Submitted:
27 November 2024
Posted:
28 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Background and Overview of Blockchain Technology
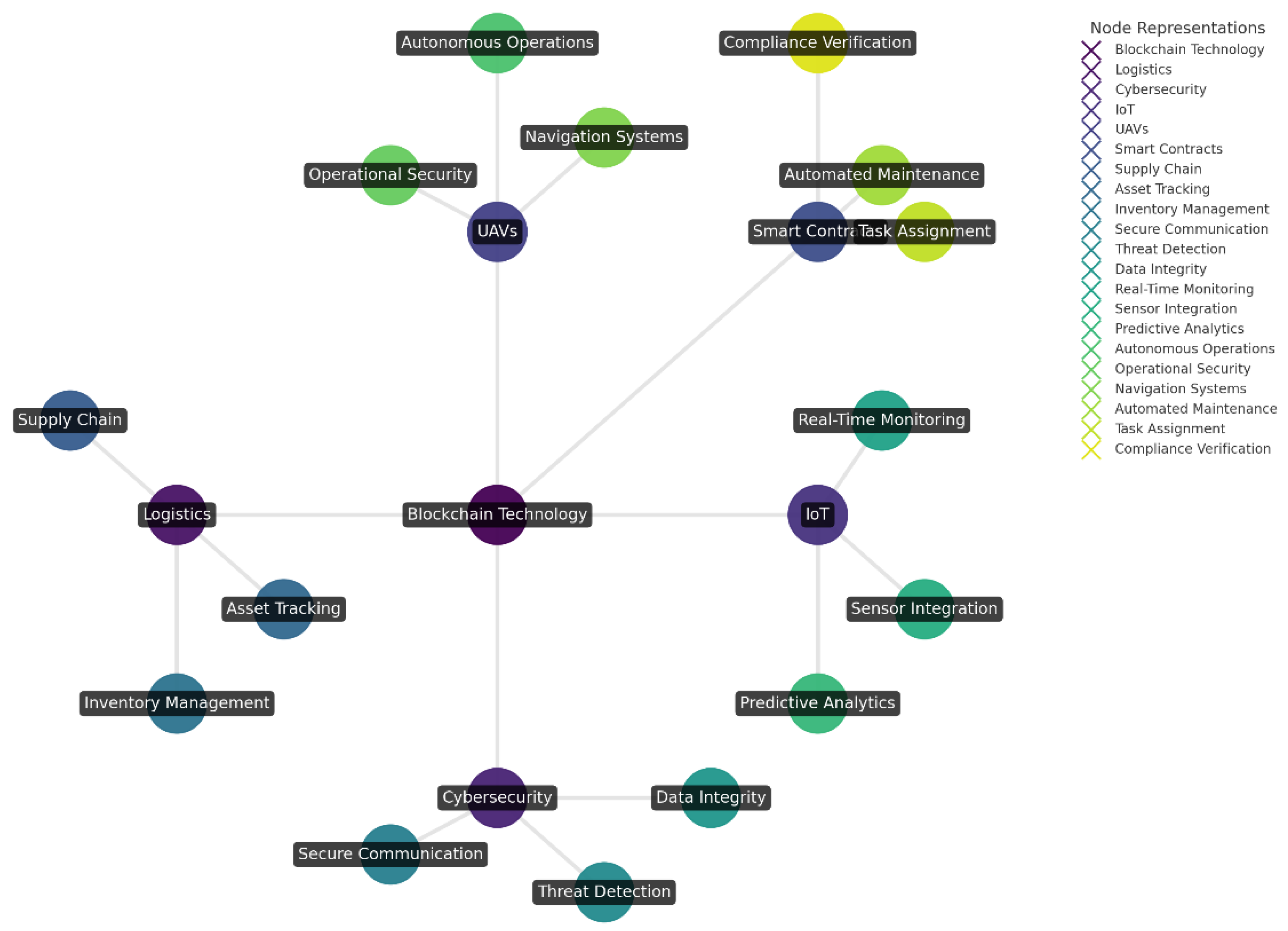
2. Military Applications of Blockchain Technology
2.1. Supply Chain Management
2.2. Secure Communication and Data Sharing
2.3. Research Questions
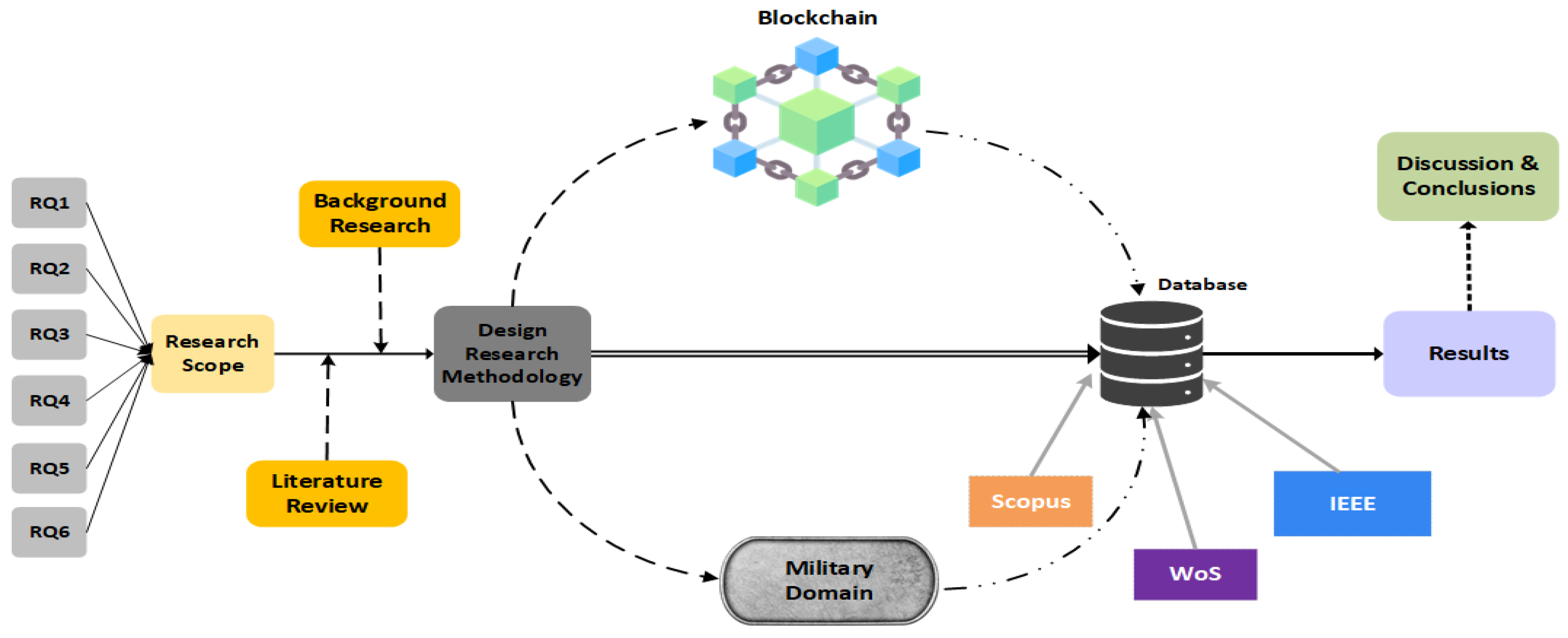
3. Materials and Methods
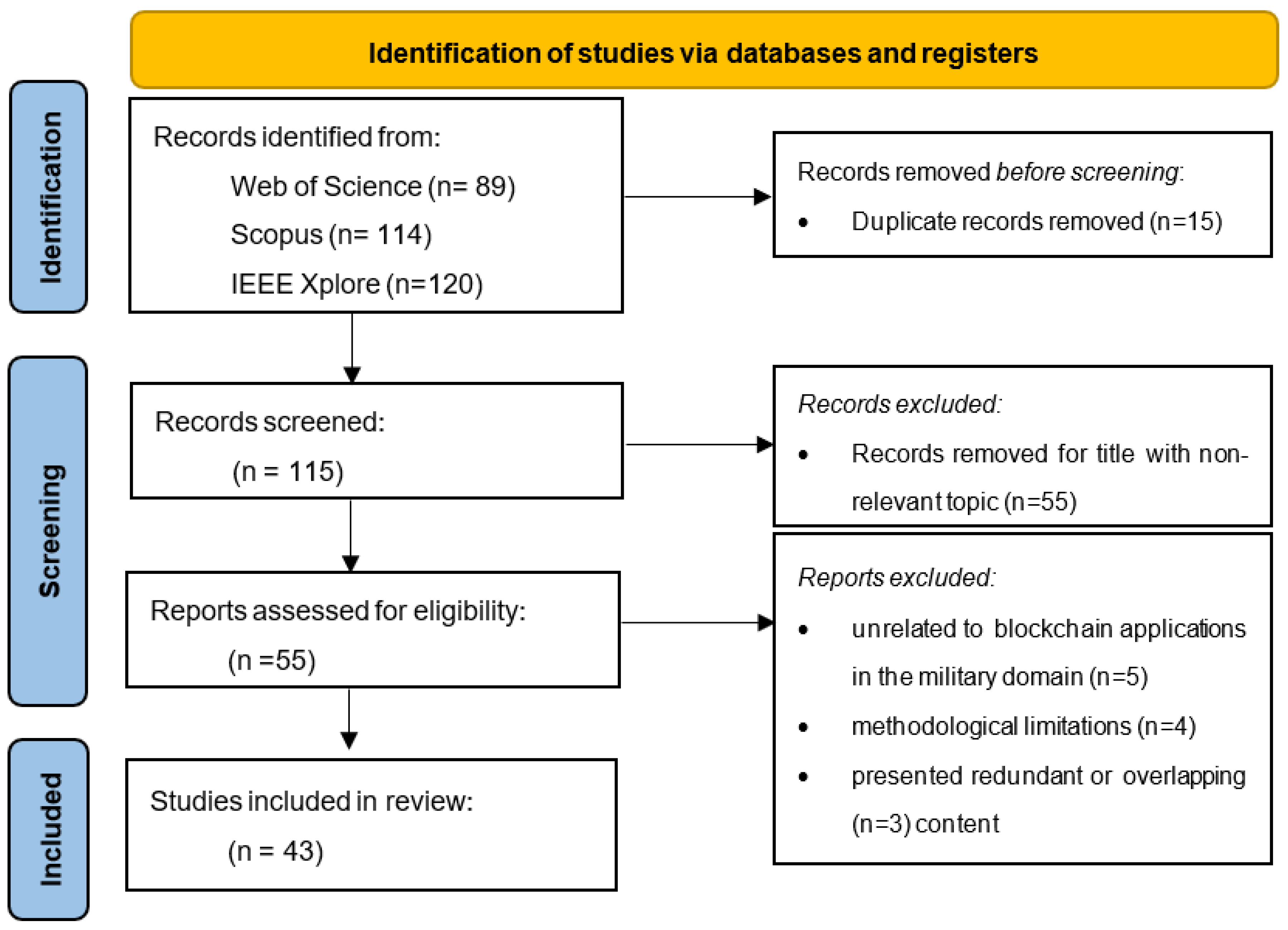
- 5 articles were unrelated to blockchain applications in the military domain.
- 4 articles had methodological limitations, such as insufficient data or lack of rigor.
- 3 articles presented redundant or overlapping content.
3.1. Search Strategy
3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
| Authors | Study Objectives | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Abed et al., (2020) [51] | 1. To develop a secure file approach using blockchain technology to protect against unauthorized access and manipulation of log files. 2. To provide proof of log file manipulation and non-repudiation. 3. To test the effectiveness of the proposed blockchain-based approach by comparing it to a scenario without blockchain protection. |
- The blockchain technique prevents log file manipulation because the attacker cannot determine the correct hash value. - Without blockchain, the log file can be manipulated by the attacker without being detected. - The blockchain technique provides proof of log manipulation and non-repudiation. |
| Abualigah et al., (2021) [52] | - Provide a comprehensive review of the Internet of Drones (IoD) and its applications - Examine the deployments and integration of IoD, including areas such as privacy protection, security, neural networks, blockchain, and optimization - Identify and discuss the hot research topics and problems in the IoD domain to guide future research |
- The paper provides a comprehensive review of the applications of the Internet of Drones (IoD) in various domains, including smart cities, cloud and fog computing, unmanned aerial vehicles, wireless sensor networks, mobile computing, and business paradigms. - The paper also reviews the integration of IoD with technologies such as privacy protection, security authentication, neural networks, blockchain, and optimization-based methods. - The paper discusses the current hot research topics and problems in the field of IoD to help guide future research in this area. |
| Aggarwal et al., (2021) [53] | 1. Provide a broad survey of 6G technology and its architecture, requirements, and use cases 2. Present a solution taxonomy for UAV communication applications 3. Propose a blockchain-envisioned security solution and 6G-enabled network connectivity for UAV communication |
- The paper presents a survey of the architecture, requirements, and use cases of 6G technology for UAV communication. - The paper proposes a blockchain-envisioned security solution and 6G-enabled network connectivity for UAV communication to address the challenges of traditional UAV communication methods. - The paper provides a solution taxonomy based on the applications of UAV communication. |
| Akter et al., (2023) [54] | - Develop a blockchain-integrated CNN-based framework (IoMT-Net) for identifying and tracking unauthorized/illegal UAVs in the Internet of Military Things (IoMT) system - Use blockchain technology to prevent illicit access, data manipulation, and illegal intrusions in the IoMT system - Utilize a CNN model to analyze RF signals from an antenna array to determine the Direction of Arrival (DoA) for localizing illegal UAVs |
- The study proposes a blockchain-integrated framework to prevent unauthorized access and data manipulation in the Internet of Military Things (IoMT) system. - The study proposes a convolutional neural network (CNN) model to analyze RF signals and localize unauthorized UAVs in the IoMT system. - The proposed CNN model achieved high accuracy (97.63%) in estimating the direction of arrival of the RF signals, outperforming other state-of-the-art models. |
| Aldossri et al., (2024) [55] | - Investigating the integration of lightweight blockchain and fog computing technologies to enhance the security of drone operations - Investigating the integration of lightweight blockchain and fog computing technologies to enhance the operational efficiency of drone operations - Providing a thorough summary of existing research on the application, challenges, and potential of integrating lightweight blockchain and fog computing into drone systems |
- The paper presents a systematic review of the integration of lightweight blockchain and fog computing technologies to enhance the security and operational efficiency of drones. - The review highlights the significant potential of this integration to advance the capabilities and reliability of drones in critical applications. - The paper aims to provide a comprehensive summary of the existing research on how the integration of lightweight blockchain and fog computing can redefine the security and operational frameworks of drone usage. |
| Amran et al., (2022) [56] | 1. Investigate using UAVs with wireless repeaters to boost weak signals in remote/isolated areas during emergencies 2. Protect the transmitted data from interference and manipulation using blockchain technology 3. Optimize the localization and clustering of UAVs using a swarm intelligence algorithm (SIL) |
- Increasing the number of UAVs reduces execution time, redundancy, and localization inaccuracy. - Syncing data via blockchain may save time. - Exploring other nature-inspired localization algorithms in combination with blockchain could lead to further improvements in the future. |
| Asuncion et al., (2021) [57] | 1. Identify a specific Department of Defense use case for blockchain technology 2. Extrapolate the requirements for this use case 3. Assess the different layers of the blockchain stack to identify the existing state of the art 4. Undertake a gap analysis of the technology for this context 5. Describe and implement a platform that addresses the identified challenges and requirements for the Department of Defense use case |
- The paper describes the development of a platform that connects transactions from two separate blockchain systems (Consensys Quorum and Hyperledger Fabric) to enable transparent part tracking across the military and supplier networks. - The platform uses a graph-based approach to preserve privacy while enabling full transparency. - The paper also discusses the evolution of blockchain technology and the emergence of enterprise-level blockchain systems. |
| Bera et al., (2020) [58] | - Identify the challenges and issues in applying blockchain technology to 5G-based IoT-enabled Internet of Drones (IoD) environments - Propose and analyze a new blockchain-based secure framework for data management among IoD communication entities |
- The paper identifies challenges and issues with applying blockchain technology in a 5G-IoT-enabled Internet of Drones (IoD) environment. - The paper proposes and analyzes a new blockchain-based secure framework for data management in the IoT-enabled IoD environment. - The proposed blockchain-based framework is able to resist several potential attacks and offers better security, functionality, and lower communication and computation overhead compared to other related schemes. |
