Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
04 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
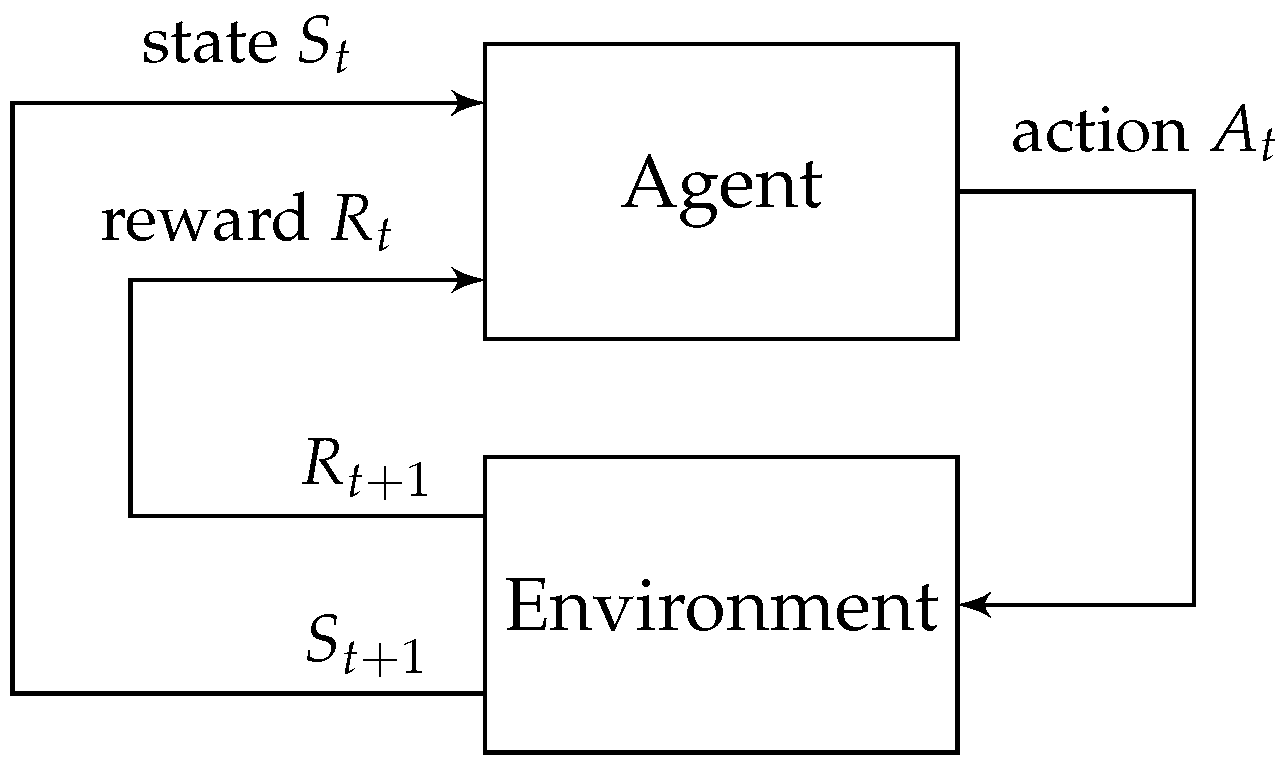
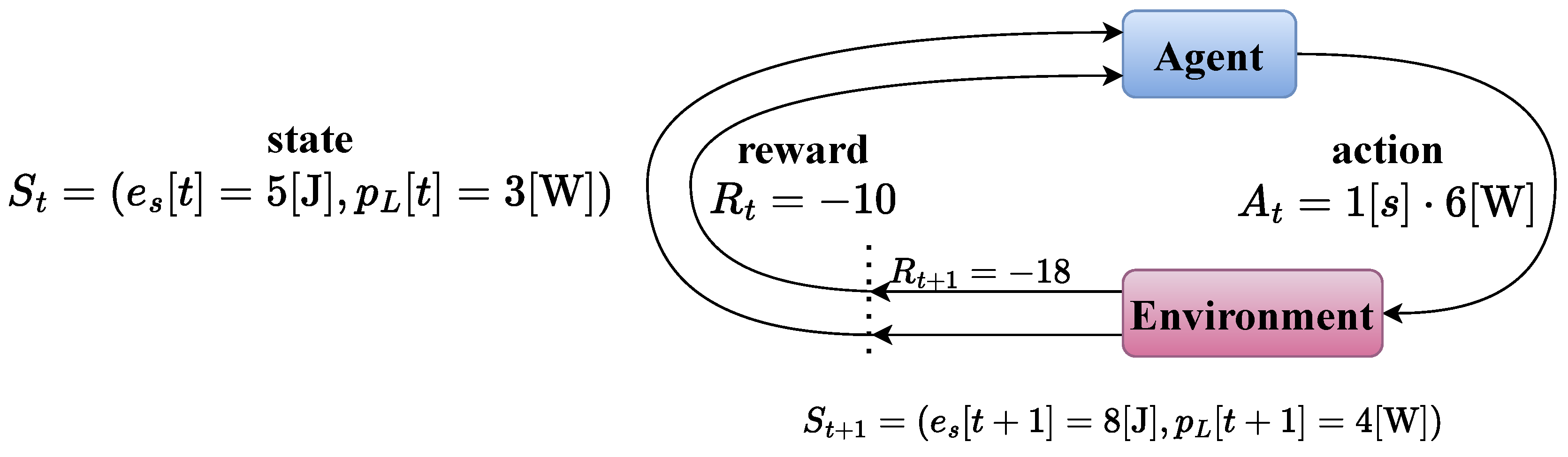
2. Technical Background on Reinforcement Learning
2.1. Markov Decision Processes
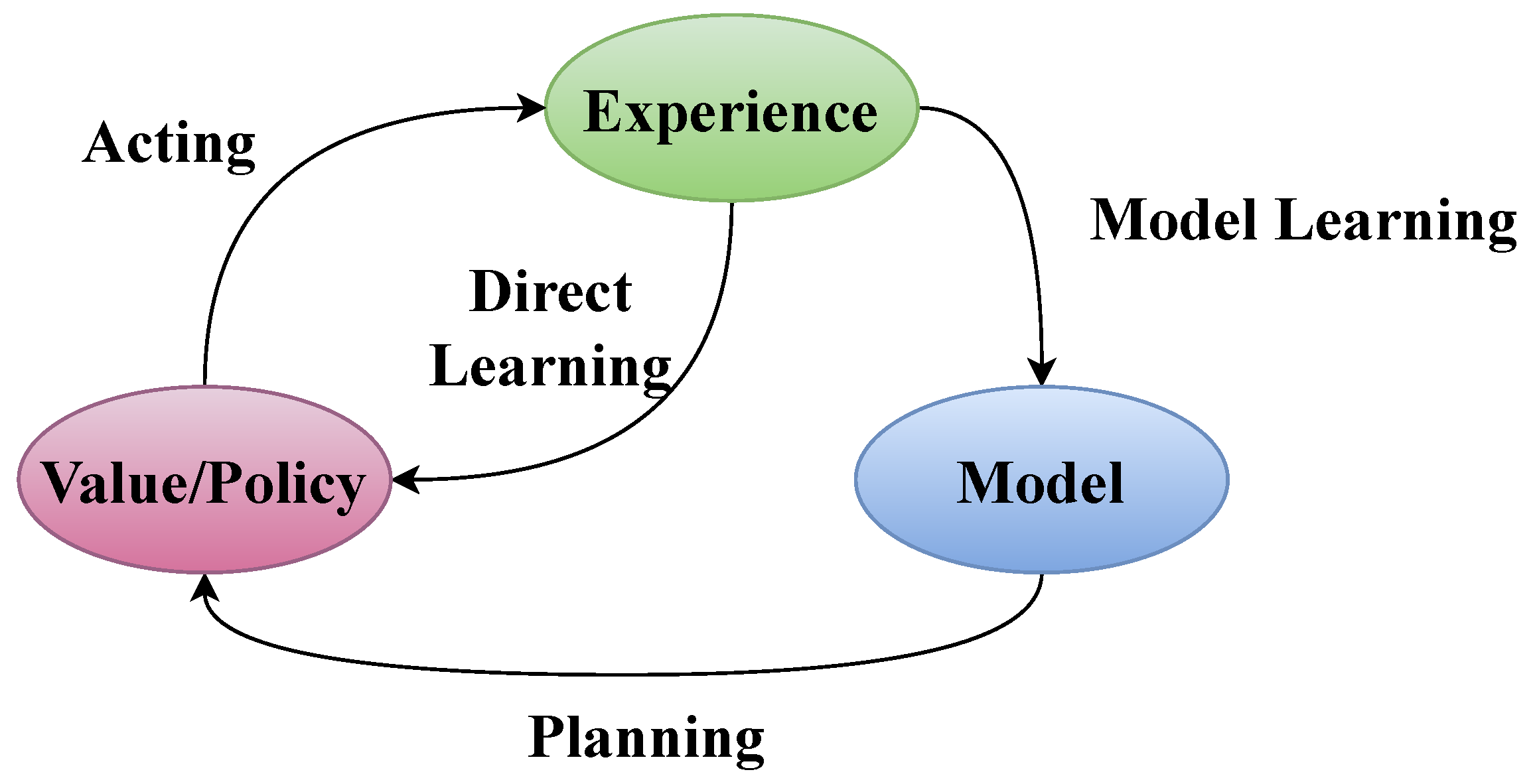
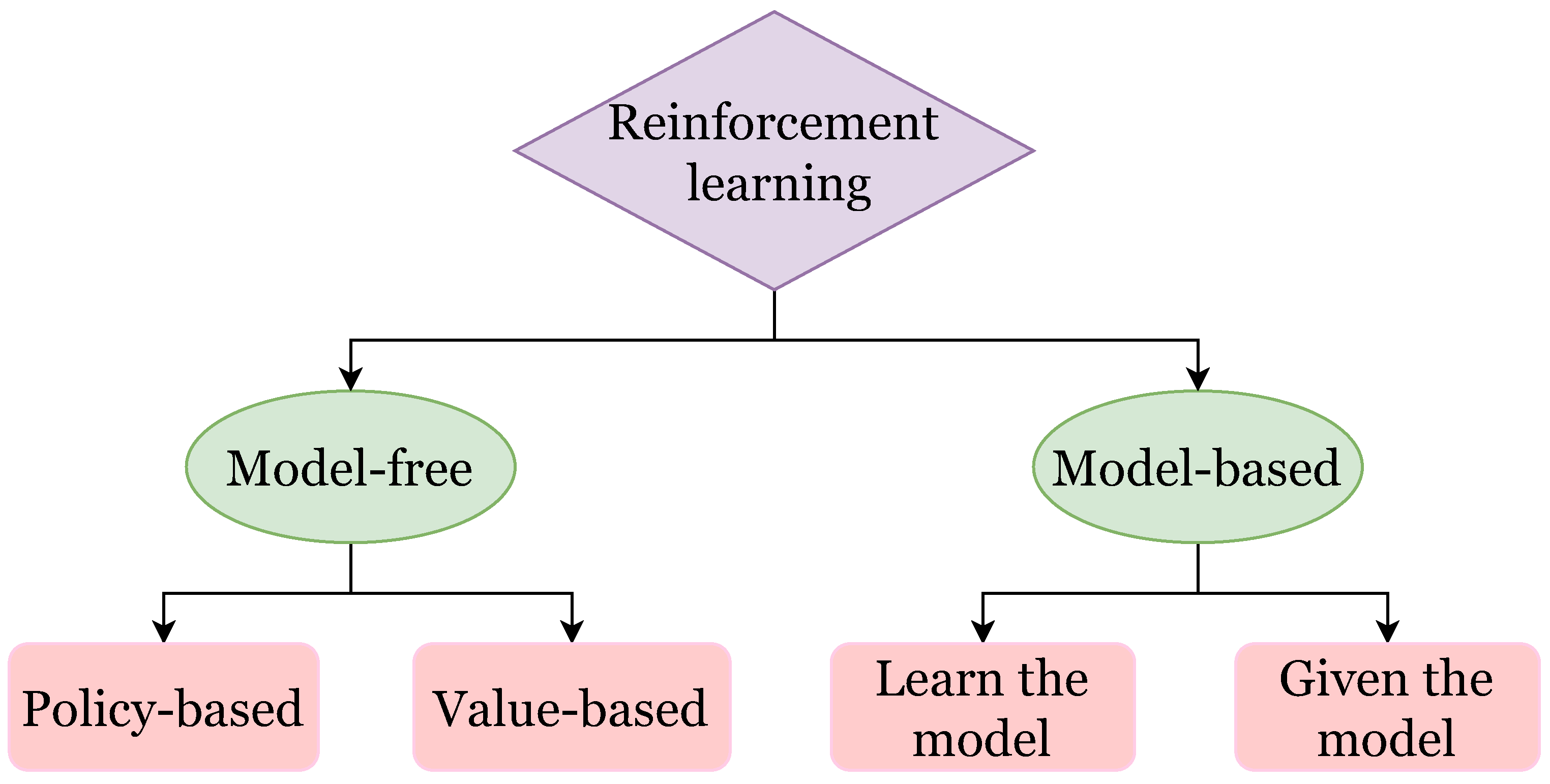
2.2. Model Based and Model Free Reinforcement Learning
2.3. Model Computation
2.3.1. Dynamic Programming
2.3.2. Model Predictive Control (MPC)
2.4. Policy Learning Basic Concepts
2.4.1. Value Function
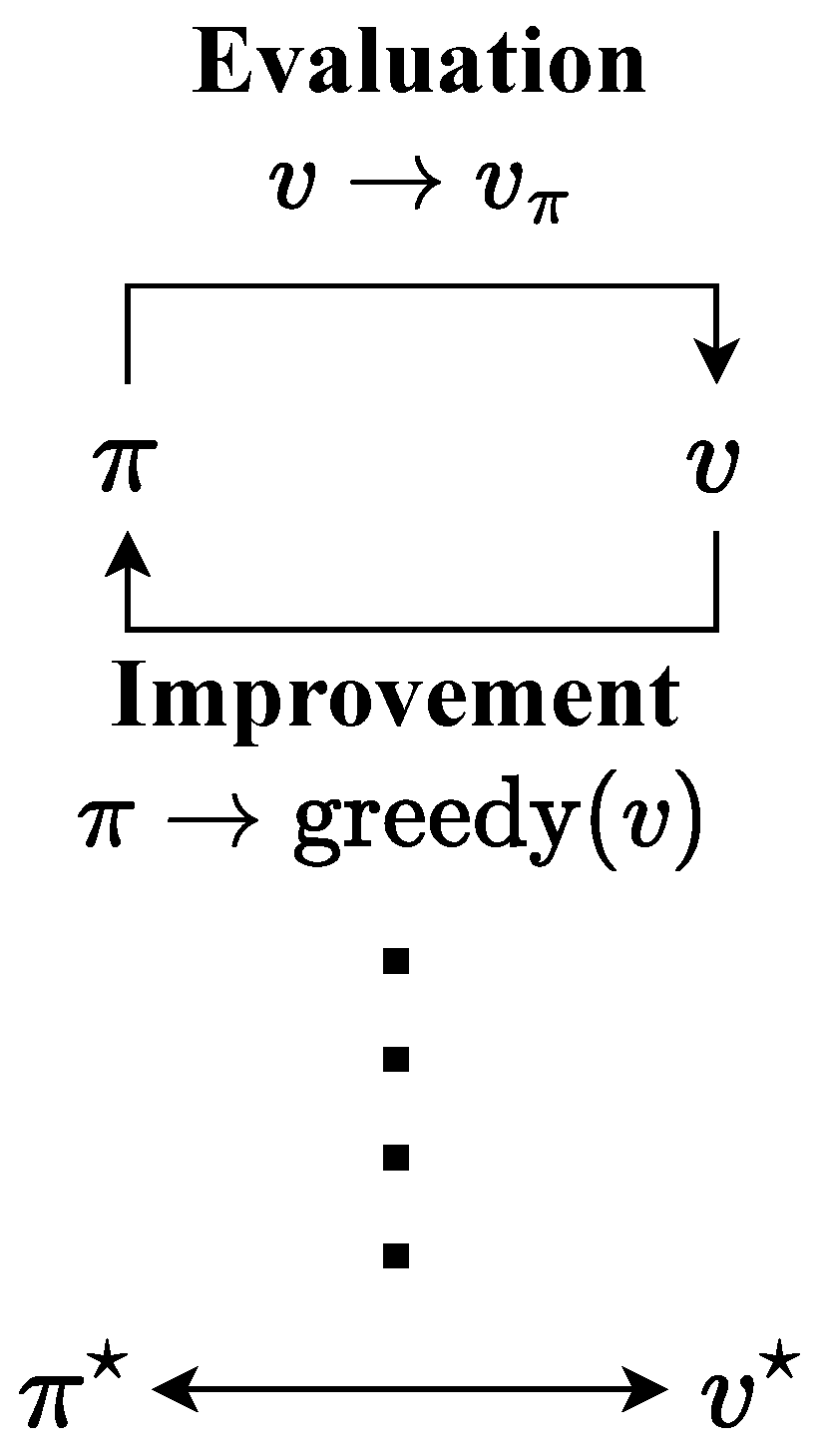
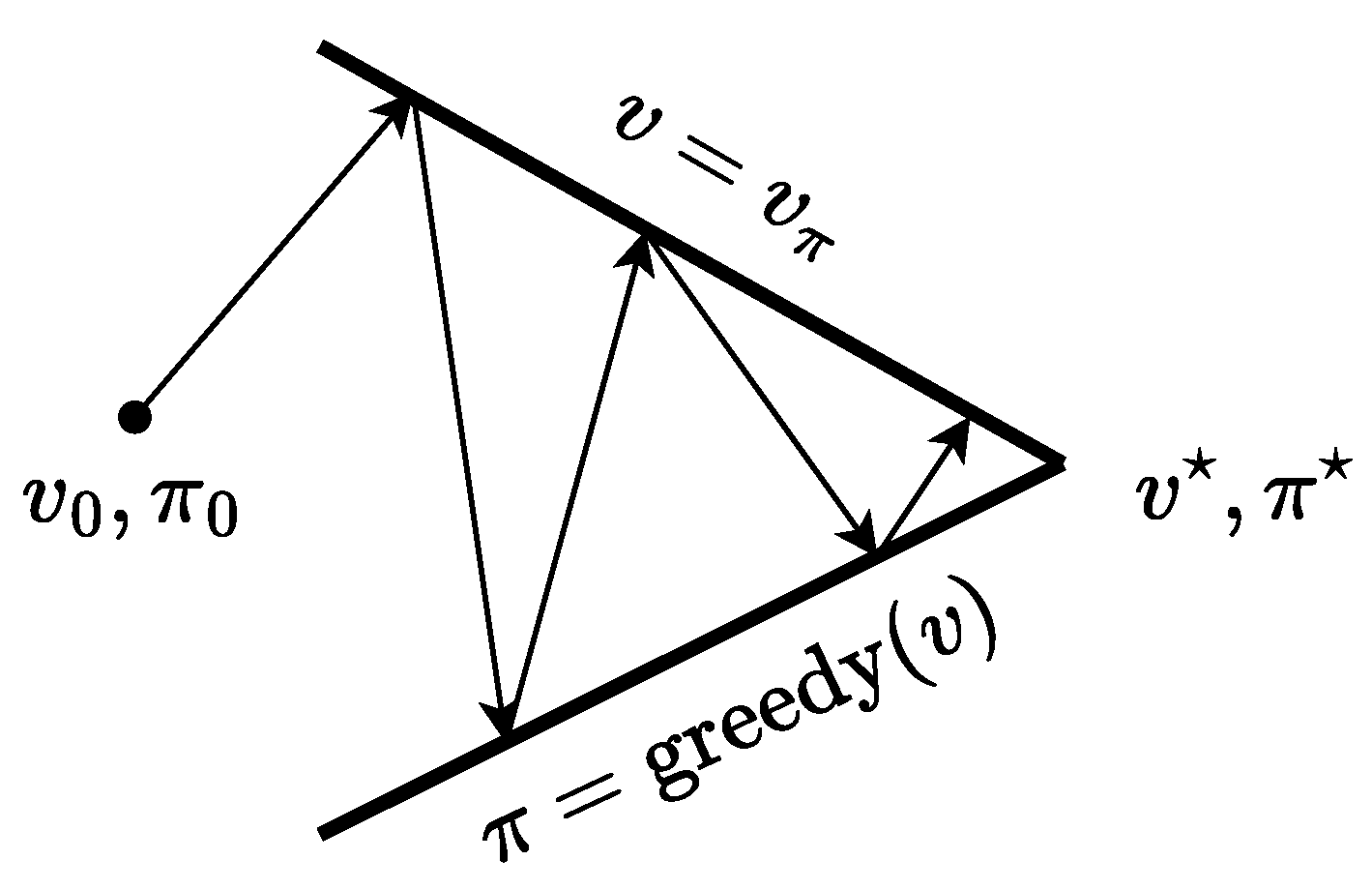
2.4.2. Policy Iteration
2.4.3. Value Iteration
2.4.4. Policy Gradient
3. Model-Based Paradigm
3.1. Energy Markets Management
3.2. Power Grid Stability and Control
3.3. Building Energy Management
3.4. Electrical Vehicles
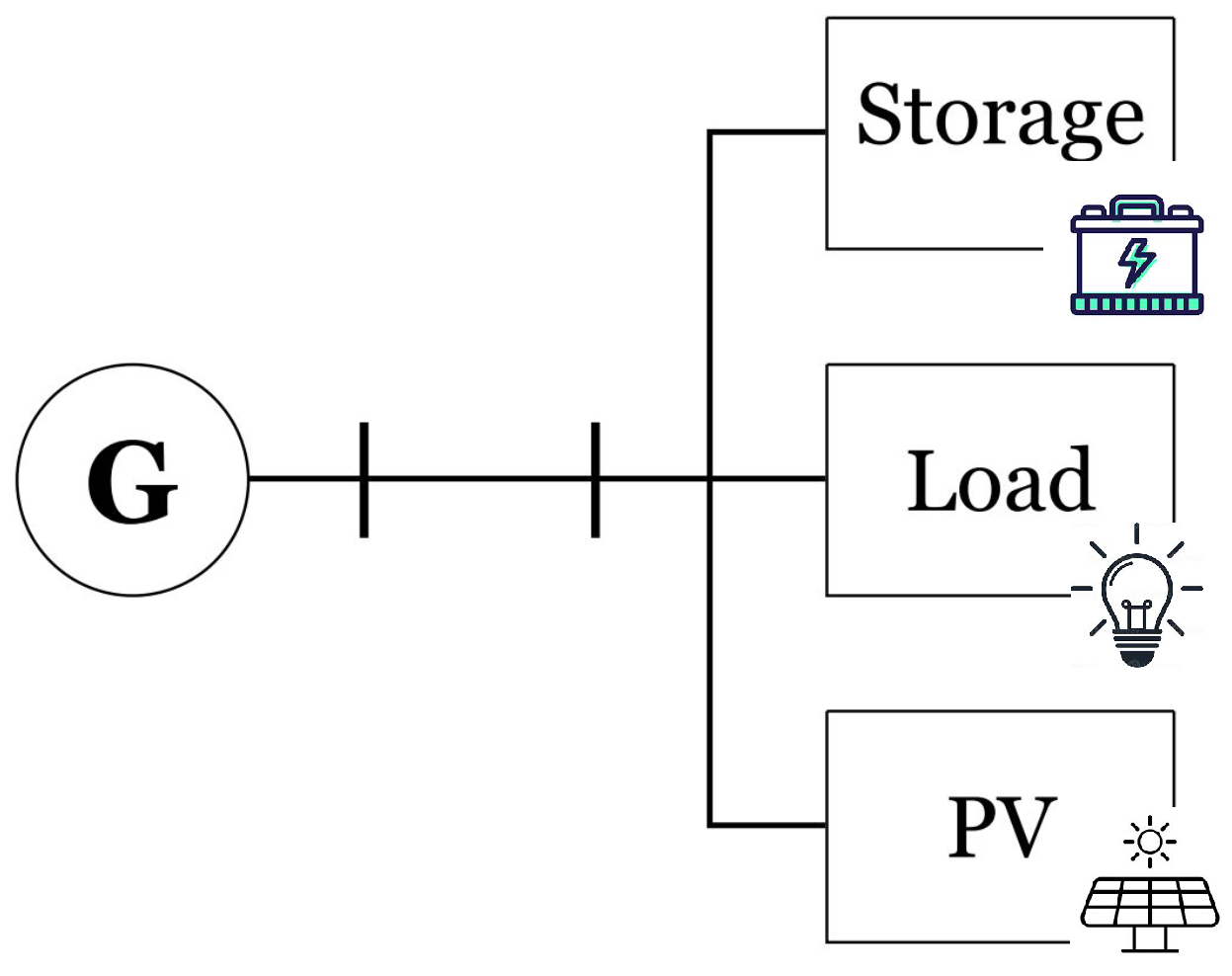
3.5. Energy Storage Management
3.6. Prominent Trends
4. Model-Free Paradigms
4.1. Energy Markets Management
4.2. Power Grid Stability and Control
4.3. Building Energy Management
4.4. Electrical Vehicles
4.5. Energy Storage Management
4.6. Prominent Trends
5. Comparison and Discussion
6. Challenges and Future Research Work
6.1. Challenges
6.1.1. Limited Real-World Data And Standardized Tools
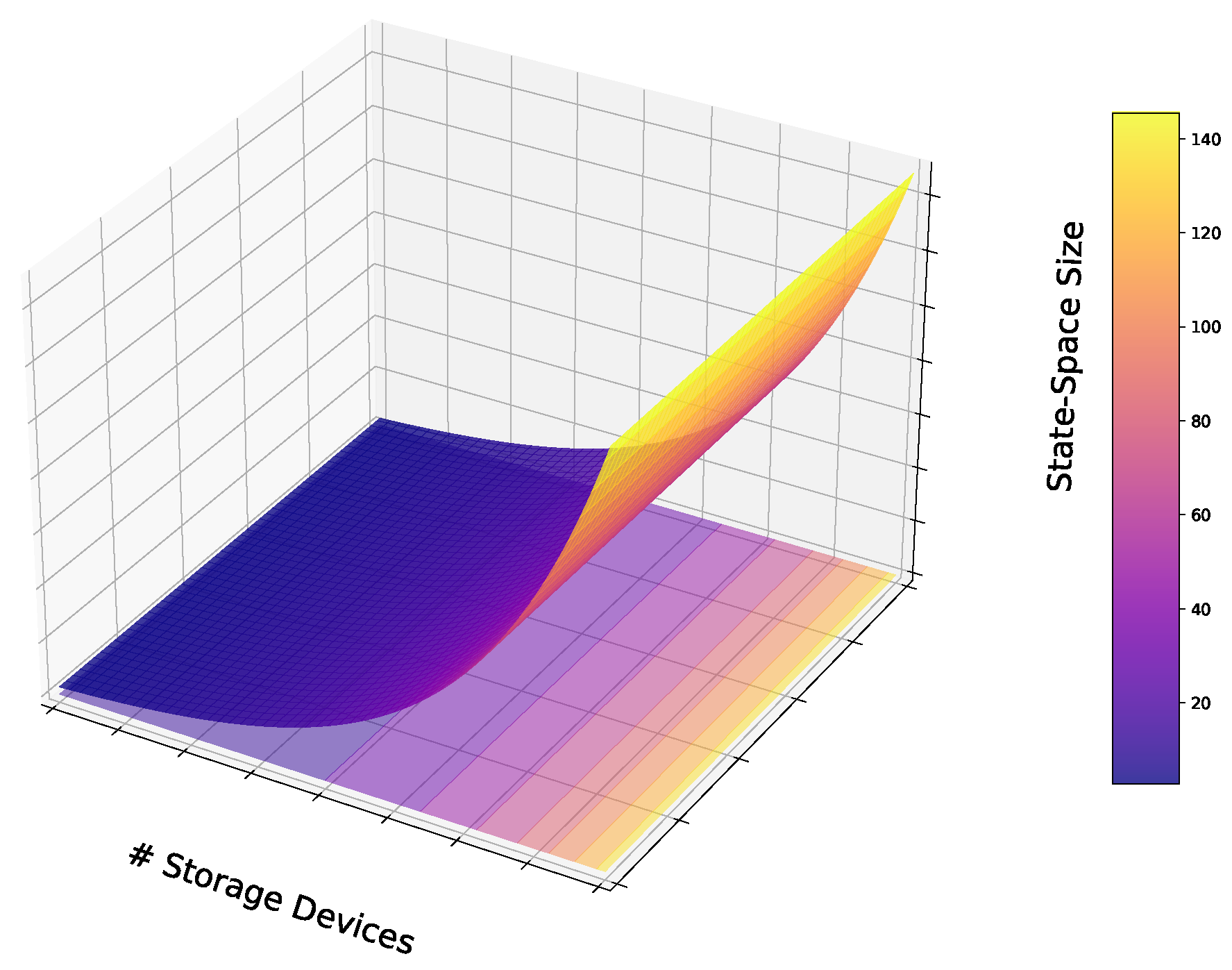
6.1.2. Limited Scalability, Generalization, And The Curse Of Dimensionality
6.1.3. Limited Robustness And Safety For Real-Time Applications
6.2. Future Work
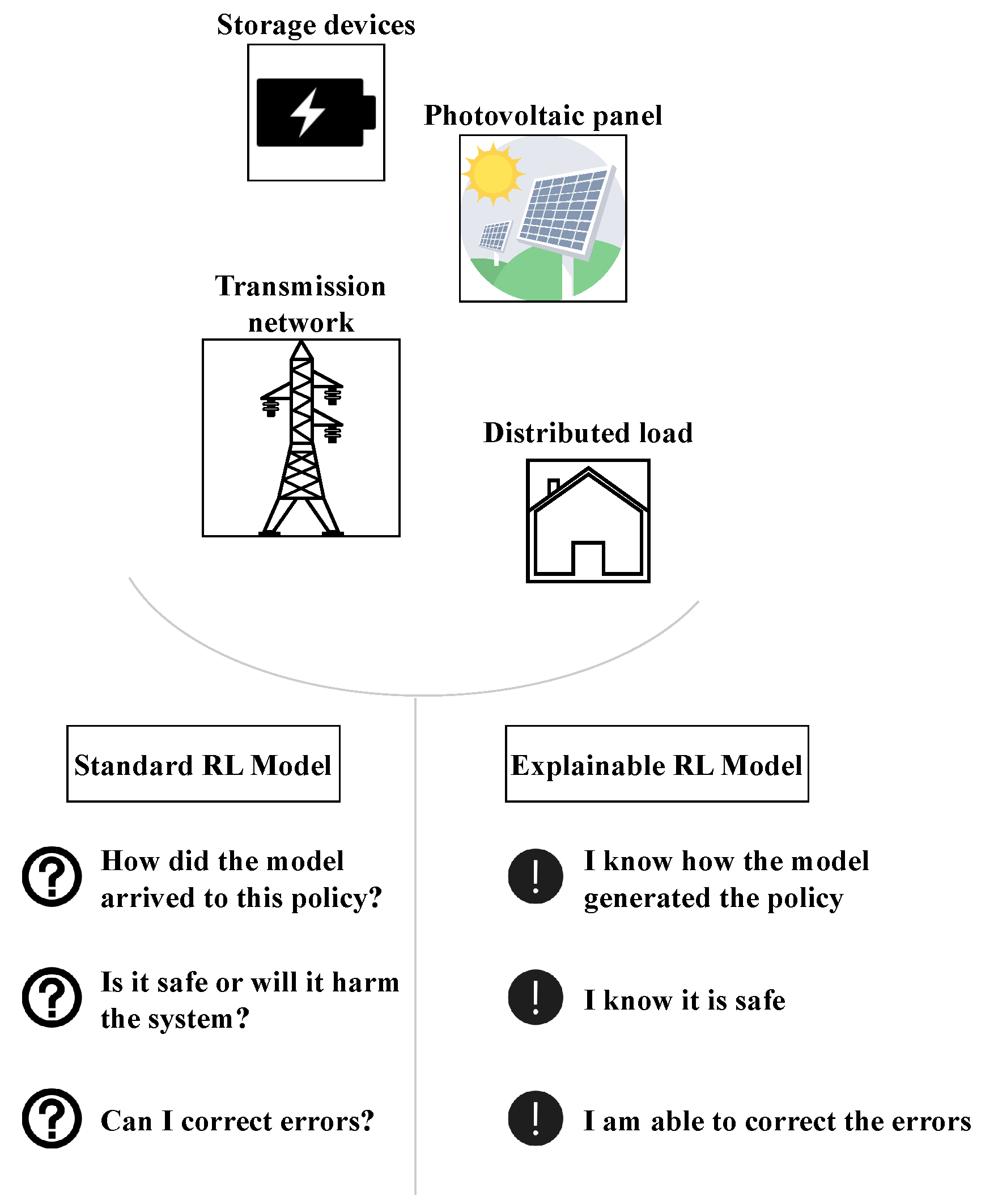
6.2.1. Explainability
6.2.2. Neural Architecture Search
6.2.3. Physics-Informed Neural Networks
6.2.4. Public Data-Sets
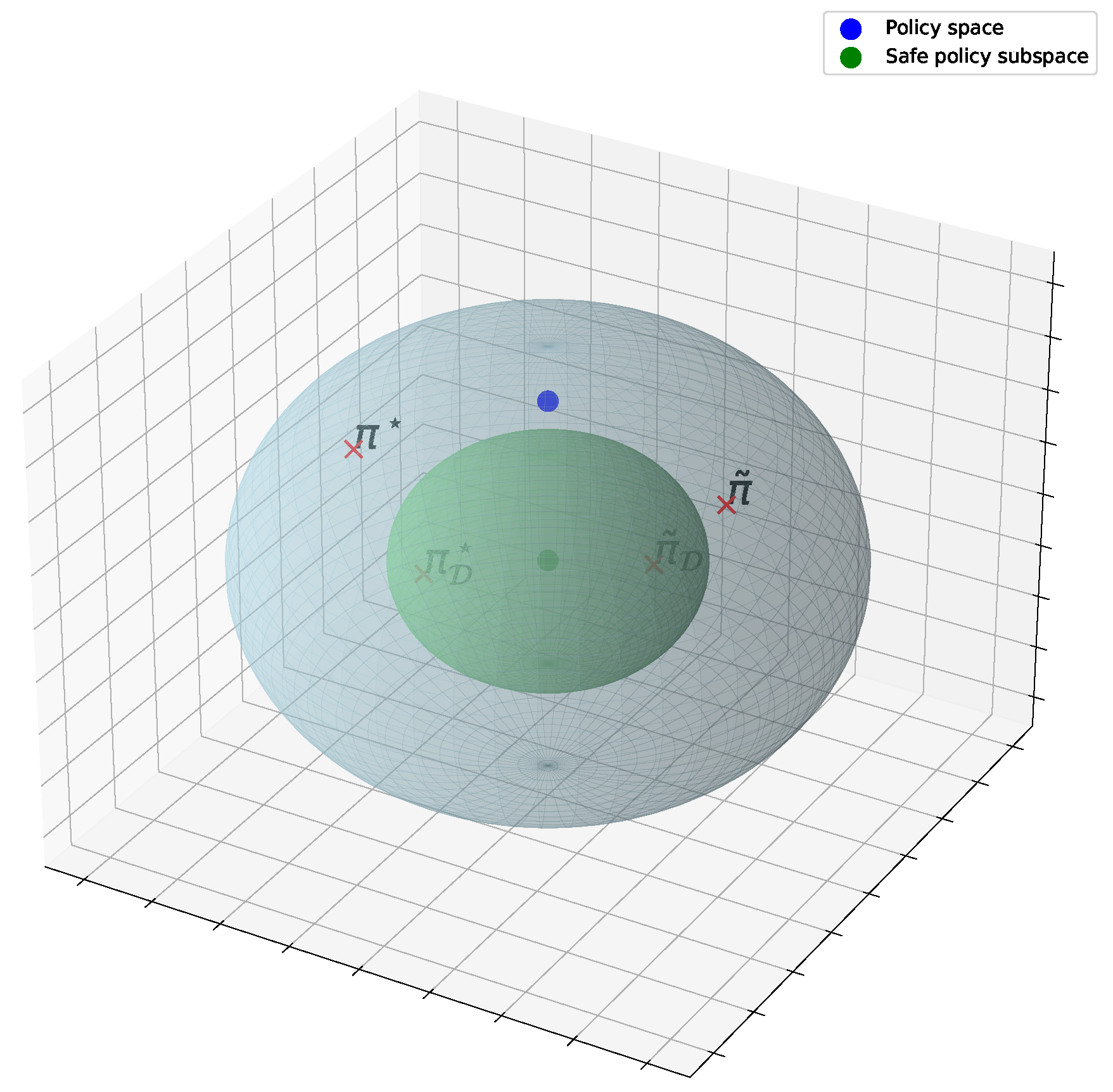
6.2.5. Safety For Real-Time Applications
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RL | Reinforcement learning |
| MDP | Markov decision process |
| EM | Energy market |
| GSAC | Grid stability and control |
| BEM | Building energy management |
| EV | Electric vehicle |
| ESS | Energy storage system |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| MG | Micro-grid |
| DR | Demand-response |
| ET | Energy trading |
| AC | Actor-critic & varitations |
| PG | Policy gradient & varitations |
| QL | Q-learning & varitations |
References
- Schneider, N. Population growth, electricity demand and environmental sustainability in Nigeria: Insights from a vector auto-regressive approach. International Journal of Environmental Studies 2022, 79, 149–176. [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.A.; Sohag, K.; Abdullah, S.M.S.; Jaafar, M. CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic and population growth in Malaysia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 41, 594–601. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. Exploring the effects of economic growth, population density and international trade on energy consumption and environmental quality in India. International Journal of Energy Sector Management 2020-10-08, 14, 1177–1203. [CrossRef]
- Comello, S.; Reichelstein, S.; Sahoo, A. The road ahead for solar PV power. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 92, 744–756. [CrossRef]
- Fathima, A.H.; Palanisamy, K. Energy storage systems for energy management of renewables in distributed generation systems. Energy Management of Distributed Generation Systems 2016, 157. [CrossRef]
- Heldeweg, M.A.; Séverine Saintier. Renewable energy communities as ‘socio-legal institutions’: A normative frame for energy decentralization? Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2020, 119, 109518. [CrossRef]
- Urishev, B. Decentralized Energy Systems, Based on Renewable Energy Sources. Applied Solar Energy 2019, 55, 207–212. [CrossRef]
- Yaqoot, M.; Diwan, P.; Kandpal, T.C. Review of barriers to the dissemination of decentralized renewable energy systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 58, 477–490. [CrossRef]
