1. Introduction
Nootropics are a class of neurologically active compounds purported to enhance cognitive abilities such as memory, focus and learning, hence the associated term, ‘
smart drugs’ [
1]. Both synthetically derived (e.g. Ritalin, Piracetam, Modafinil) and naturally occurring compounds (e.g. caffeine, medicinal mushrooms) are taken by a growing proportion of the adult population for these performance enhancing effects to aid with the demands of everyday modern life (e.g. rapid decision-making, creativity, productivity) [
2,
3,
4,
5]. Natural nootropics are considered to have less side effects and more potential widespread health benefits compared to synthetic compounds [
4,
6]; consequently, they have been of recent interest for their use in both clinical and healthy populations [
1,
7,
8].
Among clinical human and animal studies, plant-derived extracts have been shown to improve neural and behavioural markers of health and performance including perceptual-motor function, learning, language comprehension and memory [
1,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The mechanisms by which these nootropics restore cognitive abilities varies widely but commonly involves increasing the supply and efficiency of use of energetic resources in the brain (e.g. increased cerebral blood flow, positive allosteric modulation of acetylcholine and glutamate receptors and inhibition of monoamine oxidases) [
8,
12,
13,
14]. Hence, it is understandable that these substances would have impactful effects among cognitively impaired cohorts that typically present with reduced energetic resources or efficiency of resource allocation (e.g. aging, Alzheimer’s disease) [
15,
16,
17]. Nonetheless, within the healthy working age adult population, the interest in nootropic supplements has grown considerably recently for their purported ability to improve cognitive performance [
2,
3,
12,
18], with noteworthy self-reported accounts of their benefits [
6,
8,
19]. However, it is currently unclear how well the impactful results from nootropic supplements found predominantly among clinical human and animal studies can be generalised to the healthy population as cognitive enhancers as a significant number of the available studies in this group demonstrate minimally effective, contrasting or even contradictory behavioural results [
1,
6,
8,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. To exemplify this point, nootropic effects have been observed to vary across age groups as a function of the underlying cognitive deficits associated with senescence [
8,
23,
25], suggesting a restorative rather than enhancing effect of nootropic compounds [
6,
11]. Consequently, among high functioning, younger adults with adequate dietary regimes which likely function near their optimal state already, this
‘normalising’ effect would be expected to be less pronounced, leading to more subtle changes in overall cognitive performance. Statistically speaking, the relatively small effect sizes from such subtle behavioural changes following supplementation likely explains the discrepancies in previous research, however it does not explain the overwhelmingly positive self-reports and growing interest in these compounds among healthy adults [
1,
2,
3,
5,
6,
8,
19]. These performance changes, although subtle in magnitude, may in fact be of considerable significance subjectively and may be underpinned by more pronounced effects neurologically. The energetic dynamics of the brain which nootropics likely effect can be cast through the mathematical lens of information theory [
26,
27], where information sharing across neuronal populations abstractly represents the electrophysiological dynamics of cognitive processes and consequentially, the metabolic constraints underpinning them.
Therefore, in the current study we aimed to investigate the efficacy of nootropic compounds in the healthy adult population to shed light mechanistically on these discrepancies in previous research and provide a neurocomputational explanation for the self-reports of improved wellbeing with nootropic consumption. Towards this objective, we devised a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled experiment (pre-registration:
https://osf.io/25afe) that aimed to address this current research gap by combining behavioural experimentation with neuroscientific enquiry to answer the following research question:
What effect does a commercially available nootropic supplement have on perceptual decision-making performance (i.e. the ability to make rapid decisions based on sensory information) and brain network interdependencies (i.e. the collective interactions between brain regions)?
To answer this research question, we employed a computerised experimental paradigm testing participants visual perceptual decision-making while concurrently capturing brain activity using electroencephalography (EEG). We implemented this cognitive test pre- and post- 60 days of daily supplementation with the Mind Lab Pro supplement. Our analytical approach consisted of applying multivariate information-theoretic measures to identify salient differences in brain networks interdependencies that could be explained by the supplement regime. Prior to the experimental period, we hypothesized that this supplementation regime would result in negligible behavioural changes but more pronounced effects on the brain network interdependencies underlying perceptual decision-making, thereby explaining discrepancies in previous research and the growing interest and self-reports of improved wellbeing among healthy adults.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment, Selection, and Randomisation Schedule
Participant recruitment strategies included poster advertisements in the local community, mass email notifications through approved University channels and word-of-mouth. Potential candidates were provided with a brief outline of the experimental protocol and asked to contact the experimental lead for further information and screening. Interested candidates were provided with an information sheet and given time to ask questions before informed consent was obtained.
Eligibility screening of participants was guided by the following inclusion criteria: (i) be between 20-59 years old, (ii) be right-handed and (iii) be able to cease taking other dietary supplements for two months. Exclusion criteria included: (i) currently consuming a nootropic supplement, (ii) any known musculoskeletal, or neurological medical conditions or cognitive impairments (iii) have a known diagnosis of epilepsy/history of seizures and (iv) have a known hearing or visual condition that affects daily life function.
Following successful screening, participants were pseudo randomly assigned on a 1:1 ratio basis to the treatment or control groups. Both the experimental lead and participants were blinded to the assignment of treatment and control groups. Only the principal investigator was aware of group assignment but was not involved in experimental collection or analysis. After completing the experiment, each participant received a £50 retail voucher. Following the completion of data collection and preliminary data analyses, both the experimental lead and participants were subsequently unblinded to group assignments.
Full ethical permission was gained from the Faculty of Biological Sciences ethics committee, University of Leeds (BIOSC22-022).
2.2. Interventional Compound
The treatment group received a commercially available Mind Lab Pro supplement (
https://mindlabpro.com) while the control group were given a matched placebo comprised of an inactive cellulose substance. Participants of both groups were asked to consume two capsules per day (the lowest range of the recommended daily dose by the supplement manufacturer) continuously for 60 days, preferably in the morning with breakfast. Table.1 below provides a full list of the included ingredients for a two-capsule serving. They were asked to maintain their regular diet throughout supplementation and to immediately report any adverse effects.
2.3. Experimental Task
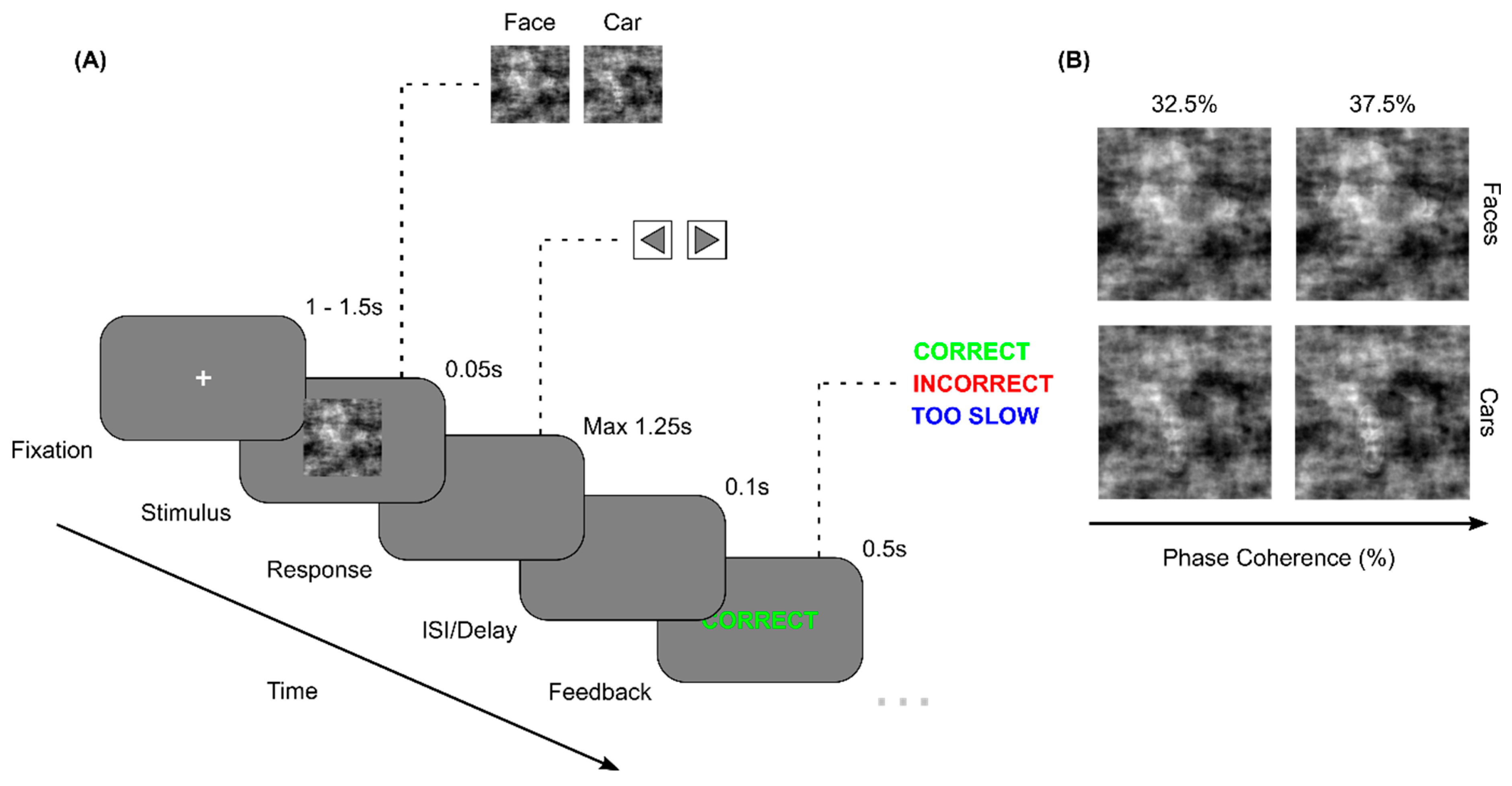
The day prior to and as soon as possible following the supplementation period, participants took part in a computerised cognitive task assessing their visual perceptual decision-making (
Figure 1) [
28]. In this experiment, a working memory task was also performed by the participants which was not analysed in the current study. However, it is worth noting that the order of these separate experimental tasks was randomised across participants to prevent any carry-over effects (i.e. learning, fatigue).