| Deebak et al., (2023) [59] | - Develop a blockchain-based remote mutual authentication (B-RMA) system for IoT devices and cloud networks - Evaluate the security efficiency and privacy protection of the proposed B-RMA system - Analyze the communication metrics (execution time, throughput, overhead ratio) of the B-RMA system |
- The proposed blockchain-based remote mutual authentication (B-RMA) system can be integrated with IoT environments and decentralize user authentication. - The paper evaluates the security and privacy benefits of the proposed B-RMA system through an informal security analysis. - The results show the B-RMA system achieves a scalable environment. |
| Dubey et al., (2022) [60] | - Examine the effects of blockchain technology (BCT) on information alignment and coordination in humanitarian supply chains - Investigate the moderating effect of intergroup leadership on the relationships between BCT, information alignment, and coordination |
- Blockchain technology (BCT) has a significant positive effect on information alignment and coordination among humanitarian organizations. - Intergroup leadership does not have a significant moderating effect on the relationship between BCT and information alignment/coordination. - Interdependence among humanitarian organizations has a significant positive effect on information alignment and coordination. |
| Ghimire et al., (2021) [61] | - Integrate blockchain technology with software-defined Internet of Unmanned Vehicles (IoUV) for military/battlefield applications - Provide trustworthy command and control operations in IoUV using blockchain - Increase trust, accountability, and reduce friction among different military units in the battlefield |
- The paper proposes a sharding-enabled blockchain framework for software-defined Internet of Unmanned Vehicles (IoUV) in the battlefield. - The blockchain technology helps to provide trustworthy command and control operations in IoUV and stores those operations in tamper-resistant digital ledgers. - The proposed framework aims to increase the trust and accountability, and to reduce business friction among different units involved in the battlefield. |
| Gumaei et al., (2021) [62] | - Develop a framework that combines blockchain, deep recurrent neural networks (DRNN), and edge computing for 5G-enabled drone identification and flight mode detection - Remotely sense and collect raw RF signals of drones under different flight modes, use this data to train a DRNN model, and distribute the trained model on edge devices for drone and flight mode detection - Use blockchain to ensure data integrity and secure data transmission |
- The DRNN model developed in the proposed framework can accurately detect drones and their flight modes from real-world RF signals. - The framework involves collecting drone RF signal data, training a DRNN model on a cloud server, and deploying the model on edge devices for real-time detection. - Blockchain is used in the framework to ensure the integrity and security of the data transmission. |
| Gupta et al., (2020) [63] | 1. Present a comprehensive survey on securing drone communication 2. Propose a blockchain-based secure and intelligent drone communication architecture that utilizes 5G and AI techniques 3. Incorporate a healthcare-based case study using the proposed architecture |
- The authors propose a blockchain-based secure and intelligent drone communication architecture that utilizes 5G and AI technologies. - The proposed architecture uses IPFS for data storage, which improves network performance, security, privacy, and reduces transaction costs. - The proposed architecture enables efficient drone communication with dynamic, flexible, and real-time decision-making capabilities through 5G and AI technologies. |
| Han et al., (2022) [64] | - Propose a blockchain-based UAV identity management model (B-UIM-M) to address security issues like single point of failure and lack of reliable authentication - Design a blockchain-based distributed identity authentication scheme based on the B-UIM-M model - Develop a secure communication architecture and protocols based on blockchain to ensure secure data transmission |
- The paper proposes a blockchain-based UAV identity management model (B-UIM-M) to address security issues such as single point of failure and lack of reliable authentication mechanisms. - The paper establishes a distributed identity authentication scheme based on distributed identity identifiers (DIDs) under the B-UIM-M model. - The paper proposes a secure communication architecture based on blockchain and a set of secure transmission protocols to ensure the secure transmission of UAV communication data. |
| Harbi et al., (2022) [65] | - Analyze the current research on using blockchain technology to secure Internet of Drones (IoD) environments - Classify the reviewed studies based on blockchain type- Compare the reviewed studies on various factors - Identify how blockchain can provide security for IoD - Discuss open issues and challenges in combining blockchain and IoD |
- Blockchain technology can provide fundamental security features for IoD networks, including authentication, privacy-preserving, confidentiality, integrity, and access control. - The paper compares the reviewed studies on blockchain for IoD security across different factors. - The paper identifies open issues and challenges in combining blockchain and IoD technologies. |
| Hassija et al., (2020) [66] | - Develop a framework for secure and reliable energy trading between UAVs and charging stations - Enable UAVs to buy energy from charging stations using tokens - Allow UAVs to borrow tokens from charging stations if they don't have enough to buy energy |
- The proposed model allows UAVs to buy energy from charging stations using tokens, and to borrow tokens if needed, with interest or late fees. - A game-theoretic model is used to decide the energy buying strategy for UAVs. - The proposed framework provides increased utility for both UAVs and charging stations in a secure and cost-optimal manner, compared to conventional approaches. |
| Hu et al., (2021) [67] | - Propose a new type of UAV network architecture that combines SDN and blockchain technology (named SUV) - Ensure the SUV network can quickly build and adjust UAV networks based on application requirements and communication environment - Ensure the SUV network has desirable features like flexibility, survivability, security, and programmability, making it suitable for 5G-oriented UAV networking |
- The main finding is the proposal of a new UAV network architecture called SUV, which combines SDN and blockchain technology to address the limitations of traditional mobile self-organizing networks. - SUV can quickly build UAV networks according to application requirements and has features such as flexibility, survivability, security, and programmability, making it suitable for 5G-oriented UAV networking. |
| Hughes et al., (2017) [68] | 1. Discuss the need to consider the societal impact of blockchain technology 2. Highlight the importance of inclusivity in the development of blockchain to avoid widening the digital divide 3. Explore the moral obligation to develop blockchain in a way that prevents abuse of trust by states and institutions 4. Examine the potential for blockchain to enable civil intervention in human rights issues |