- Avancini, D.B.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Martins, S.G.; Rabêlo, R.A.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Solic, P. Energy meters evolution in smart grids: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 217, 702–715. [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, I.; Abido, M.A.; Khalid, M.; Savkin, A.V. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances in Smart Grids: A Sustainable Future with Renewable Energy Resources. Energies 2020, 13, e25705. [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.A.; Ouahada, K.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. A Review of Machine Learning Approaches to Power System Security and Stability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 113512–113531. [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Ernst, R.; Klaer, B.; Hacker, I.; Henze, M. Cybersecurity in Power Grids: Challenges and Opportunities. Sensors 2021, 21. [CrossRef]
- Yohanandhan, R.V.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Manoharan, P.; Mihet-Popa, L. Cyber-Physical Power System (CPPS): A Review on Modeling, Simulation, and Analysis With Cyber Security Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 151019–151064. [CrossRef]
- Guerin, T.F. Evaluating expected and comparing with observed risks on a large-scale solar photovoltaic construction project: A case for reducing the regulatory burden. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 74, 333–348. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Alzate, J.; Barrera, J. Regulatory design and incentives for renewable energy. Journal of Regulatory Economics 2011, 41, 315–336. [CrossRef]
- Glavic, M. (Deep) Reinforcement learning for electric power system control and related problems: A short review and perspectives. Annual Reviews in Control 2019, 48, 22–35. [CrossRef]
- Perera, A.; Kamalaruban, P. Applications of reinforcement learning in energy systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 137, 110618. [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, M.; Al-Greer, M.; Short, M. Reinforcement Learning-Based Intelligent Control Strategies for Optimal Power Management in Advanced Power Distribution Systems: A Survey. Energies 2023, 16. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qu, G.; Tang, Y.; Low, S.; Li, N. Reinforcement Learning for Selective Key Applications in Power Systems: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2935–2958. [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement learning: An introduction; MIT press, 2018.
- Graesser, L.; Keng, W. Foundations of Deep Reinforcement Learning: Theory and Practice in Python; Addison-Wesley data and analytics series, Addison-Wesley, 2020.
- Qiang, W.; Zhongli, Z. Reinforcement learning model, algorithms and its application. International Conference on Mechatronic Science, Electric Engineering and Computer (MEC); , 2011; pp. 1143–1146. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, Z.; Başar, T., Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning: A Selective Overview of Theories and Algorithms. In Handbook of Reinforcement Learning and Control; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 321–384. [CrossRef]
- Moerland, T.M.; Broekens, J.; Plaat, A.; Jonker, C.M. Model-based Reinforcement Learning: A Survey. Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning 2023, 16, 1–118. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q. Model-based or model-free, a review of approaches in reinforcement learning. 2020 International Conference on Computing and Data Science (CDS); , 2020; pp. 219–221. [CrossRef]
- Freed, B.; Wei, T.; Calandra, R.; Schneider, J.; Choset, H. Unifying Model-Based and Model-Free Reinforcement Learning with Equivalent Policy Sets. Reinforcement Learning Journal 2024, 1, 283–301.
