Submitted:
03 October 2024
Posted:
04 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
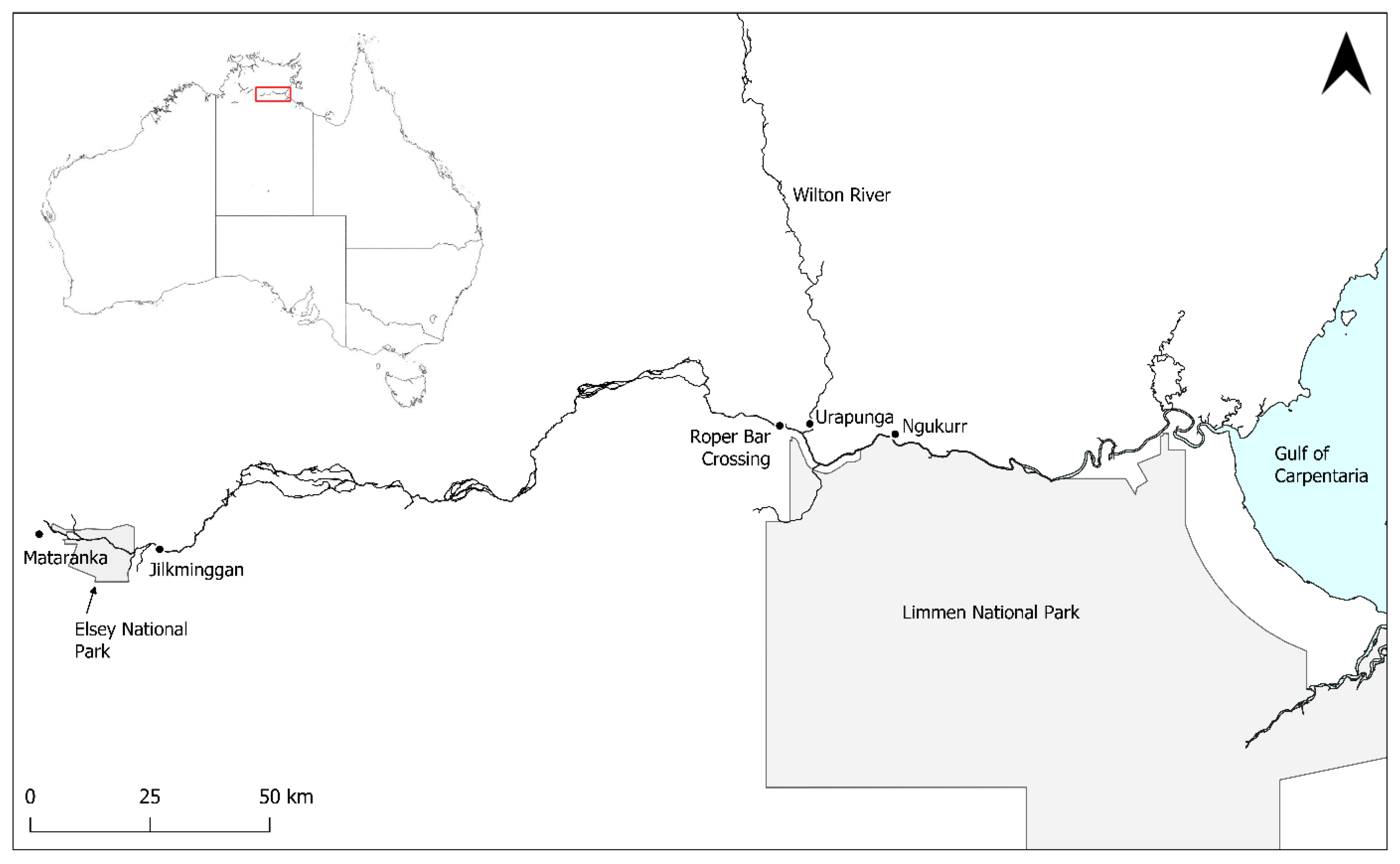
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Elasmobranch Surveys
2.3. Literature and Data Review
3. Results
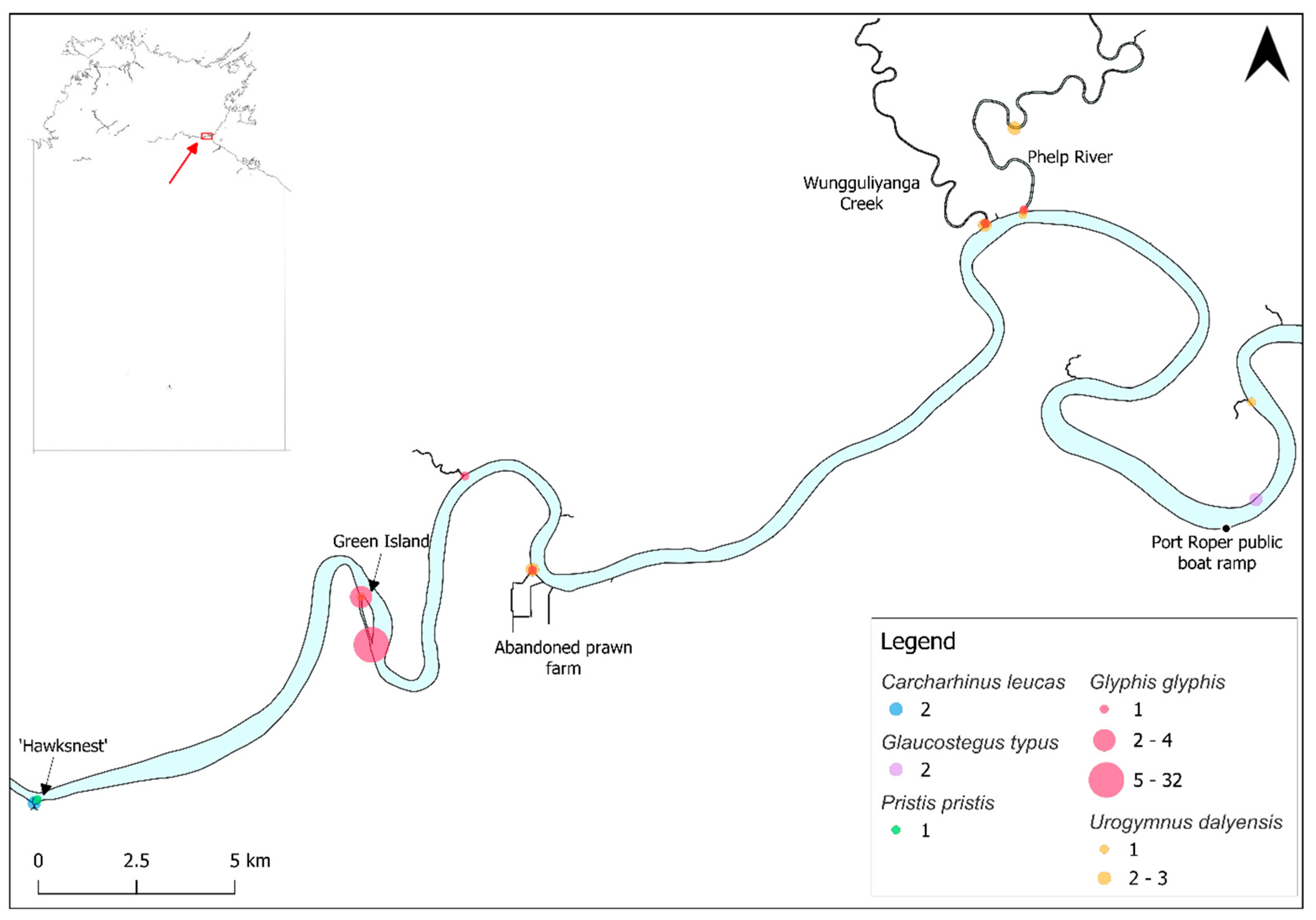
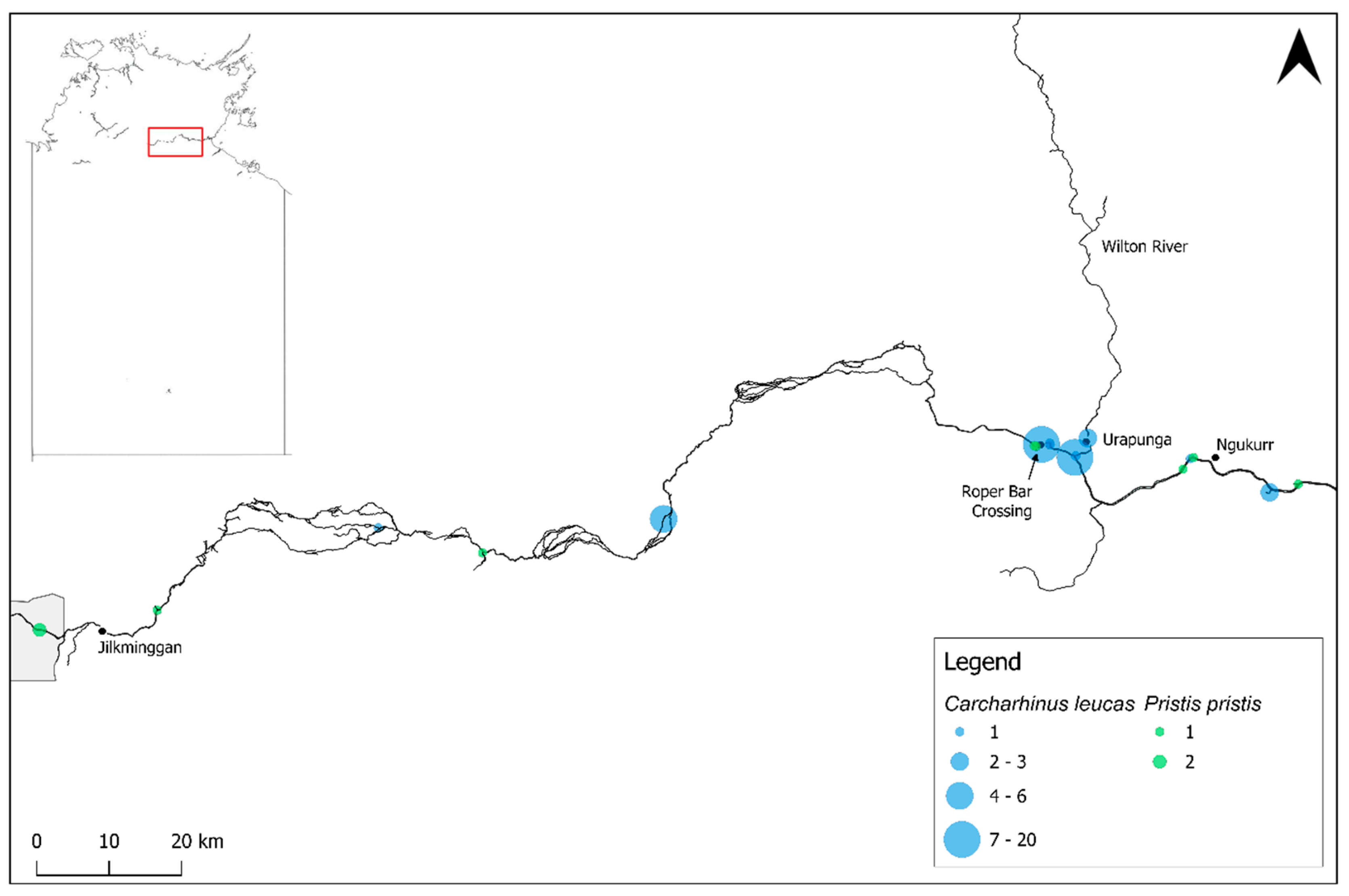
3.1. Carcharhinus leucas
3.2. Glaucostegus typus
3.3. Glyphis glyphis
3.4. Pristis pristis
3.5. Urogymnus dalyensis
| Species | IUCN Red List/ EPBC Act Category | Number recorded | Size range (cm) | Depth (m) | Salinity (PSS) | Turbidity (NTU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carcharhinus leucas | VU/nl | 50 | 68.0–139.5 | 0.8–21.0 | 0.06–1.3 | <3.2–44.0 |
| Glaucostegus typus | CR/nl | 2 | 100.0 | <1.0 | 29.38 | 19 |
| Glyphis glyphis | VU/CR | 40 | 53.5–125.0 | 1.2–9.5 | 5.8–20.8 | 15.0–439.0 |
| Pristis pristis | CR/VU | >11 | 100.0–340.0 | <2.0–5.0 | <1.0 | 4 |
| Urogymnus dalyensis | LC/nl | 14 | 83.0–129.5 | 2.8–7.8 | 5.8–26.1 | <58.0–292.0 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guisan, A. and Thuiller, W. (2005). Predicting species distribution: offering more than simple habitat models. Ecology Letters, 8(9):993–1009. [CrossRef]