- Blockchain technology should be developed with the broader societal needs in mind, not just the interests of a few. - Inclusivity is crucial in the development of blockchain technology to avoid exacerbating digital divides. - Blockchain technology could be leveraged to support human rights and civil intervention in certain contexts. |
| Jadav et al., (2023) [69] | - Develop a secure and efficient system for data acquisition and dissemination in military operations using UAVs - Propose a blockchain and machine learning-based secure and intelligent UAV communication system (called "Block-USB") that can handle large amounts of data and secure sensitive military data from intruders and malicious actors |
- The proposed "Block-USB" system, which combines blockchain and machine learning (ML) technologies, can secure UAV-based military operations and data dissemination in 6G networks. - The Block-USB system uses off-chain storage (IPFS) to improve the blockchain's storage capacity. - The Block-USB system outperforms traditional 4G/5G and non-IPFS-based systems in terms of classification accuracy, communication latency, and data scalability. |
| Javed et al., (2022) [70] | - Propose a blockchain-based authentication scheme that uses blockchain as a certificate authority and transactions as certificates, in order to reduce the high maintenance costs associated with traditional certificate-based authentication schemes. - Develop an authentication scheme based on Hyperelliptic Curve Cryptography (HECC), which provides the same level of security as other cryptographic schemes but with a smaller key size. - Provide a security analysis of the proposed scheme, demonstrating its resistance to various active and passive attacks. - Compare the performance of the proposed scheme with existing similar schemes, and show that the proposed scheme is more efficient in terms of computation and communication costs. |
- The proposed scheme has significantly lower computation cost (40.479 ms) compared to two existing schemes (107.962 ms and 81.295 ms). - The proposed scheme has lower communication overhead (320 bits) compared to two existing schemes (1952 bits and 3040 bits). - The lower computation cost and communication overhead of the proposed scheme make it more practical for resource-constrained IoD networks compared to the existing schemes. |
| Koulianos et al., (2023) [71] | - Develop a secure and efficient system for drone swarms to exchange data and coordinate movements using blockchain technology - Introduce a novel leader-election mechanism for drone swarms using blockchain nodes - Develop a smart contract for decentralized decision-making on swarm formation based on mission requirements - Design the smart contract to be lightweight and easily deployable |
- The proposed blockchain-based system for secure communication and formation control in drone swarms was successfully implemented and tested through simulation, with highly encouraging results. - The blockchain-based approach has the potential to enhance the security and decision-making capabilities of drone swarm systems. - The simulation results suggest that the proposed model could serve as a starting point for developing advanced, secure drone swarm systems. |
| Lis et al., (2019) [72] | - Analyze the economic aspects of cybersecurity for critical infrastructure - Evaluate the economic implications of cybersecurity efforts and cyberattacks - Explore methods to determine optimal investment in critical infrastructure cybersecurity - Propose solutions to develop sustainable, efficient and resilient critical infrastructure systems |
- A comprehensive economic analysis of cybersecurity must consider both direct and indirect costs of cybersecurity measures as well as the expected damages from cyberattacks. - Developing a holistic economic framework to capture the costs, benefits, and consequences of cyberattacks and cybersecurity efforts can inform future policymaking. - Critical infrastructure providers often lack sufficient incentive to invest in cybersecurity beyond their own organization, necessitating government intervention through regulation and standards. |
| Manikandan et al., (2022) [73] | - Develop a new algorithm called RUPOA that can provide an optimal path for a swarm of UAVs - Integrate concepts of UAV energy rate and authentication to enhance secure and efficient path planning - Ensure the algorithm can generate an optimal path in less time and adapt to generate a new optimal path under security attacks - Achieve a higher attack mitigation percentage compared to existing algorithms |
- The proposed RUPOA algorithm generates an optimal path in less execution time and is capable of generating the next optimal path under security attacks. - The proposed algorithm aims to reduce the distance of communication among the neighbor nodes and maintains a routing table to track the position and energy of all the neighbor nodes. - The attack mitigation percentage of the proposed algorithm is optimal compared to existing algorithms. |
| Mohril et al., (2021) [74] | - Develop a comprehensive maintenance management framework for military equipment that addresses military-specific maintenance challenges - Maintain maintenance data with high granularity and accuracy, including for the lowest maintainable units - Store maintenance data in a highly secure environment - Leverage blockchain technology to make the maintenance management framework "comprehensive and future ready" |
- The proposed blockchain-enabled maintenance management framework aims to maintain highly detailed and accurate maintenance data for military equipment. - The framework discusses how blockchain technology can be used to address the challenges of military equipment maintenance. - The framework utilizes smart contracts to automate monitoring and validation of maintenance data with minimal human intervention. |
| Nyangaresi et al., (2024) [75] | - To address the security vulnerabilities of the Internet of Drones (IoD) system, particularly the insecure wireless communication channels and the risk of drone capture and cloning - To develop a secure authentication protocol for IoD that uses Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) and biometrics to withstand typical IoD attacks such as impersonation, replay, de-synchronization and spoofing |
- A new PUF and biometric-based authentication protocol for the Internet of Drones is presented. - The protocol is formally proven to have a robust negotiated session key using the Real or Random (RoR) model. - The protocol is shown to be able to withstand common IoD attacks like impersonation, replay, de-synchronization, and spoofing. - The protocol has lower computation, energy, and communication costs compared to other approaches. |
| Oláh et al., (2023) [76] | - Develop a secure and scalable registration protocol for the Internet of Drones (IoD) using PUF and blockchain technology - Provide a formal security analysis of the proposed registration protocol using the ProVerif tool - Provide an informal security analysis of the proposed protocol - Evaluate the efficiency and practicality of the proposed solution through a proof-of-concept implementation and analysis |
- The proposed solution was evaluated against existing solutions in terms of key exchange, efficiency, physical security, data security, and availability of security analysis and implementation. - The paper presents a real-world implementation and prototype of the proposed solution, as well as a comparison of the LoRa technology used against other communication alternatives. |
