Submitted:
24 October 2024
Posted:
25 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
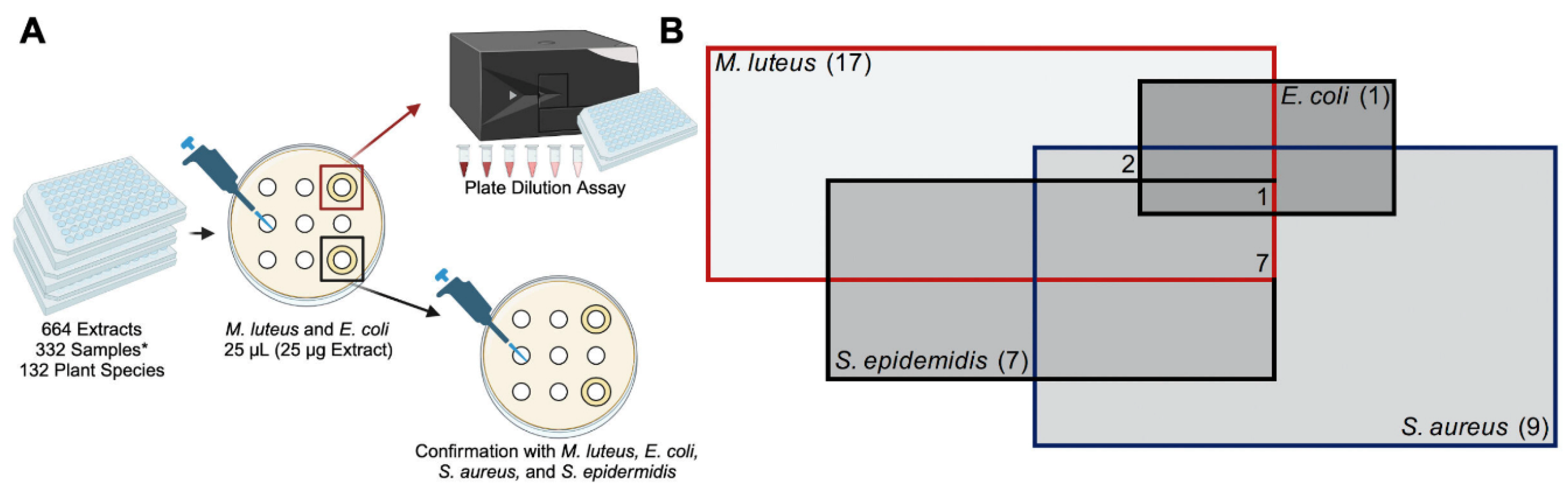
2.1. Experimental Overview and Identification of TCM Plant Extracts with Antimicrobial Properties
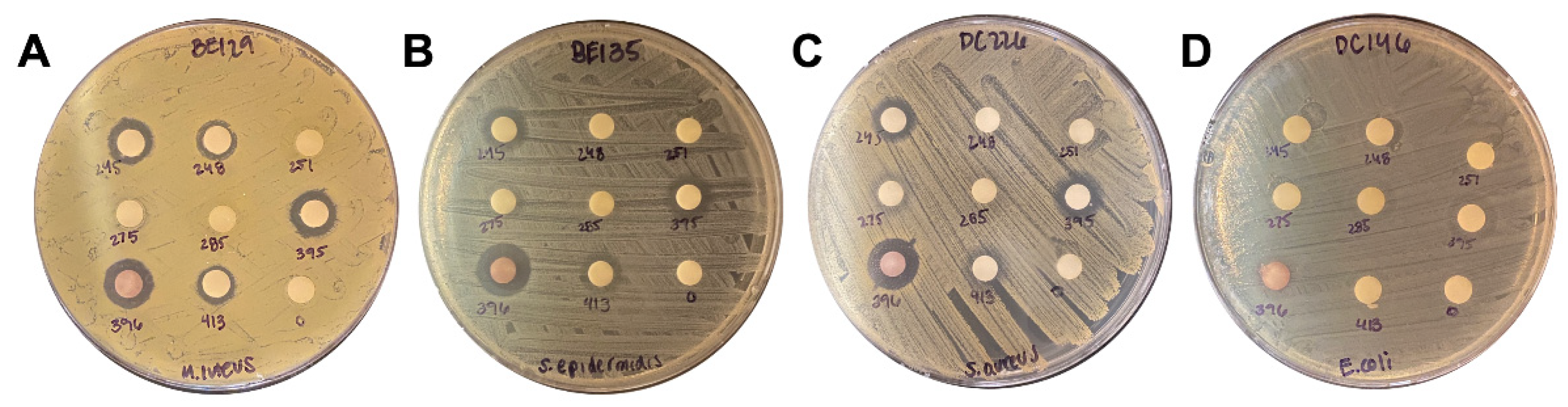
2.2. Extract Screen Reveals 17 TCM Plant Species with Antimicrobial Properties
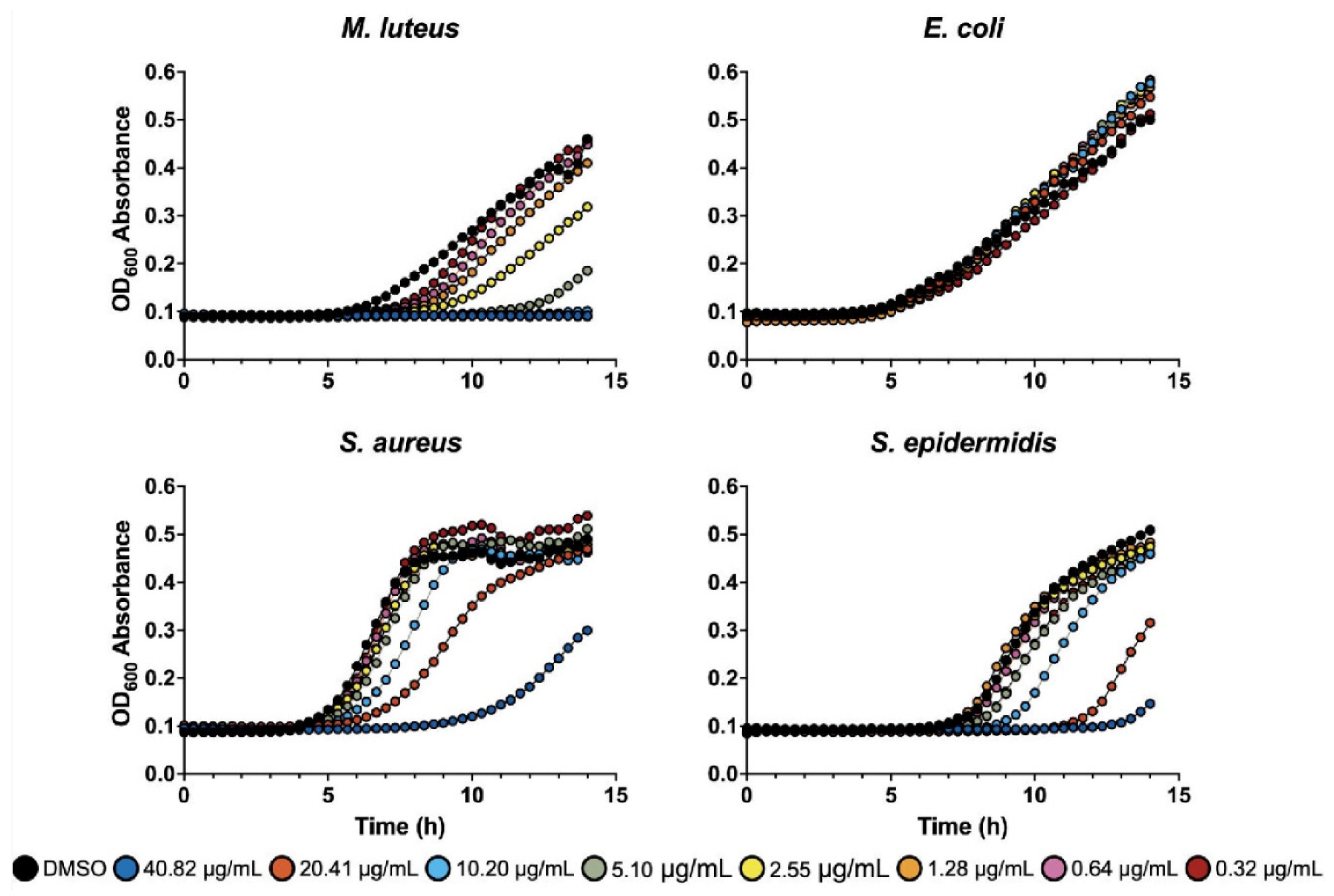
2.3. Liquid Assay
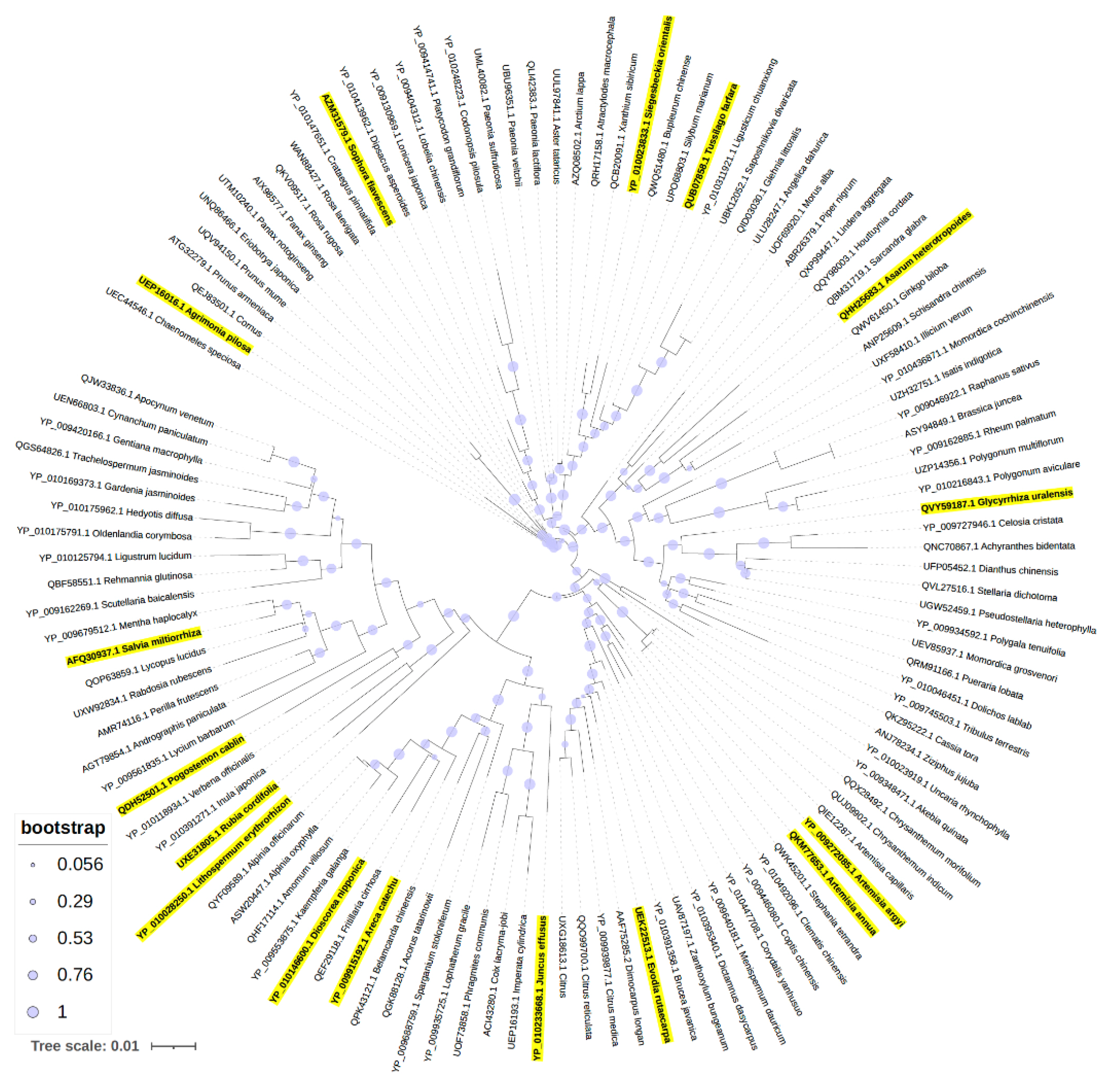
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Active Components of TCM Plant Extracts
3. Discussion
3.1. TCM Plant-Derived Antimicrobials
3.2. Antimicrobial Activities of TCM Plant Extracts
3.3. Active Components of TCM Plant Extracts
| *Family. | Genus | Species | Common Name | Chinese Name | Tested for Antimicrobial Activity [Citation] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compositae | Asarum | heterotropoides | Wild Ginger | 細辛 | Ralstonia solanacearum, Xanthomonas oryzae, Pseudomonas syringae, Xanthomonas axonopodis [28]; Fusobacterium nucleatum, Prevotella intermedia, Porphyromonas gingivalis [98]. Clostridioides difficile, Clostridium paraputrificum, Clostridium perfringens, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacteroides fragilis, Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium [27]; Listeria monocytogenes [99]; Staphylococcus epidermidis, Micrococcus luteus, Corynebacterium jeikeium, Corynebacterium xerosis, Propionibacterium freudenreichii [100] |
| Boraginaceae | Lithospermum | erythrorhizon | Purple Gromwell | 紫草 | Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus thuringiensis, Clavibacter michiganensis, Agrobacterium radiobacter, Agrobacterium rhizogenes, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Bulkholderia cepacian, Erwinia herbicola, Ralstonia solanacearum [62]; Staphylococcus aureus, Micrococcus roseus, Micrococcus luteus, Bacillus subtilis [30] |
