Submitted:
09 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Overview of Research Design
Study Participants
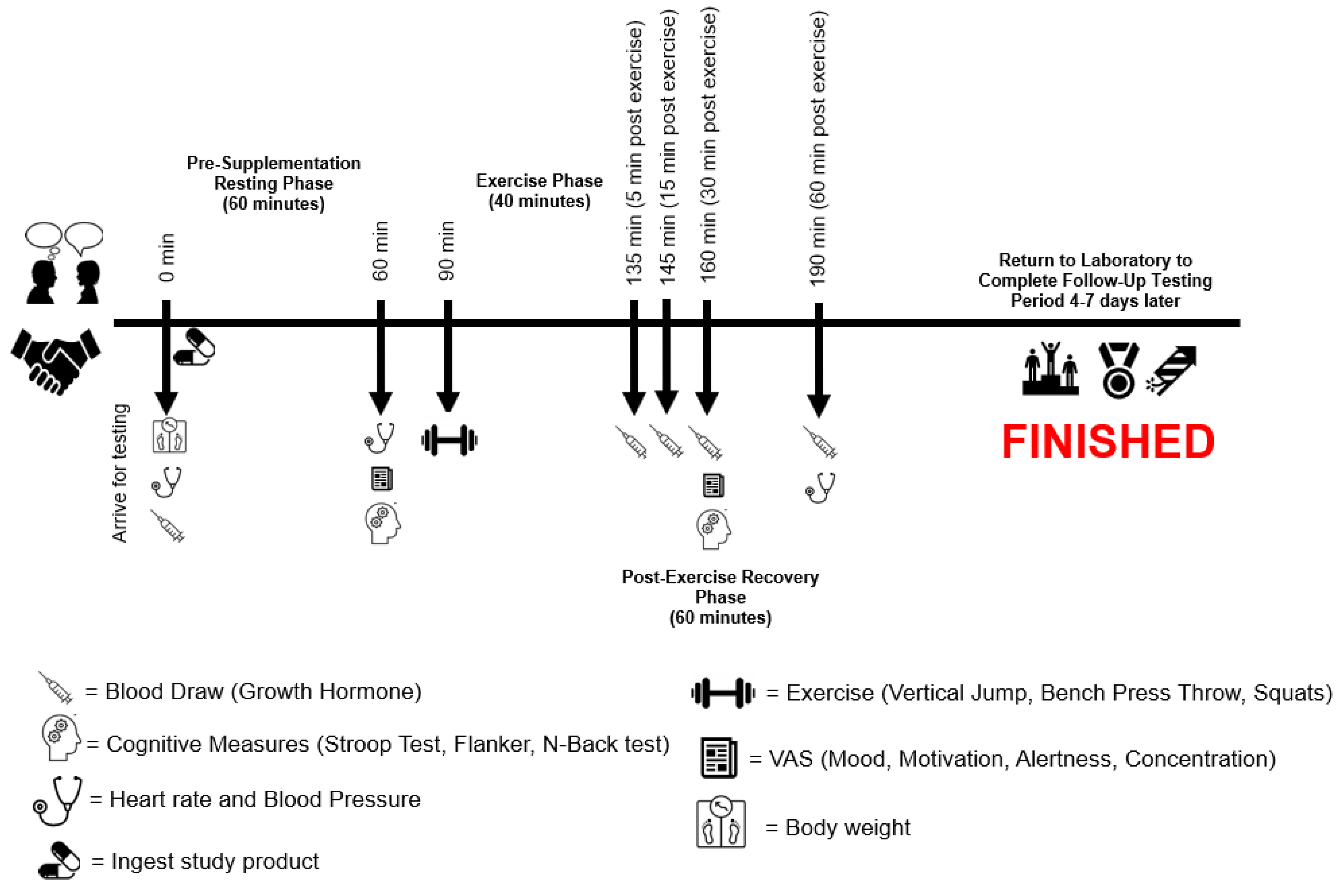
Procedures
Anthropometrics
Body Composition
Dietary Intake and Physical Activity Monitoring
Venous Blood Collection
Supplementation Protocol
Visual Analog Scales
Cognitive Performance
Exercise Performance
Resistance Exercise Protocol
Serum and Whole Blood Analysis
Adverse Events
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
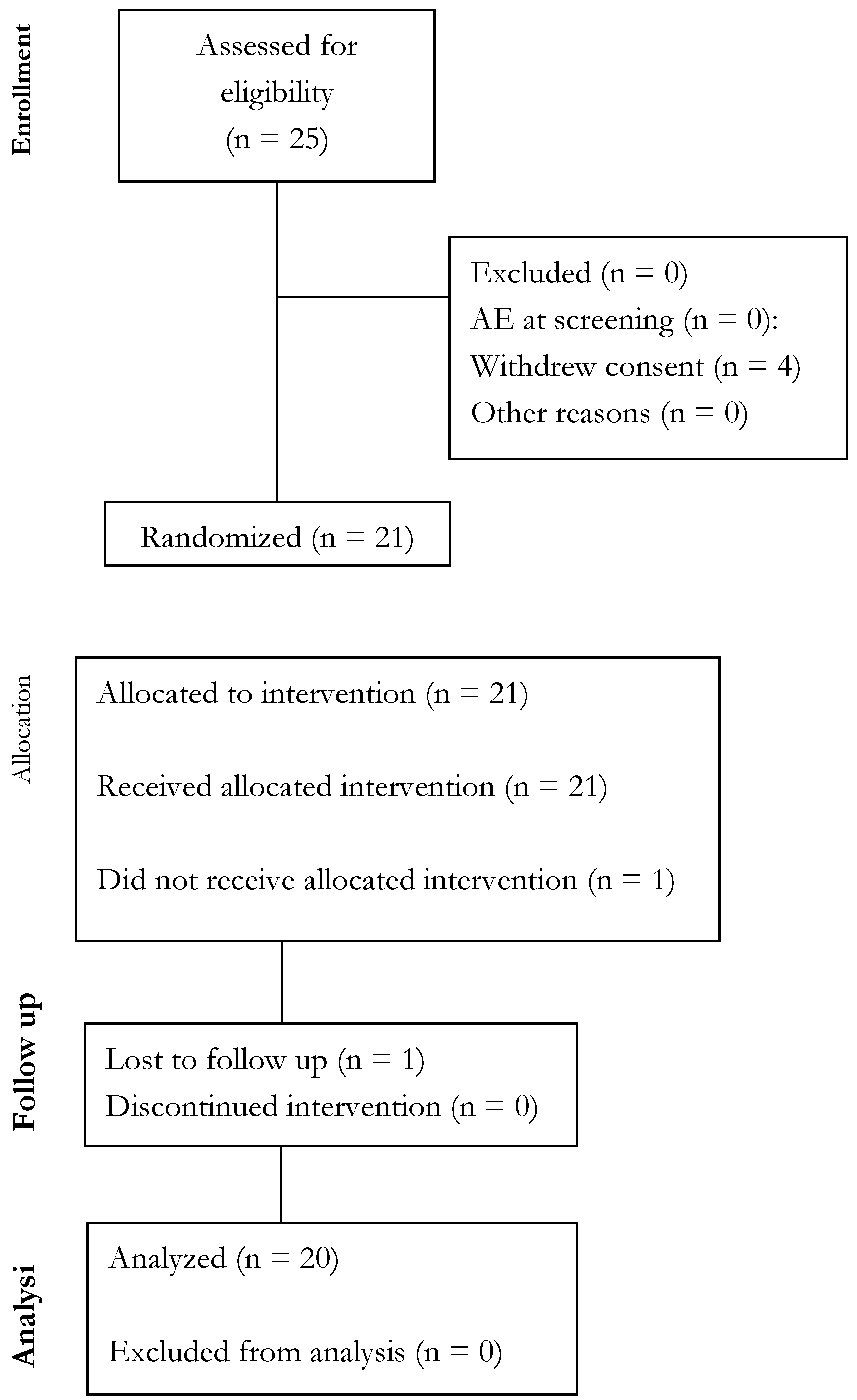
Compliance & Adverse Events (AEs)
Body Mass & Hemodynamics
Cognitive Performance
Visual Analog Scales
Physical Performance
Growth Hormone
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kansakar, U.; Trimarco, V.; Mone, P.; Varzideh, F.; Lombardi, A.; Santulli, G. Choline Supplements: An Update. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1148166. [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Okubo, T.; Sato, K.; Fujita, S.; Goto, K.; Hamaoka, T.; Iemitsu, M. Glycerophosphocholine Enhances Growth Hormone Secretion and Fat Oxidation in Young Adults. Nutrition 2012, 28, 1122–1126. [CrossRef]
- Bellar, D.; LeBlanc, N.R.; Campbell, B. The Effect of 6 Days of Alpha Glycerylphosphorylcholine on Isometric Strength. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2015, 12, 42. [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Takata, K.; Matsubara, K.; Kataoka, Y. Alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine Increases Motivation in Healthy Volunteers: A Single-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Human Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2091. [CrossRef]