| Pandey et al., (2022) [77] | - Provide a comprehensive survey of security issues in UAV-aided networks - Describe a taxonomy of security intrusions and secrecy performance metrics - Discuss techniques to mitigate security threats using various wireless communication technologies - Explore the role of emerging technologies like machine learning, SDN, and blockchain in UAV security |
- The paper provides a comprehensive review of security issues and mitigation techniques in UAV communications. - It discusses how various wireless communication technologies, such as mmWave, NOMA, and MIMO, can be used to enhance the security of UAV communications. - The paper also explores the potential of emerging technologies, like machine learning, software-defined networks, and blockchain, to improve the security of UAV-aided communications. |
| Salor et al., (2023) [78] | 1. Identify emerging 5G and 6G technologies that can enhance tactical communications 2. Provide a comprehensive overview of these technologies and their potential military applications 3. Offer a framework for understanding how these technologies can be applied in various tactical scenarios or use cases 4. Serve as a starting point for future research on using civilian technologies to advance military development |
- Emerging technologies like network virtualization, software-defined networks, IoT, blockchain, AI, semantic communications, and neuromorphic processors can enhance the security, performance, and practicality of tactical communications and military applications. - The paper serves as a foundational analysis and analytical framework to guide future research initiatives in improving tactical communications. |
| Samanth et al., (2022) [79] | - Review recent UAV frameworks that have been designed and tested using the AirSim simulator - Review different secure IoD communication frameworks that have used various cryptography concepts and have been implemented in real-time or using network simulators |
- UAV frameworks should be tested in simulators like AirSim before real-world deployment. - There is a need for secure IoD communication frameworks that do not compromise performance. - The study reviewed various secure IoD communication frameworks that have been implemented using different cryptographic techniques. |
| Sarkar et al., (2023) [80] | - To devise a technique to share k secret images among n participants (n ≥ k) such that only k or more participants can collaborate to recover the original k secret images - To use a spanning tree approach with Prufer sequences to generate the share images for each participant - To store the share images in a blockchain using the interplanetary file system to provide distributed storage and eliminate single points of failure |
- The paper proposes a blockchain-based (k,n) multi-secret image sharing scheme that uses Prufer sequences to generate share images for each participant. - The scheme stores the share images in a blockchain, which provides distributed storage and prevents cheating by allowing participants to verify each other's shares. - The scheme allows for lossless reconstruction of the original k secret images, making it suitable for sensitive applications where data integrity is critical. |
| Shahidinejad et al., (2024) [81] | - Develop a cost-effective blockchain-based key exchange protocol for secure communication between drones in different domains of the Internet of Drones (IoD) - Use Chebyshev's chaotic map as the cryptographic system and store only the public keys of the drones on the blockchain ledger to reduce storage and computational overhead - Ensure the proposed protocol meets the essential security requirements for IoD, such as anonymity and unlinkability, while complying with the Canetti and Krawczyk adversary model |
- The paper presents a new blockchain-assisted authentication protocol for secure cross-domain communications in the Internet of Drones (IoD) that aims to address the limitations of previous approaches. - The proposed protocol uses Chebyshev's chaotic map as the cryptographic system and stores only the public keys of the drones on the blockchain, which reduces the storage and computational overhead compared to previous approaches. - The paper claims that the proposed protocol meets the security requirements of the Canetti and Krawczyk adversary model and provides anonymity and unlinkability, which are essential for IoD applications. |
| Shahzad et al., (2022) [82] | 1. Discuss the need for faster and more secure 6G communication networks to support real-time applications. 2. Propose a blockchain-based solution to enhance security and privacy in 6G communication networks. 3. Describe a novel smart contract mechanism and a digital signature methodology to authenticate and secure the blockchain. |
- The paper proposes a novel smart contract mechanism and a digital signature methodology to enhance the security and authentication of blockchain-based systems for 6G communication in tactile networks. - The paper emphasizes the importance of securing sensitive data and eliminating design flaws in order to achieve robust security in blockchain-based systems. - The paper proposes the use of cryptographic algorithms such as SHA-256, SHA-512, and ZK-SNARKS to achieve authenticity and integrity in the proposed blockchain-based solution. |
| Sobb et al., (2020) [83] | - Examine the uniqueness of military supply chains 4.0 and their integration with new technologies - Outline the emerging concepts of Supply Chain 4.0 and link them to commercial and military needs - Highlight the need for semantic modeling to understand threats and opportunities in this space - Outline the underpinning technologies and their intersections in the context of increasing technological interdependence |
- Supply chain 4.0 integrates manufacturing and IT processes but suffers from cyber risks like lack of standards and security issues. - Military supply chains have unique requirements like readiness and flexibility compared to commercial supply chains. - The paper discusses the impact of emerging technologies like blockchain, IoT, and AI on supply chain 4.0 and the associated cyber security challenges. |
| Stanley-Lockman et al., (2019) [84] | 1) Build on the concept of the Revolution in Military Logistics (RML) defined by the U.S. Army in 1999. 2) Analyze how emerging critical technologies may facilitate a paradigmatic shift in land-based combat service support. 3) Assess the merits, vulnerabilities, and cultural difficulties of transforming future military logistics by integrating these technologies. |
- The chapter discusses how emerging technologies, including AI, alternative energy, AR, additive manufacturing, robotics, blockchain, and IoT, can enable a transformation of military logistics to make it more agile, modular, seamless, controlled, and sustainable. - The chapter assesses the potential benefits as well as the vulnerabilities and cultural challenges of integrating these technologies into operational concepts and organizational structures to transform future military logistics. - The chapter conceives of logistics transformation as a prerequisite for broader military transformation at the tactical, operational, and strategic levels. |