- Moore, C., Drazen, J.C., Radford, B.T., Kelley, C. and Newman, S.J. (2016). Improving essential fish habitat designation to support sustainable ecosystem-based fisheries management. Marine Policy, 69:32–41. [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.D., Feldheim, K.A., Papastamatiou, Y.P. and Hueter, R.E. (2015). There and back again: a review of residency and return migrations in sharks, with implications for population structure and management. Annual Review of Marine Science, 7:547–570. [CrossRef]
- Hyde, C.A., Notarbartolo di Sciara, G., Sorrentino, L., Boyd, C., Finucci, B., Fowler, S.L., Kyne, P.M., Leurs, G., Simpfendorfer, C.A., Tetley, M.J., Womersley, F. and Jabado, R.W. (2022). Putting sharks on the map: a global standard for improving shark area-based conservation. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9:968853. [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S.L., Cazalis, V., Dudley, N., Hoffman, M., Rodrigues, A.S.L., Stolton, S., Visconti, P., Woodley, S., Kingston, N., Lewis, E., Maron, M., Strassburg, B.B.N., Wenger, A., Jonas, H.D., Venter, O. and Watson, J.E.M. (2020). Area-based conservation in the twenty-first century. Nature, 586:217–227. [CrossRef]
- IUCN. (2024). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2024-1. https://www.icunredlist.org.
- Compagno, L.J.V. and Cook, S.F. (1995). The exploitation and conservation of freshwater elasmobranchs: status of taxa and prospects for the future. Journal of Aquariculture and Aquatic Sciences, 12:62–90.
- Grant, M.I., Kyne, P.M., Simpfendorfer, C.A., White, W.T. and Chin, A. (2019). Categorising use patterns of non-marine environments by elasmobranchs and a review of their extinction risk. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 29(3):689–710. [CrossRef]
- Constance, J.M., Garcia, E.A., Pillans, R.D., Udyawer, V. and Kyne, P.M. (2024). A review of the life history and ecology of euryhaline and estuarine sharks and rays. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 34:65–89. [CrossRef]
- White, W.T. and Kyne, P.M. (2010). The status of chondrichthyan conservation in the Indo-Australiasian region. Journal of Fish Biology, 76(9):2090–2117. [CrossRef]
- Kyne, P.M., Jabado, R.W., Rigby, C.L., Dharmadi, Gore, M.A., Pollock, C.M., Herman, K.B., Cheok, J., Ebert, D.A., Simpfendorfer, C.A. and Dulvy, N.K. (2020). The thin edge of the wedge: extremely high extinction risk in wedgefishes and giant guitarfishes. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 30:1337–1361. [CrossRef]
- Bateman, R.L., Morgan, D.L., Wueringer, B.E., McDavitt, M. and Lear, K.O. (2024). Collaborative methods identify a remote global diversity hotspot of threatened, large-bodied rhino rays. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 34(1):e4047. [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, G.P. and Finlayson, C.M. (2008). General Introduction. In: Lukacs, G.P. and Finlayson, C.M. (eds) A Compendium of Ecological Information on Australia’s Northern Tropical Rivers. Sub-project 1 of Australia’s Tropical Rivers – an integrated data assessment and analysis (DET18). A report to Land & Water Australia, National Centre for Tropical Wetland Research, Townsville, Queensland.
