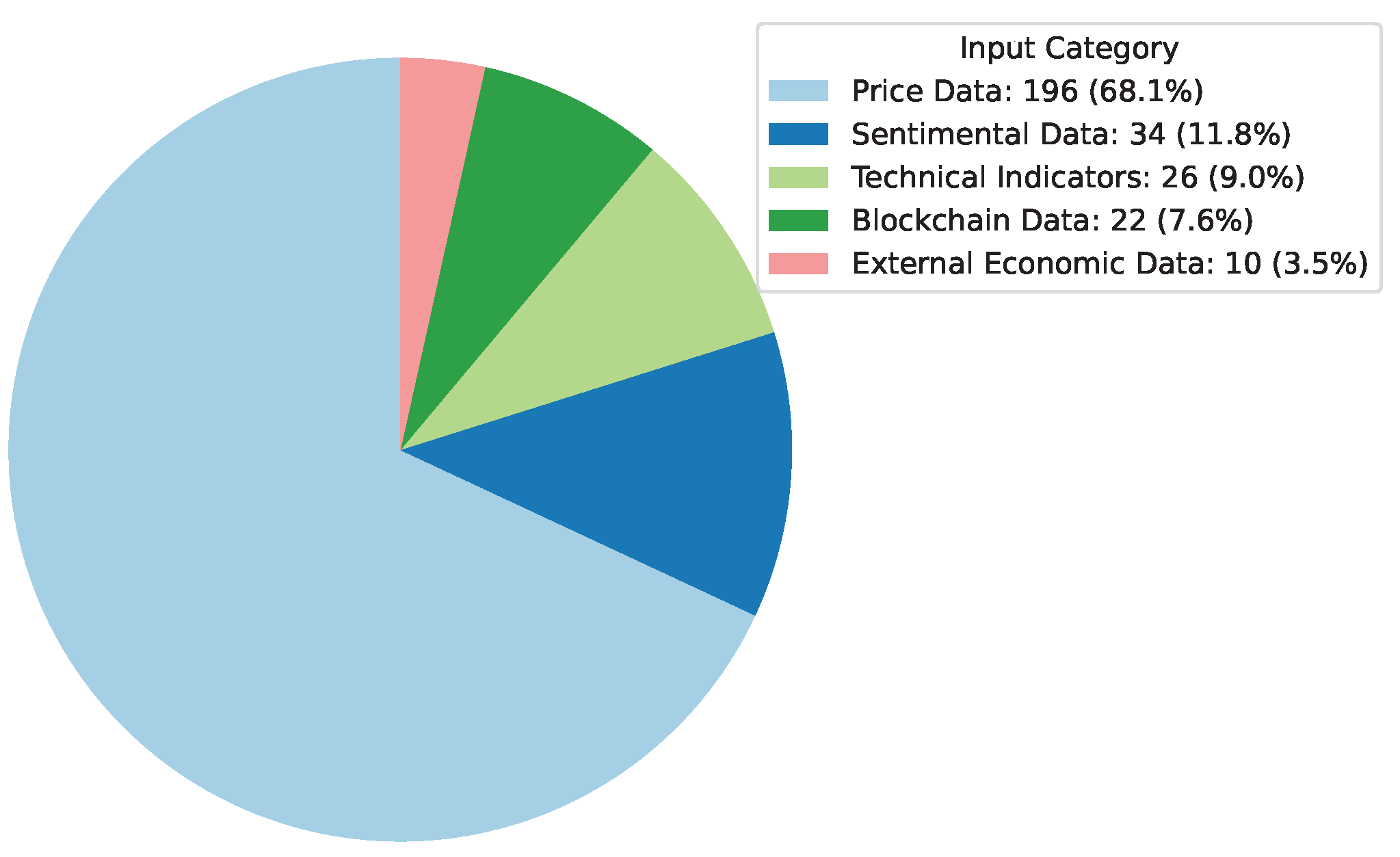
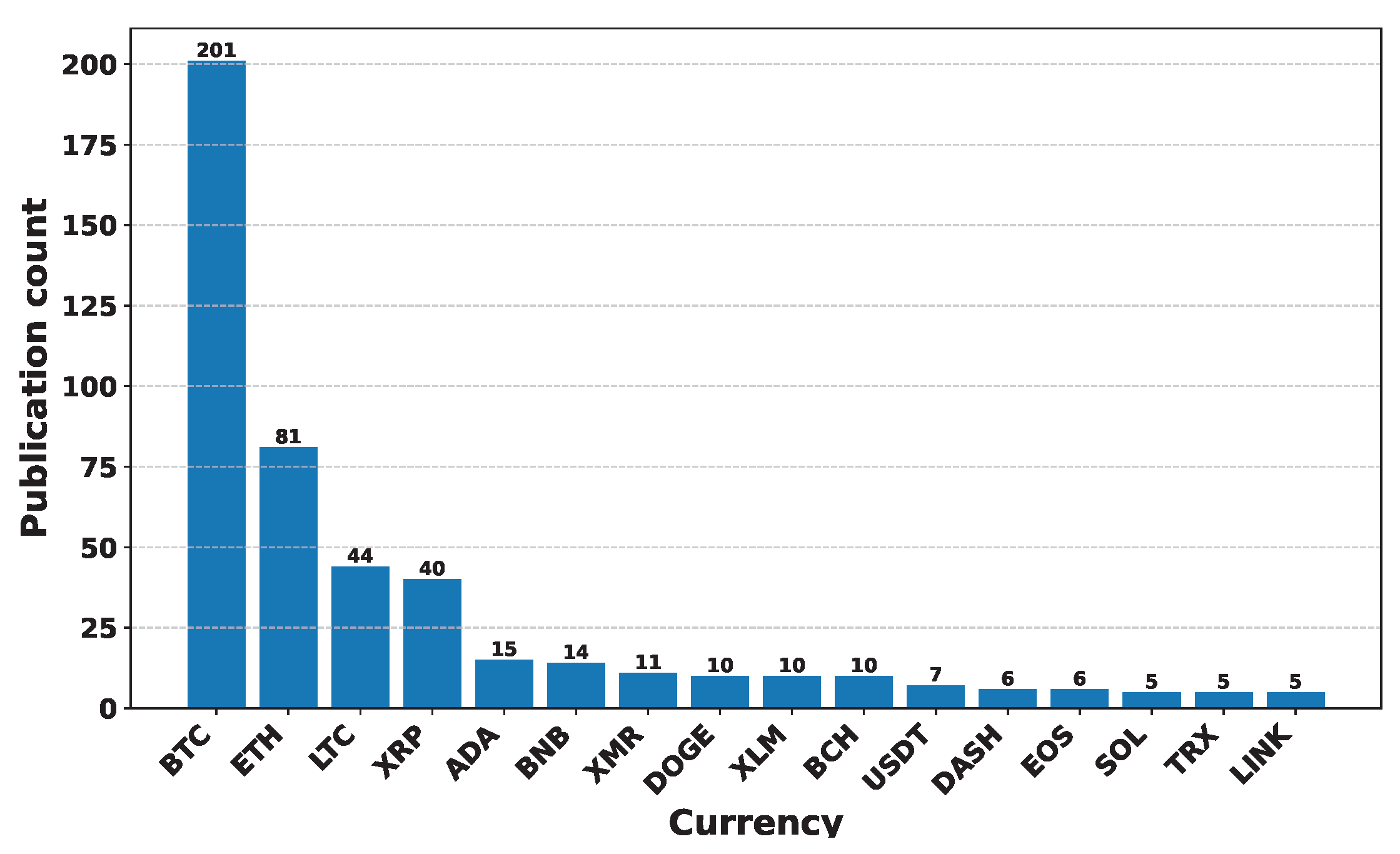
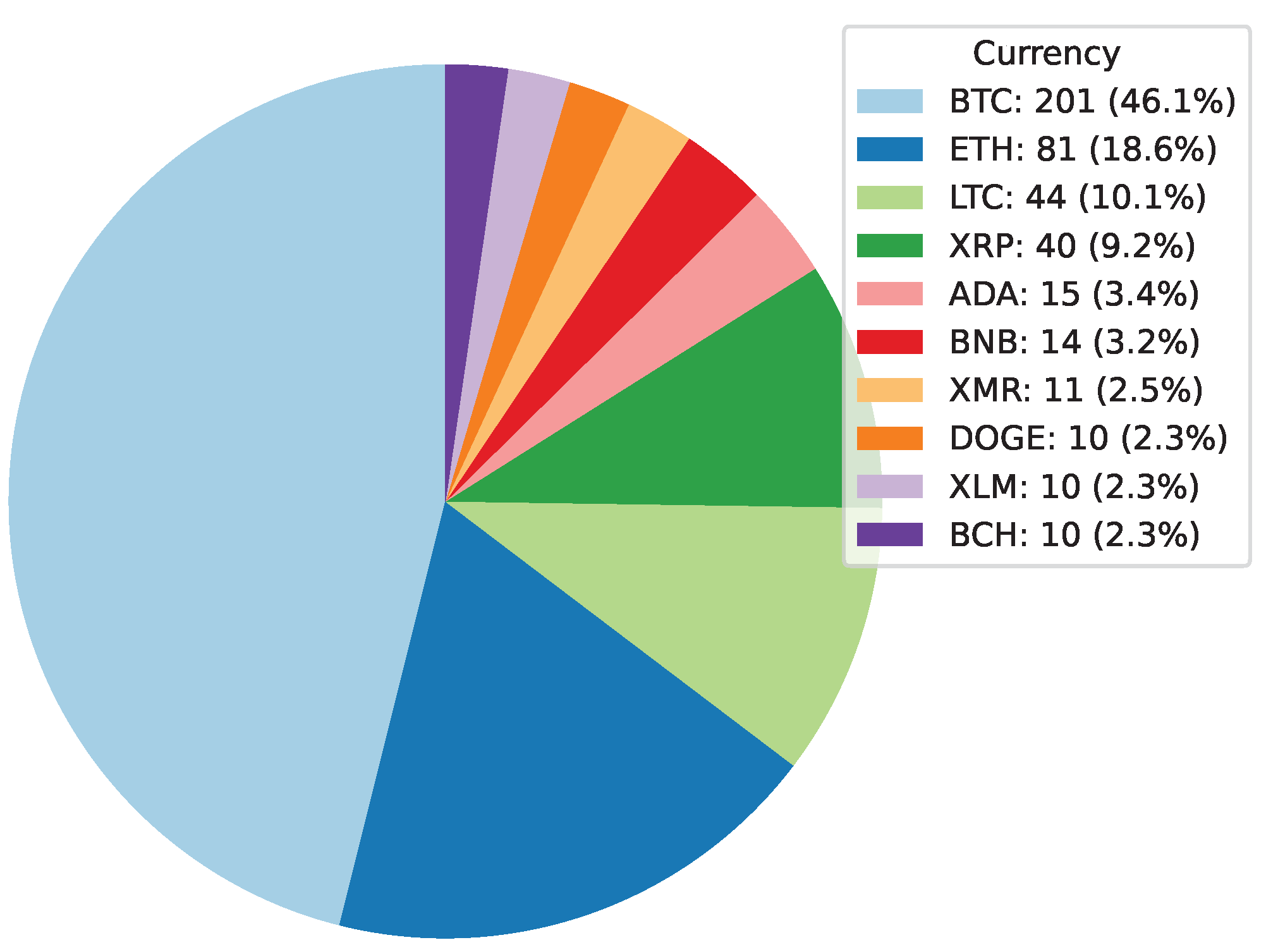
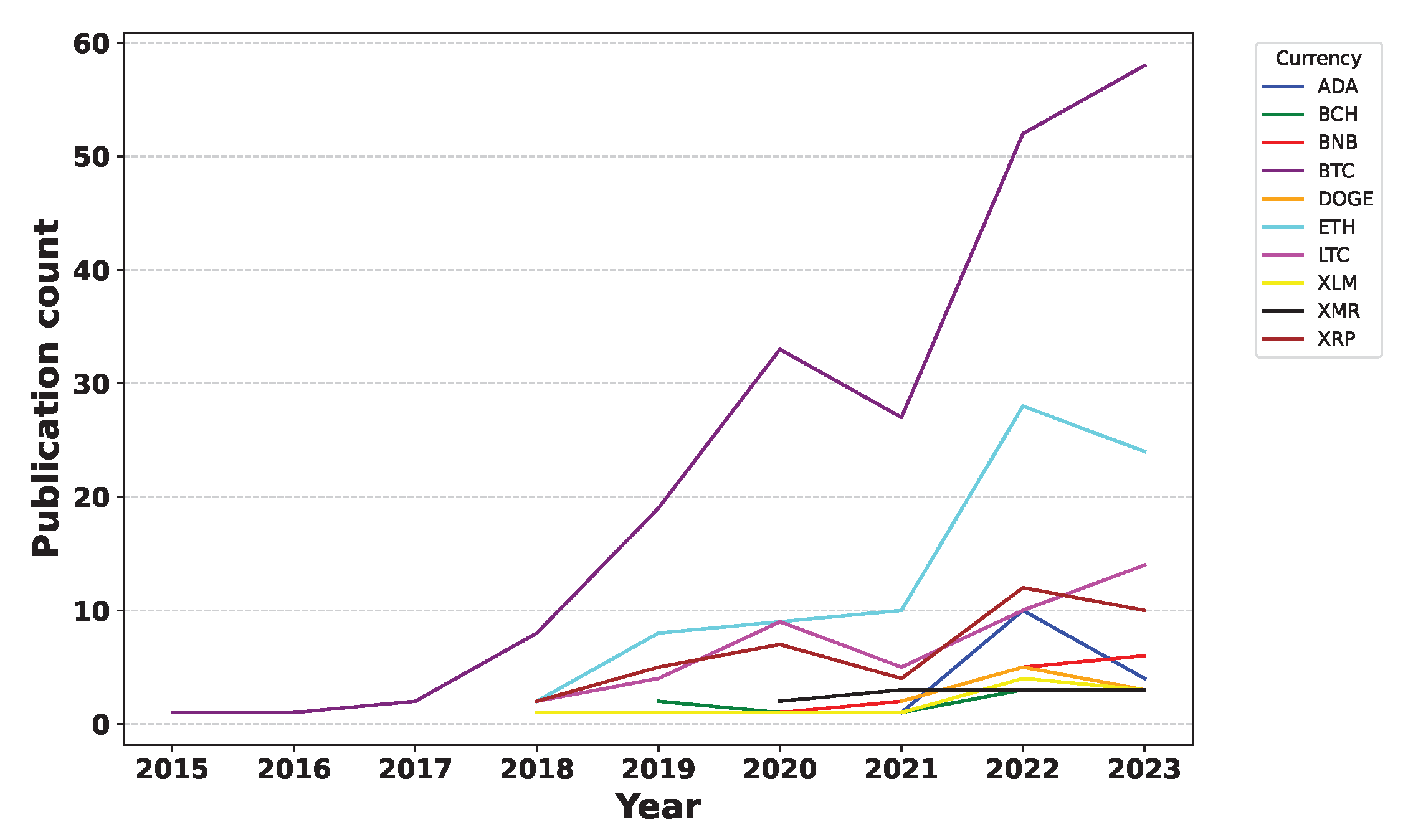
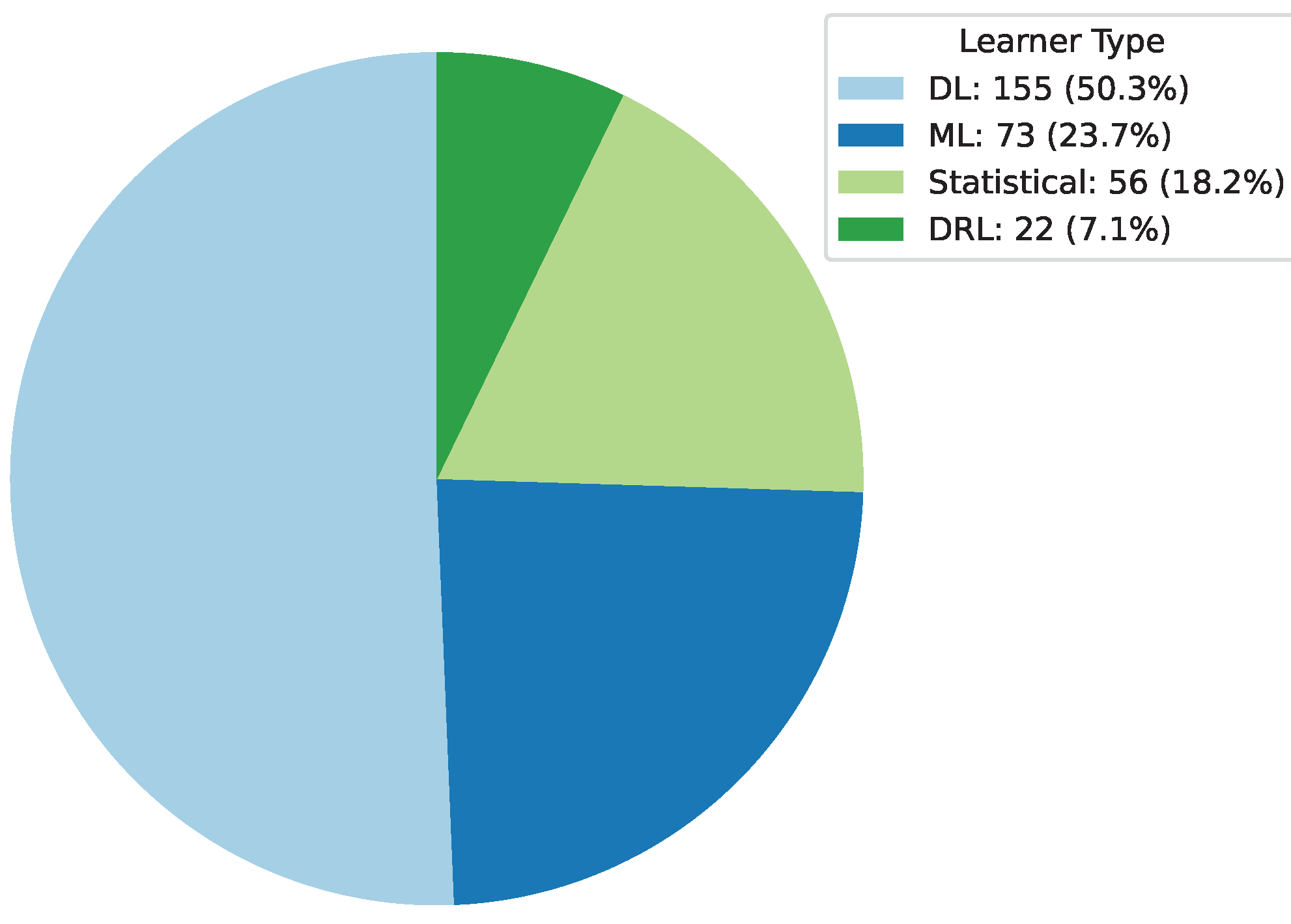
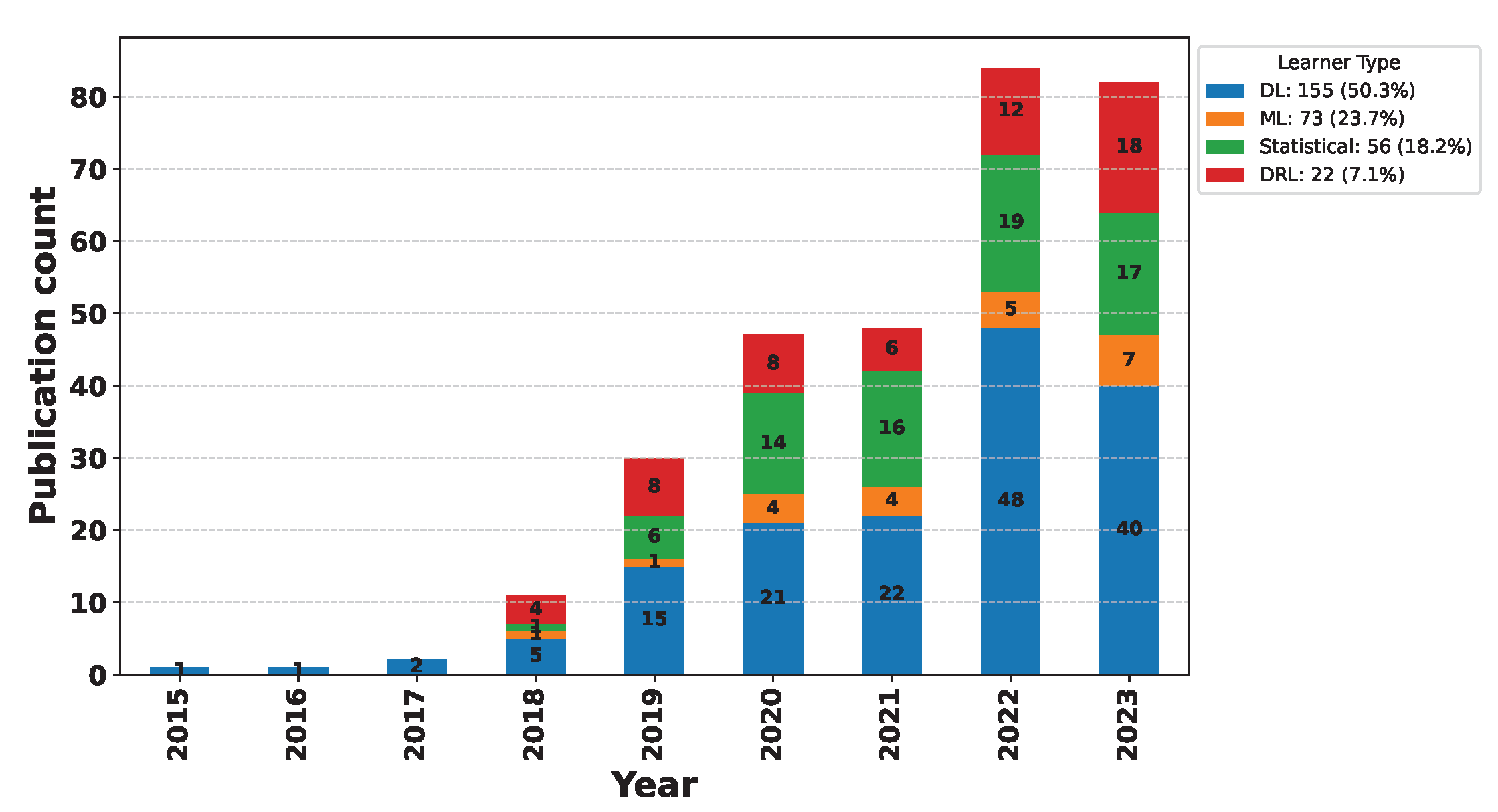