| Torky et al., (2022) [85] | 1. Optimize the scheduling of drone charging to maximize the number of charged drones and minimize the number of "dead" drones. 2. Investigate the use of a novel blockchain protocol to authenticate and verify drone charging transactions. |
- The PSO algorithm was effective in optimizing drone routes and preventing collisions during charging flights with low error rates. - The proposed scheduling methodology achieved a 96.8% success rate in drone charging cases. - The proposed blockchain protocol was efficient in managing drone charging transactions with low latency, allowing rapid and valid transactions. |
| Vashistha et al., (2022) [86] | - To develop a blockchain-based solution called eChain to address the problem of counterfeit electronic devices - To transform the existing supply chain into a trustworthy distributed ledger framework using eChain - To generate device provenance records from the blockchain that can be used to classify authentic and counterfeit electronic devices |
- eChain generates blockchain-based device provenance records that can be used to classify authentic and counterfeit electronic devices. - A fully functional prototype of the eChain system was developed to demonstrate the feasibility and efficacy of the proposed blockchain-based solution for electronic device authenticity verification. |
| Vestergaard et al., (2021) [87] | Not mentioned (the abstract does not explicitly state any "study objectives" or goals of the paper) | Not mentioned (the abstract does not present any specific "main findings" or conclusions) |
| Wang et al., (2022) [88] | - Develop a blockchain-based solution to protect 3D printing models from unauthorized tampering - Create a whitelist of approved 3D models that can be verified before printing - Demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed solution through an attack-defense experiment |
- The paper proposes using blockchain technology to store the "fingerprints" of 3D models and verify the "fingerprints" before printing to prevent illegal tampering. - The blockchain-based approach can ensure the security and credibility of 3D-printed products by creating a whitelist of approved models. - The combination of blockchain and 3D printing can help build a trusted manufacturing environment and realize more flexible manufacturing. |
| Wu et al., (2020) [89] | - Review existing blockchain-based solutions for privacy preservation in 5G-enabled drone communications - Introduce the architecture for 5G-enabled drone communications and blockchain |
- 5G-enabled drones have potential applications in military and civilian settings, such as monitoring and tracking individuals. - There are security and privacy considerations that need to be addressed in 5G-enabled drone communications. - The paper reviews existing blockchain-based solutions for facilitating privacy preservation in 5G-enabled drone communications, and discusses relevant legislation, regulations, challenges, and open issues. |
| Yang et al., (2022) [90] | 1) Conduct a comprehensive review of security issues and solutions for the Internet of Drones (IoD) 2) Discuss IoD-related security requirements 3) Identify the latest advancements in IoD security research |
- The paper reviews various security technologies for the Internet of Drones (IoD), with a focus on authentication techniques and blockchain-based solutions. - The paper identifies the challenges faced by current IoD security methodologies and provides recommendations for future research directions in this area. - The paper concludes that appropriate security measures are necessary to address IoD security issues, and that new security solutions should balance the level of security and cost efficiency. |
| Yazdinejad et al., (2020) [91] | - Integrate blockchain and SDN to address challenges in IoT networks - Propose a secure and energy-efficient blockchain-enabled SDN architecture for IoT networks - Use a cluster structure and new routing protocol in this architecture - Use public and private blockchains for P2P communication, eliminating proof-of-work - Implement an efficient authentication method with distributed trust for resource-constrained IoT devices |
- The proposed routing protocol based on a cluster structure has higher throughput, lower delay, and lower energy consumption compared to several classic routing protocols. - The proposed blockchain-enabled SDN architecture outperforms classic blockchain approaches. |
| Yazdinejad et al., (2020) [92] | - Develop a secure authentication model with low latency for drones in smart cities using blockchain technology - Apply a zone-based architecture and a customized decentralized consensus (DDPOS) to enable drones to authenticate without requiring reauthentication - Improve security and reduce latency in the Internet of Drones (IoD) |
- The proposed architecture improves security and reduces latency for the Internet of Drones. - The proposed architecture outperforms other models in terms of performance metrics like packet loss, throughput, and latency. - The proposed architecture can detect 97.5% of attacks by malicious drones while airborne. |
| Zhu et al., (2020) [93] | - Provide a systematic understanding of cyberattacks and cyber defenses related to the Internet of Battlefield Things (IoBT) - Improve cybersecurity awareness for IoBT - Advance the development of appropriate security mechanisms for IoBT |
- The paper identifies and characterizes three main types of cyberattacks on military IoBT systems: multiple entry-point and single device hacking, risks from unmanned aerial vehicles, and collateral damage. - The paper also identifies three main types of cyber defense strategies to address these threats: comply to connect, blockchain, and artificial cyber hunters. - The overall goal of the paper is to provide a systematic review of cyberattacks and cyber defenses related to the Internet of Battlefield Things (IoBT) in order to improve cybersecurity awareness and advance the development of appropriate security mechanisms. |
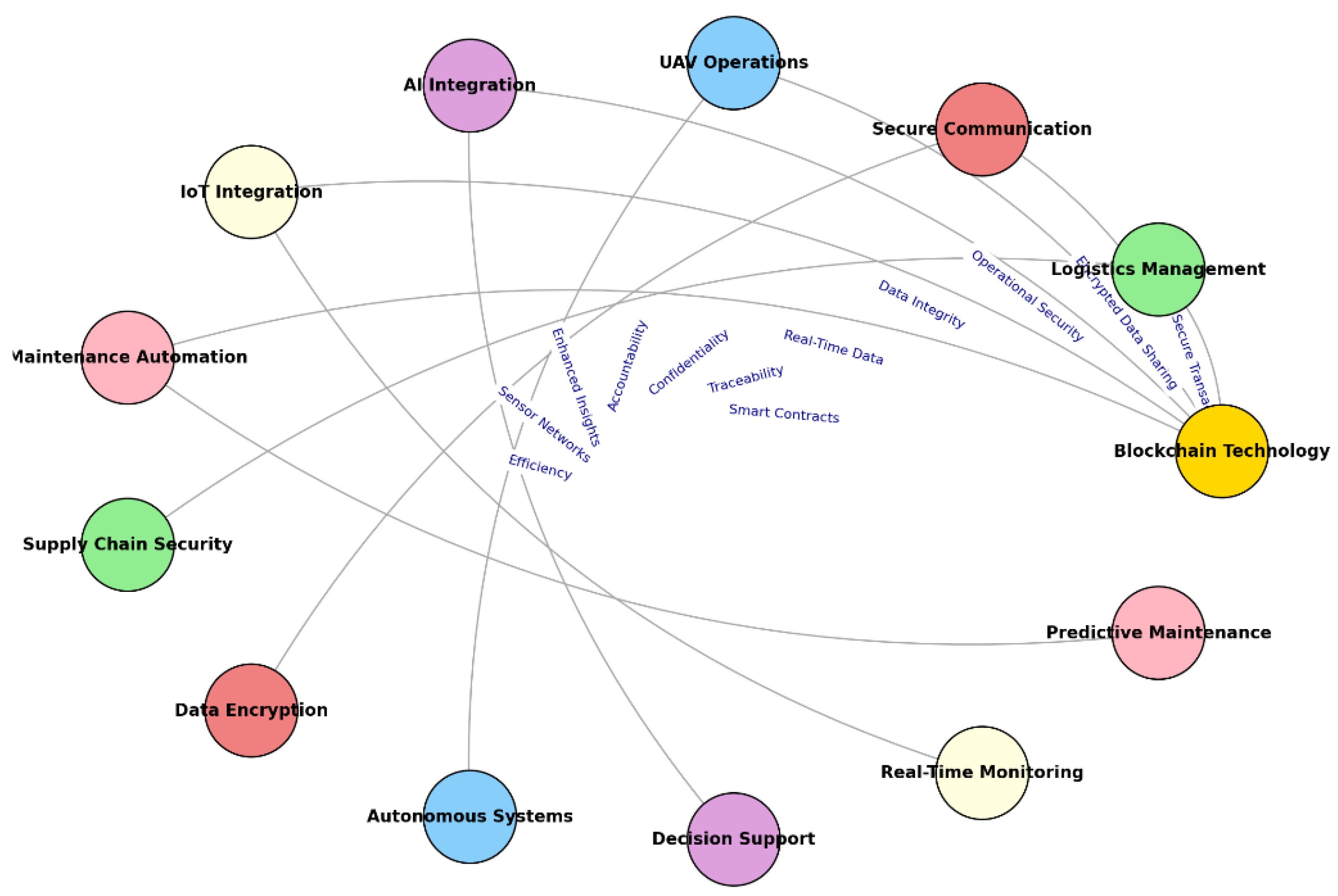
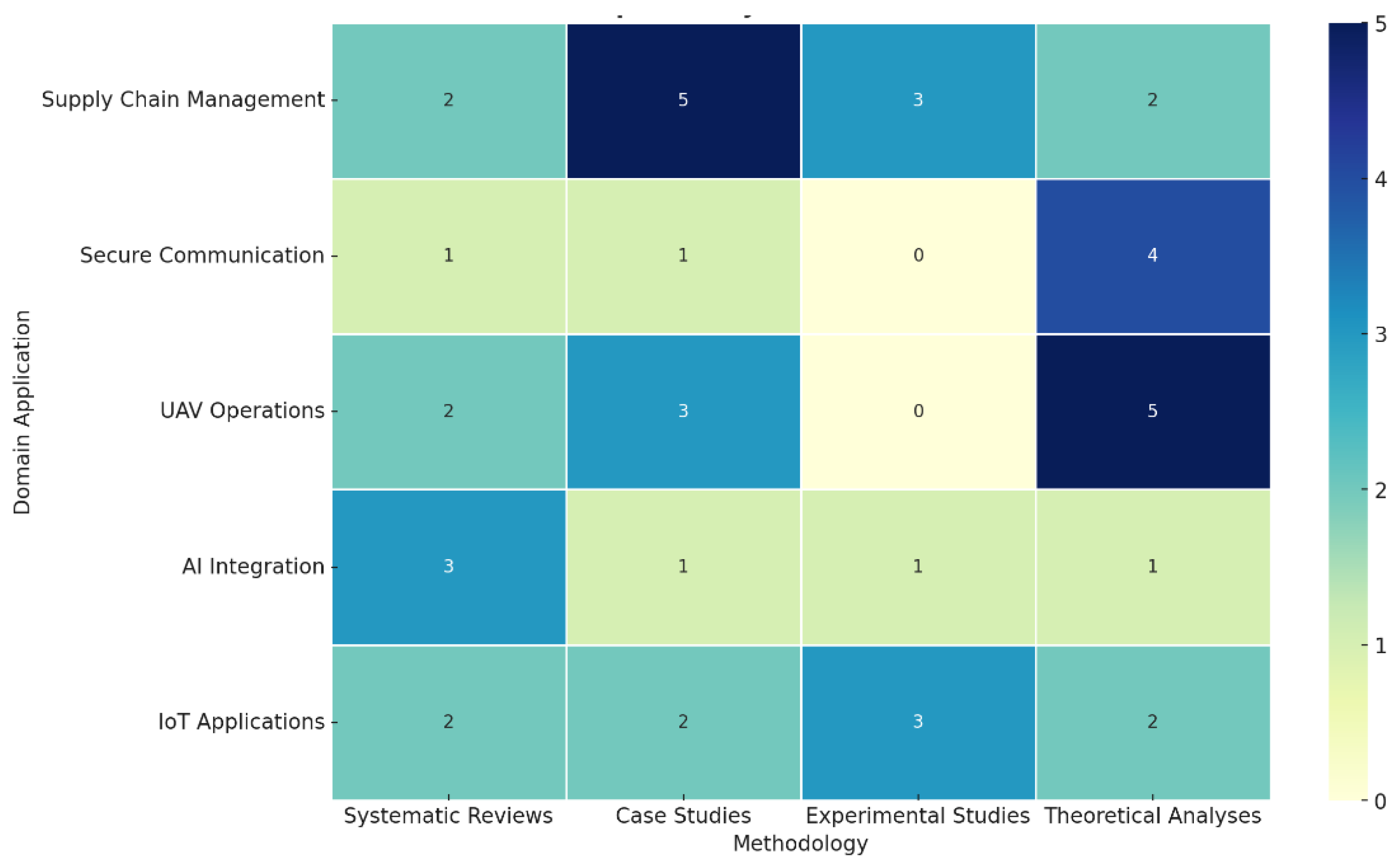
4. Results
5. Discussion
Scalability Solutions for Blockchain Deployment in Military Supply Chains
Enhancing Military Logistics with Blockchain Technology: Benefits and Transformations
Blockchain-Enabled Interoperability in Military Logistics: Challenges and Opportunities
Unlocking Blockchain's Potential in Transforming Military Operations
Integrating Blockchain Technology into Modern Warfare Strategies
Enhancing Military AI Capabilities through Blockchain Integration
Blockchain Applications in Defense: Enhancing Security, Transparency, and Efficiency
Limitations of Blockchain Technology in Defense Applications
Ethical Considerations of Blockchain Technology in Military Applications
Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, S. I. (2022). Artificial intelligence at the operational level of war. Defense & Security Analysis. [CrossRef]
- Mattingsdal, J. , Johnsen, B. H., & Espevik, R. (2023). Threat conditions on police and military commanders' preferences for urgent and offensive actions: An analysis of decision-making at the operational level of war. Military Psychology. [CrossRef]
