Submitted:
02 October 2024
Posted:
03 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
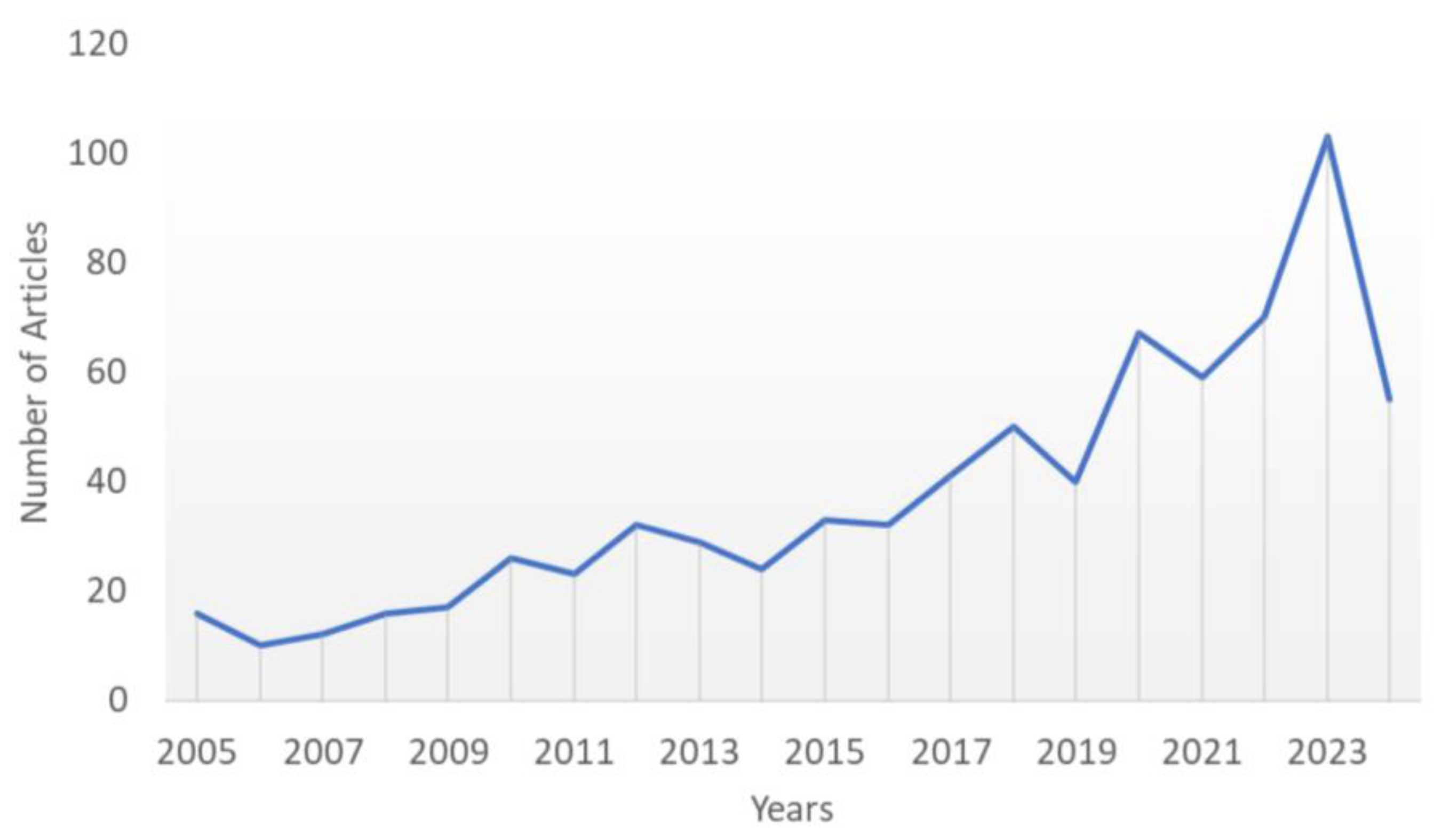
1. Introduction
2. The Contribution of Soil Yeasts to Plant Health
3. The Ecological Importance of Yeasts Beyond Soil
4. Impacts of Pesticides on Yeast Microbiota
5. Yeasts as Potential Bioremediators
6. Engineering Yeasts for Pesticide Degradation
7. Concluding Remarks: Use of Yeasts from a Sustainable Agriculture Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, V.; Mol, H.G.J.; Zomer, P.; Tienstra, M.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Pesticide Residues in European Agricultural Soils – A Hidden Reality Unfolded. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 653, 1532–1545. [CrossRef]
- Szpyrka, E.; Książek-Trela, P.; Bielak, E.; Słowik-Borowiec, M. The Influence of Commercial Yeast Preparations on the Degradation of Herbicide Mixtures in the Soil and the Effect on the Shell Pea (Pisum Sativum L.) Cultivation. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 2024, 24, 2509–2519. [CrossRef]
- Fenner, E.D.; Scapini, T.; da Costa Diniz, M.; Giehl, A.; Treichel, H.; Álvarez-Pérez, S.; Alves, S.L. Nature’s Most Fruitful Threesome: The Relationship between Yeasts, Insects, and Angiosperms. Journal of Fungi 2022, 8, 984. [CrossRef]
- Giehl, A.; dos Santos, A.A.; Cadamuro, R.D.; Tadioto, V.; Guterres, I.Z.; Prá Zuchi, I.D.; Minussi, G. do A.; Fongaro, G.; Silva, I.T.; Alves, S.L. Biochemical and Biotechnological Insights into Fungus-Plant Interactions for Enhanced Sustainable Agricultural and Industrial Processes. Plants 2023, 12, 2688. [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, R.N.; Mei, Y.Z.; Andicoechea, J.; Manson, J.S.; Irwin, R.E. Consequences of a Nectar Yeast for Pollinator Preference and Performance. Funct Ecol 2017, 31, 613–621. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.-H. Microbial Eco-Physiological Indicators to Asses Soil Quality. Agric Ecosyst Environ 2003, 98, 285–293. [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.G. dos. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos; Embrapa, 2018; ISBN 9788570358004. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/1094003/sistema-brasileiro-de-classificacao-de-solos (accessed on 10/09/2024).