| Compositae | Tussilago | farfara | Coltsfoot | 款冬花 | Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus [101]; Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus [102];. Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella enterica, Shigella sonnei, Yersinia enterocolitia, Bacillus thuringiensis, Clostridium perfringens, Haemophilus influenzae, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus [103]; Escherichia coli, Serratia rubidaea, Staphylococcus epidermis, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus raffinosus [104] |
| Compositae | Echinops | latifolius | Globe Thistle | 驴欺口 | None |
| Compositae | Artemisia | annua | Sweet Wormwood | 青蒿 | Haemophilus inflenzae, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Micrococcus luteus [105]; Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Micrococcus luteus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella enteritidis, Shigella sp. [33]; Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus thuringiensis [106]; Enterococcus hirae [107]; Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli [108]; Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Bacillus cereus, Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa [109]; Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus cereus, Micrococcus luteus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhi, Pseudomonas aeruginosa [110] |
| Compositae | Artemisia | argyi | Mugwort | 艾草 | Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Listeria monocytogenes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus agalactiae [86]; Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, Salmonella enteritidis [111] |
| Compositae | Sigesbeckia | orientalis | St. Paul’s Wort | 豨莶 | Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli [39]; Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus oralis, Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa [40] |
| Dioscoreaceae | Dioscorea | nipponica | Japanese Yam | 穿龙薯蓣 | Bacillus subtilis, S. aureus, Proteus vulgaris, Salmonella Typhimurium [77] |
| Juncaceae | Juncus | effusus | Soft Rush | 灯心草 | Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis [41]; Micrococcus luteus, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus [42] |