- Mattingsdal, J. , Espevik, R., Johnsen, B. H., & Hystad, S. (2023). Exploring why police and military commanders do what they do: An empirical analysis of decision-making in hybrid warfare. Armed Forces & Society. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J. (2023). Automating the OODA loop in the age of intelligent machines: Reaffirming the role of humans in command-and-control decision-making in the digital age. Defence Studies. [CrossRef]
- Horyń, W. , Bielewicz, M., & Joks, A. (2021). AI-supported decision-making process in multidomain military operations. In Artificial Intelligence and Its Contexts: Security, Business, and Governance (pp. 93-107). Cham: Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Bolton, C. R. , & Prescott, M. R. (2024). Commander's critical information requirements: Crucial for decision-making and joint synchronization. Joint Force Quarterly.
- Theodorakopoulos, L. , Theodoropoulou, A., & Halkiopoulos, C. (2024). Enhancing Decentralized Decision-Making with Big Data and Blockchain Technology: A Comprehensive Review. Applied Sciences, 14(16), 7007. [CrossRef]
- Halkiopoulos, C. , Antonopoulou, H., & Kostopoulos, N. (2023). Utilizing Blockchain Technology in Various Applications to Secure Data Flows. A Comprehensive Analysis. Technium: Romanian Journal of Applied Sciences and Technology, 11, 44–55. [CrossRef]
- Aoun, A. , Ilinca, A., Ghandour, M., & Ibrahim, H. (2021). A review of Industry 4.0 characteristics and challenges, with potential improvements using blockchain technology. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 162, 107746. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A. A. , Laghari, A. A., Li, P., Dootio, M. A., & Karim, S. (2023). The collaborative role of blockchain, artificial intelligence, and industrial internet of things in digitalization of small and medium-size enterprises. Scientific Reports. [CrossRef]
- Reghunadhan, R. (2020). Ethical considerations and issues of blockchain technology-based systems in war zones: A case study approach. In Handbook of Research on Blockchain Technology. [CrossRef]
- Gousteris, S. , Stamatiou, Y. C., Halkiopoulos, C., Antonopoulou, H., & Kostopoulos, N. (2023). Secure Distributed Cloud Storage based on the Blockchain Technology and Smart Contracts. Emerging Science Journal, 7(2), 469–479. [CrossRef]
- Krichen, M. , Ammi, M., Mihoub, A., & Almutiq, M. (2022). Blockchain for modern applications: A survey. Sensors. [CrossRef]
- Kassen, M. (2022). Blockchain and e-government innovation: Automation of public information processes. Information Systems. [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, Y. , Arnautović, E., Parezanović, V., & Svetinovic, D. (2023). AI and blockchain synergy in aerospace engineering: An impact survey on operational efficiency and technological challenges. IEEE Access. [CrossRef]
- Khoshavi, N. , Tristani, G., & Sargolzaei, A. (2021). Blockchain applications to improve operation and security of transportation systems: A survey. Electronics. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. , & Kim, S. (2021). Blockchain as a cyber defense: Opportunities, applications, and challenges. IEEE Access. [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K. , Aseeri, A. O., & Shah, M. A. (2022). A blockchain-based authentication solution for 6G communication security in tactile networks. Electronics. [CrossRef]
- Jain, A. , Barke, S., Garg, M., Gupta, A., Narwal, B., Mohapatra, A. K.,... & Srivastava, G. (2024). A walkthrough of blockchain-based internet of drones architectures. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. [CrossRef]
- Kendall, A. , Das, A., Nagy, B., Johnson, B., & Ghosh, A. (2022). Using hyperledger fabric blockchain to improve information assurance of IoT devices for AI model development. In Advances in Blockchain Technology for Cyber Physical Systems (pp. 233-259). Cham: Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, M. , Mukkamala, R., & Olariu, S. (2024). Autonomous strike UAVs in support of homeland security missions: Challenges and preliminary solutions. IEEE Access. [CrossRef]
- Bothra, P. , Karmakar, R., Bhattacharya, S., & De, S. (2023). How can applications of blockchain and artificial intelligence improve performance of Internet of Things?-A survey. Computer Networks. [CrossRef]
- Theodorakopoulos, L. , Theodoropoulou, A., & Stamatiou, Y. (2024). A State-of-the-Art Review in Big Data Management Engineering: Real-Life Case Studies, Challenges, and Future Research Directions. Eng, 5(3), 1266–1297. [CrossRef]
- Bagga, P. , Das, A. K., Chamola, V., & Guizani, M. (2022). Blockchain-envisioned access control for internet of things applications: A comprehensive survey and future directions. Telecommunication Systems. [CrossRef]
- Stamatiou, Y. , Halkiopoulos, C., & Antonopoulou, H. (2023). A Generic, Flexible Smart City Platform focused on Citizen Security and Privacy. Proceedings of the 27th Pan-Hellenic Conference on Progress in Computing and Informatics. [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D., Alwin, L., Neeraja, P., Lawrence, K. D., & Pathari, V. (2022). A private Ethereum blockchain implementation for secure data handling in Internet of Medical Things. Journal of Reliable Intelligent Environments, 8(4), 379-396. [CrossRef]
- Surya, S. , Elakya, R., & Selvanayaki, S. (2024). Synergizing aerospace efficiency: Blockchain and AI integration for enhanced security in flight data management. In AI and Blockchain Optimization Techniques in Aerospace Engineering (pp. 181-192). IGI Global. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S. , & Muthulakshmi, P. (2023). Artificial intelligence-blockchain-enabled technology for Internet of Things: Research statements, open issues, and possible applications in the near future. Privacy Preservation of Genomic and Medical Data (pp. 433-480). [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. , Imtiaz, S., Parvaiz, G. S., Hussain, A., & Bae, J. (2021). Integration of Internet of Things with blockchain technology to enhance humanitarian logistics performance. IEEE Access. [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A., Akhavan, P., Philsofian, M., & Darabi, A. (2022). Investigating the effect of using blockchain technology on collaborative interactions and performance improvement in the defense industry supply chain. The Journal of Industrial Management Perspective, 12(45), 109-134. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R. W. , Hasan, H., Yaqoob, I., Salah, K., Jayaraman, R., & Omar, M. (2021). Blockchain for aerospace and defense: Opportunities and open research challenges. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 151, 106982. [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R. , Gunasekaran, A., & Foropon, C. R. (2024). Improving information alignment and coordination in humanitarian supply chain through blockchain technology. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 37(3), 805-827. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. , Li, Y., Ge, W., & Shen, X. (2022, July). Military application of blockchain technology for future battlefield operations. In International Conference on Cloud Computing, Internet of Things, and Computer Applications (CICA 2022) (Vol. 12303, pp. 352-362). SPIE. [CrossRef]
- Reyes, P. M., Gravier, M. J., Jaska, P., & Visich, J. K. (2022). Blockchain impacts on global supply chain operational and managerial business value processes. IEEE Engineering Management Review, 50(3), 123-140. [CrossRef]