- Moreira, G.A.M. Diversidade e Ecologia de Leveduras em Solos Brasileiros; Tese de doutorado apresentada ao Programa de Pós-Graduação de Biologia Microbiana do Instituto de Ciências Biológicas, Universidade de Brasília – UnB. 2019.
- Álvarez-Pérez, S. Ecology: Yeasts on Their Natural Environment. In Yeasts: From Nature to Bioprocesses; Bentaham Science, 2022; pp. 27–57.
- Fernandez-San Millan, A.; Farran, I.; Larraya, L.; Ancin, M.; Arregui, L.M.; Veramendi, J. Plant Growth-Promoting Traits of Yeasts Isolated from Spanish Vineyards: Benefits for Seedling Development. Microbiol Res 2020, 237, 126480. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.C.O.; Safar, S.V.B.; Marques, A.R.; Medeiros, A.O.; Santos, A.R.O.; Carvalho, C.; Lachance, M.-A.; Sampaio, J.P.; Rosa, C.A. The Diversity and Extracellular Enzymatic Activities of Yeasts Isolated from Water Tanks of Vriesea Minarum, an Endangered Bromeliad Species in Brazil, and the Description of Occultifur Brasiliensis f.a., Sp. Nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 597–611. [CrossRef]
- Bright, J.P.; Karunanadham, K.; Maheshwari, H.S.; Karuppiah, E.A.A.; Thankappan, S.; Nataraj, R.; Pandian, D.; Ameen, F.; Poczai, P.; Sayyed, R.Z. Seed-Borne Probiotic Yeasts Foster Plant Growth and Elicit Health Protection in Black Gram (Vigna Mungo L.). Sustainability 2022, 14, 4618. [CrossRef]
- Sarabia, M.; Jakobsen, I.; Grønlund, M.; Carreon-Abud, Y.; Larsen, J. Rhizosphere Yeasts Improve P Uptake of a Maize Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Association. Applied Soil Ecology 2018, 125, 18–25. [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.R.; Resende, A.A.; Gomes, F.C.O.; Santos, A.R.O.; Rosa, C.A.; Duarte, A.A.; de Lemos-Filho, J.P.; dos Santos, V.L. Plant Growth–Promoting Traits of Yeasts Isolated from the Tank Bromeliad Vriesea Minarum L.B. Smith and the Effectiveness of Carlosrosaea Vrieseae for Promoting Bromeliad Growth. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 2021, 52, 1417–1429. [CrossRef]
- Braus, G.H. Aromatic Amino Acid Biosynthesis in the Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae: A Model System for the Regulation of a Eukaryotic Biosynthetic Pathway. Microbiol Rev 1991, 55, 349–370. [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Arreaza, A.; Acosta, H.; Quiñones, W.; Concepción, J.L.; Michels, P.A.M.; Avilán, L. Extracellular Functions of Glycolytic Enzymes of Parasites: Unpredicted Use of Ancient Proteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2014, 193, 75–81. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Yook, S.; Koh, H.; Rao, C. V; Jin, Y.-S. Engineering Xylose Metabolism in Yeasts to Produce Biofuels and Chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2021, 67, 15–25. [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.P.; Hunter, A.; Kashpur, O.; Normanly, J. Aberrant Synthesis of Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Triggers Morphogenic Transition, a Virulence Trait of Pathogenic Fungi. Genetics 2010, 185, 211–220. [CrossRef]
- Toyn, J.H.; Gunyuzlu, P.; White, W.H.; Thompson, L.A.; Hollis, G.F. A Counterselection for the Tryptophan Pathway in Yeast: 5-Fluoroanthranilic Acid Resistance. Yeast 2000, 16, 553–560. [CrossRef]
- Tzin, V.; Galili, G. The Biosynthetic Pathways for Shikimate and Aromatic Amino Acids in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Arabidopsis Book 2010, 8, e0132. [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Garbeva, P.; Raaijmakers, J.M. The Rhizosphere Microbiome: Significance of Plant Beneficial, Plant Pathogenic, and Human Pathogenic Microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2013, 37, 634–663. [CrossRef]
- Khunnamwong, P.; Lertwattanasakul, N.; Jindamorakot, S.; Suwannarach, N.; Matsui, K.; Limtong, S. Evaluation of Antagonistic Activity and Mechanisms of Endophytic Yeasts against Pathogenic Fungi Causing Economic Crop Diseases. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 2020, 65, 573–590. [CrossRef]
- Chen, O.; Yi, L.; Deng, L.; Ruan, C.; Zeng, K. Screening Antagonistic Yeasts against Citrus Green Mold and the Possible Biocontrol Mechanisms of Pichia Galeiformis (BAF03). J Sci Food Agric 2020, 100, 3812–3821. [CrossRef]
