Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
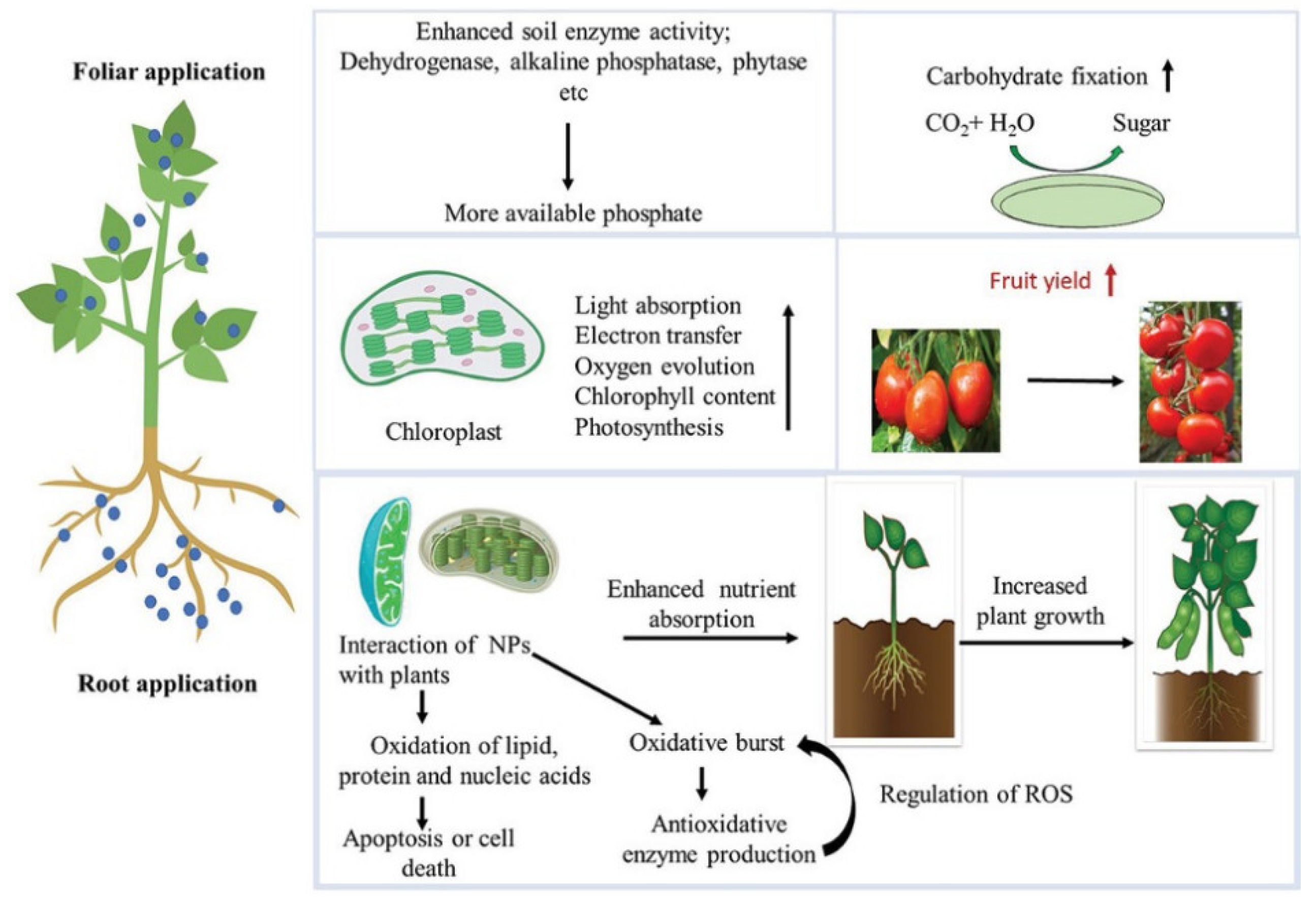
2. Plants Growth
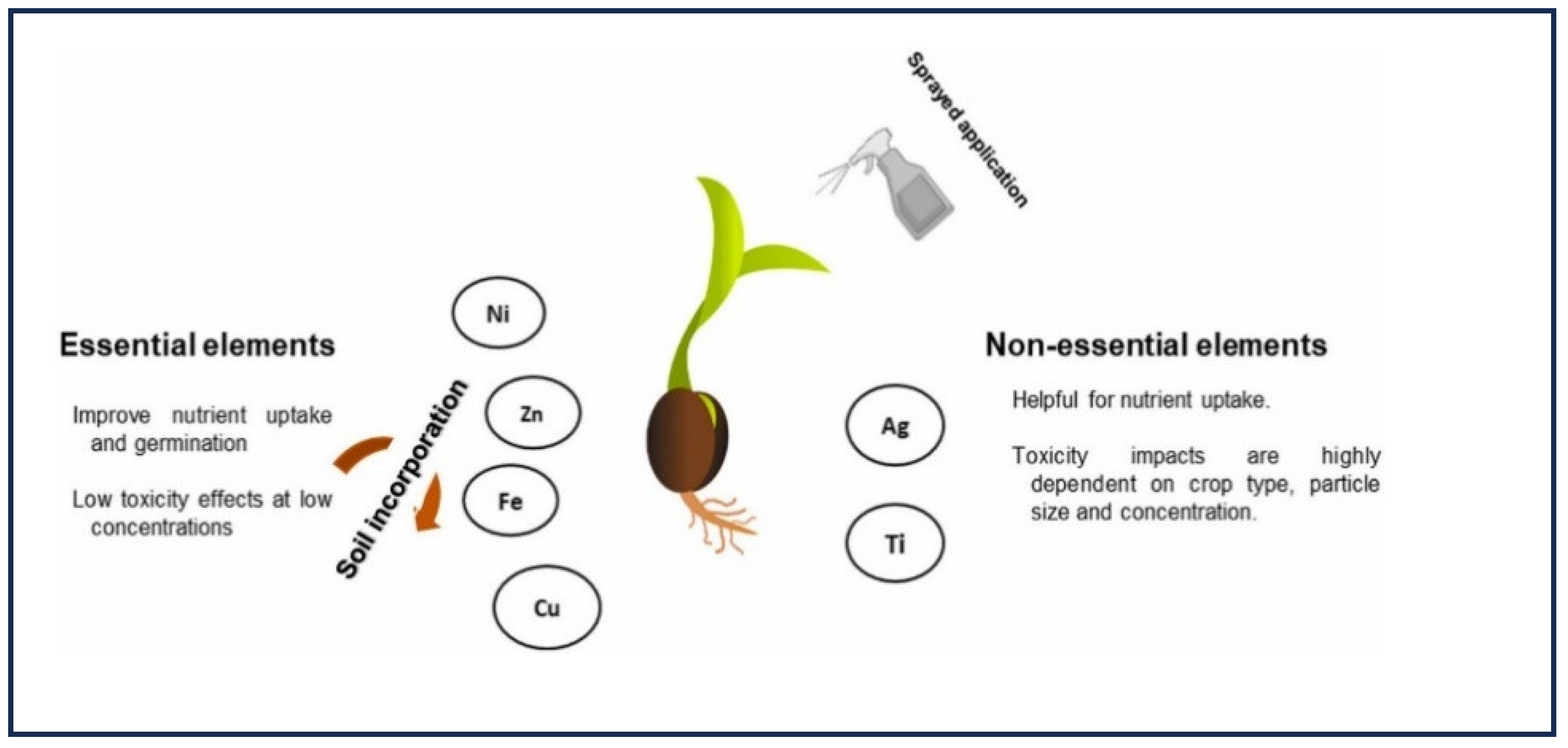
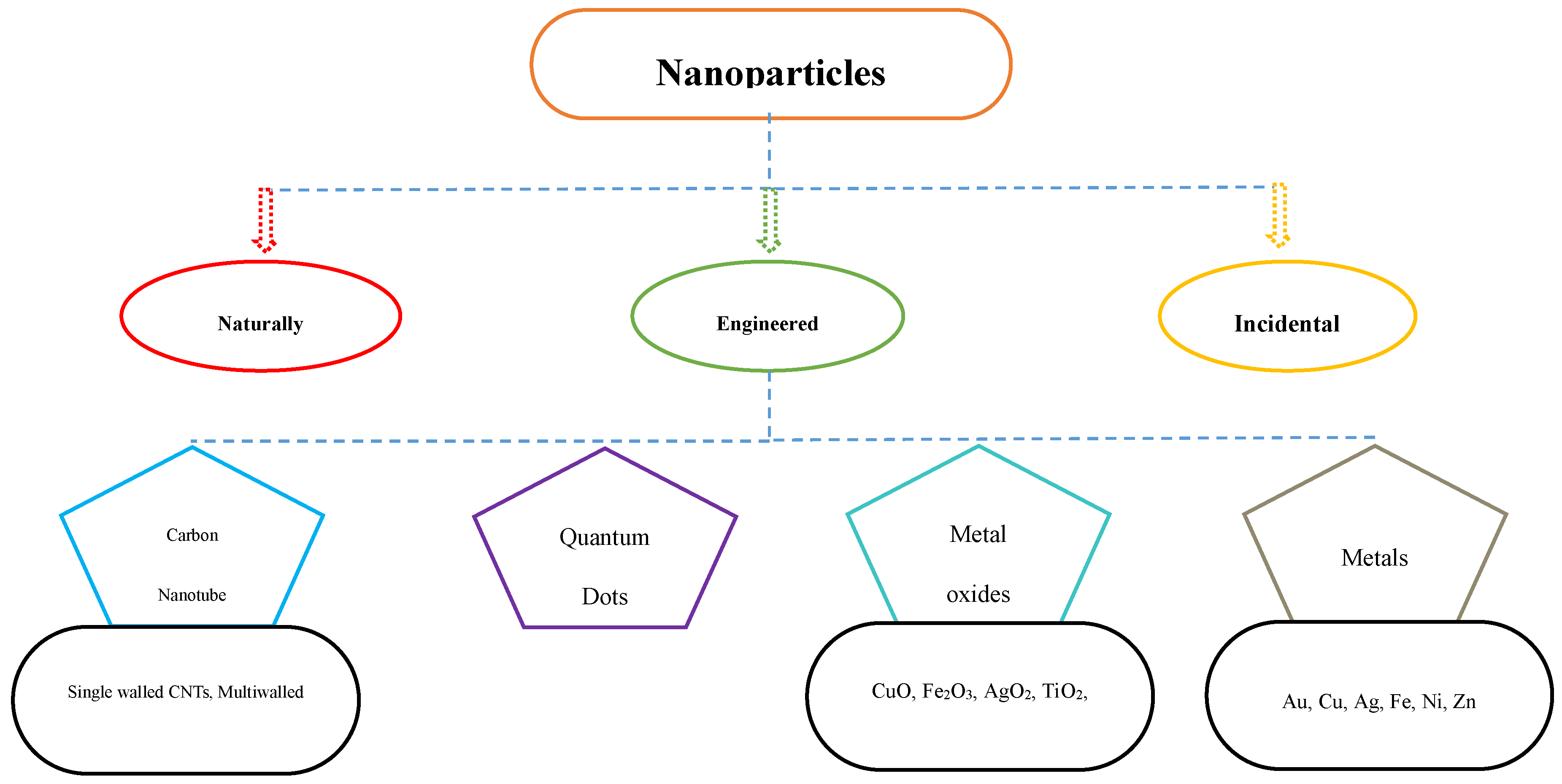
3. Nanoparticle Absorption by Plants
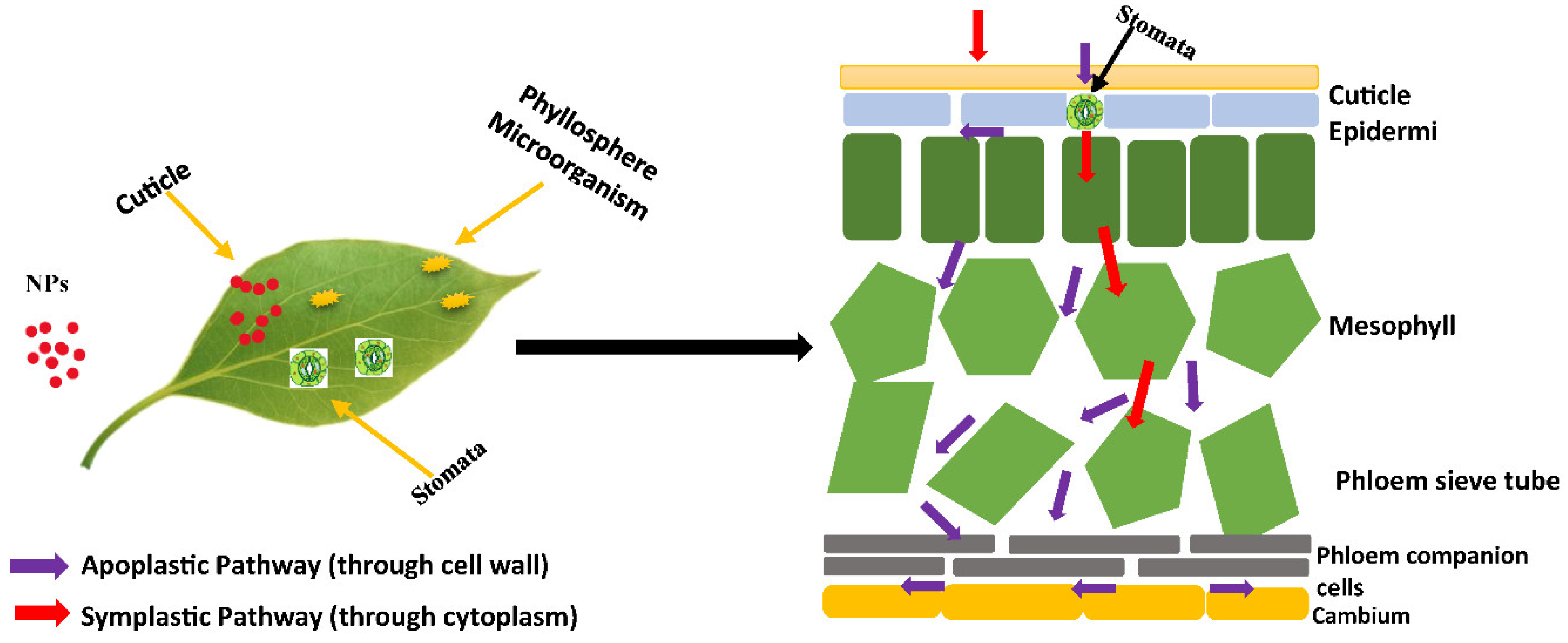
3.1. Foliar Uptake and Translocation of Nanoparticles
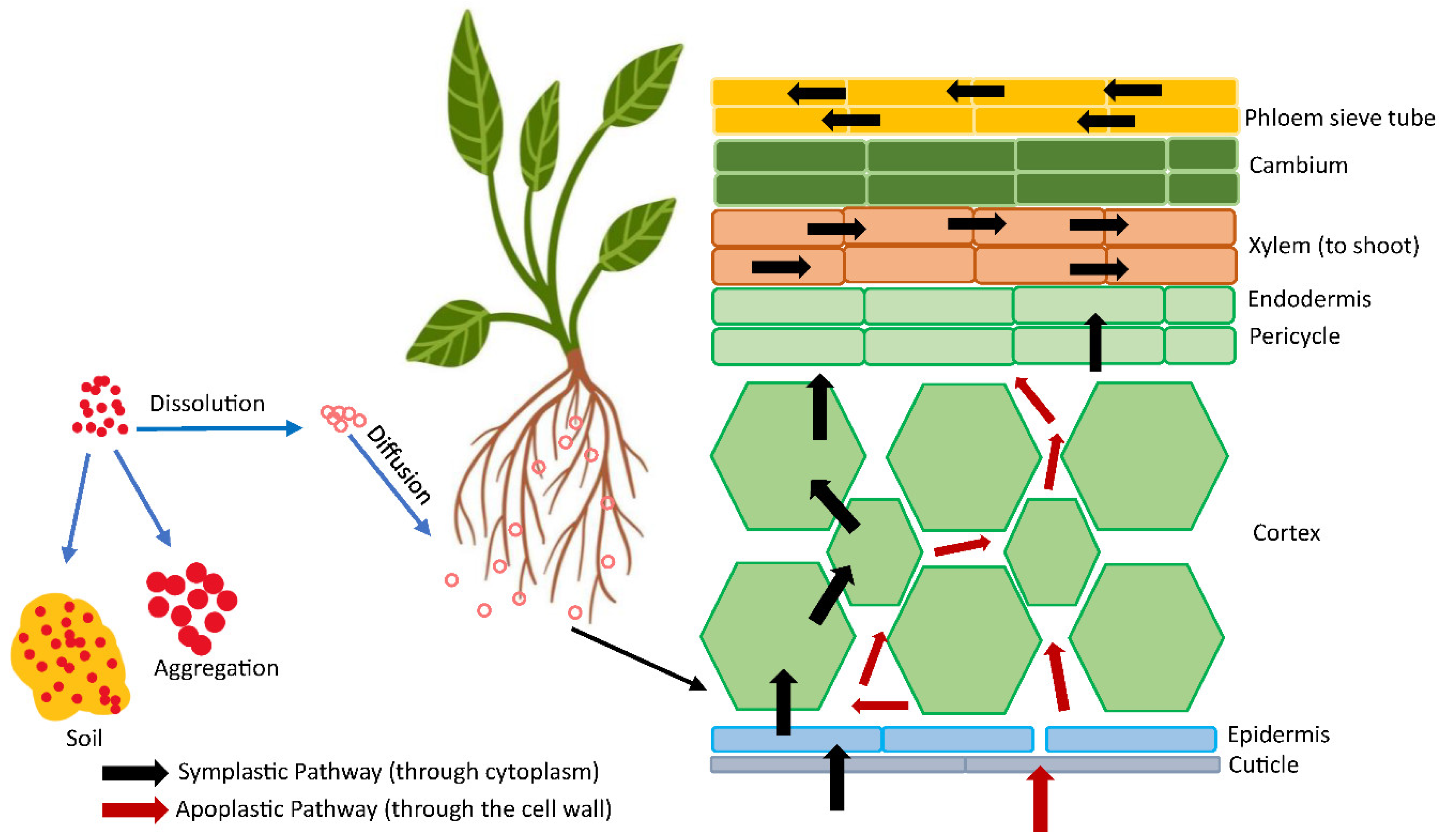
3.2. Transformation and Uptake of Nanoparticles by Root
4. Transformation of Nanoparticles
4.1. Transformation in Soil
- Leaching: NPs being washed away by water, potentially entering groundwater or nearby water sources.
- Dissolution: NPs breaking down into smaller species or ions, losing their nanoparticle properties.
- Adsorption: NPs adhering to surfaces, such as soil particles or plant cell walls, reducing their availability.
- Degradation: NPs being broken down by chemical or biological processes, such as oxidation or enzymatic activity.
- Uptake and internalization: NPs being taken up by plants or microorganisms, reducing their external concentration.
-
Sedimentation: NPs settling out of solution due to gravity, reducing their concentration in the surrounding medium.
- ➢