2.3.1. Stimuli
The stimuli consisted of 18 face (Face Database; Max Plank Institute of Biological Cybernetics3) and 18 car (sourced from the Internet) grayscale images, adapted from previous studies [
28,
29,
30,
31], were retrieved to use as visual stimuli (image size: 512 × 512 pixels; bit depth: 8 bits/pixel) (
Figure 1(A)). Each original image had its background removed before being transferred onto a uniform grey background (RGB: [115 115 115]), and were equated for spatial contrast, frequency, luminance, and total number of frontal and side views (i.e., a maximum of ±45°) to ensure identical magnitude spectra (i.e., average magnitude spectrum of all images in the database). All images had their corresponding phase spectra manipulated using the weighted mean phase technique7, 8, altering their image phase coherence, and therefore characterizing phase coherence percentage and the quantity of visual sensory evidence available. Two levels of visual sensory evidence; 32.5% and 37.5% phase coherence, were selected to manipulate image classification difficulty (
Figure 1(B)). A Stone 64-bit based workstation (CPU: i7-9700; RAM 500GB SSD), running Windows Professional 7 (Linux-x86_64-bit) and PsychoPy presentation software (v3.8.10) controlled the stimulus display (RGB: [128 128 128]). Images were presented on an Iiyama ProLite B2484HSU 24-inch monitor (resolution: 1920 × 1080 pixels; refresh rate: 75 Hz). Participants were positioned 60cm from the monitor, and each image subtended approximately 8 × 8 degrees of visual angle.
2.3.2. Behavioural Task
Participants performed an object categorization task in which they classified whether faces or cars were embedded in a series of images1, 2 (
Figure 1). Each trial began with a white (RGB: [255 255 255]) fixation cross presented on-screen for a randomized duration between 1 - 1.5s. Then a visual stimulus was presented for 50ms. Participants were instructed to make their response as soon as they had reached a decision (i.e., as quickly and accurately as they could), with a response deadline set for 1.25s. Participants responded by pressing the correctly assigned key (i.e., left and right arrow presses for faces and cars respectively) using their right index and middle fingers. Following an inter-stimulus interval (ISI; delay) of 100ms, they then received visual feedback following each response for 500ms. Three possible outcome statements, in block capitals, were presented as feedback: (1) correct (RGB: [0 255 0]), (2) incorrect (RGB: [255 0 0]), and (3) too slow (RGB: [0 0 255]), for correct, incorrect, and timed-out responses (i.e., exceeding the response deadline of 1.25s) respectively. Single-trial Reaction Times (RTs) and choice accuracy (i.e., correct and incorrect) were collected as metrics of decision-making performance, with timed-out responses (i.e.., exceeding the response deadline of 1.25s) treated as incorrect. In total, participants completed 576 trials per session, consisting of four blocks of 144 trials each, with a 60 second rest period between blocks. Within each block, trials were divided equally between face and car images (imType) (i.e., 72 face and 72 car trials per block) and the two levels of stimulus phase coherence (imCoh) (i.e., 72 37.5% and 72 32.5% trials per block). The entire task lasted approximately 25-30 minutes.
2.4. EEG Recording and Pre-Processing
EEG signals were recorded in a sound-attenuated room using a 64-channel Brian Visions amplifier system and Analyzer software at a sampling frequency of 1000Hz.
Following data capture, the EEG signals were processed in Matlab software using the EEGLab toolbox [
32]
. More specifically, following each data capture session, we firstly re-referenced the EEG signals to the average of all channels. We then band-pass filtered the signals within the 0.5Hz-200Hz range. To remove power line noise, we subsequently applied spectrum interpolation (code taken from the Fieldtrip toolbox [
33]
) at 50Hz and its corresponding harmonics up to 200Hz [
34]
. To remove muscle and eye artifacts along with any remaining channel and line noise, we applied independent component analysis and, following an automated classification procedure, removing artefactual components identified with >90% certainty threshold. Stimulus-locked epochs (0-800ms post stimulus presentation) were extracted and averaged across trials for each participant to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of the EEG signals. Finally, to enhance the spatial resolution of the EEG data for subsequent functional connectivity analyses in the EEG source space, we extracted the surface Laplacian for each participants data using a custom Matlab script [
35]
.
2.5. Higher-Order Brain Network Interdependencies
Cognitive processes like perceptual decision-making involve complex interdependencies between different networks of neuronal populations operating across a range of frequency bands [
36]. To provide a thorough mechanistic account of brain network interdependencies following nootropic supplementation, we therefore analysed the EEG signals from the representative stimulus-locked trial of each participant separately within the Delta (0.5-4Hz), Theta (4-8Hz), Alpha (8-12Hz), Beta (12-30Hz) and Gamma (30-40Hz) frequency bands and extracted brain networks at multiple scales to localise the putative nootropic effects. This Delta band range was chosen even though the temporal resolution of the stimulus-locked trials was 1.25Hz (i.e. 1/800ms trial length = 1.25Hz temporal resolution) as it was found in preliminary analyses that the partially represented cycles in the lower delta frequencies contributed significantly to the analysis output. Meanwhile, the gamma frequency range selected was based on the gamma frequency ranges available with EEG that are less prone to artifact [
37]. Temporal waveforms for each frequency band were extracted using a low and high-pass bi-directional Butterworth filter combination with zero-phase distortion (‘
filtfilt’ function in Matlab). To provide a comprehensive insight into the changes induced by nootropic supplementation in the brain, we adopted a recently proposed greedy search algorithm (GSA) to identify higher-order networks of interdependencies between brain regions in a computationally efficient way that are maximally different between experimental groups [
38]. More specifically, beginning with the representative stimulus-locked trial for each participant from the follow-up session, we firstly quantified the interdependence between all possible triplets of EEG channels. These interdependencies were quantified using two distinct information-theoretic measures of multivariate correlation strength, the Total Correlation (TC) and the Dual Total Correlation (DTC) [
39,
40]. TC (Equation.1) and DTC (Equation.2) are non-negative multivariate generalisation of Mutual Information (MI), which for a system of
random variables denoted as
, can be expressed in terms of entropies () as:
Here for TC (Equation.1), the sum of the Shannon entropies of individual variable in
(
) is contrasted against their joint Shannon entropy (
. Meanwhile for DTC (Equation.2),
is contrasted against the sum of the conditional Shannon entropies (
. The mathematical differences between these multivariate measures of MI results in the emphases of distinct types of collective interdependence. More specifically, TC quantifies the shared information in a system that is similar across variables (i.e. the collective constraints [
41]), while DTC, also known as the binding information [
42], quantifies the shared randomness across a system (i.e. complementary information) [
41]. Hence, the subtraction of these two quantities (Equation.3), a measure known as the O-Information (Ω) [
41], quantifies the net balance between synergy and redundancy in a system (positive Ω values suggest predominantly redundant system interactions while negative values suggest net synergistic interactions). Through the application of TC, DTC and Ω to networks of EEG source signals here, we aimed to provide important insight into the collective interactions of multiple brain regions and the types of statistical relationships they manifest along with the changes induced in these characteristics with nootropic supplementation.