- Cabañas, C.M.; Hernández, A.; Martínez, A.; Tejero, P.; Vázquez-Hernández, M.; Martín, A.; Ruiz-Moyano, S. Control of Penicillium Glabrum by Indigenous Antagonistic Yeast from Vineyards. Foods 2020, 9, 1864. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kareem, M.Marwa.; Zohri, A.-N.A.; Nasr, S.A.E.E. Novel Marine Yeast Strains as Plant Growth-Promoting Agents Improve Defense in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum) against Fusarium Oxysporum. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection 2021, 128, 973–988. [CrossRef]
- Lara-Capistran, L.; Zulueta-Rodriguez, R.; Castellanos-Cervantes, T.; Reyes-Perez, J.J.; Preciado-Rangel, P.; Hernandez-Montiel, L.G. Efficiency of Marine Bacteria and Yeasts on the Biocontrol Activity of Pythium Ultimum in Ancho-Type Pepper Seedlings. Agronomy 2020, 10, 408. [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, L.P.; Cunha, T. da; da Silva, A.C.; Kupper, K.C. Biocontrol Ability and Putative Mode of Action of Yeasts against Geotrichum Citri-Aurantii in Citrus Fruit. Microbiol Res 2016, 188–189, 72–79. [CrossRef]
- Golubev, W.I.; Kulakovskaya, T. V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kulakovskaya, E. V.; Golubev, N. V. Antifungal Cellobiose Lipid Secreted by the Epiphytic Yeast Pseudozyma Graminicola. Microbiology (N Y) 2008, 77, 171–175. [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.M.; Stets, M.I.; Mazzetto, A.M.; Andrade, F.D.; Pileggi, S.A. V.; Fávero, P.R.; Cantú, M.D.; Carrilho, E.; Carneiro, P.I.B.; Pileggi, M. Degradation of 2,4-D Herbicide by Microorganisms Isolated from Brazilian Contaminated Soil. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 2007, 38, 522–525. [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.M.; Ryu, C.-M. Foliar Application of the Leaf-Colonizing Yeast Pseudozyma Churashimaensis Elicits Systemic Defense of Pepper against Bacterial and Viral Pathogens. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 39432. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B. Induced Resistance in Peach Fruit as Treated by Pichia Guilliermondii and Their Possible Mechanism. Int J Food Prop 2020, 23, 34–51. [CrossRef]
- Simova, E.D.; Frengova, G.I.; Beshkova, D.M. Synthesis of Mannose-Rich Exopolysaccharide by Rhodotorula Glutinis 16P Co-Cultured with Yeast or Bacteria. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 2000, 55, 540–545. [CrossRef]
- Grigorova, D.; Simova, E.; Pavlova, K.; Frengova, G.; Beshkova, D. Polysaccharides Production by Yeast in Whey Ultrafiltrate. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 1994, 8, 31–37. [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H.; Shukla, S.P.; Engl, T.; Weiss, B.; Fischer, R.; Steiger, S.; Heckel, D.G.; Kaltenpoth, M.; Vilcinskas, A. The Digestive and Defensive Basis of Carcass Utilization by the Burying Beetle and Its Microbiota. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 15186. [CrossRef]
- Varotto Boccazzi, I.; Ottoboni, M.; Martin, E.; Comandatore, F.; Vallone, L.; Spranghers, T.; Eeckhout, M.; Mereghetti, V.; Pinotti, L.; Epis, S. A Survey of the Mycobiota Associated with Larvae of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia Illucens) Reared for Feed Production. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0182533. [CrossRef]
- Al Naggar, Y.; Singavarapu, B.; Paxton, R.J.; Wubet, T. Bees under Interactive Stressors: The Novel Insecticides Flupyradifurone and Sulfoxaflor along with the Fungicide Azoxystrobin Disrupt the Gut Microbiota of Honey Bees and Increase Opportunistic Bacterial Pathogens. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 849, 157941. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Keesey, I.W.; Hansson, B.S.; Knaden, M. Gut Microbiota Affects Development and Olfactory Behavior in Drosophila Melanogaster. Journal of Experimental Biology 2019. [CrossRef]
- de Lima Targino, H.M.; Silva, V.S.L.; Escobar, I.E.C.; Ribeiro, P.R. de A.; Gava, C.A.T.; Fernandes-Júnior, P.I. Maize-Associated Meyerozyma from the Brazilian Semiarid Region Are Effective Plant Growth-Promoting Yeasts. Rhizosphere 2022, 22, 100538. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-San Millan, A.; Larraya, L.; Farran, I.; Ancin, M.; Veramendi, J. Successful Biocontrol of Major Postharvest and Soil-Borne Plant Pathogenic Fungi by Antagonistic Yeasts. Biological Control 2021, 160, 104683. [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 15/09/2024).