| Lamiaceae | Pogostemon | cablin | Patchouli | 广藿香 | Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus oralis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus constellatus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus mitis [112]; Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella sp. [113] |
| Labiatae | Salvia | miltiorrhiza | Red Sage | 丹参 | Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas syringae, Ralstonia solanacearum, Xanthomonas vesicatoria, Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus haemolyticus [114] |
| Fabaceae | Glycyrrhiza | uralensis | Chinese Licorice | 甘草 | Streptococcus mutans [115]; Staphylococcus aureus [116] |
| Fabaceae | Sophora | flavescens | Sophora Root | 苦参 | Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Salmonella Typhimurium, Proteus vulgaris, Escherichia coli [117]; Streptococcus mutans [118] |
| Compositae | Areca | catechu | Areca Palm | 檳榔 | Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus [119] |
| Rosaceae | Agrimonia | pilosa | Chinese Agrimony | 龙芽草 | Listeria monocytogenes, Streptococcus enteritidis, Escherichia coli [120] |
| Rubiaceae | Rubia | cordifolia | Indian Madder | 茜草 | Erwinia herbicola, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Xanthamonas campestris [121]; Bacillus cereus, Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus subtilis, Micrococcus luteus, Mycobacterium luteum, Staphylococcus aureus, P. aeruginosa [70] |
| Rutaceae | Evodia | rutaecarpa | Evodia Fruit | 吳茱萸 | Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus [53]; Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Bacillus subtilis [68] |
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. TCM Plant Extracts
4.3. Bacteria and Culture
4.4. Disk Diffusion Assay
4.5. Plate Dilution Assay
4.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.7. Compound Structure Similarity
4.8. Lipinski Rule of Five
4.9. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. 2019.