In the current study, we used a gaussian copula-based method to generate lower-bound estimates of TC and DTC and consequently Ω [
43]
.
Returning to the GSA adopted from recent work [
38]
, having quantified all pairwise interdependencies between EEG channels within a specific frequency band for each participant, we quantified the standardised mean difference for each pair between treatment and control groups using the Cohen’s d effect size (Equation.4) [
44]
. Here, and
are the average TC, DTC or Ω values from the treatment and control groups respectively while
is the pooled standard deviation where
(
) and
(
) are the variance and the sample size of the control (treatment) group respectively. A positive (negative) value for
therefore represents the effects direction, indicating increases (decreases) in brain network interdependencies following the intervention. As both the positive and negative values of Ω were of interest in the current study, we reversed the signs of the estimated Ω values (i.e -(
)) and re-applied the GSA to identify maximally discriminative redundant and synergistic brain networks.
We then used this pairwise computation as the basis for subsequent computations at the higher interaction order of triplets by identifying the pair with the maximum (minimum) effect sizes and determining all possible triplet subsets that contain the identified pair of EEG channels. This procedure was further redeployed in a stepwise manner at successively higher interaction orders up to 16-channel networks, representing 1/4 of the entire scalp map and well within the range of reliable Ω estimation [
38,
45]. In doing so, we were able to identify large brain networks that maximally discriminated between experimental groups, both in the direction of greater and less network interdependencies among the treatment group compared to the control group, while avoiding the combinatorial explosion inherent to computing higher-order interactions.
Having identified the brain networks most different between groups at the follow-up session across multiple interaction orders, be they significantly higher or lower than the control group, we then worked backwards to compute the same brain networks found to be significantly discriminative at follow-up but from the pre-session EEG data. These baseline values were then included as a covariate in separate Analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) models for each frequency band and interaction order alongside experimental group affiliation as a fixed factor and the follow-up session TC or DTC values as the dependent variable (SPSS Statistics 28 software). This enabled us to control for baseline differences to effectively ascertain whether these group differences at follow-up are genuine nootropic effects or could be simply explained by differences present from the outset of the experiment.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
For behavioural analyses, trials where participants responded <300ms or >1200ms post stimulus presentation were discarded as “
fast guesses” and “
attentional lapses” respectively [
46]. The median RT for each participant at baseline and follow-up was calculated from the correct trials only while the percentage of total trials correct was also taken to summarise choice accuracy. These summary statistics were employed in Mann-Whitney U tests to determine statistical differences between groups. Further, to determine if specific features of the perceptual decision-making task were influenced by the nootropic, the choice speed and accuracies were also summarised in the same way but from easy and hard trials (i.e. high and low imCoh respectively) and the different imType trials (i.e. face and car images) only. Statistical significance was set a priori to p<0.05. False discovery rates (FDR) during the ANCOVA procedures (see ‘
Higher-order brain network interdependencies’ of the Materials and Methods section) were controlled separately for models testing greater than (i.e. maximal Cohen’s d) and less than (i.e. minimal Cohen’s d) brain network interdependencies using the Benjamini & Hochberg approach [
47]. All ANCOVA models met the assumption of homoskedasticity as per the White’s test (p>0.05).
3. Results
37 participants (treatment group=19 participants, control group= 18 participants) were successfully recruited, however, 5 participants (treatment group= 2 participants, controls group=3 participants) voluntarily withdrew before the supplementation period ended, leaving 32 participants (treatment group=17 participants, controls group=15 participants) as the study sample. No significant differences between groups were present for age (treatment group: 38±8.3, control group: 31.7±10.3 (p>0.05)) while a relatively even gender split was found in both groups (Treatment group: M=10/F=7, Control group: M=8/F=7). Of the two participants from the treatment group that withdrew, neither self-reported adverse effects, demonstrating an overall good tolerance for the supplement across the cohort. Participants were assessed 3.66±3.2 days after their scheduled supplementation period was complete and self-reported good adherence to the supplementation regime.
3.1. Nootropic Supplementation Did Not Improve Perceptual Decision-Making Performance.
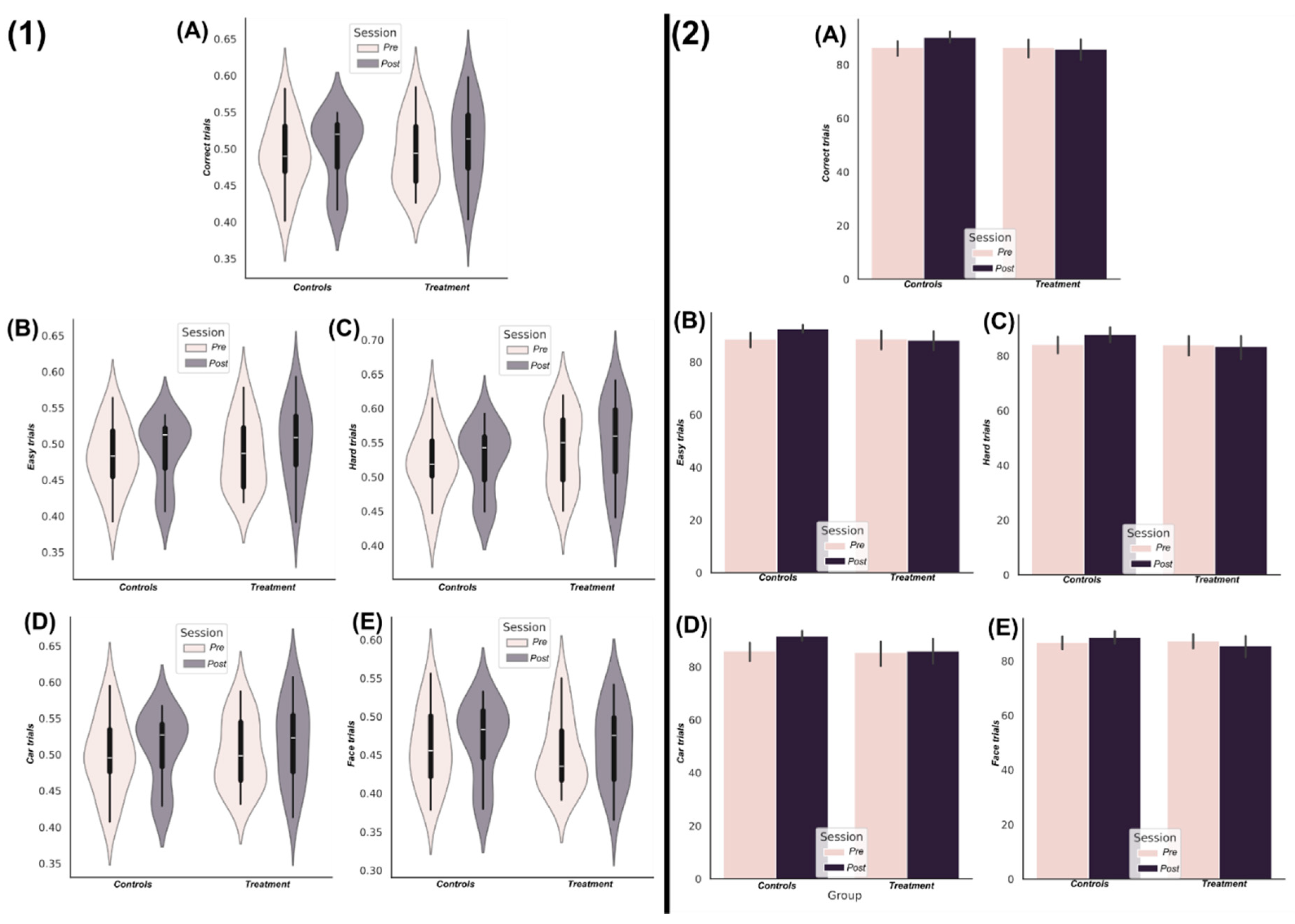
We found no statistically significant differences within or between experimental groups (p>0.05) across correct trials of any image type or difficulty level (
‘Correct trials’ Figure 2.1-2(A)), high imCoh trials (
‘Easy trials’ Figure 2.1-2(B)), low imCoh trials (
‘Hard trials’ Figure 2.1-2(C)), Car imType trials (
‘Car trials’ Figure 2.1-2(D)) or Face imType trials (
‘Face trials’ Figure 2.1-2(E)) for choice speed (
Figure 2.1) or choice accuracy (
Figure 2.2). Both groups typically demonstrated slower reaction times at follow-up compared to baseline, however this increase was lower in the treatment group. This resulted in the treatment group demonstrating typically faster reaction times at follow-up compared to controls except for hard trials (see
Figure 2.1(A-B,D-E)). However, no evidence was found for an improvement in choice reaction times due to nootropic supplementation. For choice accuracies, both groups scored highly at both sessions (>80% of trial correct on average), suggesting the task was well within their capabilities. The control group demonstrated a slight improvement in the percentage of trials correct at follow-up compared to baseline, a trend that generalised across all imType and imCoh trials. This coincides with the subtle increase in reaction times in this same group, suggesting a change in the speed-accuracy bias across the intervention in this group. Meanwhile, the treatment group demonstrated no noticeable changes in choice accuracy following the intervention and had typically lower choice accuracy than the control group.
