Submitted:
23 October 2024
Posted:
24 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
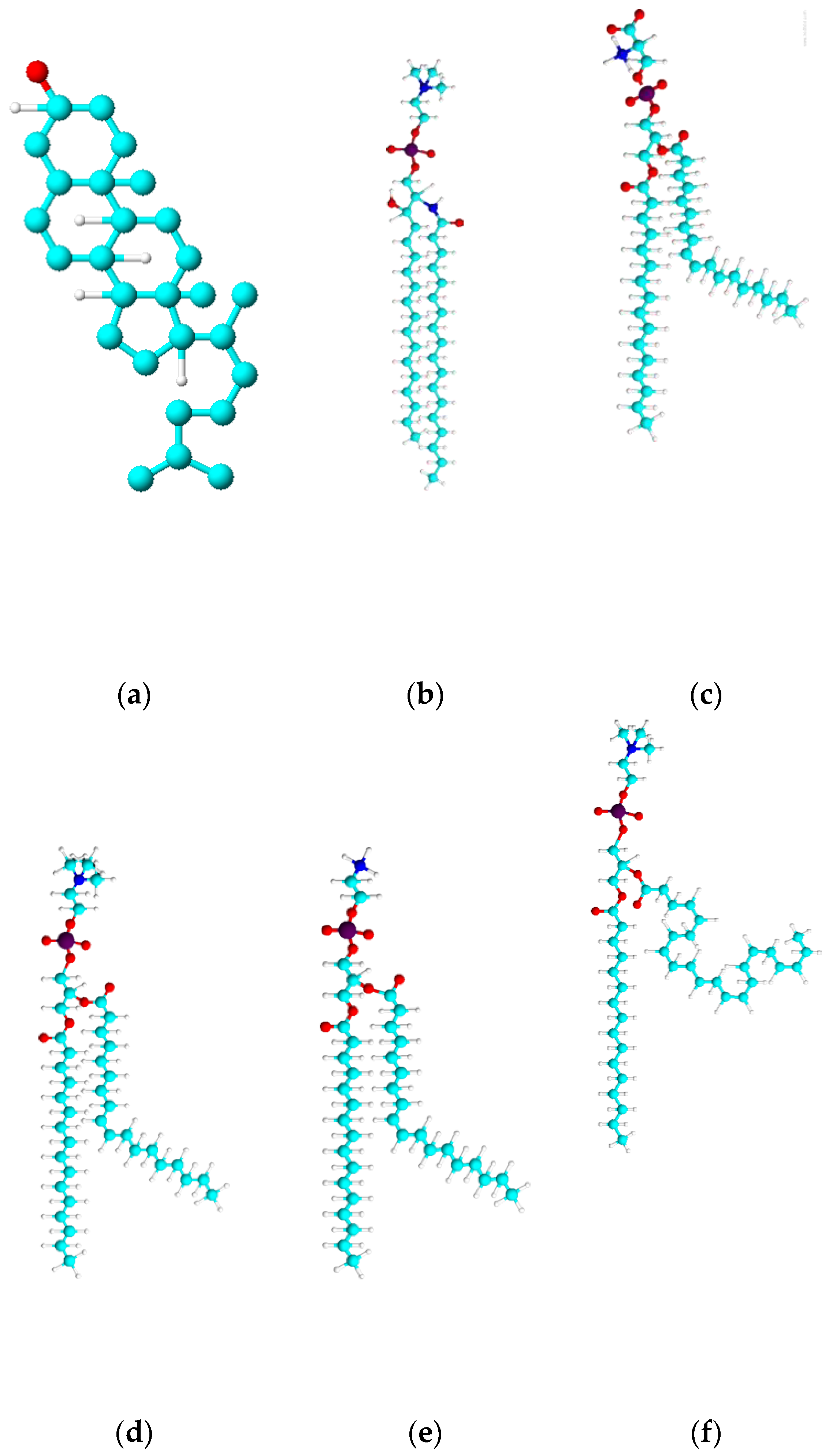
2.1. Materials
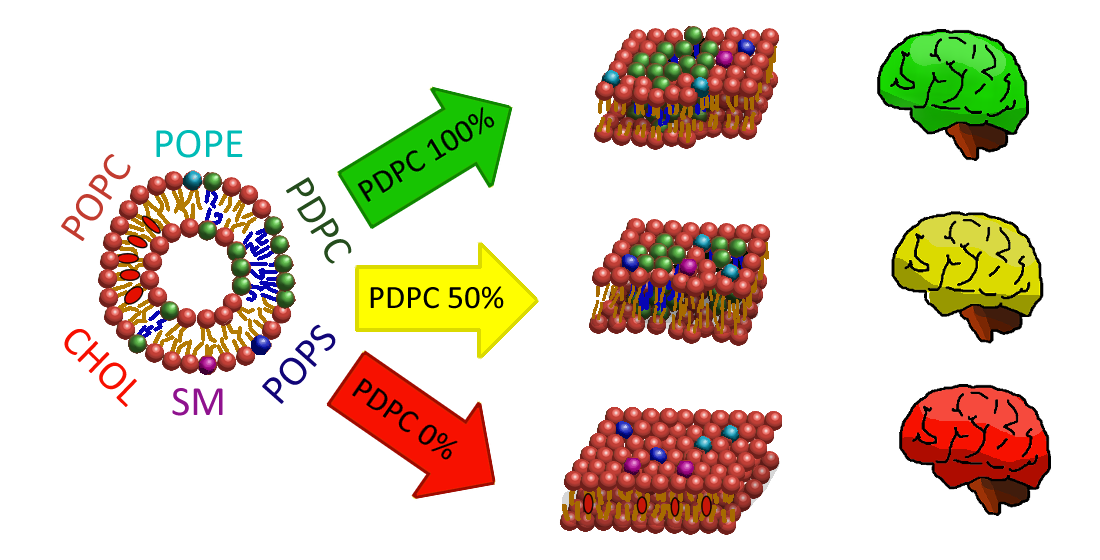
2.2. Model Lipid Membrane Preparation
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta Potential
2.3.3. Measurement of Ultrasound Velocity and Density
2.3.4. Data Analisis
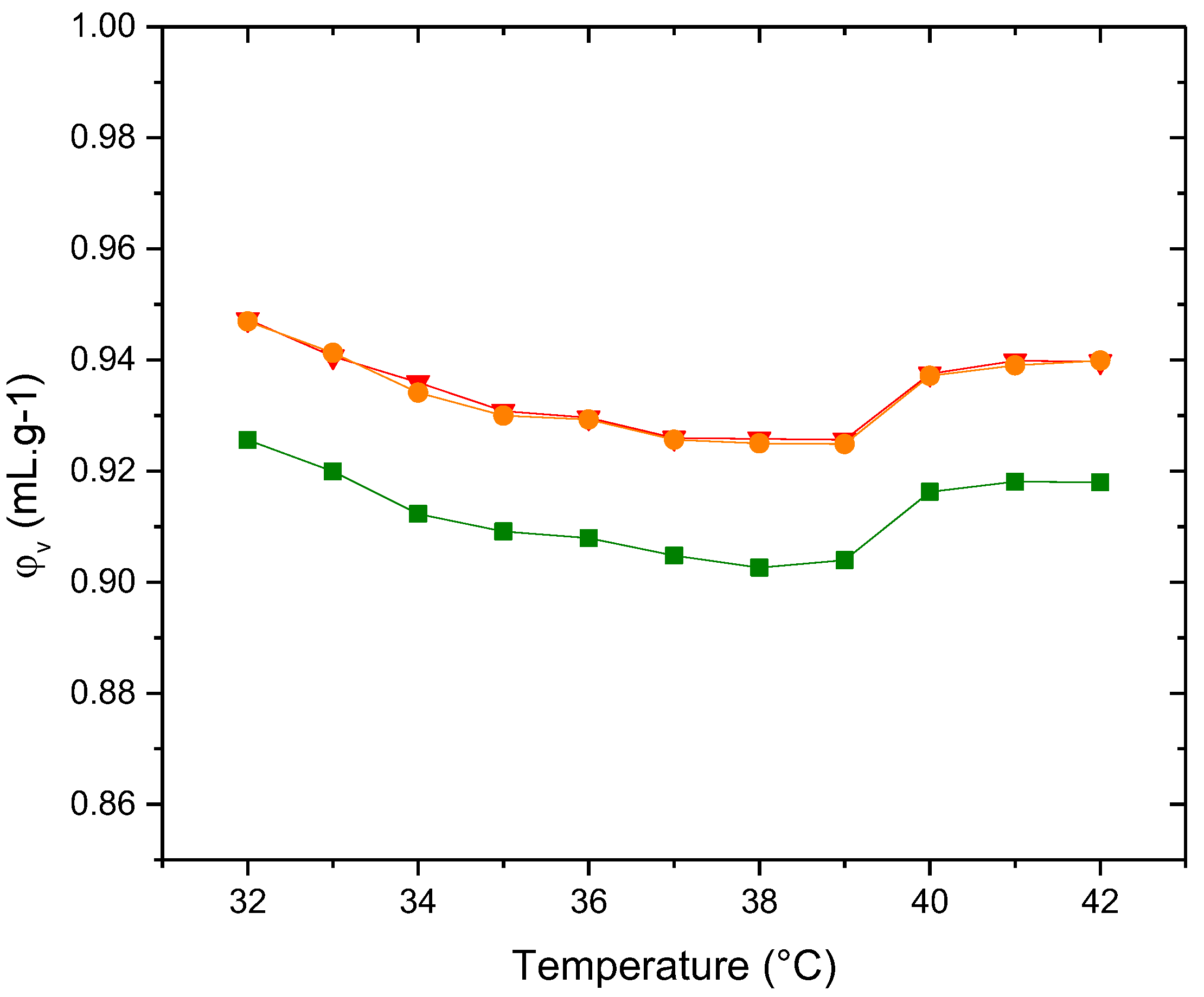
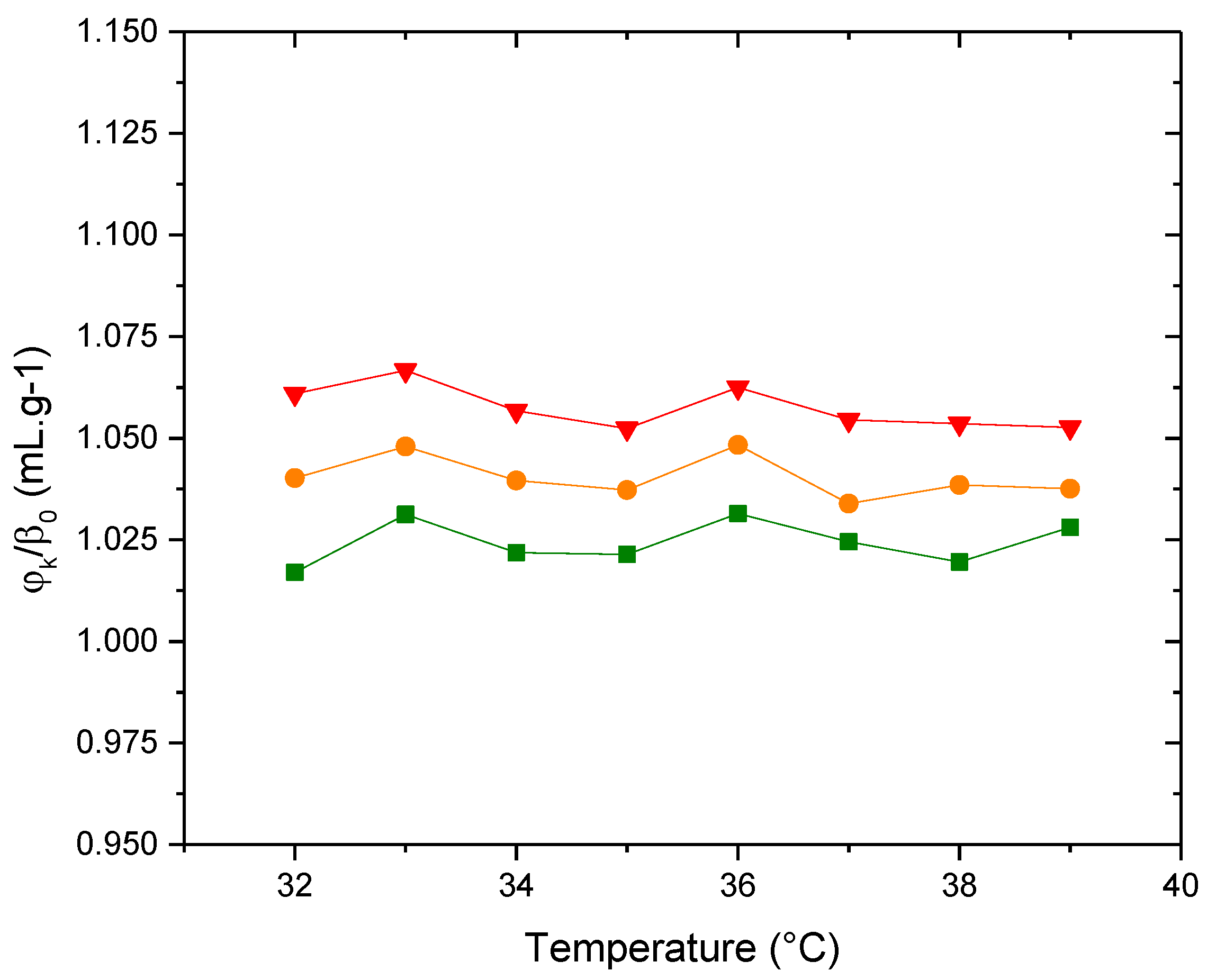
3. Results and discussion
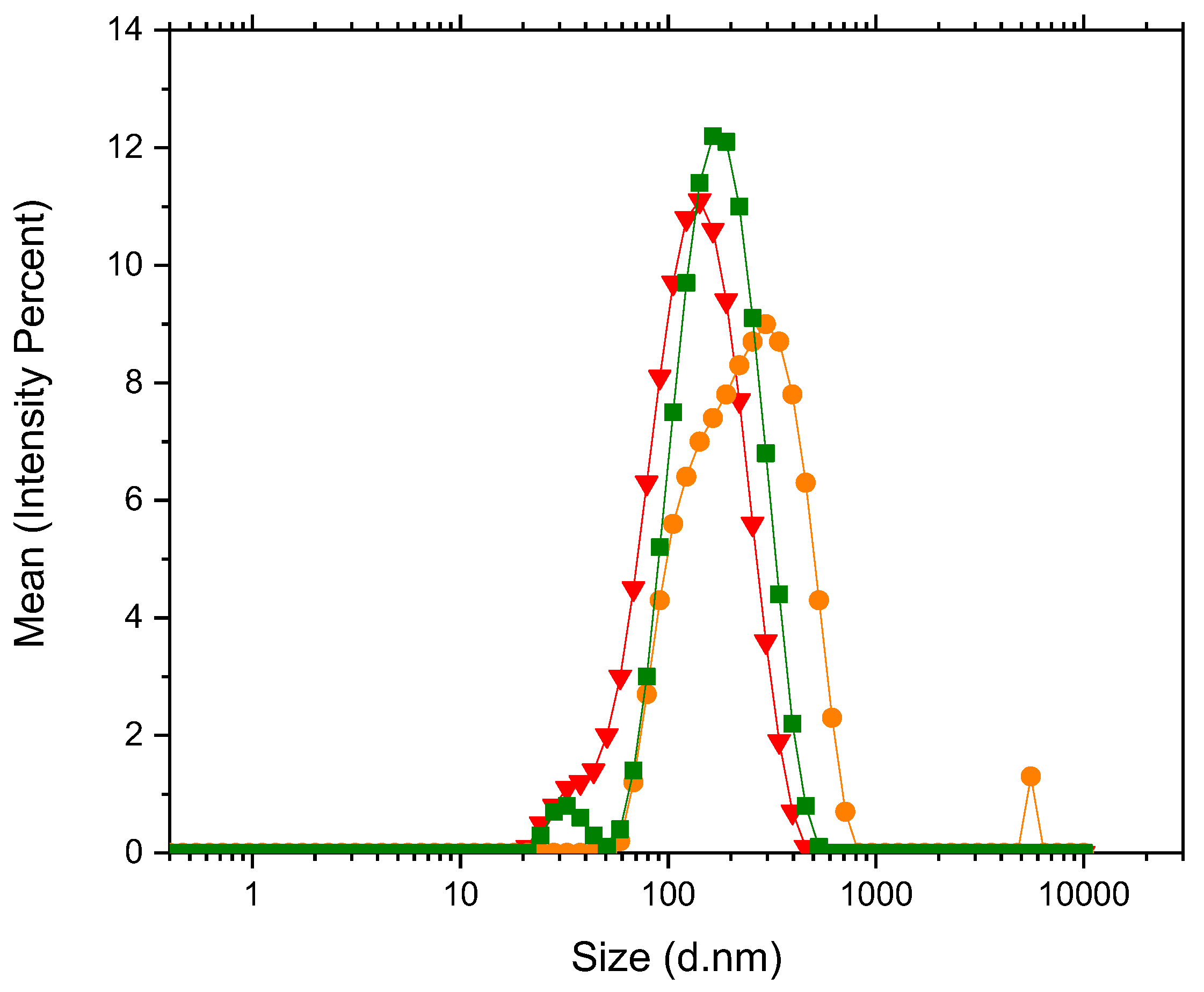
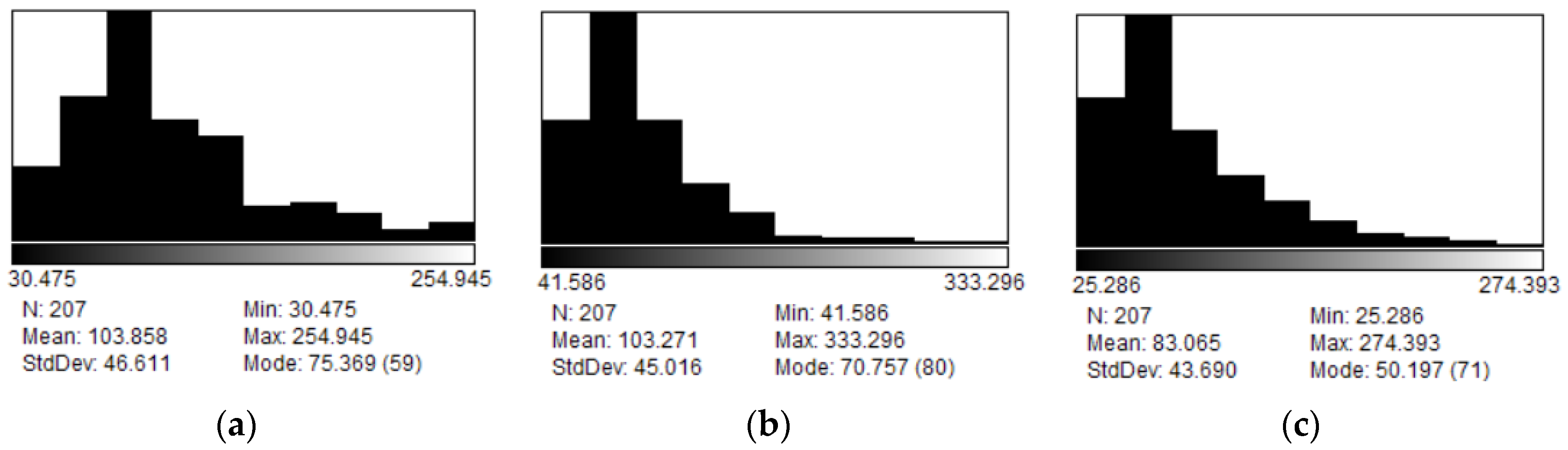
3.1. DLS
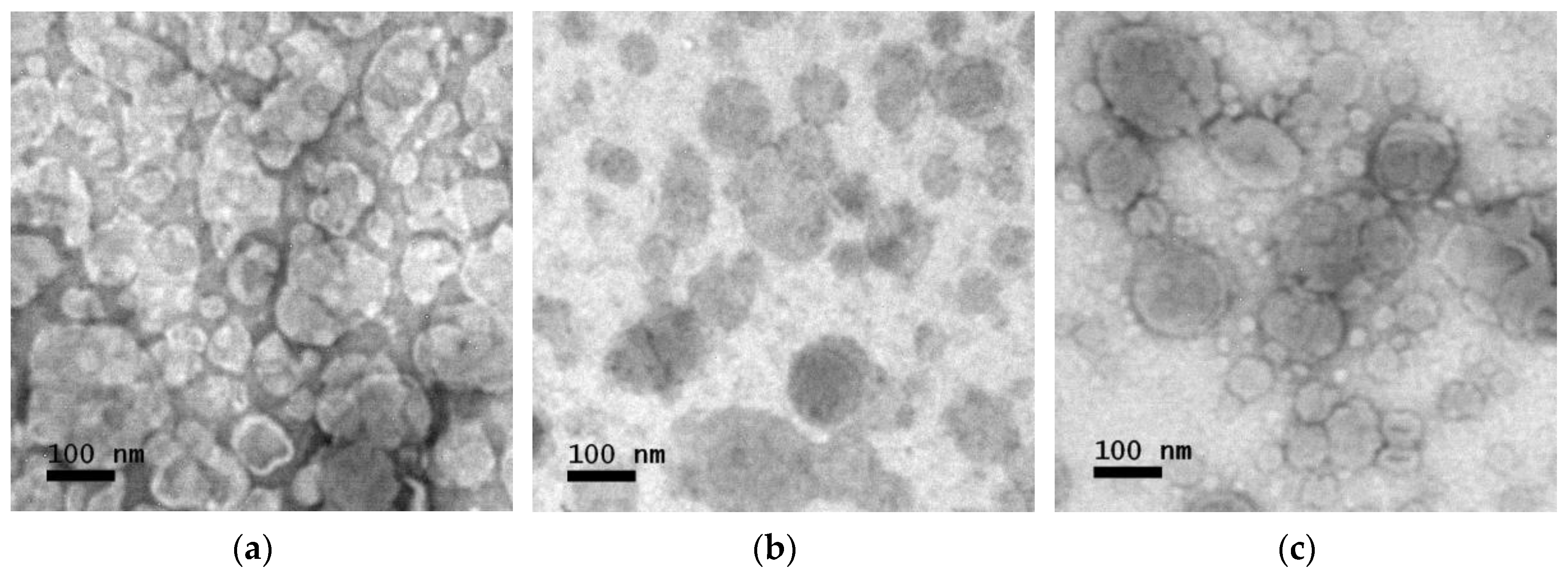
3.2. TEM
3.3. Consecutive Addition of Lipids
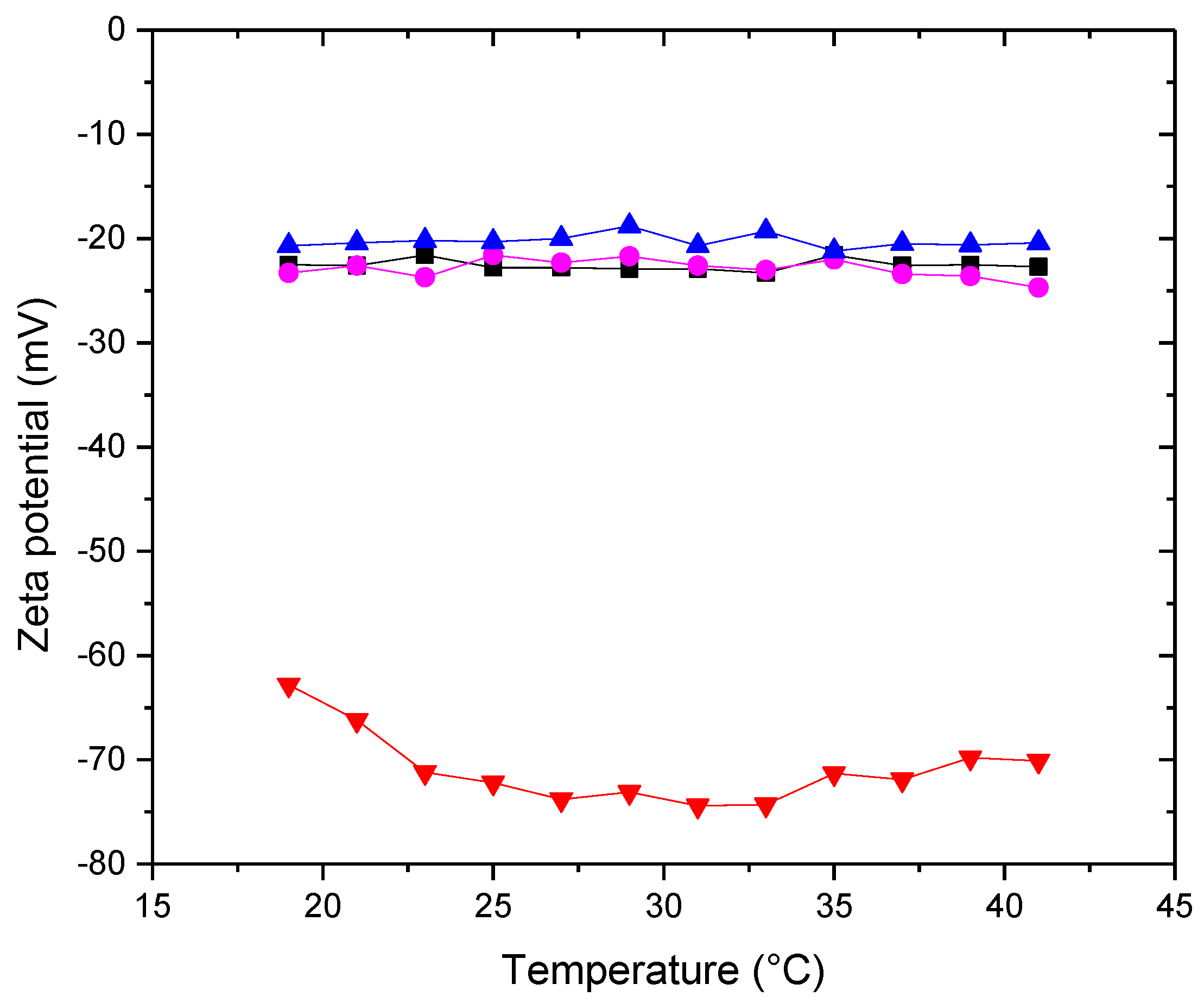
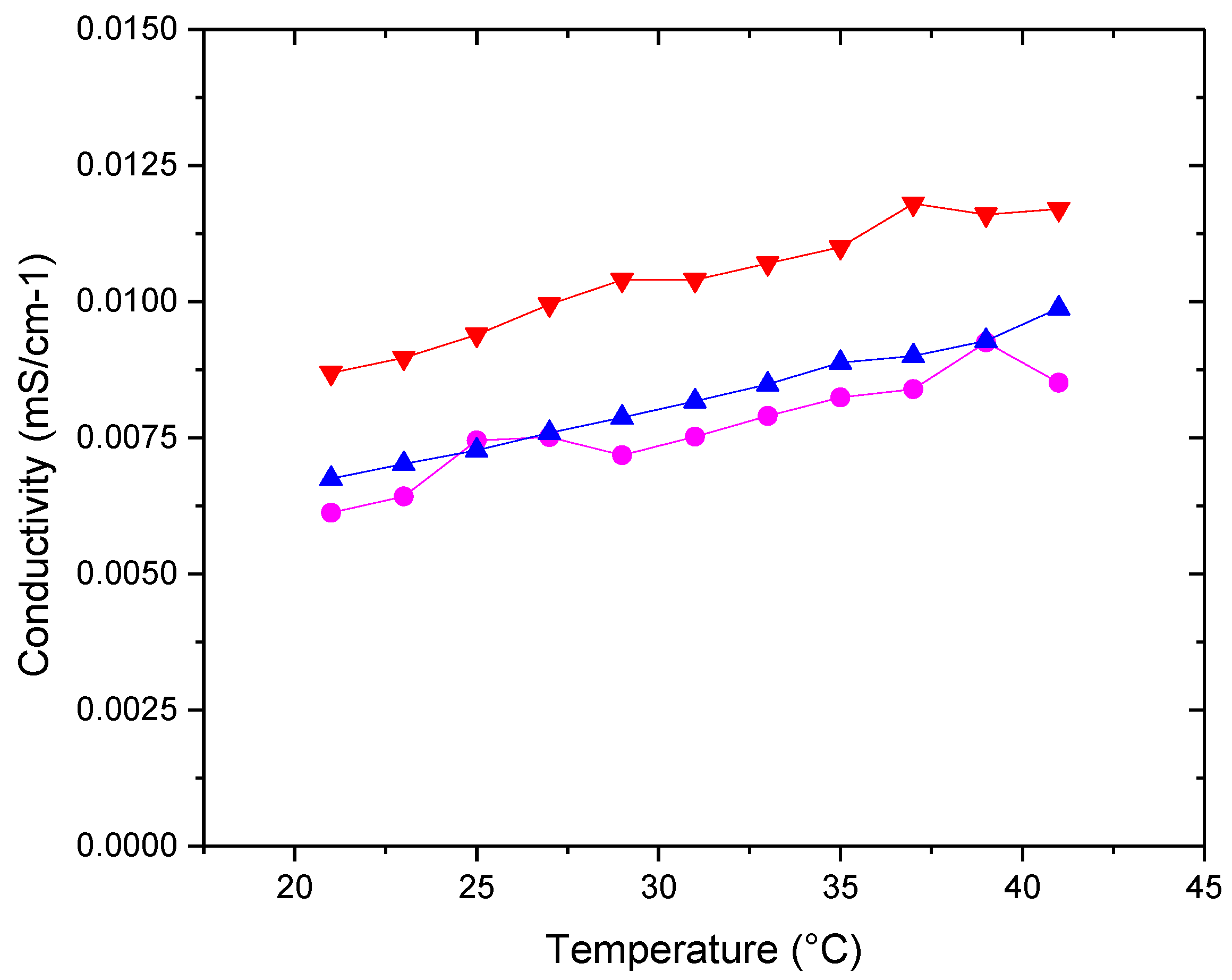
3.3.1. Zeta Potential and Conductivity
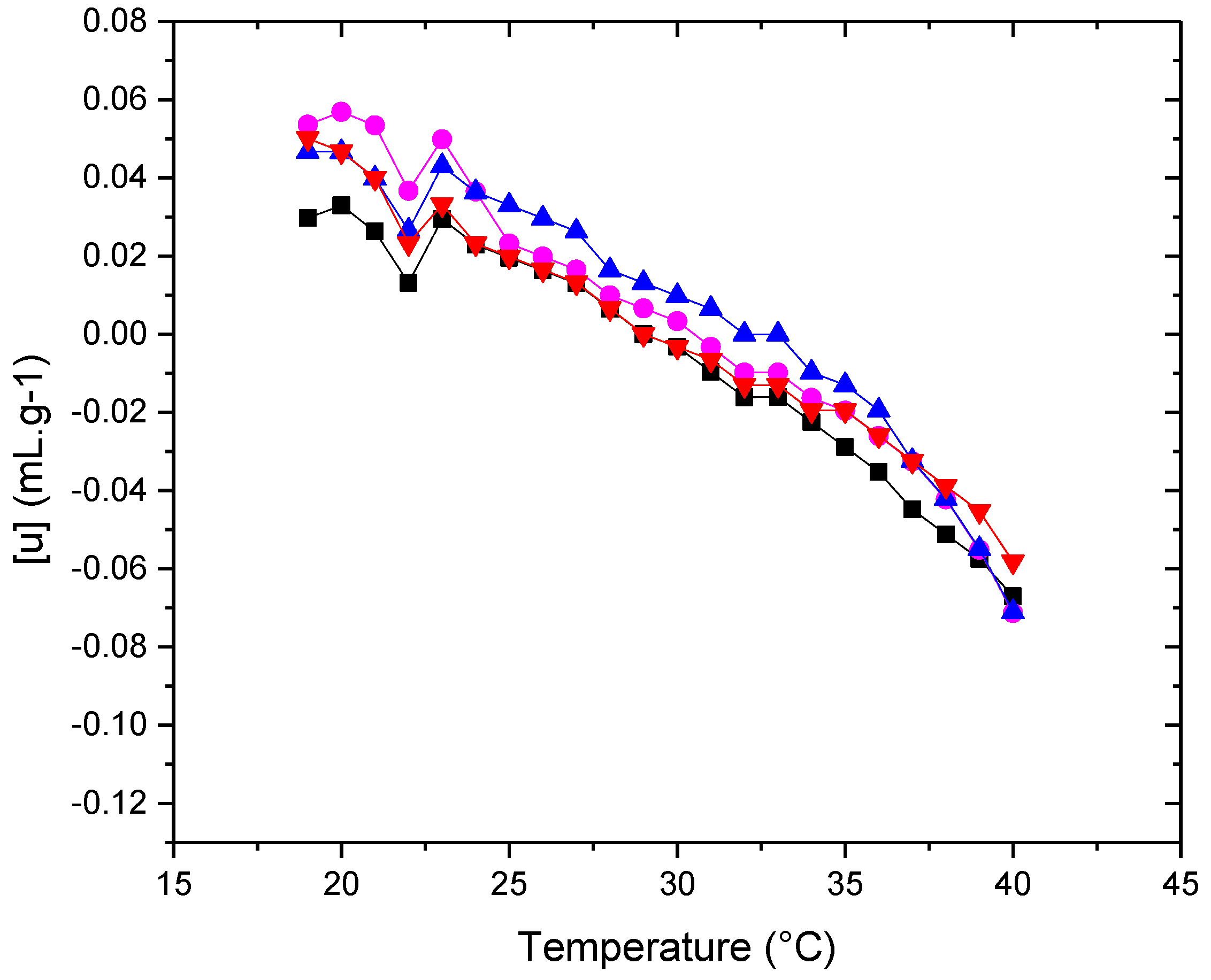
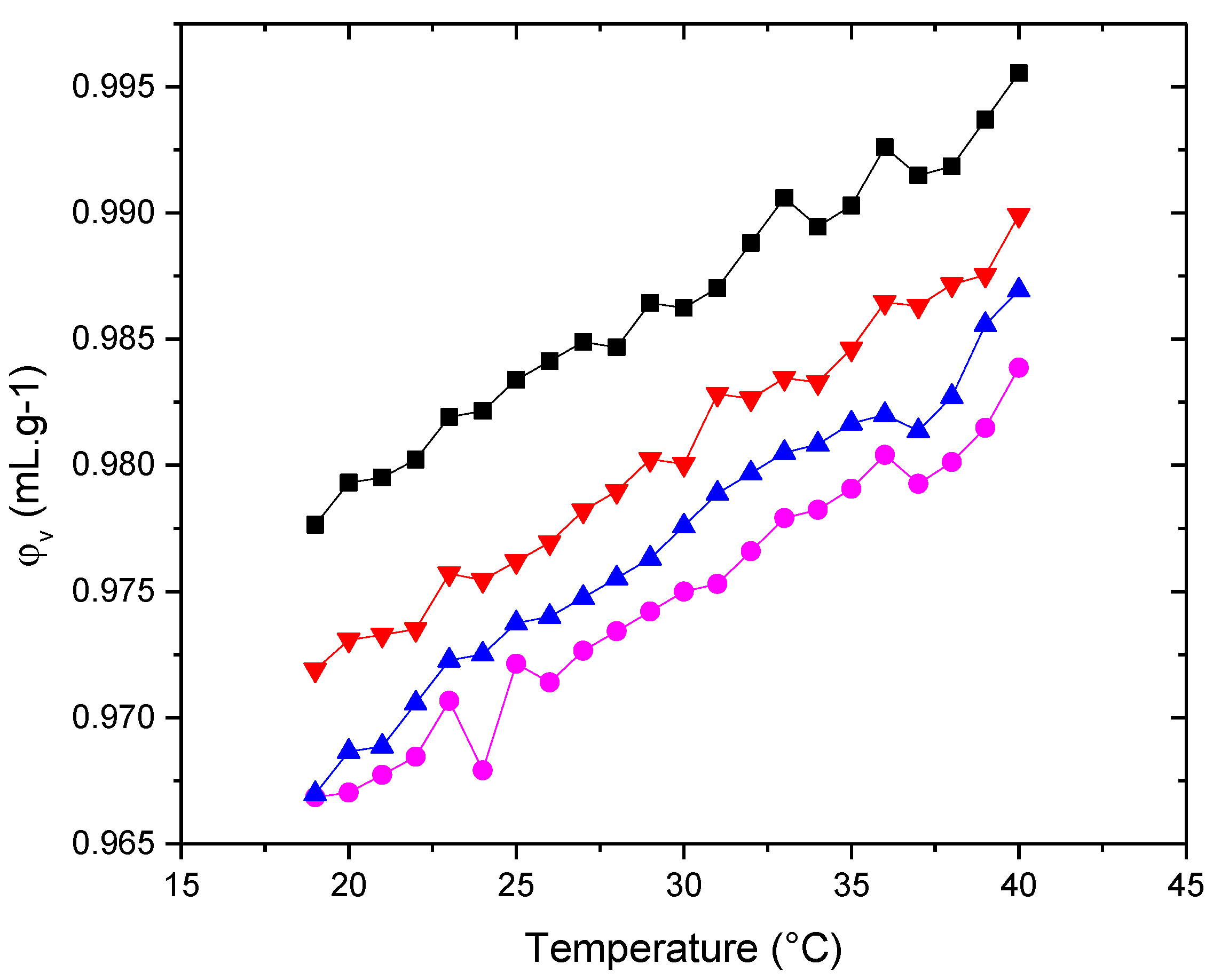
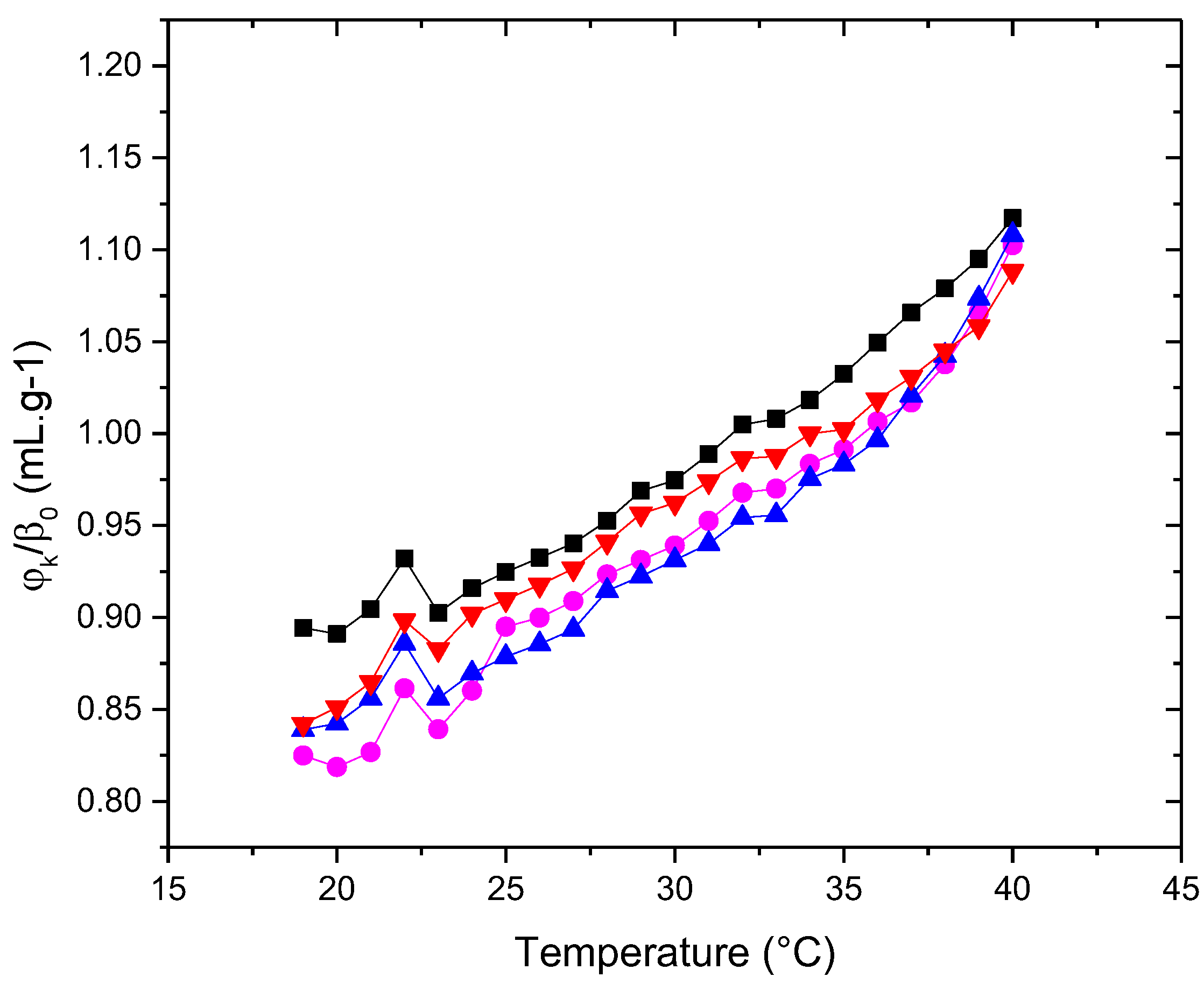
3.3.2. Molecular Acustic
3.4. Membranes with PDPC
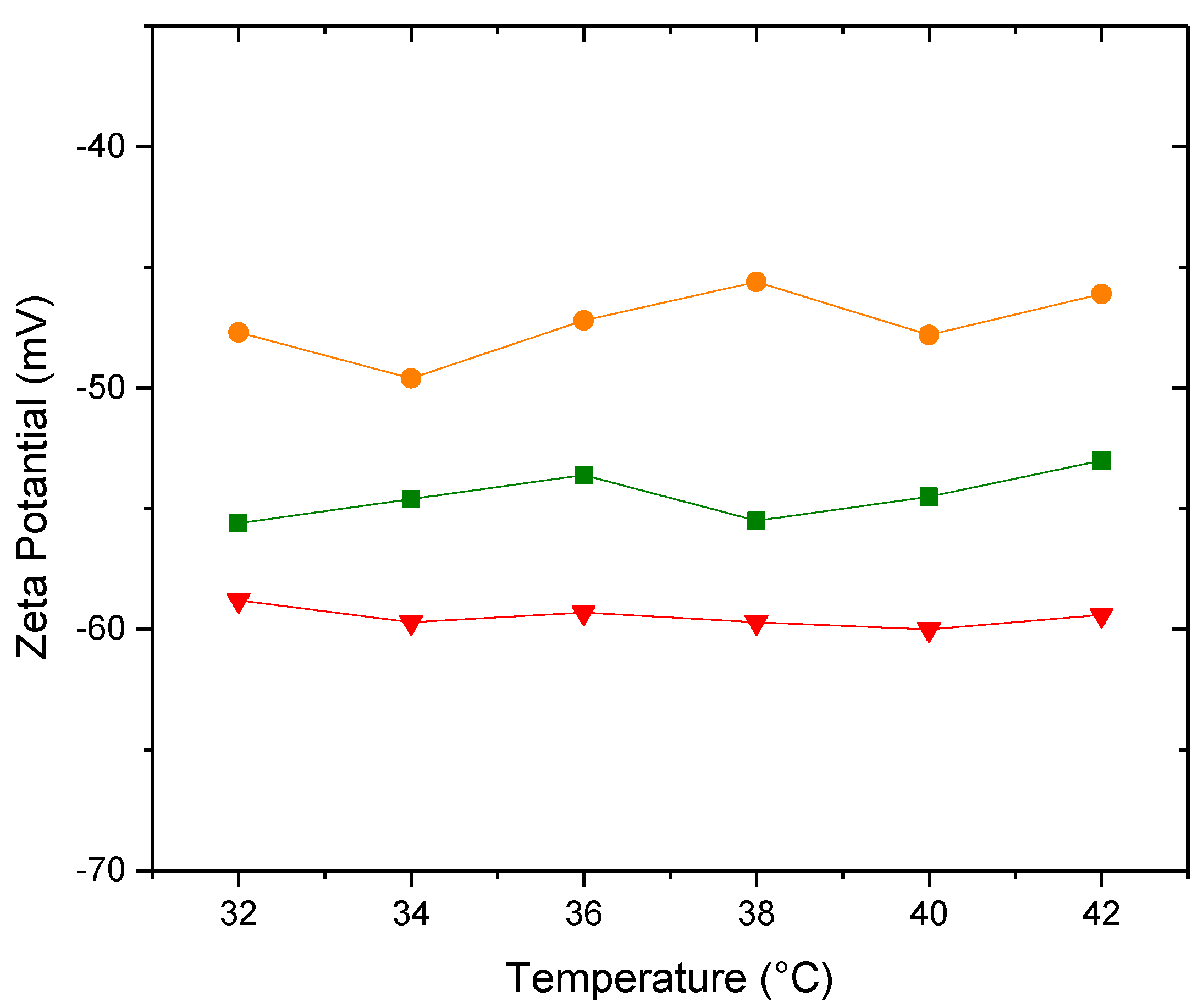
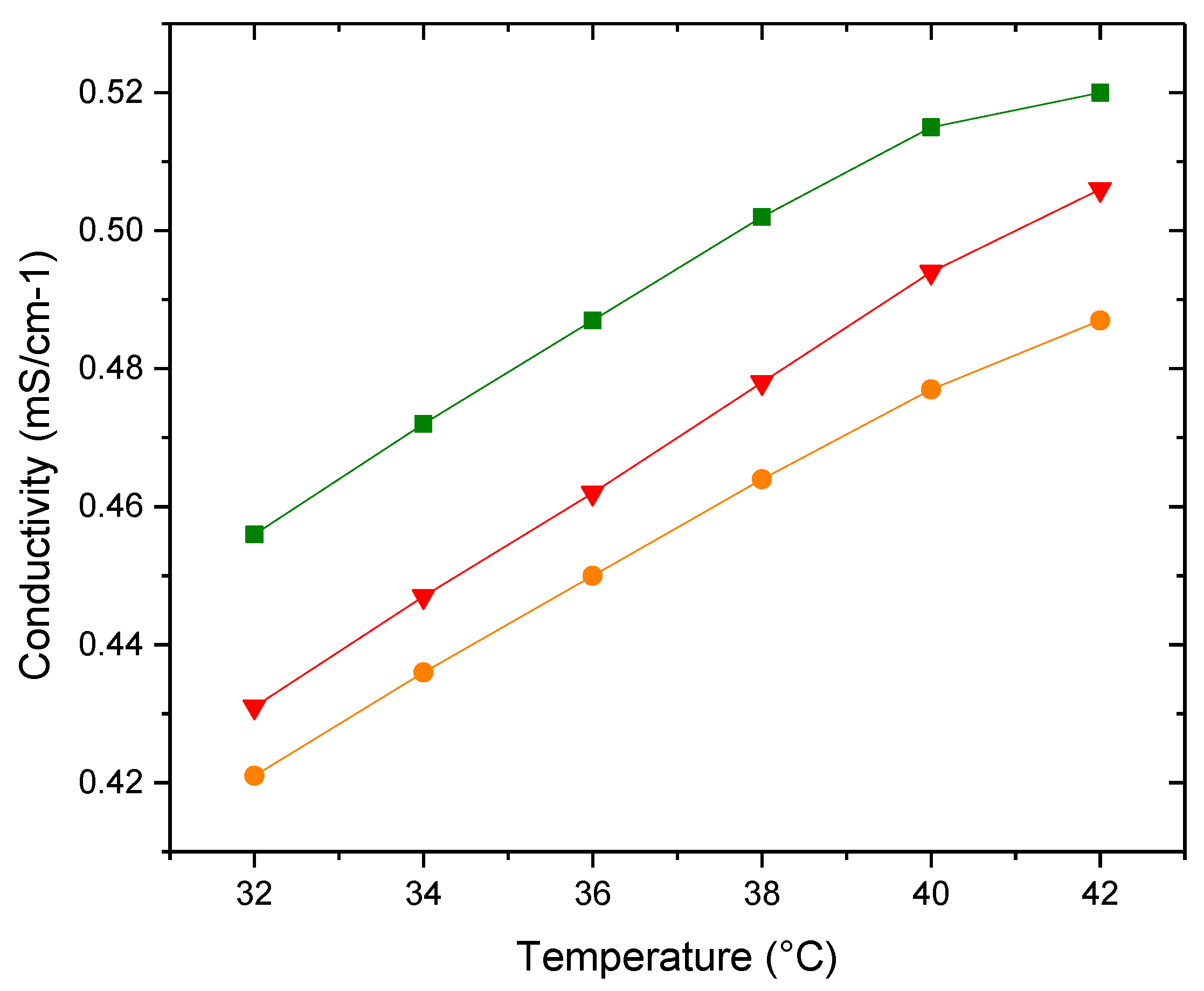
3.4.1. Zeta Potential and Conductivity
3.4.2. Molecular Acustic
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, J.S.; Sampson E., L. Lipid composition of the normal human brain: gray matter, white matter, and myelin. J. Lipid Res. 1965, 6, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.S.; Sampson E., L. Fatty acid and fatty aldehyde composition of the major brain lipids in normal human gray matter, white matter, and myelin. J. Lipid Res. 1965, 6, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata Ooi K-L; Vacy K. ; Boon W. C.. Fatty acids and beyond: Age and Alzheimer’s disease related changes in lipids reveal the neuro-nutraceutical potential of lipids in cognition. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 149, 105143. [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-S.; Hung, C.-F.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Chen, K.-C.; Chen, N.-C. Higher Serum DHA and Slower Cognitive Decline in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: Two-Year Follow-Up. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, A. J.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. What is the evidence for dietary-induced DHA deficiency in human brains? Nutrients 2022, 15, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schacky, C. Importance of EPA and DHA blood levels in brain structure and function. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousparou, C.; Fyrilla, M.; Stephanou, A.; Patrikios, I. DHA/EPA (Omega-3) and LA/GLA (Omega-6) as bioactive molecules in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, J. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): an ancient nutrient for the modern human brain. Nutrients 2011, 3, 529–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virk, R.; Cook, K.; Cavazos, A.; Wassall, S. R.; Gowdy, K. M.; Shaikh, S. R. ; How Membrane Phospholipids Containing Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Oxidation Products Orchestrate Lipid Raft Dynamics to Control Inflammation, J. Nutr., 2024, 154, 2862–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, I.; Paananen, R. O.; Fábián, B.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Javanainen, M. ; The Two Faces of the Liquid Ordered Phase. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13(5), 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.R.; Dumaual, A.C.; Castillo, A.; LoCascio, D.; Siddiqui, R.A.; Stillwell, W.; Wassall, S.R. ; Oleic and docosahexaenoic acid differentially phase separate from lipid raft molecules: A comparative NMR, DSC, AFM and detergent extraction study. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 1752–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, V. I.; Sierra, M. B.; Alarcon, L. M.; Verde, A. R.; Appignanesi, G. A.; Morini, M. A. A certain proportion of docosahexaenoic acid tends to