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. The Lancet 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, O.I., A.; Berthe, F.C.J.; Le Gall, F.; Marquez, P. Drug-Resistant Infections: A Threat to Our Economic Future (Vol. 2): Final Report (English); Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- J, O.N. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: Final report and recommendations.; 2016.
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: bacterial pathogens of public health importance to guide research, development and strategies to prevent and control antimicrobial resistance; 2024.
- Ruekit, S.; Srijan, A.; Serichantalergs, O.; Margulieux, K.R.; Mc Gann, P.; Mills, E.G.; Stribling, W.C.; Pimsawat, T.; Kormanee, R.; Nakornchai, S.; et al. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant ESKAPEE pathogens from clinical samples in Chonburi, Thailand (2017–2018). BMC infectious diseases 2022, 22, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Årdal, C.; Balasegaram, M.; Laxminarayan, R.; McAdams, D.; Outterson, K.; Rex, J.H.; Sumpradit, N. Antibiotic development — economic, regulatory and societal challenges. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2020, 18, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J.; Wunderink, R.; Gilbert, D.N. Novel approaches are needed to develop tomorrow's antibacterial therapies. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2015, 191, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czyz, D.M.; Potluri, L.P.; Jain-Gupta, N.; Riley, S.P.; Martinez, J.J.; Steck, T.L.; Crosson, S.; Shuman, H.A.; Gabay, J.E. Host-directed antimicrobial drugs with broad-spectrum efficacy against intracellular bacterial pathogens. mBio 2014, 5, e01534–01514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dove, A.S.; Dzurny, D.I.; Dees, W.R.; Qin, N.; Nunez Rodriguez, C.C.; Alt, L.A.; Ellward, G.L.; Best, J.A.; Rudawski, N.G.; Fujii, K.; et al. Silver nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of aminoglycosides against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 1064095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorski, A.; Miedzybrodzki, R.; Wegrzyn, G.; Jonczyk-Matysiak, E.; Borysowski, J.; Weber-Dabrowska, B. Phage therapy: Current status and perspectives. Medicinal research reviews 2020, 40, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Chen, X. Current Promising Strategies against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infections. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, D.M.; Harris, E.S.; Littlefield, B.A.; Cao, S.; Craycroft, J.A.; Scholten, R.; Bayliss, P.; Fu, Y.; Wang, W.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Developing a library of authenticated Traditional Chinese Medicinal (TCM) plants for systematic biological evaluation--rationale, methods and preliminary results from a Sino-American collaboration. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wu, W.; Hou, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, Z. A review: antimicrobial properties of several medicinal plants widely used in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Food Quality and Safety 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, X.; Qiao, F.; Guo, J.; Deng, S. Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine and its Active Ingredients on Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 837907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-García, M.; Sol, C.; de Nova, P.J.G.; Puyalto, M.; Mesas, L.; Puente, H.; Mencía-Ares, Ó.; Miranda, R.; Argüello, H.; Rubio, P.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of a selection of organic acids, their salts and essential oils against swine enteropathogenic bacteria. Porcine Health Management 2019, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, T.; Lores, M.; de Miguel, T. Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols and Natural Polyphenolic Extracts on Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Cushnie, B.; Lamb, A.J. Alkaloids: An overview of their antibacterial, antibiotic-enhancing and antivirulence activities. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2014, 44, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Lamb, A.J. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2005, 26, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlem Junior, M.A.; Nguema Edzang, R.W.; Catto, A.L.; Raimundo, J.M. Quinones as an Efficient Molecular Scaffold in the Antibacterial/Antifungal or Antitumoral Arsenal. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Wong, Y.K.; Li, Y.; Liao, F.; Jiang, T.; Tu, Y. Artemisinin, the Magic Drug Discovered from Traditional Chinese Medicine. Engineering 2019, 5, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.Z.; Miller, L.H. The discovery of artemisinin and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Sci China Life Sci 2015, 58, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Ausubel, F.M. Prospects for plant-derived antibacterials. Nature biotechnology 2006, 24, 1504–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berida, T.I.; Adekunle, Y.A.; Dada-Adegbola, H.; Kdimy, A.; Roy, S.; Sarker, S.D. Plant antibacterials: The challenges and opportunities. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.; Miao, G. Strategies, Achievements, and Potential Challenges of Plant and Microbial Chassis in the Biosynthesis of Plant Secondary Metabolites. Molecules 2024, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumalsamy, H.; Jung, M.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Ahn, Y.J. Growth-Inhibiting and morphostructural effects of constituents identified in Asarum heterotropoides root on human intestinal bacteria. BMC complementary and alternative medicine 2013, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Kong, D.; He, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Feng, J.; Yan, H. Phenanthrene Derivatives from Asarum heterotropoides Showed Excellent Antibacterial Activity against Phytopathogenic Bacteria. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2021, 69, 14520–14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, D.-Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, S.-W.; Cha, S.-W.; Park, H.-W.; Kim, G.-S.; Kwon, D.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Han, S.