Submitted:
30 October 2024
Posted:
31 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
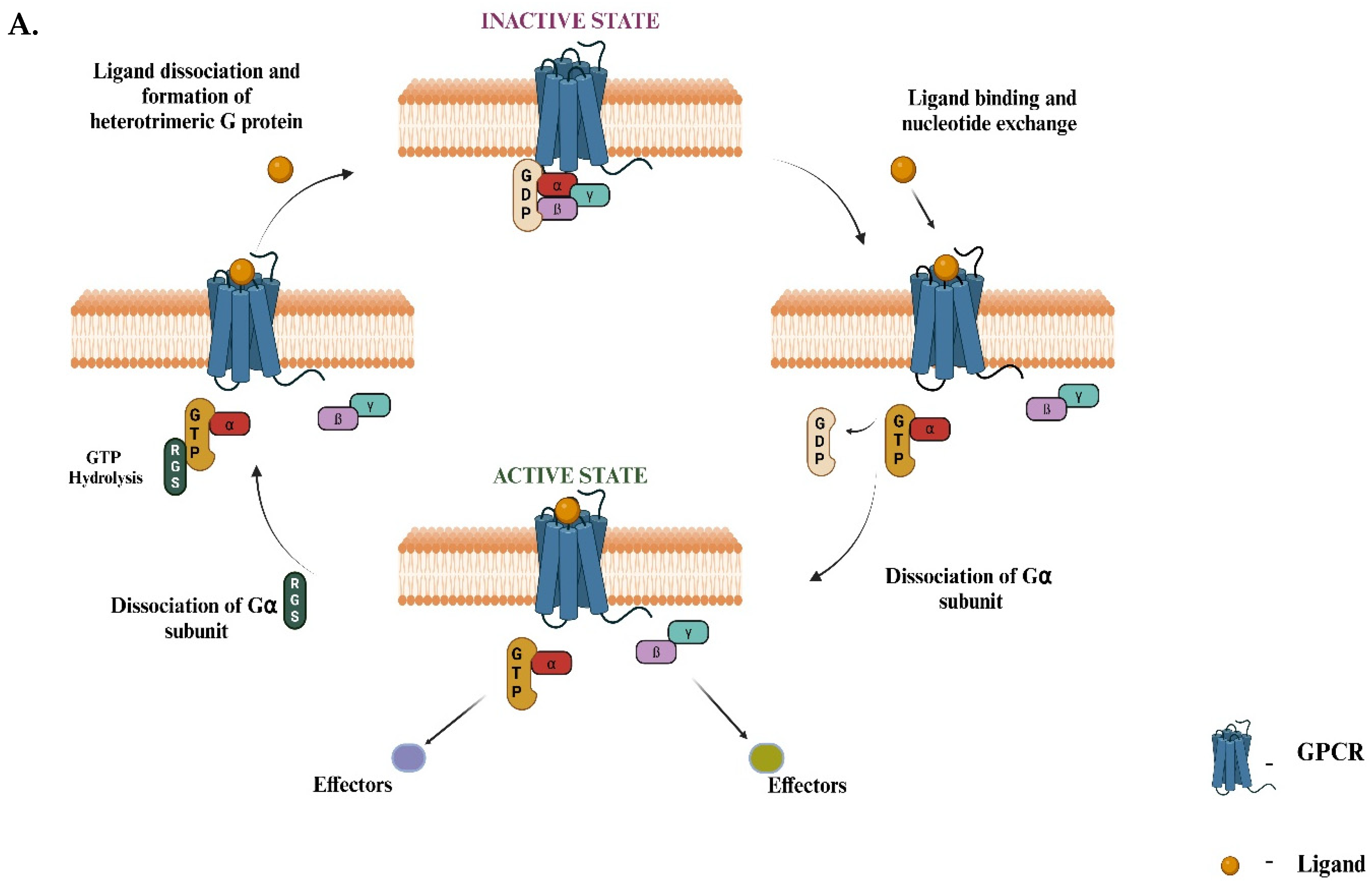
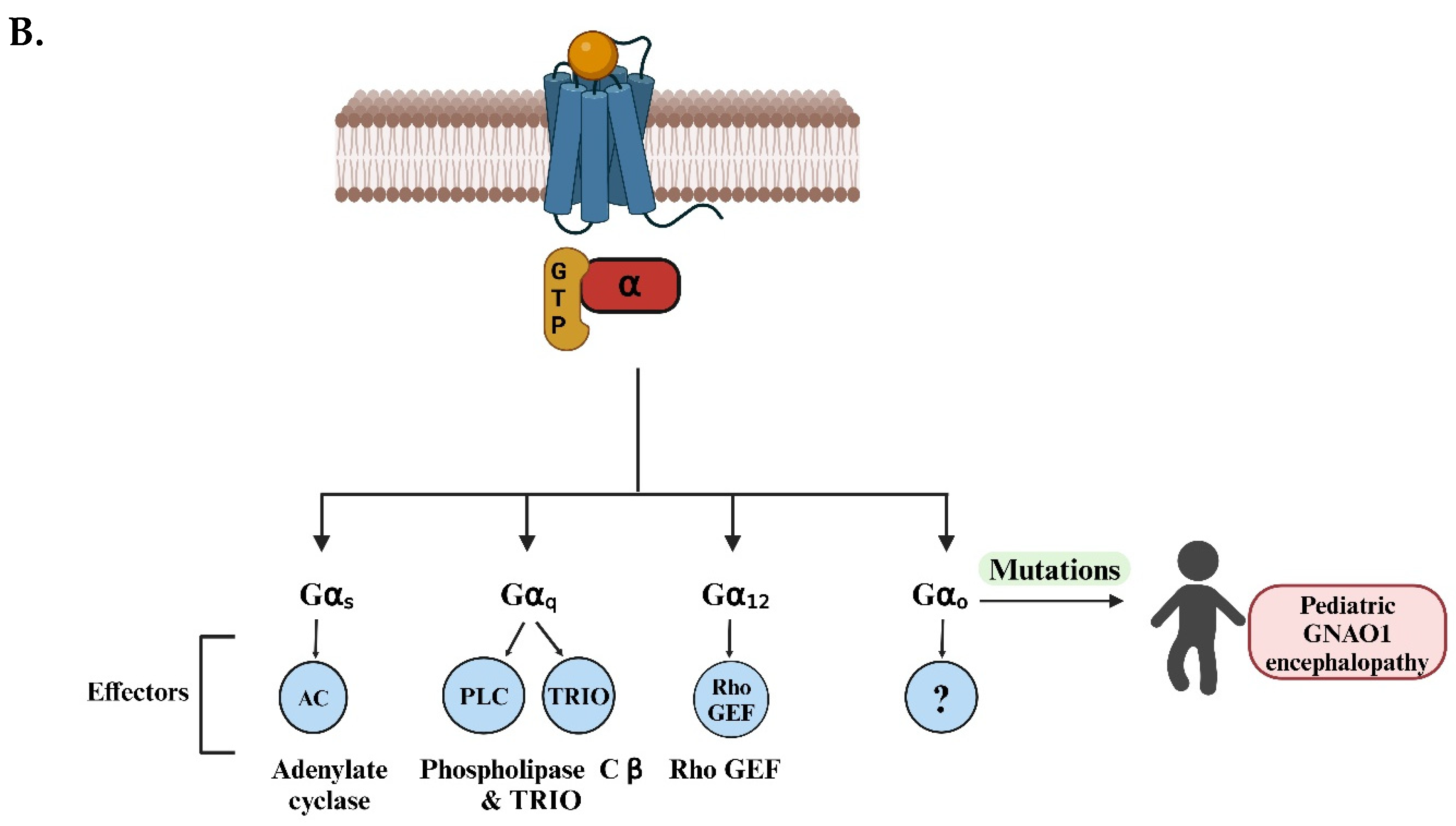
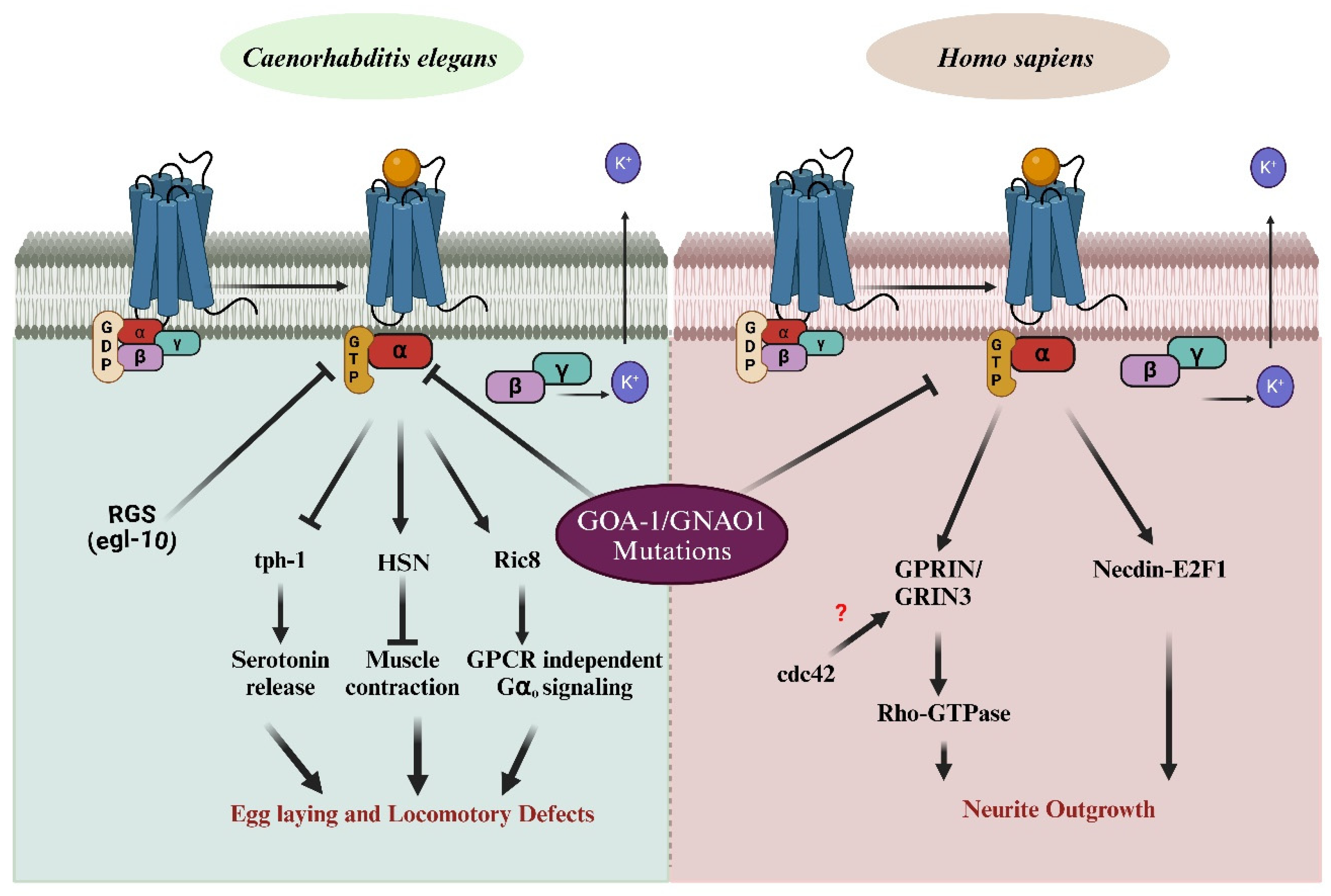
1. Gαo Signaling Pathway Is Associated with GNAO1 Encephalopathy
2. Current Status of GNAO1 Encephalopathy
2.1. GNAO1 Encephalopathy: Current Treatments and Clinical Insights
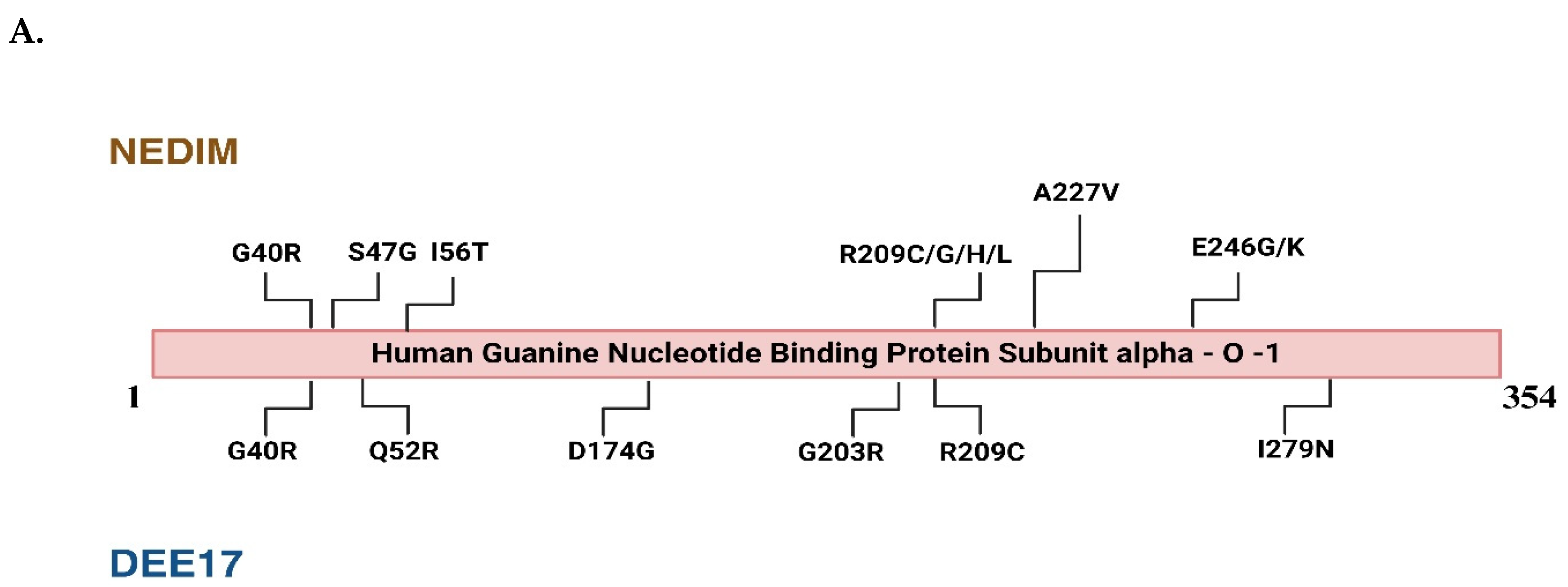
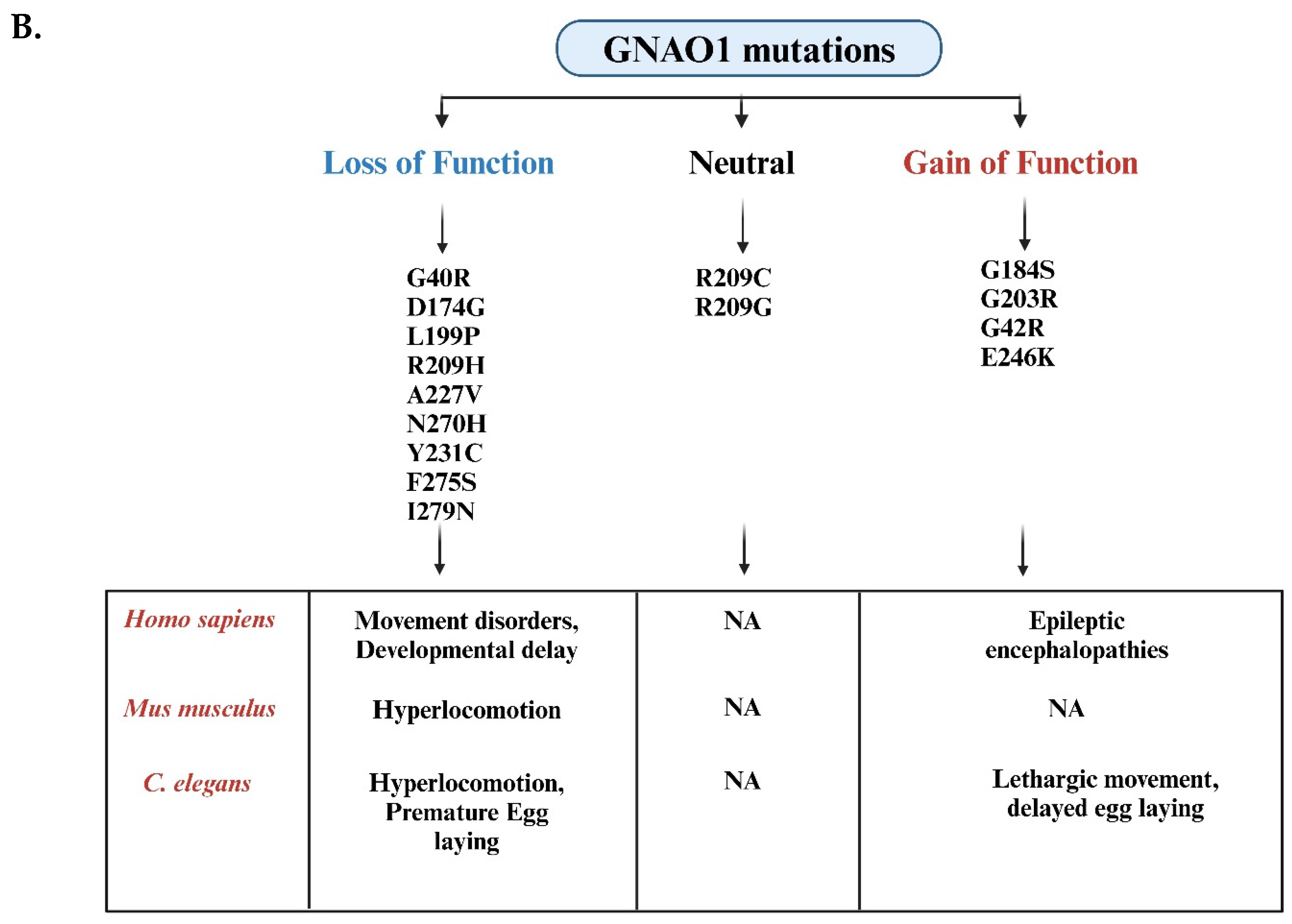
2.2. GNAO1 Encephalopathy: Mutation Analysis and Phenotypic Defects
3. C. elegans as an Advanced Model System to Study GNAO1 Mutations
4. Conclusion and Perspective
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- ADCY5—Adenylyl cyclase type 5
- CRISPR—Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats
- DAG—Diacylglycerol
- DBS—Deep brain stimulation
