Submitted:
17 October 2024
Posted:
17 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
LC Sequences
Statistics
Structural Analysis
Results
N-Glycosylation Sequons are Enriched in AL-Associated κ LCs
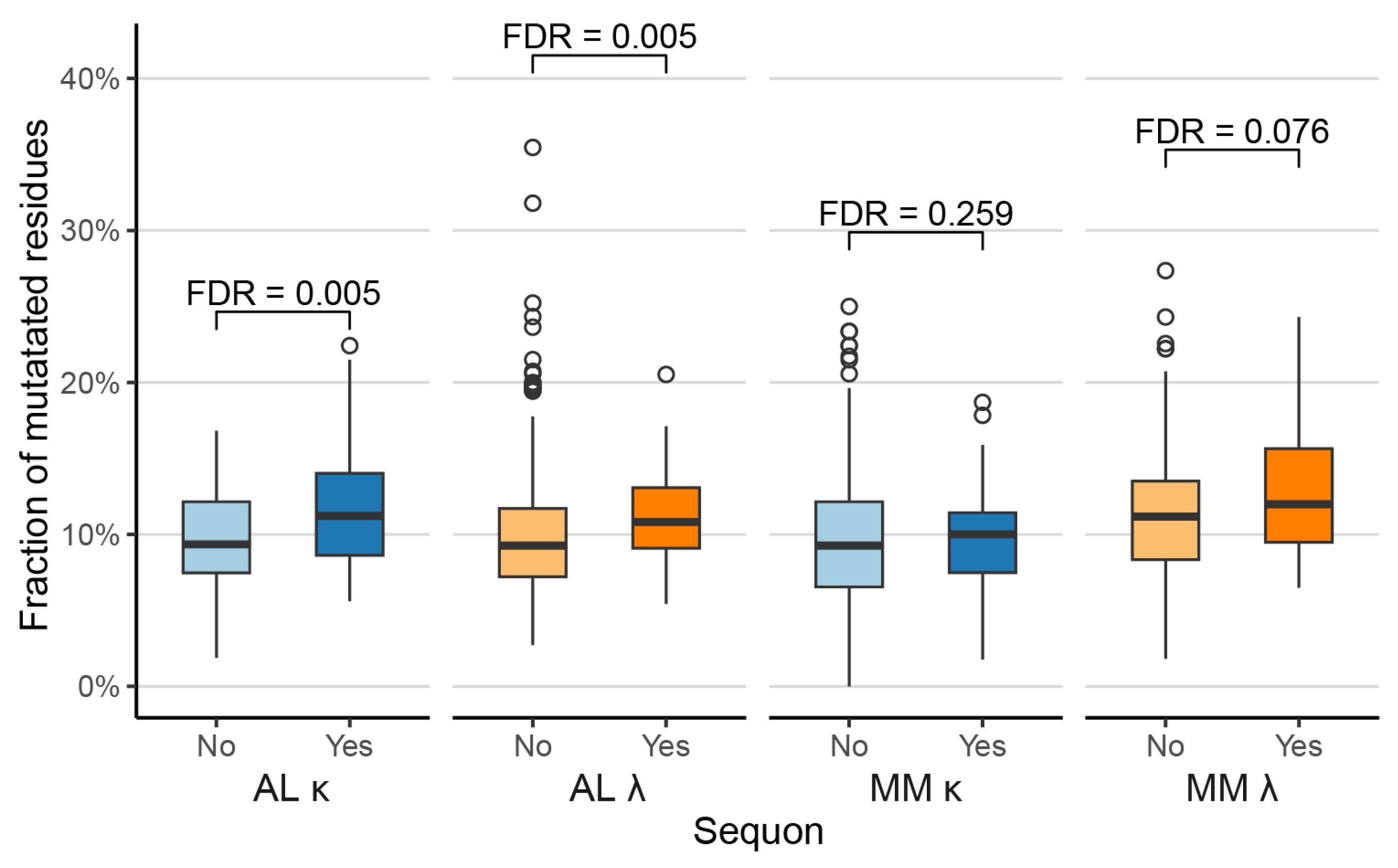
Sequons are Associated with Increased Proportions of Mutated Residues
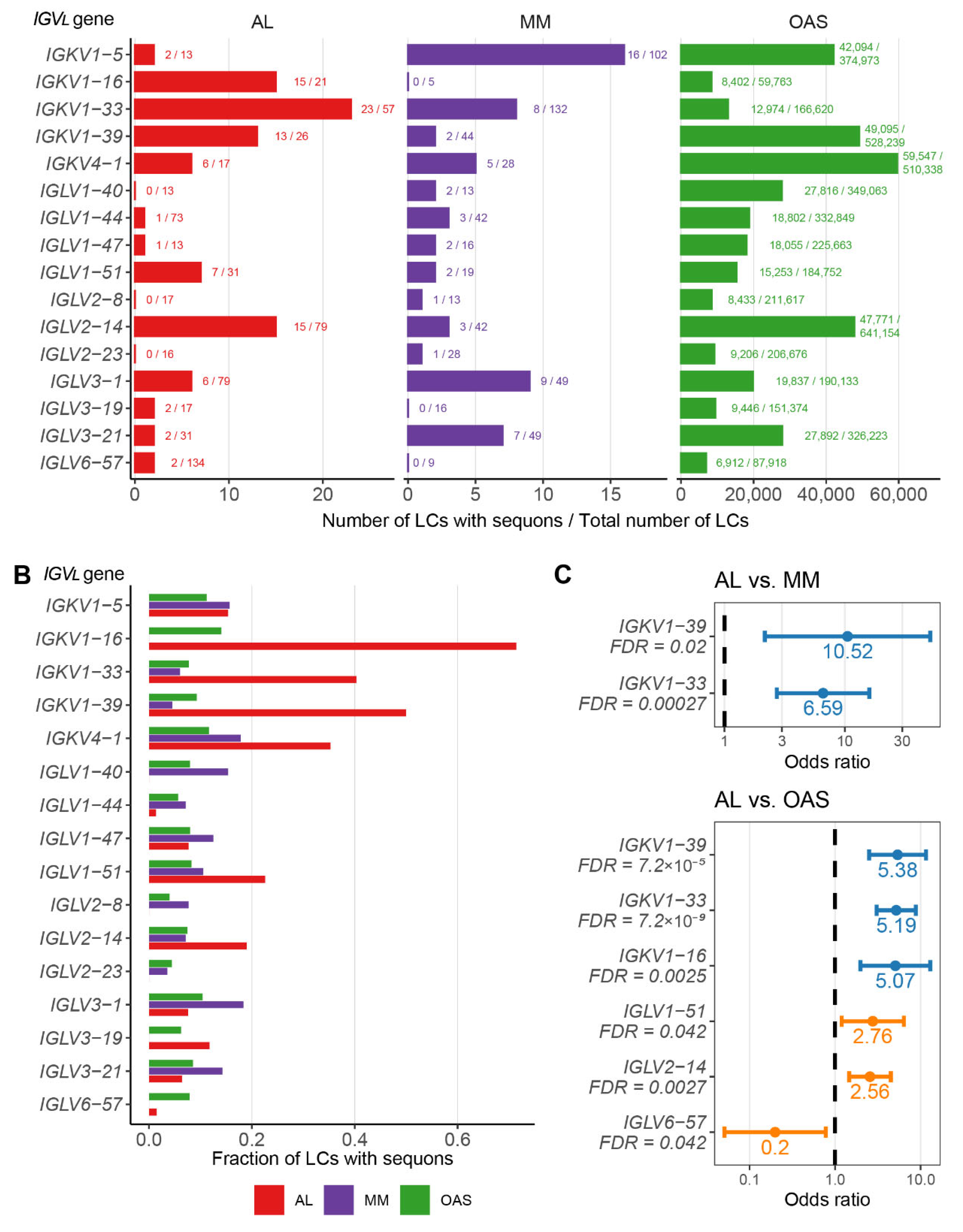
AL LCs Derived from a Subset of Precursor Genes are Enriched in Sequons
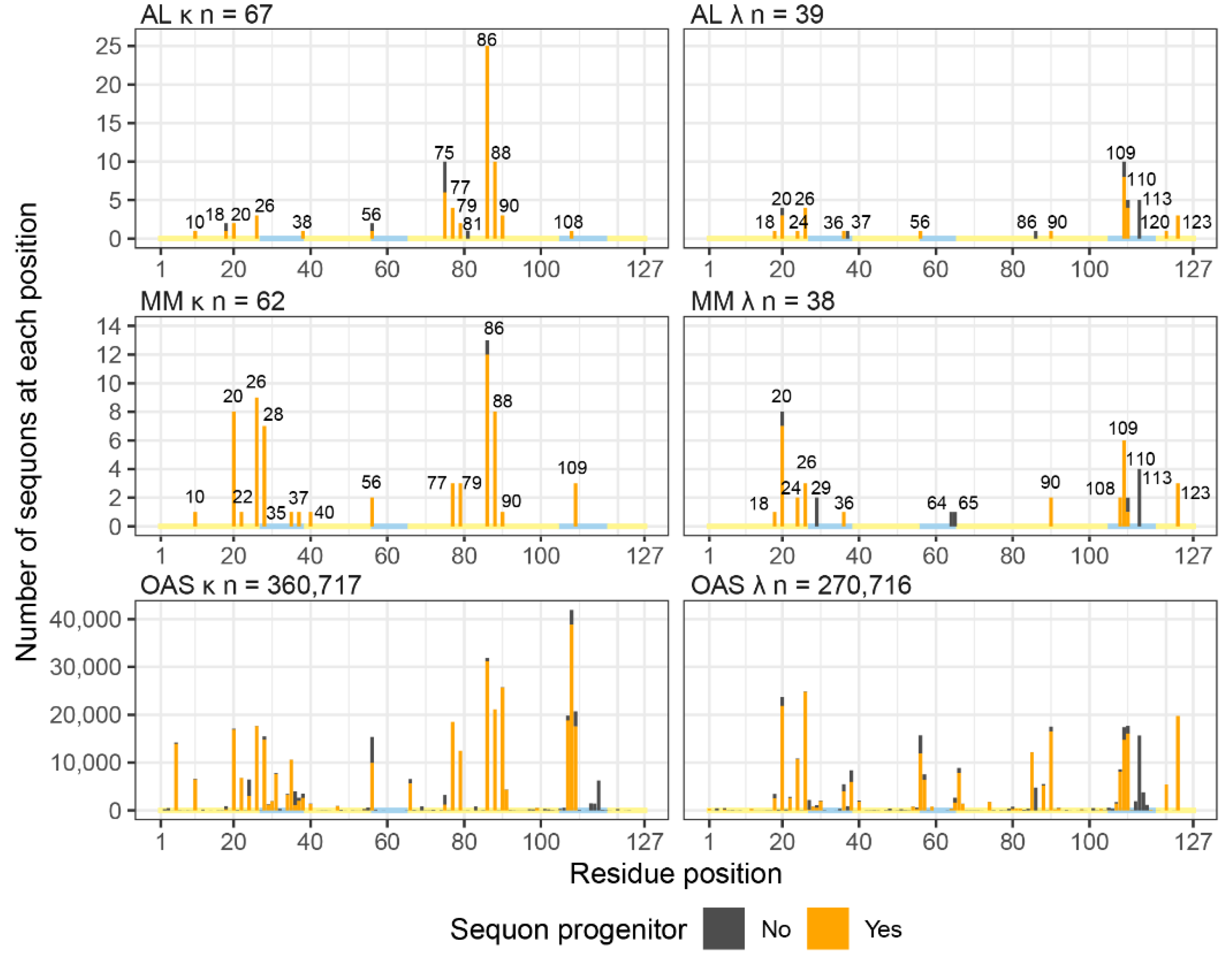
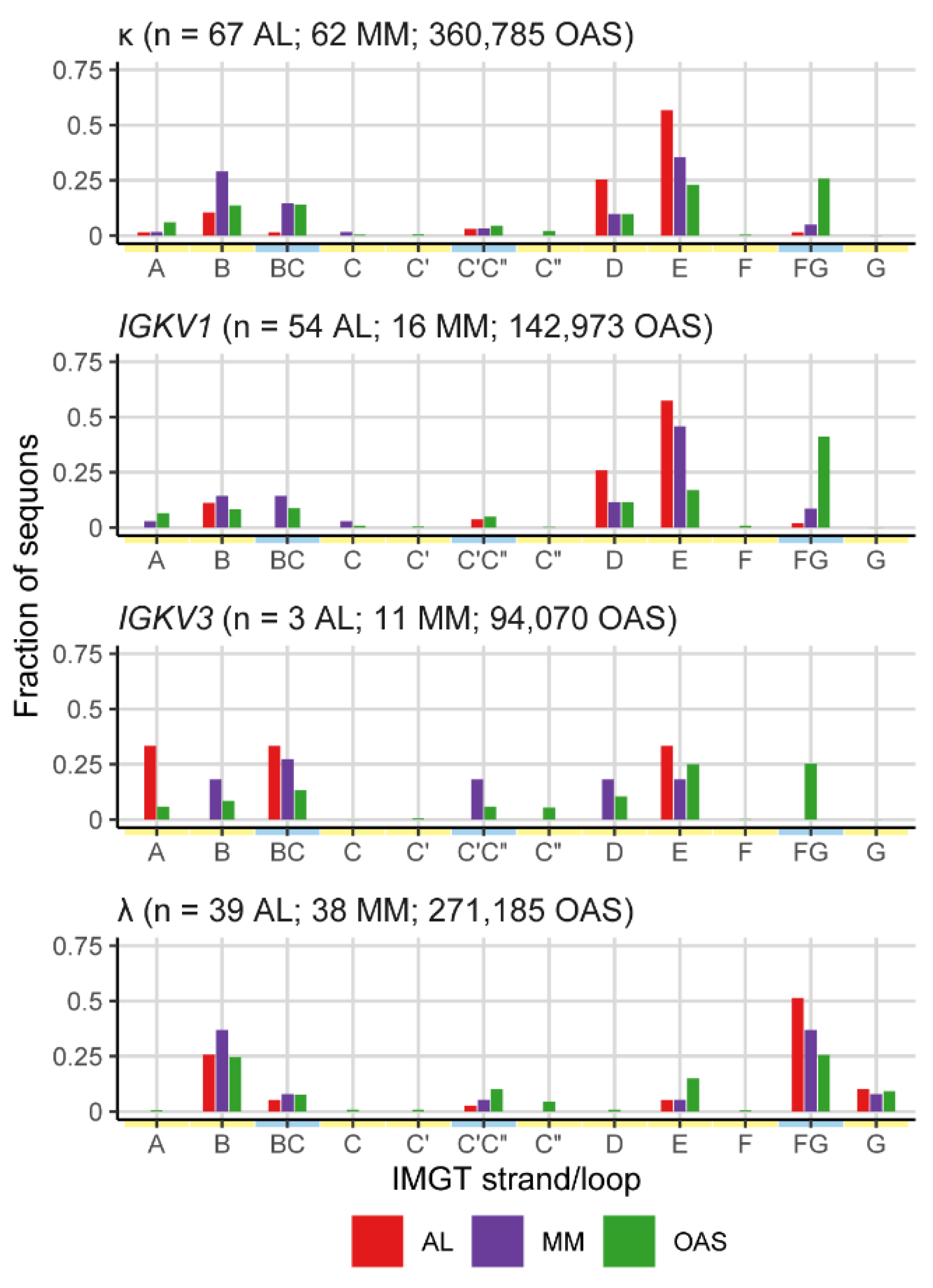
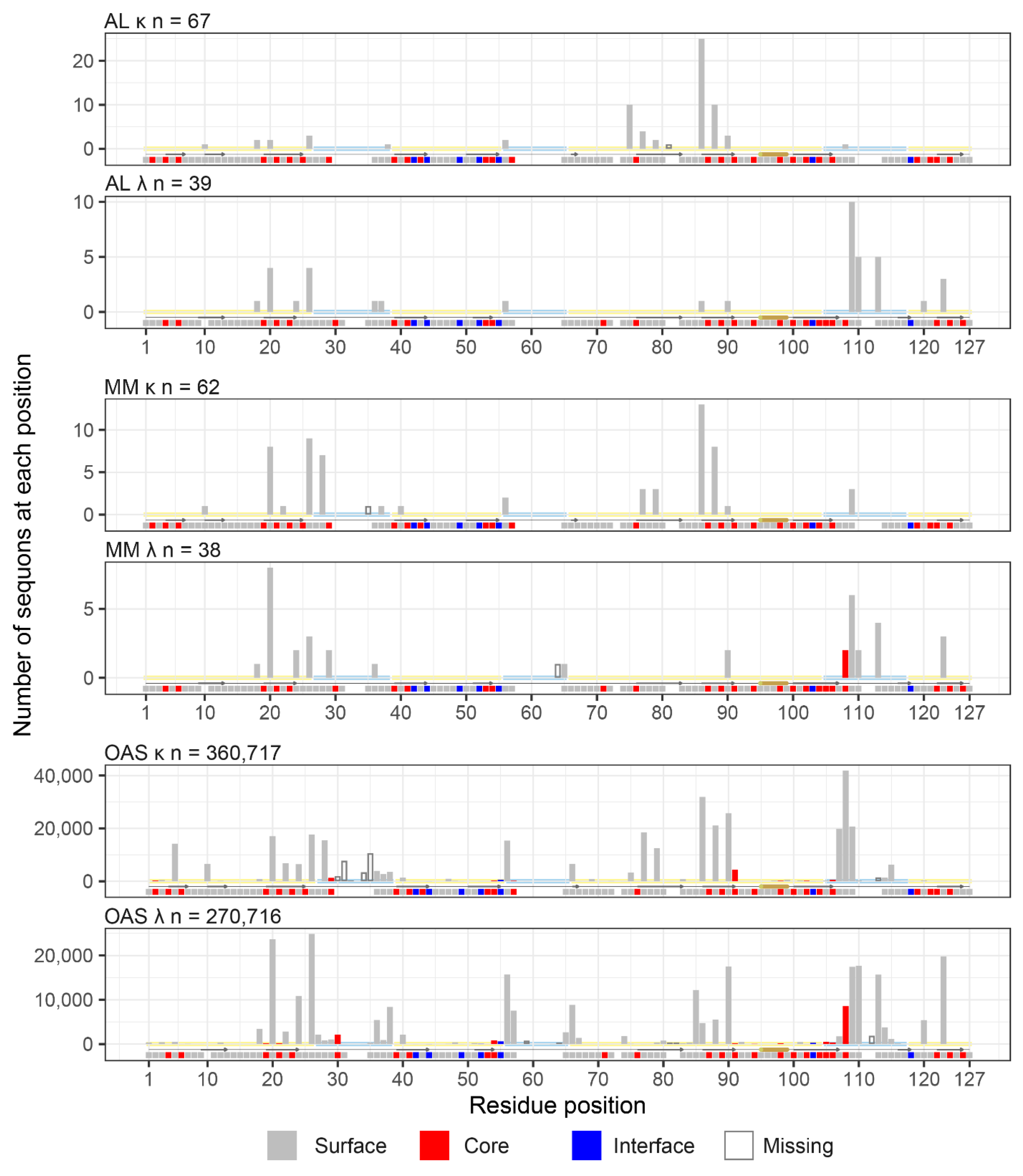
Sequons in AL and MM LCs Occur in Similar Positions
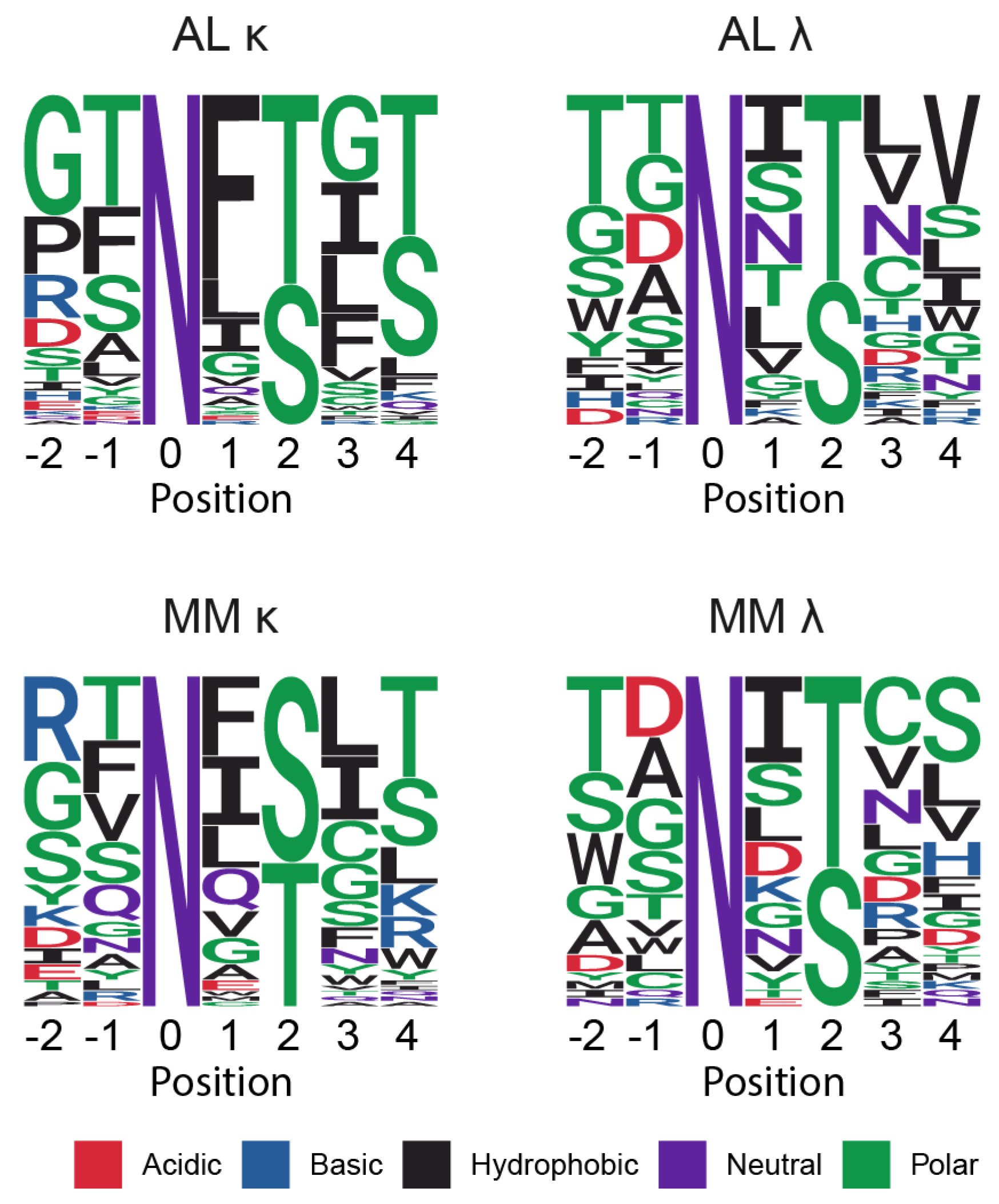
Sequons Occur in Similar Sequence Contexts
NxC Sequons Occur in LC CDRs
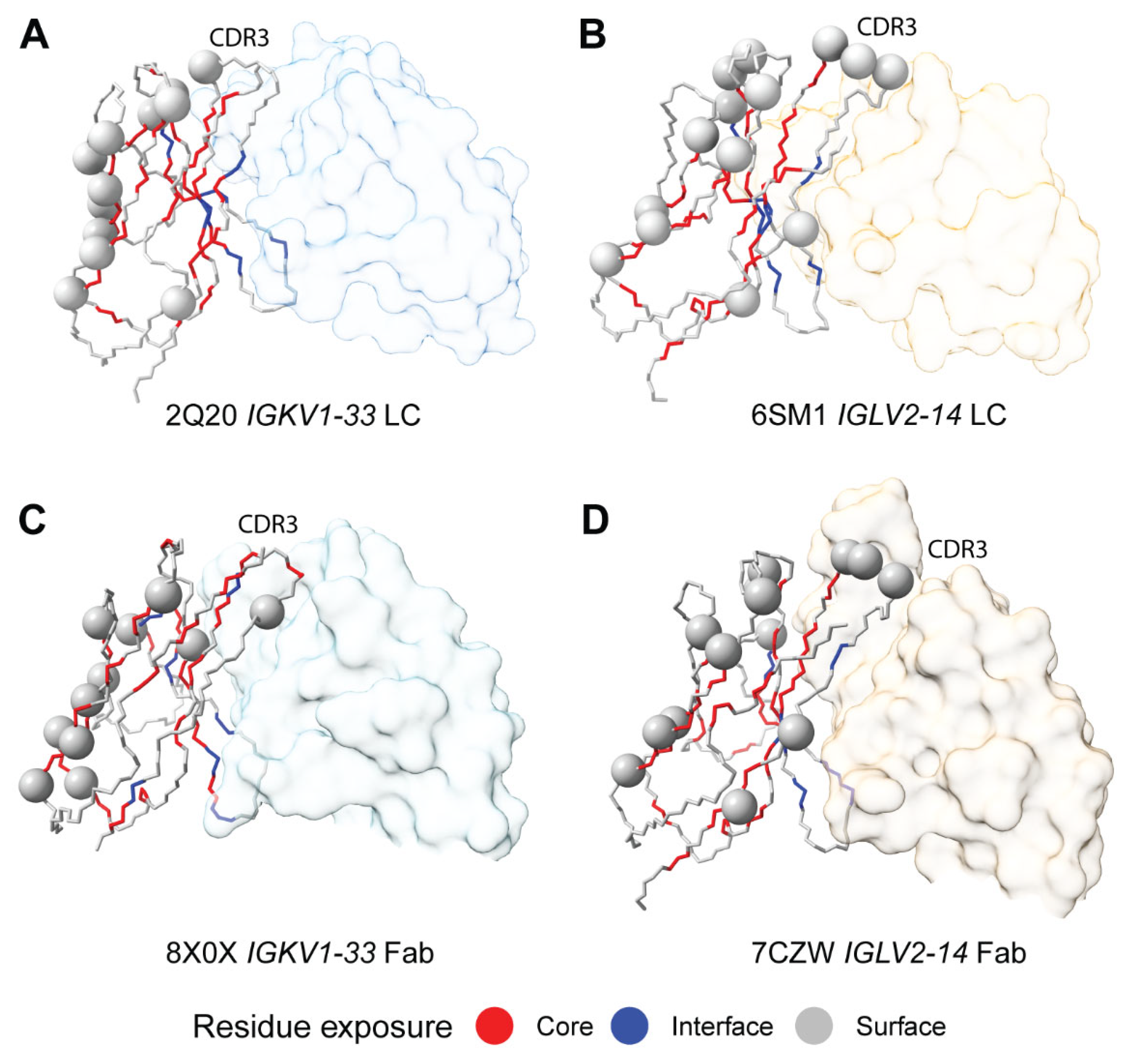
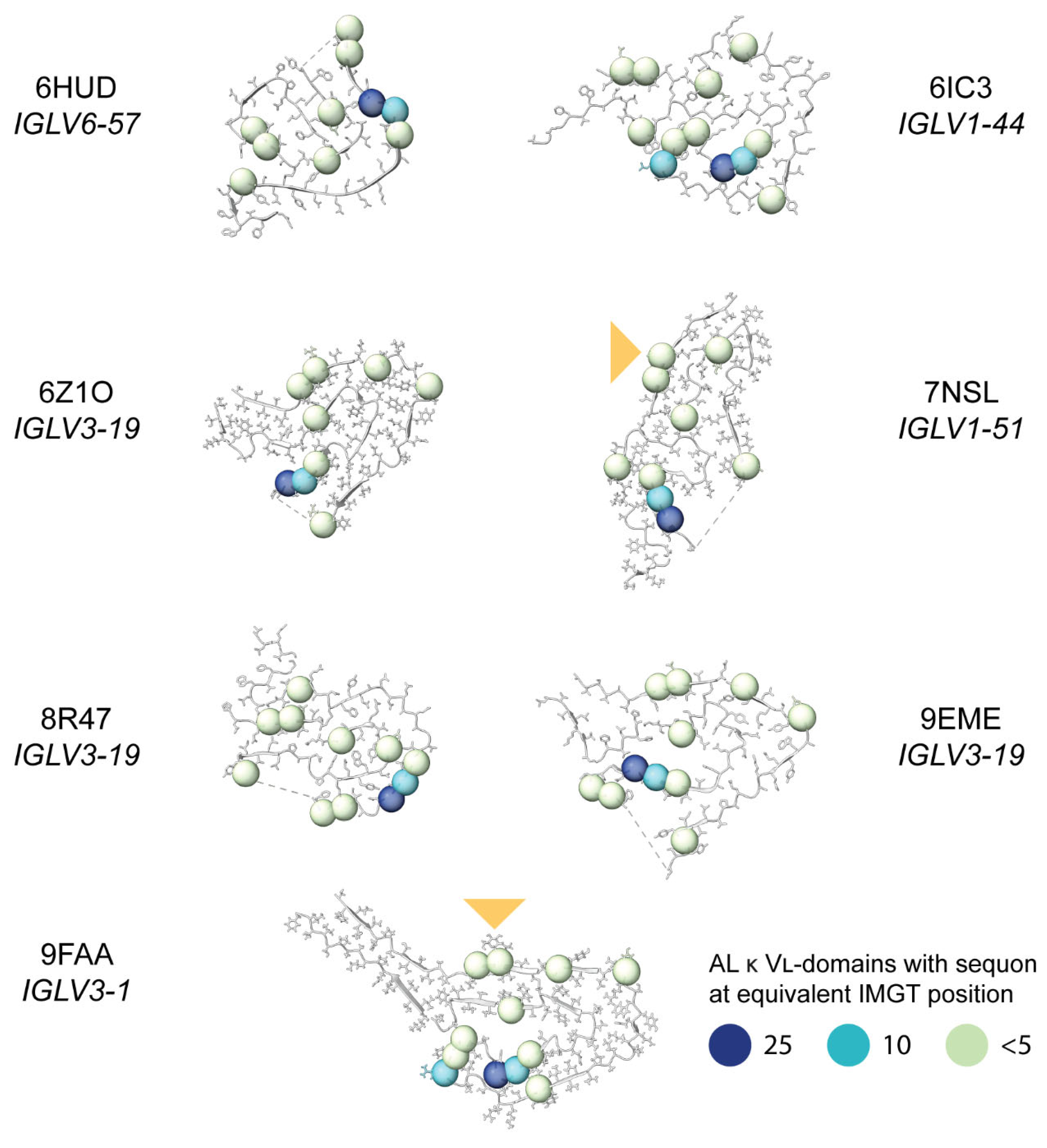
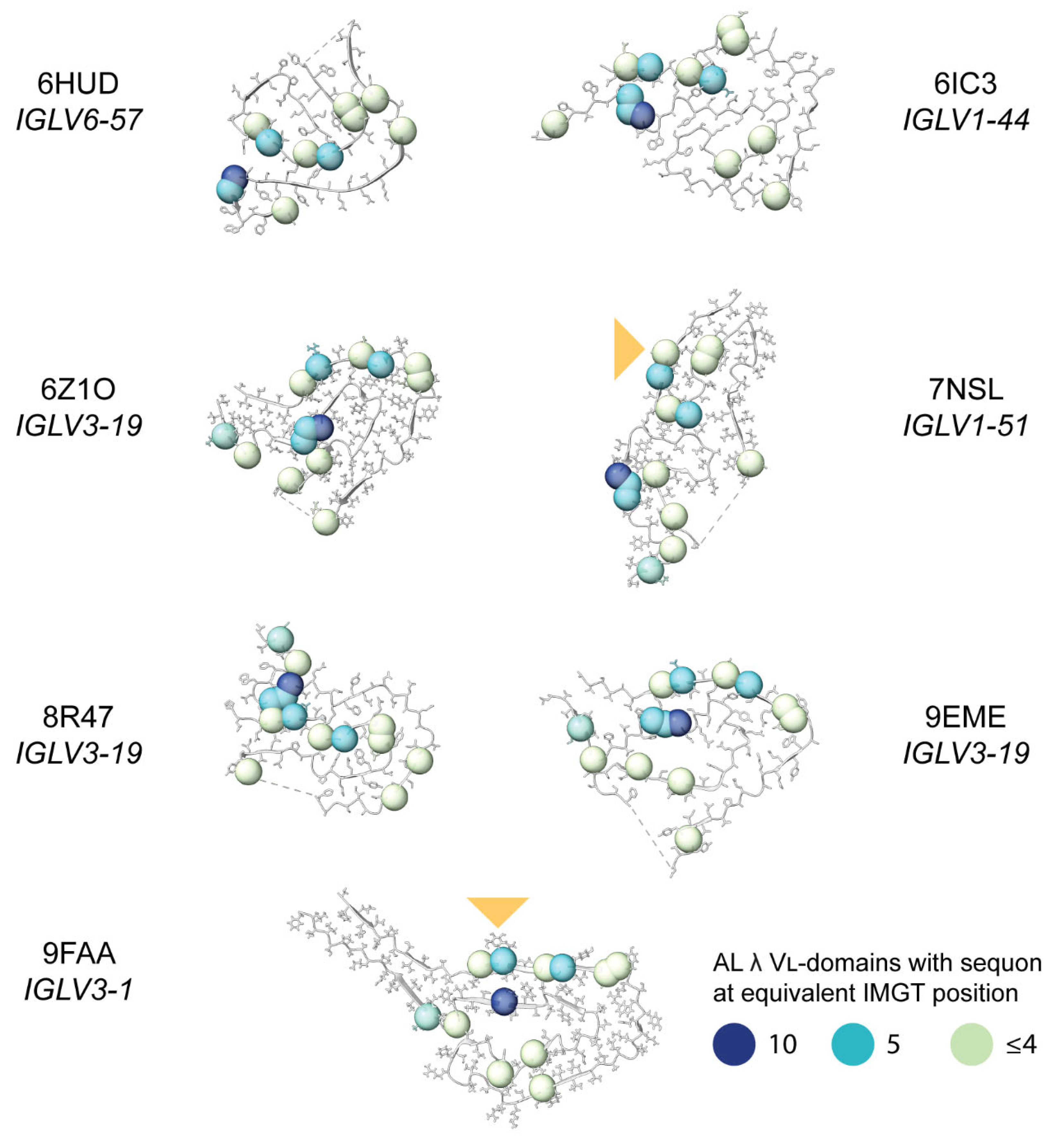
Sequon Positions are Compatible with Native Antibody Structures
Sequon Positions Differ in Their Environment among AL Fibril Structures
Discussion
Acknowledgements
References