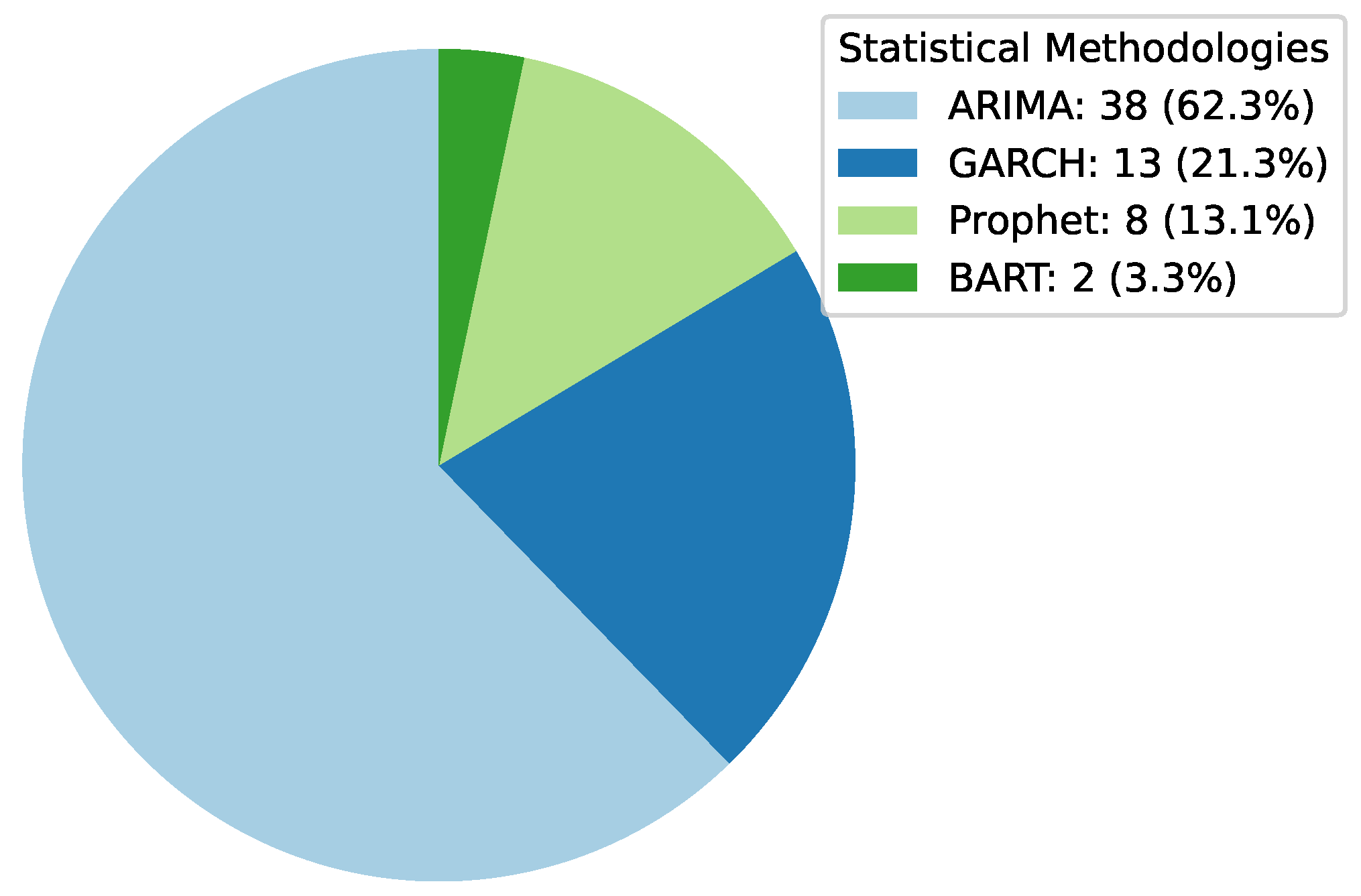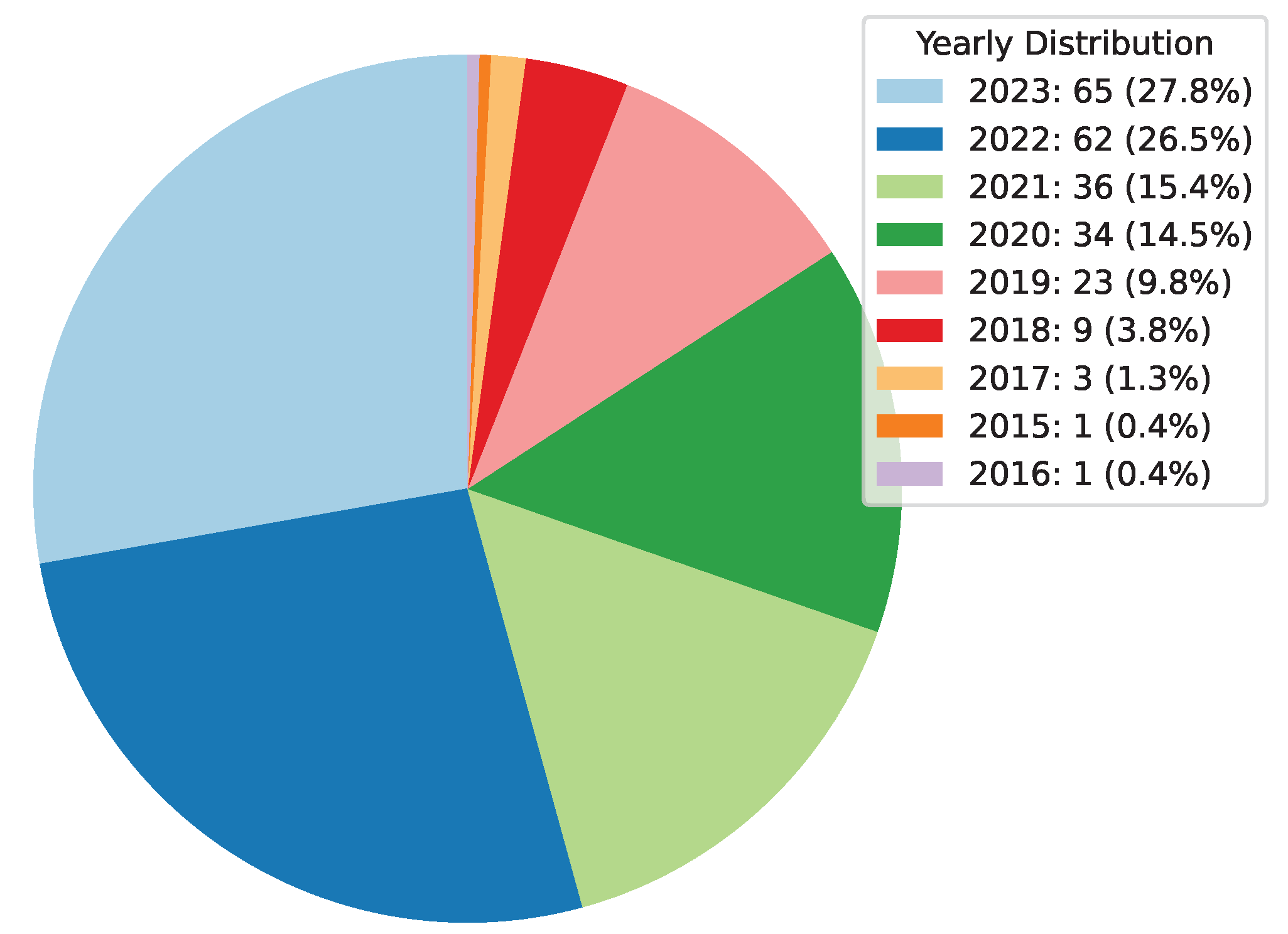Deep Learning has become a powerful tool in predicting cryptocurrency prices due to its capability to capture complex patterns and dependencies in data. In this survey paper, various applications of DL techniques such as Recurrent Neural Networks, Convolutional Neural Networks, Long Short-Term Memory Networks, Artificial Neural Networks, Multilayer Perceptrons, Gated Recurrent Units, and Transformers are explored for cryptocurrency forecasting.