- DEE-17—Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy-17
- EEG—Electroencephalography
- GABA—Gamma-aminobutyric acid
- GDP- Guanosine diphosphate
- GNAO1—G-protein subunit alpha-O-1
- GPCR—G-protein-coupled receptor
- GTP- Guanosine triphosphate
- HSN—Hermaphrodite-specific motor neuron
- MRI—Magnetic resonance imaging
- NEDIM—Neurodevelopmental disorder with involuntary movements
- PKC—Protein kinase C
- RGS—Regulator of G-protein signaling
- RNAi—RNA interference
References
- Zhang M, Chen T, Lu X, Lan X, Chen Z, Lu S. G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): advances in structures, mechanisms, and drug discovery. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 10;9(1):88. [CrossRef]
- Clapham DE, Neer EJ. G protein beta gamma subunits. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1997; 37:167-203. [CrossRef]
- Villaseca S, Romero G, Ruiz MJ, Pérez C, Leal JI, Tovar LM, Torrejón M. Gαi protein subunit: A step toward understanding its non-canonical mechanisms. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 24; 10:941870. [CrossRef]
- Wickman K, Clapham DE. Ion channel regulation by G proteins. Physiol Rev. 1995 Oct;75(4):865-85. [CrossRef]
- Jiang M, Bajpayee NS. Molecular mechanisms of Go signaling. Neurosignals. 2009;17(1):23-41. [CrossRef]
- Hepler JR, Gilman AG. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383-7. [CrossRef]
- Wettschureck N, Offermanns S. Mammalian G proteins and their cell type-specific functions. Physiol Rev. 2005 Oct;85(4):1159-204. [CrossRef]
- Ju H, Lee S, Kang S, Kim SS, Ghil S. The alpha subunit of Go modulates cell proliferation and differentiation through interactions with Necdin. Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Jul 10; 12:39. [CrossRef]