- Bayón, L.; Grau, J.; Ruiz, M.; Suárez, P. A comparative economic study of two configurations of hydro-wind power plants. Energy 2016, 112, 8–16. [CrossRef]
- Riffonneau, Y.; Bacha, S.; Barruel, F.; Ploix, S. Optimal power flow management for grid connected PV systems with batteries. IEEE Transactions on sustainable energy 2011, 2, 309–320. [CrossRef]
- Powell, W.B. Approximate Dynamic Programming: Solving the curses of dimensionality; John Wiley & Sons, 2007.
- Zargari, N.; Ofir, R.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Belikov, J.; Levron, Y. An Optimal Control Method for Storage Systems With Ramp Constraints, Based on an On-Going Trimming Process. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology 2023, 31, 493–496. [CrossRef]
- García, C.E.; Prett, D.M.; Morari, M. Model predictive control: Theory and practice—A survey. Automatica 1989, 25, 335–348. [CrossRef]
- Schwenzer, M.; Ay, M.; Bergs, T.; Abel, D. Review on model predictive control: An engineering perspective - The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology; SpringerLink, 2021. [Accessed 13-05-2024].
- Morari, M.; Garcia, C.E.; Prett, D.M. Model predictive control: Theory and practice. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 1988, 21, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Kakade, S.M.; Lee, J.D.; Mahajan, G. On the Theory of Policy Gradient Methods: Optimality, Approximation, and Distribution Shift. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2021, 22, 1–76. [CrossRef]
- Sanayha, M.; Vateekul, P. Model-based deep reinforcement learning for wind energy bidding. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 136, 107625. [CrossRef]
- Wolgast, T.; Nieße, A. Approximating Energy Market Clearing and Bidding With Model-Based Reinforcement Learning. ArXiv 2023, abs/2303.01772. [CrossRef]
- Sanayha, M.; Vateekul, P. Model-Based Approach on Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning With Multiple Clusters for Peer-To-Peer Energy Trading. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 127882–127893. [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, J.; Shi, R.; He, Y.; Wu, M. Enhancing renewable energy certificate transactions through reinforcement learning and smart contracts integration. Scientific Reports 2024, 14. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xia, Q.; Chi, Y.; Lei, C.; Zhou, N. Federated reinforcement learning for Short-Time scale operation of Wind-Solar-Thermal power network with nonconvex models. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2024, 158, 109980. [CrossRef]
- Nanduri, V.; Das, T.K. A Reinforcement Learning Model to Assess Market Power Under Auction-Based Energy Pricing. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2007, 22, 85–95. [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Kordabad, A.B.; Gros, S. Energy management in residential microgrid using model predictive control-based reinforcement learning and Shapley value. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 119, 105793. [CrossRef]
- Ojand, K.; Dagdougui, H. Q-Learning-Based Model Predictive Control for Energy Management in Residential Aggregator. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 2022, 19, 70–81. [CrossRef]
- company, N.P. Nord Pool wholesale electricity market data, 2024. [Online] Available https://data.nordpoolgroup.com/auction/day-ahead/prices?deliveryDate=latest¤cy=EUR&aggregation=Hourly&deliveryAreas=AT, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- company, A. Australia gird data, 2024. [Online] Available https://www.ausgrid.com.au/Industry/Our-Research/Data-to-share/Average-electricity-use, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Chinese listed companies, C. Carbon emissions data, 2024. [Online] Available https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-60527-3/tables/1, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Hiskens, I. IEEE PES task force on benchmark systems for stability controls, 2013.