This study explores the evolution of Deep Learning models, their performance, and the valuable insights they offer in predicting cryptocurrency prices. By thoroughly investigating the use of Deep Learning techniques in cryptocurrency forecasting, this research paper aims to reveal patterns and dynamics within cryptocurrency markets. This will enable more precise predictions in the rapidly changing landscape of digital currencies.
6.2.4. Recurrent Neural Network
In 2016, Sean et al. [
97] conducted a research study to predict Bitcoin prices within a 24-hour time horizon. Their approach centered on the implementation of Recurrent Neural Networks, coupled with various other Deep Learning algorithms as discussed in
Section 6. They utilized both price data and blockchain data as their input features, creating a comprehensive model for their predictions. In contrast, in 2018, Ze Shen et al. [
98] ventured into Bitcoin price prediction using a distinct strategy. They solely relied on price data in OHLC (Open, High, Low, Close) format to forecast Bitcoin prices over a 24-hour time horizon. Their research involved deploying Deep Learning techniques, including RNN, alongside other Statistical models as discussed in
Section 8. Interestingly, [
98] found that the Recurrent Neural Network method outperformed other applied methods in terms of predictive accuracy, as evidenced by their performance metrics, which included Root Mean Square Error and Mean Absolute Error.
In 2020, Aniruddha et al. [
99], along with Dane et al. [
100], embarked on research endeavors dedicated to predicting cryptocurrency prices. These studies took different approaches [
99] hinged their research on price data and blockchain data to predict Bitcoin prices. [
100], on the other hand, employed price data and sentimental data to predict the prices of BTC, XRP, and LTC within a 24-hour time horizon. Both studies shared a common research methodology involving Recurrent Neural Networks and various Deep Learning algorithms discussed in
Section 6. However, the specific data sources they used set them apart. In their respective conclusions, [
100] noted that including Google Trends data did not yield significant performance improvements in their models. These studies enrich our understanding of cryptocurrency price prediction, emphasizing the role of data sources and their impact on predictive outcomes.
In 2021, cryptocurrency research progressed with the works of Daniel et al. [
101] and Dante et al. [
102] both dedicated to predicting cryptocurrency prices within a 24-hour time horizon. Their common choice for input features was price data, yet the specifics of their approaches varied [
101] leveraged OHLCV data and changes in the percentage of the U.S. dollar to predict the prices of an extensive range of cryptocurrencies, including BTC, ETH and more. [
102] utilized OHLC data, volume data (from and to), conversion type, and conversion symbol to predict the prices of BTC, ETH and more. Both research studies implemented Recurrent Neural Networks in combination with various Machine Learning algorithms, as discussed in
Section 5, and Deep Learning algorithms outlined in
Section 6. Notably, [
101] achieved impressive accuracy ranging from 88% to 100% in their models, highlighting the power of their approach. On the other hand, [
102] surpassed traditional Machine Learning methods with their Deep Learning models, underscoring the efficacy of Deep Learning in cryptocurrency price prediction. These studies contribute to the ever-expanding body of cryptocurrency research, showcasing advancements in accuracy and methodology.
In 2022, the timeline of cryptocurrency research continued to evolve with several significant contributions as Monish et al. [
103] and Chuen et al. [
74] conducted research aimed at predicting cryptocurrency prices. They approached this task by utilizing the closing price as their primary input feature. Monish et al. [
103] stood out by considering both 30-day and 90-day time horizons to predict the price of ETH. Their methodology involved the implementation of Recurrent Neural Networks in conjunction with Deep Learning, Machine Learning, and Statistical models discussed in
Section 6,
Section 5,
Section 8.
Chuen et al. [
74] focused on a 24-hour time horizon to predict the prices of three different cryptocurrencies, namely BTC, ETH, and XRP. They also utilized RNN and explored various Deep Learning, Machine Learning, and Statistical models outlined in the relevant
Section 6,
Section 5,
Section 8. Meanwhile, Hashem et al. [
104] delved into predicting the price of Bitcoin over a 24-hour time horizon. Their approach involved using price data and market capitalization as input features. They also relied on Recurrent Neural Networks as their chosen methodology, supplemented with other Deep Learning algorithms. n the same year Ema et al. [
77], focused on Bitcoin price prediction over a 1-hour time horizon. They utilized price data, specifically OHLCV, as their input features for their model. Adding to the 2022 research landscape, Patnaikuni et al. [
105] conducted a study dedicated to predicting the price of Bitcoin within a 24-hour time horizon. Their research methodology involved price data, specifically OHLCV, as input features, which were processed using Recurrent Neural Networks, alongside other Deep Learning and Machine Learning methods as discussed in
Section 6,
Section 5,
Section 8. These studies collectively contribute to the ongoing advancement of cryptocurrency price prediction, showcasing the diversity of approaches and methodologies employed in the field during the year 2022.
In 2023, cryptocurrency research was expanded more with the study of Dzaki et al. [
106], J. Sasikumara et al. [
107], and K. Tejasri et al. [
108]. These studies were dedicated to predicting the prices of Bitcoin, with [
106] extending their scope to include ETH in their price-prediction models. Their primary input features consisted of price data and market capitalization data, forming the foundation of their analyses. The common thread in their research methodology was the utilization of Recurrent Neural Networks and other Deep Learning algorithms, as discussed in
Section 6. These advanced techniques allow for a more in-depth analysis of cryptocurrency price trends and patterns. Of particular note, K. Tejasri et al. [
108] observed that the Recurrent Neural Network proved to be effective in predicting Bitcoin prices over a 24-hour time horizon. Their comprehensive evaluation encompassed critical performance metrics, including Mean Squared Error, Mean Absolute Percentage Error, and Root Mean Square Error. These studies in 2023 continue to contribute to the evolving field of cryptocurrency research, emphasizing the effectiveness of advanced neural network models like RNN in predicting cryptocurrency prices.
In the same year 2023, Madhusekhar Yadla et al. [
109] and Tiago et al. [
88] contributed to the ongoing exploration of cryptocurrency price prediction. Madhusekhar Yadla et al. [
109] focused on predicting Bitcoin prices by leveraging both price data and sentimental data. Their research revealed that Recurrent Neural Networks outperformed Long Short-Term Memory Networks in their predictive models. Simultaneously, Tiago et al. [
88] conducted a research study to predict Bitcoin prices over a 24-hour time horizon. Their methodology revolved around RNN, complemented by other Deep Learning and Statistical methods, as discussed in
Section 6 and
Section 8. They utilized closing prices as their primary input feature. In their respective conclusions, Tiago et al. [
88] noted that RNN provided smoother forecasting results but encountered challenges in capturing significant price spikes.