3.2. Information Sharing Across Brain Networks Is Enhanced Following Nootropic Supplementation.
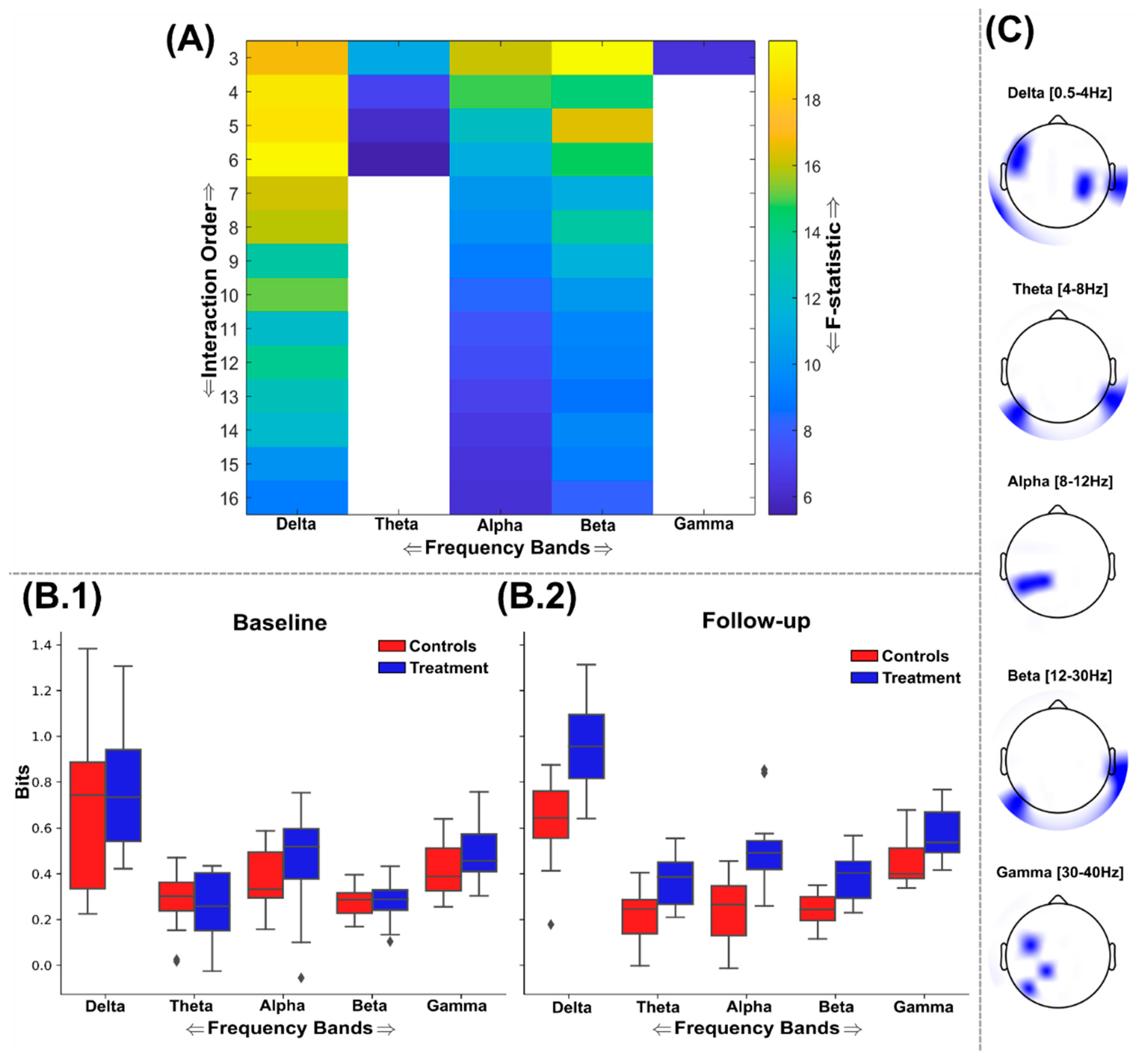
The application of TC and DTC as part of a GSA to the representative stimulus-locked trials of participants identified maximally discriminative brain networks across a range of interaction orders and frequency ranges (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). All the identified brain network interdependencies quantified using TC and DTC were in favour of enhanced information sharing among the treatment group at follow-up compared to controls, controlling for baseline differences. No minimally discriminative (i.e. greater information sharing among the control group) were found for TC or DTC, therefore results in this direction are not illustrated here.
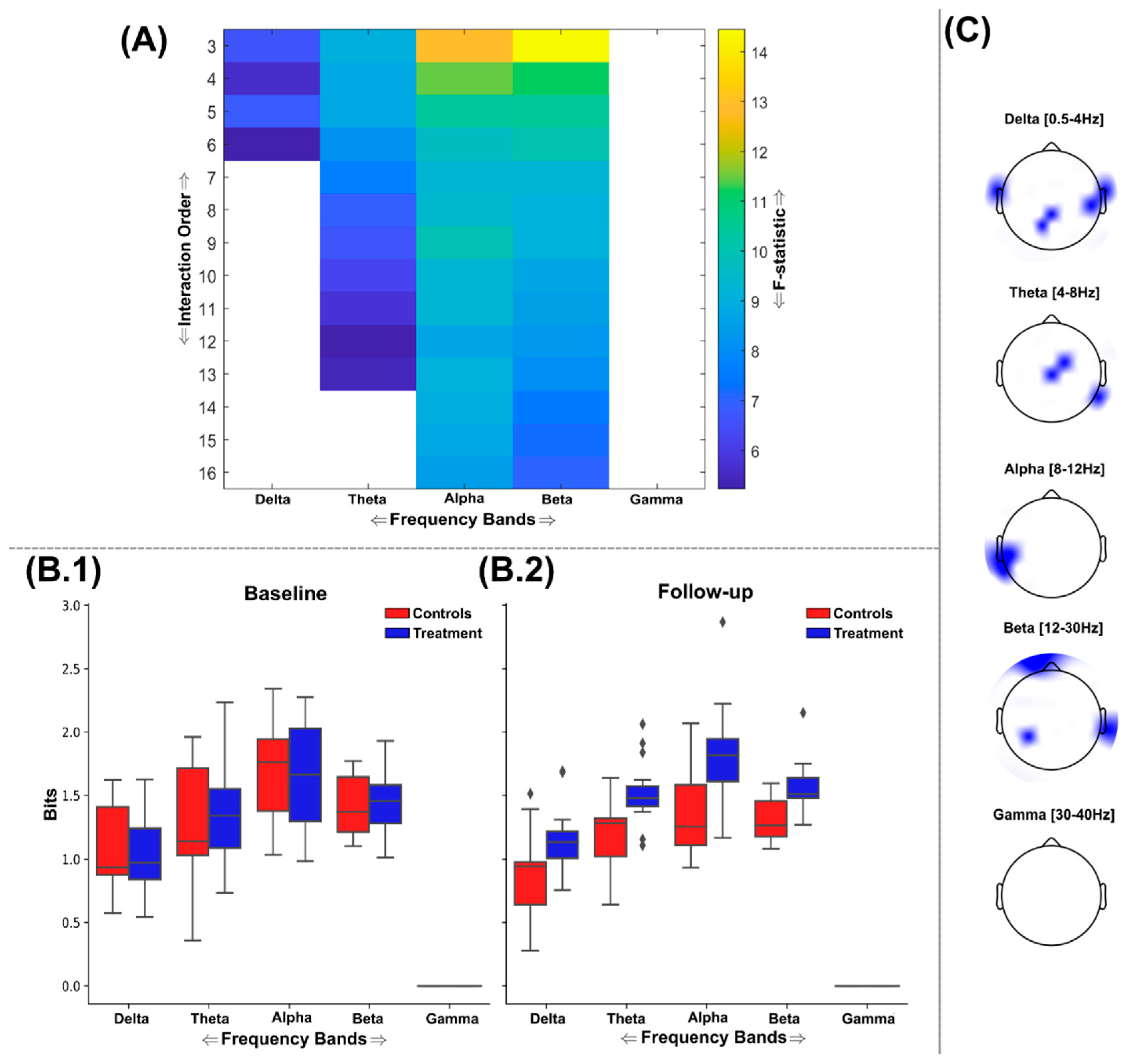
Beginning with the findings from TC (
Figure 3), following FDR correction (critical value for p=0.031) significantly greater network interdependencies were found in all frequency bands except the Gamma band (
Figure 3(A)). Typical TC value ranges within baseline and follow-up sessions for both groups (controls=red, treatment=blue) for all significant frequency bands are illustrated in
Figure 3(B.1-2) respectively. The most discriminative networks from the significant frequency bands were of a relatively low interaction order (see
Figure 3(C) for the scalp topography with the most discriminative brain networks highlighted). The delta band demonstrated significantly enhanced TC among treatment group participants up to 6
th order (
Figure 3(A)), however the 4
th order brain network was most discriminative here (F= 5.61, (p=0.0152)). This brain network consisted of EEG sources covering the left and right frontotemporal and the centroparietal region (
Figure 3(C)). Meanwhile, the theta, alpha and beta bands all demonstrated significantly enhanced information sharing for brain networks up to the 13
th order for theta, and 16
th order for both alpha and beta bands (
Figure 3(A)). However, the most discriminative brain networks for all three frequencies were consistently composed of triplets of EEG sources (Theta: F= 9.1 (p=0.0059), Alpha: F= 12.95 (p=0.0014), Beta: F=14.5 (p<0.001)) (