- Sani, S. , Schaefer, D., & Milisavljevic-Syed, J. (2022). Strategies for achieving pre-emptive resilience in military supply chains. Procedia CIRP. [CrossRef]
- Raja Santhi, A. , & Muthuswamy, P. (2022). Influence of blockchain technology in manufacturing supply chain and logistics. Logistics. [CrossRef]
- Park, A. , & Li, H. (2021). The effect of blockchain technology on supply chain sustainability performances. Sustainability. [CrossRef]
- Al-Zaqeba, M., Jarah, B., Ineizeh, N., Almatarneh, Z., & Jarrah, M. A. A. L. (2022). The effect of management accounting and blockchain technology characteristics on supply chains efficiency. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 10(3), 973-982. [CrossRef]
- Batwa, A. , & Norrman, A. (2020). A framework for exploring blockchain technology in supply chain management. Operations and Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 13. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, U., Rishiwal, V., Tanwar, S., Chaudhary, R., Sharma, G., Bokoro, P. N., & Sharma, R. (2022). Blockchain technology for secure supply chain management: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access, 10, 85493-85517. [CrossRef]
- Hariguna, T., Durachman, Y., Yusup, M., & Millah, S. (2021). Blockchain technology transformation in advancing future change. Blockchain Frontier Technology, 1(01), 13-20. [CrossRef]
- Andrii, D. , Zarina, P., Oleh, S., Olena, P., & Dmytro, R. (2024, April). Management of Transport and Logistics Systems: Problems Under Conditions of Military Operations. In International Conference on Business and Technology (pp. 363-373). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland. [CrossRef]
- Katina, P. F. , & Gheorghe, A. V. (2023). Blockchain-enabled resilience: An integrated approach for disaster supply chain and logistics management. [CrossRef]
- Wamba, S. F. , & Queiroz, M. M. (2020). Blockchain in the operations and supply chain management: Benefits, challenges and future research opportunities. International Journal of Information Management. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R., Wang, W., Kumar, J., Yang, T., Khan, A., Ali, W., & Ali, I. (2021). An integration of blockchain and AI for secure data sharing and detection of CT images for the hospitals. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 87, 101812. [CrossRef]
- Wan, P. K. , Huang, L., & Holtskog, H. (2020). Blockchain-enabled information sharing within a supply chain: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. , Zheng, Z., Jiang, W., & Tang, S. (2021). Blockchain-enabled data sharing in supply chains: Model, operationalization, and tutorial. Production and Operations Management, 30. [CrossRef]
- Shen, M. , Duan, J., Zhu, L., Zhang, J., Du, X., & Guizani, M. (2020). Blockchain-based incentives for secure and collaborative data sharing in multiple clouds. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 38. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. , Crespo, R. G., & Martínez, O. S. (2020). Enhancing privacy and data security across healthcare applications using blockchain and distributed ledger concepts. Healthcare. [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Moher, D. Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: Development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. J. Clin. Epidemiology 2021, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, N. , & Hasan, S. (2020). A Proactive Secure File Approach Using a Blockchain Technique. [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L. , Diabat, A., Sumari, P., & Gandomi, A. (2021). Applications, Deployments, and Integration of Internet of Drones (IoD): A Review. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P. , & Dixit, S. (2021). Blockchain-Envisioned UAV Communication Using 6G Networks: Open Issues, Use Cases, and Future Directions. [CrossRef]
- Akter, F. , Malik, M., & Rahman, S. (2023). IoMT-Net: Blockchain-Integrated Unauthorized UAV Localization Using Lightweight Convolution Neural Network for Internet of Military Things. [CrossRef]
- Aldossri, K. , & Saleh, H. (2024). Advancing Drone Operations Through Lightweight Blockchain and Fog Computing Integration: A Systematic Review. [CrossRef]
- Amran, R. , & Hassan, N. (2022). Efficient and Secure WiFi Signal Booster via Unmanned Aerial Vehicles WiFi Repeater Based on Intelligence-Based Localization Swarm and Blockchain. [CrossRef]
- Asuncion, A. , Hernandez, D., & Sato, K. (2021). Connecting Supplier and DoD Blockchains for Transparent Part Tracking. [CrossRef]
- Bera, B. , Saha, S., Das, A., & Kumar, N. (2020). Blockchain-Envisioned Secure Data Delivery and Collection Scheme for 5G-Based IoT-Enabled Internet of Drones Environment. [CrossRef]
- Deebak, B. , & Al-Turjman, F. (2023). A Lightweight Blockchain-Based Remote Mutual Authentication for AI-Empowered IoT Sustainable Computing Systems. [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R. , Bryde, D., & Kapur, R. (2022). Improving Information Alignment and Coordination in Humanitarian Supply Chain Through Blockchain Technology. [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, N. , & Kumar, P. (2021). Sharding-Enabled Blockchain for Software-Defined Internet of Unmanned Vehicles in the Battlefield. [CrossRef]
- Gumaei, A. , & Khalil, I. (2021). Deep Learning and Blockchain with Edge Computing for 5G-Enabled Drone Identification and Flight Mode Detection. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. , Jain, V., & Aggarwal, P. (2020). Fusion of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence for Secure Drone Networking Underlying 5G Communications. [CrossRef]
- Han, D. , Kim, S., & Choi, J. (2022). Identity Management and Authentication of a UAV Swarm Based on Blockchain. [CrossRef]
- Harbi, S. , Alshammari, M., & Ahmed, A. (2022). A Systematic Literature Review of Blockchain Technology for Internet of Drones Security. [CrossRef]
- Hassija, V. , Gupta, A., & Singh, R. (2020). A Distributed Framework for Energy Trading Between UAVs and Charging Stations for Critical Applications. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. , Zhang, J., & Li, Z. (2021). Building Agile and Resilient UAV Networks Based on SDN and Blockchain. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J. , & Smith, T. (2017). Blockchain, The Greater Good, and Human and Civil Rights. [CrossRef]
- Jadav, S. , Patel, D., & Sharma, N. (2023). Blockchain-Based Secure and Intelligent Data Dissemination Framework for UAVs in Battlefield Applications. [CrossRef]
- Javed, F. , Iqbal, K., & Raza, M. (2022). An Efficient Authentication Scheme Using Blockchain as a Certificate Authority for the Internet of Drones. [CrossRef]
- Koulianos, S. , & Papadopoulos, E. (2023). Blockchain Technology for Secure Communication and Formation Control in Smart Drone Swarms. [CrossRef]
- Lis, M. , & Balogh, G. (2019). Cyberattacks on Critical Infrastructure: An Economic Perspective. [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M. , & Narayanan, S. (2022). Optimized Path Planning Strategy to Enhance Security Under Swarm of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. [CrossRef]
- Mohril, R. S. , Solanki, B. S., & Lad, B. K. (2021). Blockchain Enabled Maintenance Management Framework for Military Equipment. [CrossRef]
- Nyangaresi, P. , & Mutunga, R. (2024). A Biometric and Physically Unclonable Function-Based Authentication Protocol for Payload Exchanges in Internet of Drones. [CrossRef]