- Mendel JE, Korswagen HC, Liu KS, Hajdu-Cronin YM, Simon MI, Plasterk RH, Sternberg PW. Participation of the protein Go in multiple aspects of behavior in C. elegans. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1652-5. [CrossRef]
- Ségalat L, Elkes DA, Kaplan JM. Modulation of serotonin-controlled behaviors by Go in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1648-51. [CrossRef]
- Miller KG, Alfonso A, Nguyen M, Crowell JA, Johnson CD, Rand JB. A genetic selection for Caenorhabditis elegans synaptic transmission mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Oct 29;93(22):12593-8. [CrossRef]
- Collins KM, Koelle MR. Postsynaptic ERG potassium channels limit muscle excitability to allow distinct egg-laying behavior states in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 9;33(2):761-75. [CrossRef]
- Cuppen E, van der Linden AM, Jansen G, Plasterk RH. Proteins interacting with Caenorhabditis elegans Galpha subunits. Comp Funct Genomics. 2003;4(5):479-91. [CrossRef]
- Koelle MR. Neurotransmitter signaling through heterotrimeric G proteins: insights from studies in C. elegans. WormBook. 2018 Dec 11;2018:1-52. [CrossRef]
- Wang D, Dao M, Muntean BS, Giles AC, Martemyanov KA, Grill B. Genetic modeling of GNAO1 disorder delineates mechanisms of Gαo dysfunction. Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Feb 21;31(4):510-522. [CrossRef]
- Briere L, Thiel M, Sweetser DA, Koy A, Axeen E. GNAO1-Related Disorder. 2023 Nov 9. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2024. PMID: 37956232. DOI is not available. Available from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37956232/.