Figure 3(A)). For the theta band, this triplet consisted of two EEG sources over the central lobe and one on the right temporal lobe (
Figure 3(C)), while the alpha band triplet consisted of EEG sources originating from the left temporal lobe only. Finally for the beta band, which demonstrated the most significant difference between groups at follow-up controlling for baseline differences, the triplet was composed of more widespread EEG sources from the frontal, right temporal and parietal brain regions.
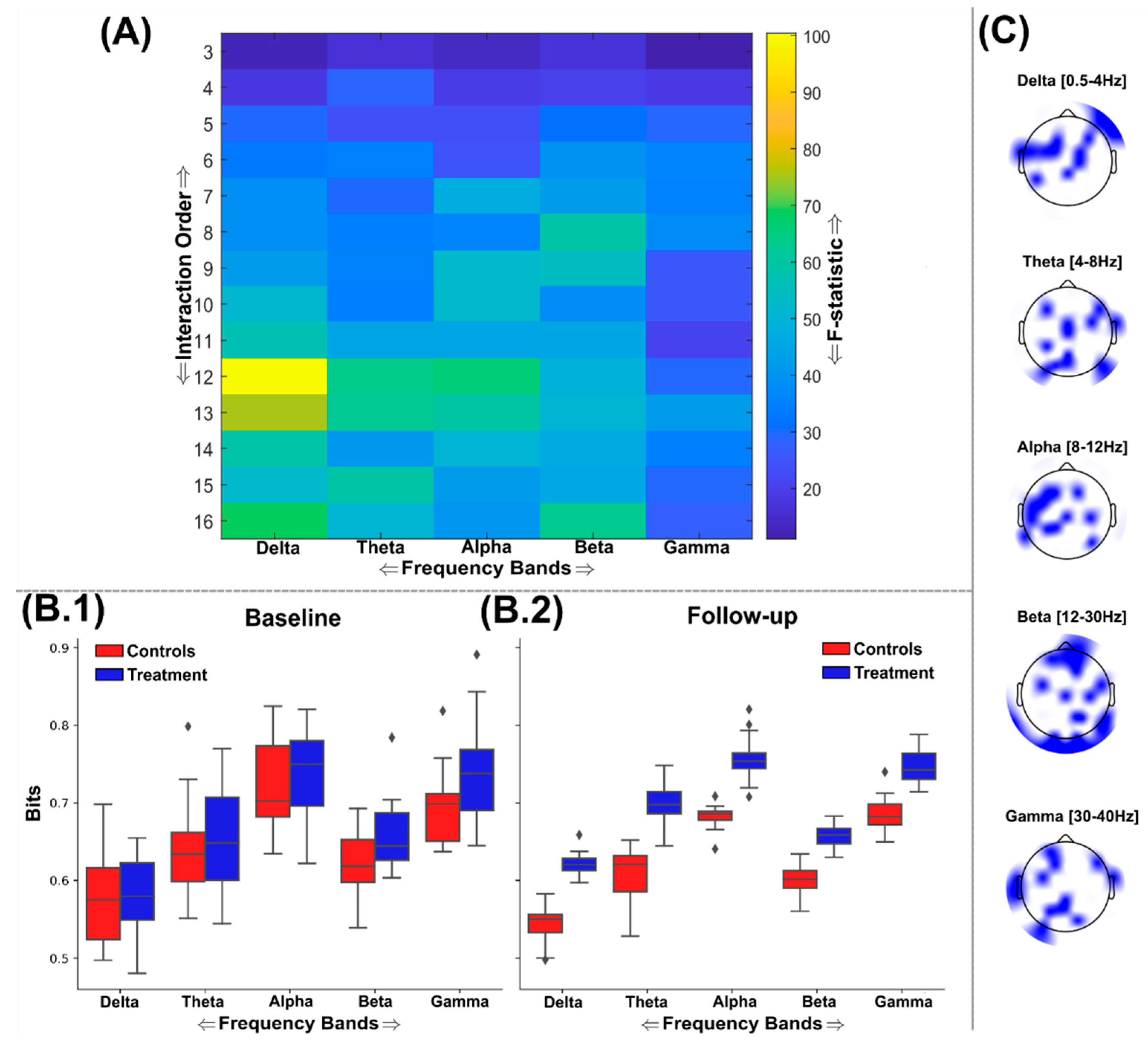
The nootropics effect of information sharing across brain networks was much more widespread and significant when quantified using DTC (
Figure 4(A-C)), suggesting the nootropic enhanced the sharing of complementary information more so than redundant information. All five frequency bands here displayed significantly enhanced information sharing (FDR critical value: p=0.0027), but in contrast to TC (
Figure 3), here these differences steadily increased for the most part as a function of interaction order (
Figure 4(A)). This trend was especially obvious for the beta band, where the highest order network analysed was also the most discriminative (F=63.04 (p<0.00001)) (
Figure 4(A)). Interdependencies between 12 EEG sources within the delta band demonstrated the most significant group differences (F= 100.41 (p<0.00001)), followed by 12
th order network interdependencies within the alpha (F=65.98 (p<0.00001)) and theta (F=63.76 (p<0.00001)) bands. The gamma band was noticeably lower in terms of its group differences, with a 13
th order network of EEG sources demonstrating the highest discrimination in this frequency range (F= 42.4 (p<0.00001)). Based on these results it is likely that significance enhancements to information sharing would be found in higher order brain networks than analysed here. As found in the TC results (
Figure 3(B)), the alpha band provided the greatest amount of shared information across the intervention while the delta band typically provided the least bits of information (the bits of information were normalised by the interaction order for comparability) (
Figure 4(B.1-2)).