6.2.5. Long Short Term Memory
In 2016, Sean et al. [
97] conducted a study to predict Bitcoin’s price. Their research strategy included the utilization of Recurrent Neural Networks and Long Short-Term Memory models. What set their approach apart was the incorporation of both price data and blockchain data as inputs, aimed at enhancing predictive accuracy. To evaluate the model’s performance, Sean et al. [
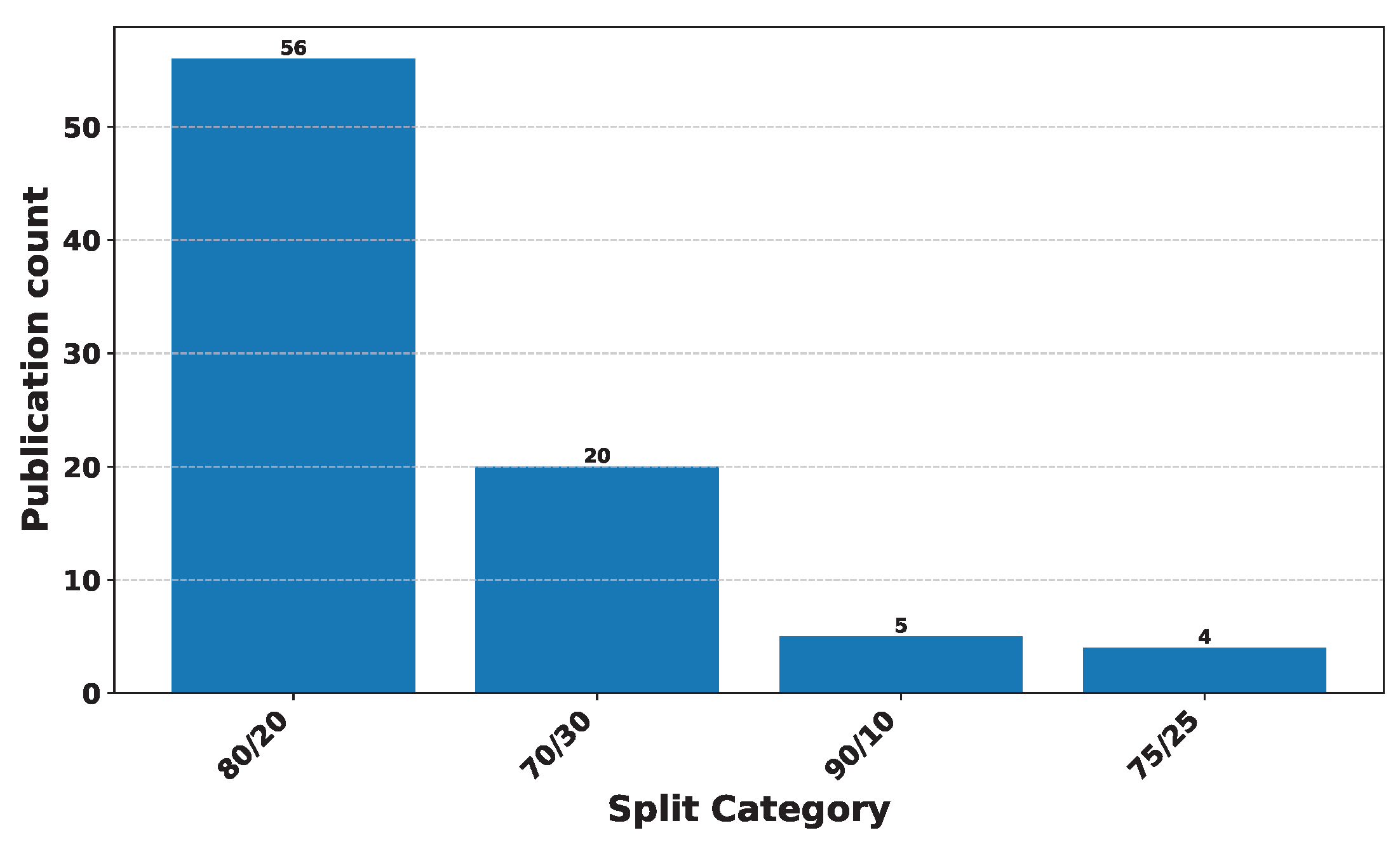
97] divided their dataset into training and testing sets, following an 80/20 ratio. The dataset they employed encompassed a time range spanning from the 19th of August 2013 to the 19th of July 2016. The findings from their study were remarkable, as the LSTM model outperformed other methods, achieving the highest classification accuracy at 52% and a Root Mean Square Error of 8%. This research represented a pivotal moment in cryptocurrency price prediction, showcasing the potential of advanced neural network models in addressing the complex task of forecasting cryptocurrency prices.
In 2018, Kejsi et al. [
110] carried out a comprehensive study aimed at predicting the price of Bitcoin. Their approach was notably multifaceted, incorporating price data, blockchain data, and sentimental data to enhance their predictive model. To forecast Bitcoin’s price over varying time horizons (30 days and 60 days), the researchers employed Long Short-Term Memory networks, known for their effectiveness in modeling sequential data. The dataset utilized for their study spanned from 2014 to September 2018, with the last two months reserved for prediction purposes. This temporal division ensured the model’s evaluation of unseen data, a crucial step in assessing its real-world applicability. The researchers used Root Mean Square Error and Mean Absolute Error as performance metrics to gauge the model’s accuracy and precision.
In 2019, Suhwan et al. [
90] conducted an insightful study with the primary goal of predicting Bitcoin’s price. To achieve this, they utilized Long Short-Term Memory networks. A distinctive aspect of their research was the utilization of blockchain data, covering the period from November 29, 2011, to December 31, 2018, as a crucial input feature for training the LSTM model. This extensive historical data provided valuable insights into Bitcoin’s price behavior. Their research methodology integrated LSTM alongside other Deep Learning methods discussed in
Section 6, reflecting a comprehensive approach to cryptocurrency price prediction. To rigorously assess the model’s performance, [
90] adopted a dataset split, allocating an 80% portion for training and 20% for testing. They also conducted backtesting to validate the model’s predictive capabilities. The outcomes of their research revealed that there was no clear standout among the various algorithms employed. However, the results obtained were notably comparable, demonstrating the robustness of these approaches. Particularly noteworthy was the effectiveness of Deep Learning models in predicting Bitcoin’s price, further establishing their relevance in cryptocurrency price prediction.
In the same year,, Do-Hyung et al. [
54] delved into the realm of time series classification for cryptocurrency price trends, focusing on a 10-minute time frame. Their study encompassed eight different cryptocurrencies, namely BTC, ETH, and more. The dataset utilized in their research comprised essential metrics, including open, high, low, close, and volume, spanning from June 9, 2017, to May 8, 2018. To classify and analyze these cryptocurrency price trends effectively, their research methodology integrated Long Short-Term Memory networks alongside other Machine Learning algorithms, as discussed in
Section 5. This diverse approach aimed to capture the complexities of cryptocurrency markets. In terms of performance evaluation, their study employed crucial metrics such as Accuracy, Recall, Precision, and F1-score. The findings of their research were noteworthy, as they indicated that LSTM outperformed traditional Machine Learning models, resulting in approximately a 7% performance improvement.
Also in 2019, Hector et al. [
111] embarked on a study that centered around the prediction of high-frequency trends for Bitcoin, focusing on a 1-minute time frame. To achieve this, they harnessed Long Short-Term Memory networks in combination with various Deep Learning architectures. Their study leveraged technical indicators and OHLC (Open, High, Low, Close) data, encompassing the period from January 1, 2020, to September 30, 2020. The dataset was thoughtfully divided into three segments: 70% for training, 15% for validation, and the remaining 15% for testing. This division allowed for a comprehensive assessment of the model’s performance, encompassing unseen data.
Table 5.
Average testing accuracy bitcoin [
111].
Table 5.
Average testing accuracy bitcoin [
111].
| Model |
Accuracy |
| MLP |
57.84% |
| LSTM |
57.55% |
| CNN |
51.14% |
| CNN-LSTM |
57.29% |
In 2019, Agha et al. [
112] conducted a study in which they utilized LSTM, along with other Deep Learning algorithms, to predict Bitcoin prices. Notably, their research demonstrated that LSTM consistently outperformed the alternative methods they employed. The primary performance metric they used for evaluation was Mean Squared Error.
In 2019, Anh-Dung et al. [
113] conducted a study focused on predicting the price of Ether using LSTM over a 24-hour time horizon. They employed OHLC data and sentiment data from news sources, covering the period from 30 July 2017 to 5 October 2018. The dataset was divided into an 80% portion for training and the remaining portion for testing. Remarkably, their research revealed that LSTM exhibited strong predictive performance, even when not incorporating sentiment scores from news data.
Takuya et al. [
114] conducted research focused on predicting cryptocurrency price trends using OHLC (Open, High, Low, Close) and blockchain data. They considered different time intervals, specifically 1-minute and 30-minute ranges, covering the period from 13 June 2013 to 18 March 2017. In this study, they employed LSTM along with other algorithms and evaluated their models using metrics such as accuracy, recall, precision, and F1-score. Interestingly, LSTM did not emerge as the top-performing model within the implemented methods. The profit rates derived from RSM outperformed those from LSTM; however, they did not surpass those of the buy-and-hold strategy during the testing data period. Consequently, they do not offer a viable basis for algorithmic trading.
In 2019, George et al. [
115] conducted a study aiming to examine and predict the price of Bitcoin over a 24-hour time horizon. To accomplish this, they incorporated both blockchain and price data. Their research compared the effectiveness of LSTM and ARIMA models for predicting Bitcoin prices. The study’s conclusion highlighted LSTM as the more proficient model for this specific forecasting task.
Ashwini et al. [
116] conducted a study in 2019 to forecast various cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, Ether , and Litecoin, over a 24-hour time horizon. Their research findings indicated that the LSTM model consistently outperformed alternative forecasting methodologies, such as Prophet and ARIMA.
Yan Li et al. [
91] in 2019 embarked on a research endeavor to predict Bitcoin prices. They harnessed price data and external economic data, covering a dataset ranging from 30 December 2016 to 31 August 2018. The study focused on predicting prices over 3-day intervals. Their findings underscored the effectiveness of a CNN-LSTM hybrid neural network, which emerged as a valuable tool for cryptocurrency price prediction.