- Marcus, L.; Soileau, J.; Judge, L.W.; Bellar, D. Evaluation of the Effects of Two Doses of Alpha Glycerylphosphorylcholine on Physical and Psychomotor Performance. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2017, 14, 39. [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, A. Brain Neurotransmitters in Aging and Dementia: Similar Changes across Diagnostic Dementia Groups. Gerontology 1987, 33, 159–167. [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Cantone, M.; D’Amico, E.; Fisicaro, F.; Puglisi, V.; Vinciguerra, L.; Bella, R.; Vicari, E.; Malaguarnera, G. Acetyl-L-Carnitine in Dementia and Other Cognitive Disorders: A Critical Update. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1389. [CrossRef]
- Hudson, S.; Tabet, N. Acetyl-L-Carnitine for Dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003, 2003, CD003158. [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Amenta, F.; Gallai, V. Choline Alphoscerate in Cognitive Decline and in Acute Cerebrovascular Disease: An Analysis of Published Clinical Data. Mech Ageing Dev 2001, 122, 2041–2055. [CrossRef]
- Passeri, M.; Cucinotta, D.; Bonati, P.A.; Iannuccelli, M.; Parnetti, L.; Senin, U. Acetyl-L-Carnitine in the Treatment of Mildly Demented Elderly Patients. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 1990, 10, 75–79.
- Rai, G.; Wright, G.; Scott, L.; Beston, B.; Rest, J.; Exton-Smith, A.N. Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Study of Acetyl-l-Carnitine in Patients with Alzheimer’s Dementia. Curr Med Res Opin 1990, 11, 638–647. [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo Sangiorgi, G.; Barbagallo, M.; Giordano, M.; Meli, M.; Panzarasa, R. Alpha-Glycerophosphocholine in the Mental Recovery of Cerebral Ischemic Attacks. An Italian Multicenter Clinical Trial. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1994, 717, 253–269. [CrossRef]