- Ke, P.C.; Zhou, R.; Serpell, L.C.; Riek, R.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Lashuel, H.A.; Gazit, E.; Hamley, I.W.; Davis, T.P.; Fändrich, M.; et al. Half a Century of Amyloids: Past, Present and Future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5473–5509. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blancas-Mejía, L.M.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Systemic Amyloidoses. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 745–774. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxbaum, J.N.; Eisenberg, D.S.; Fändrich, M.; McPhail, E.D.; Merlini, G.; Saraiva, M.J.M.; Sekijima, Y.; Westermark, P. Amyloid Nomenclature 2024: Update, Novel Proteins, and Recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) Nomenclature Committee. Amyloid 2024, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Radamaker, L.; Karimi-Farsijani, S.; Andreotti, G.; Baur, J.; Neumann, M.; Schreiner, S.; Berghaus, N.; Motika, R.; Haupt, C.; Walther, P.; et al. Role of Mutations and Post-Translational Modifications in Systemic AL Amyloidosis Studied by Cryo-EM. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6434. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, T.; Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Speranzini, V.; Sicking, K.; Milazzo, M.; Mazzini, G.; Rognoni, P.; Caminito, S.; Milani, P.; Marabelli, C.; et al. Helical Superstructures between Amyloid and Collagen in Cardiac Fibrils from a Patient with AL Amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-50686-2. [CrossRef]
- Braakman, I.; Bulleid, N.J. Protein Folding and Modification in the Mammalian Endoplasmic Reticulum. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 71–99. [CrossRef]
- Sanchorawala, V. Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 2295–2307. [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo-Yauner, L.; Herrera, G.A.; Perez Carreon, J.I.; Turbat-Herrera, E.A.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, F.J.; Ruiz Zamora, R.A. Role of the Mechanisms for Antibody Repertoire Diversification in Monoclonal Light Chain Deposition Disorders: When a Friend Becomes Foe. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1203425. [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J.; Wall, J.S. The Process of Amyloid Formation Due to Monoclonal Immunoglobulins. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2020, 34, 1041–1054. [CrossRef]
- Feige, M.J.; Hendershot, L.M.; Buchner, J. How Antibodies Fold. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 35, 189–198. [CrossRef]
- Desikan, K.R.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; Hough, A.; Waldron, T.; Jagannath, S.; Siegel, D.; Barlogie, B.; Tricot, G. Incidence and Impact of Light Chain Associated (AL) Amyloidosis on the Prognosis of Patients with Multiple Myeloma Treated with Autologous Transplantation. Leuk. Lymphoma 1997, 27, 315–319. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Buadi, F.; Hayman, S.R.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.K. Clinical Features and Treatment Response of Light Chain (AL) Amyloidosis Diagnosed in Patients with Previous Diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 232–238. [PubMed]
- Bodi, K.; Prokaeva, T.; Spencer, B.; Eberhard, M.; Connors, L.H.; Seldin, D.C. AL-Base: A Visual Platform Analysis Tool for the Study of Amyloidogenic Immunoglobulin Light Chain Sequences. Amyloid 2009, 16, 1–8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourelis, T.V.; Dasari, S.; Theis, J.D.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; Kurtin, P.J.; Gertz, M.A.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Zenka, R.M.; Dogan, A.; Dispenzieri, A. Clarifying Immunoglobulin Gene Usage in Systemic and Localized Immunoglobulin Light-Chain Amyloidosis by Mass Spectrometry. Blood 2017, 129, 299–306. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.; Nau, A.N.; Wong, S.; Spencer, B.H.; Shen, Y.; Hua, A.; Bullard, M.J.; Sanchorawala, V.; Prokaeva, T. An Updated AL-Base Reveals Ranked Enrichment of Immunoglobulin Light Chain Variable Genes in AL Amyloidosis. bioRxiv 2024, 2024.09.11.612490.