- When dealing with sandy soil, it’s worth noting that NPs tend to undergo oxidation due to the higher oxygen content. For instance, the presence of an Ag2O layer around Ag NPs can lead to the dissolution and subsequent release of Ag+ (Li et al. 2017).
- ➢
- The weathering process can have a significant impact on the availability of copper nanoparticles in soil, as well as its uptake and movement within lettuce plants (Servin et al. 2017).
4.2. Plant-Mediated Transformation of NPs
- ➢
- A complicated process produces differences in organic matter, mineral components, soil pH, and microbial community that alter the transformations of NPs during their dissolution and transformation in the rhizosphere. Many chemical reactions, including dissolution, accompany the change of metal-based NPs, which may also include sulfidation, phosphorylation, chelation, or reduction (Zhang et al. 2020).
- ➢
- The chemical modification of NPs at the Phyllosphere via interactions with the epiphytes (bacteria, fungus, and yeast) on the surface of the leaf might alter the aggregation state (Zhang et al. 2020).
- ➢
- Depending on the species of plant, the kind and degree of NP transformation may differ. As an example, the root exudates of cucumbers (Cucumis sativus) are firmly bound to by CuO NPs (∼40 nm), which causes the transformation of CuO NPs to Cu(I) and Cu (II) and decreases the absorption and buildup of Cu (Huang et al. 2017).
5. Physiological Effects of Nanoparticles in Plants
6. Impression of Different NPs on the Physiological Processes for Plant Development, Growth, and Maturation
6.1. Copper Nanoparticles
6.2. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
6.3. Silver Nanoparticles
6.4. Carbon Nanotubes
- Enhanced growth and biomass production (e.g., TiO2 NPs)
- Improved photosynthesis and light absorption (e.g., ZnO NPs)
- Increased water uses efficiency and drought tolerance (e.g., SiO2 NPs)
- Enhanced nutrient uptake and transport (e.g., Fe3O4 NPs)
- Altered hormone regulation and signaling (e.g., Au NPs)
- Increased stress tolerance and antioxidant activity (e.g., CeO2 NPs)
- Modified cell wall composition and structure (e.g., Ag NPs)
- Changed gene expression and regulation (e.g., CuO NPs)
7. Nanoparticles Influence the Structure and Function of Plants’ Photosynthetic Systems
- Ag NPs (silver nanoparticles)
- CuO NPs (copper oxide nanoparticles)
- ZnO NPs (zinc oxide nanoparticles)
- Damaging chloroplasts and disrupting electron transport chains
- Reducing light absorption and pigment content
- Altering stomatal aperture and gas exchange
- Inducing oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses
- TiO2 NPs (titanium dioxide nanoparticles)
- SiO2 NPs (silicon dioxide nanoparticles)
- Fe3O4 NPs (iron oxide nanoparticles)
- Increasing light absorption and scattering
- Improving electron transport and ATP production
- Enhancing stomatal conductance and CO2 uptake
- Reducing oxidative stress and promoting antioxidant activity
8. Nanoparticles and Antioxidant Capacity
9. Conclusion
Author Contribution
Data availability statement
Conflict of interest
References
- Abu-Hamdah R, Cho WJ, Cho SJ, Jeremic A, Kelly M, Ilie, AE, Jena, BP (2004) Regulation of the water channel aquaporin-1: isolation and reconstitution of the regulatory complex. Cell biology international, 28(1), 7-17. [CrossRef]
- Achari GA, Zakane RN, Kowshik, M (2020) Eco-friendly Nanomaterials in Agriculture: Biofortification, Plant Growth Promotion, and Phytopathogen Control. Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications, 1-22.