- Morgan, D.L., Whitty, J.M., Phillips, N.M., Thorburn, D.C., Chaplin, J.A., and McAuley, R. (2011). North-western Australia as a hotspot for endangered elasmobranchs with particular reference to sawfishes and the Northern River Shark. Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia, 94:345–358.
- Grill, G., Lehner, B., Lumsdon, A.E., MacDonald, G.K., Zarfl, C. and Liermann, C.R. (2015). An index-based framework for assessing patterns and trends in river fragmentation and flow regulation by global dams at multiple scales. Environmental Research Letters, 10:015001. [CrossRef]
- Braccini, M., Molony, B. and Blay, N. (2019). Patterns in abundance and size of sharks in northwestern Australia: cause for optimism. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 77(1):72–82. [CrossRef]
- Midgley, S. H. (1979). The Roper River system, Limmen Bight River system, Rosie Creek system in the Northern Territory. Report to the Fisheries Division, Department of Primary Production of the Northern Territory, Nambour.
- Dally, G. and Larson, H.K. (2008). Roper River (Elsey and Moroak Stations) Freshwater Fishes Survey. MAGNT Research Report No. 12, Museum and Art Galleries of the Northen Territory, Darwin.
- Hammer, M., Williams, R. and Dally, G. (2012). Fishes of Wongalara Sanctuary. Museum and Art Gallery of the Northern Territory, Darwin.
- Petheram, C., McMahon, T.A. and Peel, M.C. (2008). Flow characteristics of rivers in northern Australia: Implications for development. Journal of Hydrology, 357:93–111. [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, D.C., Morgan, D.L., Rowland, A.J. and Gill, H. (2004). Elasmobranchs in the Fitzroy River, Western Australia. Report to the National Heritage Trust. Centre for Fish and Fisheries Research, Murdoch University, Perth, Western Australia.
- Pillans, R.D., Stevens, J.D., Kyne, P.M. and Salini, J. (2009). Observations on the distribution, biology, short-term movements and habitat requirements of river sharks Glyphis spp. in northern Australia. Endangered Species Research, 10:321–332. [CrossRef]
- Feutry, P., Kyne, P.M., Pillans, R.D., Chen, X., Naylor, G.J.P. and Grewe, P.M. (2014). Mitogenomics of the Speartooth Shark challenges ten years of control region sequencing. BMC Evolutional Biology, 14:232. [CrossRef]
- Feutry, P., Berry, O., Kyne, P.M., Pillans, R.D., Hillary, R.M., Grewe, P.M., Marthick, J.R., Johnson, G., Gunasekera, R.M., Bax, N.J. and Bravington, M. (2017). Inferring contemporary and historical genetic connectivity from juveniles. Molecular Ecology, 26:444–456. [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, D.C., Peverell, S., Stevens, J.D., Last, P.R. and Rowland, A.J. (2003). Status of Freshwater and Estuarine Elasmobranchs in Northern Australia. Unpublished Report to the National Heritage Trust, Canberra.
- Faulks, J.J. (2001). Roper River Catchment: an assessment of the physical and ecological condition of the Roper River and its major tributaries. Technical Report 36/2001, Natural Resources Division, Department of Lands, Planning and Environment, Katherine, Northern Territory.
- Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO). (2023). Watson, I., Petheram, C. Bruce, C. and Chilcott, C. (eds.). Water resource assessment for the Roper catchment: A report from the CSIRO Roper River Water Resource Assessment for the National Water Grid. CSIRO, Australia.
- Messel, H., Vorlicek, G.C., Wells, A.G., Green, W.J. and Johnson, A. (1980). Surveys of Tidal River Systems in the Northern Territory and their Crocodile Populations, Volume 12. Pergamon Press.
- Environmental Data and Analysis Branch: Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (DCCEEW). (2023). Indigenous Protected Areas September 2023. Retrieved from https://www.niaa.gov.au/sites/default/files/ipa-national-map-sep-2023.pdf. Accessed 28th February 2024.