revert structural and dynamical effects of cholesterol on lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edidin, M. Shrinknig patches and slippery rafts: scales of domains in the plasma membrane. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebecauer, M.; Amaro, M.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Sarmento, M.J.; Šachl, R.; Cwiklik L., Hof M. Membrane Lipid Nanodomains. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11259–11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnun, J. J.; Bittman, R.; Shaikh, S. R.; Wassall, S. R. DHA Modifies the Size and Composition of Raftlike Domains: A Solid-State 2H NMR Study. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybar, P.; Krivanek, R.; Samuely, T.; Lewis, R.N.A.H. , McElhaney, R.N., Study of the interaction of an α-helical transmembrane peptide with phosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes by means of densimetry and ultrasound velocimetry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2007, 1768, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hianik, T.; Passechnik, V.I. Bilayer Lipid Membranes: Structure and Mechanical Properties, 1st ed.; Academic Publishers: The Netherlands: Kluwer, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, M.B.; Pedroni, V.I.; Buffo, F.E.; Disalvo, E.A.; Morini, M.A. The use of zetapotential as a tool to study phase transitions in binary phosphatidylcholines mixtures. Colloids Surf., B 2016, 142, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.; Katti, P.; Biete, M.; Mungai, M.; AshShareef, S.; Neikirk, K.; Garza Lopez, E.; Vue, Z.; Christensen, T.A.; Beasley, H.K.; et al. A Universal Approach to Analyzing Transmission Electron Microscopy with ImageJ. Cells 2021, 10, 2177–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvazyan, A. P. ; Ultrasonic Velocimetry of Biological Compounds. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chern. 1991, 20, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PandeA. H.; Qin S.; Tatulian S.A., Membrane Fluidity Is a Key Modulator of Membrane Binding, Insertion, and Activity of 5-Lipoxygenase. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 4084–4094. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.C.; Straume, M.; Litman, B.J. Role of sn-1-saturated, sn-2-polyunsaturated phospholipids in control of membrane receptor conformational equilibrium: effects of cholesterol and acyl chain unsaturation on the metarhodopsin I / metarhodopsin II equilibrium. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morini, M.A.; Sierra, M.B.; Pedroni, V.I.; Alarcon, L.M.; Appignanesi, G.A.; . Disalvo, E.A. Influence of temperature, anions and size distribution on the zeta potential of DMPC, DPPC and DMPE lipid vesicles. Colloids Surf., B 2015, 131, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, S.A.; Bostick, D.; Berkowitz, M.L. Complexation of phosphatidylcholine lipids with cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magarkar, A.; Dhawan, V., Kallinteri; Rog., T., Bunker A. Cholesterol level affects surface charge of lipid membranes in saline solution. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, M. B.; Pedroni, V. I.; Buffo, F. E.; Disalvo, E. A.; Morini, M. A. The use of zeta potential as a tool to study phase transitions in binary phosphatidylcholines mixtures. Colloids Surf. B. 2016, 142, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic A., A.; Balanc B., D.; Ota, A.; Grabnar P., A.; Djordjevic V., B.; Savikin K., P.; Bugarski B., M.; Nedovic V., A.; Ulrih N., P. Comparative effects of cholesterol and β-sitosterol on the liposome membrane characteristics. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1800039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Aranda, F.; Ortiz, A.; Martínez, V.; Carvajal, M.; Teruel, J. Molecular aspects of the interaction between plants sterols and