- Acharya P, Jayaprakasha GK, Crosby KM, Jifon JL, Patil BS (2019) Green-synthesized nanoparticles enhanced seedling growth, yield, and quality of onion (Allium cepa L.). ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 7(17), 14580-14590. [CrossRef]
- Ali SS, Al-Tohamy R, Koutra E, Moawad MS, Kornaros M, Mustafa AM, Sun, J (2021) Nanobiotechnological advancements in agriculture and food industry: Applications, nanotoxicity, and future perspectives. Science of the Total Environment, 792, 148359. [CrossRef]
- Ali S, Mehmood, A, Khan N (2021) Uptake, translocation, and consequences of nanomaterials on plant growth and stress adaptation. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2021, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Almutairi ZM (2016) Effect of nano-silicon application on the expression of salt tolerance genes in germinating tomato (‘Solanum lycopersicum’L.) seedlings under salt stress. Plant Omics, 9(1), 106-114.
- Aqeel U, Aftab T, Khan MMA, Naeem M, Khan MN (2022) A comprehensive review of impacts of diverse nanoparticles on growth, development and physiological adjustments in plants under changing environment. Chemosphere, 291, 132672. [CrossRef]
- Arnott A, Galagedara L, Thomas R, Cheema M, Sobze JM (2021) The potential of rock dust nanoparticles to improve seed germination and seedling vigor of native species: A review. Science of The Total Environment, 775, 145139. [CrossRef]
- Ashraf SA, Siddiqui AJ, Abd Elmoneim OE, Khan MI, Patel M, Alreshidi M, Adnan M (2021) Innovations in nanoscience for the sustainable development of food and agriculture with implications on health and environment. Science of the Total Environment, 768, 144990. [CrossRef]
- Avellan A, Yun J, Morais BP, Clement ET, Rodrigues SM, Lowry GV (2021) Critical review: Role of inorganic nanoparticle properties on their foliar uptake and in planta translocation. Environmental science & technology, 55(20), 13417-13431. [CrossRef]
- Awasthi G, Singh T, Tiwari Y, Awasthi A, Tripathi RD, Shrivastava S, Awasthi KK (2020) A review on nanotechnological interventions for plant growth and production. Materials Today: Proceedings, 31, 685-693. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee K, Pramanik P, Maity A, Joshi DC, Wani SH, Krishnan P (2019) Methods of using nanomaterials to plant systems and their delivery to plants (mode of entry, uptake, translocation, accumulation, biotransformation and barriers). In Advances in Phyto nanotechnology (pp. 123-152). Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Beal T, Massiot E, Arsenault JE, Smith MR, Hijmans RJ (2017) Global trends in dietary micronutrient supplies and estimated prevalence of inadequate intakes. PloS one, 12(4), e0175554. [CrossRef]
- Bombin S, LeFebvre M, Sherwood J, Xu Y, Bao Y, Ramonell KM (2015) Developmental and reproductive effects of iron oxide nanoparticles in Arabidopsis thaliana. International journal of molecular sciences, 16(10), 24174-24193. [CrossRef]
- Chanu TT, Upadhyaya H (2019). Zn oxide nanoparticle-induced responses on plants: a physiological perspective. In Nanomaterials in plants, algae and microorganisms (pp. 43-64). Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Chaud M, Souto EB, Zielinska A, Severino P, Batain F, Oliveira-Junior J, Alves T. (2021) Nanopesticides in agriculture: Benefits and challenge in agricultural productivity, toxicological risks to human health and environment. Toxics, 9(6), 131. [CrossRef]
- Choukri M, Abouabdillah A, Bouabid R, Abd-Elkader OH, Pacioglu O, Boufahja F, Bourioug M (2022) Zn application through seed priming improves productivity and grain nutritional quality of silage corn. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 29(12), 103456. [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal SS, Sharma V, Mandal A, Naresh RK, Verma G (2021) Improving soil micronutrient availability under organic farming. In Advances in organic farming (pp. 93-114). Woodhead Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Elsherif DE, Abd-ElShafy E, Khalifa AM (2023) Impacts of ZnO as a nanofertilizer on fenugreek: some biochemical parameters and SCoT analysis. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, 21(1), 52. [CrossRef]
- Fan X, Cao X, Zhou H, Hao L, Dong W, He C, Zheng Y (2020) Carbon dioxide fertilization effect on plant growth under soil water stress associates with changes in stomatal traits, leaf photosynthesis, and foliar nitrogen of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Environmental and Experimental Botany, 179, 104203. [CrossRef]
- Fatima F, Hashim A, Anees S (2021) Efficacy of nanoparticles as nanofertilizer production: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(2), 1292-1303.
