Submitted:
12 November 2024
Posted:
13 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Uncovering the genetic characteristics of important traits in wheat cultivars is essential for targeted wheat breeding. Here, a liquid 100K single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) chip panel, integrating markers of known function, was selected and used to analyze genetic characteristics for 115 spring wheat cultivars from a high-altitude region of China. A total of 102 reported functional markers closely related to important traits were identified, including 54 related to yield and grain quality and 33 associated with disease resistance and stress tolerance. Of the cultivars, 58.3% contained multiple marker genes, ranging in number between 20 and 29. Genetic structure analysis revealed that the cultivars were grouped into five subgroup. Genome-wide association studies identified 218 significant loci on 20 chromosomes, with the exception of chromosome 3D, associated with nine traits and which explained 14.15%–29% of phenotypic variance, with 199 potential candidate genes being annotated for the nine traits studied. Notably, 21 previously unidentified candidate genes, with associated SNPs, were closely associated with seven traits, explaining 14.26%–19.86% of the phenotypic variance. The current study revealed the genetic characteristics of spring wheat cultivars from a high-altitude region of China. This will provide a reference for spring wheat breeding for high-altitude regions and promote the fine-mapping of new genetic loci controlling important traits.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction and SNP Genotyping
2.3. Evaluation of Agronomic Traits
2.4. Population Structure and GWAS
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Phenotypic Variation and Functional Markers
3.2. Analysis of Genetic Structure
3.3. Genome-Wide Association Study of Agronomic Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayer PE, Petereit J, Durant É, Monat C, Rouard M, Hu H, Chapman B, Li C, Cheng S, Batley J, Edwards D. Wheat Panache: A pangenome graph database representing presence-absence variation across sixteen bread wheat genomes. Plant Genome. 2022, 15, e20221.
- Gao Y, An K, Guo W, Chen Y, Zhang R, Zhang X, Chang S, Rossi V, Jin F, Cao X, Xin M, Peng H, Hu Z, Guo W, Du J, Ni Z, Sun Q, Yao Y. The endosperm-specific transcription factor TaNAC019 regulates glutenin and starch accumulation and its elite allele improves wheat grain quality. Plant Cell. 2021,33(3),603-622.
- Wang H, Bernardo A, St Amand P, Bai G, Bowden RL, Guttieri MJ, Jordan KW. Skim exome capture genotyping in wheat. Plant Genome. 2023, 16(4), e20381.
- Guo Z, Yang Q, Huang F, Zheng H, Sang Z, Xu Y, Zhang C, Wu K, Tao J, Prasanna BM, Olsen MS, Wang Y, Zhang J, Xu Y. Development of high-resolution multiple-SNP arrays for genetic analyses and molecular breeding through genotyping by target sequencing and liquid chip. Plant Commun. 2021,2(6),100230.
- Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Ren, Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, K.; Zou, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Development of multiple SNP marker panels affordable to breeders through genotyping by target sequencing (GBTS) in maize. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 37 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqiang N, Zihan L,Zhang FengtingYuan ShaohuaBai JianfangLiu YongjieLi YanmeiZhang HengZhang HuishuZhao ChangpingSong XiyueZhang Liping.Identification and validation of major-effect quantitative trait locus QMS-5B associated with male sterility in photo-thermo-sensitive genic male sterile wheat[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 2023, 136(12).
- Mohamed IES, Kamal NM, Mustafa HM, Abdalla MGA, Elhashimi AMA, Gorafi YSA, Tahir ISA, Tsujimoto H, Tanaka H. Identification of Glu-D1 Alleles and Novel Marker-Trait Associations for Flour Quality and Grain Yield Traits under Heat-Stress Environments in Wheat Lines Derived from Diverse Accessions of Aegilops tauschii. Int J Mol Sci. 2022,23(19),12034.
- Negisho K, Shibru S, Pillen K, Ordon F, Wehner G. Genetic diversity of Ethiopian durum wheat landraces. PLoS One. 2021, 16(2), e0247016.