- Radamaker, L.; Baur, J.; Huhn, S.; Haupt, C.; Hegenbart, U.; Schönland, S.; Bansal, A.; Schmidt, M.; Fändrich, M. Cryo-EM Reveals Structural Breaks in a Patient-Derived Amyloid Fibril from Systemic AL Amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 875. [CrossRef]
- Radamaker, L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Annamalai, K.; Huhn, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Schönland, S.O.; Fritz, G.; Schmidt, M.; Fändrich, M. Cryo-EM Structure of a Light Chain-Derived Amyloid Fibril from a Patient with Systemic AL Amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1103. [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Farsijani, S.; Pfeiffer, P.B.; Banerjee, S.; Baur, J.; Kuhn, L.; Kupfer, N.; Hegenbart, U.; Schönland, S.O.; Wiese, S.; Haupt, C.; et al. Light Chain Mutations Contribute to Defining the Fibril Morphology in Systemic AL Amyloidosis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5121. [CrossRef]
- Swuec, P.; Lavatelli, F.; Tasaki, M.; Paissoni, C.; Rognoni, P.; Maritan, M.; Brambilla, F.; Milani, P.; Mauri, P.; Camilloni, C.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of Cardiac Amyloid Fibrils from an Immunoglobulin Light Chain AL Amyloidosis Patient. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1269. [CrossRef]
- Puri, S.; Schulte, T.; Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Mazzini, G.; Caminito, S.; Pappone, C.; Anastasia, L.; Milani, P.; Merlini, G.; Bolognesi, M.; et al. The Cryo-EM Structure of Renal Amyloid Fibril Suggests Structurally Homogeneous Multiorgan Aggregation in AL Amyloidosis. J. Mol. Biol. 2023, 435, 168215. [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J. Transient Disorder along Pathways to Amyloid. Biophys. Chem. 2022, 281, 106711. [CrossRef]
- Kazman, P.; Vielberg, M.-T.; Pulido Cendales, M.D.; Hunziger, L.; Weber, B.; Hegenbart, U.; Zacharias, M.; Köhler, R.; Schönland, S.; Groll, M.; et al. Fatal Amyloid Formation in a Patient’s Antibody Light Chain Is Caused by a Single Point Mutation. Elife 2020, 9, doi:10.7554/eLife.52300. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, E.M.; Randles, E.G.; Aboagye, A.K.; Thompson, J.R.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Structural Insights into the Role of Mutations in Amyloidogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30950–30956. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurle, M.R.; Helms, L.R.; Li, L.; Chan, W.; Wetzel, R. A Role for Destabilizing Amino Acid Replacements in Light-Chain Amyloidosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1994, 91, 5446–5450. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, G.J.; Kelly, J.W. The Kinetic Stability of a Full-Length Antibody Light Chain Dimer Determines Whether Endoproteolysis Can Release Amyloidogenic Variable Domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 4280–4297. [CrossRef]
- Klimtchuk, E.S.; Gursky, O.; Patel, R.S.; Laporte, K.L.; Connors, L.H.; Skinner, M.; Seldin, D.C. The Critical Role of the Constant Region in Thermal Stability and Aggregation of Amyloidogenic Immunoglobulin Light Chain. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 9848–9857. [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J. Mechanisms of Disease: Monoclonal Immunoglobulin Deposition. Amyloidosis, Light Chain Deposition Disease, and Light and Heavy Chain Deposition Disease. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 1992, 6, 323–346. [CrossRef]
- Lavatelli, F.; Natalello, A.; Marchese, L.; Ami, D.; Corazza, A.; Raimondi, S.; Mimmi, M.C.; Malinverni, S.; Mangione, P.P.; Palmer, M.T.; et al. Truncation of the Constant Domain Drives Amyloid Formation by Immunoglobulin Light Chains. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107174. [CrossRef]
- Mazzini, G.; Ricagno, S.; Caminito, S.; Rognoni, P.; Milani, P.; Nuvolone, M.; Basset, M.; Foli, A.; Russo, R.; Merlini, G.; et al. Protease-Sensitive Regions in Amyloid Light Chains: What a Common Pattern of Fragmentation across Organs Suggests about Aggregation. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 494–506. [CrossRef]
- Lavatelli, F.; Mazzini, G.; Ricagno, S.; Iavarone, F.; Rognoni, P.; Milani, P.; Nuvolone, M.; Swuec, P.; Caminito, S.; Tasaki, M.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Characterization of Light Chain Fragmentation Sites in Cardiac AL Amyloidosis: Insights into the Timing of Proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 16572–16584. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Prokaeva, T.; Connors, L.H.; Costello, C.E. Oxidative Post-Translational Modifications of an Amyloidogenic Immunoglobulin Light Chain Protein. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 416, 71–79. [CrossRef]
- Connors, L.H.; Jiang, Y.; Budnik, M.; Théberge, R.; Prokaeva, T.; Bodi, K.L.; Seldin, D.C.; Costello, C.E.; Skinner, M. Heterogeneity in Primary Structure, Post-Translational Modifications, and Germline Gene Usage of Nine Full-Length Amyloidogenic Kappa1 Immunoglobulin Light Chains. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 14259–14271. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.; Wally, J.; Walsh, M.T.; Skinner, M.; Costello, C.E. Identification and Location of a Cysteinyl Posttranslational Modification in an Amyloidogenic Kappa1 Light Chain Protein by Electrospray Ionization and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 295, 45–56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omtvedt, L.A.; Bailey, D.; Renouf, D.V.; Davies, M.J.; Paramonov, N.A.; Haavik, S.; Husby, G.; Sletten, K.; Hounsell, E.F. Glycosylation of Immunoglobulin Light Chains Associated with Amyloidosis. Amyloid 2000, 7, 227–244. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveteraas, T.; Sletten, K.; Westermark, P. The Amino Acid Sequence of a Carbohydrate-Containing Immunoglobulin-Light-Chain-Type Amyloid-Fibril Protein. Biochem. J 1985, 232, 183–190. [CrossRef]
- Fykse, E.M.; Sletten, K.; Husby, G.; Cornwell, G.G., 3rd The Primary Structure of the Variable Region of an Immunoglobin IV Light-Chain Amyloid-Fibril Protein (AL GIL). Biochem. J 1988, 256, 973–980. [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.J. Four Structural Risk Factors Identify Most Fibril-Forming Kappa Light Chains. Amyloid 2000, 7, 200–211. [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.J.; Weiss, D.T.; Solomon, A. Structural Bases of Light Chain-Related Pathology. In The Antibodies; CRC Press, 1999; pp. 175–208 ISBN 9780429180620.