- Fincheira P, Tortella G, Duran N, Seabra AB, Rubilar O (2020) Current applications of nanotechnology to develop plant growth inducer agents as an innovation strategy. Critical reviews in biotechnology, 40(1), 15-30. [CrossRef]
- Geisler-Lee J, Wang Q, Yao Y, Zhang W, Geisler M, Li K, Ma X (2013) Phytotoxicity, accumulation and transport of silver nanoparticles by Arabidopsis thaliana. Nanotoxicology, 7(3), 323-337. [CrossRef]
- Godoy F, Olivos-Hernández K, Stange C, Handford M (2021) Abiotic stress in crop species: improving tolerance by applying plant metabolites. Plants, 10(2), 186. [CrossRef]
- González-Feijoo R, Rodríguez-Seijo A, Fernández-Calviño D, Arias-Estévez M, Arenas-Lago D (2023) Use of three different nanoparticles to reduce Cd availability in soils: effects on germination and early growth of Sinapis alba L. Plants, 12(4), 801. [CrossRef]
- Gupta SD, Agarwal A, Pradhan S (2018) Phytostimulatory effect of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on rice seedling growth: An insight from antioxidative enzyme activities and gene expression patterns. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 161, 624-633. [CrossRef]
- Hong J, Wang C, Wagner DC, Gardea-Torresdey JL, He F, Rico CM (2021) Foliar application of nanoparticles: mechanisms of absorption, transfer, and multiple impacts. Environmental Science: Nano, 8(5), 1196-1210. [CrossRef]
- Hossain Z, Mustafa G, Sakata K, Komatsu S (2016) Insights into the proteomic response of soybean towards Al2O3, ZnO, and Ag nanoparticles stress. Journal of hazardous materials, 304, 291-305. [CrossRef]
- Hu P, An J, Faulkner MM, Wu H, Li Z, Tian X, Giraldo JP (2020) Nanoparticle charge and size control foliar delivery efficiency to plant cells and organelles. ACS nano, 14(7), 7970-7986. [CrossRef]
- Huang Y, Zhao L, Keller AA (2017) Interactions, transformations, and bioavailability of nano-copper exposed to root exudates. Environmental science & technology, 51(17), 9774-9783. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal M, Raja NI, Mashwani ZUR, Hussain M, Ejaz M, Yasmeen F (2019) Effect of silver nanoparticles on growth of wheat under heat stress. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions A: Science, 43, 387-395.
- Iqbal M, Umar S, Mahmooduzzafar (2019) Nano-fertilization to enhance nutrient use efficiency and productivity of crop plants. Nanomaterials and plant potential, 473-505.
- Kah M, Tufenkji N, White JC (2019) Nano-enabled strategies to enhance crop nutrition and protection. Nature nanotechnology, 14(6), 532-540.
- Karimi N, Behbahani M, Dini G, Razmjou A (2018) Enhancing the secondary metabolite and anticancer activity of Echinacea purpurea callus extracts by treatment with biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 9(4), 045009. [CrossRef]
- Kaur N, Kaur J, Grewal SK, Singh I (2019) Effect of heat stress on antioxidative defense system and its amelioration by heat acclimation and salicylic acid pre-treatments in three pigeonpea genotypes. Indian Journal of Agricultural Biochemistry, 32(1), 106-110. [CrossRef]
- Khan I, Awan SA, Rizwan M, Hassan ZU, Akram MA, Tariq R, Xie W (2022) Nanoparticle’s uptake and translocation mechanisms in plants via seed priming, foliar treatment, and root exposure: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(60), 89823-89833.
- Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian journal of chemistry, 12(7), 908-931. [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum MU (2011) Does enhanced photosynthesis enhance growth? Lessons learned from CO2 enrichment studies. Plant physiology, 155(1), 117-124. [CrossRef]
- Larue C, Veronesi G, Flank AM, Surble S, Herlin-Boime N, Carrière M (2012) Comparative uptake and impact of TiO2 nanoparticles in wheat and rapeseed. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A, 75(13-15), 722-734. [CrossRef]
- Lei Z, Mingyu S, Xiao W, Chao L, Chunxiang Q, Liang C, Fashui H (2008) Antioxidant stress is promoted by nano-anatase in spinach chloroplasts under UV-B radiation. Biological Trace Element Research, 121, 69-79. [CrossRef]
- Li WR, Sun TL, Zhou SL, Ma YK, Shi QS, Xie XB, Huang XM (2017) A comparative analysis of antibacterial activity, dynamics, and effects of silver ions and silver nanoparticles against four bacterial strains. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 123, 304-310. [CrossRef]
- Liu R, Zhang H, Lal R (2016) Effects of stabilized nanoparticles of copper, Zn, manganese, and iron oxides in low concentrations on lettuce (Lactuca sativa) seed germination: nanotoxicants or nanonutrients. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 227, 1-14.
- Mazhar Z, Akhtar J, Alhodaib A, Naz T, Zafar MI, Iqbal MM, Naz I (2023) Efficacy of ZnO nanoparticles in Zn fortification and partitioning of wheat and rice grains under salt stress. Scientific reports, 13(1), 2022.
- Mitra G (2017) Essential plant nutrients and recent concepts about their uptake. Essential plant nutrients: Uptake, use efficiency, and management, 3-36.
- Mittler R (2017) ROS is good. Trends in plant science, 22(1), 11-19. [CrossRef]
- Natasha N, Shahid M, Bibi I, Iqbal J, Khalid S, Murtaza B, Arshad M (2022) Zn in soil-plant-human system: A data-analysis review. Science of the Total Environment, 808, 152024. [CrossRef]
- Omanović-Mikličanin M, Maksimović (2016) Nanosensors applications in agriculture and food industry. Glas Hem. Technol. Bosne Herceg., 47, pp. 59-70.