- Yang Y, Chai Y, Zhang X, Lu S, Zhao Z, Wei D, Chen L, Hu Y G. Multi-locus GWAS of quality traits in bread wheat: mining more candidate genes and possible regulatory network. Front Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1091.
- Yang H, Xiang S H, Liu L, Yang X, Shu Y J, He Q Y. Genome-wide association analysis of growth period traits in soybean of Sichuan and Chongqing. Acta Agron Sin. (in Chinese with English abstract). 2023, 49, 2727–2742.
- Huang X H, Zhao Y, Wei X H, Li C Y, Wang A H, Zhao Q, Li W J, Guo Y L, Deng L W, Zhu C R, Fan D L, Lu Y Q, Weng Q J, Liu K Y, Zhou T Y, Jing Y F, Si L Z, Dong G J, Huang T, Lu T T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J Y, Han B. Genome-wide association study of flowering time and grain yield traits in a worldwide collection of rice germplasm. Nat Genet. 2012, 44, 32–39.
- Chen J H, Zhang F Y, Zhao C J, Lv G G, Sun C W, Pan Y B, Guo X Y, Chen F. Genome-wide association study of six quality traits reveals the association of the TaRPP13L1 gene with flour colour in Chinese bread wheat. Plant Biotechnol J. (in Chinese with English abstract). 2019, 17, 2106–2122.
- Gao L, Meng C S, Yi T F, Xu K, Cao H W, Zhang S H, Yang X J, Zhao Y. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic basis of yield- and quality-related traits in wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 1–11.
- Kumar A, Mantovani E E, Simsek S, Jain S L, Elias E M, Mergoum M. Genome-wide genetic dissection of wheat quality and yield related traits and their relationship with grain shape and size traits in an elite × non-adapted bread wheat cross. PLoS One. 2019, 14, e0221826.
- Lou H Y, Zhang R Q, Liu Y T, Guo D D, Zhai S S, Chen A Y, Zhang Y F, Xie C J, You M S, Peng H R, Liang R Q, Ni Z F, Sun Q X, Li B Y. Genome-wide association study of six quality-related traits in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under two sowing conditions. Theor Appl Genet. 2021, 134, 399–418.
- Ageeva EV, Leonova IN, Likhenko IE. Пoлегание пшеницы: генетические и экoлoгические фактoры и спoсoбы преoдoления [Lodging in wheat: genetic and environmental factors and ways of overcoming]. Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genet Selektsii. 2020,24(4),356-362.
- Yu J M, Pressoir G, Briggs W H, Bi I V, Yamasaki M, Doebley J F, McMullen M D, Gaut B S, Nielsen D M, Holland J B, Kresovich S, Buckler E S. A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet. 2006, 38, 203–208.
- Zhu Y L, Wang S X, Zhao L X, Zhang D X, Hu J B, Cao X L, Yang Y J, Chang C, Ma C X, Zhang H P. Exploring molecular markers of preharvest sprouting resistance gene using wheat intact spikes by association analysis. Acta Agron Sin, 2014, 40, 1725–1732, (in Chinese with English abstract).
- Sun X, Xie Y, Xu K, et al. Regulatory networks of the F-box protein FBX206 and OVATE family proteins modulate brassinosteroid biosynthesis to regulate grain size and yield in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany. 2024, 75(3),789-801.
- Sano H, Youssefian S. A novel ras-related rgp1 gene encoding a GTP-binding protein has reduced expression in 5-azacytidine-induced dwarf rice[J]. Molecular and General Genetics MGG. 1991, 228, 227–232.
- Saini DK, Chopra Y, Singh J, Sandhu KS, Kumar A, Bazzer S, Srivastava P. Comprehensive evaluation of mapping complex traits in wheat using genome-wide association studies. Mol Breed. 2021,42(1),1.