- company, E. Belgium grid data, 2024. [Online] Available https://www.elia.be/en/grid-data/, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- company, C. Chicago electricity price data, 2024. [Online] Available https://hourlypricing.comed.com/live-prices/, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Yin, T.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Tan, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q. Accelerated Derivative-Free Deep Reinforcement Learning for Large-Scale Grid Emergency Voltage Control. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2022, 37, 14–25. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, R.R.; Yin, T.; Du, Y.; Huang, R.; Tan, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q. Efficient learning of power grid voltage control strategies via model-based Deep Reinforcement Learning - machine learning. SpringerLink 2023, 113, 2675–2700. [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Zhao, J.; Hu, W.; Ding, F.; Yu, N.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Z. Model-free voltage control of active distribution system with PVs using surrogate model-based deep reinforcement learning. Applied Energy 2022, 306, 117982. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, R.; Hao, W.; Tan, J.; Fan, R.; Huang, Z. Adaptive Power System Emergency Control Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1171–1182. [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yi, Z.; Shi, D.; Lin, C.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z. Reinforcement-Learning-Based Optimal Control of Hybrid Energy Storage Systems in Hybrid AC–DC Microgrids. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2019, 15, 5355–5364. [CrossRef]
- Totaro, S.; Boukas, I.; Jonsson, A.; Cornélusse, B. Lifelong control of off-grid microgrid with model-based reinforcement learning. Energy 2021, 232, 121035. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xu, Y. Real-Time Optimal Power Flow: A Lagrangian Based Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2020, 35, 3270–3273. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yue, D.; Dou, C.; Xie, X.; Li, K.; Hancke, G.P. Resilient Optimal Defensive Strategy of TSK Fuzzy-Model-Based Microgrids’ System via a Novel Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2023, 34, 1921–1931. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, R.; Hao, W.; Tan, J.; Fan, R.; Huang, Z. Adaptive Power System Emergency Control Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1171–1182. [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, J.; Niknam, T.; Azizipanah-Abarghooee, R.; Arroyo, J.M. Scenario-based dynamic economic emission dispatch considering load and wind power uncertainties. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2013, 47, 351–367. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yue, D.; Xie, X.; Dou, C.; Sun, F. Gradient decent based multi-objective cultural differential evolution for short-term hydrothermal optimal scheduling of economic emission with integrating wind power and photovoltaic power. Energy 2017, 122, 748–766. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lam, K.P. A deep reinforcement learning method for model-based optimal control of HVAC systems. SURFACE at Syracuse University 2018. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chong, A.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lam, K.P. Whole building energy model for HVAC optimal control: A practical framework based on deep reinforcement learning. Energy and Buildings 2019, 199, 472–490. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Cai, Z.; Bergés, M. Gnu-rl: A precocial reinforcement learning solution for building hvac control using a differentiable mpc policy. Proceedings of the 6th ACM international conference on systems for energy-efficient buildings, cities, and transportation; , 2019; pp. 316–325.