- Omara AED, Elsakhawy T, Alshaal T, El-Ramady H, Kovács Z, Fári M (2019) Nanoparticles: a novel approach for sustainable agro-productivity. Environment, Biodiversity and Soil Security, 3(2019), 29-62. [CrossRef]
- Patel DK, Kim HB, Dutta SD, Ganguly K, Lim KT (2020) Carbon nanotubes-based nanomaterials and their agricultural and biotechnological applications. Materials, 13(7), 1679. [CrossRef]
- Pelegrino MT, Kohatsu MY, Seabra AB, Monteiro LR, Gomes DG, Oliveira HC, Lange CN (2020) Effects of copper oxide nanoparticles on growth of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) seedlings and possible implications of nitric oxide in their antioxidative defense. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 1-14.
- Peteu SF, Oancea F, Sicuia OA, Constantinescu F, Dinu S (2010) Responsive polymers for crop protection. Polymers, 2(3), 229-251. [CrossRef]
- Plaksenkova I, Kokina I, Petrova A, Jermaļonoka M, Gerbreders V, Krasovska M (2020) The impact of Zn oxide nanoparticles on cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and miRNA expression in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. The Scientific World Journal, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Poddar K, Sarkar D, Sarkar A (2020) Nanoparticles on photosynthesis of plants: effects and role. Green Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Biomedical Applications, 273-287.
- Rahmani N, Radjabian T, Soltani BM (2020) Impacts of foliar exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes on physiological and molecular traits of Salvia verticillata L., as a medicinal plant. Plant physiology and biochemistry, 150, 27-38. [CrossRef]
- Rajput VD, Minkina T, Kumari A, Harish, Singh VK, Verma KK, Keswani C (2021) Coping with the challenges of abiotic stress in plants: New dimensions in the field application of nanoparticles. Plants, 10(6), 1221. [CrossRef]
- Rajput VD, Minkina T, Suskova S, Mandzhieva S, Tsitsuashvili V, Chapligin V, Fedorenko A (2018) Effects of copper nanoparticles (CuO NPs) on crop plants: a mini review. Bio Nanoscience, 8, 36-42.
- Rico CM, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2015) Chemistry, biochemistry of nanoparticles, and their role in antioxidant defense system in plants. Nanotechnology and plant sciences: nanoparticles and their impact on plants, 1-17.
- Rodríguez-Seijo A, Soares C, Ribeiro S, Amil BF, Patinha C, Cachada A, Pereira R (2022) Nano-Fe2O3 as a tool to restore plant growth in contaminated soils–Assessment of potentially toxic elements (bio) availability and redox homeostasis in Hordeum vulgare L. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 425, 127999. [CrossRef]
- Rui M, Ma C, Rui Y, Fan X (2016) Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Frontiers in plant science, 7, 195361. [CrossRef]
- Salama HM (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticles in some crop plants, common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and corn (Zea mays L.). Int Res J Biotechnol, 3(10), 190-197.
- Samadi S, Saharkhiz MJ, Azizi M, Samiei L, Ghorbanpour M (2020) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes stimulate growth, redox reactions and biosynthesis of antioxidant metabolites in Thymus daenensis celak. in vitro. Chemosphere, 249, 126069. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt J (2015) Nanoparticle-induced membrane pore formation studied with lipid bilayer arrays. Biophysical Journal, 108(2), 344a-345a.
- Schymura S, Fricke T, Hildebrand H, Franke K (2017) Elucidating the role of dissolution in CeO2 nanoparticle plant uptake by smart radiolabeling. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 56(26), 7411-7414. [CrossRef]
- Servin AD, Pagano L, Castillo-Michel H, De la Torre-Roche R, Hawthorne J, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, White JC (2017) Weathering in soil increases nanoparticle CuO bioaccumulation within a terrestrial food chain. Nanotoxicology, 11(1), 98-111. [CrossRef]
- Singh A, Singh S, Prasad SM, Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Ahmad P, Chauhan DK, Prasad SM (2016) Silicon and Nanotechnology Role in Agriculture and Future Perspective in Silicon in Plants in Advances and Future Prospects, CRC Press, p. 392 . [CrossRef]
- Singh Y, Sodhi RS, Singh PP, Kaushal S (2022) Biosynthesis of NiO nanoparticles using Spirogyra sp. cell-free extract and their potential biological applications. Materials Advances, 3(12), 4991-5000. [CrossRef]
- Slomberg DL, Schoenfisch MH (2012) Silica nanoparticle phytotoxicity to Arabidopsis thaliana. Environmental science & technology, 46(18), 10247-10254. [CrossRef]
- Song GuanLing SG, Hou WenHua HW, Gao Yuan GY, Wang Yan WY, Lin Lin LL, Zhang ZhiWei ZZ, Wang HaiXia WH (2016) Effects of CuO nanoparticles on Lemna minor.
- Song U, Kim J (2020) Zn oxide nanoparticles: a potential micronutrient fertilizer for horticultural crops with little toxicity. Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology, 61(3), 625-631.
- Su, Y., Ashworth, V., Kim, C., Adeleye, A. S., Rolshausen, P., Roper, C., ... & Jassby, D. (2019). Delivery, uptake, fate, and transport of engineered nanoparticles in plants: a critical review and data analysis. Environmental Science: Nano, 6(8), 2311-2331.