- Jingwei Zhou, Bowei Ye, Pengfei Zhang, Yuqing Zhang, Min Hao, Yuruo, Chan Yuan, Zhikang Li, Shunda Li, Xianchun He, Zhonghu He, Hongjun Zhang, Caixia Lan. Identification and evaluation of stripe rust resistance in 153 wheat germplasm from domestic and international sources [J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica. 2024, 57(01),18-33.(in Chinese with English abstract).
- Marchal C, Zhang J, Zhang P, Fenwick P, Steuernagel B, Adamski NM, Boyd L, McIntosh R, Wulff BBH, Berry S, Lagudah E, Uauy C. BED-domain-containing immune receptors confer diverse resistance spectra to yellow rust. Nat Plants. 2018, 4(9),662-668.
- Shao M, Bai G, Rife TW, Poland J, Lin M, Liu S, Chen H, Kumssa T, Fritz A, Trick H, Li Y, Zhang G. QTL mapping of pre-harvest sprouting resistance in a white wheat cultivar Danby. Theor Appl Genet. 2018,131(8),1683-1697.
- Brinton J, Uauy C. A reductionist approach to dissecting grain weight and yield in wheat. J Integr Plant Biol. 2019, 61(3), 337–358.
- Kong X, Wang F, Wang Z, Gao X, Geng S, Deng Z, Zhang S, Fu M, Cui D, Liu S, Che Y, Liao R, Yin L, Zhou P, Wang K, Ye X, Liu D, Fu X, Mao L, Li A. Grain yield improvement by genome editing of TaARF12 that decoupled peduncle and rachis development trajectories via differential regulation of gibberellin signalling in wheat. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023, 21(10), 1990–2001.
- Morris, CF. Determinants of wheat noodle color. J Sci Food Agric. 2018, 98(14), 5171–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaDuca H, Farwell KD, Vuong H, Lu HM, Mu W, Shahmirzadi L, Tang S, Chen J, Bhide S, Chao EC. Exome sequencing covers >98% of mutations identified on targeted next-generation sequencing panels. PLoS One. 2017,12(2),e0170843.
- Jin X, Feng B, Xu Z, Fan X, Liu J, Liu Q, Zhu P, Wang T. TaAAP6-3B, a regulator of grain protein content selected during wheat improvement. BMC Plant Biol. 2018,18(1),71.