- Nakamura K, Kodera H, Akita T, Shiina M, Kato M, Hoshino H, Terashima H, Osaka H, Nakamura S, Tohyama J, Kumada T, Furukawa T, Iwata S, Shiihara T, Kubota M, Miyatake S, Koshimizu E, Nishiyama K, Nakashima M, Tsurusaki Y, Miyake N, Hayasaka K, Ogata K, Fukuda A, Matsumoto N, Saitsu H. De Novo mutations in GNAO1, encoding a Gαo subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins, cause epileptic encephalopathy. Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Sep 5;93(3):496-505. [CrossRef]
- Collins KM, Bode A, Fernandez RW, Tanis JE, Brewer JC, Creamer MS, Koelle MR. Activity of the C. elegans egg-laying behavior circuit is controlled by competing activation and feedback inhibition. Elife. 2016 Nov 16;5:e21126. [CrossRef]
- Sáez González, M., Kloosterhuis, K., van de Pol, L., Baas, F., & Mikkers, H. (2023). Phenotypic Diversity in GNAO1 Patients: A Comprehensive Overview of Variants and Phenotypes. Human mutation, 2023, Article 6628283. [CrossRef]
- Ling W, Huang D, Yang F, Yang Z, Liu M, Zhu Q, Huang J, Zhou R, Chen X. Treating GNAO1 mutation-related severe movement disorders with oxcarbazepine: a case report. Transl Pediatr. 2022 Sep;11(9):1577-1587. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Zhang Q, Wang J, Liu J, Yang W, Yan X, Ouyang Y, Yang H. Both subthalamic and pallidal deep brain stimulation are effective for GNAO1-associated dystonia: three case reports and a literature review. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2022 Apr 29; 15:17562864221093507. [CrossRef]
- Ananth AL, Robichaux-Viehoever A, Kim YM, Hanson-Kahn A, Cox R, Enns GM, Strober J, Willing M, Schlaggar BL, Wu YW, Bernstein JA. Clinical Course of Six Children With GNAO1 Mutations Causing a Severe and Distinctive Movement Disorder. Pediatr Neurol. 2016 Jun; 59:81-4. [CrossRef]
- Danti FR, Galosi S, Romani M, Montomoli M, Carss KJ, Raymond FL, Parrini E, Bianchini C, McShane T, Dale RC, Mohammad SS, Shah U, Mahant N, Ng J, McTague A, Samanta R, Vadlamani G, Valente EM, Leuzzi V, Kurian MA, Guerrini R. GNAO1 encephalopathy: Broadening the phenotype and evaluating treatment and outcome. Neurol Genet. 2017 Mar 21;3(2):e143. [CrossRef]
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998 Feb 19;391(6669):806-11. [CrossRef]
- Caplen NJ. RNAi as a gene therapy approach. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2003 Jul;3(4):575-86. [CrossRef]
- Davis ME, Zuckerman JE, Choi CH, Seligson D, Tolcher A, Alabi CA, Yen Y, Heidel JD, Ribas A. Evidence of RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted nanoparticles. Nature. 2010 Apr 15;464(7291):1067-70. [CrossRef]
- Lunev EA, Shmidt AA, Vassilieva SG, Savchenko IM, Loginov VA, Marina VI, Egorova TV, Bardina MV. [Effective Viral Delivery of Genetic Constructs to Neuronal Culture for Modeling and Gene Therapy of GNAO1 Encephalopathy]. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2022 Jul-Aug;56(4):604-618. Russian. [CrossRef]
- Klementieva NV, Lunev EA, Shmidt AA, Loseva EM, Savchenko IM, Svetlova EA, Galkin II, Polikarpova AV, Usachev EV, Vassilieva SG, Marina VI, Dzhenkova MA, Romanova AD, Agutin AV, Timakova AA, Reshetov DA, Egorova TV, Bardina MV. RNA Interference Effectors Selectively Silence the Pathogenic Variant GNAO1 c.607 G > A In Vitro. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2024 Apr;34(2):90-99. [CrossRef]
- Koval A, Larasati YA, Savitsky M, Solis GP, Good JM, Quinodoz M, Rivolta C, Superti-Furga A, Katanaev VL. In-depth molecular profiling of an intronic GNAO1 mutant as the basis for personalized high-throughput drug screening. Med. 2023 May 12;4(5):311-325.e7. [CrossRef]
- Silachev D, Koval A, Savitsky M, Padmasola G, Quairiaux C, Thorel F, Katanaev VL. Mouse models characterize GNAO1 encephalopathy as a neurodevelopmental disorder leading to motor anomalies: from a severe G203R to a milder C215Y mutation. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Jan 28;10(1):9. [CrossRef]
- Locke CJ, Williams SN, Schwarz EM, Caldwell GA, Caldwell KA. Genetic interactions among cortical malformation genes that influence susceptibility to convulsions in C. elegans. Brain Res. 2006 Nov 20;1120(1):23-34. [CrossRef]