- NT Fisheries (NTF). (2023). Commercial Barramundi Fishery Harvest Strategy. Department of Industry, Tourism and Trade, Darwin.
- Castro, J.I. (1993). The shark nursery of Bulls Bay, South Carolina, with a review of the shark nurseries of the southeastern coast of the United States. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 38:37–48. [CrossRef]
- Atlas of Living Australia (ALA). (2024). Atlas of Living Australia. Available from https://www.ala.org.au. Accessed 17th May 2024.
- iNaturalist. (2024). iNaturalist. Available from https://www.inaturalist.org. Accessed 17th May 2024.
- Last, P.R., White, W.T., de Carvalho, M.R., Séret, B., Stehmann, M.F. W. and Naylor, G.J.P. (2016). Rays of the World. CSIRO Publishing, Clayton South.
- Department of Environment, Parks and Water Security (DEPWS). (2022). Aquatic Ecosystems Baseline Report: Strategic Regional Environmental and Baseline Assessment for the Beetaloo Sub-basin. Technical Report 30/2022. Flora and Fauna Division, Department of Environment, Parks and Water Security, Northern Territory Government. Berrimah, Northern Territory.
- Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (DCCEEW). (2024). Species Profile and Threats Database: EPBC Act List of Threatened Fauna. Available from https://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/sprat/public/publicthreatenedlist.pl?wanted=fauna#fishes_critically_endangered. Accessed 5th September 2024.
- Kyne, P.M., Rigby, C.L., Dharmadi, Gutteridge, A.N. and Jabado, R.W. (2019). Glaucostegus typus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T104061138A68623995. [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, D.C., Morgan, D.L., Rowland, A.J., and Gill, H.S. (2007). Freshwater sawfish Pristis microdon Latham, 1794 (Chondrichthyes: Pristidae) in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Zootaxa, 1471:27–41.
- Kyne, P.M., Oetinger, M., Grant, M.I. and Feutry, P. (2021). Life history of the Critically Endangered largetooth sawfish: a compilation of data for population assessment and demographic modelling. Endangered Species Research, 44:79–88. [CrossRef]
- White, W.T., Appleyard, S.A., Sabub, B., Kyne, P.M., Harris, M., Lis, R., Baje, L., Usu, T., Smart, J.J., Corrigan, S., Yang, L. and Naylor, G.J.P. (2015). Rediscovery of the threatened river sharks, Glyphis garricki and G. glyphis, in Papua New Guinea. PLoS ONE, 10(10):e0140075. [CrossRef]
- Jenson, N.H. (1976). Reproduction of the bull shark, Carcharhinus leucas, in the Lake Nicaragua-Rio San Juan system. In: Thorson, T.B. (ed.) Investigations of the Ichthyofauna of Nicaraguan Lakes. University of Nebraska, Lincoln.
- Cliff, G. and Dudley, S.F.J. (1991). Sharks caught in the protective gill nets of Natal, South Africa. 4. The bull shark Carcharhinus leucas Valenciennes. South African Journal of Marine Science, 10:253–270. [CrossRef]
- Pirog, A., Magalon, H., Poirout, T. and Jaquemet, S. (2019). Reproductive biology, multiple paternity and polyandry of the bull shark Carcharhinus leucas. Journal of Fish Biology, 95(5):1195–1206. [CrossRef]
- Lyon, B.J., Dwyer, R.G., Pillans, R.D., Campbell, H.A. and Franklin, C.E. (2017). Distribution, seasonal movements and habitat utilisation of an endangered shark, Glyphis glyphis, from northern Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 573:203–213. [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, D.C. and Rowland, A.J. (2008). Juvenile bull sharks Carcharhinus leucas (Valenciennes, 1839) in northern Australian rivers. The Beagle, Records of the Museum and Art Galleries of the Northern Territory, 24:79–86. [CrossRef]
- Kyne, P.M., Smart, J.J. and Johnson, G. (2022). Extremely low sample size allows age and growth estimation in a rare and threatened shark. bioRxiv preprint. [CrossRef]
- Kyne, P.M., Rigby, C.L., Darwall, W.R.T., Grant, I. and Simpfendorfer, C. (2021). Glyphis glyphis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: e.T39379A68624306. [CrossRef]
- West, L.D., Stark, K.E., Dysart, K. and Lyle, J.M. (2022). Survey of recreational fishing in the Northern Territory: 2018 to 2019. Northern Territory Fisheries, Department of Industry, Tourism and Trade, Darwin.