-H. The Mechanism Underlying the Antibacterial Activity of Shikonin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2015, 2015, 520578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, G.; Sakakibara, F.; Yazaki, K.; Tabata, M. Isolation of Deoxyshikonin, an Antidermatophytic Principle from Lithospermum erythrorhizon Cell Cultures. Journal of natural products 1988, 51, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, M.-A.; Côté, H.; Pichette, A.; Ripoll, L.; Legault, J. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of Tussilago farfara (L.) essential oil from Quebec, Canada. Natural product research 2020, 34, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Evangelopoulos, D.; Bhakta, S.; Gray, A.I.; Seidel, V. Antitubercular activity of Arctium lappa and Tussilago farfara extracts and constituents. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2014, 155, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulović, N.S.; Randjelović, P.J.; Stojanović, N.M.; Blagojević, P.D.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.Z.; Ilić, I.R.; Djordjević, V.B. Toxic essential oils. Part II: Chemical, toxicological, pharmacological and microbiological profiles of Artemisia annua L. volatiles. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2013, 58, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donato, R.; Santomauro, F.; Bilia, A.R.; Flamini, G.; Sacco, C. Antibacterial activity of Tuscan Artemisia annua essential oil and its major components against some foodborne pathogens. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2015, 64, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 신승원. In vitro Effects of Essential Oils from Aerial Parts of Artemisia annus L. Against Antibiotic-Susceptible and -Resistance Strains of Salmenella typhimurium. YAKHAK HOEJI 2007, 51, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Marinas, I.C.; Oprea, E.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Badea, I.A.; Buleandra, M.; Lazar, V. Chemical Composition and Antipathogenic Activity of Artemisia annua Essential Oil from Romania. Chemistry & biodiversity 2015, 12, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivarsen, E.; Fretté, X.C.; Christensen, K.B.; Christensen, L.P.; Engberg, R.M.; Grevsen, K.; Kjaer, A. Bioassay-Guided Chromatographic Isolation and Identification of Antibacterial Compounds from Artemisia annua L. That Inhibit Clostridium perfringens Growth. Journal of AOAC International 2014, 97, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Xiang, H.; Qiu, H.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; Tong, S. Screening and identification of antibacterial components in Artemisia argyi essential oil by TLC–direct bioautography combined with comprehensive 2D GC × GC-TOFMS. Journal of Chromatography B 2024, 1234, 124026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Lei, J.; Yu, J. Biological activity of extracts and active compounds isolated from Siegesbeckia orientalis L. Industrial Crops and Products 2016, 94, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Kirenol production in hairy root culture of Siegesbeckea orientalis and its antimicrobial activity. Pharmacogn Mag 2012, 8, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, F.; Okamoto, M.; Towers, G.H.N. Antimicrobial DNA-binding Photosensitizers from the Common Rush, Juncus effusus. Photochemistry and photobiology 2002, 76, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, L.L.; Zhang, X.; Gong, X.W.; Zhu, D.L.; Xu, X.H.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.L. Three new phenanthrenes with antimicrobial activities from the aerial parts of Juncus effusus. Fitoterapia 2018, 130, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Wan, F.; Xiong, L.; Peng, C.; Dai, M.; Chen, J. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of Pogostone. Chinese medical journal 2014, 127, 4001–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Noh, J.-G.; Hong, S.-D. Antibacterial Activities of Cryptotanshinone and Dihydrotanshinone I from a Medicinal Herb, Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 1999, 63, 2236–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-C.; Ding, Z.-S.; Dai, J.-S.; Chen, N.-P.; Gong, X.-W.; Ma, L.-F.; Qian, C.-D. New Insights Into the Antibacterial Mechanism of Cryptotanshinone, a Representative Diterpenoid Quinone From Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Chen, D.; Wu, T. Minor compounds of the high purity salvianolic acid B freeze-dried powder from Salvia miltiorrhiza and antibacterial activity assessment. Natural product research 2018, 32, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Chen, L.; Heber, D.; Shi, W.; Lu, Q.-Y. Antibacterial Compounds from Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Journal of natural products 2006, 69, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villinski, J.R.; Bergeron, C.; Cannistra, J.C.; Gloer, J.B.; Coleman, C.M.; Ferreira, D.; Azelmat, J.; Grenier, D.; Gafner, S. Pyrano-isoflavans from Glycyrrhiza uralensis with Antibacterial Activity against Streptococcus mutans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. Journal of natural products 2014, 77, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, H. Antimicrobial Effects of Sophora flavescens Alkaloids on Metronidazole-Resistant Gardnerella vaginalis in Planktonic and Biofilm Conditions. Current microbiology 2023, 80, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Jiang, C.; Dai, W.; Jing, H.; Du, X.; Peng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Effects of different extraction on the antibacterial and antioxidant activities of phenolic compounds of areca nut (husks and seeds). Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 2022, 16, 1502–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaki, M.; Kashihara, M.; Ishiguro, K.; Takagi, S. Antimicrobial Principles of Xian he cao (Agrimonia pilosa). Planta medica 1989, 55, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, S.; Watanabe, S.; Kawabata, J.; Tahara, S.; Mizutani, J. Antimicrobial catechin derivatives of Agrimonia pilosa. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, B.; Wu, F.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liang, S. Bitterness and antibacterial activities of constituents from Evodia rutaecarpa. BMC complementary and alternative medicine 2017, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Chang, M.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Lin, H.-C.; Tsai, H.-P.; Yang, C.