Moving into 2020, Ihyak et al. [
117] conducted a comprehensive study aimed at forecasting Bitcoin’s price over a 24-hour time horizon. Their chosen methodology for this task was LSTM, and they relied on price data. The dataset utilized in their research extended from 2014 to 2020. To assess the predictive accuracy of their model, they adopted performance metrics such as Root Mean Square Error and Mean Absolute Percentage Error. Impressively, their LSTM-based model achieved outstanding results, boasting an accuracy rate of 97%, a MAPE error of 2.52%, and an RMSE of 329.15.
In 2020, [
118,
119,
120,
121,
122,
123] explored the use of LSTM among other methodologies for cryptocurrency price prediction. [
122] delved into the realm of cryptocurrency price prediction, focusing on a very short time horizon of 5 seconds. Their research involved the application of LSTM and other techniques discussed in sections related to Statistical models
8. Notably, LSTM emerged as a promising model within this ultra-short-term context. Other researchers, including [
118,
119,
120,
121,
122,
123], undertook studies to predict cryptocurrency prices over a 24-hour time horizon. These studies also employed LSTM along with various other methodologies discussed in the sections on Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Statistical models
5,
Section 6 and
Section 8. Among these researchers, some observed that LSTM outperformed alternative algorithms, emphasizing its effectiveness in cryptocurrency price prediction.
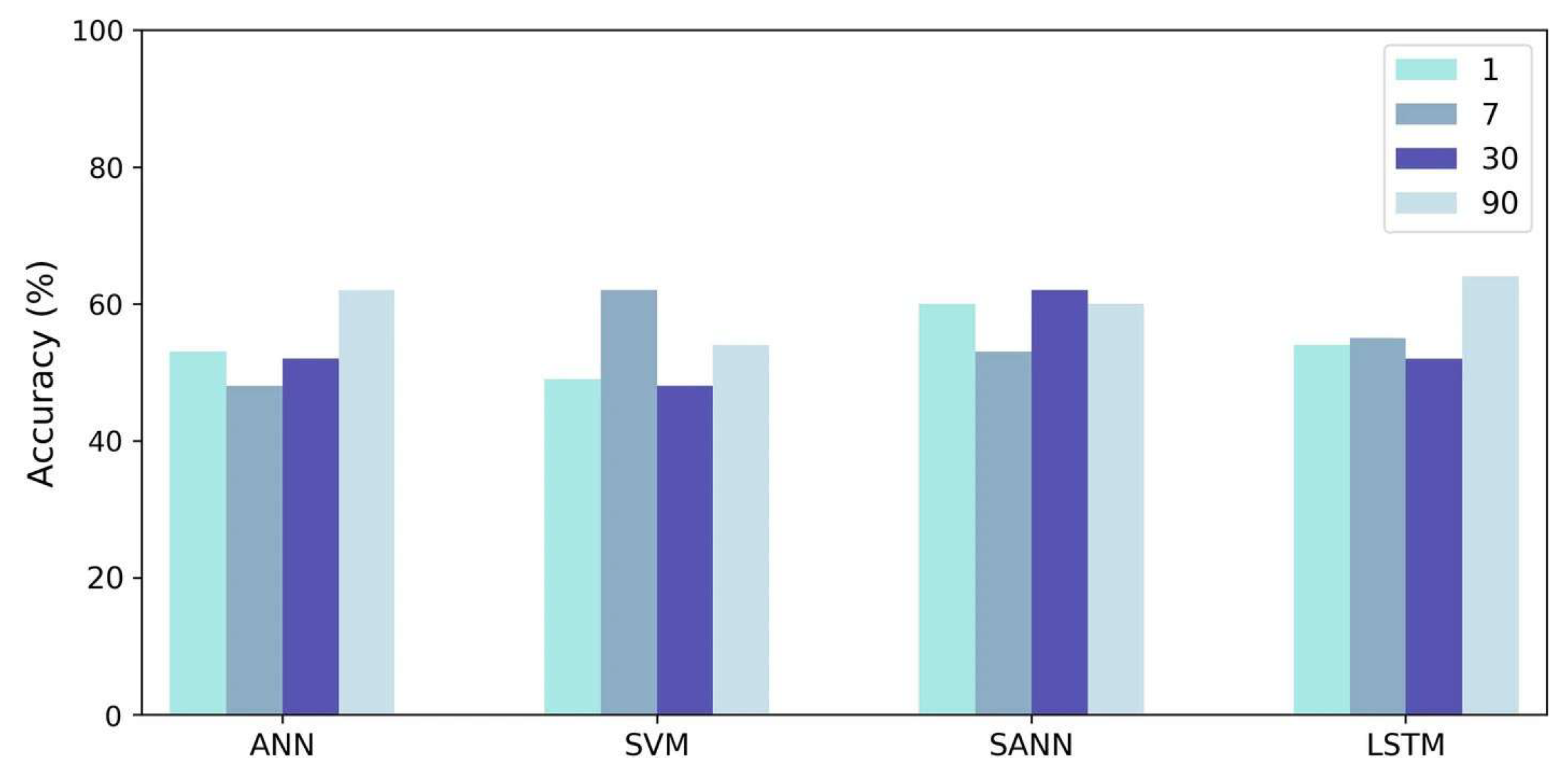
In 2020 Mohammed et al. [
42] conducted a comprehensive research study focused on predicting Bitcoin prices. Their approach encompassed the utilization of Blockchain data and price data to forecast Bitcoin prices over various time intervals, ranging from 1 day to 90 days. This extensive analysis featured the implementation of Long Short-Term Memory along with other algorithms, as discussed in the respective sections dedicated to Machine Learning and Deep Learning
5 and
6. The dataset under scrutiny spanned from 2013 to 2017 and was segmented into different time chunks to facilitate in-depth analysis. The researchers meticulously divided this dataset into training and testing subsets, following an 80/20 ratio, ensuring a robust evaluation of their predictive models. What sets this study apart is its observation of LSTM’s superior performance in cryptocurrency price prediction. Specifically, LSTM achieved an impressive 65% accuracy rate for next-day Bitcoin price predictions, showcasing its prowess in short-term forecasting. Furthermore, LSTM demonstrated consistent accuracy levels, ranging from 62% to 64%, for forecasts extending from the 7th day to the 90th day. In terms of forecasting accuracy, this study reported Mean Absolute Percentage Error scores, highlighting a remarkable 1.44% for 1-day predictions and a range of 2.88% to 4.10% for the extended horizons, namely from the 7th to the 90th day.
In the same year 2020, Tapan et al. [
76] undertook a significant research study aimed at predicting Bitcoin prices. Their approach involved the utilization of Long Short-Term Memory, a popular Deep Learning model, as well as other Machine Learning methodologies, which were discussed in the relevant section on Machine Learning
5. To bolster their predictive models, the researchers leveraged a unique dataset comprising a broad spectrum of tweets. These tweets were categorized into positive, neutral, and negative sentiment groups, each linked to corresponding mapped average Bitcoin prices. This distinctive dataset allowed the researchers to explore the intricate relationship between sentiment expressed in tweets and Bitcoin price predictions.
In 2021, Patrick et al. [
37] embarked on a comprehensive research study to forecast Bitcoin prices. Their approach was multifaceted, incorporating technical indicators, sentiment data, and blockchain data to generate predictive models. The study spanned various time horizons, including 1 minute, 5 minutes, 15 minutes, and 60 minutes, thereby catering to different trading strategies and preferences. The performance of these predictive models was evaluated using the accuracy metric. The findings of the study indicated that, particularly for the 60-minute time horizon, Long Short-Term Memory emerged as the top-performing algorithm among all those implemented. This means that LSTM exhibited the highest accuracy when compared to the other algorithms discussed in the sections about Machine Learning and Deep Learning
5 and
6.
In 2021 [
124,
125] conducted separate research studies to predict the prices of Bitcoin and Dogecoin. They utilized price data as their primary input feature, aiming to forecast cryptocurrency prices using various time horizons and sentiment data. [
124] focused on Bitcoin and employed both 1-minute and 1-hour time horizons to capture minute-to-minute and hourly price dynamics. To evaluate the performance of their predictive models, they utilized the Root Mean Square Error as a metric. Their results demonstrated impressive accuracy, with an RMSE score of 0.014 for minute-level data and 0.018 for hourly data, highlighting the precision of their predictive models. [
125] concentrated on Dogecoin and adopted a 24-hour time horizon to assess and predict its price dynamics over a longer duration. Like [
124] they employed RMSE as their performance evaluation metric, although specific RMSE scores were not provided in the available information. A noteworthy conclusion drawn from both studies was that Long Short-Term Memory emerged as the top-performing algorithm, particularly when focusing on a 60-minute time horizon. LSTM demonstrated the highest accuracy when compared to other Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms discussed in the respective studies.
In the same year 2021, Sardar et al. [
126] and [
127] focused on predicting the price of Bitcoin over a 24-hour time horizon. They employed Long Short-Term Memory along with other Deep Learning and Machine Learning algorithms to enhance their predictive models. [
126] evaluated the performance of their models using metrics such as Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1, while [
127] used metrics like Mean Squared Error, Mean Absolute Percentage Error, Accuracy, and Precision for performance assessment. while [
102] extended their study to predict the prices of multiple cryptocurrencies, including BTC, ETH, and more. Similar to the previous studies, they also utilized LSTM models in combination with different Deep Learning and Machine Learning algorithms for price prediction. In [
102] study, they employed performance evaluation metrics such as Root Mean Square Error and Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) to assess their models’ accuracy. Notably, their findings indicated that multivariate LSTM outperformed other models in terms of predictive performance, suggesting its suitability for cryptocurrency price prediction across multiple currencies.