- Goulart, A.C.P.; Nunes, J.C. da S. Evolução e Cenário Atual Do Tratamento de Sementes de Soja Com Fungicidas No Brasil. Revista Cultivar:Embrapa 2021.
- International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database Most Recent Cases of Herbicide Resistant Weeds Entered into the Database.
- Guo, L.; Li, R.; Chen, W.; Dong, F.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y. The Interaction Effects of Pesticides with Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Their Fate during Wine-Making Process. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138577. [CrossRef]
- Wachowska, U.; Irzykowski, W.; Jędryczka, M. Agrochemicals: Effect on Genetic Resistance in Yeasts Colonizing Winter Wheat Kernels. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2018, 162, 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Jawich, D.; Hilan, C.; Saliba, R.; Lteif, R.; Strehaiano, P. Effects of Some Pesticides on Two Yeast Strains <Em>Saccharomyces Cerevisiae</Em> and <Em>Metschnikowia Pulcherrima</Em> OENO One 2005, 39, 67. [CrossRef]
- Čuš, F.; Raspor, P. The Effect of Pyrimethanil on the Growth of Wine Yeasts. Lett Appl Microbiol 2008, 47, 54–59. [CrossRef]
- Viegas, C.A.; Cabral, M.G.; Teixeira, M.C.; Neumann, G.; Heipieper, H.J.; Sá-Correia, I. Yeast Adaptation to 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Involves Increased Membrane Fatty Acid Saturation Degree and Decreased OLE1 Transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005, 330, 271–278. [CrossRef]
- Marchi, G.; Carvalho, E.; Tadeu, S.M.; Guimarães, G. Documentos 227 Herbicidas: Mecanismos de Ação e Uso Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária Embrapa Cerrados Ministério Da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. 2008.
- Cabral, M.G.; Viegas, C.A.; Teixeira, M.C.; Sá-Correia, I. Toxicity of Chlorinated Phenoxyacetic Acid Herbicides in the Experimental Eukaryotic Model Saccharomyces Cerevisiae: Role of PH and of Growth Phase and Size of the Yeast Cell Population. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 47–54. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Telo, J.P.; Duarte, N.F.; Sá-Correia, I. The Herbicide 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid Induces the Generation of Free-Radicals and Associated Oxidative Stress Responses in Yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004, 324, 1101–1107. [CrossRef]
- Barney, J.B.; Winans, M.J.; Blackwood, C.B.; Pupo, A.; Gallagher, J.E.G. The Yeast Atlas of Appalachia: Species and Phenotypic Diversity of Herbicide Resistance in Wild Yeast. Diversity (Basel) 2020, 12, 139. [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; He, M.M.; Shin, K.; Mai, V.; Jeong, K.C.; Finckh, M.R.; Morris, J.G. Environmental and Health Effects of the Herbicide Glyphosate. Science of The Total Environment 2018, 616–617, 255–268. [CrossRef]
- Braconi, D.; Possenti, S.; Laschi, M.; Geminiani, M.; Lusini, P.; Bernardini, G.; Santucci, A. Oxidative Damage Mediated by Herbicides on Yeast Cells. J Agric Food Chem 2008, 56, 3836–3845. [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, A.; Cumming, J.R.; Gallagher, J.E.G. Mitochondrial Metabolism Is Central for Response and Resistance of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae to Exposure to a Glyphosate-Based Herbicide. Environmental Pollution 2020, 262, 114359. [CrossRef]
- Lescano, M.; Fussoni, N.; Vidal, E.; Zalazar, C. Biodegradation of Pesticide-Contaminated Wastewaters from a Formulation Plant Employing a Pilot Scale Biobed. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 807, 150758. [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, K.; Gerginova, M.; Peneva, N.; Dincheva, I.; Alexieva, Z. Biodegradation and Utilization of the Pesticides Glyphosate and Carbofuran by Two Yeast Strains. Processes 2023, 11, 3343. [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.N.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Becker, J.D.; Viegas, C.A. Comparative Analysis of Transcriptomic Responses to Sub-Lethal Levels of Six Environmentally Relevant Pesticides in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 871–889. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Fernandes, A.R.; Mira, N.P.; Becker, J.D.; Sá-Correia, I. Early Transcriptional Response of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae to Stress Imposed by the Herbicide 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid. FEMS Yeast Res 2006, 6, 230–248. [CrossRef]
- 59. National Library of Medicine Pub Chem: Explore Chemistry. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 15/09/2024).