- Dexter PM, Caldwell KA, Caldwell GA. A predictable worm: application of Caenorhabditis elegans for mechanistic investigation of movement disorders. Neurotherapeutics. 2012 Apr;9(2):393-404. [CrossRef]
- Lee TY, Yoon KH, Lee JI. NGT-3D: a simple nematode cultivation system to study Caenorhabditis elegans biology in 3D. Biol Open. 2016 Apr 15;5(4):529-34. [CrossRef]
- Opperman KJ, Mulcahy B, Giles AC, Risley MG, Birnbaum RL, Tulgren ED, Dawson-Scully K, Zhen M, Grill B. The HECT Family Ubiquitin Ligase EEL-1 Regulates Neuronal Function and Development. Cell Rep. 2017 Apr 25;19(4):822-835. [CrossRef]
- Polikarpova AV, Egorova TV, Lunev EA, Tsitrina AA, Vassilieva SG, Savchenko IM, Silaeva YY, Deykin AV, Bardina MV. CRISPR/Cas9-generated mouse model with humanizing single-base substitution in the Gnao1 for safety studies of RNA therapeutics. Front Genome Ed. 2023 Apr 3; 5:1034720. [CrossRef]
- Savitsky M, Solis GP, Kryuchkov M, Katanaev VL. Humanization of Drosophila Gαo to Model GNAO1 Paediatric Encephalopathies. Biomedicines. 2020 Oct 6;8(10):395. [CrossRef]
- Di Rocco M, Galosi S, Lanza E, Tosato F, Caprini D, Folli V, Friedman J, Bocchinfuso G, Martire A, Di Schiavi E, Leuzzi V, Martinelli S. Caenorhabditis elegans provides an efficient drug screening platform for GNAO1-related disorders and highlights the potential role of caffeine in controlling dyskinesia. Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Mar 21;31(6):929-941. [CrossRef]
- Ravi B, Zhao J, Chaudhry SI, Signorelli R, Bartole M, Kopchock RJ, Guijarro C, Kaplan JM, Kang L, Collins KM. Presynaptic Gαo (GOA-1) signals to depress command neuron excitability and allow stretch-dependent modulation of egg laying in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 2021 Aug 9;218(4):iyab080. [CrossRef]
- Muntean BS, Masuho I, Dao M, Sutton LP, Zucca S, Iwamoto H, Patil DN, Wang D, Birnbaumer L, Blakely RD, Grill B, Martemyanov KA. Gαo is a major determinant of cAMP signaling in the pathophysiology of movement disorders. Cell Rep. 2021 Feb 2;34(5):108718. [CrossRef]
- Baik JH, Picetti R, Saiardi A, Thiriet G, Dierich A, Depaulis A, Le Meur M, Borrelli E. Parkinsonian-like locomotor impairment in mice lacking dopamine D2 receptors. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):424-8. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H., Wu, XR., Wewer, U. et al. Murine muscular dystrophy caused by a mutation in the laminin α2 (Lama2) gene. Nat Genet 8, 297–302 (1994). [CrossRef]
- Chase DL, Pepper JS, Koelle MR. Mechanism of extrasynaptic dopamine signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Neurosci. 2004 Oct;7(10):1096-103. [CrossRef]
- Allen NE, Sherrington C, Paul SS, Canning CG. Balance and falls in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of the effect of exercise and motor training. Mov Disord. 2011 Aug 1;26(9):1605-15. [CrossRef]
- Ségalat L, Elkes DA, Kaplan JM. Modulation of serotonin-controlled behaviors by Go in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1995 Mar 17;267(5204):1648-51. [CrossRef]
- Jiang M, Bajpayee NS. Molecular mechanisms of go signaling. Neurosignals. 2009;17(1):23-41. [CrossRef]
- Meijer, I. A., Miravite, J., Kopell, B. H., & Lubarr, N. (2017). Deep Brain Stimulation in an Additional Patient with ADCY5 -Related Movement Disorder. Journal of Child Neurology, 32(4), 438-439. [CrossRef]
- Mencacci NE, Erro R, Wiethoff S, Hersheson J, Ryten M, Balint B, Ganos C, Stamelou M, Quinn N, Houlden H, Wood NW, Bhatia KP. ADCY5 mutations are another cause of benign hereditary chorea. Neurology. 2015 Jul 7;85(1):80-8. [CrossRef]
- Kelly M, Park M, Mihalek I, Rochtus A, Gramm M, Pérez-Palma E, Axeen ET, Hung CY, Olson H, Swanson L, Anselm I, Briere LC, High FA, Sweetser DA; Undiagnosed Diseases Network; Kayani S, Snyder M, Calvert S, Scheffer IE, Yang E, Waugh JL, Lal D, Bodamer O, Poduri A. Spectrum of neurodevelopmental disease associated with the GNAO1 guanosine triphosphate-binding region. Epilepsia. 2019 Mar;60(3):406-418. [CrossRef]
- Allen, A. S., Berkovic, S. F., Cossette, P., Delanty, N., Dlugos, D., Eichler, E. E., Epstein, M. P., Glauser, T., Goldstein, D. B., Han, Y., Heinzen, E. L., Hitomi, Y., Howell, K. B., Johnson, M. R., Kuzniecky, R., Lowenstein, D. H., Lu, Y. F., Madou, M. R. Z., Marson, A. G., ... Winawer, M. R. (2013). De novo mutations in epileptic encephalopathies. Nature, 501(7466), 217-221. [CrossRef]