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-M. Topoisomerase I Inhibitor Evodiamine Acts As an Antibacterial Agent against Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Planta medica 2013, 79, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.-L.; Xu, S.; Shan, Y.; Yin, M.; Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, Q.-Z. Three new quinazolines from Evodia rutaecarpa and their biological activity. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, M.M. Plant products as antimicrobial agents. Clinical microbiology reviews 1999, 12, 564–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Marquez, L.; Crandall, W.J.; Risener, C.J.; Quave, C.L. Recent advances in the discovery of plant-derived antimicrobial natural products to combat antimicrobial resistant pathogens: insights from 2018-2022. Natural product reports 2023, 40, 1271–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassagne, F.; Samarakoon, T.; Porras, G.; Lyles, J.T.; Dettweiler, M.; Marquez, L.; Salam, A.M.; Shabih, S.; Farrokhi, D.R.; Quave, C.L. A Systematic Review of Plants With Antibacterial Activities: A Taxonomic and Phylogenetic Perspective. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 586548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Grkovic, T.; Evans, J.R.; Thornburg, C.C.; Akee, R.K.; Thompson, J.R.; Whitt, J.A.; Harris, M.J.; Loyal, J.A.; Britt, J.R.; et al. The NCI library of traditional Chinese medicinal plant extracts - Preliminary assessment of the NCI-60 activity and chemical profiling of selected species. Fitoterapia 2019, 137, 104285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.; Saitis, T.; Shareef, R.; Harb, C.; Lakhani, M.; Ahmad, Z. Shikonin and Alkannin inhibit ATP synthase and impede the cell growth in Escherichia coli. International journal of biological macromolecules 2023, 253, 127049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Kou, M.; Shi, C.; Peng, X.; Wang, X. Control of Foodborne Staphylococcus aureus by Shikonin, a Natural Extract. Foods 2021, 10, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, L.A.; Michaels, P.J.; Flores, H.E. Cell-specific production and antimicrobial activity of naphthoquinones in roots of lithospermum erythrorhizon. Plant physiology 1999, 119, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Jiang, X.; Han, Y.; Feng, L.; Sun, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, T. An effective antimicrobial strategy of colistin combined with the Chinese herbal medicine shikonin against colistin-resistant Escherichia coli. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, e0145923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Chae, H.S.; Kang, O.H.; Kwon, D.Y. Synergistic Antibacterial Activity with Conventional Antibiotics and Mechanism of Action of Shikonin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarosh, D.B.; Galvin, J.W.; Nay, S.L.; Peña, A.V.; Canning, M.T.; Brown, D.A. Anti-inflammatory activity in skin by biomimetic of Evodia rutaecarpa extract from traditional Chinese medicine. Journal of dermatological science 2006, 42, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, P.; Kim, S.H. Evodiamine Inhibits Helicobacter pylori Growth and Helicobacter pylori-Induced Inflammation. International journal of molecular sciences 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, M.; Tripathi, S.K.; Zengin, G.; Biswal, B.K. Evodiamine as an anticancer agent: a comprehensive review on its therapeutic application, pharmacokinetic, toxicity, and metabolism in various cancers. Cell Biol Toxicol 2023, 39, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-X.; Zan, K.; Shi, S.-P.; Zeng, K.-W.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Xiao, C.-L.; Gao, H.-Y.; Wu, L.-J.; Tu, P.-F. Quinolone alkaloids with antibacterial and cytotoxic activities from the fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa. Fitoterapia 2013, 89, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Martínez, F.J.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Encinar, J.A.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.C.; Micol, V. Antimicrobial Capacity of Plant Polyphenols against Gram-positive Bacteria: A Comprehensive Review. Current medicinal chemistry 2020, 27, 2576–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Ghosh, A.; Hazra, B. Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Ventilago madraspatana Gaertn., Rubia cordifolia Linn. and Lantana camara Linn.: isolation of emodin and physcion as active antibacterial agents. Phytotherapy research: PTR 2005, 19, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Chen, Q.; Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, A.; Lai, J.; Chen, J.; Mei, Q.; et al. A comprehensive review of Rubia cordifolia L.: Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, and clinical applications. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 965390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ezati, P.; Rhim, J.W. Alizarin: Prospects and sustainability for food safety and quality monitoring applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2023, 223, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, G.; Shukla, M.; Kaul, G.; K, R.; Chopra, S.; Pandey, R. Characterization and antimicrobial evaluation of anthraquinones and triterpenes from Rubia cordifolia. Journal of Asian natural products research 2023, 25, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, A.; Murakami, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Amoh, T.; Hirao, K.; Hosokawa, Y.; Hinode, D.; Miyake, Y.; Yumoto, H. Anti-Inflammatory and Protective Effects of Juncus effusus L. Water Extract on Oral Keratinocytes. BioMed research international 2022, 2022, 9770899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lai, K.H.; Hsu, Y.M.; Hwang, T.L.; Lin, C.C.; Fülöp, F.; Wu, Y.C.; Yu, S.Y.; et al. Estrogenic and anti-neutrophilic inflammatory phenanthrenes from Juncus effusus L. Natural product research 2022, 36, 3043–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, F.; Ding, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N. Four new phenanthrenoid dimers from Juncus effusus L. with cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities. Fitoterapia 2015, 105, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-B.; Kim, M.S.; Sohn, H.Y. Evaluation of Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Antithrombin Activities of the Rhizome of Various Dioscorea Species. 2010.