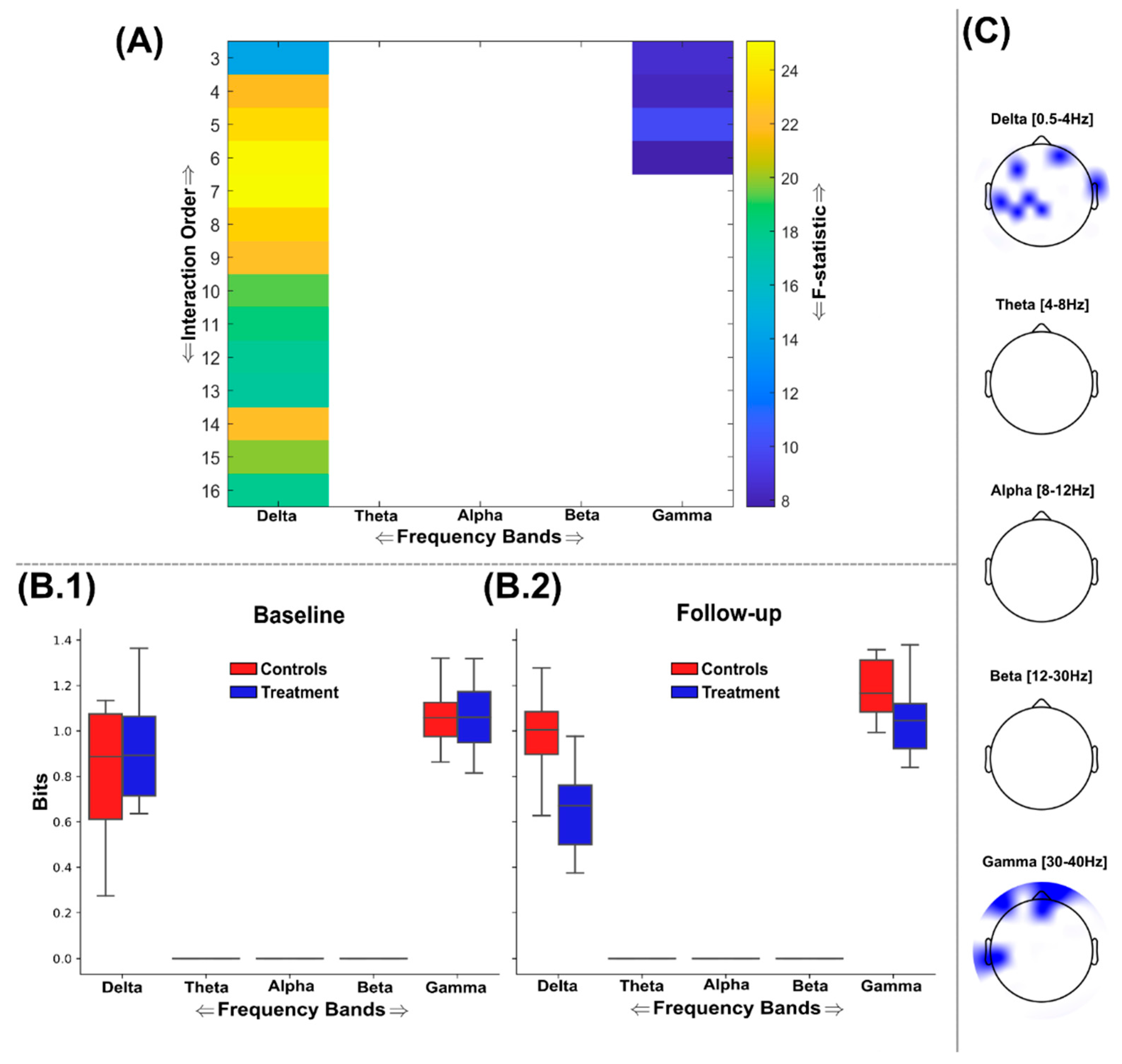
3.3. A Natural Nootropic Supplement Increases Both the Redundancy and Synergy Between Brain Regions.
The balance between redundant (i.e. informationally similar) and synergistic (i.e. informationally complementary) interdependencies in the brain pre- and post- supplementation with a nootropic or placebo was quantified using the O-Information (Ω), revealing salient group differences across multiple interaction orders and frequency bands that all favoured the treatment group in terms of increased redundancy and synergy (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). As with the TC and DTC results (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4), no significant differences were found in favour of greater redundancy or synergy among the control group, hence findings favouring the treatment group only are illustrated here. We found that the discriminative networks of EEG sources identified were redundancy dominated (i.e. positive Ω values) across sessions and groups for both the redundancy (
Figure 5) and synergy (
Figure 6) analyses. Therefore, the boxplots in
Figure 6(B.1-2) of the synergy analysis depict a significant decrease in redundant information (corresponding to an increase in synergistic information) for the treatment group (blue boxes) compared to controls (red boxes) within the delta and gamma frequency bands.
Significantly increased redundancy was found in all frequency bands following FDR correction (Critical value: p=0.0278), where three frequency bands (i.e. delta, alpha and beta) were shown to comprise of significantly different redundancy for network interaction orders up to the maximum analysed here (i.e. 16 channels) (
Figure 5(A)). Meanwhile, the theta and gamma bands demonstrated a much lower prevalence for this nootropic effect, demonstrating significantly greater redundancy up to the 6
th and 3
rd interaction orders respectively (
Figure 5(A)). As found in the TC results (
Figure 3), these differences were most significant at lower interaction orders, suggesting local information processing at specific brain regions was enhanced post-supplementation. Indeed, the delta band was the only frequency range where the most significant network was composed of more than three EEG sources, with the 6
th order being most significant (F=19.6 (p<0.001)). This band also demonstrated the largest amount of redundant information across sessions and groups (displayed in normalized bits (
Figure 5(B.1-2)) and incorporated left frontotemporal and right temporoparietal regions (
Figure 5(C)). The beta band triplet was the most different between groups (F= 19.76 (p<0.001)) and included occipital and right temporal-occipital brain regions (
Figure 5(C)).
The significant reductions in redundancy (increases in synergy) found among the treatment group were frequency band specific, with the predominant effects found in the delta band followed by the gamma band (FDR Critical value: p=0.0101) (
Figure 6(A)). All other frequency bands did not demonstrate any nootropic effects. The delta band demonstrated its most significantly different network interdependencies at the 7
th interaction order (F=25.1 (p<0.0001)), however these significant differences continued in a mostly consistent way up to the maximum 16
th order analysed here (
Figure 6(A)). Indeed, this effect more pronounced than that found of the statistical differences found within the delta band or any other band among the maximally redundant networks (
Figure 5), suggesting an overall effect in the direction of increased synergy for the delta band. This most significantly different brain network in the delta band was composed of EEG sources scattered across frontal, temporal, and parietal brain regions (
Figure 6(C)). Meanwhile for the gamma band, the 5
th order network was most significantly different (F= 9.9 (p=0.0043)) and was more focussed around the frontal and left temporal brain regions (
Figure 6(C)).
4. Discussion
This randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study investigated the effects of a plant-based nootropic supplement on visual perceptual-decision making performance and brain network interdependencies in a healthy adult cohort. Through a visual categorisation task where participants performed consecutive trials of rapid perceptual decision-making based on visual stimuli (i.e. face vs. car images) while EEG signals were concurrently captured, we analysed changes in perceptual decision-making performance (i.e. choice accuracy and reaction times) and the underlying brain network interdependencies following 60 days of nootropic supplementation. Supporting our a priori hypothesis, we found evidence for pronounced neurophysiological changes despite no significant behavioural improvements (i.e. choice accuracy or choice reaction times). Specifically, we found broadband changes in brain network interdependencies of various interaction orders that suggest nootropic supplementation increased the strength of complementary and similar statistical dependencies between brain regions, resulting in an overall enhancement of brain network cohesion and computational capacity. The findings presented here offer a neurocomputational explanation for the increased interest in and positive self-reports of using nootropic supplements in healthy adult cohorts despite the inconclusive behavioural effects found in the literature.