- Dortch-Carnes J, Potter DE. Delta-opioid agonist-stimulated inositol phosphate formation in isolated, rabbit iris-ciliary bodies: role of G(i/o) proteins and Gbetagamma-subunits. Exp Eye Res. 2003 Dec;77(6):647-52. [CrossRef]
- Gill A, Hammes SR. G beta gamma signaling reduces intracellular cAMP to promote meiotic progression in mouse oocytes. Steroids. 2007 Feb;72(2):117-23. [CrossRef]
- Borlikova G, Endo S. Inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) and brain functions. Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Aug;40(1):73-86. [CrossRef]
- Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S, Patel J, Cordeiro D, Hewson S, Callen D, Donner EJ, Hahn CD, Kannu P, Kobayashi J, Minassian BA, Moharir M, Siriwardena K, Weiss SK, Weksberg R, Snead OC 3rd. Diagnostic yield of genetic testing in epileptic encephalopathy in childhood. Epilepsia. 2015 May;56(5):707-16. [CrossRef]
- Miclea D, Peca L, Cuzmici Z, Pop IV. Genetic testing in patients with global developmental delay / intellectual disabilities. A review. Clujul Med. 2015;88(3):288-92. [CrossRef]
- Tanis, J. E., Moresco, J. J., Lindquist, R. A., & Koelle, M. R. (2008). Regulation of serotonin biosynthesis by the G proteins Gαo and Gαq controls serotonin signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics, 178(1), 157-169. [CrossRef]
- Solis GP, Koval A, Valnohova J, Kazemzadeh A, Savitsky M, Katanaev VL. Neomorphic Gαo mutations gain interaction with Ric8 proteins in GNAO1 encephalopathies. J Clin Invest. 2024 Jun 14;134(15):e172057. [CrossRef]
- Koelle MR. A new family of G-protein regulators—the RGS proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;9(2):143-7. [CrossRef]
- Savoia Claudia, Pujol Julien B, Vaucher Angelique, Marchi Umberto De, Rieker Claus, Heikkilä, Eija, Núñez Galindo, Antonio, Dayon Loïc, Dioum, Elhadji M. GPRIN1 modulates neuronal signal transduction and affects mouse-learning behavior,” Mar. 30, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Taira R, Akamine S, Okuzono S, Fujii F, Hatai E, Yonemoto K, Takemoto R, Kato H, Masuda K, Kato TA, Kira R, Tsujimura K, Yamamura K, Ozaki N, Ohga S, Sakai Y. Gnao1 is a molecular switch that regulates the Rho signaling pathway in differentiating neurons. Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 24;14(1):17097. [CrossRef]
- Ju H, Lee S, Kang S, Kim SS, Ghil S. The alpha subunit of Go modulates cell proliferation and differentiation through interactions with Necdin. Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Jul 10; 12:39. [CrossRef]
- Solis GP, Kozhanova TV, Koval A, Zhilina SS, Mescheryakova TI, Abramov AA, Ishmuratov EV, Bolshakova ES, Osipova KV, Ayvazyan SO, Lebon S, Kanivets IV, Pyankov DV, Troccaz S, Silachev DN, Zavadenko NN, Prityko AG, Katanaev VL. Pediatric Encephalopathy: Clinical, Biochemical and Cellular Insights into the Role of Gln52 of GNAO1 and GNAI1 for the Dominant Disease. Cells. 2021 Oct 14;10(10):2749. [CrossRef]
- JoJo Yang QZ, Porter BE, Axeen ET. GNAO1-related neurodevelopmental disorder: Literature review and caregiver survey. Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2022 Dec 31; 21:100582. [CrossRef]
- Wang D, Dao M, Muntean BS, Giles AC, Martemyanov KA, Grill B. Genetic modeling of GNAO1 disorder delineates mechanisms of Gαo dysfunction. Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Feb 21;31(4):510-522. [CrossRef]
- Miller KG, Emerson MD, Rand JB. Goalpha and diacylglycerol kinase negatively regulate the Gqalpha pathway in C. elegans. Neuron. 1999 Oct;24(2):323-33. [CrossRef]
- Saitsu H, Fukai R, Ben-Zeev B, Sakai Y, Mimaki M, Okamoto N, Suzuki Y, Monden Y, Saito H, Tziperman B, Torio M, Akamine S, Takahashi N, Osaka H, Yamagata T, Nakamura K, Tsurusaki Y, Nakashima M, Miyake N, Shiina M, Ogata K, Matsumoto N. Phenotypic spectrum of GNAO1 variants: epileptic encephalopathy to involuntary movements with severe developmental delay. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016 Jan;24(1):129-34. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