- Bilia, A.R.; Santomauro, F.; Sacco, C.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Donato, R. Essential Oil of Artemisia annua L.: An Extraordinary Component with Numerous Antimicrobial Properties. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine: eCAM 2014, 2014, 159819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Vörös-Horváth, B.; Bencsik, T.; Micalizzi, G.; Mondello, L.; Horváth, G.; Kőszegi, T.; Széchenyi, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Different Artemisia Essential Oil Formulations. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, S.G.; Rao, R.V. Antiviral and Immunomodulation Effects of Artemisia. Medicina (Kaunas) 2021, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nature medicine 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Lalarizo Rakoto, M.; Marodon, C.; Bedoui, Y.; Nakab, J.; Simon, E.; Hoarau, L.; Savriama, S.; Strasberg, D.; Guiraud, P.; et al. Artemisia annua, a Traditional Plant Brought to Light. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbarg, H.; Mehdipour Moghaddam, M.J. Antibacterial Potency of Medicinal Plants including Artemisia annua and Oxalis corniculata against Multi-Drug Resistance E. coil. BioMed research international 2021, 2021, 9981915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordean, M.E.; Ungur, R.A.; Toc, D.A.; Borda, I.M.; Marțiș, G.S.; Pop, C.R.; Filip, M.; Vlassa, M.; Nasui, B.A.; Pop, A.; et al. Antibacterial and Phytochemical Screening of Artemisia Species. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Qu, L.B.; Bi, Y.F.; Pan, C.X.; Yang, R.; Zeng, H.J. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of chloroform fraction from aqueous extract of mugwort leaves (Artemisia argyi L.) against Staphylococcus aureus. Letters in applied microbiology 2022, 74, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, R.; You, M.; Chen, N.; Sun, L.; Chen, N. The antimicrobial effect and mechanism of the Artemisia argyi essential oil against bacteria and fungus. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 2024, 55, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, R.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Song, D. Effects of Traditional Chinese Herbal Feed Additive on Production Performance, Egg Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, Immunity and Intestinal Health of Laying Hens. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, J.; Yang, C.; Kang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Use of fermented Chinese medicine residues as a feed additive and effects on growth performance, meat quality, and intestinal health of broilers. Front Vet Sci 2023, 10, 1157935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Ma, J.; Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jin, X.; Yan, S.; Shi, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, B. Effects of Artemisia annua L. Water Extract on Growth Performance and Intestinal Related Indicators in Broilers. J Poult Sci 2023, 60, 2023024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, R.L.; Ball, M.E.E.; Linton, M.; Pinkerton, L.; Kelly, C.; Lester, J.; Donaldson, C.; Balta, I.; Tunney, M.M.; Corcionivoschi, N.; et al. The Effects of Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb, Anemone chinensis Bunge, and Smilax glabra Roxb on Broiler Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Gastrointestinal Tract Microorganisms. Animals (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Tan, D.; Gong, X.; Ji, H.; Wang, K.; Lei, Q.; Zhao, G. An Extract of Artemisia argyi Leaves Rich in Organic Acids and Flavonoids Promotes Growth in BALB/c Mice by Regulating Intestinal Flora. Animals (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Tang, T.; Chen, Q.; Yan, Z.; Peng, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Fermented Chinese Herbal Medicine Promoted Growth Performance, Intestinal Health, and Regulated Bacterial Microbiota of Weaned Piglets. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.P.; Feng, D.Y.; Xia, M.H.; He, X.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Tan, H.Z.; Zou, S.G.; Ou, X.H.; Zheng, T.; Cao, Y.; et al. Effects of a traditional Chinese medicine formula supplementation on growth performance, carcass characteristics, meat quality and fatty acid profiles of finishing pigs. Livestock Science 2017, 202, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Luo, J.; Fu, D.; Zhao, X.; Bunlue, K.; Xu, Z.; Qu, M. Traditional chinese medicine prescriptions enhance growth performance of heat stressed beef cattle by relieving heat stress responses and increasing apparent nutrient digestibility. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 2014, 27, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadras, F.; Velisek, J.; Zuskova, E. An update about beneficial effects of medicinal plants in aquaculture: A review. Vet Med (Praha) 2023, 68, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Yin, F.; Hou, Y.; Yin, Y. Review: Chinese herbs as alternatives to antibiotics in feed for swine and poultry production: Potential and challenges in application. Canadian Journal of Animal Science 2014, 94, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.L.A.R.; De Menezes, I.R.A.; Sousa, A.K.; Farias, P.A.M.; dos Santos, F.A.V.; Freitas, T.S.; Figueredo, F.G.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Carvalho, D.T.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; et al. In vitro and in silico antibacterial evaluation of coumarin derivatives against MDR strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Microbial pathogenesis 2023, 177, 106058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, H.; Peng, L.; Zhen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; He, D.; Li, X. Orthogonal test design for optimization of the extraction of essential oil from Asarum heterotropoides var. Mandshuricum and evaluation of its antibacterial activity against periodontal pathogens. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Hwang, I.H.; Kim, D.C.; Kang, S.C.; Jang, T.S.; Lee, S.H.; Na, M. Anti-listerial compounds from Asari Radix. Archives of pharmacal research 2010, 33, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Moon, J.N.; Saravana, P.S.; Tilahun, A.; Chun, B.S. Composition of Asarum heterotropoides var. mandshuricum radix oil from different extraction methods and activities against human body odor-producing bacteria. J Food Drug Anal 2016, 24, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokoska, L.; Polesny, Z.; Rada, V.; Nepovim, A.; Vanek, T. Screening of some Siberian medicinal plants for antimicrobial activity. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2002, 82, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Song, K.; Cha, S.H.; Cho, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, Y. Sesquiterpenoids from Tussilago farfara Flower Bud Extract for the Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Possessing Antibacterial and Anticancer Activities. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanišová, E.; Kačániová, M.; Petrová, J.; Frančáková, H.; Tokár, M. The evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial effect of Tussilago farfara L. and Cetraria islandica L. Scientific Papers Animal Science and Biotechnologies 2016, 49, 46–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kacaniova, M.; Hleba, L.; Petrová, J.; Felšöciová, S.; Pavelková, A.; Miklášová, K.; Bobková, A.; Čuboň, J. Antimicrobial activity of Tussilago farfara L. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences 2013, 2, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Ćavar, S.; Maksimović, M.; Vidic, D.; Parić, A. Chemical composition and antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of essential oil of Artemisia annua L. from Bosnia. Industrial Crops and Products 2012, 37, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, L. Composition and antimicrobial activity of essential oil from the aerial part of Artemisia annua. J Medicin Plants Res 2011, 5, 3629–3633. [Google Scholar]
- Juteau, F.; Masotti, V.; Bessière, J.M.; Dherbomez, M.; Viano, J. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Artemisia annua essential oil. Fitoterapia 2002, 73, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VERDIAN, R.M.; SADAT, E.E.; HAJI, A.A.; Fazeli, M.; PIRALI, H.M. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of Artemisia annua L. essential oil from Iran. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Massiha, A.; Majid Khoshkholgh-Pahlaviani, M.; Issazadeh, K.; Bidarigh, S.; Zarrabi, S. Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils and Plant Extracts of Artemisia (Artemisia annua L.) In Vitro. Zahedan J Res Med Sci 2013, 15, e92933. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.C.; Dutta, B.; Pant, D.; Joshi, P.; Lohar, D. In vitro antibacterial activity of Artemisia annua Linn. growing in India. International Journal of Green Pharmacy (IJGP) 2009, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Ge, D.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; Liu, J.; Li, F. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activities of Artemisia argyi Lévl. et Vant Essential Oils Extracted by Simultaneous Distillation-Extraction, Subcritical Extraction and Hydrodistillation. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.R. Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Patchouli Essential Oil Extracted From Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. (lamiaceae). 2014.