In 2021 Dino et al. [
128] conducted a study to forecast Bitcoin’s price over a 24-hour time horizon. They employed Long Short-Term Memory as a primary component of their predictive model. The study used Mean Squared Error as the primary performance metric. Their findings suggested that LSTM is effective in predicting Bitcoin’s price, highlighting its suitability for this specific cryptocurrency. Additionally, Liping et al. [
129] and Ashutosh et al. [
41] also conducted research studies aimed at predicting the price of Bitcoin. They utilized price data and implemented LSTM along with other algorithms to predict Bitcoin’s price over different time horizons. [
41] employed performance evaluation metrics such as Accuracy, R2, and MSE to assess their predictive models. In contrast, [
129] primarily used MSE as their performance metric to evaluate the accuracy of their price predictions.
Reem K et al. [
130] conducted a research study in 2021, focused on predicting the price of Bitcoin using various predictive models, including Long Short-Term Memory in conjunction with other Deep Learning algorithms. They considered price data for Bitcoin over different time horizons, including 4 hours, 12 hours, and 24 hours. To assess the performance of their predictive models, the researchers utilized several performance evaluation metrics, including Root Mean Squared Error , Mean Absolute Percentage Error, and R-squared. Their study’s results and conclusions indicated that the LSTM-based model performed exceptionally well when forecasting Bitcoin prices over 4-hour intervals. The specific performance metrics for this model included a MAPE of 0.63, RMSE of 0.0009, MSE of 9e-07, MAE of 0.0005, and an impressive R2 value of 0.994. These findings highlighted the effectiveness of LSTM in accurately predicting Bitcoin prices, especially over short-term intervals.
In 2021 Alvin et al. [
131] Alvin et al. [Ravichandran2021] researched to predict the price of Bitcoin over a 24-hour time horizon. They implemented LSTM alongside other machine-learning algorithms. Their performance metrics included Mean Absolute Error and Mean Squared Error. The results demonstrated a low error rate of approximately 0.08%, indicating the model’s ability to make accurate price predictions. In the same year, Hari et al. [
132] also used LSTM in their research study to forecast the price of Bitcoin over a 24-hour time horizon. They employed various performance metrics such as Accuracy, Recall, Precision, and ST. Their study concluded that utilizing a large dataset with LSTM can significantly enhance the accuracy of Bitcoin price predictions.
Dimitrios et al. [
79] implemented LSTM and Machine Learning algorithms to predict the price of Ether over a 24-hour time horizon. They leveraged blockchain data and technical indicators to make their predictions. Performance metrics included Mean Absolute Error, Root Mean Squared Error, Mean Absolute Percentage Error, and R-squared. Their findings indicated that LSTM outperformed the Machine Learning algorithms in forecasting ETH prices. Following this, Olena et al. [
133] conducted a study aimed at predicting the prices of both Bitcoin and Ether. They worked with 1-minute-level open price data. Their research concluded that LSTM excelled compared to other algorithms for modeling exchange rates.
As 2022 started, Kamran et al. [
134] conducted a study to predict the prices of four different cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin and Ether. Their research methodology involved using price data and technical indicators as input features. They applied LSTM and various other deep-learning methods. To assess the performance of their models, they used metrics such as Mean Squared Error, Root Mean Squared Error, Mean Absolute Error, and the coefficient of determination. The study’s findings revealed that the LSTM-based strategy was the most effective in predicting cryptocurrency prices.
In 2022, researchers in the field of cryptocurrency analysis continued their endeavors to predict the prices of various cryptocurrencies, with a focus on Bitcoin and Ether. Three notable studies, conducted by [
135,
136], and [
104], stand out in this regard. These studies utilized price data and employed a range of algorithms, including LSTM, as well as other Deep Learning and Statistical models, which were discussed in
Section 6 Section 8. The primary objective of these studies was to forecast cryptocurrency prices, particularly over a 24-hour time horizon. After extensive analysis and experimentation, the researchers observed that LSTM-based strategies were more effective and yielded better results in predicting the prices of these digital assets.
In 2022, Bhaskar [
137] conducted a study aimed at predicting cryptocurrency prices, particularly Bitcoin, by utilizing both price data and technical indicators. The methodology involved employing LSTM and other Deep Learning strategies discussed in
Section 6. This study considered various time horizons, including 3 days, 5 days, and 7 days, to forecast price movements. The performance metrics used to evaluate the models encompassed MAE, RMSE, and MAPE. Additionally, during the same year in 2022, Mamoona et al. [
138] conducted a similar research study to predict Bitcoin’s price. Like [
137] study, this research also utilized price data and technical indicators. The models employed included LSTM, along with some other Deep Learning methods discussed in
Section 6, as well as Statistical models discussed in
Section 8. [
138] extended their analysis to time horizons of 7 days, 14 days, and 21 days. Notably, this study explored different combinations of hybrid models, ultimately identifying LSTM as a crucial component of the best-performing model.
In the same year, several research studies were conducted to predict the price of Bitcoin also using sentiment data as their input feature. Zelal et al. [
139], L.J et al. [
140], and AyÅŸenur et al. [
141] focused on leveraging sentiment data to forecast Bitcoin’s price movements over a 24-hour time horizon. They employed LSTM as the primary strategy for predicting Bitcoin’s price based on sentiment data. Concurrently, Huali et al. , Yiyang et al. [
143], and Gil et al. [
30] undertook research projects that also incorporated sentiment data alongside price data for Bitcoin price prediction. Their primary strategy was the utilization of LSTM, combined with other Deep Learning strategies discussed in the Deep Learning
Section 6. Notably, both [
142] and [
143] concluded that LSTM was the most effective algorithm for predicting Bitcoin’s price when using sentiment and price data. Furthermore, in the same year, another study sought to predict the price of Bitcoin by integrating price data, sentiment data, and technical indicators data as input features. Zi et al. [
144] implemented a combination of LSTM and GRU, which is further discussed in the Deep Learning section. They applied this strategy to predict Bitcoin’s price over two different time horizons: 30 minutes and 24 hours. The performance metrics used in their study included MSE, MAE, MAPE, and sMAPE, with their findings indicating particularly good results for the shorter time horizon of 30 minutes.
Figure 14.
Data collection and pre-processing steps [
139].
Figure 14.
Data collection and pre-processing steps [
139].
[
142] In 2022, several research studies focused on predicting the prices of Bitcoin over various time horizons, with a specific emphasis on the 24-hour period. These studies included authors such as [
105,
145,
146,
147], and [
148]. While [
145] extended their analysis to include cryptocurrencies such as ETH and ADA, [
103] specifically targeted Bitcoin price predictions over different timeframes, including 1 day, 7 days, 30 days, and 90 days. The input features for these studies primarily revolved around price data. To predict cryptocurrency prices, the authors employed various strategies, including LSTM and other methodologies discussed in
Section 6,
Section 5, and
Section 8 of their respective research papers. Across these studies, LSTM consistently outperformed the other implemented strategies, showcasing its effectiveness in cryptocurrency price prediction. Notably, [
146] reported an impressive accuracy rate of 95.7% and achieved low RMSE scores of 0.05, as well as an error loss of 0.00065.
In 2022, a series of research studies were conducted by authors like [
58,
63,
77,
149,
150] with a focus on predicting the prices of various cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin being the primary target. These studies employed a range of Deep Learning and Machine Learning algorithms, but LSTM was prominently featured across different time horizons. Most of these studies were designed to forecast cryptocurrency prices over a 24-hour time horizon, except for [
77] and [
149], which specifically examined 1-hour price predictions. The input features commonly included OHLC (Open, High, Low, Close) data and trading volume. Among these studies, LSTM emerged as the preferred choice for cryptocurrency price prediction, with some, like [
149], reporting remarkable results. For instance, [
149] achieved an impressive correlation value of R=96.73% during training and 96.09% during testing when forecasting cryptocurrency prices. Various performance metrics, such as Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1, MSE (Mean Squared Error), RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error), and NRMSE (Normalized RMSE), were employed to evaluate the models’ performance.
In 2022, Ravikant et al. [
151] conducted a research study aimed at predicting the prices of both cryptocurrencies and stocks. They utilized price data, which included open, low, close, high, and volume. Their chosen methodology was LSTM, and their analysis covered cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ether, and Ripple, as well as stocks like Tesla, TCS, Google, Apple, and Infosys. Performance evaluation was based on metrics including MAE, MSE, RMSE, and R2. Notably, they achieved an RMSE score of 0.061 for cryptocurrencies and 0.029 for stocks.
In 2022, [
103,
152,
153] conducted research studies focused on predicting the prices of Ether over a 24-hour time horizon. While [
152] utilized open, low, close, high, and volume as input features, [
103,
153] exclusively used the close price as their input feature. A common element in their methodologies was the use of LSTM, other than this also discussed in
Section 6 Section 8. The studies employed performance metrics such as MAPE, RMSE, MAE, ME, R2, and MSE, with [
103] study demonstrating the best results through the use of LSTM and Bi-LSTM.
In 2022, researchers including [
154,
155,
156] conducted studies aimed at predicting the prices of Bitcoin over a 24-hour time horizon. These studies utilized close prices as their input features for price prediction and employed LSTM as the primary methodology. The performance metrics in these studies focused on RMSE and MSE. Additionally, in 2022, [
157] conducted a study to predict Bitcoin prices over both 1-hour and 24-hour time horizons. The study highlighted the importance of tuning hyperparameters, specifically emphasizing the need for small learning rates and dropout values for the 24-hour predictions, while larger values were more suitable for the 1-hour forecasts.