- Kumar, A.; Trefault, N.; Olaniran, A.O. Microbial Degradation of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid: Insight into the Enzymes and Catabolic Genes Involved, Their Regulation and Biotechnological Implications. Crit Rev Microbiol 2014, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Patriarcheas, D.; Momtareen, T.; Gallagher, J.E.G. Yeast of Eden: Microbial Resistance to Glyphosate from a Yeast Perspective. Curr Genet 2023, 69, 203–212. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Y.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Insights into the Microbial Degradation and Resistance Mechanisms of Glyphosate. Environ Res 2022, 215, 114153. [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, F.; Rahman, S.A. Biodegradation of Carbofuran; A Review. Journal of Environmental Microbiology and Toxicology 2020, 8, 50–57. [CrossRef]
- Kocárek, M.; Artikov, H.; Vorisek, K.; Boruvka, L. Pendimethalin Degradation in Soil and Its Interaction with Soil Microorganisms. Soil and Water Research 2016, 11, 213–219. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tang, Z.; Bao, H.; Wu, D.; Deng, X.; Guo, G.; Ye, B.-C.; Dai, B. Degradation of Pendimethalin by the Yeast YC2 and Determination of Its Two Main Metabolites. RSC Adv 2019, 9, 491–497. [CrossRef]
- Abigail, E.A.; Abdul Salam, J.; Das, N. Atrazine Degradation in Liquid Culture and Soil by a Novel Yeast Pichia Kudriavzevii Strain Atz-EN-01 and Its Potential Application for Bioremediation. J Appl Pharm Sci 2013, 3, 35–43. [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, M.; Jurcoane, S.; Maftei, D.; Pui, A.; Dumitras-Hutanu, C.A.; Gradinaru, R. Yeast Biodegradation of Some Pesticide Dinitrophenols. Rom Biotechnol Lett 2013, 18, 8151.
- Alves Jr, S.L.; Treichel, H.; Basso, T.O.; Stambuk, B.U. Are Yeasts “Humanity’s Best Friends”? In Yeasts: From Nature to Bioprocesses; Bentaham Science, 2022; pp. 431–458.
- Bobate, S.; Bokade, P.; Bajaj, A. Engineered Yeasts as Biocatalysts for Pesticide Degradation. In Advances in Yeast Biotechnology for Biofuels and Sustainability; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 449–474.
- Imaishi, H.; Matumoto, S. Isolation and Functional Characterization in Yeast of CYP72A18, a Rice Cytochrome P450 That Catalyzes (ω-1)-Hydroxylation of the Herbicide Pelargonic Acid. Pestic Biochem Physiol 2007, 88, 71–77. [CrossRef]
- Shiota, N.; Kodama, S.; Inui, H.; Ohkawa, H. Expression of Human Cytochromes P450 1A1 and P450 1A2 as Fused Enzymes with Yeast NADPH-Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2000, 64, 2025–2033. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, E.; Fuzimoto, K.; Imaishi, H. Expression of Arabidopsis Thaliana Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase, CYP71A12, in Yeast Catalyzes the Metabolism of Herbicide Pyrazoxyfen. Plant Biotechnology 2007, 24, 393–396. [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Zhou, Q.; Li, G.; Tao, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, P.; Yang, T.