- Lv Q, Li L, Meng Y, Sun H, Chen L, Wang B, Li X. Wheat E3 ubiquitin ligase TaGW2-6A degrades TaAGPS to affect seed size. Plant Sci. 2022, 320, 111274.
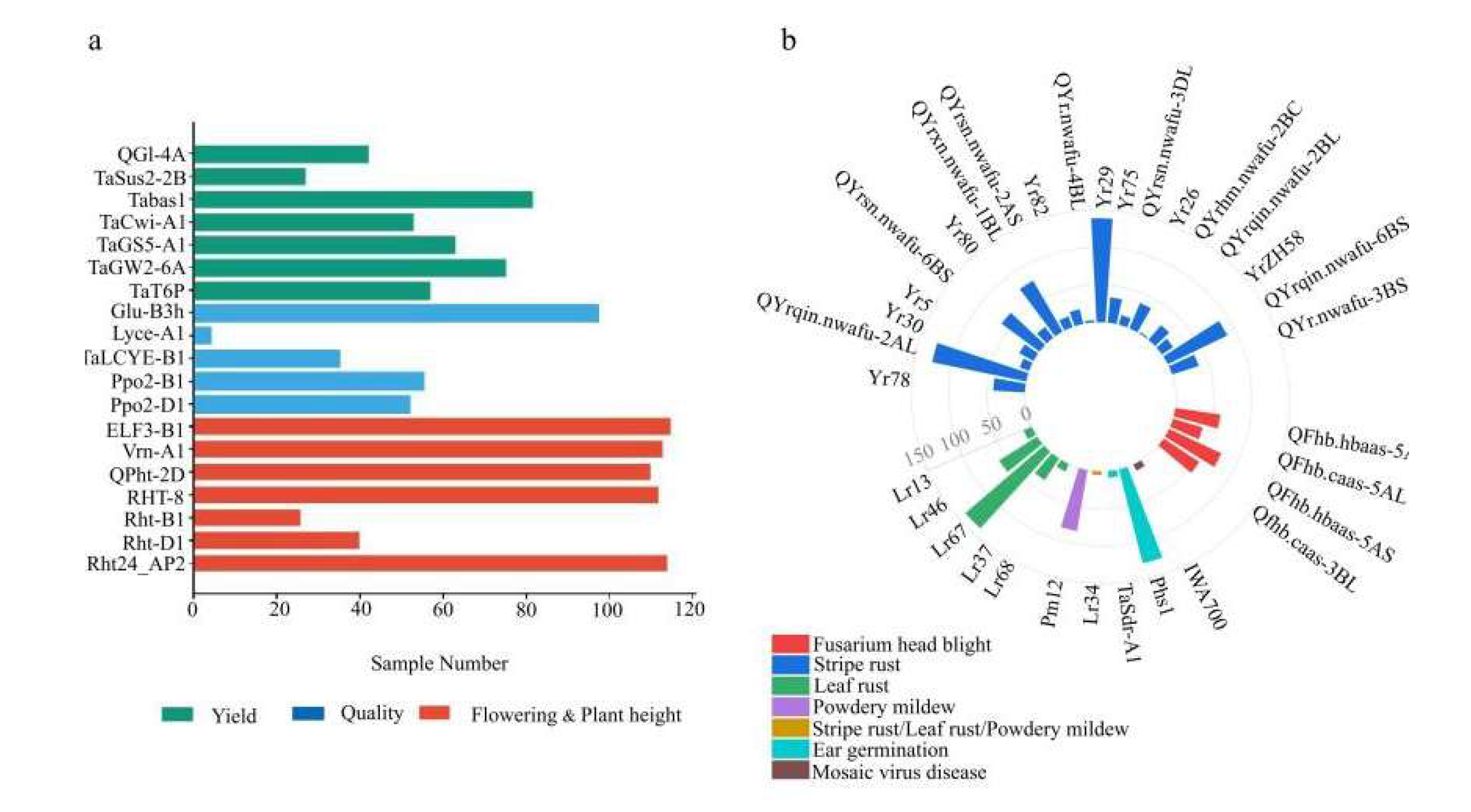
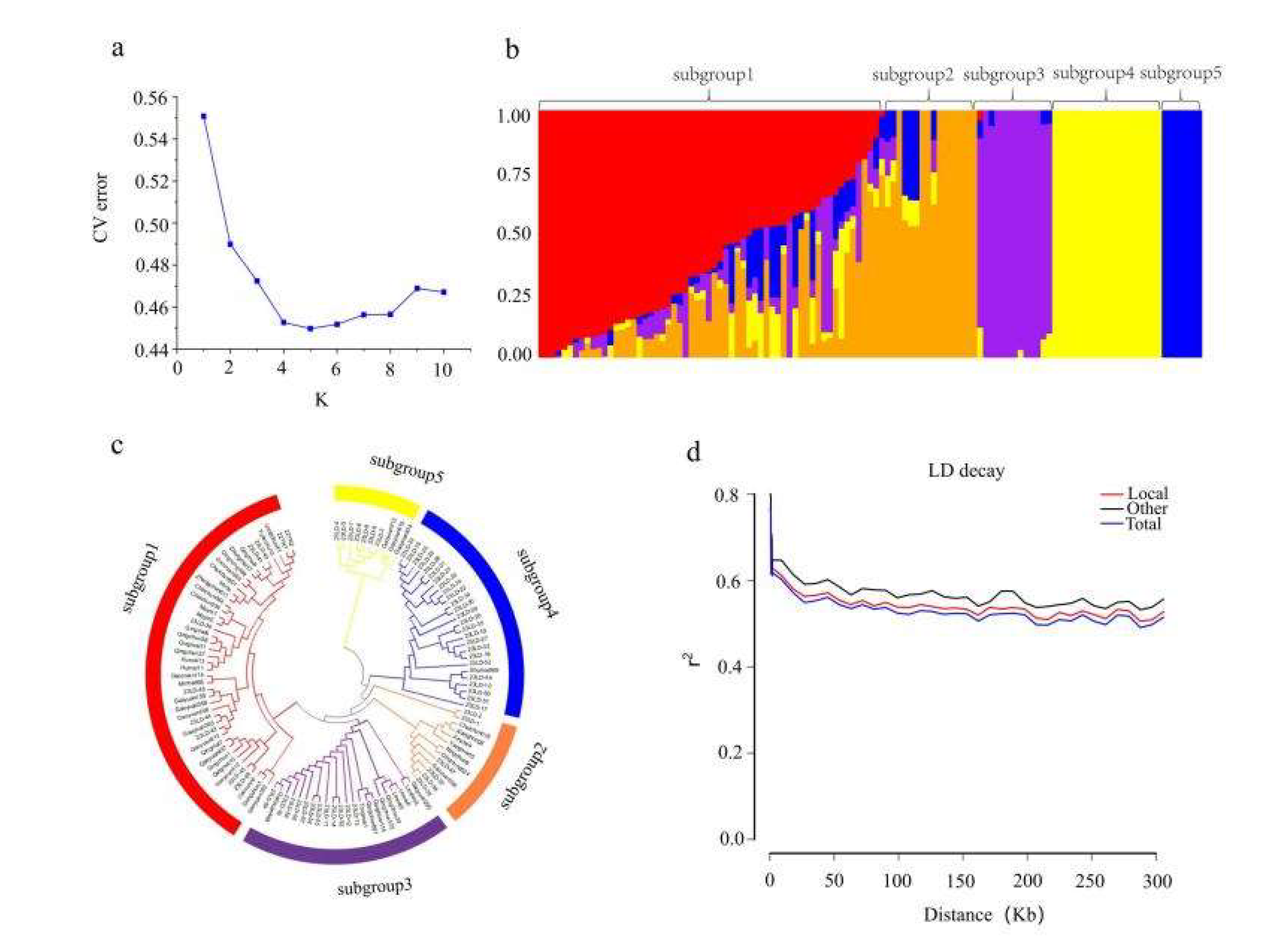
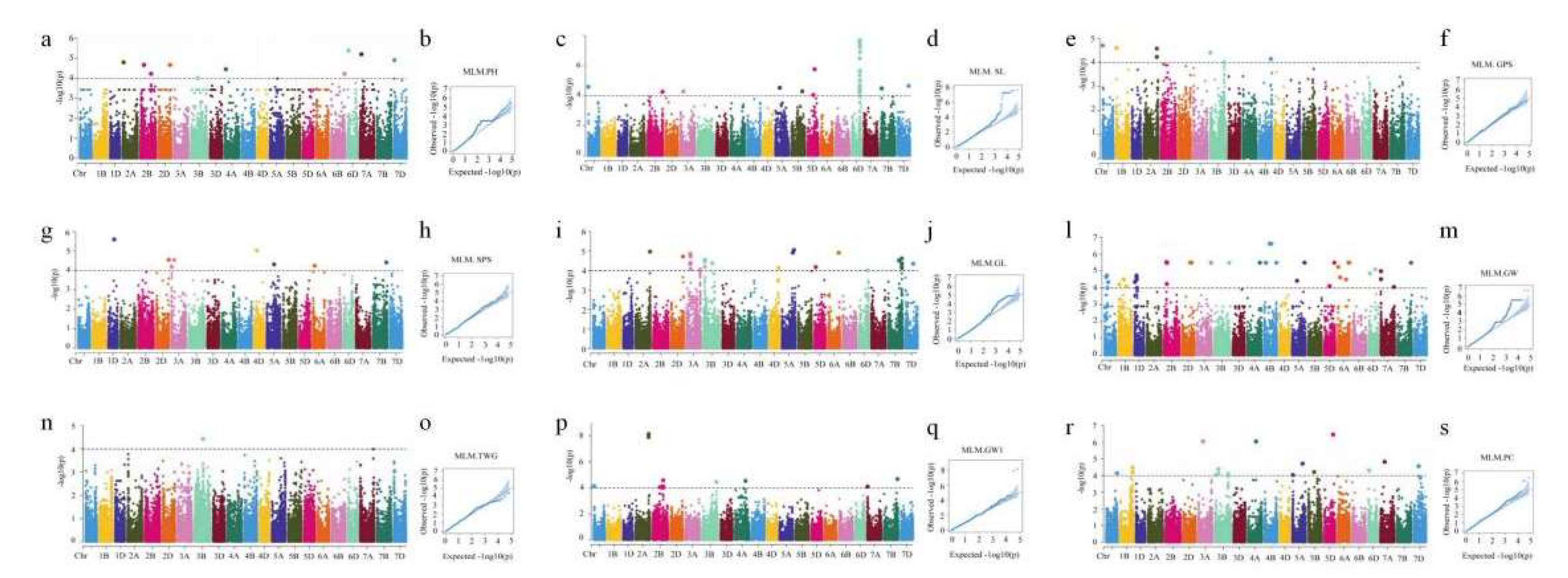
| Trait | Year | Range | Mean±SD | Variance | Skewness | Kurtosis | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height (cm) | 2023 | 52.00-133.00 | 88.01±12.25 | 188.02 | 0.44 | 0.49 | 0.15 |
| 2024 | 53.00–135.00 | 87.81±13.75 | 189.06 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.16 | |
| Spike length (cm) | 2023 | 5.80–17.36 | 9.78±2.11 | 5.67 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.20 |
| 2024 | 5.80–18.00 | 9.81±2.44 | 5.96 | 0.62 | 0.46 | 0.25 | |
| Number of grains per spike | 2023 | 26.00–97.00 | 54.86±14.60 | 218.79 | 0.36 | −0.09 | 0.21 |
| 2024 | 27.00–96.00 | 55.54±15.20 | 231.16 | 0.47 | −0.14 | 0.27 | |
| Number of spikelets/spike | 2023 | 9.87.–22.65 | 14.68±2.12 | 8.01 | 0.48 | 0.31 | 0.12 |