- Bunn, J.A.; Crossley, A.; Timiney, M.D. Acute Ingestion of Neuromuscular Enhancement Supplements Do Not Improve Power Output, Work Capacity, and Cognition. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2018, 58, 974–979. [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.G.; Gordon, J.; Thornton, A.; Byars, A.; Lubker, J.; Bartlett, M.; Byrd, M.; Oliver, J.; Simbo, S.; Rasmussen, C.; et al. The Effects of IQPLUS Focus on Cognitive Function, Mood and Endocrine Response before and Following Acute Exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition 2011, 8, 16. [CrossRef]
- Canal, N.; Franceschi, M.; Alberoni, M.; Castiglioni, C.; De Moliner, P.; Longoni, A. Effect of L-Alpha-Glyceryl-Phosphorylcholine on Amnesia Caused by Scopolamine. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 1991, 29, 103–107.
- Ziegenfuss, T.; Landis, J.; Hofheins, J. Acute Supplementation with Alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine Augments Growth Hormone Response to, and Peak Force Production during, Resistance Exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition 2008, 5, P15. [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.N. Effects of Branched Chain Amino Acids, l-Citrulline, and Alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine Supplementation on Exercise Performance in Trained Cyclists: A Randomized Crossover Trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2023, 20, 2214112. [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, W.G. The Effects of α-GPC Supplementation on Growth Hormone, Fat Loss, and Body Composition in Overweight Adults.