- Drgoňa, J.; Picard, D.; Kvasnica, M.; Helsen, L. Approximate model predictive building control via machine learning. Applied Energy 2018, 218, 199–216. [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.; Manna, C.; Spiessens, F.; Helsen, L. Reinforced model predictive control (RL-MPC) for building energy management. Applied Energy 2022, 309, 118346. [CrossRef]
- Drgoňa, J.; Tuor, A.; Skomski, E.; Vasisht, S.; Vrabie, D. Deep learning explicit differentiable predictive control laws for buildings. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 14–19. [CrossRef]
- Kowli, A.; Mayhorn, E.; Kalsi, K.; Meyn, S.P. Coordinating dispatch of distributed energy resources with model predictive control and Q-learning. Coordinated Science Laboratory Report no. UILU-ENG-12-2204, DC-256 2012.
- Bianchi, C.; Fontanini, A. TMY3 Weather Data for ComStock and ResStock, 2021. [Online] Available https://data.nrel.gov/submissions/156, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Blum, D.; Arroyo, J.; Huang, S.; Drgoňa, J.; Jorissen, F.; Walnum, H.T.; Chen, Y.; Benne, K.; Vrabie, D.; Wetter, M.; others. Building optimization testing framework (BOPTEST) for simulation-based benchmarking of control strategies in buildings. Journal of Building Performance Simulation 2021, 14, 586–610. [CrossRef]
- company, N. Wind data, 2024. [Online] Available https://www.nrel.gov/wind/data-tools.html, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Lee, H.; Cha, S.W. Energy management strategy of fuel cell electric vehicles using model-based reinforcement learning with data-driven model update. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 59244–59254.
- Chiş, A.; Lundén, J.; Koivunen, V. Reinforcement learning-based plug-in electric vehicle charging with forecasted price. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2016, 66, 3674–3684.
- Zhang, F.; Yang, Q.; An, D. CDDPG: A deep-reinforcement-learning-based approach for electric vehicle charging control. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 8, 3075–3087.
- Cui, L.; Wang, Q.; Qu, H.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Ge, L. Dynamic pricing for fast charging stations with deep reinforcement learning. Applied Energy 2023, 346, 121334.
- Xing, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Z. A graph reinforcement learning-based decision-making platform for real-time charging navigation of urban electric vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2022, 19, 3284–3295.
- Qian, T.; Shao, C.; Wang, X.; Shahidehpour, M. Deep reinforcement learning for EV charging navigation by coordinating smart grid and intelligent transportation system. IEEE transactions on smart grid 2019, 11, 1714–1723.
- Vandael, S.; Claessens, B.; Ernst, D.; Holvoet, T.; Deconinck, G. Reinforcement learning of heuristic EV fleet charging in a day-ahead electricity market. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1795–1805.
- Jin, J.; Xu, Y. Optimal policy characterization enhanced actor-critic approach for electric vehicle charging scheduling in a power distribution network. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 12, 1416–1428.
- Qian, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Shi, Y.; Chen, W. Federated Reinforcement Learning for Electric Vehicles Charging Control on Distribution Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2023.
- Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Pedram, M. Accurate component model based optimal control for energy storage systems in households with photovoltaic modules. 2013 IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech); , 2013; pp. 28–34. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Hong, M. Machine Learning Based Optimization Model for Energy Management of Energy Storage System for Large Industrial Park. Processes 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zou, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, F. Reinforcement learning of adaptive energy management with transition probability for a hybrid electric tracked vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2015, 62, 7837–7846. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liu, T. Implementation of real-time energy management strategy based on reinforcement learning for hybrid electric vehicles and simulation validation. PloS one 2017, 12, e0180491. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, T.; Qi, X.; Barth, M. Reinforcement learning for hybrid and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle energy management: Recent advances and prospects. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine 2019, 13, 16–25. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X. Deep reinforcement learning-based optimal data-driven control of battery energy storage for power system frequency support. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2020, 14, 6071–6078. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Pedram, M. Adaptive control for energy storage systems in households with photovoltaic modules. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2014, 5, 992–1001.
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Hong, M. Machine learning-based energy system model for tissue paper machines. Processes 2021, 9, 655.
- Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Pedram, M. A Near-Optimal Model-Based Control Algorithm for Households Equipped With Residential Photovoltaic Power Generation and Energy Storage Systems. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy 2016, 7, 77–86. [CrossRef]
- company, N. Measurement and Instrumentation Data Center, 2021. [Online] Available https://midcdmz.nrel.gov/apps/sitehome.pl?site=LMU, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- company, B. Baltimore load profile data, 2021. [Online] Available https://supplier.bge.com/electric/load/profiles.asp, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Liu, T.; Zou, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, F. Reinforcement learning–based energy management strategy for a hybrid electric tracked vehicle. Energies 2015, 8, 7243–7260. [CrossRef]
- Baah, G.K.; Podgurski, A.; Harrold, M.J. The Probabilistic Program Dependence Graph and Its Application to Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 2010, 36, 528–545. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Qiu, D.; Wu, X.; Strbac, G.; Ward, J. Model-Free Real-Time Autonomous Control for a Residential Multi-Energy System Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3068–3082. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; May, D.; Gül, M.; Musilek, P. Reinforcement learning-driven local transactive energy market for distributed energy resources. Energy and AI 2022, 8, 100150. [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Kremers, E.; Mengelkamp, E.M.; Eberbach, J.; Weinhardt, C. Reinforcement learning in local energy markets. Energy Informatics 2021, 4, 7. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Attentive Convolutional Deep Reinforcement Learning for Optimizing Solar-Storage Systems in Real-Time Electricity Markets. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2024, 20, 7205–7215. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Luo, F.; Li, C. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning-based autonomous decision-making framework for community virtual power plants. Applied Energy 2024, 360, 122813. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Papadaskalopoulos, D.; Yuan, Q.; Tang, Y.; Strbac, G. Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Coordinated Energy Trading and Flexibility Services Provision in Local Electricity Markets. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2023, 14, 1541–1554. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Su, W. Indirect Customer-to-Customer Energy Trading With Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 10, 4338–4348. [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Li, Y. Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Distributed Energy Management and Strategy Optimization of Microgrid Market. Sustainable Cities and Society 2021, 74, 103163. [CrossRef]
- Harrold, D.J.; Cao, J.; Fan, Z. Renewable energy integration and microgrid energy trading using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Applied Energy 2022, 318, 119151. [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Xiang, C.; Yu, M.; Tan, K.T.; Lee, T.H. Online Optimal Power Scheduling of a Microgrid via Imitation Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 861–876. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Irwin, D. SunDance: Black-box Behind-the-Meter Solar Disaggregation. Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Future Energy Systems; , 2017; e-Energy ’17, p. 45–55. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Cecchet, E.; Shenoy, P.J.; Albrecht, J.R. Smart: An Open Data Set and Tools for Enabling Research in Sustainable Homes, 2012. [Online] Available https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:6562225, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- company, A. Electricity distribution and prices data, 2024. [Online] Available https://aemo.com.au/en/energy-systems/electricity/national-electricity-market-nem/data-nem/data-dashboard-nem, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Operator, C.I.S. California electrical power system operational data, 2024. [Online] Available https://www.caiso.com/, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Duan, J.; Shi, D.; Diao, R.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Bian, D.; Yi, Z. Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Autonomous Voltage Control for Power Grid Operations. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2020, 35, 814–817. [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Zhao, J.; Hu, W.; Yu, N.; Ding, F.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Z. Deep Reinforcement Learning Enabled Physical-Model-Free Two-Timescale Voltage Control Method for Active Distribution Systems. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 149–165. [CrossRef]
- Diao, R.; Wang, Z.; Shi, D.; Chang, Q.; Duan, J.; Zhang, X. Autonomous Voltage Control for Grid Operation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. 2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM); , 2019; pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, R.; Jeyasurya, B. Reinforcement Learning Based Real-Time Wide-Area Stabilizing Control Agents to Enhance Power System Stability. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2013, 4, 489–497. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cui, M.; Li, F.; Yin, S.; Wang, X. Model-Free Emergency Frequency Control Based on Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2021, 17, 2336–2346. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Mukherjee, S.; Sticht, C. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Model-Free On-Line Dynamic Multi-Microgrid Formation to Enhance Resilience. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2557–2567. [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, F. Intelligent Multi-Microgrid Energy Management Based on Deep Neural Network and Model-Free Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1066–1076. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lee, W.; Diao, R.; Shi, D. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Real-time AC Optimal Power Flow Considering Uncertainties. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2022, 10, 1098–1109. [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Hu, W.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Approach for Optimal Power Flow of Distribution Networks Embedded with Renewable Energy and Storage Devices. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2021, 9, 1101–1110. [CrossRef]
- Birchfield, A.B.; Xu, T.; Gegner, K.M.; Shetye, K.S.; Overbye, T.J. Grid Structural Characteristics as Validation Criteria for Synthetic Networks. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2017, 32, 3258–3265. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, K.; Zhu, L.; Qian, M. Novel Detection Scheme Design Considering Cyber Attacks on Load Frequency Control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14, 1932–1941. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Long, S.; Li, X. Model-free control method based on reinforcement learning for building cooling water systems: Validation by measured data-based simulation. Energy and Buildings 2020, 218, 110055. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Bernstein, A.; Chintala, R.; Graf, P.; Jin, X.; Biagioni, D. Two-stage reinforcement learning policy search for grid-interactive building control. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 1976–1987. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Biagioni, D.; Cai, M.; Graf, P.; Rahman, S. An Edge-Cloud Integrated Solution for Buildings Demand Response Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2021, 12, 420–431. [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, E.; Mocanu, D.C.; Nguyen, P.H.; Liotta, A.; Webber, M.E.; Gibescu, M.; Slootweg, J.G. On-Line Building Energy Optimization Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 10, 3698–3708. [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q. Deep reinforcement learning for building HVAC control. Proceedings of the 54th annual design automation conference 2017; , 2017; pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shen, C.; Yue, D.; Jiang, T.; Guan, X. Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for HVAC Control in Commercial Buildings. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2021, 12, 407–419. [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Song, A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.Y. Development of an HVAC system control method using weather forecasting data with deep reinforcement learning algorithms. Building and Environment 2024, 248, 111069. [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Li, J.; Wen, Y. DeepComfort: Energy-Efficient Thermal Comfort Control in Buildings Via Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 7, 8472–8484. [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Marzullo, T.; Zhang, X.; Henze, G. Reinforcement learning building control approach harnessing imitation learning. Energy and AI 2023, 14, 100255. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Qiu, D.; Wu, X.; Strbac, G.; Ward, J. Model-Free Real-Time Autonomous Control for a Residential Multi-Energy System Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3068–3082. [CrossRef]
- Ruelens, F.; Claessens, B.J.; Quaiyum, S.; De Schutter, B.; Babuška, R.; Belmans, R. Reinforcement Learning Applied to an Electric Water Heater: From Theory to Practice. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3792–3800. [CrossRef]
- weather service, T. Weather data, 2024. [Online] Available https://en.tutiempo.net/climate/ws-486980.html, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- company, D. Thermal comfort field measurements, 2024. [Online] Available https://datadryad.org/stash/dataset/, Accessed September 19, 2024. [CrossRef]
- company, P.S. Consumption data, 2024. [Online] Available https://www.pecanstreet.org/, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- company, E. Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Data, 2024. [Online] Available https://www.eia.gov/consumption/commercial/data/2012/bc/cfm/b6.php, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Ulrike Jordan, K.V. Hot-Water Profiles, 2001. [Online] Available https://sel.me.wisc.edu/trnsys/trnlib/iea-shc-task26/iea-shc-task26-load-profiles-description-jordan.pdf, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, F.; Tang, B.; Fan, W. Effective charging planning based on deep reinforcement learning for electric vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2020, 22, 542–554.
- Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Xing, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T. A modified rainbow-based deep reinforcement learning method for optimal scheduling of charging station. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1884.
- Wang, S.; Bi, S.; Zhang, Y.A. Reinforcement learning for real-time pricing and scheduling control in EV charging stations. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2019, 17, 849–859.
- Qian, T.; Shao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Shahidehpour, M. Enhanced coordinated operations of electric power and transportation networks via EV charging services. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 3019–3030.
- Zhao, Z.; Lee, C.K. Dynamic pricing for EV charging stations: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2021, 8, 2456–2468.
- Sadeghianpourhamami, N.; Deleu, J.; Develder, C. Definition and evaluation of model-free coordination of electrical vehicle charging with reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 11, 203–214.
- Yeom, K. Model predictive control and deep reinforcement learning based energy efficient eco-driving for battery electric vehicles. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 34–42.