- Aisyah, Y.; Yunita, D.; Amanda, A. Antimicrobial activity of patchouli (Pogostemon cablin Benth) citronella (Cymbopogon nardus), and nutmeg (Myristica fragrans) essential oil and their mixtures against pathogenic and food spoilage microbes. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021, 667, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lou, J.; Mou, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L. Diterpenoid tanshinones and phenolic acids from cultured hairy roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge and their antimicrobial activities. Molecules 2011, 16, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Choi, Y.R.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, M.K. Antimicrobial Effects against Oral Pathogens and Cytotoxicity of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Extract. Plants (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Ji, Y.J.; Yu, M.H.; Bo, M.H.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, S.P.; Lee, I.S. Antimicrobial effect and resistant regulation of Glycyrrhiza uralensis on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Natural product research 2009, 23, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, I.; Yang, W.Y.; Chung, S.C.; Kim, T.Y.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. In vitro sortase A inhibitory and antimicrobial activity of flavonoids isolated from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Archives of pharmacal research 2011, 34, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Park, S.-N.; Ahn, S.-J.; Seo, Y.-W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lim, Y.K.; Freire, M.O.; Cho, E.; Kook, J.-K. Antimicrobial effect of sophoraflavanone G isolated from Sophora flavescens against mutans streptococci. Anaerobe 2013, 19, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Sultana, P.; Islam, M.S.; Mahmud, M.T.; Rashid, M.M.O.; Foysal; Hossen. Comparative Antimicrobial Activity of Areca catechu Nut Extracts using Different Extracting Solvents. Bangladesh Journal of Microbiology 2016, 31, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurray, R.L.; Ball, M.E.E.; Tunney, M.M.; Corcionivoschi, N.; Situ, C. Antibacterial Activity of Four Plant Extracts Extracted from Traditional Chinese Medicinal Plants against Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli, and Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, K.; Ramya Lalam, R.L.; Varaprasad Bobbarala, V.B. Antimicrobial agents from Rubia cordifolia and Glycyrrhiza glabra against phytopathogens of Gossypium. International Journal of PharmTech Research 2009, 1, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Molecular biology and evolution 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): a resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic acids research 2023, 51, D678–d689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic acids research 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, T.W.; Cao, Y.; Girke, T. ChemMine tools: an online service for analyzing and clustering small molecules. Nucleic acids research 2011, 39, W486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic acids research 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetko, I.V.; Tanchuk, V.Y. Application of Associative Neural Networks for Prediction of Lipophilicity in ALOGPS 2.1 Program. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences 2002, 42, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetko, I.V.; Gasteiger, J.; Todeschini, R.; Mauri, A.; Livingstone, D.; Ertl, P.; Palyulin, V.A.; Radchenko, E.V.; Zefirov, N.S.; Makarenko, A.S.; et al. Virtual computational chemistry laboratory--design and description. Journal of computer-aided molecular design 2005, 19, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spot # | Genus | Species | M. luteus* | --- | S. aureus | S. epidermidis |
| 20 | Tussilago | farfara | 10 | --- | --- | --- |
| 27 | Asarum | heterotropoides | 10 | --- | 12.6 | --- |
| 33 | Evodia | rutaecarpa | 17.6 | --- | 11.6 | 10.8 |
| 42 | Rubia | cordifolia | 11.6 | --- | --- | --- |
| 55 | Dioscorea | nipponica | 9.7 | --- | --- | --- |
| 83 | Dioscorea | nipponica | 11.6 | --- | --- | --- |
| 95 | Echinops | latifolius | 10.9 | --- | 11.8 | --- |
| 201 | Artemisia | annua | 19.4 | --- | --- | --- |
| 245 | Glycyrrhiza | uralensis | 12.6 | --- | 11.7 | 11.6 |
| 248 | Areca | catechu | 10.6 | --- | --- | --- |
| 251 | Artemisia | argyi | 11 | --- | --- | --- |
| 275 | Juncus | effusus | 10.2 | --- | 11.2 | --- |
| 285 | Artemisia | argyi | 8.4 | --- | --- | --- |
| 395 | Juncus | effusus | 13 | --- | 13.2 | 11.8 |
| 396 | Lithospermum | erythrorhizon | 14 | 9.5 | 13.9 | 14.8 |
| 413 | Sophora | flavescens | 12.2 | --- | 11.2 | 11.4 |
| 415 | Juncus | effusus | 11.2 | --- | 11.4 | --- |
| 416 | Rubia | cordifolia | 12 | --- | --- | --- |
| 424 | Evodia | rutaecarpa | 19 | --- | 9.8 | --- |
| 456 | Agrimonia | pilosa | 11.4 | --- | 12.2 | 10.6 |
| 460 | Lithospermum | erythrorhizon | 12.6 | --- | 10.2 | 12.4 |
| 694 | Salvia | miltiorrhiza | 12.2 | --- | 9.81 | 15.6 |
| 704 | Siegesbeckia | orientalis | 9.4 | --- | --- | --- |
| 727 | Evodia | rutaecarpa | 18.4 | --- | 11 | 11.8 |
| 749 | Pogostemon | cablin | 21.4 | --- | --- | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