- Dispenzieri, A.; Larson, D.R.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Kyle, R.A.; Kumar, S.K.; Kourelis, T.; Arendt, B.; Willrcih, M.; Dasari, S.; Murray, D. N-Glycosylation of Monoclonal Light Chains on Routine MASS-FIX Testing Is a Risk Factor for MGUS Progression. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2749–2753. [CrossRef]
- Nevone, A.; Girelli, M.; Mangiacavalli, S.; Paiva, B.; Milani, P.; Cascino, P.; Piscitelli, M.; Speranzini, V.; Cartia, C.S.; Benvenuti, P.; et al. An N-Glycosylation Hotspot in Immunoglobulin κ Light Chains Is Associated with AL Amyloidosis. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2076–2085. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Murray, D.; Dasari, S.; Milani, P.; Barnidge, D.; Madden, B.; Kourelis, T.; Arendt, B.; Merlini, G.; Ramirez-Alvarado, M.; et al. Assay to Rapidly Screen for Immunoglobulin Light Chain Glycosylation: A Potential Path to Earlier AL Diagnosis for a Subset of Patients. Leukemia 2019, 33, 254–257. [CrossRef]
- Mellors, P.W.; Dasari, S.; Kohlhagen, M.C.; Kourelis, T.; Go, R.S.; Muchtar, E.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.K.; Buadi, F.K.; Willrich, M.A.V.; et al. MASS-FIX for the Detection of Monoclonal Proteins and Light Chain N-Glycosylation in Routine Clinical Practice: A Cross-Sectional Study of 6315 Patients. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 50. [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.D.; Kohlhagen, M.C.; Ladwig, P.M.; Dasari, S.; Kumar, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Willrich, M.A.V.; Murray, D.L. Characterizing M-Protein Light Chain Glycosylation via Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 109–110, 11–16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.N.; Wormald, M.R.; Sim, R.B.; Rudd, P.M.; Dwek, R.A. The Impact of Glycosylation on the Biological Function and Structure of Human Immunoglobulins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 21–50. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Bovenkamp, F.S.; Hafkenscheid, L.; Rispens, T.; Rombouts, Y. The Emerging Importance of IgG Fab Glycosylation in Immunity. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 1435–1441. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Bovenkamp, F.S.; Derksen, N.I.L.; Ooijevaar-de Heer, P.; van Schie, K.A.; Kruithof, S.; Berkowska, M.A.; van der Schoot, C.E.; IJspeert, H.; van der Burg, M.; Gils, A.; et al. Adaptive Antibody Diversification through N-Linked Glycosylation of the Immunoglobulin Variable Region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2018, 115, 1901–1906. [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.J. Role of N-Oligosaccharide Endoplasmic Reticulum Processing Reactions in Glycoprotein Folding and Degradation. Biochem. J 2000, 348 Pt 1, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Varki, A. Biological Roles of Oligosaccharides: All of the Theories Are Correct. Glycobiology 1993, 3, 97–130. [CrossRef]
- Kraus, A.; Hoyt, F.; Schwartz, C.L.; Hansen, B.; Artikis, E.; Hughson, A.G.; Raymond, G.J.; Race, B.; Baron, G.S.; Caughey, B. High-Resolution Structure and Strain Comparison of Infectious Mammalian Prions. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 4540-4551.e6. [CrossRef]
- Culyba, E.K.; Price, J.L.; Hanson, S.R.; Dhar, A.; Wong, C.-H.; Gruebele, M.; Powers, E.T.; Kelly, J.W. Protein Native-State Stabilization by Placing Aromatic Side Chains in N-Glycosylated Reverse Turns. Science 2011, 331, 571–575. [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.R.; Culyba, E.K.; Hsu, T.-L.; Wong, C.-H.; Kelly, J.W.; Powers, E.T. The Core Trisaccharide of an N-Linked Glycoprotein Intrinsically Accelerates Folding and Enhances Stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 3131–3136. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Enck, S.; Price, J.L.; Powers, D.L.; Powers, E.T.; Wong, C.-H.; Dyson, H.J.; Kelly, J.W. Structural and Energetic Basis of Carbohydrate–Aromatic Packing Interactions in Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9877–9884. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-J.; Luo, J.; O’Neil, K.T.; Kang, J.; Lacy, E.R.; Canziani, G.; Baker, A.; Huang, M.; Tang, Q.M.; Raju, T.S.; et al. Structure-Based Engineering of a Monoclonal Antibody for Improved Solubility. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2010, 23, 643–651. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Bovenkamp, F.S.; Derksen, N.I.L.; van Breemen, M.J.; de Taeye, S.W.; Ooijevaar-de Heer, P.; Sanders, R.W.; Rispens, T. Variable Domain N-Linked Glycans Acquired During Antigen-Specific Immune Responses Can Contribute to Immunoglobulin G Antibody Stability. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 740. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.H.; Boyles, F.; Deane, C.M. Observed Antibody Space: A Diverse Database of Cleaned, Annotated, and Translated Unpaired and Paired Antibody Sequences. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 141–146. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaltsuk, A.; Leem, J.; Kelm, S.; Snowden, J.; Deane, C.M.; Krawczyk, K. Observed Antibody Space: A Resource for Data Mining Next-Generation Sequencing of Antibody Repertoires. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2502–2509. [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.-P.; Lefranc, G. Immunoglobulins or Antibodies: IMGT® Bridging Genes, Structures and Functions. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 319. [CrossRef]
- Schanz, M.; Liechti, T.; Zagordi, O.; Miho, E.; Reddy, S.T.; Günthard, H.F.; Trkola, A.; Huber, M. High-Throughput Sequencing of Human Immunoglobulin Variable Regions with Subtype Identification. PLoS One 2014, 9, e111726. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.T.; Adams, K.D.; Briggs, A.W.; Timberlake, S.C.; Vigneault, F.; Kleinstein, S.H. Hierarchical Clustering Can Identify B Cell Clones with High Confidence in Ig Repertoire Sequencing Data. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2489–2499. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Schramm, C.A.; Kong, R.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Mullikin, J.C.; Mascola, J.R.; Kwong, P.D.; Shapiro, L. Gene-Specific Substitution Profiles Describe the Types and Frequencies of Amino Acid Changes during Antibody Somatic Hypermutation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 537. [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Bombardi, R.G.; Branchizio, A.; Kose, N.; Matta, P.; Sevy, A.M.; Sinkovits, R.S.; Gilchuk, P.; Finn, J.A.; Crowe, J.E., Jr High Frequency of Shared Clonotypes in Human B Cell Receptor Repertoires. Nature 2019, 566, 398–402. [CrossRef]
- Simonich, C.A.; Doepker, L.; Ralph, D.; Williams, J.A.; Dhar, A.; Yaffe, Z.; Gentles, L.; Small, C.T.; Oliver, B.; Vigdorovich, V.; et al. Kappa Chain Maturation Helps Drive Rapid Development of an Infant HIV-1 Broadly Neutralizing Antibody Lineage. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2190. [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, J.A.; Stathopoulos, P.; Zhou, J.Q.; Chen, L.; Gilbert, T.J.; Bolen, C.R.; Barohn, R.J.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Ciafaloni, E.; Broering, T.J.; et al. Dysregulation of B Cell Repertoire Formation in Myasthenia Gravis Patients Revealed through Deep Sequencing. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1460–1473. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.-P. Nomenclature of the Human Immunoglobulin Kappa (IGK) Genes. Exp. Clin. Immunogenet. 2001, 18, 161–174. [CrossRef]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing Available online: https://www.R-project.org/.
- RStudio Team Posit Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. Journal of Open Source Software 2019, 4, 1686. [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Stringr: Simple, Consistent Wrappers for Common String Operations; 2022;
- Wagih, O. ggseqlogo: A `ggplot2’ Extension for Drawing Publication-Ready Sequence Logos; 2017;
- Petrescu, A.-J.; Milac, A.-L.; Petrescu, S.M.; Dwek, R. a.; Wormald, M.R. Statistical Analysis of the Protein Environment of N-Glycosylation Sites: Implications for Occupancy, Structure, and Folding. Glycobiology 2004, 14, 103–114. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Brunak, S. Prediction of Glycosylation across the Human Proteome and the Correlation to Protein Function. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2002, 310–322.