- Dorokhova, M.; Martinson, Y.; Ballif, C.; Wyrsch, N. Deep reinforcement learning control of electric vehicle charging in the presence of photovoltaic generation. Applied Energy 2021, 301, 117504.
- Wen, Z.; O’Neill, D.; Maei, H. Optimal demand response using device-based reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2312–2324.
- Lee, S.; Choi, D.H. Reinforcement learning-based energy management of smart home with rooftop solar photovoltaic system, energy storage system, and home appliances. Sensors 2019, 19, 3937.
- Yan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X. Deep reinforcement learning-based optimal data-driven control of battery energy storage for power system frequency support. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2020, 14, 6071–6078. [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Harrold, D.; Fan, Z.; Morstyn, T.; Healey, D.; Li, K. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Energy Storage Arbitrage With Accurate Lithium-Ion Battery Degradation Model. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 4513–4521. [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.H.; Hussain, A.; Kim, H.M. Double Deep Q -Learning-Based Distributed Operation of Battery Energy Storage System Considering Uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2020, 11, 457–469. [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.H.; Hussain, A.; Kim, H.M. Q-Learning-Based Operation Strategy for Community Battery Energy Storage System (CBESS) in Microgrid System. Energies 2019, 12. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Su, W. Local Energy Trading Behavior Modeling With Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62806–62814. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Q.; Tao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Sidorov, D. Deep reinforcement learning based energy storage management strategy considering prediction intervals of wind power. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 145, 108608. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Erol-Kantarci, M. Correlated deep q-learning based microgrid energy management. 2020 IEEE 25th International Workshop on Computer Aided Modeling and Design of Communication Links and Networks (CAMAD); , 2020; pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, H. Real-time energy management of a microgrid using deep reinforcement learning. Energies 2019, 12, 2291. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hu, X. A bi-level control for energy efficiency improvement of a hybrid tracked vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14, 1616–1625. [CrossRef]
- government, U. UK wholesale electricity market prices, 2024. [Online] Available https://tradingeconomics.com/united-kingdom/electricity-price, Accessed September 19, 2024.
- Lopes, J.P.; Hatziargyriou, N.; Mutale, J.; Djapic, P.; Jenkins, N. Integrating distributed generation into electric power systems: A review of drivers, challenges and opportunities. Electric Power Systems Research 2007, 77, 1189–1203. [CrossRef]
- Pfenninger, S.; Hawkes, A.; Keirstead, J. Energy systems modeling for twenty-first century energy challenges. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2014, 33, 74–86. [CrossRef]
- Nafi, N.S.; Ahmed, K.; Gregory, M.A.; Datta, M. A survey of smart grid architectures, applications, benefits and standardization. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2016, 76, 23–36. [CrossRef]
- Ustun, T.S.; Hussain, S.M.S.; Kirchhoff, H.; Ghaddar, B.; Strunz, K.; Lestas, I. Data Standardization for Smart Infrastructure in First-Access Electricity Systems. Proceedings of the IEEE 2019, 107, 1790–1802. [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Xu, Y. Robustness Verification for Machine-Learning-Based Power System Dynamic Security Assessment Models Under Adversarial Examples. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems 2022, 9, 1645–1654. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yau, D.K. CoRE: Constrained Robustness Evaluation of Machine Learning-Based Stability Assessment for Power Systems. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2023, 10, 557–559. [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tan, R. Vulnerability Analysis, Robustness Verification, and Mitigation Strategy for Machine Learning-Based Power System Stability Assessment Model Under Adversarial Examples. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 1622–1632. [CrossRef]
- Machlev, R.; Zargari, N.; Chowdhury, N.; Belikov, J.; Levron, Y. A review of optimal control methods for energy storage systems - energy trading, energy balancing and electric vehicles. Journal of Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101787. [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, R.; Jeyasurya, B. Reinforcement Learning Based Real-Time Wide-Area Stabilizing Control Agents to Enhance Power System Stability. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2013, 4, 489–497. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lee, W.; Diao, R.; Shi, D. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Real-time AC Optimal Power Flow Considering Uncertainties. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2022, 10, 1098–1109. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Xu, Y. Real-Time Optimal Power Flow: A Lagrangian Based Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2020, 35, 3270–3273. [CrossRef]
- Machlev, R.; Heistrene, L.; Perl, M.; Levy, K.; Belikov, J.; Mannor, S.; Levron, Y. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) techniques for energy and power systems: Review, challenges and opportunities. Energy and AI 2022, 9, 100169. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P.D.; Gao, T.; Gao, D.W. Explainable AI in Deep Reinforcement Learning Models for Power System Emergency Control. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems 2022, 9, 419–427. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P.D.; Gao, T.; Gao, D.W. Explainable AI in Deep Reinforcement Learning Models for Power System Emergency Control. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems 2022, 9, 419–427. [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Xiao, Y.; Chang, X.; Huang, P.y.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. A Comprehensive Survey of Neural Architecture Search: Challenges and Solutions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–34. [CrossRef]
- Jalali, S.M.J.; Osório, G.J.; Ahmadian, S.; Lotfi, M.; Campos, V.M.A.; Shafie-khah, M.; Khosravi, A.; Catalão, J.P.S. New Hybrid Deep Neural Architectural Search-Based Ensemble Reinforcement Learning Strategy for Wind Power Forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2022, 58, 15–27. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kapuza, I.; Baimel, D.; Belikov, J.; Levron, Y.; Machlev, R. Neural Architecture Search (NAS) for designing optimal power quality disturbance classifiers. Electric Power Systems Research 2023, 223, 109574. [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J. Applications of Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Power Systems - A Review. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2023, 38, 572–588. [CrossRef]