- Oláh, J. , & Kovács, P. (2023). Secure Registration Protocol for the Internet of Drones Using Blockchain and Physical Unclonable Function Technology. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R. , & Mishra, K. (2022). Security Threats and Mitigation Techniques in UAV Communications: A Comprehensive Survey. [CrossRef]
- Salor, H. , & Wong, L. (2023). Harnessing the Potential of Emerging Technologies to Break down Barriers in Tactical Communications. [CrossRef]
- Samanth, R. , Gupta, N., & Sharma, P. (2022). Security in Internet of Drones: A Comprehensive Review. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S. , & Mukherjee, R. (2023). Blockchain-Based Authenticable (k,n) Multi-Secret Image Sharing Scheme. [CrossRef]
- Shahidinejad, A. , & Davoodi, M. (2024). Anonymous Blockchain-Assisted Authentication Protocols for Secure Cross-Domain IoD Communications. [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A. , & Malik, F. (2022). A Blockchain-Based Authentication Solution for 6G Communication Security in Tactile Networks. [CrossRef]
- Sobb, T. , Turnbull, B., & Moustafa, N. (2020). Supply Chain 4.0: A Survey of Cyber Security Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions. [CrossRef]
- Stanley-Lockman, Z. , & Greenberg, M. (2019). Revisiting the Revolution in Military Logistics: Technological Enablers Twenty Years On. [CrossRef]
- Torky, M. , & Hassanein, A. (2022). Scheduling and Securing Drone Charging System Using Particle Swarm Optimization and Blockchain Technology. [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, M. , Raj, P., & Shukla, K. (2022). eChain: A Blockchain-Enabled Ecosystem for Electronic Device Authenticity Verification. [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, J. , Jensen, T., & Andersen, M. (2021). Blockchain for International Security: An Introduction. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. , Liu, Y., & Li, Q. (2022). Using Blockchain to Protect 3D Printing from Unauthorized Model Tampering. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. , Dai, H., Wang, H., & Ruan, K. K. (2020). Blockchain-Based Privacy Preservation for 5G-Enabled Drone Communications. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. , Zhou, X., & Lin, H. (2022). A Review on Security Issues and Solutions of the Internet of Drones. [CrossRef]
- Yazdinejad, A. , & Gandomi, A. (2020). An Energy-Efficient SDN Controller Architecture for IoT Networks With Blockchain-Based Security. [CrossRef]
- Yazdinejad, A. , & Gandomi, A. (2020). Enabling Drones in the Internet of Things With Decentralized Blockchain-Based Security. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. , Lu, Z., & Li, S. (2020). An invisible warfare with the internet of battlefield things: A literature review. [CrossRef]
- Al Sadawi, A. , Hassan, M. S., & Ndiaye, M. (2021). A survey on the integration of blockchain with IoT to enhance performance and eliminate challenges. IEEE Access. [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N. (2020). Demystifying blockchain: A critical analysis of challenges, applications and opportunities. International Journal of Information Management. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. , Hua, H., Wei, Z., & Cao, J. (2022). Challenges of blockchain in new generation energy systems and future outlooks. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 135. [CrossRef]
- Akram, S. V. , Malik, P. K., Singh, R., Anita, G., & Tanwar, S. (2020). Adoption of blockchain technology in various realms: Opportunities and challenges. Security and Privacy, 3. [CrossRef]
- Alam, S. , Shuaib, M., Khan, W. Z., Garg, S., Kaddoum, G., Hossain, M. S., & Zikria, Y. B. (2021). Blockchain-based initiatives: current state and challenges. Computer Networks, 198. [CrossRef]
- Zou, J. , He, D., Zeadally, S., Kumar, N., Wang, H., & Choo, K. R. (2021). Integrated blockchain and cloud computing systems: A systematic survey, solutions, and challenges. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 54. [CrossRef]
- Durneva, P. , Cousins, K., & Chen, M. (2020). The current state of research, challenges, and future research directions of blockchain technology in patient care: Systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research. [CrossRef]
- Rissanen, R. , Pulli, P., Sinkkonen, M., & Vaittinen, S. (2023). Lessons learned in cross-border data exchange in health services across Nordic and Baltic countries. Reference incomplete; data unavailable.
- Kifokeris, D. , & Koch, C. (2022). The proof-of-concept of a blockchain solution for construction logistics integrating flows: Lessons from Sweden. Blockchain for Construction. [CrossRef]
- Proskurovska, A. (2023). Re-inventing housing finance with blockchain: The case of Sweden. Geoforum. [CrossRef]
- Karaszewski, R. (2021). The use of blockchain technology in public sector entities management: An example of security and energy efficiency. [CrossRef]
- Holm, K. , & Goduscheit, R. C. (2023). Exploring the opportunities of blockchain-enabled coopetition: Learnings from the wind turbine industry. International Journal of Technology Management, 93. [CrossRef]
- Theodorakopoulos, L. , Karras, A., Theodoropoulou, A., & Kampiotis, G. (2024). Benchmarking Big Data Systems: Performance and Decision-Making Implications in Emerging Technologies. Technologies, 12(11), 217. [CrossRef]
- Al-Swidi, A. K. , Al-Hakimi, M. A., Al Halbusi, H., Al Harbi, J. A., & Al-Hattami, H. M. (2024). Does blockchain technology matter for supply chain resilience in dynamic environments? The role of supply chain integration. PLOS ONE, 19. [CrossRef]
- Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, I., Yıldız, B., Çiğdem, Ş., & Činčikaitė, R. (2021). An integrated impact of blockchain on supply chain applications. Logistics, 5(2), 33. [CrossRef]
- Stamatiou, Y. C. , Halkiopoulos, C., Giannoulis, A., & Antonopoulou, H. (2022). Utilizing a Restricted Access e-Learning Platform for Reform, Equity, and Self-development in Correctional Facilities. Emerging Science Journal, 6, 241–252. [CrossRef]
- Adrian Gheorghe, F. S. A. P. , & Unal Tatar, O. F. K. (2021). Blockchain for a resilient, efficient, and effective supply chain: Evidence from cases.
- GOODS, N. O. N. C. (2023). Mobilizing military supply chains with distributed ledger technologies-Volume 2. DRDC-RDDC.Wenger, A., Cavelty, M. D., & Jasper, U. (2020). The politics and science of the future: Assembling future knowledge and integrating it into public policy and governance. In The Politics and Science of Prevision (pp. 229-251). Routledge. [CrossRef]
- Kimbell, L. , & Vesnić-Alujević, L. (2020). After the toolkit: Anticipatory logics and the future of government. Policy Design and Practice. [CrossRef]
- King, J. , Holmes, R., Burkholder, S., Holzman, J., & Suedel, B. (2022). Advancing nature-based solutions by leveraging Engineering With Nature® strategies and landscape architectural practices in highly collaborative settings. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 18. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M. L. , Cabrera, A. T., & Del Pulgar, M. L. G. (2020). Guidelines from the heritage field for the integration of landscape and heritage planning: A systematic literature review. Landscape and Urban Planning, 204. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





