Submitted:
28 November 2024
Posted:
29 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
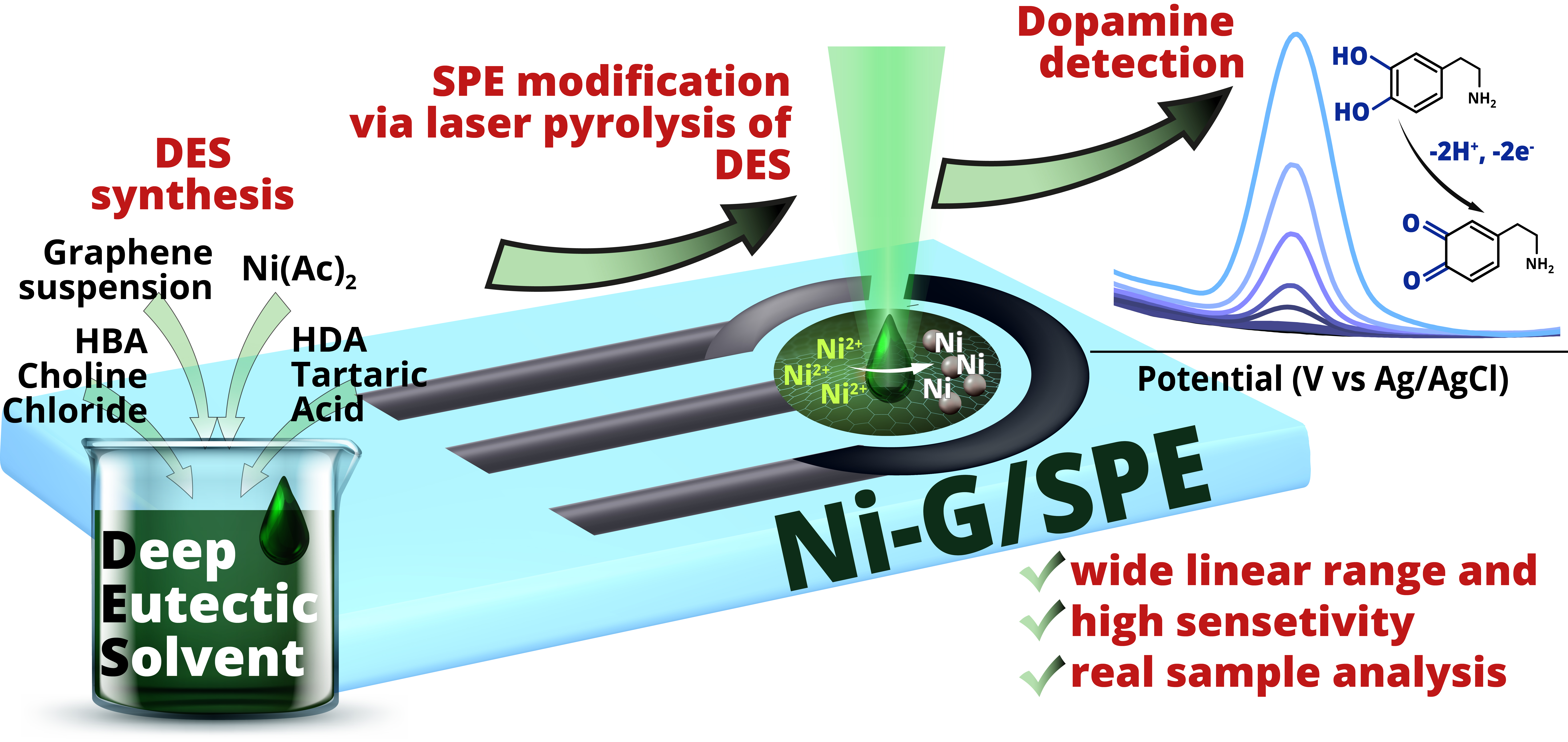
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Deep Eutectic Solvent
2.3. Electrode Fabrication
2.4. Nelder-Mead Algorithm
2.5. Characterization Techniques
2.6. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of Ni-G/SPE via Laser-Assisted Synthesis Using the Nelder–Mead Optimization Approach
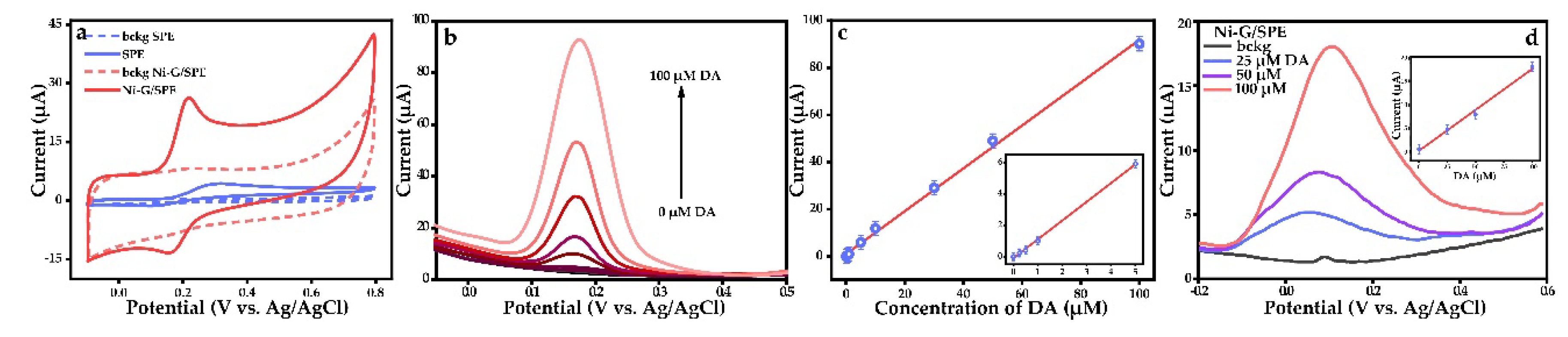
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Ni-G/SPE and Dopamine Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, S.J.; Christofferson, A.J.; Greaves, T.L.; Mcconville, C.F.; Bryant, G.; Elbourne, A. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science Bulk and interfacial nanostructure and properties in deep eutectic solvents : Current perspectives and future directions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2430–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Mayor, Á.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Herrera-Herrera, A. V.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Deep eutectic solvents. The new generation of green solvents in analytical chemistry. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134.
- Calvo-Flores, F.G.; Mingorance-Sánchez, C. Deep Eutectic Solvents and Multicomponent Reactions: Two Convergent Items to Green Chemistry Strategies. ChemistryOpen 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, D. V; Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents : Sustainable Media for Nanoscale and Functional Materials. 2014.
- Khandelwal, S.; Tailor, Y.K.; Kumar, M. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as eco-friendly and sustainable solvent/catalyst systems in organic transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S. Deep eutectic solvents as versatile media for the synthesis of noble metal nanomaterials. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Chipatecua Godoy, Y. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Assisted Synthesis of Au Nanostars Supported on Graphene Oxide as an Efficient Substrate for SERS-Based Molecular Sensing. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Hayyan, M. Potential applications of deep eutectic solvents in nanotechnology : Part II. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, S.H.; Ruddy, D.A.; Pylypenko, S.; Richards, R.M. Deep eutectic solvent approach towards nickel / nickel nitride nanocomposites. Catal. Today 2018, 306, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Rong, K.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Fang, Y. Deep eutectic solvent assisted facile synthesis of low-dimensional hierarchical porous high-entropy oxides. 2022, 15, 2756–2763.