- Misyris, G.S.; Venzke, A.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Power Systems. 2020 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM); , 2020; pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Sami, N.M.; Naeini, M. Machine learning applications in cascading failure analysis in power systems: A review. Electric Power Systems Research 2024, 232, 110415. [CrossRef]
- Miraftabzadeh, S.M.; Foiadelli, F.; Longo, M.; Pasetti, M. A Survey of Machine Learning Applications for Power System Analytics. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2019 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC / I&CPS Europe); , 2019; pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Bedi, G.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K.; Singh, R.; Brooks, R.R.; Wang, K.C. Review of Internet of Things (IoT) in Electric Power and Energy Systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2018, 5, 847–870. [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.T.; Nguyen Thi, M.S.; Truong, D.N.; Hoang, A.Q.; Tran, P.N.; Bui, N.A. Applying IoT Platform to Design a Data Collection System for Hybrid Power System. 2021 International Conference on System Science and Engineering (ICSSE); , 2021; pp. 181–184. [CrossRef]
- Sayed, H.A.; Said, A.M.; Ibrahim, A.W. Smart Utilities IoT-Based Data Collection Scheduling. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 2024, 49, 2909–2923. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qu, G.; Tang, Y.; Low, S.; Li, N. Reinforcement Learning for Selective Key Applications in Power Systems: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2935–2958. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, H. Learning to Operate Distribution Networks With Safe Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2022, 13, 1860–1872. [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.L.; Mukherjee, S.; Yin, T.; Huang, R.; Tan, J.; Huang, Q. Safe Reinforcement Learning for Emergency Load Shedding of Power Systems. 2021 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM); , 2021; pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Gooi, H.B.; Wang, T.; Tang, Y. Edge Intelligence for Smart Grid: A Survey on Application Potentials. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems 2023, 9, 1623–1640. [CrossRef]
- Sodhro, A.H.; Pirbhulal, S.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Mechanism for Edge Computing-Based Industrial Applications. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2019, 15, 4235–4243. [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gupta, B.B.; Tian, Z. An Edge-AI Based Forecasting Approach for Improving Smart Microgrid Efficiency. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2022, 18, 7946–7954. [CrossRef]
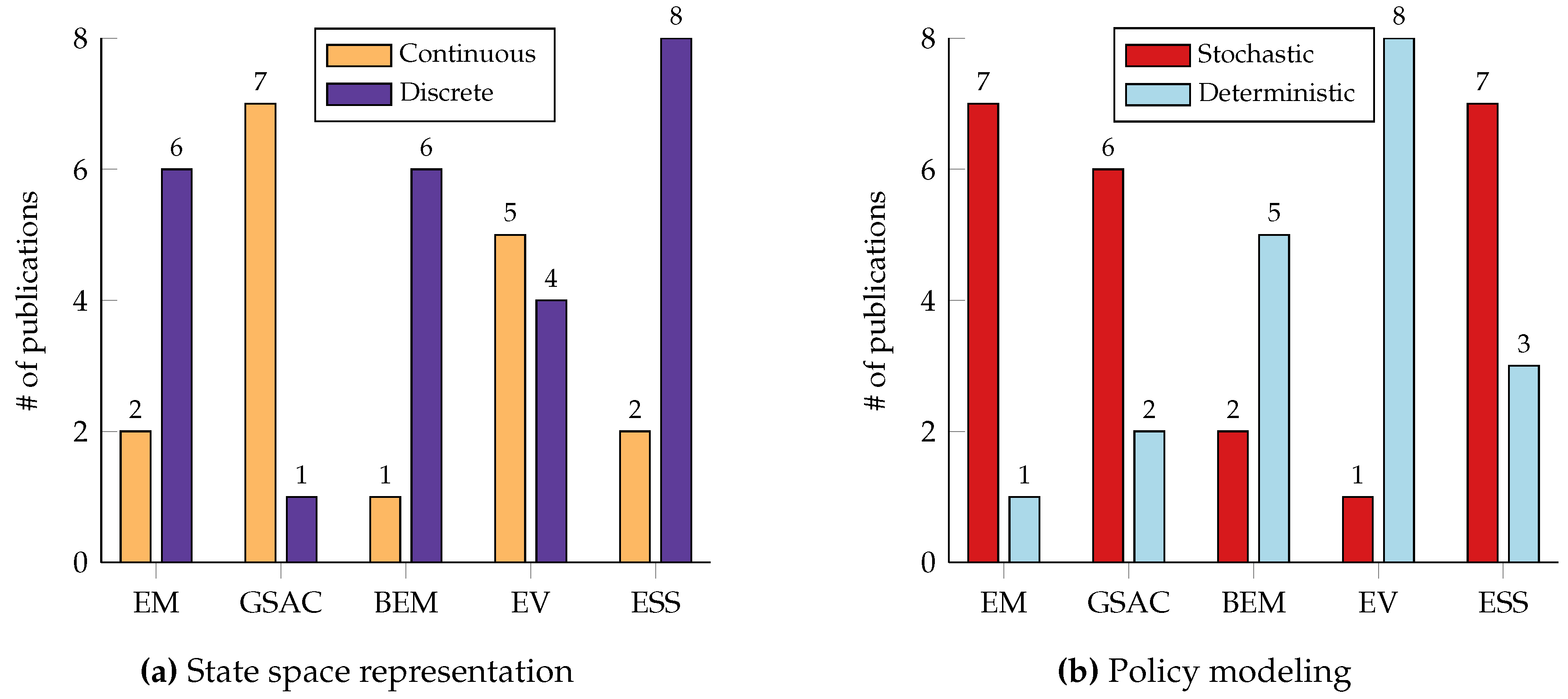
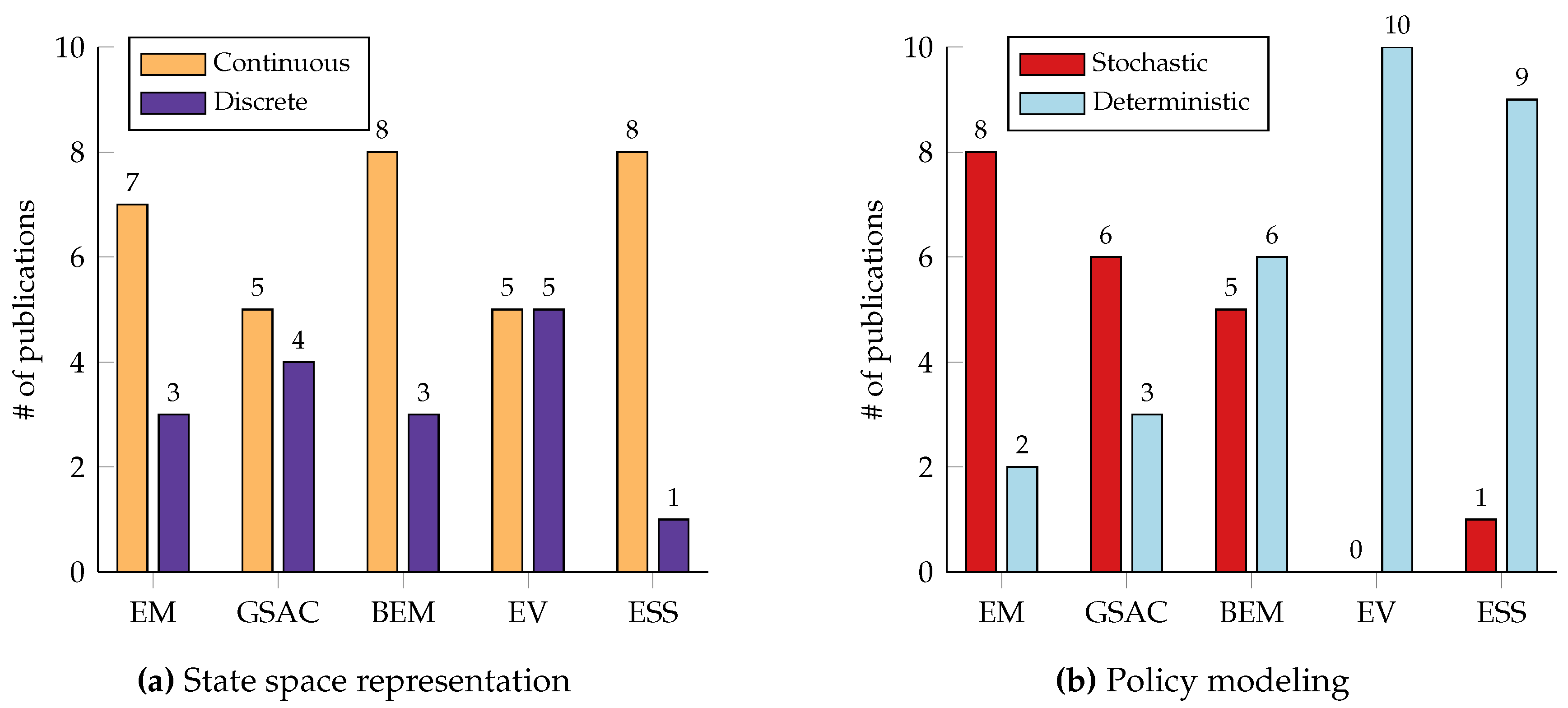
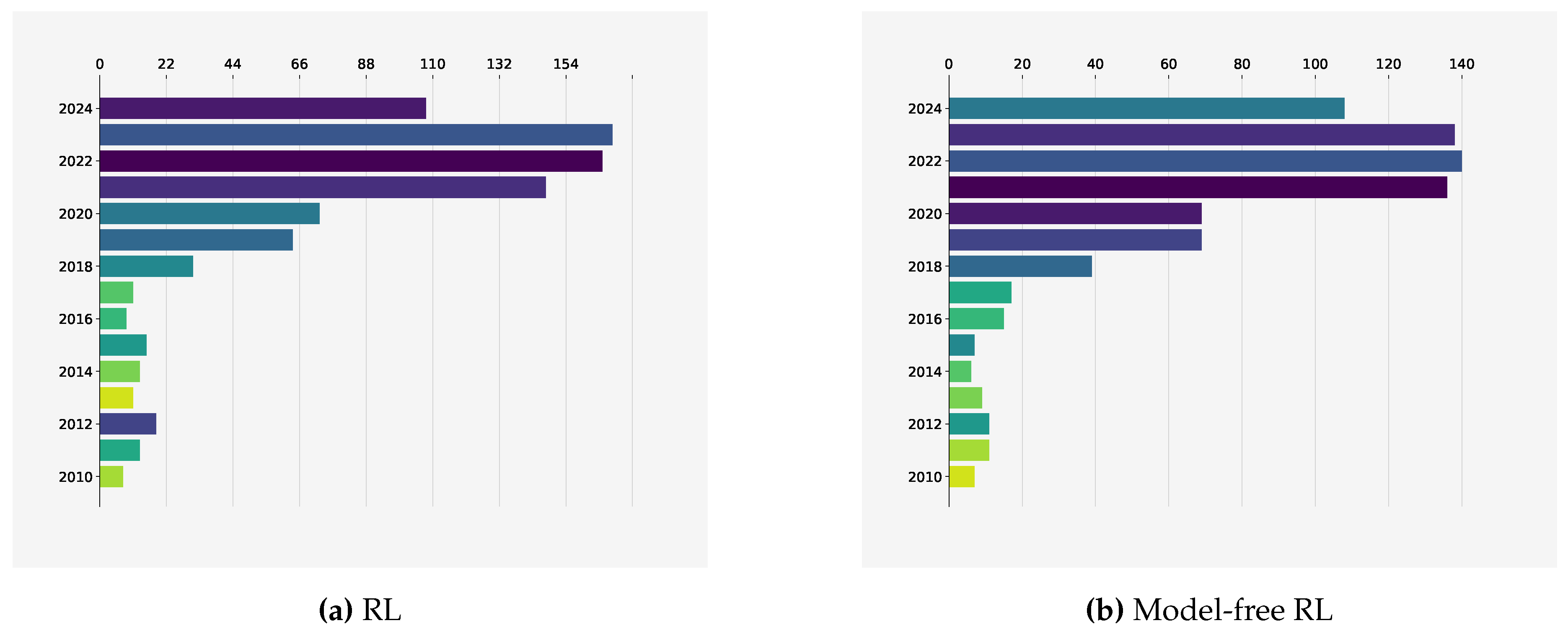
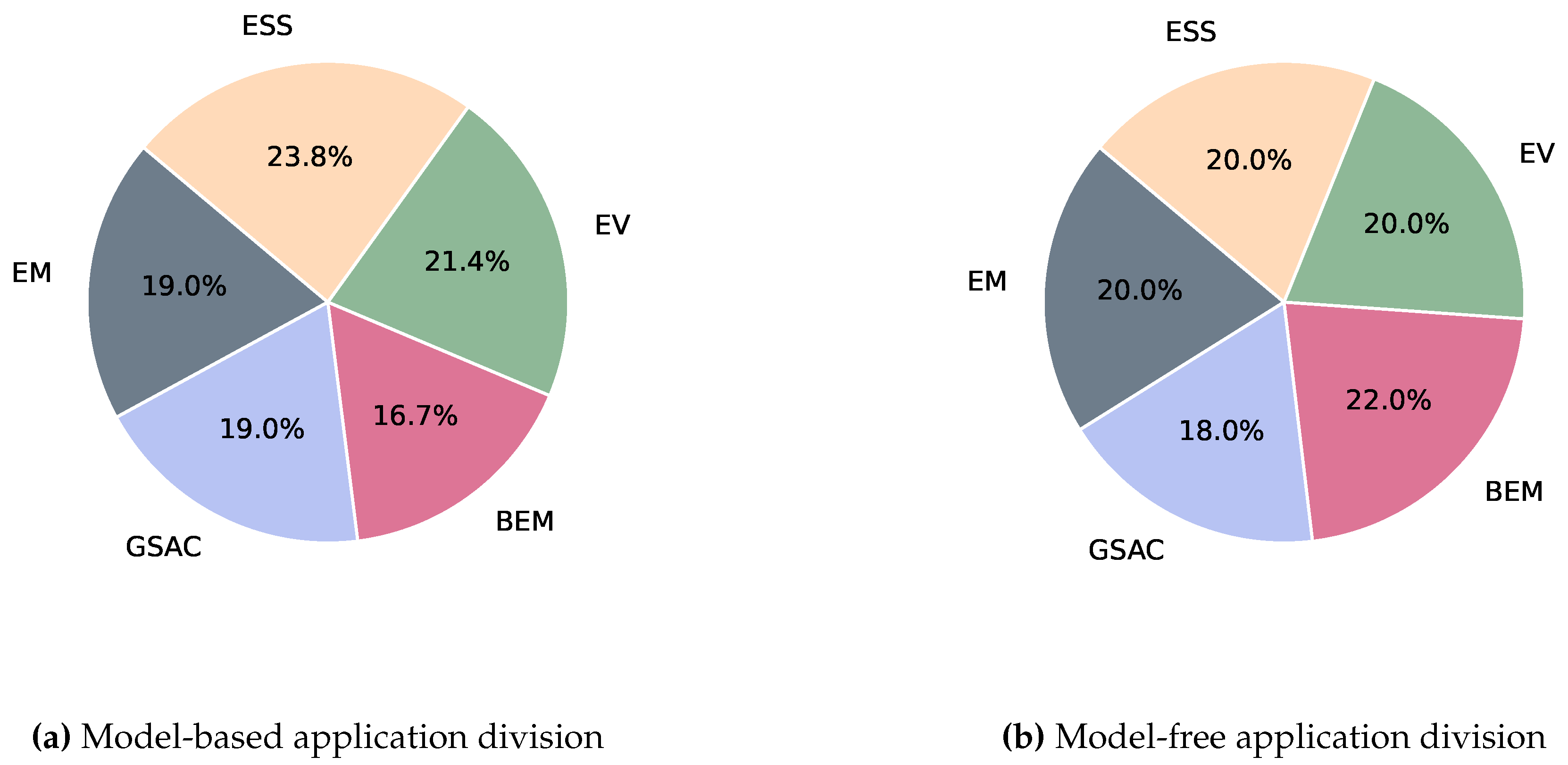
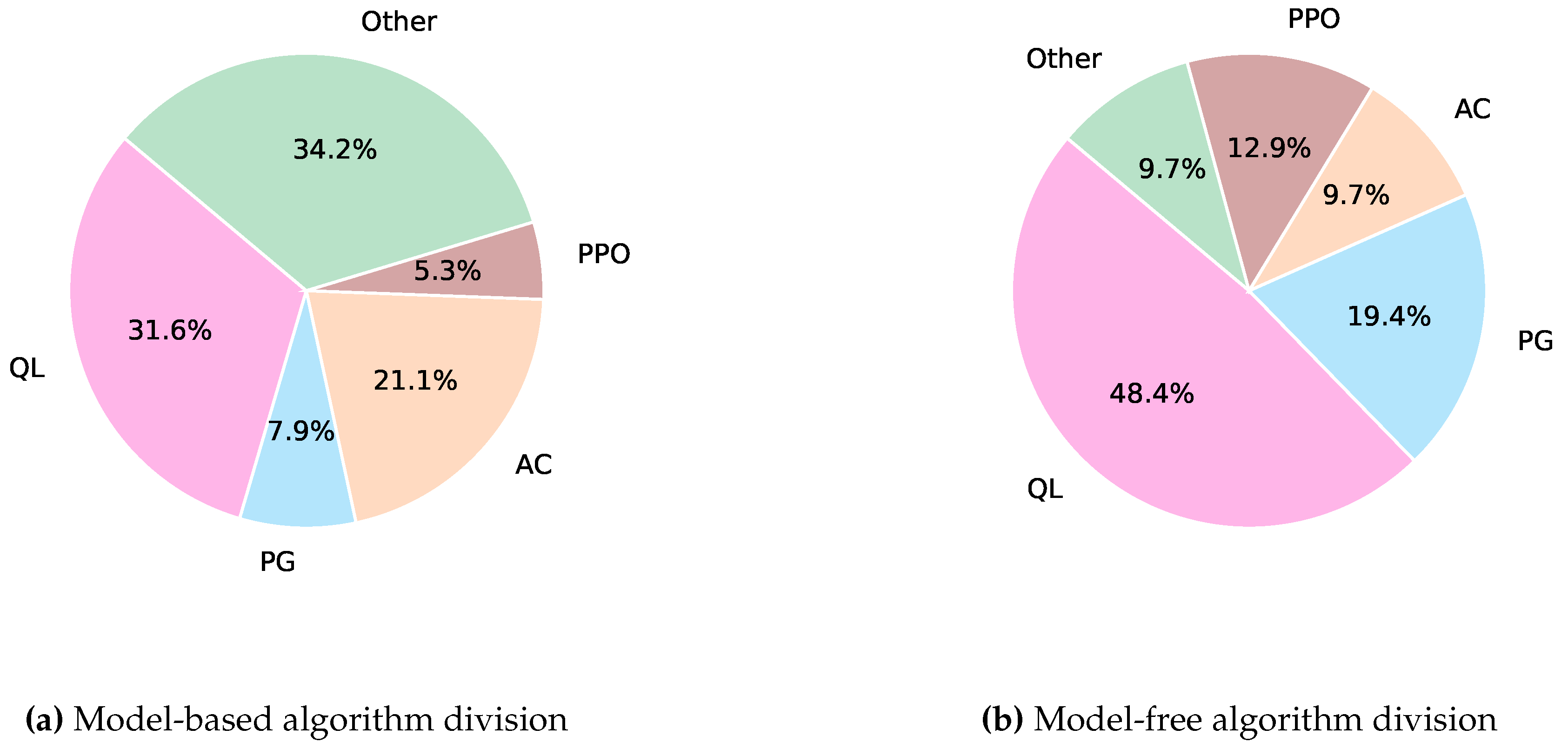
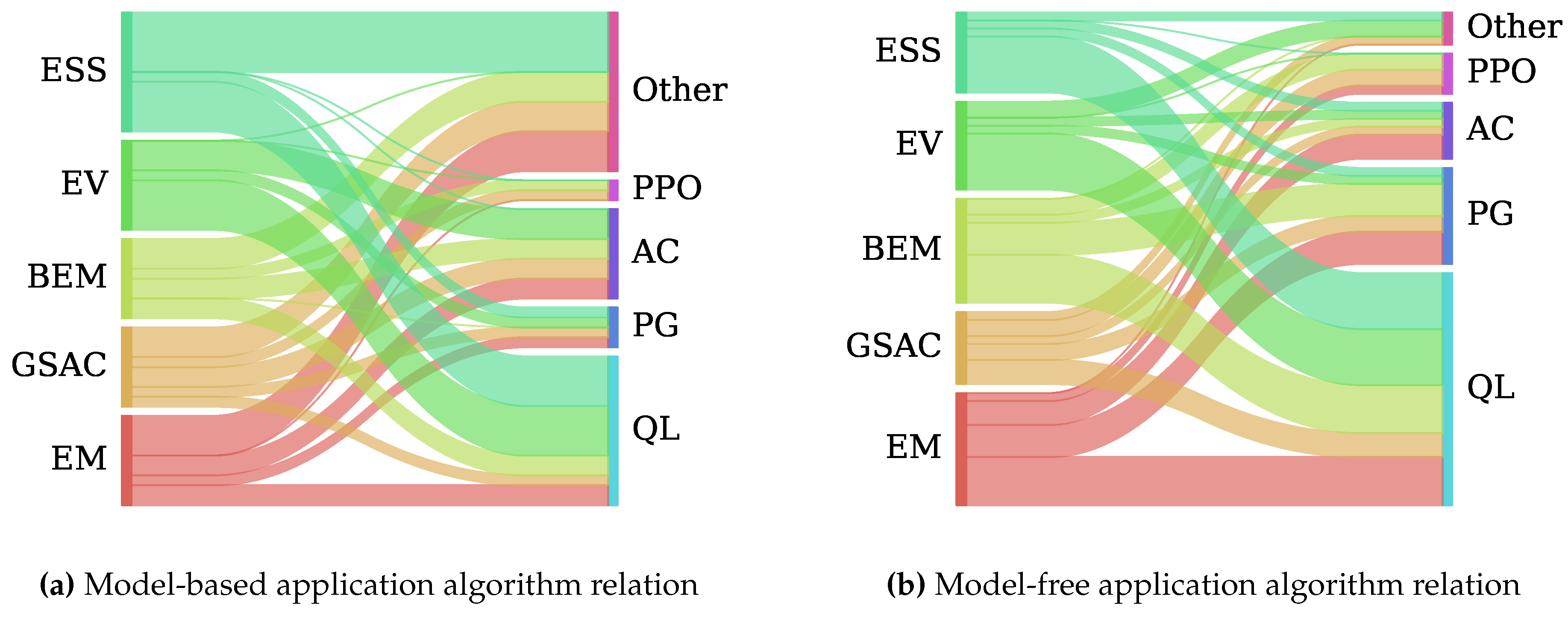
| Problem | States | Actions | Reward |
|---|---|---|---|
| EM | System operator decides upon a power flow distribution | Firms set their bid | The firms’ rewards are the net profit achieved |
| GSAC | Voltage levels at different nodes | Adjusting the output of power generators | Cost of deviating from nominal voltage levels |
| BEM | Indoor temperature and humidity levels | Adjusting thermostat setpoints for heating and cooling | Cost of electricity |
| EV | Traffic conditions and route information | Selecting a route based on traffic and charging station availability | Cost of charging, considering electricity prices and charging station fees |
| ESS | Battery state of charge and current consumer power demand | The controller decides how much power to produce using the generator | The power generation cost the controller must pay |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset & simulator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [35] | ET | AC | Continuous | Deterministic | [43] |
| [37] | ET | AC | Discrete | Stochastic | [44] |
| [38] | ET | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | [45] |
| [40] | ET | Other | Discrete | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [41] | ET | PG, Other | Continuous | Deterministic | Real data |
| [36] | Dispatch | PG | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [39] | Dispatch | AC, Other | Continuous | Deterministic | [46,47] |
| [42] | DR, Microgrid | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Real data, [48] |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [49] | Voltage control | Other | Continuous | Stochastic | IEEE 300, IEEE 9, [57] |
| [50] | Voltage control | Other | Continuous | Stochastic | IEEE 300 |
| [51] | Voltage control | AC | Continuous | Deterministic | IEEE 123 |
| [52] | Voltage control | QL | Continuous | Stochastic | IEEE 39, [57] |
| [53] | Microgrid | Other | Discrete | Deterministic | HIL platform “dSPACE MicroLabBox” |
| [54] | Microgrid | PPO | Continuous | Stochastic | Empirical measurments |
| [56] | Power flow, Microgrid | AC | Continuous | Stochastic | [58,59] |
| [55] | Power flow | PG | Continuous | Stochastic | IEEE 118 |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [60] | HVAC | AC | Discrete | Deterministic | [67] |
| [61] | HVAC | AC | Continuous | Stochastic | Real data [Upon request] |
| [63] | HVAC | Other | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [65] | HVAC | Other | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [64] | HVAC | QL, Other | Discrete | Deterministic | [68] |
| [62] | HVAC | PPO | Discrete | Stochastic | “EnergyPlus” |
| [66] | Dispatch | QL, Other | Discrete | Deterministic | [69], Simulated data |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [70] | Power flow | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | MATLAB simulation |
| [71] | Charge control | QL | Mixed | Deterministic | Historic prices |
| [72] | Charge control | PG | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [73] | Charge control | AC | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [74] | Charge control | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Open street map, ChargeBar |
| [75] | Charge control | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [77] | Charge scheduling | AC | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [78] | Charge control | AC | Continuous | Stochastic | Historic prices |
| [76] | Load balancing | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [87] | Smart Grid | QL | Discrete | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [79] | Smart Grid | Other | Discrete | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [85] | Smart Grid | Other | Discrete | Stochastic | [88,89] |