- La Monica, M.B.; Raub, B.; Ziegenfuss, E.J.; Hartshorn, S.; Grdic, J.; Gustat, A.; Sandrock, J.; Ziegenfuss, T.N. Acute Effects of Naturally Occurring Guayusa Tea and Nordic Lion’s Mane Extracts on Cognitive Performance. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5018. [CrossRef]
- La Monica, M.B.; Raub, B.; Malone, K.; Hartshorn, S.; Grdic, J.; Gustat, A.; Sandrock, J. Methylliberine Ingestion Improves Various Indices of Affect but Not Cognitive Function in Healthy Men and Women. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4509. [CrossRef]
- Jonides, J.; Schumacher, E.H.; Smith, E.E.; Lauber, E.J.; Awh, E.; Minoshima, S.; Koeppe, R.A. Verbal Working Memory Load Affects Regional Brain Activation as Measured by PET. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 1997, 9, 462–475. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, H.L.; Cesareo, K.R.; Raub, B.; Kedia, A.W.; Sandrock, J.E.; Kerksick, C.M.; Ziegenfuss, T.N. Effects of Hemp Extract on Markers of Wellness, Stress Resilience, Recovery and Clinical Biomarkers of Safety in Overweight, But Otherwise Healthy Subjects. Journal of Dietary Supplements 2020, 17, 561–586. [CrossRef]
- Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Kedia, A.W.; Sandrock, J.E.; Raub, B.J.; Kerksick, C.M.; Lopez, H.L. Effects of an Aqueous Extract of Withania Somnifera on Strength Training Adaptations and Recovery: The STAR Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1807. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.R.; Rohwer, W.D. The Stroop Color-Word Test: A Review. Acta Psychologica 1966, 25, 36–93. [CrossRef]
- Kane, M.J.; Engle, R.W. Working-Memory Capacity and the Control of Attention: The Contributions of Goal Neglect, Response Competition, and Task Set to Stroop Interference. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 2003, 132, 47–70. [CrossRef]
- Scarpina, F.; Tagini, S. The Stroop Color and Word Test. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Z.; Li, L. A Coordinate-Based Meta-Analysis of the n-Back Working Memory Paradigm Using Activation Likelihood Estimation. Brain Cogn 2019, 132, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.S.; Beck, T.W.; DeFreitas, J.M.; Dillon, M.A. Test-Retest Reliability of Barbell Velocity during the Free-Weight Bench-Press Exercise. J Strength Cond Res 2011, 25, 171–177. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Ratamess, N.A.; Kang, J.; Rashti, S.L.; Faigenbaum, A.D. Effect of Betaine Supplementation on Power Performance and Fatigue. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2009, 6, 7. [CrossRef]
- Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Cesareo, K.; Raub, B.; Kedia, A.W.; Sandrock, J.E.; Kerksick, C.M.; Ferrando, A.A.; Lopez, H.L. Effects of an Amylopectin-Chromium Complex Plus Whey Protein on Strength and Power After Eight Weeks of Resistance Training. JEN 2021, 4. [CrossRef]
- Beckenholdt, S.E.; Mayhew, J.L. Specificity among Anaerobic Power Tests in Male Athletes. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 1983, 23, 326–332.
- Stone, M.H.; Byrd, R.; Tew, J.; Wood, M. Relationship between Anaerobic Power and Olympic Weightlifting Performance. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 1980, 20, 99–102.
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A. Hormonal Responses and Adaptations to Resistance Exercise and Training. Sports Med 2005, 35, 339–361. [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Nindl, B.C. Recovery Responses of Testosterone, Growth Hormone, and IGF-1 after Resistance Exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2017, 122, 549–558. [CrossRef]
- Gatti, G.; Barzaghi, N.; Acuto, G.; Abbiati, G.; Fossati, T.; Perucca, E. A Comparative Study of Free Plasma Choline Levels Following Intramuscular Administration of L-Alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine and Citicoline in Normal Volunteers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 1992, 30, 331–335.
- Ceda, G.P.; Ceresini, G.; Denti, L.; Marzani, G.; Piovani, E.; Banchini, A.; Tarditi, E.; Valenti, G. Alpha-Glycerylphosphorylcholine Administration Increases the GH Responses to GHRH of Young and Elderly Subjects. Horm Metab Res 1992, 24, 119–121. [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Marchitelli, L.; Gordon, S.E.; Harman, E.; Dziados, J.E.; Mello, R.; Frykman, P.; McCurry, D.; Fleck, S.J. Hormonal and Growth Factor Responses to Heavy Resistance Exercise Protocols. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990, 69, 1442–1450. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.M.; Hoffman, J.R.; Townsend, J.R.; Jajtner, A.R.; Boone, C.H.; Beyer, K.S.; Baker, K.M.; Wells, A.J.; Mangine, G.T.; Robinson, E.H.; et al. Intramuscular Anabolic Signaling and Endocrine Response Following High Volume and High Intensity Resistance Exercise Protocols in Trained Men. Physiol Rep 2015, 3, e12466. [CrossRef]
| Procedure | Visit 1 (Screen) |
Visit 2 (Day 1) |
Visit 3 (Day 8) |
Visit 4 (Day 15) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informed Consent | X | |||
| Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria | X | |||
| Medical History | X | |||
| Height, weight, and BMI | X | X | X | X |
| 24-hr Dietary recall | X | |||
| CBC, CMP, Lipid Panel | X | |||
| Vitals (HR and BP) | X | |||
| Body Composition | X | |||
| Upper Body Exercise Performance | X | X | X | |
| Lower Body Exercise Performance | X | X | X | |
| Resistance Exercise Protocol | X | X | X | |
| Cognitive performance | X | X | X | X |
| Growth hormone | X | X | X | |
| Visual Analog Scales | X | X | X | |
| Vitals (HR and BP) Post-Exercise | X | X | X | |
| 24 hr Diet Records/Analysis/Repeat | X | X | X | |
| Protocol Compliance | X | X | X | |
| Dispense Test Product | X | X | X | |
| Adverse Events Monitoring | X | X | X | X |
| Variable | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 31.3 ± 11.0 |
| Height (cm) | 178.6 ± 7.3 |
| Weight (kg) | 84.6 ± 11.4 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 26.4 ± 2.5 |
| Body Fat (%) | 15.4 ± 5.6 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) | 120.7 ± 12.1 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) | 72.3 ± 9.0 |
| Resting Heart Rate (bpm) | 63.4 ± 8.7 |
| White Blood Cell Count (x103/µL) | 5.3 ± 1.4 |
| Red Blood Cell Count (x106/µL) | 5.3 ± 0.4 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15.8 ± 0.7 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 46.5 ± 2.1 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 90.0 ± 9.8 |
| Blood Urea Nitrogen (mg/dL) | 16.8 ± 5.3 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| BUN/Creatinine ratio | 91.8 ± 16.9 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73) | 14.7 ± 3.5 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 140.8 ± 1.9 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.5 ± 0.4 |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 103.1 ± 2.0 |
| CO2 (mmol/L) | 23.9 ± 1.5 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.5 ± 0.3 |
| Total Protein (g/dL) | 7.1 ± 0.4 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.7 ± 0.2 |
| Globulin (g/dL) | 2.4 ± 0.3 |
| Albumin/Globulin ratio | 2.0 ± 0.3 |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.6 ± 0.3 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (IU/L) | 69.3 ± 14.4 |
| AST (IU/L) | 23.5 ± 5.7 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 25.7 ± 7.0 |
| Total Chol (mg/dL) | 162.0 ± 25.3 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 102.4 ± 112.1 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 50.0 ± 10.6 |