Through the application of multivariate measures of statistical dependency (i.e. TC and DTC) within a greedy-search algorithm (28), we consistently identified significantly greater sharing of both similar and complementary information between EEG sources among the treatment group (see
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). Remarkably, these significantly different brain networks were found across a range of spatial scales (k=3-16 channels) and frequency bands (i.e. Delta-Gamma ranges) and, through the application of the O-Information (31,35), were shown to signify an overall shift towards increased synergy in the brain following nootropic supplementation (see the greater F-statistics in
Figure 4 and
Figure 6(A) compared to
Figure 3 and
Figure 5(A)). Although the brain networks analysed here were strongly redundancy-dominated (see
Figure 6(B.1-2)) and redundancy was shown to increase across several localised EEG sources (
Figure 3 and
Figure 5), the most significant changes from baseline were found in the direction of increased complementarity (
Figure 4) and reductions in redundancy dominance (i.e. increased synergy) (
Figure 6), together suggesting improvements in both local and distributed information processing [
48]. This also suggests that the crucial balance between redundancy and synergy as functionally segregative and integrative forces respectively in dynamical systems like the brain was maintained following nootropic supplementation, thus ensuring adequate robustness (through compensatory increases in redundancy) to support the overall increase in computational capacity gained with increased synergy [
48,
49,
50]. Indeed, the prevalence of synergistic interactions has been closely linked to goal-directed learning [
51], the evolution of human intelligence and different states of consciousness [
52,
53], and contributes to metabolically efficient neural codes [
54,
55]. Hence, the main result of this study is of crucial evidentiary importance towards demonstrating the efficacy of nootropic supplements in supporting brain health in the general adult population.
However, aside from the evidence provided here for nootropic supplements supporting brain health, further work is required to fully understand their efficacy as cognitive performance enhancers. Characteristics of the task employed and limited sample size restrict the conclusions that can be made from this study in this regard. Nonetheless, the sample size of our study is similar to most of the related literature that have frequently demonstrated subtle behavioural effects [
6,
12,
20,
22,
23,
24]. This contrasts with other nootropic compounds renowned for their obvious cognitively stimulating effects (e.g. caffeine) [
23,
56], but which result in withdrawal symptoms not found among the compounds analysed here, likely due to the modulatory effect on cortical energy expenditure with caffeine consumption [
56]. The compounds analysed here perhaps come under a separate class of nootropics with more subtle effects on brain metabolism and function among healthy adults that manifest over longer timescales [
1,
8]. Furthermore, the supplements’ predominant effect on complementary cortical interdependencies in the delta frequency range here (
Figure 6) closely aligns with recent findings demonstrating global increases in synergistic brain interdependencies during meditation in the same neural oscillations [
57]. Hence, our conjecture here is that research on these nootropic compounds as performance enhancers among healthy adults should instead follow a similar vein to studies on meditation and mindfulness practices that consistently found significant effects on complex cognition (e.g. creativity, learning) [
58,
59]. This position is supported by the multimodal, integrative functions of synergy-dominated cortical regions most likely effected by the nootropic here however [
49,
53], due to the broadband prevalence of these effects among redundant brain interdependencies also (
Figure 5), does not limit the potential of these compounds in other domains [
60,
61]. Future research on these compounds in the healthy adult population should therefore examine their effects across greater supplementation durations and in more deliberate cognitive tasks.
Limitations
The conclusions drawn from this study’s behavioural findings are limited by the sample size included, although numbers are in line with other studies. This study suggests that the behavioural effects are subtle in comparison to the neurological effects of the nootropic supplement in healthy adults but does not rule out the subjective significance of any induced changes in cognitive performance, however small. The restricted temporal resolution of the stimulus-locked trials analysed here (i.e. 1.25Hz) resulted in the whole period of lower delta band frequencies not being fully represented. Nevertheless, removal of this lower delta range (0.5-1.25Hz) in preliminary analyses resulted in the correlation strength of many network interdependencies illustrated here being lost. Hence, we suggest that the partial coverage of these lower frequency ranges given in this analysis provided crucial insight into the nootropic’s effects, as evidenced by the statistically significant effects persistently shown (see
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). Future work with longer naturalistic stimulations will most likely demonstrate even more prominent nootropic effects within this delta frequency range.
Author Contributions
DOR: Participant recruitment, experimental design, data capture, processing and analysis, manuscript writing and editing. JB: Experimental design and setup, manuscript editing. ID: Supervision, resources, and manuscript editing. AU: Supervision, participant recruitment, manuscript editing.
Data Availability Statement
The data generated from this study is available upon reasonable request. Higher-order brain network dependencies and the greedy-search algorithm were quantified using custom Matlab scripts (
https://github.com/rubenherzog/high-order-fc-ml).
Conflicts of Interest
This study was independently funded by Performance Lab Group® who had no access to or influence on the presented data.
References
- Malík M, Tlustoš P. Nootropics as cognitive enhancers: types, dosage and side effects of smart drugs. Nutrients. 2022 Aug 17;14(16):3367.
- Sharif S, Guirguis A, Fergus S, Schifano F. The use and impact of cognitive enhancers among university students: a systematic review. Brain sciences. 2021 Mar 10;11(3):355.
- Cavaco AM, Ribeiro J, Nørgaard LS. Exploring the use of cognitive enhancement substances among Portuguese university students. Exploratory Research in Clinical and Social Pharmacy. 2022 Mar 1;5:100097.
- Schifano F, Catalani V, Sharif S, Napoletano F, Corkery JM, Arillotta D, Fergus S, Vento A, Guirguis A. Benefits and harms of ‘smart drugs’(nootropics) in healthy individuals. Drugs. 2022 Apr;82(6):633-47.
- Zaami S, Rinaldi R, Bersani G, Del Rio A, Ciallella C, Marinelli E. Nootropics use in the workplace. Psychiatric and ethical aftermath towards the new frontier of bioengineering. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences. 2020;24(4):2129-39.
- Roe AL, Venkataraman A. The safety and efficacy of botanicals with nootropic effects. Current neuropharmacology. 2021 Sep 9;19(9):1442.
- Chiroma SM, Taib CN, Moklas MA, Baharuldin MT, Amom Z, Jagadeesan S. The use of nootropics in Alzheimer’s disease: is there light at the end of the tunnel?. Biomedical Research and Therapy. 2019 Jan 4;6(1):2937-44.
- Lorca C, Mulet M, Arévalo-Caro C, Sanchez MÁ, Perez A, Perrino M, Bach-Faig A, Aguilar-Martínez A, Vilella E, Gallart-Palau X, Serra A. Plant-derived nootropics and human cognition: A systematic review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2023 Aug 29;63(22):5521-45.
- Brandalise F, Roda E, Ratto D, Goppa L, Gargano ML, Cirlincione F, Priori EC, Venuti MT, Pastorelli E, Savino E, Rossi P. Hericium erinaceus in neurodegenerative diseases: From bench to bedside and beyond, how far from the shoreline?. Journal of Fungi. 2023 May 10;9(5):551.
- Murphy KJ, Foley AG, O'connell AW, Regan CM. Chronic exposure of rats to cognition enhancing drugs produces a neuroplastic response identical to that obtained by complex environment rearing. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Jan;31(1):90-100.
- Vorobyov V, Kaptsov V, Kovalev G, Sengpiel F. Effects of nootropics on the EEG in conscious rats and their modification by glutamatergic inhibitors. Brain Research Bulletin. 2011 May 30;85(3-4):123-32.
- Malík M, Tlustoš P. Nootropic herbs, shrubs, and trees as potential cognitive enhancers. Plants. 2023 Mar 18;12(6):1364.
- Das T, Saha SC, Sunita K, Majumder M, Ghorai M, Mane AB, Prasanth DA, Kumar P, Pandey DK, Al-Tawaha AR, Batiha GE. Promising botanical-derived monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors: Pharmacological aspects and structure-activity studies. South African Journal of Botany. 2022 May 1;146:127-45.
- Suliman NA, Mat Taib CN, Mohd Moklas MA, Adenan MI, Hidayat Baharuldin MT, Basir R. Establishing natural nootropics: recent molecular enhancement influenced by natural nootropic. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2016;2016(1):4391375.
- Drachman DA. Aging of the brain, entropy, and Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2006 Oct 24;67(8):1340-52.
- Aanerud J, Borghammer P, Chakravarty MM, Vang K, Rodell AB, Jonsdottir KY, Møller A, Ashkanian M, Vafaee MS, Iversen P, Johannsen P. Brain energy metabolism and blood flow differences in healthy aging. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism. 2012 Jul;32(7):1177-87.
- Ryu WI, Bormann MK, Shen M, Kim D, Forester B, Park Y, So J, Seo H, Sonntag KC, Cohen BM. Brain cells derived from Alzheimer’s disease patients have multiple specific innate abnormalities in energy metabolism. Molecular Psychiatry. 2021 Oct;26(10):5702-14.
- Solomon TM, Leech J, deBros GB, Murphy CA, Budson AE, Vassey EA, Solomon PR. A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, parallel group, efficacy study of alpha BRAIN® administered orally. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental. 2016 Mar;31(2):135-43.