| 2024 | 10.00–24.00 | 15.70±2.68 | 7.18 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.17 | |
| Grain length (mm) | 2023 | 4.98–7.96 | 5.99±0.79 | 0.18 | 0.01 | –0.19 | 0.04 |
| 2024 | 5.31–7.74 | 6.47±0.49 | 0.24 | 0.08 | –0.27 | 0.08 | |
| Grain width (mm) | 2023 | 2.83–4.17 | 3.06±0.27 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 3.06 | 0.03 |
| 2024 | 2.91–4.59 | 3.48±0.24 | 0.06 | 0.75 | 3.85 | 0.07 | |
| Thousand-grain weight (g) | 2023 | 28.15–62.89 | 49.56±5.79 | 47.88 | 0.19 | –0.03 | 0.12 |
| 2024 | 28.79–63.21 | 45.07±6.99 | 48.94 | 0.21 | –0.08 | 0.16 | |
| Protein content (%) | 2023 | 10.58–15.23 | 12.12±1.01 | 1.61 | 0.63 | –0.04 | 0.09 |
| 2024 | 11.49–16.73 | 13.42±1.31 | 1.71 | 0.78 | –0.07 | 0.10 | |
| Grain weight/spike (g) | 2023 | 0.93–4.96 | 2.18±0.66 | 0.49 | 0.52 | –0.09 | 0.29 |
| 2024 | 0.95–5.06 | 2.53±0.87 | 0.76 | 0.60 | –0.19 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