- Lowry, M., Steffe, A. and Williams, D. (2006). Relationships between bait collection, bait type and catch: a comparison of the NSW trailer-boat and gamefish-tournament fisheries. Fisheries Research, 778(2–3):266–275. [CrossRef]
- Kyne, P.M. and Feutry, P. (2017). Recreational fishing impacts on threatened river sharks: a potential conservation issue. Ecological Management & Restoration, 18(3):209–213. [CrossRef]
- Field, I.C., Tillet, B.J., Charters, R., Johnson, G.J., Bukworth, R.C., Meekan, M.G. and Bradshaw, C.J.A. (2013). Distribution, relative abundance and risks from fisheries to threatened Glyphis sharks and sawfishes in northern Australia. Endangered Species Research, 21:171–180. [CrossRef]
- Pillans, R.D., Fry, G.C., Carlin, G.D. and Patterson, T.A. (2022). Bycatch of a Critically Endangered shark Glyphis glyphis in a crab pot fishery: implications for management. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9:787634. [CrossRef]
- Tillett, B.J., Field, I.C., Bradshaw, C.J.A., Johnson, G., Buckworth, R.C., Meekan, M.G. and Ovenden, J.R. (2012). Accuracy of species identification by fisheries observers in a north Australia shark fishery. Fisheries Research, 127–128:109–115. [CrossRef]
- Prime Minister and Cabinet (PMC). (2007). National plan for water security. Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet. Retrieved from https://www.crcsi.com.au/assets/Resources/f21ceb9e-2258-4f40-9e11-50fa80ee940e.pdf. Accessed on 11th April 2024.
- Northern Territory Government (NTG). (2023). Territory Water Plan: A Plan to Deliver Water Security for all Territorians, Now and into the Future. Office of Water Security, Darwin.
- Northern Territory Government (NTG). (2023). Georgina Wiso Water Allocation Plan 2023–2031. Water Resources Division, Department of Environment, Parks and Water Security, Darwin.
- Grill, G., Lehner, B., Thieme, M., Geenen, B., Tickner, D., Antonelli. F., Babu, S., Borrelli, P., Cheng, L., Crochetiere, H., Ehalt Macedo, H., Filgueiras, R., Goichot, M., Higgins, J., Hogan, Z., Lip, B., McClain, M.E., Meng, J., Mulligan, M., Nilsson, C., Olden, J.D., Opperman, J.J., Petry, P., Reidy Liermann, C., Sáenz, L., Salinas-Rodríuez, S., Schelle, P., Schmitt, R.J.P., Snider, J., Tan, F., Tockner, K., Valdujo, P.H., van Soesbergen, A. and Zarfl, C. (2019). Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers. Nature, 569:215–221. [CrossRef]
- Lear, K.O., Morgan, D.L., Whitty, J.M., Beatty, S.J. and Gleiss, A.C. (2021). Wet season flood magnitude drives resilience to dry season drought of a euryhaline elasmobranch in a dry-land river. Science of the Total Environment, 750:142234. [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, N. (2004). The changing nature of Australian droughts. Climate Change, 63:323–336. [CrossRef]
- Bates, B.C., Hope, P., Ryan, B., Smith, I. and Charles, S. (2008). Key findings from the Indian Ocean climate initiative and their impact on policy development in Australia. Climate Change, 89:339–354. [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.A., Hillary, R.M., Kyne, P.M., Pillans, R.D., Gunasekera, R.M., Marthick, J.R., Johnson, G.J. and Feutry, P. (2022). Rapid assessment of adult abundance and demographic connectivity from juvenile kin pairs in a critically endangered species. Science Advances, 8:eadd1679. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