| [81] | EV | QL | Discrete | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [90] | EV | QL, Other | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [82] | EV | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [83] | EV | QL, Other | Discrete | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [80] | Renewable energy | Other [91] | Discrete | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [84] | Battery ESS, frequency support | PG, AC | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [86] | Energy system modeling | Other | Discrete | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [92] | ET | PG | Continuous | Deterministic | Real data |
| [93] | ET | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | [102,103] |
| [95] | ET | PG | Continuous | Deterministic | [104] |
| [96] | ET | AC | Continuous | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [97] | ET | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Real data |
| [99] | Microgrid, Dispatch | QL | Continuous | Stochastic | [105] |
| [100] | Microgrid | PG | Continuous | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| [101] | Microgrid | Other | Continuous | Deterministic | Real and Simulated data |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [106] | Voltage control | PG | Continuous | Stochastic | Powerflow & Short circuit Assessment Tool (PSAT), 200-bus system [115] |
| [107] | Voltage control | AC | Continuous | Stochastic | IEEE 33-, 123-, and 342-node systems |
| [108] | Voltage control | QL | Discrete | Stochastic | IEEE 14-bus system |
| [109] | Frequency control | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulted data |
| [110] | Frequency control | PG | Discrete | Deterministic | Kundur’s 4-unit-13 bus system, New England 68-bus system, [116] |
| [111] | Microgrid | QL | Continuous | Stochastic | 7-bus system and the IEEE 123-bus system |
| [112] | Microgrid | Other | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [113] | Power flow | PPO | Continuous | Stochastic | Illinois 200-bus system |
| [114] | Power flow | PPO | Continuous | Stochastic | Simulated data, West Denmark wind data |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [117] | HVAC | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [125] | HVAC | PPO | Continuous | Deterministic | “EnergyPlus” |
| [121] | HVAC | QL | Continuous | Stochastic | “EnergyPlus” |
| [123] | HVAC | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [124] | HVAC | PG | Continuous | Stochastic | [128,129] |
| [122] | HVAC | AC | Continuous | Stochastic | [130] |
| [118] | HVAC,DR | PPO | Continuous | Deterministic | “EnergyPlus” |
| [120] | HVAC, DR | QL, PG | Continuous | Stochastic | [130] |
| [119] | DR | QL, PG | Discrete | Deterministic | [131] |
| [126] | Dispatch | PG | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [127] | Dispatch | QL | Continuous | Stochastic | [47,132] |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [133] | Scheduling | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | “Open street map”, “ChargeBar” |
| [134] | Scheduling | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [135] | Scheduling | Other | Continuous | Deterministic | Historic data |
| [136] | Scheduling | Other | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [138] | Scheduling | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | “ElaadNL” |
| [137] | Cost reduction | Other | Mixed | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [139] | Cost reduction | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [142] | Cost reduction | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [141] | DR | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated |
| [140] | SoC control | QL, PG | Continuous | Deterministic | Historic data |
| Ref. | Application | Algorithm | State-space | Policy | Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [145] | Microgrids | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [146] | Microgrids | QL | Discrete | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [149] | Microgrids | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [150] | Microgrids | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | [105] |
| [148] | Frequency control | Other | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [143] | Frequency control | PG, AC | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [144] | Energy trading | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | [152] |
| [147] | Energy trading | QL | Continuous | Deterministic | Simulated data |
| [151] | EV | QL | Continuous | Stochastic | Simulated data |
| RL expressions | Power systems application expressions |
|---|---|
| “model-based” | “energy market management” |
| OR | OR |
| “model learning” | “voltage control” |
| OR | OR |
| “model-free” | “frequency control” |
| OR | OR |
| “data-driven” | “reactive power control” |
| AND/OR | OR |
| “reinforcement learning” | “grid stability” |
| OR | |
| “microgrid” | |
| OR | |
| “building energy management” | |
| OR | |
| “building” | |
| OR | |
| “electrical vehicles” | |
| OR | |
| “EV” | |
| OR | |
| “energy storage control problems” | |
| OR | |
| “battery energy storage system” | |
| OR | |
| “local energy trading” |
| QL | PG | AC | PPO | Other | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MB | MF | MB | MF | MB | MF | MB | MF | MB | MF | |
| ESS | 5 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 1 |
| EV | 5 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| BEM | 2 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 |
| GSAC | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| EM | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| Category | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Lack of standardization | Lack of real-world data for different control tasks in power systems. No qualitative simulator to efficiently integrate between accurate physical models of energy systems and reinforcement learning libraries. No standardized benchmarks algorithms or datasets that represent a quality norm for various reinforcement learning algorithms. |
| Lack of generalization | Lack of data causes limited generalization ability in model-free algorithms. Complex models in power systems are difficult to learn, thus model-based algorithms converge to inaccurate model, which does not generalize well. As the state or action variables increase, there is an exponential growth in the computational requirements of the model. |
| Limited safety | Model-free methods produce suboptimal policy due to small acquired data, which may not perform well when unexpected events occur. The complexity of the environment’s dynamics causes model-based algorithms to produce suboptimal policies, jeopardizing the stability of the system when uncertainty is encountered. During training the models focus on exploration and perform mainly random actions, in real-time applications for power systems it may be catastrophic and lead to blackouts. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