| VLDL (mg/dL) | 18.6 ± 16.8 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 93.4 ± 21.1 |
| LDL/HDL | 1.9 ± 0.4 |
| Total/HDL | 3.5 ± 1.0 |
| Treatment | HD | LD | PL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severity | |||
| Mild | 2 | ||
| Moderate | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Severe | |||
| Relationship to Study Treatment (Product) | |||
| Unlikely | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Possible | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Probable | |||
| Relationship to Test Article (Procedural) | |||
| Unlikely | |||
| Possible | |||
| Probable | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Body Systems and AEs | |||
| Gastrointestinal | |||
| Emesis (regurgitate) | 1 | 2 | |
| Nausea | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Retching (dry heaving) | 1 | ||
| Nervous | |||
| Cephalalgia (headache) | 1 | ||
| Cardiovascular | |||
| Presyncope (lightheaded) | 3 | 2 | |
| Total Number of Adverse Events Experienced During Study | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Total Number of Subjects Experiencing AEs: n (%) | 2/20 (10%) | 4/21 (19%) | 4/20 (20%) |
| 0 min Post-Ingestion | 60 min Post Ingestion | 30 min Post Exercise | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) | HD | 121.1 ± 10.3 | 121.1 ± 11.4 | 116.4 ± 12.1 |
| LD | 120.1 ± 9.3 | 120.4 ± 7.9 | 115.3 ± 11.6 | |
| PL | 123.1 ± 10.7 | 121.0 ± 9.8 | 116.9 ± 12.3 | |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mm Hg) | HD | 74.9 ± 8.0 | 74.6 ± 7.4 | 73.5 ± 8.3 |
| LD | 72.5 ± 8.6 | 77.5 ± 8.5† | 71.9 ± 8.3† | |
| PL | 73.6 ± 7.2 | 76.8 ± 7.1 | 71.1 ± 7.0† | |
| Heart Rate (beats/min) | HD | 62.6 ± 11.4 | 58.9 ± 10.2† | 72.6 ± 12.0† |
| LD | 62.7 ± 8.7 | 60.7 ± 8.6 | 74.1 ± 8.6† | |
| PL | 61.3 ± 10.4 | 59.5 ± 9.7 | 74.2 ± 12.4† |
| HD | LD | PL | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
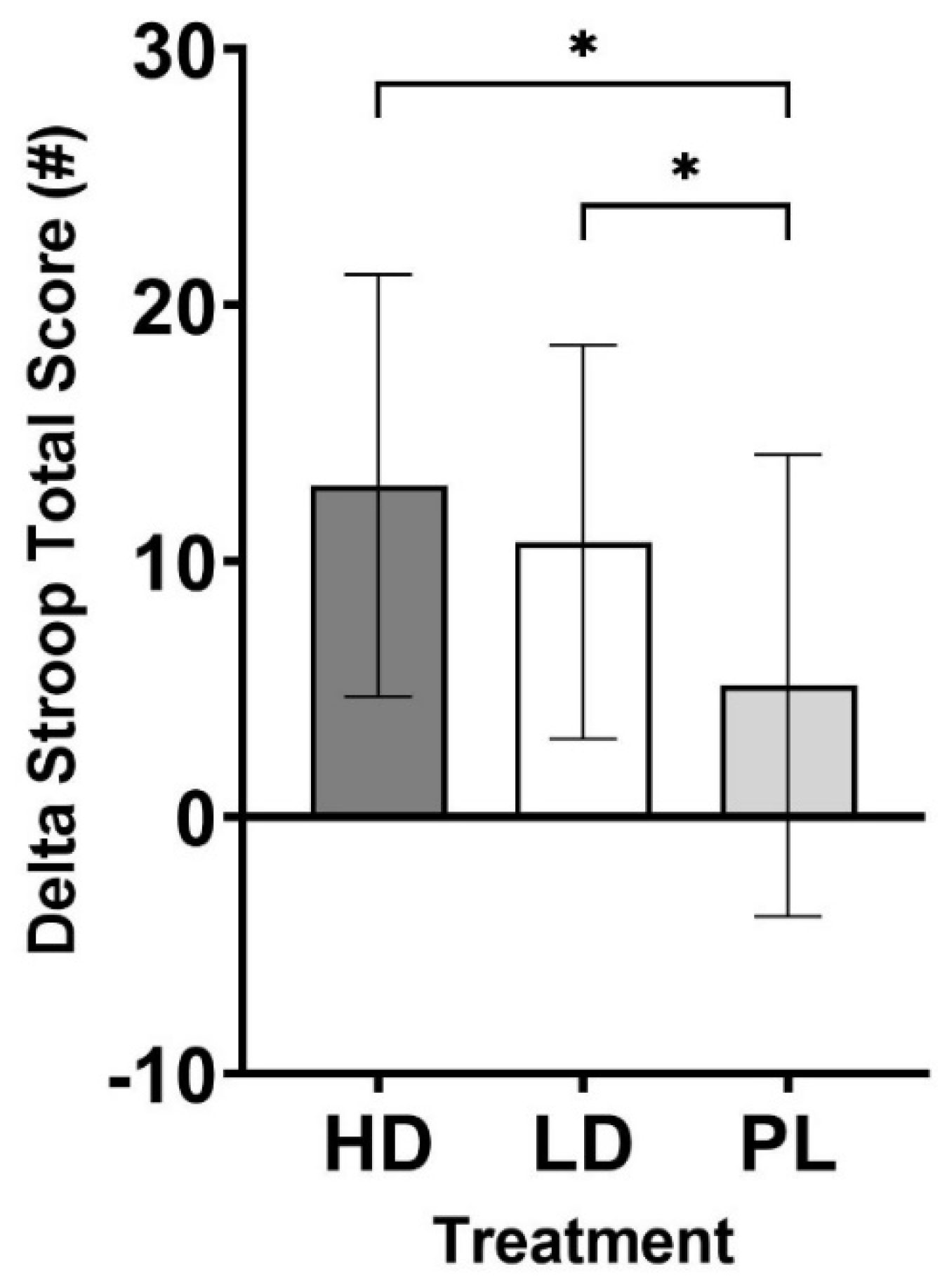
| Stroop Total Score | 13.0 ± 8.2** | 10.8 ± 7.7** | 5.2 ± 9.0 | 0.016 |
| Stroop Accuracy | 0.29 ± 0.85‡ | -0.58 ± 0.90 | -0.16 ± 1.35 | 0.073 |
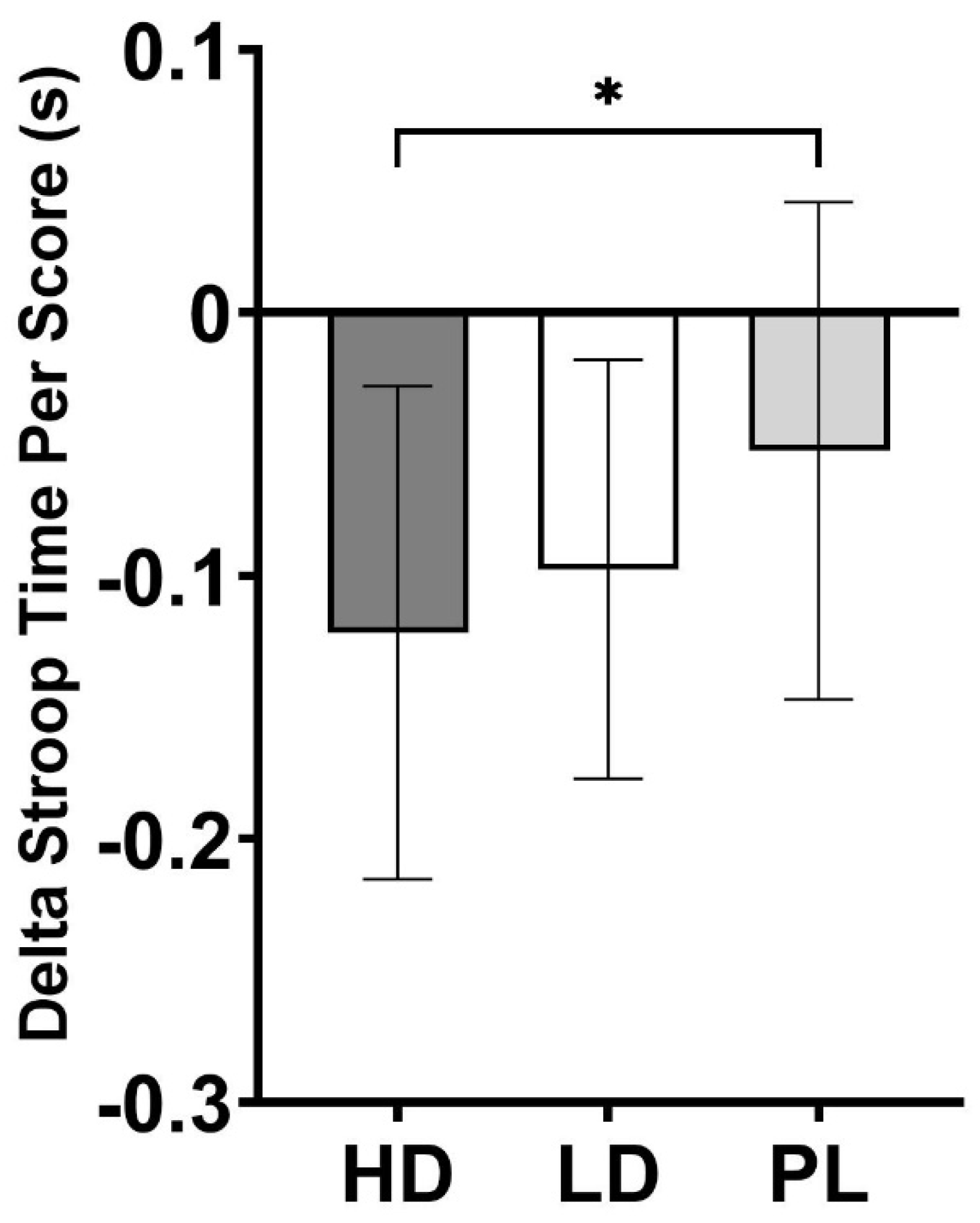
| Stroop Time Per Score (s) | -0.12 ± 0.09** | -0.10 ± 0.08* | -0.05 ± 0.09 | 0.030 |
| Flanker Compatible Accuracy (%) | -1.24 ± 3.1 | -0.16 ± 2.57 | 0.00 ± 2.26 | 0.376 |
| Flanker Compatible Reaction Time (ms) | -51.2 ± 53.9** | -13.0 ± 97.2 | -13.0 ± 51.6 | 0.126 |
| Flanker Incompatible Accuracy (%) | -0.63 ± 2.97 | 0.00 ± 3.03 | -0.78 ± 1.99 | 0.754 |
| Flanker Incompatible Reaction Time (ms) | -39.2 ± 60.1 | -18.2 ± 107 | -14.1 ± 48.8 | 0.467 |