- Dunbar, J.; Deane, C.M. ANARCI: Antigen Receptor Numbering and Receptor Classification. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 298–300. [CrossRef]
- Pagès, H.; Aboyoun, P.; Gentleman, R.; DebRoy, S. Biostrings: Efficient Manipulation of Biological Strings; 2022;
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1995, 57, 289–300. [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.C.; Goddard, T.D.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Pearson, Z.J.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Tools for Structure Building and Analysis. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4792. [CrossRef]
- Topham, C.M.; Smith, J.C. Tri-Peptide Reference Structures for the Calculation of Relative Solvent Accessible Surface Area in Protein Amino Acid Residues. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2015, 54, 33–43. [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.L.; Goulet, D.R.; Teplyakov, A.; Gilliland, G.L. Antibody Structure and Function: The Basis for Engineering Therapeutics. Antibodies (Basel) 2019, 8, 55. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mohapatra, A.; Nguyen, H.T.V.; Schimanski, L.; Kit Tan, T.; Rijal, P.; Chen, C.-P.; Cheng, S.-H.; Lee, W.-H.; Chou, Y.-C.; et al. The Presence of Broadly Neutralizing Anti-SARS-CoV-2 RBD Antibodies Elicited by Primary Series and Booster Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012246. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Wang, R.; Ju, B.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, P.; Zhou, B.; et al. Structural Basis for Bivalent Binding and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Human Potent Neutralizing Antibodies. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 517–525. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokaeva, T.; Spencer, B.; Kaut, M.; Ozonoff, A.; Doros, G.; Connors, L.H.; Skinner, M.; Seldin, D.C. Soft Tissue, Joint, and Bone Manifestations of AL Amyloidosis: Clinical Presentation, Molecular Features, and Survival. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3858–3868. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.N.; Chen, W.; Antonopoulos, A.; Hanson, S.R.; Wiseman, R.L.; Dell, A.; Haslam, S.M.; Powers, D.L.; Powers, E.T.; Kelly, J.W. Enhanced Aromatic Sequons Increase Oligosaccharyltransferase Glycosylation Efficiency and Glycan Homogeneity. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 1052–1062. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.D.; Stephens, R.M. Sequence Logos: A New Way to Display Consensus Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6097–6100. [CrossRef]
- Lowenthal, M.S.; Davis, K.S.; Formolo, T.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Phinney, K.W. Identification of Novel N-Glycosylation Sites at Noncanonical Protein Consensus Motifs. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2087–2101. [CrossRef]
- Sternke-Hoffmann, R.; Boquoi, A.; Lopez Y Niedenhoff, D.; Platten, F.; Fenk, R.; Haas, R.; Buell, A.K. Biochemical and Biophysical Characterisation of Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains Derived from an Initially Unbiased Population of Patients with Light Chain Disease. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8771. [CrossRef]
- Morgan, G.J.; Yan, N.L.; Mortenson, D.E.; Rennella, E.; Blundon, J.M.; Gwin, R.M.; Lin, C.-Y.; Stanfield, R.L.; Brown, S.J.; Rosen, H.; et al. Stabilization of Amyloidogenic Immunoglobulin Light Chains by Small Molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2019, 116, 8360–8369. [CrossRef]
- Rennella, E.; Morgan, G.J.; Kelly, J.W.; Kay, L.E. Role of Domain Interactions in the Aggregation of Full-Length Immunoglobulin Light Chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2019, 116, 854–863. [CrossRef]
- Sekijima, Y.; Wiseman, R.L.; Matteson, J.; Hammarström, P.; Miller, S.R.; Sawkar, A.R.; Balch, W.E.; Kelly, J.W. The Biological and Chemical Basis for Tissue-Selective Amyloid Disease. Cell 2005, 121, 73–85. [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Cohen, A.D.; Comenzo, R.L.; Kastritis, E.; Landau, H.J.; Libby, E.N.; Liedtke, M.; Sanchorawala, V.; Schönland, S.; Wechalekar, A.; et al. Birtamimab plus Standard of Care in Light-Chain Amyloidosis: The Phase 3 Randomized Placebo-Controlled VITAL Trial. Blood 2023, 142, 1208–1218. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apweiler, R.; Hermjakob, H.; Sharon, N. On the Frequency of Protein Glycosylation, as Deduced from Analysis of the SWISS-PROT Database. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1473, 4–8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
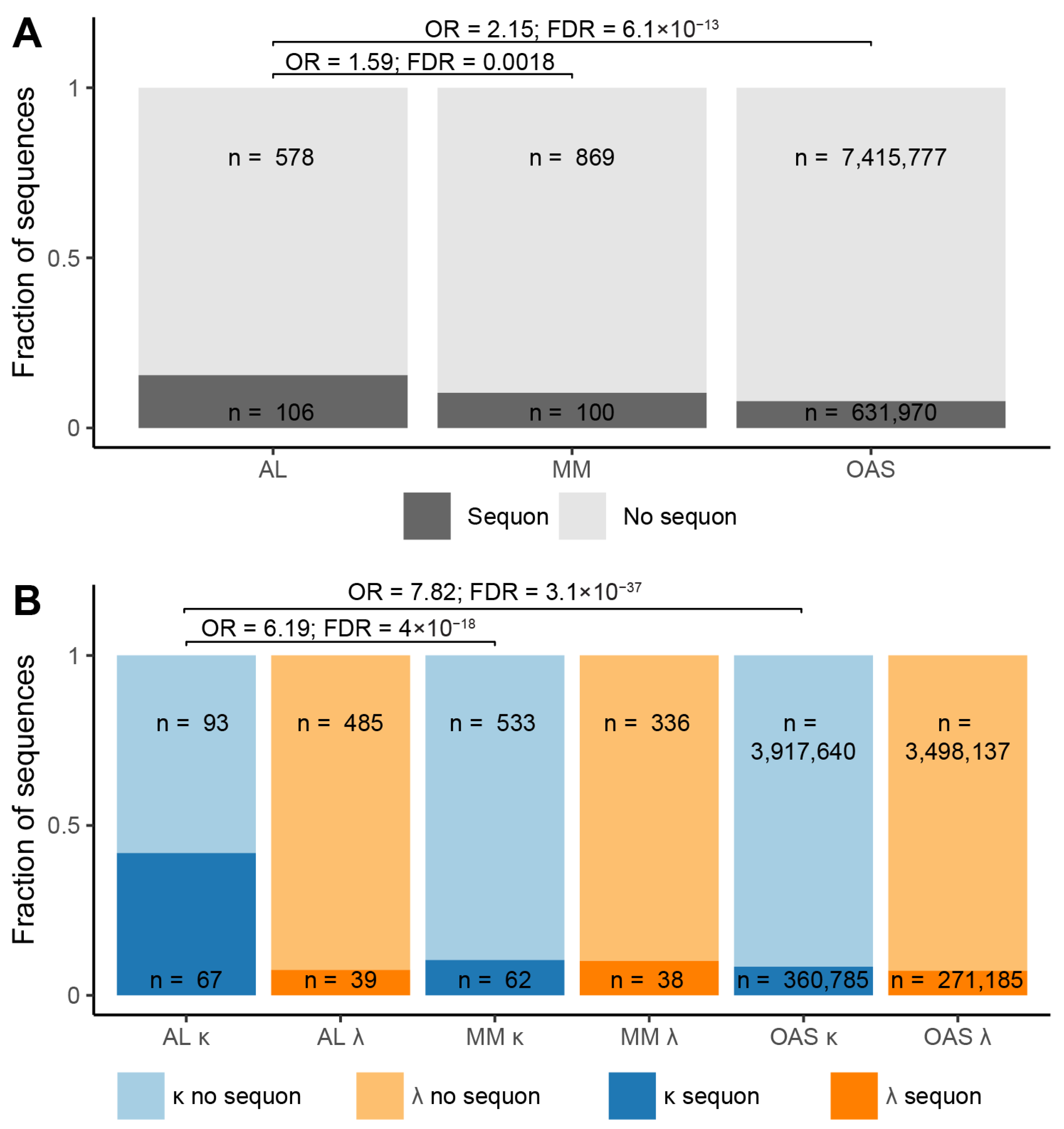
| Sequence origin | IGKV | IGLV | Total | ||||||
| Total | Sequon | No sequon | Total | Sequon | No sequon | Total | Sequon | No sequon | |
| AL subcategory | 160 | 67 41.9% | 93 58.1% |
524 |
39 7.4% |
485 92.6% |
684 | 106 15.5% |
578 84.5% |
| MM subcategory | 595 | 62 10.4% |
533 89.6% |
374 | 38 10.2% |
336 89.8% |
969 | 100 10.3% |
869 89.7% |
| OAS repertoire | 4,278,425 | 360,785 8.4% |
3,917,640 91.6% |
3,769,322 | 271,185 7.2% |
3,498,137 92.8% |
8,047,747 | 631,970 0.79% |
7,415,777 92.1% |
| AL-Base subcategory | IGVL gene | Region | Asn position (IMGT) | Sequence | Number of sequences |
| AL | IGLV2-23 | CDR3 | 114 | NTC | 1 |
| AL | IGLV3-1 | CDR1 | 38 | NAC | 2 |
| AL | IGLV3-1 | CDR1 | 38 | NVC | 2 |
| MM | IGKV1-39 | CDR1 | 36 | NTC | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