- Maria Stanley, M.; Sherlin V, A.; Wang, S.-F.; Baby, J.N.; Sriram, B.; George, M. Deep eutectic solvent assisted synthesis of molybdenum nitride entrapped graphene aerogel heterostructure with enhanced electrochemical behavior for ronidazole drug detection. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 375, 121308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, B.; N. Baby, J.; Wang, S.F.; Ranjitha M., R.; Govindasamy, M.; George, M. Eutectic Solvent-Mediated Synthesis of NiFe-LDH/Sulfur-Doped Carbon Nitride Arrays: Investigation of Electrocatalytic Activity for the Dimetridazole Sensor in Human Sustenance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 17772–17782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, J.N.; Sriram, B.; Wang, S.F.; George, M.; Govindasamy, M.; Benadict Joseph, X. Deep eutectic solvent-based manganese molybdate nanosheets for sensitive and simultaneous detection of human lethal compounds: Comparing the electrochemical performances of M-molybdate (M = Mg, Fe, and Mn) electrocatalysts. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 19719–19731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baby, J.N.; Sriram, B.; Wang, S.F.; George, M. Effect of Various Deep Eutectic Solvents on the Sustainable Synthesis of MgFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Nitrofurantoin and 4-Nitrophenol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherigui, E.A.M.; Sentosun, K.; Mamme, M.H.; Lukaczynska, M.; Terryn, H.; Bals, S.; Ustarroz, J. On the Control and Effect of Water Content during the Electrodeposition of Ni Nanostructures from Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mernissi Cherigui, E.A.; Sentosun, K.; Bouckenooge, P.; Vanrompay, H.; Bals, S.; Terryn, H.; Ustarroz, J. Comprehensive Study of the Electrodeposition of Nickel Nanostructures from Deep Eutectic Solvents: Self-Limiting Growth by Electrolysis of Residual Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilova, E.A.; Khairullina, E.M.; Shishov, A.Y.; Eltysheva, E.A.; Mikhailovskii, V.; Sinev, D.A.; Tumkin, I.I. Direct Laser Writing of Copper Micropatterns from Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Pulsed near-IR Radiation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonský, M.; Škulcová, A.; Šima, J. Use of deep eutectic solvents in polymer chemistry–a review. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestakov, D.; Khairullina, E.; Shishov, A.; Khubezhov, S.; Makarov, S.; Tumkin, I.; Logunov, L. Picosecond laser writing of highly conductive copper micro-contacts from deep eutectic solvents. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manshina, A.A.; Tumkin, I.I.; Khairullina, E.M.; Mizoshiri, M.; Ostendorf, A.; Kulinich, S.A.; Makarov, S.; Kuchmizhak, A.A.; Gurevich, E.L. The Second Laser Revolution in Chemistry: Emerging Laser Technologies for Precise Fabrication of Multifunctional Nanomaterials and Nanostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2405457, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairullina, E.M.; Ratautas, K.; Panov, M.S.; Andriianov, V.S.; Mickus, S.; Manshina, A.A.; Račiukaitis, G.; Tumkin, I.I. Laser - assisted surface activation for fabrication of flexible non - enzymatic Cu - based sensors. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, M.; Wongkaew, N. Carbon nanomaterial hybrids via laser writing for high-performance non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors: a critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6079–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Feng, B.; He, X.; Li, F.; Ding, Y.; Fei, J. Carbon nanomaterial based electrochemical sensors for biogenic amines. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givanoudi, S.; Heyndrickx, M.; Depuydt, T.; Khorshid, M.; Robbens, J.; Wagner, P. A Review on Bio- and Chemosensors for the Detection of Biogenic Amines in Food Safety Applications : The Status in 2022. 2023.
- Ahangari, H.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Ehsani, A.; Uslu, B. Latest trends for biogenic amines detection in foods: Enzymatic biosensors and nanozymes applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkourani, G.; Brouzgou, A.; Tsiakaras, P. A review on recent advancements in electrochemical detection of dopamine using carbonaceous nanomaterials. Carbon N. Y. 2023, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, D.; Fu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Biogenic amines detection in meat and meat products : the mechanisms, applications, and future trends. J. Futur. Foods 2024, 4, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairullina, E.; Shishov, A.; Gordeychuk, D.; Logunov, L.; Levshakova, A.; Sosnovsky, V.B.; Koroleva, A.; Mikhailovsky, V.; Gurevich, E.L.; Chernyshov, I.; et al. Rapid and effective method of laser metallization of dielectric materials using deep eutectic solvents with copper acetate. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 9322–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levshakova, A.S.; Khairullina, E.M.; Panov, M.S.; Ninayan, R.; Mereshchenko, A.S.; Shishov, A.; Tumkin, I.I. Modification of nickel micropatterns for sensor-active applications from deep eutectic solvents. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2023, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levshakova, A.S.; Khairullina, E.M.; Logunov, L.S.; Panov, M.S.; Mereshchenko, A.S.; Sosnovsky, V.B.; Gordeychuk, D.I.; Shishov, A.Y.; Tumkin, I.I. Highly rapid direct laser fabrication of Ni micropatterns for enzyme-free sensing applications using deep eutectic solvent. Mater. Lett. 2022, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Kwon, H.; Kang, H.; Jang, J.E.; Kwon, H.J. Laser-Induced and MOF-Derived Metal Oxide/Carbon Composite for Synergistically Improved Ethanol Sensing at Room temperature. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogolev, D.; Semyonov, O.; Metalnikova, N.; Fatkullin, M.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Slepicka, P.; Yamauchi, Y.; Guselnikova, O.; Boukherroub, R.; Postnikov, P.S. Waste PET upcycling to conductive carbon-based composite through laser-assisted carbonization of UiO-66. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Gordeychuk, D.; Logunov, L.; Levshakova, A.; Andrusenko, E.; Chernyshov, I.; Danilova, E.; Panov, M.; Khairullina, E.; Tumkin, I. Laser-induced deposition of copper from deep eutectic solvents: optimization of chemical and physical parameters. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 21896–21904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Lu, C.J.; Xia, Z.P.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Z. X-ray diffraction patterns of graphite and turbostratic carbon. Carbon N. Y. 2007, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, S.A.; Zeebaree, S.Y.S.; Zeebaree, A.Y.S.; Zebari, O.I.H.; Saeed, I.A. The efficient removal of methylene blue dye using CuO/PET nanocomposite in Aqueous solutions. Catalysts 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Choi, C.; Wu, T.S.; Ma, C.; Kang, P.; Tao, H.; Fan, Q.; Hong, S.; Liu, S.; Soo, Y.L.; et al. Carbon-supported Ni nanoparticles for efficient CO2 electroreduction. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, M.; Martín-Jimeno, F.J.; Fernández-García, M.P.; Suárez-García, F.; Paredes, J.I.; Belo, J.H.; Araújo, J.P.; Adawy, A.; Martínez-Blanco, D.; Álvarez-Alonso, P.; et al. Untangling the role of the carbon matrix in the magnetic coupling of Ni@C nanoparticles with mixed FCC/HCP crystal structures. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Nistor, V.; Nouneh, K.; Oyama, M.; Abd-Lefdil, M.; Díaz, R. XPS study of silver, nickel and bimetallic silver-nickel nanoparticles prepared by seed-mediated growth. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fortunato, M.; Cardinale, A.M.; Sarapulova, A.; Njel, C.; Dsoke, S. Electrochemical study on nickel aluminum layered double hydroxides as high-performance electrode material for lithium-ion batteries based on sodium alginate binder. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2022, 26, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; da Silva, M.M.; de Souza Santos, L.V.; Jacob, R.S.; de Vasconcelos, C.K.B.; Viana, M.M. Graphene oxide in the remediation of norfloxacin from aqueous matrix: simultaneous adsorption and degradation process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, T.; Liao, D.; Li, Q.; Song, Y.; Xue, H.; Zhang, Y. Carbon aerogels with nickel@N-doped carbon core-shell nanoclusters as electrochemical sensors for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dementjev, A.P.; De Graaf, A.; Van de Sanden, M.C.M.; Maslakov, K.I.; Naumkin, A. V.; Serov, A.A. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy reference data for identification of the C3N4 phase in carbon-nitrogen films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2000, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Si, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Lei, W.; Xia, X.; Li, J.; Wang, F. Nitrogen-doped graphene: Effect of graphitic-N on the electrochemical sensing properties towards acetaminophen. FlatChem 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johra, F.T.; Lee, J.W.; Jung, W.G. Facile and safe graphene preparation on solution based platform. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Kaneva, Aleksandra Levshakova, Ilya Tumkin, Maxim Fatkullin, Evgeny Gurevich, Alina Manshina, Raul D. Rodriguez, E.K. Simultaneous electrochemical detection of hydroquinone and catechol using flexible laser-induced metal-polymer composite electrodes. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 240. [CrossRef]
- Jorio, A.; Souza Filho, A.G. Raman Studies of Carbon Nanostructures. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 357–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deng, L.; Kinloch, I.A.; Young, R.J. Raman spectroscopy of carbon materials and their composites: Graphene, nanotubes and fibres. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhwaige, A.A.; Alhassan, S.M.; Katsiotis, M.S.; Ishida, H.; Qutubuddin, S. Interactions, morphology and thermal stability of graphene-oxide reinforced polymer aerogels derived from star-like telechelic aldehyde-terminal benzoxazine resin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, R.; Sharawi, M.S.; Dubois, C.; Tantawy, H.; Chaouki, J. Superior quality chemically reduced graphene oxide for high performance EMI shielding materials. RSC Adv. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Cao, Y.; Diao, D. Electrochemical activation of graphene sheets embedded carbon films for high sensitivity simultaneous determination of hydroquinone, catechol and resorcinol. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2020, 305, 127495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Wan, H.; Peng, X.; Zhu, Y. An ultra-sensitive electrochemical dopamine sensor based on Ni@N-doped carbon derived from COF LZU-1 microspheres. Ionics (Kiel). 2023, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhao, P.; Fei, J.; Xie, Y. A novel dopamine electrochemical sensor based on 3D flake nickel oxide/ cobalt oxide @ porous carbon nanosheets/carbon nanotubes/electrochemical reduced of graphene oxide composites modified glassy carbon electrode. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Singh, P.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, N. Electrochemical detection of dopamine by using nickel supported carbon nanofibers modified screen printed electrode. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ali Hassine, C.; Kahri, H.; Barhoumi, H. Enhancing Dopamine Detection Using Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with Graphene Oxide, Nickel and Gold Nanoparticles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Xi, X.; Wu, D.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Ji, W.; Liu, R.L. Ordered Mesoporous Carbon/Graphene/Nickel Foam for Flexible Dopamine Detection with Ultrahigh Sensitivity and Selectivity. J. Electrochem. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Tsai, Z.Y.; Chang, H.W.; Tsai, Y.C. Enhancing Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Dopamine Sensing Based on Bimetallic Nickel/Cobalt Phosphide Nanosheets. Micromachines 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheena, M.; Ratnamala, A.; Noorjahan, M.; Reddy, G.D.; Begum, G. Hierarchical graphene oxide-Ni3S2 quantum dots nanocomposites modified glassy carbon electrode for electrochemical detection of dopamine and tyrosine. Front. Mater. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althagafi, Z.T.; Althakafy, J.T.; Al Jahdaly, B.A.; Awad, M.I. Differential Electroanalysis of Dopamine in the Presence of a Large Excess of Ascorbic Acid at a Nickel Oxide Nanoparticle-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. J. Sensors 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.S.; Chiu, D.T. Controlling mass transport in microfluidic devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Mansha, M.; Alsharaa, A.; Jillani, S.M.S.; Basheer, C. Chemically modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of uric acid and ascorbic acid: A review. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76.
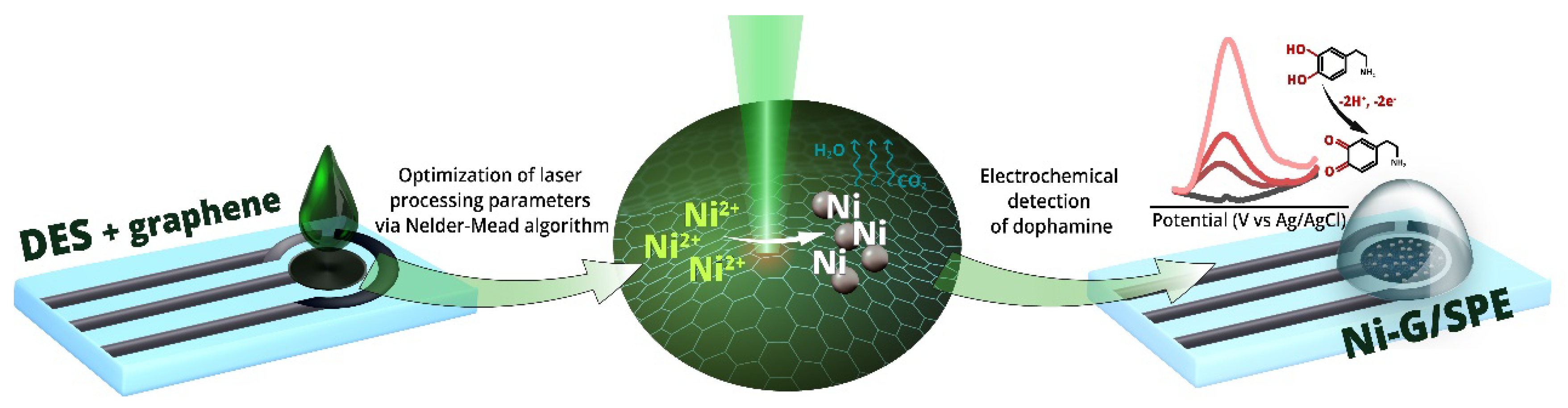
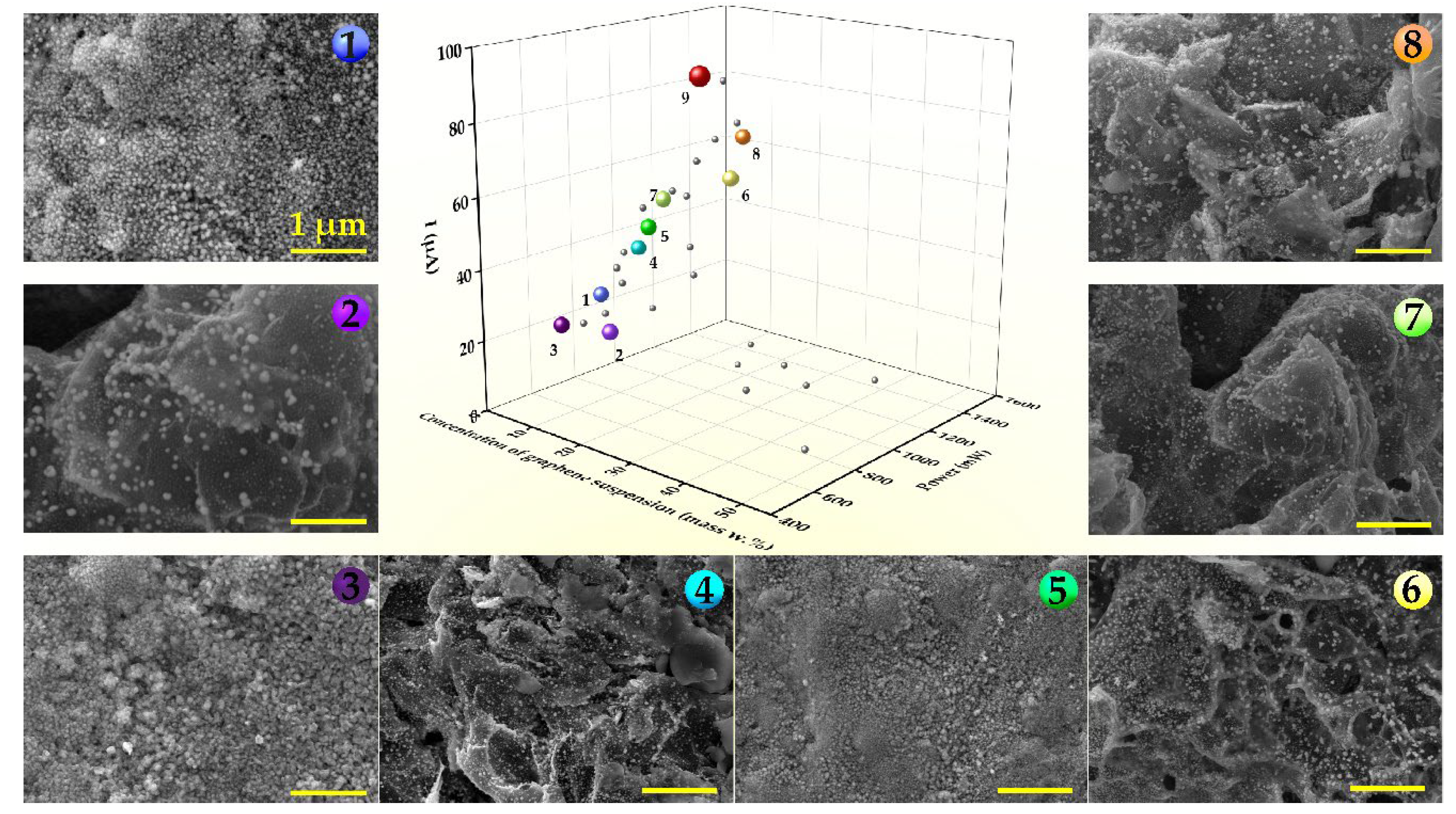
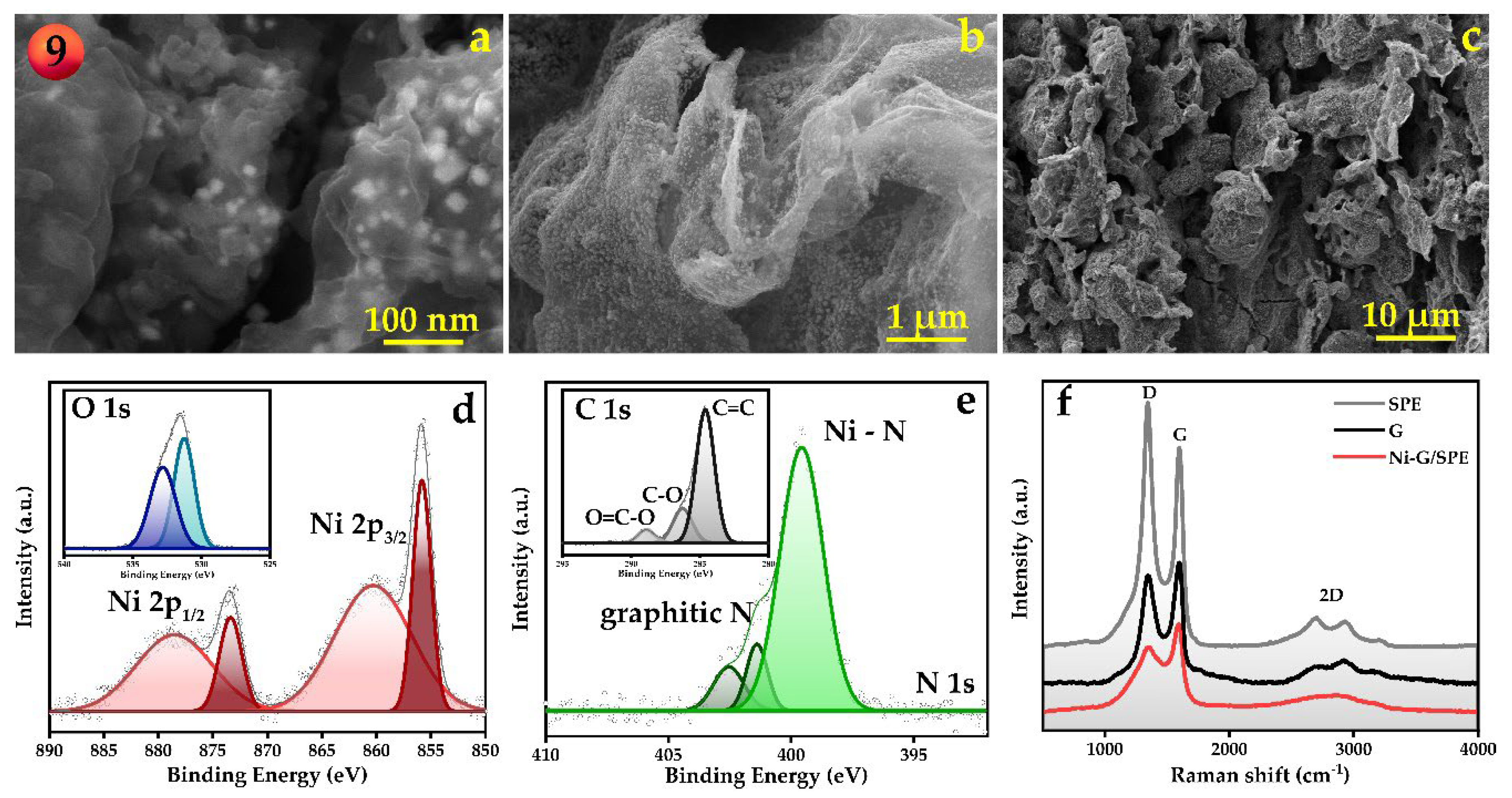
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