In 2023, a series of research studies were conducted by [
49,
67,
109,
158,
159] aiming to predict the prices of various cryptocurrencies, primarily over a 24-hour time horizon. These all studies leveraged sentiment analysis and price data as their input to forecast cryptocurrency prices. The methodologies employed in these studies encompassed various Machine Learning and Deep Learning strategies discussed in
Section 6 and
Section 5, with LSTM being one of the key methods. The findings from these studies varied, with some indicating that LSTM performed well in certain aspects but was average or relatively less effective when compared to other implemented algorithms. To evaluate the performance of their models, these studies used a range of metrics, including MAPE, MSE, R2, Forecast Bias, MAE, ME, RMSE, and MPE.
In 2023, a set of research studies conducted by [
71,
88,
95,
160] aimed to predict the prices of various cryptocurrencies over different time horizons. [
160] study focused on a 10-minute time horizon, while [
71,
88,
95] primarily used a 24-hour time horizon to forecast cryptocurrency prices. These studies employed a range of Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms, including LSTM, and utilized closing prices as their input features. Among these studies, [
71,
160] both found LSTM to be the most effective method for predicting cryptocurrency prices. [
71] study concluded that LSTM achieved an average RMSE of 0.0222 and MAE of 0.0173, while [
160] study determined that the LSTM model was the best approach for predicting both the direction and value of cryptocurrency prices at various time horizons. To evaluate the performance of their models, these studies used a variety of metrics, including RMSE, MAPE, R2, MAE, MAPE, DSTAT, and RMSE.
In 2023, a group of research studies led by [
64,
78,
161,
162] focused on predicting the prices of various cryptocurrencies using price data OHLC. These studies employed a 24-hour price time horizon for different cryptocurrencies and explored a range of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Statistical models as part of their research, as discussed in
Section 5,
Section 6, and
Section 8. Among these studies, [
78] concluded that LSTM was the most effective method for predicting the prices of different cryptocurrencies.
In the same year, 2023, a set of research studies led by [
106,
107,
108] aimed to predict the prices of various cryptocurrencies, primarily focusing on Bitcoin, over a 24-hour time horizon. They employed Recurrent Neural Networks, as discussed in
Section 6, and LSTM. The input features for their models included price data OHLC and Market Capitalization. These studies evaluated the performance using metrics such as MAPE, RMSE, and MSE. The consensus among these studies is that LSTM outperforms other methods for predicting the prices of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. For instance, in [
106], LSTM achieved an RMSE of 0.061 and a MAPE of 5.66% in predicting Bitcoin prices. When predicting ETH, LSTM obtained an RMSE of 0.036 and a MAPE score of 4.58%.
In 2023, Junwei et al. [
163] conducted a research study. Their study utilized a combination of price data, technical indicators data, and external economic indicators data as input features to predict the price of Bitcoin. They implemented LSTM along with other Machine Learning algorithms, which are discussed in
Section 5. One of the key findings of their research was that as the number of past periods for substituted explanatory variables increased, the prediction accuracy of the model decreased. This suggests that the model’s accuracy may be influenced by the historical data used for explanatory variables in predicting Bitcoin prices.
In 2023, several research studies were conducted to predict the prices of various cryptocurrencies, such as BTC, ETH, and LTC. Notably, Phumudzo et al. [
164] included all three of these cryptocurrencies in their analysis, whereas Nrusingha et al. [
165] focused specifically on Bitcoin. Additionally, Tiya et al. [
166] extended their research to cover a wide range of 10 different cryptocurrencies. These studies utilized price data, specifically OHLC (Open, High, Low, Close), as their primary input feature. To predict cryptocurrency prices, they implemented various Deep Learning and Statistical methods, including LSTM. Their choice of performance metrics included RMSE (Root Mean Square Error), MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error), and MAE (Mean Absolute Error).
6.2.6. Gated Recurrent Unit
In 2020, Xiangxi et al.[
120] and Dane et al.[
100] conducted research studies to predict the prices of different cryptocurrencies. Xiangxi et al. focused on using price data to predict the price of Bitcoin, while Dane et al. utilized both price data and sentimental data to predict the prices of BTC, XRP, and LTC. Their implementations involved the use of GRU along with other deep-learning methods. In 2021, Patrick et al. [
37] conducted a research study aiming to predict the price of Bitcoin. They employed technical indicators data, sentimental data, and blockchain data to make predictions over various time horizons, including 1-min, 5-min, 15-min, and 60-min. Their research methodology included GRU, combined with different Machine Learning and Deep Learning methods. The study’s findings indicated that the GRU model produced better predictions, particularly on 15-minute horizons when compared to other methods. In the same year, Basant et al. [
125] conducted a research study to predict the price of Dogecoin over a 24-hour time horizon. They used price data and sentimental data as their input features and implemented GRU and LSTM in their research methodology. The study’s conclusion revealed that the best results were achieved by using historical price data, excluding high and low prices, and Twitter sentiment data in the GRU model. The performance metric used in this study was RMSE. Additionally, in 2021, Ashutosh et al.[
41] and Reem et al.[
130] conducted research studies to predict the prices of Bitcoin. Their research methodologies incorporated GRU along with other Deep Learning and Machine Learning methods, as discussed in
Section 6 and
Section 5. The performance metrics used in their studies included RMSE, MAPE, Accuracy, R2, and MSE.
In 2022, several research studies were conducted to predict the prices of different cryptocurrencies over a 24-hour time horizon. Abdussalam et al.[
167], Dr. M. TanooJ et al.[
150], Chuen et al.[
74], Jens et al.[
145], and V. Derbentseva et al. [
148] all employed GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit) as part of their research methodologies, in addition to other Deep Learning and Machine Learning methods, as discussed in
Section 6 and
Section 5. Abdussalam et al.[
167] and Dr. M. TanooJ et al.[
150] concluded that GRU performs better than other implemented methods in predicting various cryptocurrencies, including BTC, ETH, ADA, and BTC, respectively. In the study by Lim et al. [
74], a 1DCNN-GRU model was proposed and found to perform better than existing methods, achieving RMSE scores of 43.933 for BTC, 3.511 for ETH, and 0.00128 for XRP. V. Derbentseva et al. [
148] also concluded in their study that GRU is the best method among others, achieving an RMSE of 2.2201 and MAPE of 0.8076. In 2022, Yiyang et al. [
143] conducted a research study to predict the price of Bitcoin over both 1-hour and 24-hour time horizons. Their research methodology included the use of price data and sentimental data as input features. In their study, GRU outperformed other models, achieving an F1 score of 0.6720 for dataset 2 without emotion. Furthermore, in 2022, Caglar et al. [
152] conducted research to predict the prices of ETH over 15-minute and 30-minute time horizons, utilizing price data. Their research methodology included GRU, along with different Deep Learning-based time series models. GRU achieved the following performance metrics: a MAPE value of 5.57651, an RMSE value of 105.81920, a MAE value of 72.15339, an ME value of 363.47583, and an R2 value of 0.97090.
In 2022, [
150] conducted a research study in which they utilized Lagged Data as their input feature for different Deep Learning models, including GRU. The study included the development of a long-short portfolio strategy based on the predictions generated by the GRU model. This portfolio strategy achieved an impressive Sharpe ratio of 3.12, indicating the effectiveness of the GRU-based predictions in enhancing portfolio performance.
In 2023 Haritha et al. [
158] conducted a research study to predict the prices of Bitcoin over the 24-hour time horizon. They use price data and sentimental data as input features for different deep-learning models. Their research methodology also includes GRU which achieves MAPE of 3.6%. In the same year, Shruthi et al. [
168] also conducted a research study to predict the prices of BTC. Their research methodology includes GRU along with other Deep Learning models. Their research concluded that GRU is best for time series prediction specifically cryptocurrency price prediction. In 2022 Tiya et al. [
166], Stefano et al. [
162] conducted a research study to predict the prices of different cryptocurrencies over the 24-hour time horizon. [
166] utilized the price data to predict the prices of 10 different cryptocurrencies while [
162] used price data to predict the price of Bitcoin. Their performance metrics include RMSE, MSE, DA, and MAE. [
166] concluded that GRU performs best and can be considered efficient and dependable amongst other implemented methods while [
162] also concluded that in case of ensemble based on GRU incorporated with the value of return or baseline prediction brings a huge improvement in results.
Table 6.
Mean square error obtained while prediction [
166].
Table 6.
Mean square error obtained while prediction [
166].
| Model |
MSE |
| LSTM |
0.0006063628663181186 |
| Bi-LSTM |
0.0013169118146140332 |
| GRU |
0.0013169118146140332 |
| Ensemble |
0.0005468361394868078 |
In 2023, Haritha et al. [
158] conducted a research study focused on predicting the prices of Bitcoin over a 24-hour time horizon. They utilized both price data and sentimental data as input features for different deep-learning models. Among their research methodologies, they also incorporated the use of GRU, which achieved a MAPE (Mean Absolute Percentage Error) of 3.6%. Similarly, in the same year, Shruthi et al. [
168] conducted a research study to predict the prices of Bitcoin. Their research methodology included the use of GRU, along with other Deep Learning models. Their research findings supported the effectiveness of GRU for time series prediction, particularly in the context of cryptocurrency price prediction. In 2022, Tiya et al. [
166] and Stefano et al. [
162] also conducted research studies aimed at predicting the prices of different cryptocurrencies over a 24-hour time horizon. While [
166] used price data to predict the prices of 10 different cryptocurrencies, [
162] specifically focused on predicting the price of Bitcoin. The performance metrics utilized in these studies included RMSE (Root Mean Square Error), MSE (Mean Square Error), DA (Directional Accuracy), and MAE (Mean Absolute Error). The research findings of [
166] concluded that GRU performed the best among the implemented methods and could be considered efficient and dependable for cryptocurrency price prediction. On the other hand, [
162] also emphasized the importance of ensembles based on GRU, particularly when incorporated with return values or baseline predictions, as it led to a significant improvement in results.