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, C.; et al. Molecular Responses Reveal That Two Glutathione S-Transferase CsGSTU8s Contribute to Detoxification of Glyphosate in Tea Plants (Camellia Sinensis). Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 277, 134304. [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M. Cell Surface Engineering of Yeast for Applications in White Biotechnology. Biotechnol Lett 2011, 33, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Ye, Y.; Du, Z.; Chen, G. Cell-Surface Engineering of Yeasts for Whole-Cell Biocatalysts. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 2021, 44, 1003–1019. [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Suye, S. -i.; Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M.; Kitaguchi, T.; Tsuchiyama, K.; Fukuda, T.; Chen, W.; Mulchandani, A. Surface Display of Organophosphorus Hydrolase on Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Biotechnol Prog 2006, 22, 939–943. [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Tsuchiyama, K.; Makishima, H.; Takayama, K.; Mulchandani, A.; Kuroda, K.; Ueda, M.; Suye, S. Improvement in Organophosphorus Hydrolase Activity of Cell Surface-Engineered Yeast Strain Using Flo1p Anchor System. Biotechnol Lett 2010, 32, 655–659. [CrossRef]
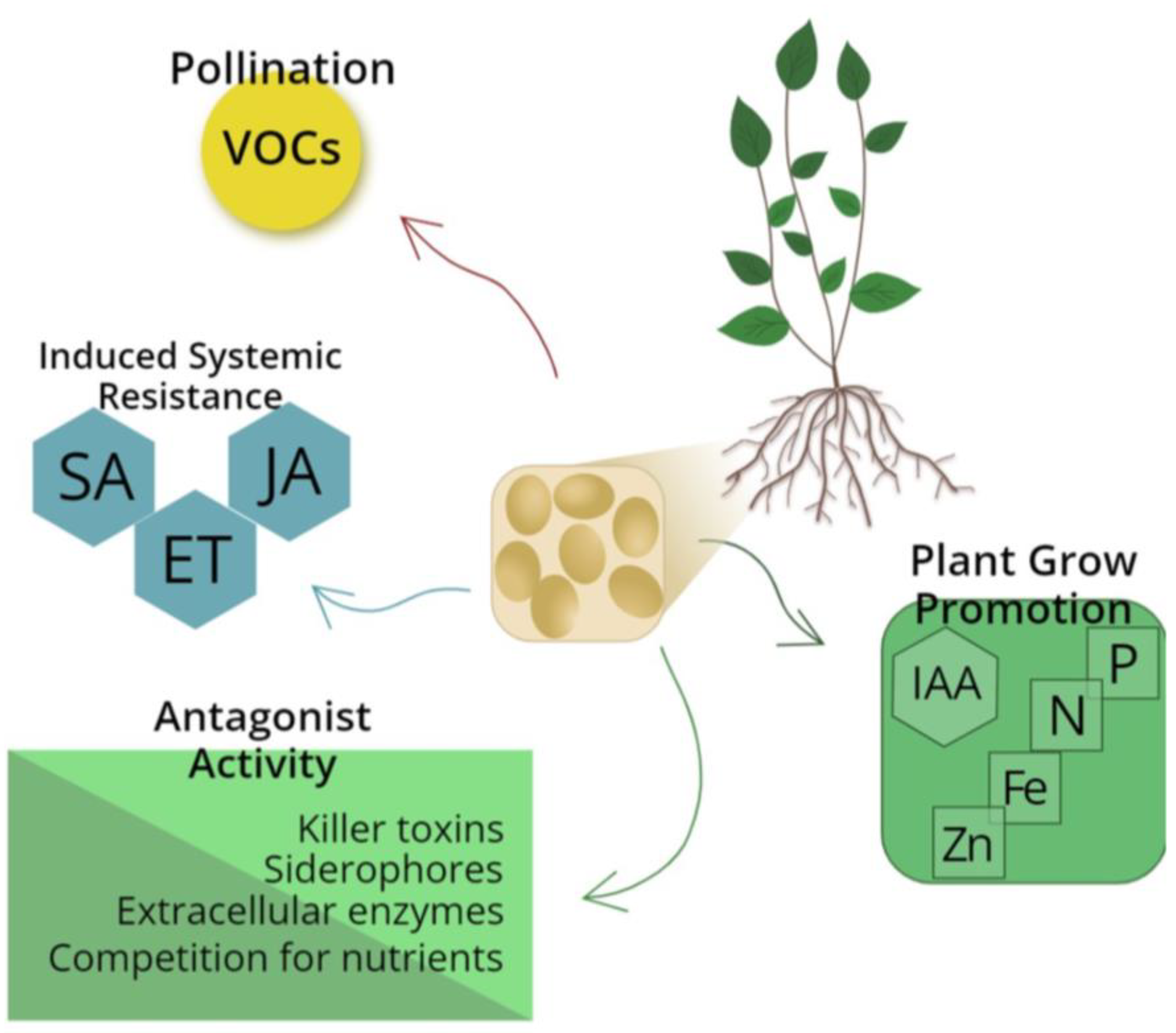
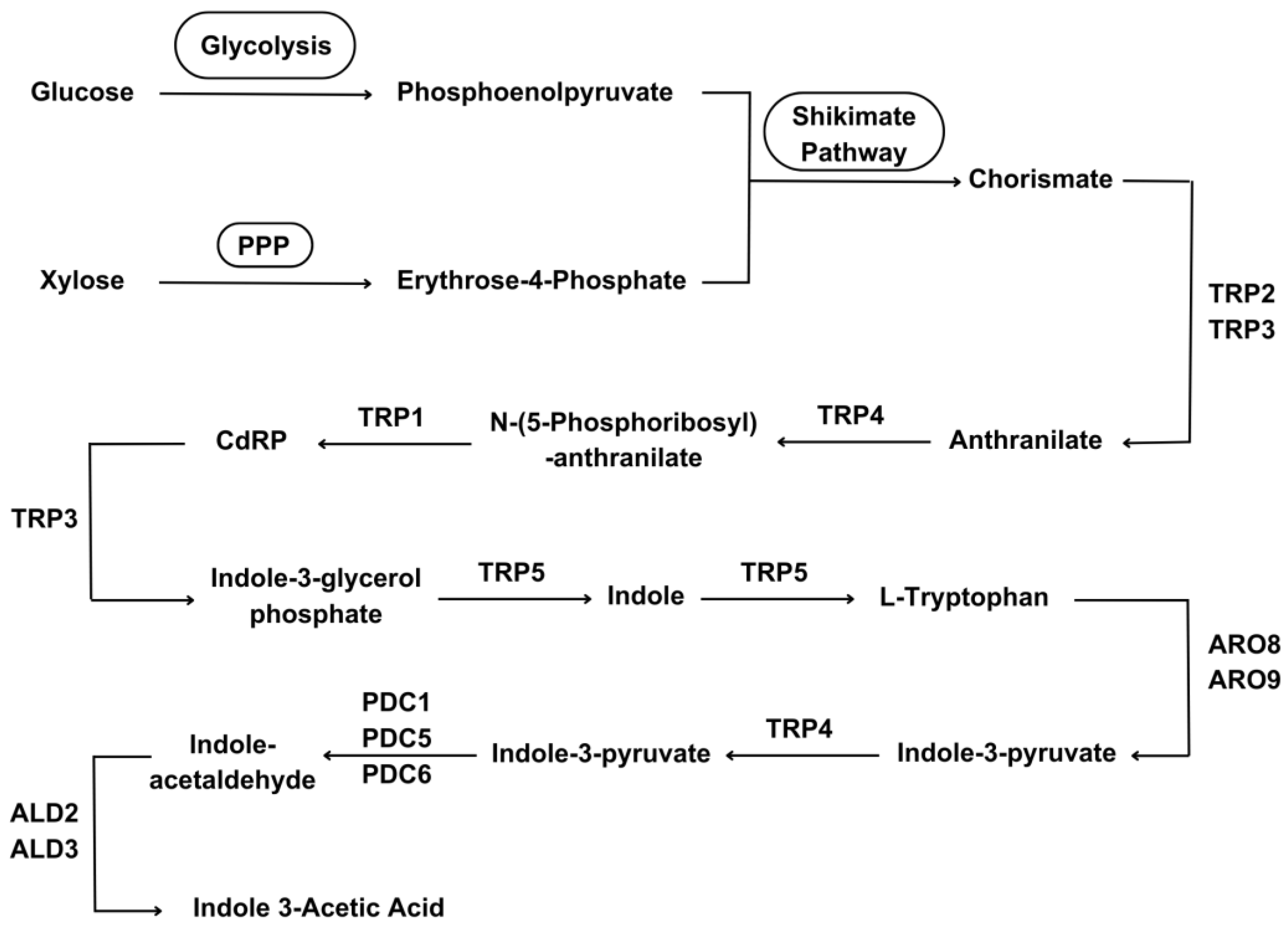
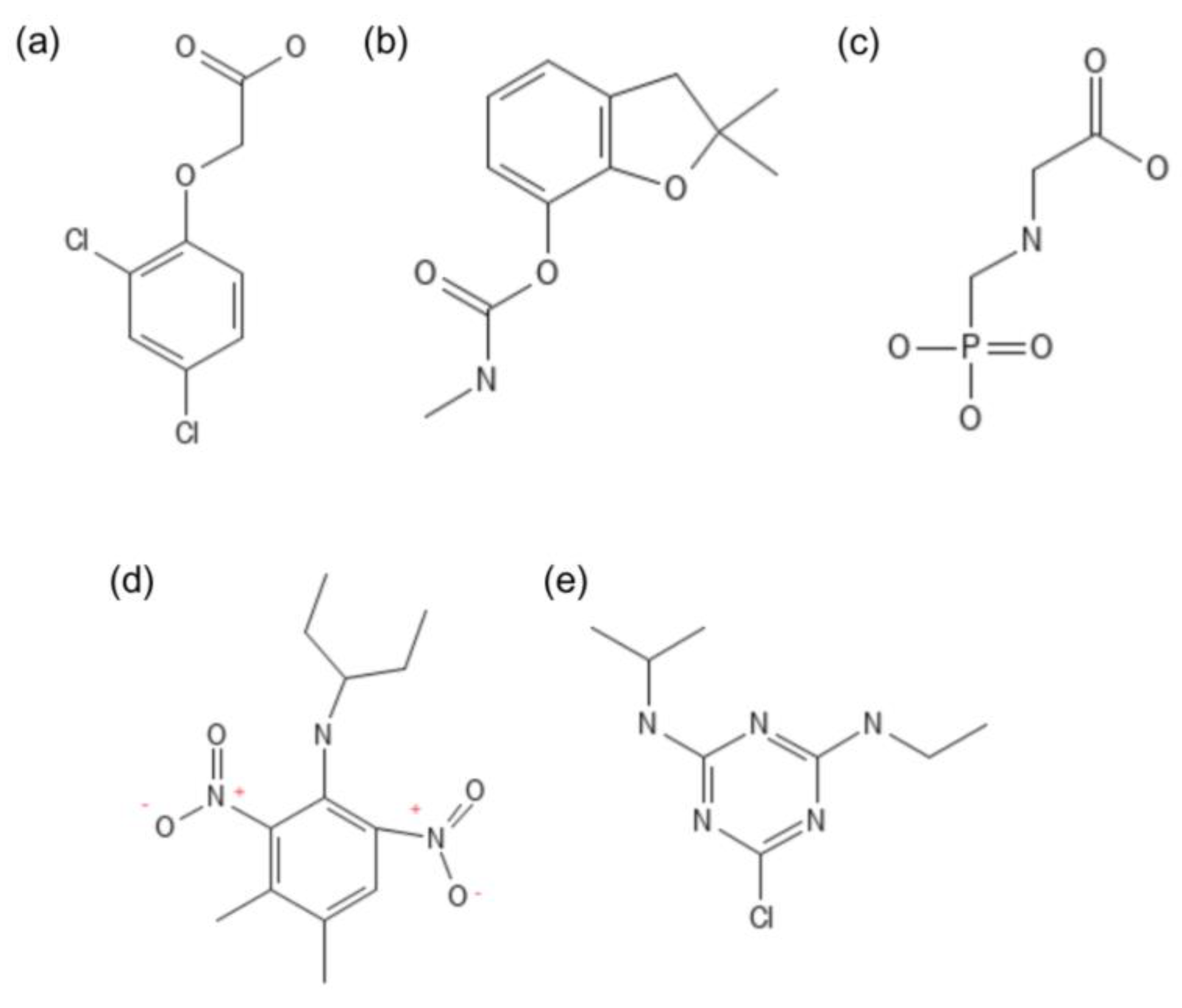
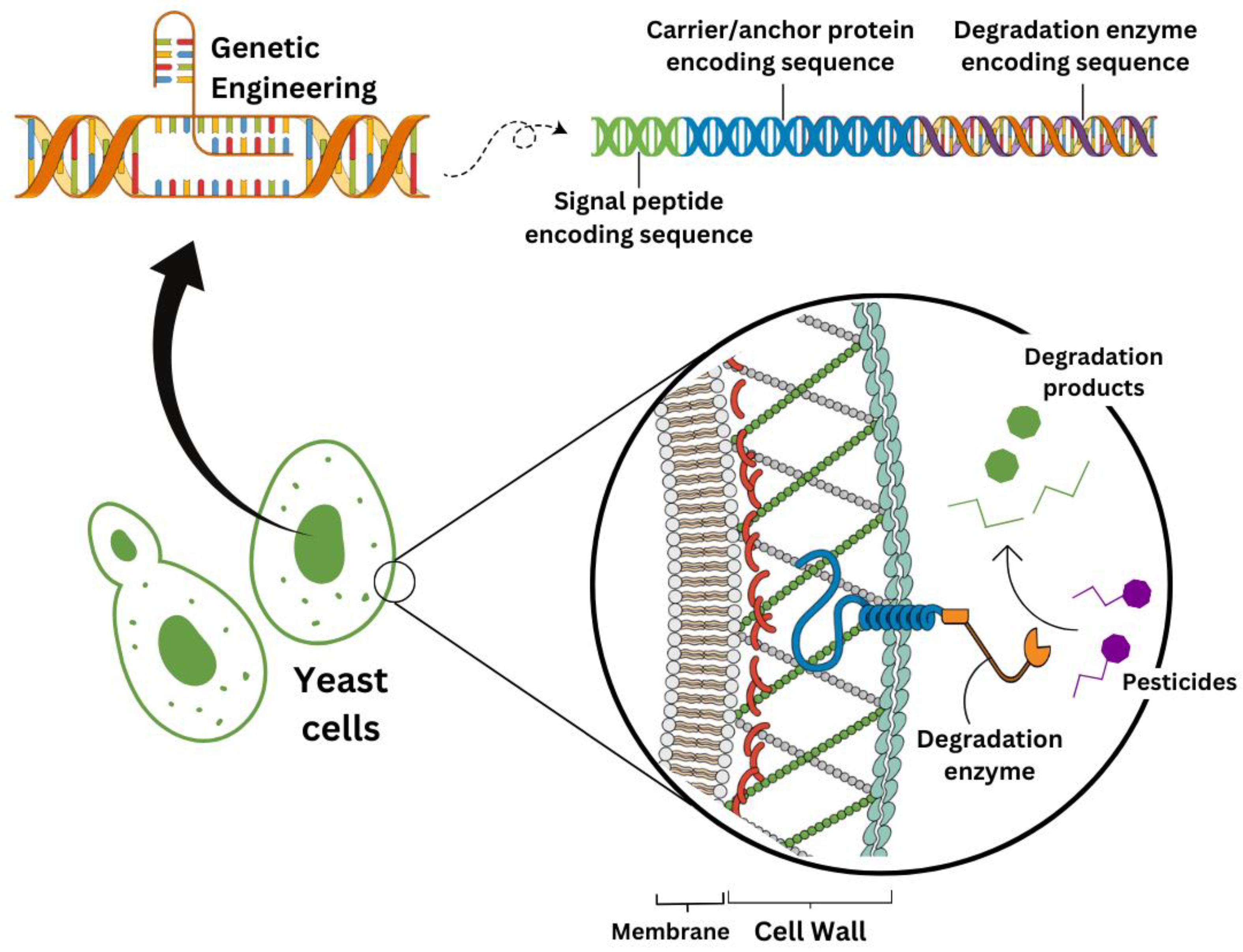