DPPC bilayers: an experimental and theoretical approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, H. A.; Disalvo, A.; Frías, M.d.l.A. Effect of cholesterol on the surface polarity and hydration of lipid interphases as measured by Laurdan fluorescence: new insights. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 178, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.; Olivia, R.; Del Vecchio, P.; Paolantoni, M.; Moressi, A.; Sassi, P. DMSO-induced perturbation of thermotropic properties of cholesterol-containing DPPC liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 3024–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharakoz, D. P.; Colotto, A.; Lohner, K.; Laggner, P. Fluid-gel interphase line tension and density fluctuations in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine multilamellar vesicles: an ultrasonic study. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 1993. 97, 9844–9851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimburg, T. Mechanical aspects of membrane thermodynamics. Estimation of the mechanical properties of lipid membranes close to the chain melting transition from calorimetry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1415, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, G.; Lonez, C.; Vandenbranden, M.; Jestin, J.; Radulescu, A.; Ruysschaert, J. ; Gutberlete,T. Stalk-free membrane fusion of cationic lipids via an interdigitated phase. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7243–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hianik, T.; Rybár, P.; Krivánek, R.; Petríková, M.; Roudna, M.; Apell, H. Specific volume and compressibility of bilayer lipid membranes with incorporated Na,K-ATPase. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2011, 30, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halstenberg, S.; Heimburg, T.; Hianik, T.; Kaatze, U.; Krivanek, R. Cholesterol-Induced Variations in the Volume and Enthalpy Fluctuations of Lipid Bilayers. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitaku, S.; Ikegami, A.; Sakanishi, A. Ultrasonic studies of lipid bilayer. phase transition in synthetic phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Biophys. Chem. 1978, 8, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde A., R. , Sierra M. B., Alarcón L. M., Pedroni V. I., Appignanesi, G. A. Morini M.A. Experimental and computational studies of the effects of free DHA on a model phosphatidylcholine membrane. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 217, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