- Rootman JM, Kiraga M, Kryskow P, Harvey K, Stamets P, Santos-Brault E, Kuypers KP, Walsh Z. Psilocybin microdosers demonstrate greater observed improvements in mood and mental health at one month relative to non-microdosing controls. Scientific Reports. 2022 Jun 30;12(1):11091.
- Canter PH, Ernst E. Ginkgo biloba is not a smart drug: an updated systematic review of randomised clinical trials testing the nootropic effects of G. biloba extracts in healthy people. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental. 2007 Jul;22(5):265-78.
- Pomeroy DE, Tooley KL, Probert B, Wilson A, Kemps E. A systematic review of the effect of dietary supplements on cognitive performance in healthy young adults and military personnel. Nutrients. 2020 Feb 20;12(2):545.
- Laws KR, Sweetnam H, Kondel TK. Is Ginkgo biloba a cognitive enhancer in healthy individuals? A meta-analysis. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental. 2012 Nov;27(6):527-33.
- Jarvis MJ. Does caffeine intake enhance absolute levels of cognitive performance?. Psychopharmacology. 1993 Jan;110:45-52.
- Abbott-Imboden C, Gonzalez Y, Utley A. Efficacy of the nootropic supplement Mind Lab Pro on memory in adults: Double blind, placebo-controlled study. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental. 2023 Jul;38(4):e2872.
- Stancheva SL, Petkov VD, Hadjiivanova CI, Petkov VV. Age-related changes of the effects of a group of nootropic drugs on the content of rat brain biogenic monoamines. General pharmacology. 1991 Jan 1;22(5):873-7.
- Sengupta B, Stemmler MB, Friston KJ. Information and efficiency in the nervous system—a synthesis. PLoS computational biology. 2013 Jul 25;9(7):e1003157.
- Zenon A, Solopchuk O, Pezzulo G. An information-theoretic perspective on the costs of cognition. Neuropsychologia. 2019 Feb 4;123:5-18.
- Philiastides MG, Sajda P. Temporal characterization of the neural correlates of perceptual decision making in the human brain. Cerebral cortex. 2006 Apr 1;16(4):509-18.
- Bolam J, Diaz JA, Andrews M, Coats RO, Philiastides MG, Astill SL, Delis I. A drift diffusion model analysis of age-related impact on multisensory decision-making processes. Scientific Reports. 2024 Jun 28;14(1):14895.
- Franzen L, Delis I, De Sousa G, Kayser C, Philiastides MG. Auditory information enhances post-sensory visual evidence during rapid multisensory decision-making. Nature communications. 2020 Oct 28;11(1):5440.
- Delis I, Onken A, Schyns PG, Panzeri S, Philiastides MG. Space-by-time decomposition for single-trial decoding of M/EEG activity. Neuroimage. 2016 Jun 1;133:504-15.
- Delorme A, Makeig S. EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. Journal of neuroscience methods. 2004 Mar 15;134(1):9-21.
- Oostenveld R, Fries P, Maris E, Schoffelen JM. FieldTrip: open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Computational intelligence and neuroscience. 2011;2011(1):156869.
- Leske S, Dalal SS. Reducing power line noise in EEG and MEG data via spectrum interpolation. Neuroimage. 2019 Apr 1;189:763-76.
- Perrin F, Pernier J, Bertrand O, Echallier JF. Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology. 1989 Feb 1;72(2):184-7.
- Wilming N, Murphy PR, Meyniel F, Donner TH. Large-scale dynamics of perceptual decision information across human cortex. Nature communications. 2020 Oct 9;11(1):5109.
- Nottage JF, Horder J. State-of-the-art analysis of high-frequency (gamma range) electroencephalography in humans. Neuropsychobiology. 2016 Feb 1;72(3-4):219-28.
- Herzog R, Rosas FE, Whelan R, Fittipaldi S, Santamaria-Garcia H, Cruzat J, Birba A, Moguilner S, Tagliazucchi E, Prado P, Ibanez A. Genuine high-order interactions in brain networks and neurodegeneration. Neurobiology of Disease. 2022 Dec 1;175:105918.
- Watanabe S. Information theoretical analysis of multivariate correlation. IBM Journal of research and development. 1960 Jan;4(1):66-82.
- Te Sun H. Nonnegative entropy measures of multivariate symmetric correlations. Information and Control. 1978;36:133-56.
- Rosas FE, Mediano PA, Gastpar M, Jensen HJ. Quantifying high-order interdependencies via multivariate extensions of the mutual information. Physical Review E. 2019 Sep;100(3):032305.
- Abdallah SA, Plumbley MD. A measure of statistical complexity based on predictive information. arXiv preprint arXiv:1012.1890. 2010 Dec 8.
- Ince RA, Giordano BL, Kayser C, Rousselet GA, Gross J, Schyns PG. A statistical framework for neuroimaging data analysis based on mutual information estimated via a gaussian copula. Human brain mapping. 2017 Mar;38(3):1541-73.
- Sawilowsky SS. New effect size rules of thumb. Journal of modern applied statistical methods. 2009 Nov 1;8:597-9.
- Gatica M, Cofré R, Mediano PA, Rosas FE, Orio P, Diez I, Swinnen SP, Cortes JM. High-order interdependencies in the aging brain. Brain connectivity. 2021 Nov 1;11(9):734-44.
- Whelan R. Effective analysis of reaction time data. The psychological record. 2008 Jul;58:475-82.
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal statistical society: series B (Methodological). 1995 Jan;57(1):289-300.
- Proca AM, Rosas FE, Luppi AI, Bor D, Crosby M, Mediano PA. Synergistic information supports modality integration and flexible learning in neural networks solving multiple tasks. PLOS Computational Biology. 2024 Jun 3;20(6):e1012178.
- Luppi AI, Rosas FE, Mediano PA, Menon DK, Stamatakis EA. Information decomposition and the informational architecture of the brain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2024 Jan 9.
- Cohen JR, D'Esposito M. The segregation and integration of distinct brain networks and their relationship to cognition. Journal of Neuroscience. 2016 Nov 30;36(48):12083-94.
- Combrisson E, Basanisi R, Neri M, Auzias G, Petri G, Marinazzo D, Panzeri S, Brovelli A. Higher-order and distributed synergistic functional interactions encode information gain in goal-directed learning. bioRxiv. 2024:2024-09.
- Luppi AI, Mediano PA, Rosas FE, Holland N, Fryer TD, O’Brien JT, Rowe JB, Menon DK, Bor D, Stamatakis EA. A synergistic core for human brain evolution and cognition. Nature Neuroscience. 2022 Jun;25(6):771-82.
- Luppi AI, Mediano PA, Rosas FE, Allanson J, Pickard J, Carhart-Harris RL, Williams GB, Craig MM, Finoia P, Owen AM, Naci L. A synergistic workspace for human consciousness revealed by integrated information decomposition. Elife. 2024 Jul 18;12:RP88173.
- Nigam S, Pojoga S, Dragoi V. Synergistic coding of visual information in columnar networks. Neuron. 2019 Oct 23;104(2):402-11.
- Brenner N, Strong SP, Koberle R, Bialek W, Steveninck RR. Synergy in a neural code. Neural computation. 2000 Jul 1;12(7):1531-52.
- Lorist MM, Tops M. Caffeine, fatigue, and cognition. Brain and cognition. 2003 Oct 1;53(1):82-94.
- Kumar P, Panda R, Sharma K, Adarsh A, Annen J, Martial C, Faymonville ME, Laureys S, Sombrun C, Ganesan RA, Vanhaudenhuyse A. Changes in high-order interaction measures of synergy and redundancy during non-ordinary states of consciousness induced by meditation, hypnosis, and auto-induced cognitive trance. NeuroImage. 2024 Jun 1;293:120623.
- Ding X, Tang YY, Tang R, Posner MI. Improving creativity performance by short-term meditation. Behavioral and Brain Functions. 2014 Dec;10:1-8.
- Moore A, Malinowski P. Meditation, mindfulness and cognitive flexibility. Consciousness and cognition. 2009 Mar 1;18(1):176-86.
- Harmony T. The functional significance of delta oscillations in cognitive processing. Frontiers in integrative neuroscience. 2013 Dec 5;7:83.
- Popov T, Steffen A, Weisz N, Miller GA, Rockstroh B. Cross-frequency dynamics of neuromagnetic oscillatory activity: two mechanisms of emotion regulation. Psychophysiology. 2012 Dec;49(12):1545-57.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).