| Flanker None Accuracy (%) | -1.25 ± 2.19 | -0.39 ± 3.07 | 0.23 ± 0.76 | 0.214 |
| Flanker None Reaction Time (ms) | -34.1 ± 56.3# | -11.5 ± 89.4 | -19.4 ± 73.4 | 0.165 |
| N-Back Score (au) | 853 ± 1973 | 828 ± 1455 | 1486 ± 2328 | 0.490 |
| N-Back Correct (#) | 7.2 ± 7.5 | 5.2 ± 5.3 | 6.5 ± 7.0 | 0.617 |
| N-Back Attempted (#) | 9.2 ± 8.5 | 6.2 ± 5.4 | 7.5 ± 6.6 | 0.395 |
| N-Back Accuracy (%) | -1.7 ± 2.5 | -0.5 ± 2.2 | -0.4 ± 3.0 | 0.241 |
| N-Back Time Per Score (ms) | -81.7 ± 107 | -71.7 ± 81.5 | -67.4 ± 55.4 | 0.951 |
| 60 min Post-Ingestion | p | 30 min Post-Exercise | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mood | HD | 7.2 ± 1.2 | 0.649 | 7.1 ± 1.3 | 0.189 |
| LD | 7.3 ± 1.4 | 7.0 ± 1.7 | |||
| PL | 7.1 ± 1.3 | 6.5 ± 1.8 | |||
| Motivation Towards Physical Exercise | HD | 6.6 ± 1.6 | 0.320 | 5.7 ± 2.4 | 0.546 |
| LD | 6.9 ± 1.4 | 5.4 ± 2.5 | |||
| PL | 6.4 ± 1.4 | 5.1 ± 2.6 | |||
| Motivation Towards Mental Exercise | HD | 6.8 ± 1.7 | 0.664 | 6.3 ± 1.9 | 0.182 |
| LD | 6.9 ± 1.6 | 6.6 ± 2.1 | |||
| PL | 6.6 ± 1.7 | 5.7 ± 2.2 | |||
| Alertness | HD | 7.2 ± 1.3 | 0.197 | 6.3 ± 2.2 | 0.860 |
| LD | 6.7 ± 2.3 | 6.3 ± 2.6 | |||
| PL | 6.2 ± 2.5 | 6.1 ± 2.6 | |||
| Concentration | HD | 7.2 ± 1.3 | 0.385 | 6.5 ± 1.7 | 0.942 |
| LD | 7.2 ± 1.4 | 6.5 ± 2.1 | |||
| PL | 6.9± 1.5 | 66. ± 1.8 |
| HD | LD | PL | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bench Press Average Power (watts) | 509 ± 94 | 527 ± 107 | 506 ± 101 | 0.198 |
| Bench Press Peak Power (watts) | 913 ± 192# | 909 ± 213 | 864 ± 202 | 0.168 |
| Bench Press Peak Velocity (m/s) | 1.36 ± 0.22 | 1.38 ± 0.23 | 1.35 ± 0.23 | 0.296 |
| Bench Press Peak Force (N) | 898 ± 168** | 915 ± 210* | 869 ± 193 | 0.159 |
| Vertical Jump Average Power (watts) | 1572 ± 263 | 1569 ± 286 | 1573 ± 278 | 0.954 |
| Vertical Jump Peak Power (watts) | 7309 ± 2719# | 8403 ± 4363* | 7546 ± 3555 | 0.085 |
| Vertical Jump Peak Velocity (m/s) | 3.45 ± 0.44* | 3.42 ± 0.45 | 3.37 ± 0.45 | 0.160 |
| Vertical Jump Peak Force (N) | 2899 ± 1155‡ | 3080 ± 1060* | 2916 ± 1192 | 0.050 |
| Time | HD | LD | PL | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 0.58 ± 1.38 | 0.72 ± 2.12† | 0.35 ± 0.59† | Group | <0.001 |
| 5 min | 9.82 ± 6.72† | 14.00 ± 12.66† | 11.63 ± 11.46† | Time | < 0.001 |
| 15 min | 9.61 ± 7.27† | 11.81 ± 10.51† | 10.60 ± 11.72† | Group x Time | 0.174 |
| 30 min | 5.99 ± 4.86† | 7.94 ± 6.43† | 8.93 ± 14.03† | ||
| 60 min | 2.73 ± 3.01 | 3.04 ± 2.42† | 3.99 ± 6.62† |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