| Yeast Species | Physiological Process | Reference |
| Aureobasidium pullulans, Myriangiales sp., Occultifur brasiliensis, Candida silvae, Cryptococcus podzolicus | Nitrogen and Carbon availability | [11] |
| Pichia kudriavzevii, Issatchenkia terricola | Phosphorus availability, IAA1 production | [12] |
| Cryptococcus flavus, Candida railenensis | Phosphorus availability | [13] |
| Meyerozyma guilliermondii, Candida zemplinina, Candida pimensis, Lachancea lanzarotensis, Rhodotorula mucilaginosa | IAA1 production | [10] |
| Kazachstania rupicola, Rhodosporidium diabovatum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae | IAA1 production | [14] |
| Yeast Species | Pathogen | Yeast Antagonist Action | Reference |
| Papiliotrema laurentii | Pythium ultimum | β-1,3-glucanase production | [26] |
| Rhodotorula minuta, Candida azyma, Aureobasidium pullulans | Georichum citri-aurantii | Competition for nutrients, β-1,3-glucanase, Chitinase, Killer activity | [27] |
| Wickerhamomyces anomalus | Rhizoctonia solani, Curvularia lunata, Fusarium moniliforme | Production of VOCs, β-1,3-glucanase, and chitinase | [22] |
| Pichia galeiformis | Penicillium digitatum | Competition for space and nutrients, VOCs production | [23] |
| Pseudozyma graminicola | Bullera hannae, Cryptococcus nemorosus, Dacrymyces stillatus, Neovossia setariae, Sporobolomyces singularis | Cellobiose-lipid production | [28] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