- Talankova-Sereda TE, Liapina KV, Shkopinskij EA, Ustinov AI, Kovalyova AV, Dulnev PG, Kucenko NI (2016) The influence of Cu and Co nanoparticles on growth characteristics and biochemical structure of Mentha longifolia in vitro Nanosci. Nanoeng., 4 (2016), pp. 31-39.
- Taylor AF, Rylott EL, Anderson CW, Bruce NC (2014) Investigating the toxicity, uptake, nanoparticle formation and genetic response of plants to gold. PLOS one, 9(4), e93793. [CrossRef]
- Tighe-Neira R, Carmora E, Recio G, Nunes-Nesi A, Reyes-Diaz M, Alberdi M, Inostroza-Blancheteau C (2018) Metallic nanoparticles influence the structure and function of the photosynthetic apparatus in plants Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 130, pp. 408-417 . [CrossRef]
- Tiwari DK, Dasgupta-Schubert N, Villaseñor Cendejas LM, Villegas J, Carreto Montoya L (2014) Borjas García SE Interfacing carbon nanotubes (CNT) with plants: enhancement of growth, water and ionic nutrient uptake in maize (Zea mays) and implications for nanoagriculture. Appl. Nanosci, 4(5), 577-591.
- Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere M, Baykal A (2019) Uptake and translocation of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and its impact on photosynthetic genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Chemosphere, 226, 110-122. [CrossRef]
- Tripathi A, Liu S, Singh PK, Kumar N, Pandey AC, Tripathi DK, Sahi S (2017) Differential phytotoxic responses of silver nitrate (AgNO3) and silver nanoparticle (AgNps) in Cucumis sativus L. Plant Gene, 11, 255-264. [CrossRef]
- Tripathi DK, Mishra RK, Singh S, Singh S, Vishwakarma K, Sharma S, Chauhan DK (2017) Nitric oxide ameliorates Zn oxide nanoparticles phytotoxicity in wheat seedlings: implication of the ascorbate–glutathione cycle. Frontiers in plant science, 8, 1. [CrossRef]
- Tripathi DK, Singh S, Singh S, Pandey R, Singh VP, Sharma NC, Chauhan DK (2017) An overview on manufactured nanoparticles in plants: uptake, translocation, accumulation and phytotoxicity. Plant physiology and biochemistry, 110, 2-12. [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk M, Morley T, Rau ML, Saghai Y (2021) A meta-analysis of projected global food demand and population at risk of hunger for the period 2010–2050. Nature Food, 2(7), 494-501. [CrossRef]
- Veena M, Puthur JT (2022) Seed nutripriming with Zn is an apt tool to alleviate malnutrition. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 44(8), 2355-2373.
- Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER, Sharma NC, Sahi SV (2017) Zn oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alleviate heavy metal-induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 110, 59-69. [CrossRef]
- Vinopal S, Ruml T, Kotrba P (2007) Biosorption of Cd2+ and Zn2+ by cell surface-engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 60(2), 96-102. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Xie X, Zhao J, Liu X, Feng W, White JC, Xing B (2012) Xylem-and phloem-based transport of CuO nanoparticles in maize (Zea mays L.). Environmental science & technology, 46(8), 4434-4441. [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen F, Razzaq A, Iqbal M, Jhanzab HM (2015) Effect of silver, copper and iron nanoparticles on wheat germination. Int. J. Biosci, 6(4), 112-117. [CrossRef]
- Younas N, Fatima I, Ahmad IA, Ayyaz MK (2023) Alleviation of Zn deficiency in plants and humans through an effective technique; biofortification: A detailed review. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43(3), 419-425. [CrossRef]
- Zhai G, Walters KS, Peate DW, Alvarez PJ, Schnoor JL (2014). Transport of gold nanoparticles through plasmodesmata and precipitation of gold ions in woody poplar. Environmental science & technology letters, 1(2), 146-151. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Yue M, Zheng X, Xie C, Zhou H, Li L (2017) Physiological effects of single-and multi-walled carbon nanotubes on rice seedlings. IEEE transactions on nano bioscience, 16(7), 563-570. [CrossRef]
- Zhang P, Guo Z, Zhang Z, Fu H, White JC, Lynch I (2020) Nanomaterial transformation in the soil–plant system: implications for food safety and application in agriculture. Small, 16(21), 2000705. [CrossRef]
- Zhao L, Ortiz C, Adeleye AS, Hu Q, Zhou H, Huang Y, Keller AA (2016) Metabolomics to detect response of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) to Cu (OH) 2 nanopesticides: oxidative stress response and detoxification mechanisms. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(17), 9697-9707. [CrossRef]
| NPs Application | Size (nm) | Plants | Concentration | Effect | References |
| Soaking | 20 to 45 | Methi | 20 to 30 mg/L | Promoted fresh and dry weights of plant | Elsherif et al. 2023 |
| Adding to soil | 20 to 60 | Wheat | 7mg/kg | Promoted plant height and tillers number | Mazhar et al. 2023 |
| Adding to soil | 20 to 60 | Rice | 10 mg/kg | Enhanced the number of tillers and height of plants | Mazhar et al. 2023 |
| In Petri dishes | 31 | Barley | 1 to 4 mg/L | Improved elongation of root, shoot and germination of seed | Plaksenkova et al. 2021 |
| To soil | More than 100 | Carrot | 1 to 100 mg/kg | Biomass of the plant is increased | Song and Kim, 2020 |
| To soil | More than 100 | Lettuce | 1 to 100 mg/kg | Biomass of the plant is increased | Song and Kim, 2020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




